|
1
|
American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts
& Figures 2018. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2018,
https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2018.html.
Accessed November 22, 2018.
|
|
2
|
Zubaidi AM, AlSubaie NM, AlHumaid AA,
Shaik SA, AlKhayal KA and AlObeed OA: Public awareness of
colorectal cancer in Saudi Arabia: A survey of 1070 participants in
Riyadh. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 21:78–83. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kuipers EJ, Grady WM, Lieberman D,
Seufferlein T, Sung JJ, Boelens PG, van de Velde CJ and Watanabe T:
Colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 1:150652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sreevalsan S and Safe S: Reactive oxygen
species and colorectal cancer. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep.
9:350–357. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Larocque K, Ovadje P, Djurdjevic S, Mehdi
M, Green J and Pandey S: Novel analogue of colchicine induces
selective pro-death autophagy and necrosis in human cancer cells.
PLoS One. 9:e870642014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim AD, Kang KA, Kim HS, Kim DH, Choi YH,
Lee SJ, Kim HS and Hyun JW: A ginseng metabolite, compound K,
induces autophagy and apoptosis via generation of reactive oxygen
species and activation of JNK in human colon cancer cells. Cell
Death Dis. 4:e7502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim JY, Yu SJ, Oh HJ, Lee JY, Kim Y and
Sohn J: Panaxydol induces apoptosis through an increased
intracellular calcium level, activation of JNK and p38 MAPK and
NADPH oxidase-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species.
Apoptosis. 16:347–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ramiro-Cortés Y, Guemez-Gamboa A and Morán
J: Reactive oxygen species participate in the p38-mediated
apoptosis induced by potassium deprivation and staurosporine in
cerebellar granule neurons. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 43:1373–1382.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hsieh CJ, Kuo PL, Hsu YC, Huang YF, Tsai
EM and Hsu YL: Arctigenin, a dietary phytoestrogen, induces
apoptosis of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells through
the ROS/p38 MAPK pathway and epigenetic regulation. Free Radic Biol
Med. 67:159–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
