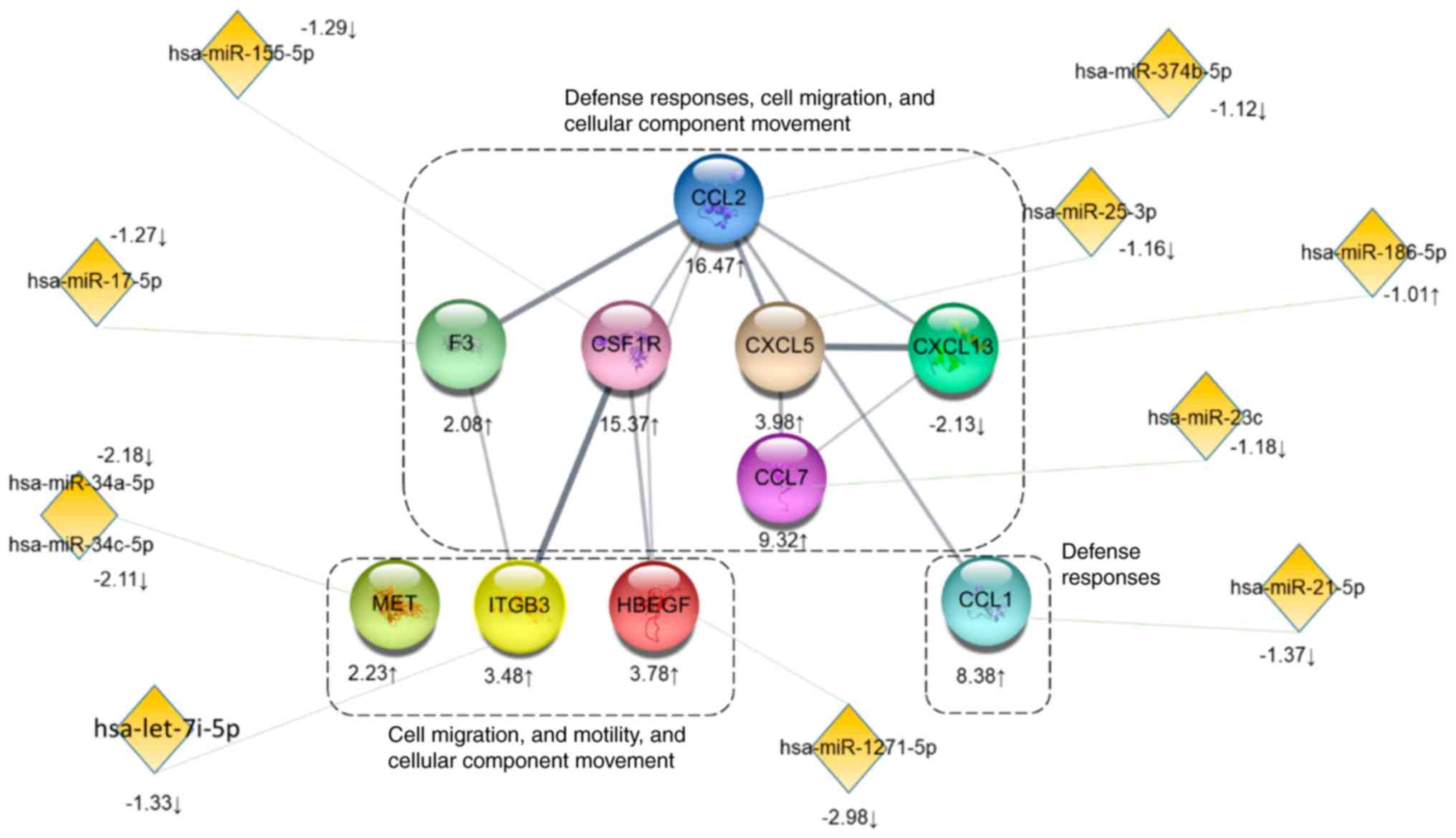
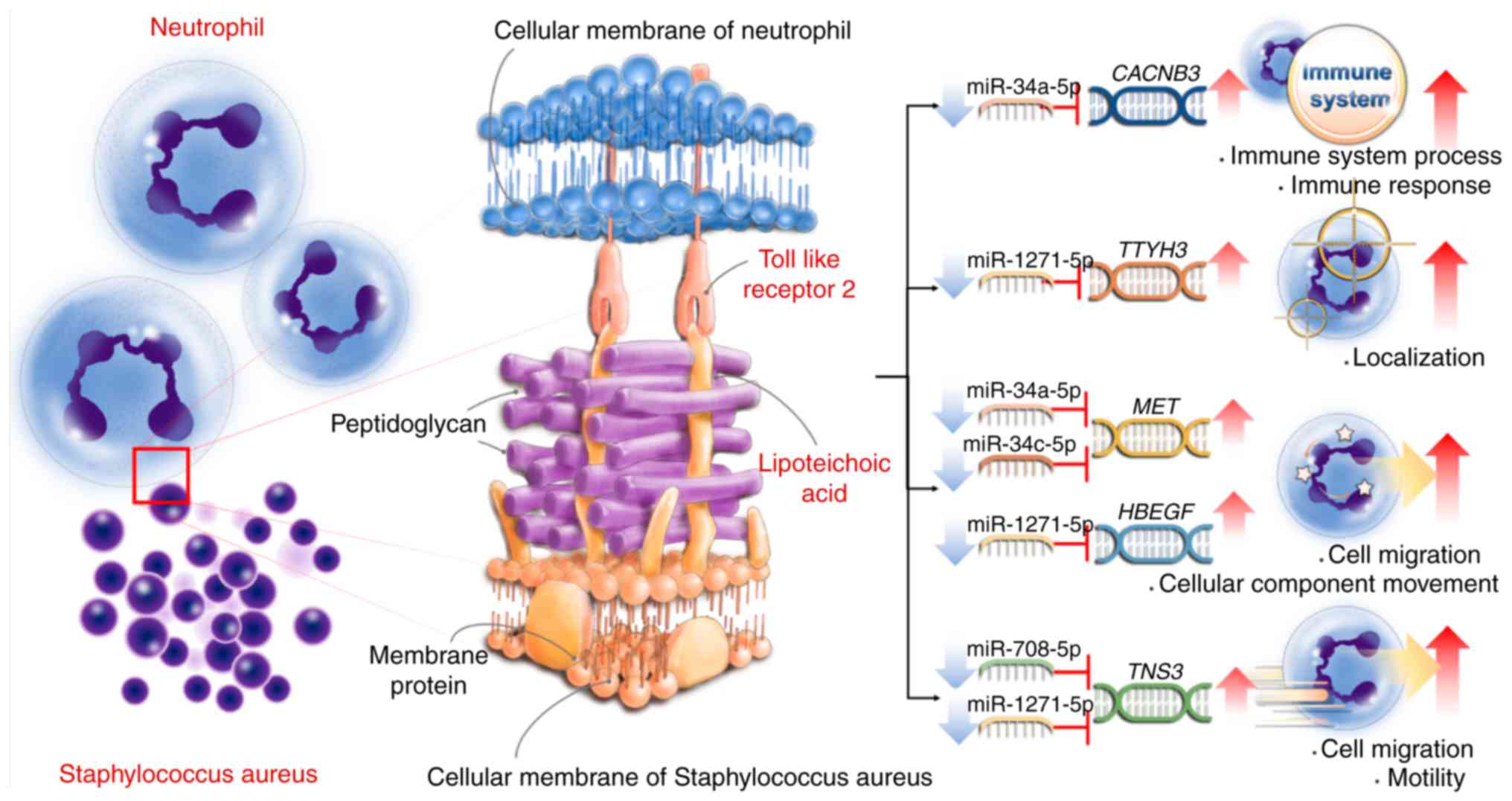
|
1
|
Brubaker SW, Bonham KS, Zanoni I and Kagan
JC: Innate immune pattern recognition: A cell biological
perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 33:257–290. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mogensen TH: Pathogen recognition and
inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 22:240–273, Table of Contents, 2009. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kawasaki T and Kawai T: Toll-like receptor
signaling pathways. Front Immunol. 5:4612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu YC, Yeh WC and Ohashi PS: LPS/TLR4
signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 42:145–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Park BS and Lee JO: Recognition of
lipopolysaccharide pattern by TLR4 complexes. Exp Mol Med.
