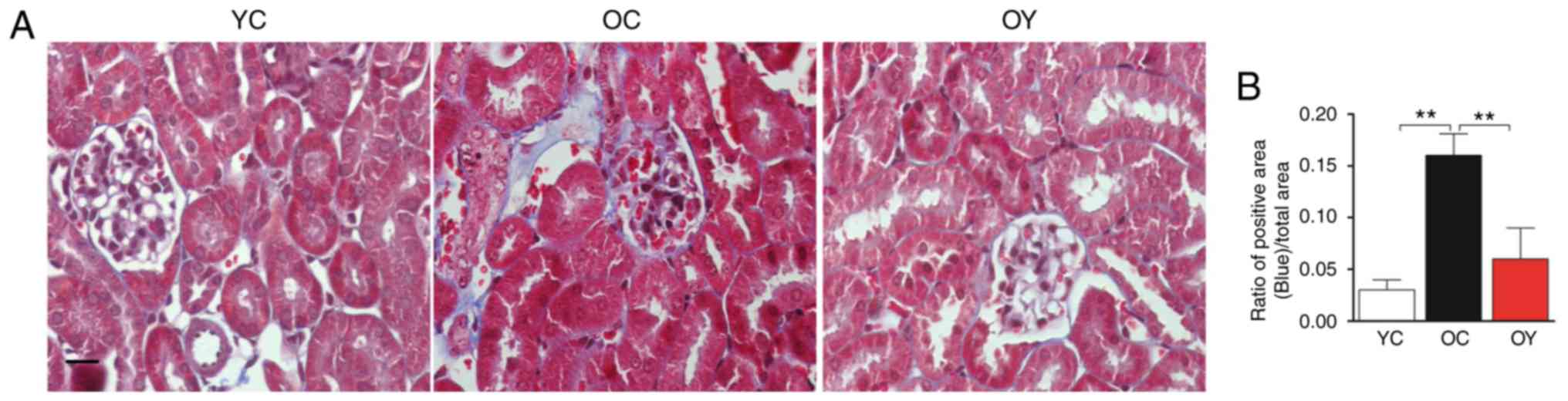
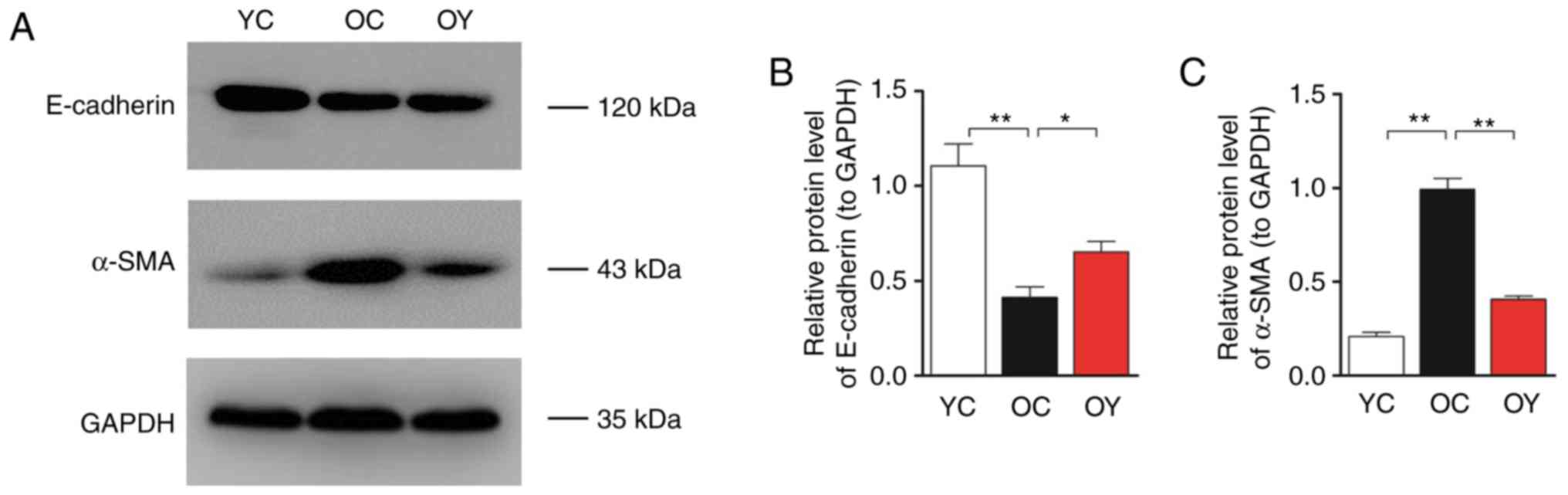
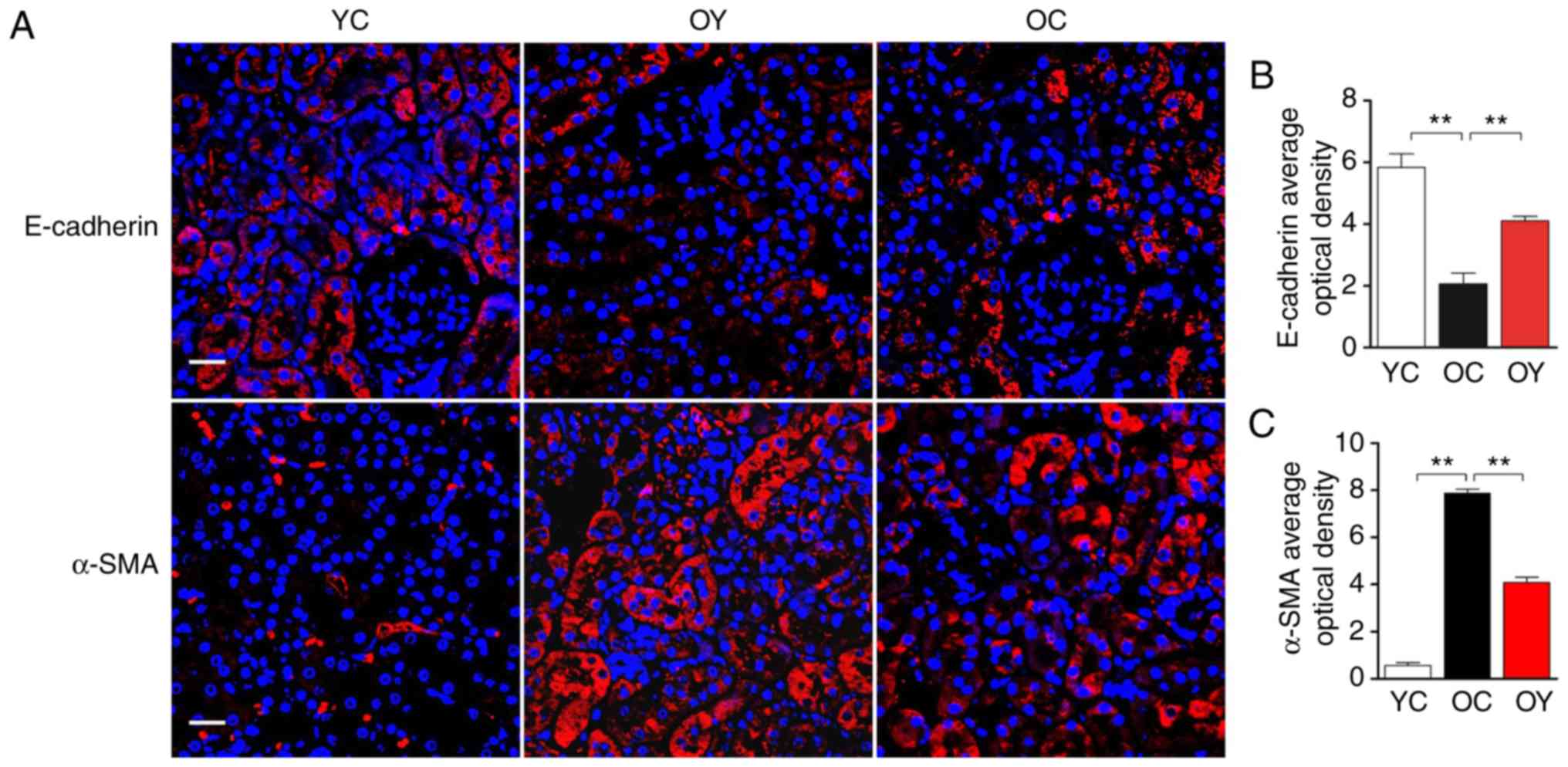
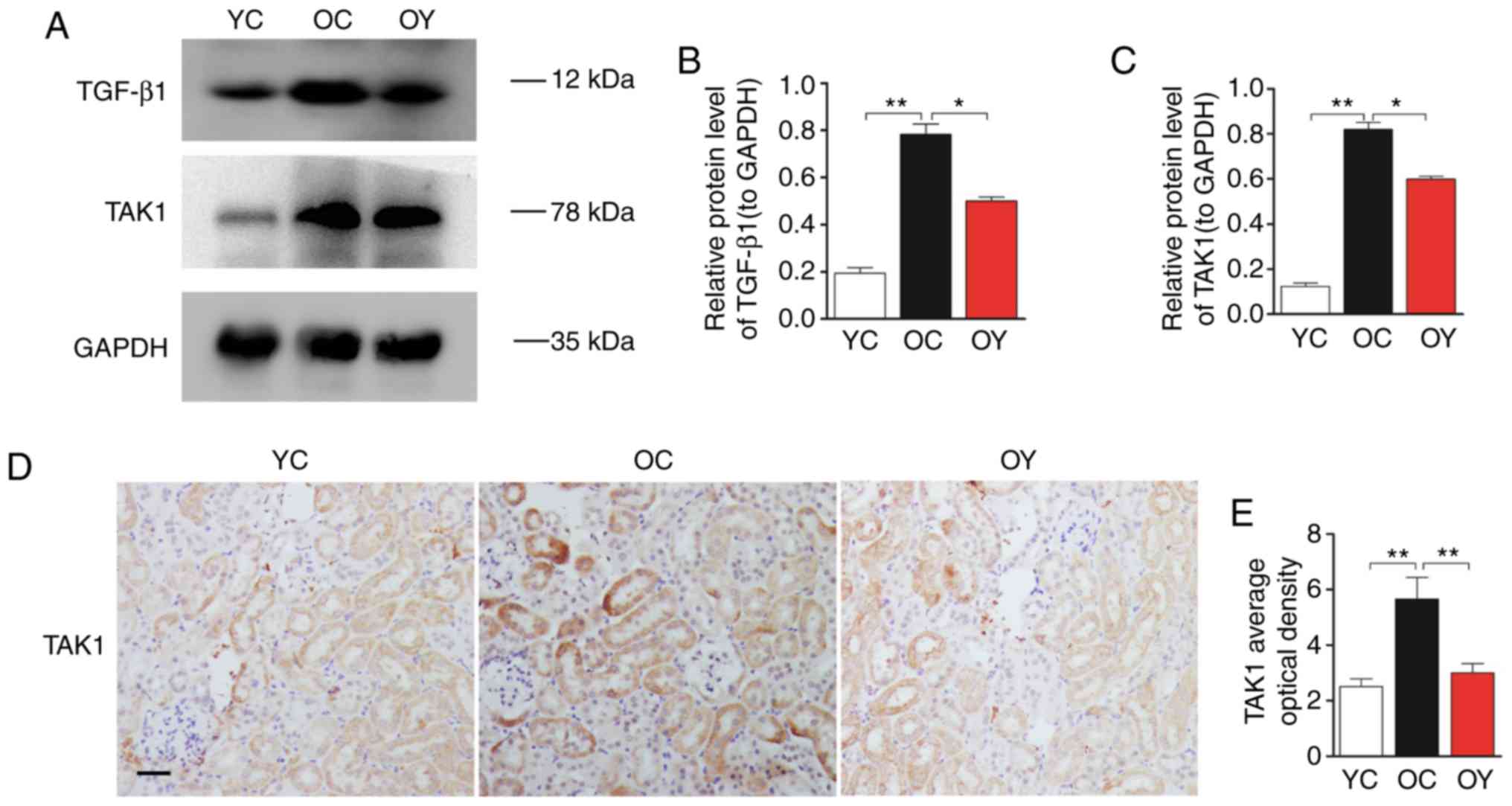
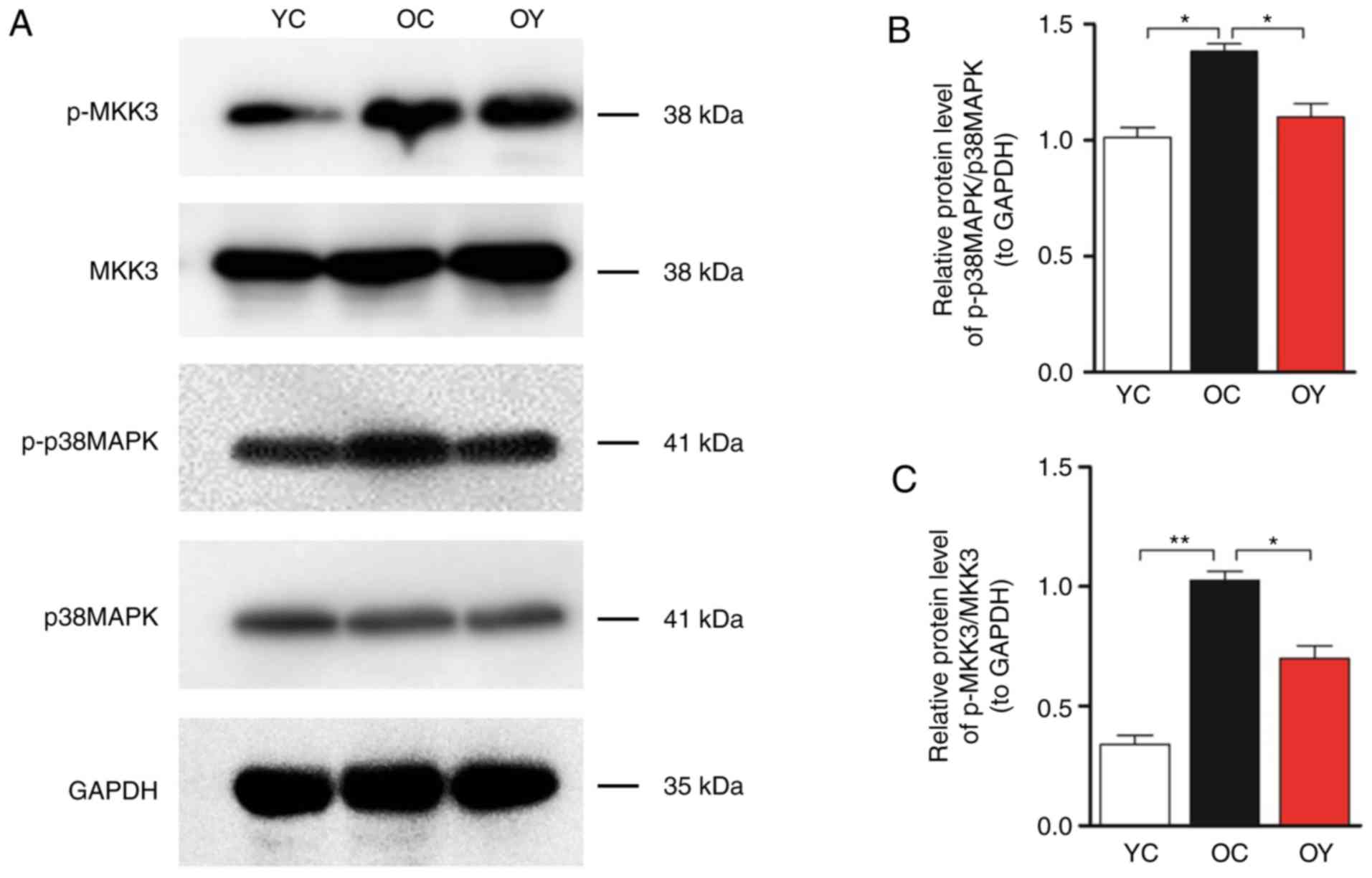
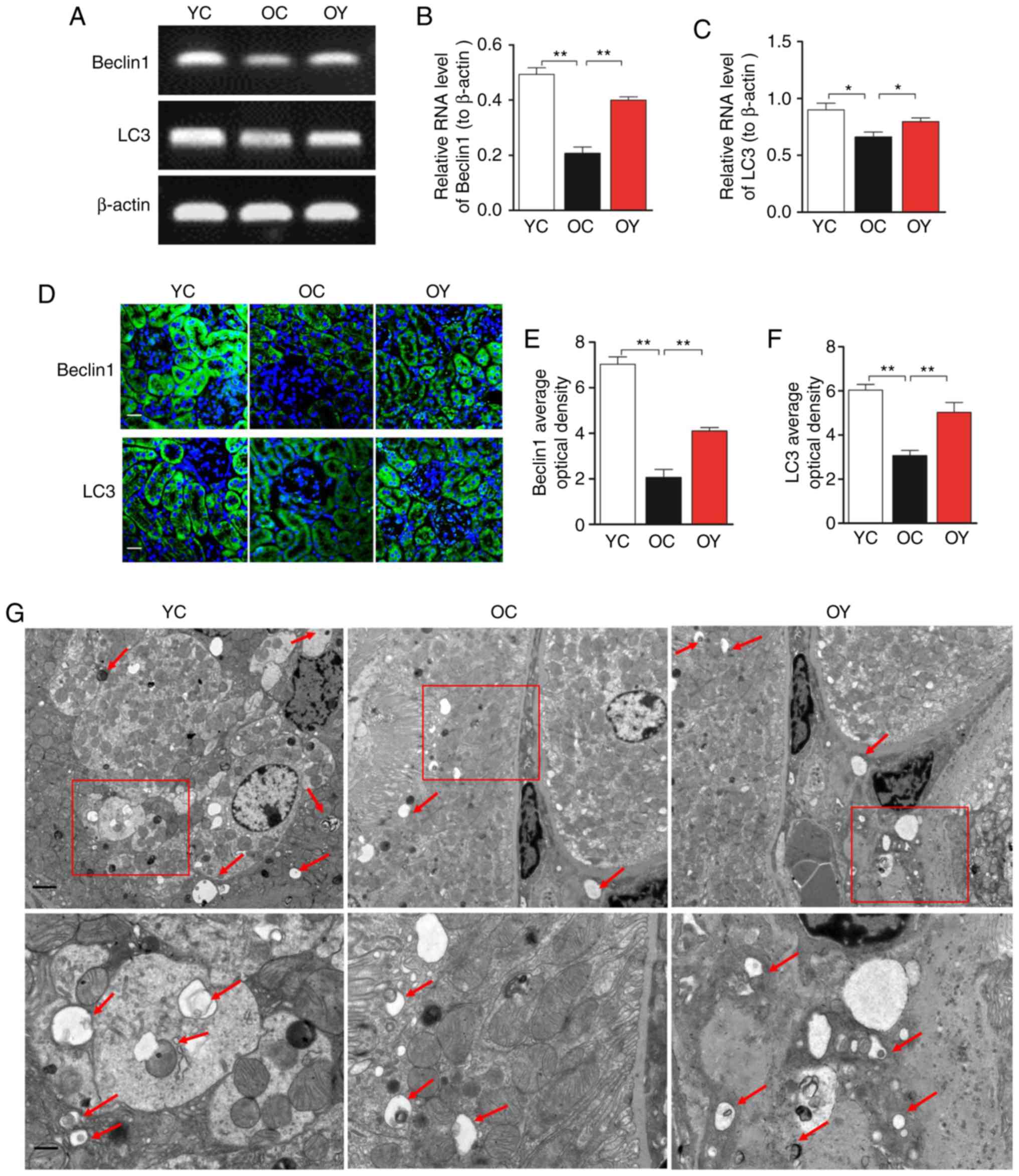
|
1
|
Liu Y: Renal fibrosis: New insights into
the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int. 69:213–217. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang HC and Fogo AB: Fibrosis and renal
