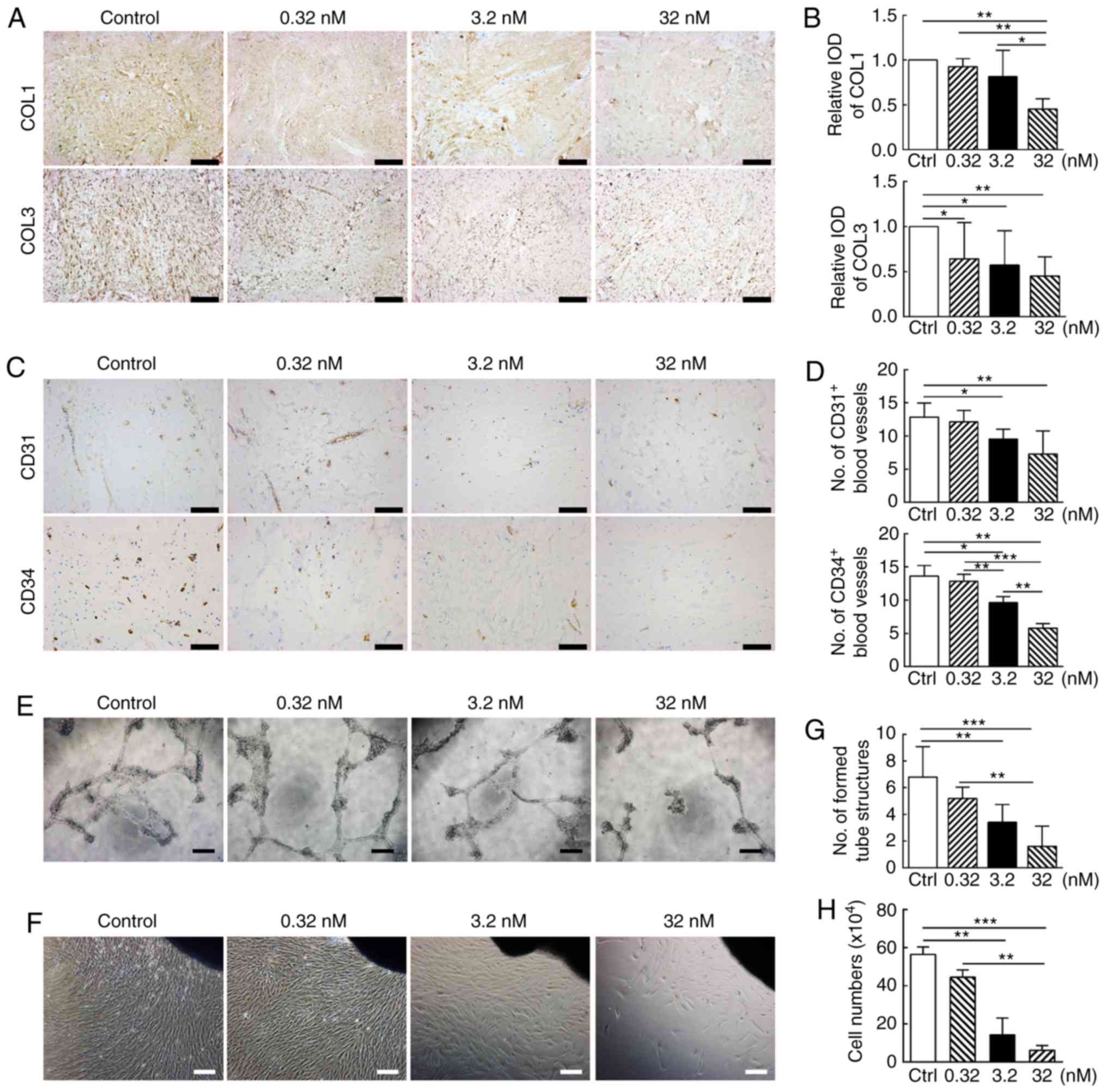
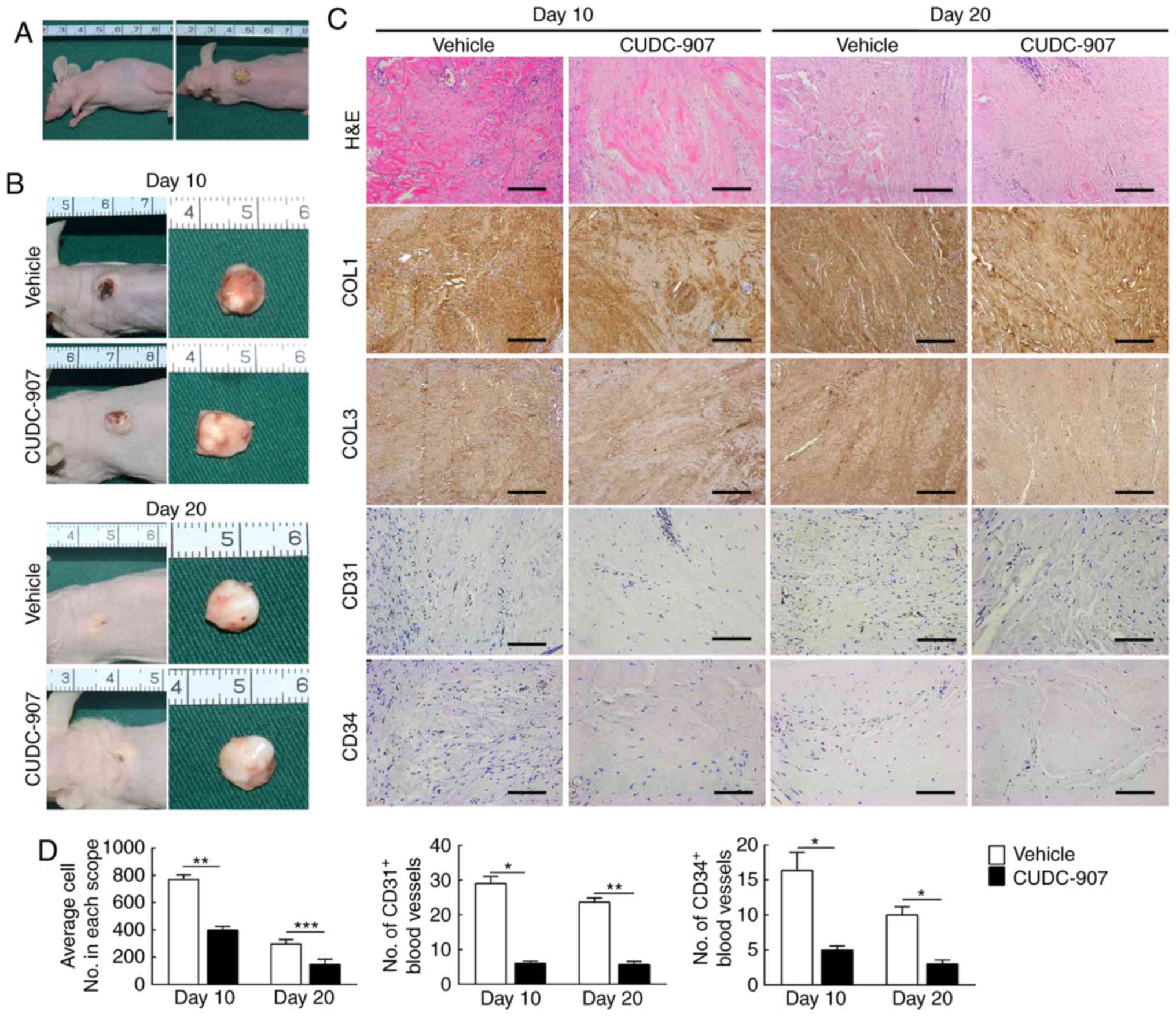
|
1
|
Ghazawi FM, Zargham R, Gilardino MS,
Sasseville D and Jafarian F: Insights into the pathophysiology of
hypertrophic scars and keloids: How do they differ? Adv Skin Wound
Care. 31:582–595. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Morelli Coppola M, Salzillo R, Segreto F
and Persichetti P: Triamcinolone acetonide intralesional injection
for the treatment of keloid scars: Patient selection and
perspectives. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 11:387–396. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Forbat E, Ali FR and Al-Niaimi F:
Treatment of keloid scars using light-, laser- and energy-based
devices: A contemporary review of the literature. Lasers Med Sci.