45:e662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seo HS, Michalek SM and Nahm MH:
Lipoteichoic acid is important in innate immune responses to
gram-positive bacteria. Infect Immun. 76:206–213. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Schwandner R, Dziarski R, Wesche H, Rothe
M and Kirschning CJ: Peptidoglycan- and lipoteichoic acid-induced
cell activation is mediated by toll-like receptor 2. J Biol Chem.
274:17406–17409. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oliveira-Nascimento L, Massari P and
Wetzler LM: The role of TLR2 in infection and immunity. Front
Immunol. 3:792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kengatharan KM, De Kimpe S, Robson C,
Foster SJ and Thiemermann C: Mechanism of gram-positive shock:
Identification of peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid moieties
essential in the induction of nitric oxide synthase, shock, and
multiple organ failure. J Exp Med. 188:305–315. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kurt-Jones EA, Mandell L, Whitney C,
Padgett A, Gosselin K, Newburger PE and Finberg RW: Role of
toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) in neutrophil activation: GM-CSF
enhances TLR2 expression and TLR2-mediated interleukin 8 responses
in neutrophils. Blood. 100:1860–1868. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lotz S, Aga E, Wilde I, van Zandbergen G,
Hartung T, Solbach W and Laskay T: Highly purified lipoteichoic
acid activates neutrophil granulocytes and delays their spontaneous
apoptosis via CD14 and TLR2. J Leukoc Biol. 75:467–477. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ginsburg I: Role of lipoteichoic acid in
infection and inflammation. Lancet Infect Dis. 2:171–179. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nathan C: Neutrophils and immunity:
Challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Immunol. 6:173–182. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hattar K, Grandel U, Moeller A, Fink L,
Iglhaut J, Hartung T, Morath S, Seeger W, Grimminger F and Sibelius
U: Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) from Staphylococcus aureus stimulates
human neutrophil cytokine release by a CD14-dependent,
Toll-like-receptor-independent mechanism: Autocrine role of tumor
necrosis factor-[alpha] in mediating LTA-induced interleukin-8
generation. Crit Care Med. 34:835–841. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Drury RE, O'Connor D and Pollard AJ: The
clinical application of MicroRNAs in infectious disease. Front
Immunol. 8:11822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu H, Lei C, He Q, Pan Z, Xiao D and Tao
Y: Nuclear functions of mammalian MicroRNAs in gene regulation,
immunity and cancer. Mol Cancer. 17:642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wen Z, Xu L, Chen X, Xu W, Yin Z, Gao X
and Xiong S: Autoantibody induction by DNA-containing immune
complexes requires HMGB1 with the TLR2/microRNA-155 pathway. J
Immunol. 190:5411–5422. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yao H, Zhang H, Lan K, Wang H, Su Y, Li D,
Song Z, Cui F, Yin Y and Zhang X: Purified Streptococcus pneumoniae
endo-peptidase O (PepO) enhances particle uptake by macrophages in
a toll-like receptor 2- and miR-155-dependent manner. Infect Immun.
85:e01012–e01016. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Xu H, Wu Y, Li L, Yuan W, Zhang D, Yan Q,
Guo Z and Huang W: MiR-344b1-3p targets TLR2 and negatively
regulates TLR2 signaling pathway. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis.
12:627–638. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Landais I, Pelton C, Streblow D,
DeFilippis V, McWeeney S and Nelson JA: Human cytomegalovirus
miR-UL112-3p targets TLR2 and modulates the TLR2/IRAK1/NFκB
signaling pathway. PLoS Pathog. 11:e10048812015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Quinn EM, Wang JH, O'Callaghan G and
Redmond HP: MicroRNA-146a is upregulated by and negatively
regulates TLR2 signaling. PLoS One. 8:e622322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bolger AM, Lohse M and Usadel B:
Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data.