aging. Kidney Int Suppl. 4:75–78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang B, Xu M, Li W, Li X, Zheng Q and Niu
X: Aerobic exercise protects against pressure overload-induced
cardiac dysfunction and hypertrophy via β3-AR-nNOS-NO activation.
PLoS One. 12:pp. e01796482017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zeina K and Jennifer T: Anatomic and
physiologic changes of the aging kidney. Clin Geriatr Med.
29:555–564. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Stone RC, Pastar I, Ojeh N, Chen V, Liu S,
Garzon KI and Tomic-Canic M: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
tissue repair and fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 365:495–506. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A,
Bochaton-Piallat ML and Gabbiani G: The myofibroblast: One
function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol. 170:1807–1816. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harikrishna T, Xu XC, Polosukhin VV,
Degryse AL, Li B, Han W, Sherrill TP, Plieth D, Neilson EG,
Blackwell TS and Lawson WE: Contribution of epithelial-derived
fibroblasts to bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 180:657–665. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Fîlfan M, Sandu RE, Zăvăleanu AD, GreşiŢă
A, Glăvan DG, Olaru DG and Popa-Wagner A: Autophagy in aging and
disease. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 58:27–31. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Samy L, Jian X and Rik D: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Biernacka A, Dobaczewski M and
Frangogiannis NG: TGF-β signaling in fibrosis. Growth Factors.