32:2145–2154. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Russell SB, Trupin KM, Rodriguez-Eaton S,
Russell JD and Trupin JS: Reduced growth-factor requirement of
keloid-derived fibroblasts may account for tumor growth. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 85:587–591. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vincent AS, Phan TT, Mukhopadhyay A, Lim
HY, Halliwell B and Wong KP: Human skin keloid fibroblasts display
bioener-getics of cancer cells. J Invest Dermatol. 128:702–709.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang Q, Yamaza T, Kelly AP, Shi S, Wang
S, Brown J, Wang L, French SW, Shi S and Le AD: Tumor-Like stem
cells derived from human keloid are governed by the inflammatory
niche driven by IL-17/IL-6 axis. PLoS One. 4:e77982009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jumper N, Paus R and Bayat A: Functional
histopathology of keloid disease. Histol Histopathol. 30:1033–1057.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Syed F, Sherris D, Paus R, Varmeh S,
Pandolfi PP and Bayat A: Keloid disease can be inhibited by
antagonizing excessive mTOR signaling with a novel dual TORC1/2
inhibitor. Am J Pathol. 181:1642–1658. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Diao J, Xia W, Yi C, Wang Y, Li B, Xia W,
Liu B, Guo S and Sun X: Trichostatin A inhibits collagen synthesis
and induces apoptosis in keloid fibroblasts. Arch Dermatol Res.
303:573–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yi D, Bihl J, Newman MS, Chen Y and Simman
R: The preliminary study of effects of tolfenamic acid on cell
proliferation, cell apoptosis, and intracellular collagen
deposition in keloid fibroblasts in vitro. Dermatol Res Pract.
2014.1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Syed F, Sanganee HJ, Bahl A and Bayat A:
Potent dual inhibitors of TORC1 and TORC2 complexes (KU-0063794 and
KU-0068650) demonstrate in vitro and ex vivo Anti-Keloid scar
activity. J Invest Dermatol. 133:1340–1350. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang W, Qu M, Xu L, Wu X, Gao Z, Gu T,
Zhang W, Ding X, Liu W and Chen Y: Sorafenib exerts an anti-keloid
activity by antagonizing TGF-β/Smad and MAPK/ERK signaling
pathways. J Mol Med (Berl). 94:1181–1194. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wong VW, You F, Januszyk M, Gurtner GC and
Kuang AA: Transcriptional profiling of rapamycin-treated
fibroblasts from hypertrophic and keloid scars. Ann Plast Surg.
72:711–719. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ong CT, Khoo YT, Mukhopadhyay A, Do DV,
Lim IJ, Aalami O and Phan TT: mTOR as a potential therapeutic
target for treatment of keloids and excessive scars. Exp Dermatol.
16:394–404. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fitzgerald O'Connor EJ, Badshah II, Addae
LY, Kundasamy P, Thanabalasingam S, Abioye D, Soldin M and Shaw TJ:
Histone deacetylase 2 is upregulated in normal and keloid scars. J
Invest Dermatol. 132:1293–1296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Van Beneden K, Mannaerts I, Pauwels M, Van
den Branden C and Van Grunsven LA: HDAC inhibitors in experimental
liver and kidney fibrosis. Fibrogen Tissue Repair. 6:12013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Miller TA, Witter DJ and Belvedere S:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 46:5097–5116. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qian C, Lai CJ, Bao R, Wang DG, Wang J, Xu
GX, Atoyan R, Qu H, Yin L, Samson M, et al: Cancer network
disruption by a single molecule inhibitor targeting both histone
deacetylase activity and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:4104–4113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mondello P, Derenzini E, Asgari Z, Philip
J, Brea EJ, Seshan V, Hendrickson RC, de Stanchina E, Scheinberg DA
and Younes A: Dual inhibition of histone deacetylases and
phosphoinositide 3-kinase enhances therapeutic activity against B
cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 8:14017–14028. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Younes A, Berdeja JG, Patel MR, Flinn I,
Gerecitano JF, Neelapu SS, Kelly KR, Copeland AR, Akins A, Clancy
MS, et al: Safety, tolerability, and preliminary activity of
CUDC-907, a first-in-class, oral, dual inhibitor of HDAC and PI3K,
in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma or multiple
myeloma: An open-label, dose-escalation, phase 1 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 17:622–631. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seifert O and Mrowietz U: Keloid scarring:
Bench and bedside. Arch Dermatol Res. 301:259–272. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang W, Li J, Wang K, Zhang Z, Zhang W,
Zhou G, Cao Y, Ye M, Zou H and Liu W: Induction of predominant
tenogenic phenotype in human dermal fibroblasts via synergistic
effect of TGF-β and elongated cell shape. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 310:C357–C372. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Arnaoutova I and Kleinman HK: In vitro
angiogenesis: Endothelial cell tube formation on gelled basement
membrane extract. Nat Protoc. 5:628–635. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ward Kischer C, Sheridan D and Pindur J:
Use of nude (athymic) mice for the study of hypertrophic scars and
keloids: Vascular continuity between mouse and implants. Anat Rec.