Bioinformatics. 30:2114–2120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim D, Langmead B and Salzberg SL: HISAT:
A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods.
12:357–360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Friedlander MR, Mackowiak SD, Li N, Chen W
and Rajewsky N: miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds
of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:37–52. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G,
Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL and Pachter L:
Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with TopHat and cufflinks. Nat Protoc. 7:562–578. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mootha VK, Lindgren CM, Eriksson KF,
Subramanian A, Sihag S, Lehar J, Puigserver P, Carlsson E,
Ridderstråle M, Laurila E, et al: PGC-1alpha-responsive genes
involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately
downregulated in human diabetes. Nat Genet. 34:267–273. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Backes C, Khaleeq QT, Meese E and Keller
A: miEAA: microRNA enrichment analysis and annotation. Nucleic
Acids Res. 44:W110–W116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pathan M, Keerthikumar S, Ang CS, Gangoda
L, Quek CY, Williamson NA, Mouradov D, Sieber OM, Simpson RJ, Salim
A, et al: FunRich: An open access standalone functional enrichment
and interaction network analysis tool. Proteomics. 15:2597–2601.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu W and Wang X: Prediction of functional
microRNA targets by integrative modeling of microRNA binding and
target expression data. Genome Biol. 20:182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Garcia DM, Baek D, Shin C, Bell GW,
Grimson A and Bartel DP: Weak seed-pairing stability and high
target-site abundance decrease the proficiency of lsy-6 and other
microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 18:1139–1146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chou CH, Shrestha S, Yang CD, Chang NW,
Lin YL, Liao KW, Huang WC, Sun TH, Tu SJ, Lee WH, et al: miRTarBase
update 2018: A resource for experimentally validated
microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D296–D302.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Gorodkin J and
Jensen LJ: Cytoscape stringApp: Network analysis and visualization
of proteomics data. J Proteome Res. 18:623–632. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Finney SJ, Leaver SK, Evans TW and
Burke-Gaffney A: Differences in lipopolysaccharide- and
lipoteichoic acid-induced cytokine/chemokine expression. Intensive
Care Med. 38:324–332. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Schröder NW, Morath S, Alexander C, Hamann
L, Hartung T, Zähringer U, Göbel UB, Weber JR and Schumann RR:
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) of Streptococcus pneumoniae and
Staphylococcus aureus activates immune cells via Toll-like receptor
(TLR)-2, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP), and CD14,
whereas TLR-4 and MD-2 are not involved. J Biol Chem.
278:15587–15594. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zeng RZ, Kim HG, Kim NR, Gim MG, Ko MY,
Lee SY, Kim CM and Chung DK: Differential gene expression profiles
in human THP-1 monocytes treated with Lactobacillus plantarum or
Staphylococcus aureus lipoteichoic acid. J Korean Soc Appl Bi.
54:763–770. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sharma S, Davis RE, Srivastva S, Nylen S,
Sundar S and Wilson ME: A subset of neutrophils expressing markers
of antigen-presenting cells in human visceral leishmaniasis. J
Infect Dis. 214:1531–1538. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen X, Li SJ, Ojcius DM, Sun AH, Hu WL,
Lin X and Yan J: Mononuclear-macrophages but not neutrophils act as
major infiltrating anti-leptospiral phagocytes during
leptospirosis. PLoS One. 12:e01810142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Long EM, Millen B, Kubes P and Robbins SM:
Lipoteichoic acid induces unique inflammatory responses when
compared to other toll-like receptor 2 ligands. PLoS One.
4:e56012009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hermeking H: The miR-34 family in cancer
and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 17:193–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Cai KM, Bao XL, Kong XH, Jinag W, Mao MR,
Chu JS, Huang YJ and Zhao XJ: Hsa-miR-34c suppresses growth and
invasion of human laryngeal carcinoma cells via targeting c-Met.