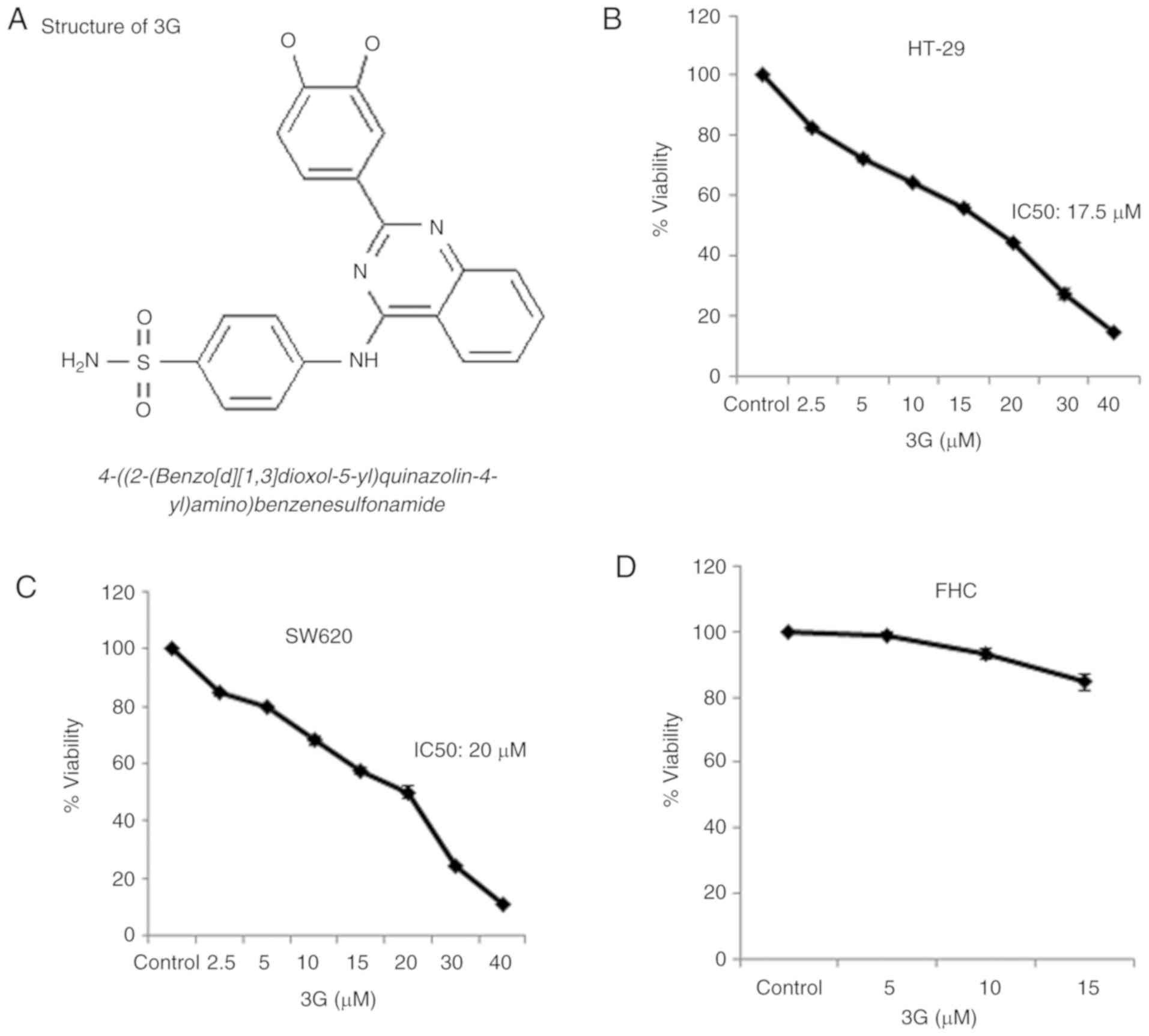
Alafeefy AM, Ahmad R, Abdulla M, Eldehna
WM, Al-Tamimi AM, Abdel-Aziz HA, Al-Obaid O, Carta F, Al-Kahtani AA
and Supuran CT: Development of certain new
2-substituted-quinazolin-4-yl-aminobenzenesulfonamide as potential
antitumor agents. Eur J Med Chem. 109:247–253. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
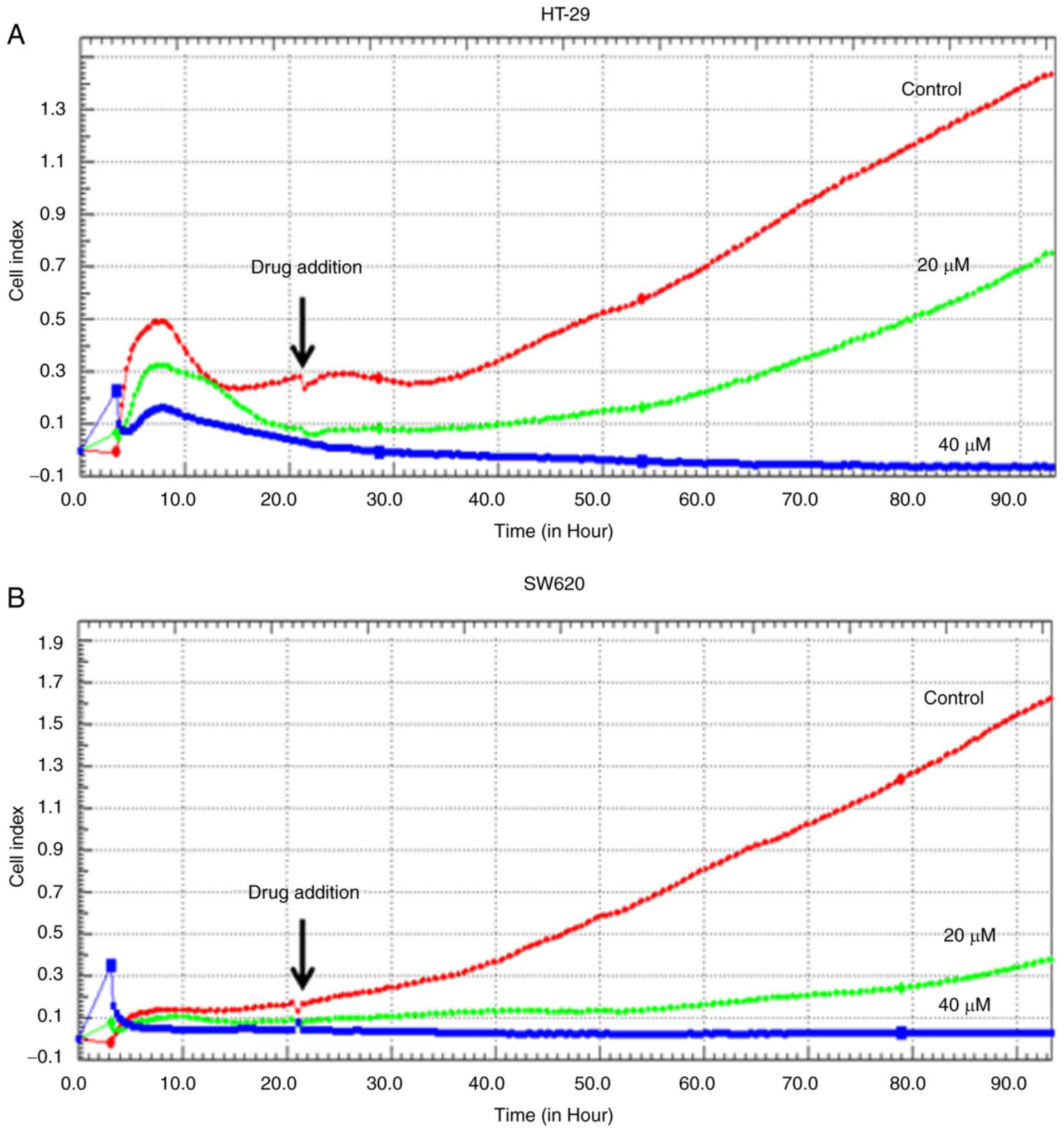
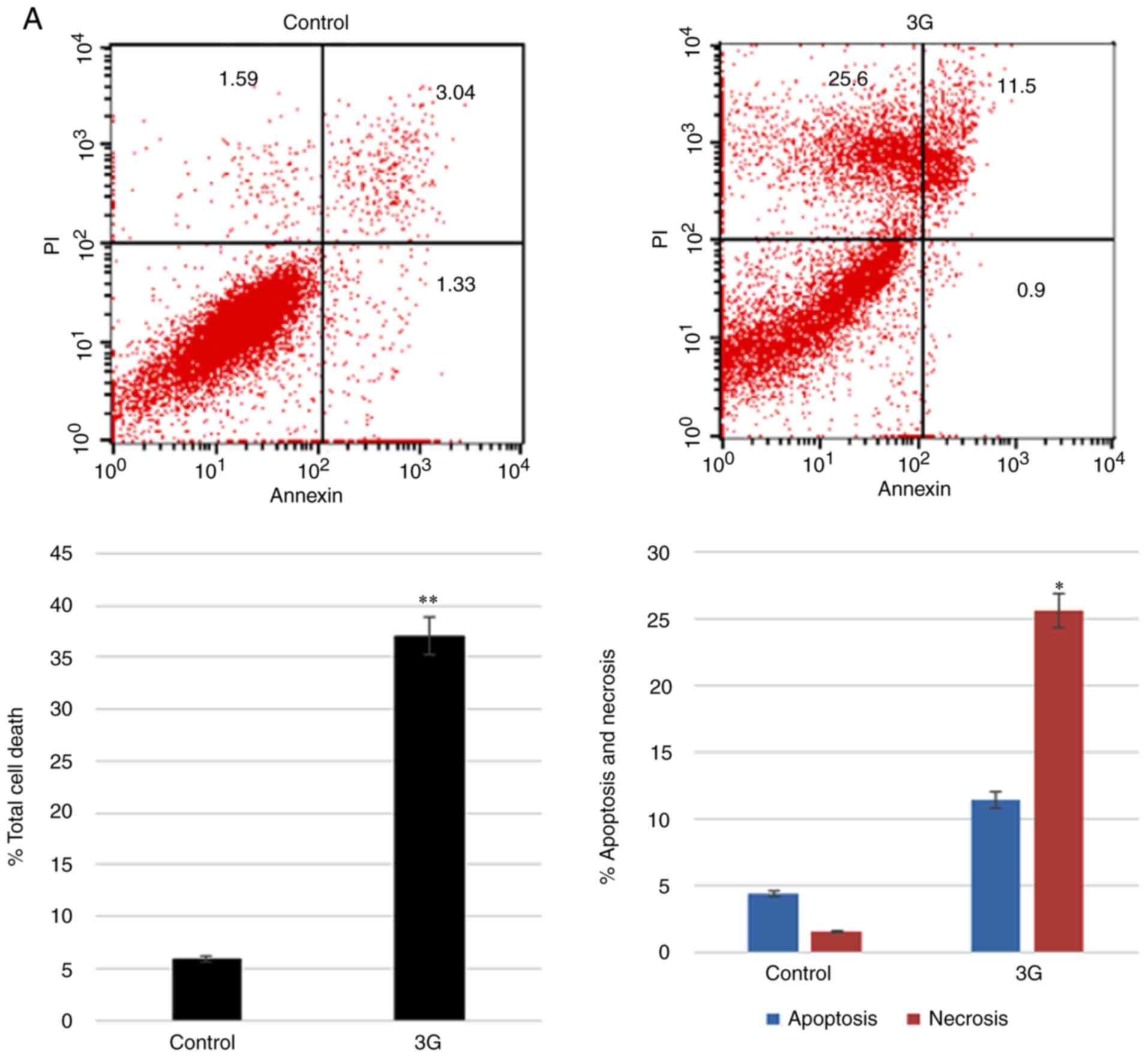
Al-Khayal K, Alafeefy A, Vaali-Mohammed
MA, Mahmood A, Zubaidi A, Al-Obeed O, Khan Z, Abdulla M and Ahmad
R: Novel derivative of aminobenzenesulfonamide (3c) induces
apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells through ROS generation and
inhibits cell migration. BMC Cancer. 17:42017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
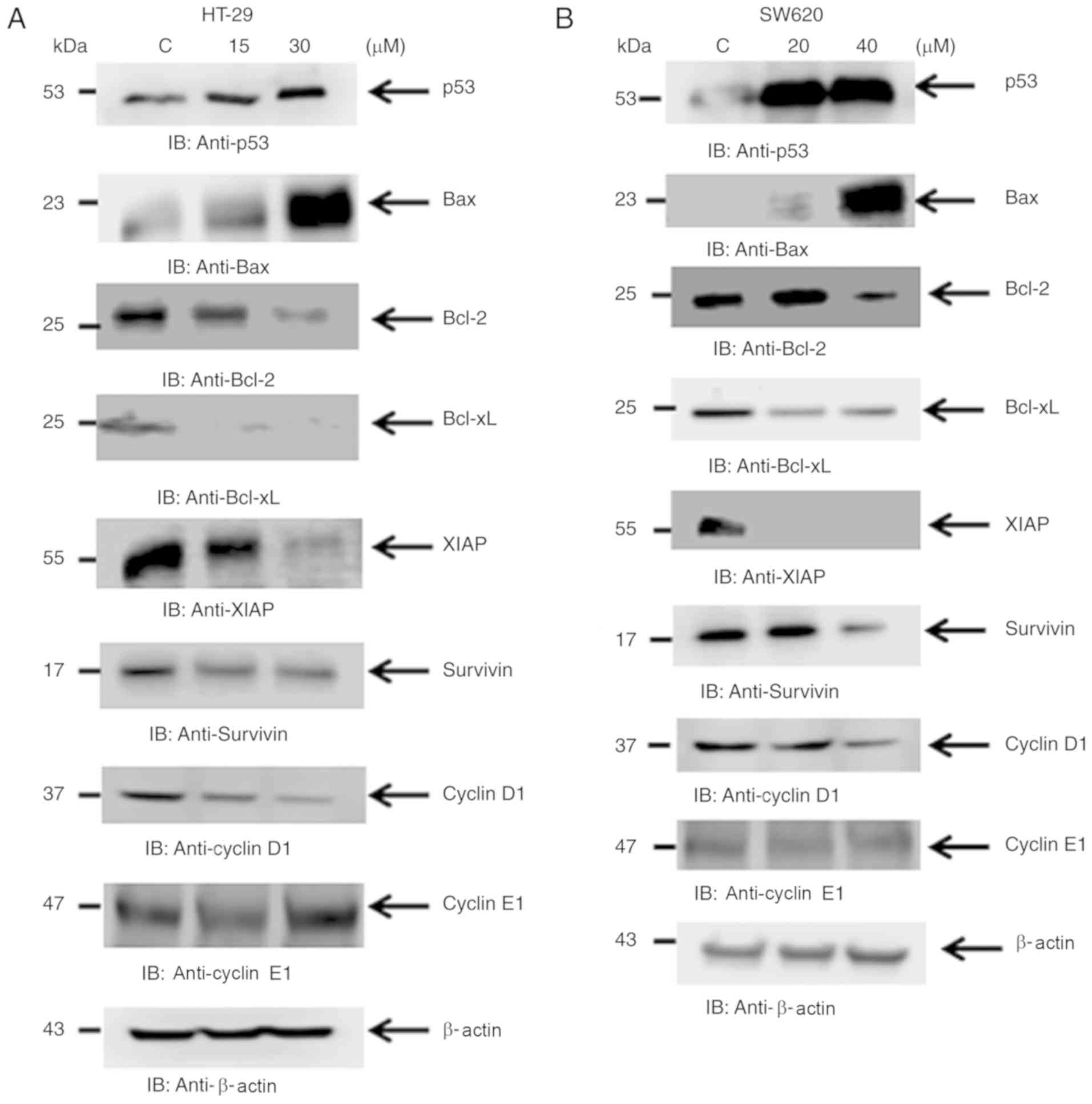
Al-Obeed O, Vaali-Mohammed MA, Eldehna WM,
Al-Khayal K, Mahmood A, Abdel-Aziz HA, Zubaidi A, Alafeefy A,
Abdulla M and Ahmad R: Novel quinazoline-based sulfonamide
derivative (3D) induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer by
inhibiting JAK2-STAT3 pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 11:3313–3322.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Olovnikov IA, Kravchenko JE and Chumakov