225:189–196. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ni C, Li C, Dong Y, Guo X, Zhang Y and Xie
Z: Anesthetic isoflurane induces DNA damage through oxidative
stress and p53 pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 54:3591–3605. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Koutsogiannaki S, Zha H and Yuki K:
Volatile anesthetic isoflurane attenuates liver injury in
experimental polymicrobial sepsis model. Transl Perioper Pain Med.
5:63–74. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Borowiak R, Reichardt W, Kurzhunov D,
Schuch C, Leupold J, Krafft AJ, Reisert M, Lange T, Fischer E and
Bock M: Initial investigation of glucose metabolism in mouse brain
using enriched 17O-glucose and dynamic
17O-MRS. NMR Biomed. 30:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Johansson N, Ahonen M and Kähäri VM:
Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion. Cell Mol Life Sci.
57:5–15. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mogili NS, Krishnaswamy VR, Jayaraman M,
Rajaram R, Venkatraman A and Korrapati PS: Altered angiogenic
balance in keloids: A key to therapeutic intervention. Transl Res.
159:182–189. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pisacane AM, Picciotto F and Risio M: CD31
and CD34 expression as immunohistochemical markers of endothelial
transdifferentiation in human cutaneous melanoma. Cell Oncol.
29:59–66. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Unahabhokha T, Sucontphunt A, Nimmannit U,
Chanvorachote P, Yongsanguanchai N and Pongrakhananon V: Molecular
signalings in keloid disease and current therapeutic approaches
from natural based compounds. Pharm Biol. 53:457–463. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bijlard E, Steltenpool S and Niessen FB:
Intralesional 5-Fluorouracil in keloid treatment: A systematic
review. Acta Derm Venerol. 95:778–782. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ud-Din S and Bayat A: New insights on
keloids, hypertrophic scars, and striae. Dermatol Clin. 32:193–209.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mari W, Alsabri SG, Tabal N, Younes S,
Sherif A and Simman R: Novel insights on understanding of keloid
scar: Article review. J Am Coll Clin Wound Spec. 7:1–7. 2016.
|
|
35
|
Andrews JP, Marttala J, Macarak E,
Rosenbloom J and Uitto J: Keloids: The paradigm of skin
fibrosis-pathomechanisms and treatment. Matrix Biol. 51:37–46.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Runyan CE, Schnaper HW and Poncelet AC:
The phosphati-dylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway enhances
Smad3-stimulated mesangial cell collagen I expression in response
to transforming growth factor-beta1. J Biol Chem. 279:2632–2639.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lopiccolo J, Blumenthal GM, Bernstein WB
and Dennis PA: Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: Effective
combinations and clinical considerations. Drug Resist Update.
11:32–50. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Carracedo A, Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J,
Rojo F, Salmena L, Alimonti A, Egia A, Sasaki AT, Thomas G, Kozma
SC, et al: Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation
through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J Clin
Invest. 118:3065–3074. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wee S, Jagani Z, Xiang KX, Loo A, Dorsch
M, Yao YM, Sellers WR, Lengauer C and Stegmeier F: PI3K pathway
activation mediates resistance to MEK inhibitors in KRAS mutant
cancers. Cancer Res. 69:4286–4293. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jia J, Zhu F, Ma X, Cao ZW, Li YX and Chen
YZ: Mechanisms of drug combinations: Interaction and network
perspectives. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:111–128. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pei Y, Liu KW, Wang J, Garancher A, Tao R,
Esparza LA, Maier DL, Udaka YT, Murad N, Morrissy S, et al: HDAC
and PI3K antagonists cooperate to inhibit growth of MYC-driven
medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell. 29:311–323. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wozniak MB, Villuendas R, Bischoff JR,
Aparicio CB, Martínez Leal JF, de La Cueva P, Rodriguez ME,
Herreros B, Martin-Perez D, Longo MI, et al: Vorinostat interferes
with the signaling transduction pathway of T-cell receptor and
synergizes with phosphoinositide-3 kinase inhibitors in cutaneous
T-cell lymphoma. Haematologica. 95:613–621. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Delcuve GP, Khan DH and Davie JR:
Targeting class I histone deacetylases in cancer therapy. Expert
Opin Ther Tar. 17:29–41. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kawada J, Ito Y, Iwata S, Suzuki M, Kawano
Y, Kanazawa T, Siddiquey MN and Kimura H: mTOR inhibitors induce
cell-cycle arrest and inhibit tumor growth in Epstein-Barr
virus-associated T and natural killer cell lymphoma cells. Clin
Cancer Res. 20:5412–5422. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cuyas E, Corominas-Faja B, Joven J and
Menendez JA: Cell cycle regulation by the nutrient-sensing
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. Methods Mol Biol.