29:196–202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ding Y, Kim SL, Lee SY, Koo JK, Wang Z and
Choi ME: Autophagy regulates TGF-β expression and suppresses kidney
fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 25:2835–2846. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Islam SS, Mokhtari RB, El Hout Y, Azadi
MA, Alauddin M, Yeger H and Farhat WA: TGF-β1 induces EMT
reprogramming of porcine bladder urothelial cells into collagen
producing fibroblasts-like cells in a Smad2/Smad3-dependent manner.
J Cell Commun Signal. 8:39–58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kaur A, Riaz M, Singh SK and Kishore U:
Human surfactant protein D suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in pancreatic cancer cells by downregulating TGF-β.
Front Immunol. 15:18442018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kajino T, Omori E, Ishii S, Matsumoto K
and Ninomiya-Tsuji J: TAK1 MAPK kinase kinase mediates transforming
growth factor-beta signaling by targeting SnoN oncoprotein for
degradation. J Biol Chem. 282:9475–9481. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choi ME, Ding Y and Kim SI: TGF-β
signaling via TAK1 pathway: Role in kidney fibrosis. Semin Nephrol.
32:244–252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li J, Chen K, Li S, Feng J, Liu T, Wang F,
Zhang R, Xu S, Zhou Y, Zhou S, et al: Protective effect of fucoidan
fromFucus vesiculosuson liver fibrosis via the TGF-β1/Smad
pathway-mediated inhibition of extracellular matrix and autophagy.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 10:619–630. 2016.
|
|
17
|
Kim SI, Na HJ, Ding Y, Wang Z, Lee SJ and
Choi ME: Autophagy promotes intracellular degradation of type I
collagen induced by transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1. J Biol
Chem. 287:11677–11688. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Banks L, Buchan TA and Dizonno V: Aerobic
exercise attenuates ageing of the athletic heart. J Physiol.
594:3183–3184. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Inoue A, Cheng XW, Huang Z, Hu L, Kikuchi
R, Jiang H, Piao L, Sasaki T, Itakura K, Wu H, et al: Exercise
restores muscle stem cell mobilization, regenerative capacity and
muscle metabolic alterations via adiponectin/AdipoR1 activation in
SAMP10 mice. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 8:370–385. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Baker EJ and Gleeson TT: The effects of
intensity on the energetics of brief locomotor activity. J Exp
Biol. 202:3081–3087. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bedford TG, Tipton CM, Wilson NC, Oppliger
RA and Gisolfi CV: Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its
changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol Respir
Environ Exerc Physiol. 47:1278–1283. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Di Felice V, Macaluso F, Montalbano A,
Gammazza AM, Palumbo D, Angelone T, Bellafiore M and Farina F:
Effects of conjugated linoleic acid and endurance training on
peripheral blood and bone marrow of trained mice. J Strength Cond
Res. 21:193–198. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
O'Sullivan ED, Hughes J and Ferenbach DA:
Renal aging: Causes and consequences. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:407–420.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hou CL, Wang MJ, Sun C, Huang Y, Jin S, Mu
XP, Chen Y and Zhu YC: Protective effects of hydrogen sulfide in
the ageing kidney. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016.7570489:2016.
|
|
25
|
Lin CH, Chen J, Ziman B, Marshall S,
Maizel J and Goligorsky MS: Endostatin and kidney fibrosis in
aging: A case for antagonistic pleiotropy? . Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 306:H1692–H1699. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sangaralingham SJ, Heublein DM, Grande JP,
Cataliotti A, Rule AD, McKie PM, Martin FL and Burnett JC Jr:
Urinary C-type natriuretic peptide excretion: A potential novel
biomarker for renal fibrosis during aging. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 301:943–952. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ning YC, Cai GY, Zhuo L, Gao JJ, Dong D,
Cui S, Feng Z, Shi SZ, Bai XY, Sun XF and Chen XM: Short-term
calorie restriction protects against renal senescence of aged rats
by increasing autophagic activity and reducing oxidative damage.