PM: Homeostatic function of the p53 tumor suppressor: Regulation of
energy metabolism and antioxidant defence. Semin Cancer Biol.
19:32–41. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shamas-Din A, Kale J, Leber B and Andrews
DW: Mechanism of action of Bcl-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 5:a0087142013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Casimiro MC, Crosariol M, Loro E, Li Z and
Pestell RG: Cyclins and cell cycle control in cancer and disease.
Genes Cancer. 3:649–657. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Altieri DC: Survivin and IAP proteins in
cell death mechanisms. Biochem J. 430:199–205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Soldani C and Scovassi AI:
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: An update.
Apoptosis. 7:321–328. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Raj L, Ide T, Gurkar AU, Foley M, Schenone
M, Li X, Tolliday NJ, Golub TR, Carr SA, Shamji AF, et al:
Selective killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targeting the
stress response to ROS. Nature. 475:231–234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zikaki K, Aggeli IK, Gaitanaki C and Beis
I: Curcumin induces the apoptotic intrinsic pathway via
upregulation of reactive oxygen species and JNKs in H9c2 cardiac
myoblasts. Apoptosis. 19:958–974. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu Z, Liang C, Zhang Z, Pan J, Xia H,
Zhong N and Li L: Para-toluenesulfonamide induces tongue squamous
cell carcinoma cell death through disturbing lysosomal stability.
Anticancer Drugs. 26:1026–1033. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saha T, Hossain MS, Saha D, Lahiri M and
Talukdar P: Chloride-mediated apoptosis-inducing activity of
bis(sulfonamide) anionophores. J Am Chem Soc. 138:7558–7567. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Agudo-López A, Prieto-García E, Alemán J,
Pérez C, Díaz-García CV, Parrilla-Rubio L, Cabrera S,
Navarro-Ranninger C, Cortés-Funes H, López-Martín JA and
Agulló-Ortuño MT: Mechanistic added value of a
trans-Sulfonamide-Platinum-Complex in human melanoma cell lines and
synergism with cis-Platin. Mol Cancer. 16:452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Armaghany T, Wilson JD, Chu Q and Mills G:
Genetic alterations in colorectal cancer. Gastrointest Cancer Res.