Int J Mol Med. 25:565–571. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dong F and Lou D: MicroRNA-34b/c
suppresses uveal melanoma cell proliferation and migration through
multiple targets. Mol Vis. 18:537–546. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hagman Z, Haflidadottir BS, Ansari M,
Persson M, Bjartell A, Edsjö A and Ceder Y: The tumour suppressor
miR-34c targets MET in prostate cancer cells. Br J Cancer.
109:1271–1278. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang F, Lu J, Peng X, Wang J, Liu X, Chen
X, Jiang Y, Li X and Zhang B: Integrated analysis of microRNA
regulatory network in nasopharyngeal carcinoma with deep
sequencing. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bavamian S, Mellios N, Lalonde J, Fass DM,
Wang J, Sheridan SD, Madison JM, Zhou F, Rueckert EH, Barker D, et
al: Dysregulation of miR-34a links neuronal development to genetic
risk factors for bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 20:573–584.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yan D, Zhou X, Chen X, Hu DN, Dong XD,
Wang J, Lu F, Tu L and Qu J: MicroRNA-34a inhibits uveal melanoma
cell proliferation and migration through downregulation of c-Met.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:1559–1565. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Guessous Li Y, Zhang F, Dipierro Y, Kefas
C, Johnson B, Marcinkiewicz E, Jiang L, Yang J, Schmittgen YTD, et
al: MicroRNA-34a inhibits glioblastoma growth by targeting multiple
oncogenes. Cancer Res. 69:7569–7576. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yan K, Gao J, Yang T, Ma Q, Qiu X, Fan Q
and Ma B: MicroRNA-34a inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of
osteosarcoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.
7:e337782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Percy MG and Grundling A: Lipoteichoic
acid synthesis and function in gram-positive bacteria. Annu Rev
Microbiol. 68:81–100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Standiford TJ, Arenberg DA, Danforth JM,
Kunkel SL, VanOtteren GM and Strieter RM: Lipoteichoic acid induces
secretion of interleukin-8 from human blood monocytes: A cellular
and molecular analysis. Infect Immun. 62:119–125. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mattsson E, Verhage L, Rollof J, Fleer A,
Verhoef J and van Dijk H: Peptidoglycan and teichoic acid from
Staphylococcus epidermidis stimulate human monocytes to release
tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6.
FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 7:281–287. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Summers C, Rankin SM, Condliffe AM, Singh
N, Peters AM and Chilvers ER: Neutrophil kinetics in health and
disease. Trends Immunol. 31:318–324. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Durand SH, Flacher V, Roméas A, Carrouel
F, Colomb E, Vincent C, Magloire H, Couble ML, Bleicher F, Staquet
MJ, et al: Lipoteichoic acid increases TLR and functional chemokine
expression while reducing dentin formation in in vitro
differentiated human odontoblasts. J Immunol. 176:2880–2887. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Park C, Lee SY, Kim HJ, Park K, Kim JS and
Lee SJ: Synergy of TLR2 and H1R on Cox-2 activation in pulpal
cells. J Dent Res. 89:180–185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Staquet MJ, Durand SH, Colomb E, Roméas A,
Vincent C, Bleicher F, Lebecque S and Farges JC: Different roles of
odonto-blasts and fibroblasts in immunity. J Dent Res. 87:256–261.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sawa Y, Tsuruga E, Iwasawa K, Ishikawa H
and Yoshida S: Leukocyte adhesion molecule and chemokine production
through lipoteichoic acid recognition by toll-like receptor 2 in
cultured human lymphatic endothelium. Cell Tissue Res. 333:237–252.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Xia X, Li Z, Liu K, Wu Y, Jiang D and Lai
Y: Staphylococcal LTA-induced miR-143 inhibits propionibacterium
acnes-mediated inflammatory response in skin. J Invest Dermatol.
136:621–630. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hsieh CH, Yang JC, Jeng JC, Chen YC, Lu
TH, Tzeng SL, Wu YC, Wu CJ and Rau CS: Circulating microRNA
signatures in mice exposed to lipoteichoic acid. J Biomed Sci.
20:22013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|