Mech Ageing Dev. 134:570–579. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reyes DRA, Gomes MJ, Rosa CM, Pagan LU,
Zanati SG, Damatto RL, Rodrigues EA, Carvalho RF, Fernandes AAH,
Martinez PF, et al: Exercise during transition from compensated
left ventricular hypertrophy to heart failure in aortic stenosis
rats. J Cell Mol Med. 23:1235–1245. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Zhou CN, Chao FL, Zhang Y, Jiang L, Zhang
L, Luo YM, Xiao Q, Chen LM and Tang Y: Sex differences in the white
matter and myelinated fibers of APP/PS1 mice and the effects of
running exercise on the sex differences of AD mice. Front Aging
Neurosci. 10:2432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kou X, Li J, Liu X, Chang J, Zhao Q, Jia
S, Fan J and Chen N: Swimming attenuates D-galactose-induced brain
aging via suppressing miR-34a-mediated autophagy impairment and
abnormal mitochondrial dynamics. J Appl Physiol.
1985.122:1462–1469. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Martínez R, Kapravelou G, López-Chaves C,
Cáceres E, Coll-Risco I, Sánchez-González C, Llopis J, Arrebola F,
Galisteo M, Aranda P, et al: Aerobic interval exercise improves
renal functionality and affects mineral metabolism in obese Zucker
rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 316:F90–F100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Peng CC, Chen KC, Hsieh CL and Peng RY:
Swimming exercise prevents fibrogenesis in chronic kidney disease
by inhibiting the myofibroblast transdifferentiation. PLoS One.
7:pp. e373882012, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
El-Wakeel SA, Rahmao RM and EI-Abhar HS:
Anti-fibrotic impact of Carvedilol in a CCl-4 model of liver
fibrosis via serum microRNA-200a/SMAD7 enhancement to bridle
TGF-β1/EMT track. Sci Rep. 8:143272018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Dong D, Cai GY, Ning YC, Wang JC, Lv Y,
Hong Q, Cui SY, Fu B, Guo YN and Chen XM: Alleviation of senescence
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in aging kidney by short-term
caloric restriction and caloric restriction mimetics via modulation
of AMPK/mTOR signaling. Oncotarget. 8:16109–16121. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qi FH, Cai PP, Liu X and Si GM:
Adenovirus-mediated P311 ameliorates renal fibrosis through
inhibition of epithelial-mesen-chymal transition via
TGF-β1-Smad-ILK pathway in unilateral ureteral obstruction rats.
Int J Mol Med. 41:3015–3023. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
De Rechter S, Decuypere JP, Ivanova E, van
den Heuvel LP, De Smedt H, Levtchenko E and Mekahli D: Autophagy in
renal diseases. Pediatr Nephrol. 31:737–752. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ceylan-Isik AF, Dong M, Zhang Y, Dong F,
Turdi S, Nair S, Yanagisawa M and Ren J: Cardiomyocyte-specific
deletion of endothelin receptor A rescues aging-associated cardiac
hypertrophy and contractile dysfunction: Role of autophagy. Basic
Res Cardiol. 108:3352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang S, Abdulla R, Lu C and Zhang L:
Inhibition of microRNA-376b protects against renal interstitial
fibrosis via inducing macrophage autophagy by upregulating Atg5 in
mice with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Blood Press Res.
43:1749–1764. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ding Y and Choi ME: Regulation of
autophagy by TGF-β: Emerging role in kidney fibrosis. Semin
Nephrol. 34:62–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sosulski ML, Gongora R, Danchuk S, Dong C,
Luo F and Sanchez CG: Deregulation of selective autophagy during
aging and pulmonary fibrosis: The role of TGFβ1. Aging Cell.
14:774–783. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ono K, Ohtomo T, Ninomiya-Tsuji J and
Tsuchiya M: A dominant negative TAK1 inhibits cellular fibrotic
responses induced by TGF-β. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
307:332–337. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim SI, Kwak JH, Zachariah M, He Y, Wang L
and Choi ME: TGF-beta-activated kinase 1 and TAK1-binding protein 1
cooperate to mediate TGF-beta1-induced MKK3-p38 MAPK activation and
stimulation of type I collagen. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
292:F1471–F1478. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|