1170:113–144. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Loos C, Syrovets T, Musyanovych A,
Mailänder V, Landfester K and Simmet T: Amino-functionalized
nanoparticles as inhibitors of mTOR and inducers of cell cycle
arrest in leukemia cells. Biomaterials. 35:1944–1953. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Du L, Risinger AL, King JB, Powell DR and
Cichewicz RH: A potent HDAC inhibitor, 1-Alaninechlamydocin, from a
Tolypocladium sp. induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in
MIA PaCa-2 cells. J Nat Prod. 77:1753–1757. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Feng W, Cai D, Zhang B, Lou G and Zou X:
Combination of HDAC inhibitor TSA and silibinin induces cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis by targeting survivin and cyclinB1/cdk1 in
pancreatic cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 74:257–264. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ramakrishnan S, Ku S, Ciamporcero E, Miles
KM, Attwood K, Chintala S, Shen L, Ellis L, Sotomayor P, Swetzig W,
et al: HDAC 1 and 6 modulate cell invasion and migration in clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 16:6172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tian H, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Li S, Liu Y and
Han X: Effects of BENC-511, a novel PI3K inhibitor, on the
proliferation and apoptosis of A549 human lung adenocarcinoma
cells. Biosci Trends. 13:40–48. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Eto S, Saeki K, Yoshitake R, Yoshimoto S,
Shinada M, Ikeda N, Kamoto S, Tanaka Y, Kato D, Maeda S, et al:
Anti-tumor effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat
on canine urothelial carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 14:e02183822019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Huang WW, Tsai SC, Peng SF, Lin MW, Chiang
JH, Chiu YJ, Fushiya S, Tseng MT and Yang JS: Kaempferol induces
autophagy through AMPK and AKT signaling molecules and causes G2/M
arrest via downregulation of CDK1/cyclin B in SK-HEP-1 human
hepatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 42:2069–2077. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Makarević J, Rutz J, Juengel E, Maxeiner
S, Tsaur I, Chun FK, Bereiter-Hahn J and Blaheta RA: Influence of
the HDAC inhibitor valproic acid on the growth and proliferation of
temsirolimus-resistant prostate cancer cells in vitro. Cancers
(Basel). 11. pp. E5662019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sun Z, Cao B and Wu J: Protease-activated
receptor 2 enhances renal cell carcinoma cell invasion and
migration via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Exp Mol Pathol.
98:382–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhou H, Jiang S, Chen J, Ren X, Jin J and
Su SB: Largazole, an inhibitor of class I histone deacetylases,
attenuates inflammatory corneal neovascularization. Eur J
Pharmacol. 740:619–626. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bian X, Liang Z, Feng A, Salgado E and
Shim H: HDAC inhibitor suppresses proliferation and invasion of
breast cancer cells through regulation of miR-200c targeting CRKL.
Biochem Pharmacol. 147:30–37. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Luo K: Signaling cross talk between
TGF-β/Smad and other signaling pathways. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 9:a0221372017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Guo W, Shan B, Klingsberg RC, Qin X and
Lasky JA: Abrogation of TGF-beta1-induced fibroblast-myofibroblast
differentiation by histone deacetylase inhibition. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 297:L864–L870. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bettinger DA, Yager DR, Diegelmann RF and
Cohen KI: The effect of TGF-beta on keloid fibroblast proliferation
and collagen synthesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 98:827–833. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Peltonen J, Hsiao LL, Jaakkola S, Sollberg
S, Aumailley M, Timpl R, Chu M and Uitto J: Activation of collagen
gene expression in keloids: Co-localization of type I and VI
collagen and transforming growth factor-beta1 mRNA. J Invest
Dermatol. 97:240–248. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lim IJ, Phan TT, Tan EK, Nguyen TT, Tran
E, Longaker MT, Song C, Lee ST and Huynh HT: Synchronous activation
of ERK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways is required for
collagen and extracellular matrix production in keloids. J Biol
Chem. 278:40851–40858. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|