5:19–27. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cherbonnel-Lasserre C and Dosanjh ML:
Suppression of apoptosis by overexpression of Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL
promotes survival and mutagenesis after oxidative damage.
Biochimie. 79:613–617. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sinicrope FA, Ruan SB, Cleary KR, Stephens
LC, Lee JJ and Levin B: Bcl-2 and p53 expression during colorectal
tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 55:237–241. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scherr AL, Gdynia G, Salou M,
Radhakrishnan P, Duglova K, Heller A, Keim S, Kautz N, Jassowicz A,
Elssner C, et al: Bcl-xL is an oncogenic driver in colorectal
cancer. Cell Death Dis. 7:e23422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mermelshtein A, Gerson A, Walfisch S,
Delgado B, Shechter-Maor G, Delgado J, Fich A and Gheber L:
Expression of D-type cyclins in colon cancer and in cell lines from
colon carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 93:338–345. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Takeuchi H, Kim J, Fujimoto A, Umetani N,
Mori T, Bilchik A, Turner R, Tran A, Kuo C and Hoon DS: X-Linked
inhibitor of apoptosis protein expression level in colorectal
cancer is regulated by hepatocyte growth factor/C-met pathway via
Akt signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7621–7628. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kalliakmanis JG, Kouvidou CH, Latoufis C,
Kouvatseas G, Anagnostakis D, Papatheodoridis G, Koskinas J and
Archimandritis A: Survivin expression in colorectal carcinomas:
Correlations with clinicopathological parameters and survival. Dig
Dis Sci. 55:2958–2964. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Arihara Y, Takada K, Kamihara Y, Hayasaka
N, Nakamura H, Murase K, Ikeda H, Iyama S, Sato T, Miyanishi K, et
al: Small molecule CP-31398 induces reactive oxygen
species-dependent apoptosis in human multiple myeloma. Oncotarget.
8:65889–65899. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Adams DJ, Boskovic ZV, Theriault JR, Wang
AJ, Stern AM, Wagner BK, Shamji AF and Schreiber SL: Discovery of
small-molecule enhancers of reactive oxygen species that are
nontoxic or cause genotype-selective cell death. ACS Chem Biol.
8:923–929. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Weidner C, Rousseau M, Plauth A, Wowro SJ,
Fischer C, Abdel-Aziz H and Sauer S: Iberis amara extract induces
intracellular formation of reactive oxygen species and inhibits
colon cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01523982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Marathe SA, Dasgupta I, Gnanadhas DP and
Chakravortty D: Multifaceted roles of curcumin: Two sides of a
coin! Expert Opin Biol Ther. 11:1485–1499. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Muqbil I, Beck FW, Bao B, Sarkar FH,
Mohammad RM, Hadi SM and Azmi AS: Old wine in a new bottle: The
warburg effect and anticancer mechanisms of resveratrol. Curr Pharm
Des. 18:1645–1654. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liou GY and Storz P: Reactive oxygen
species in cancer. Free Radic Res. 44:479–496. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cargnello M and Roux PP: Activation and
function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated
protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 75:50–83. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cumaoglu A, Dayan S, Agkaya AO, Ozkul Z
and Ozpozan NK: Synthesis and pro-apoptotic effects of new
sulfonamide derivatives via activating p38/ERK phosphorylation in
cancer cells. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 30:413–419. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kwon Y, Song J, Lee H, Kim EY, Lee K, Lee
SK and Kim S: Design, synthesis, and biological activity of
sulfonamide analogues of antofine and cryptopleurine as potent and
orally active antitumor agents. J Med Chem. 58:7749–7762. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tülüce Y, Ahmed BA, Koyuncu İ and Durgun
M: The cytotoxic, apoptotic and oxidative effects of carbonic
anhydrase IX inhibitor on colorectal cancer cells. J Bioenerg
Biomembr. 50:107–116. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|