|
1
|
Nam H, Jung H, Kim Y, Kim B, Kim KH, Park
SJ and Suh JG: Aged black garlic extract regulates lipid metabolism
by inhibiting lipogenesis and promoting lipolysis in mature 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Food Sci Biotechnol. 27:575–579. 2017.
|
|
2
|
Li Z, Le W and Cui Z: A novel therapeutic
anticancer property of raw garlic extract via injection but not
ingestion. Cell Death Discov. 4:1082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dwivedi VP, Bhattacharya D, Singh M,
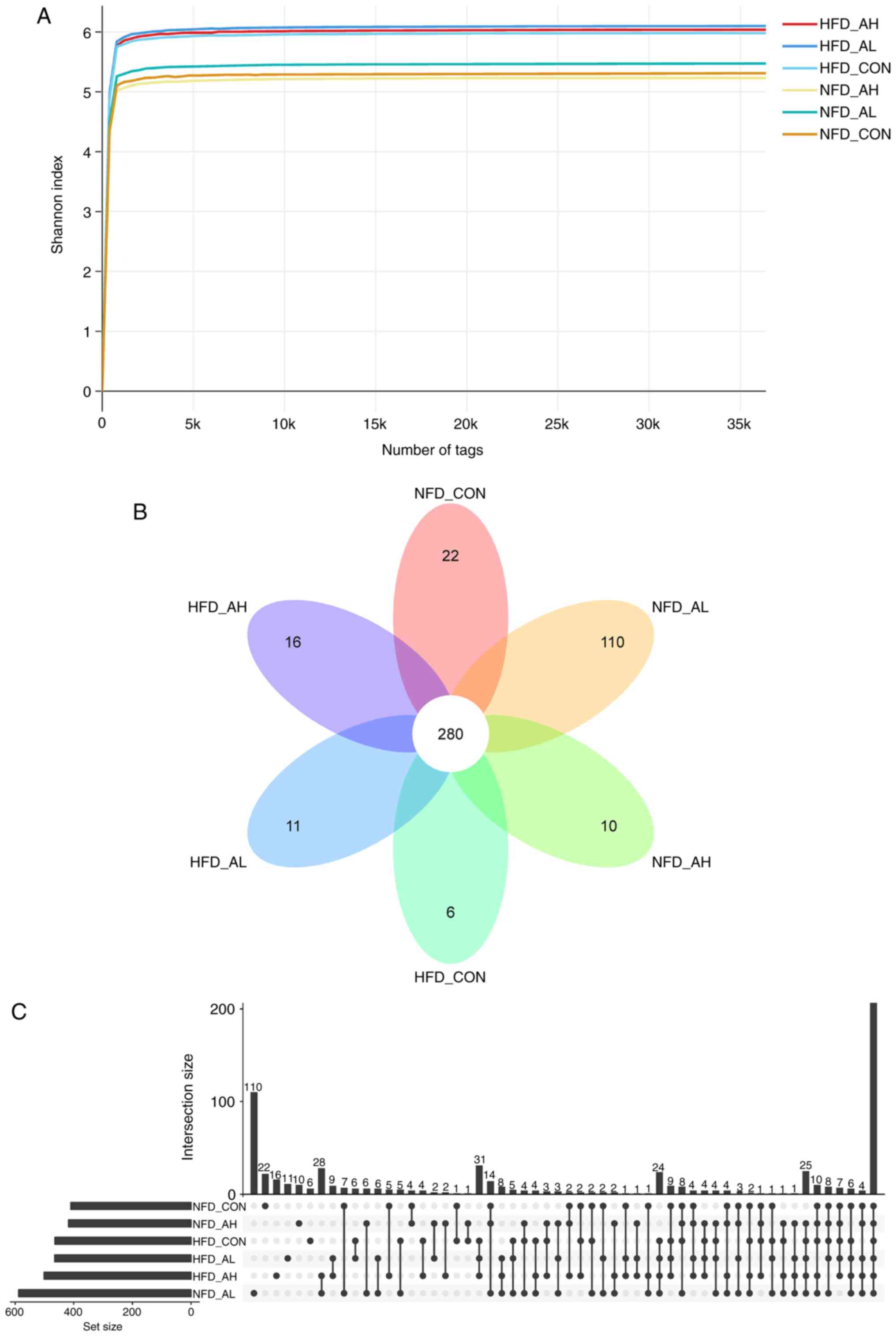
Bhaskar A, Kumar S, Fatima S, Sobia P, Kaer LV and Das G: Allicin
enhances antimicrobial activity of macrophages during Mycobacterium
tuberculosis infection. J Ethnopharmacol. 243:1116342019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Behrouj H, Ziamajidi N, Abbasalipourkabir
R, Goodarzi MT and Saidijam M: Hypoglycemic and antioxidant effects
of oral administration of garlic extract in the livers of type 1
diabetic rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 30:245–250. 2018.
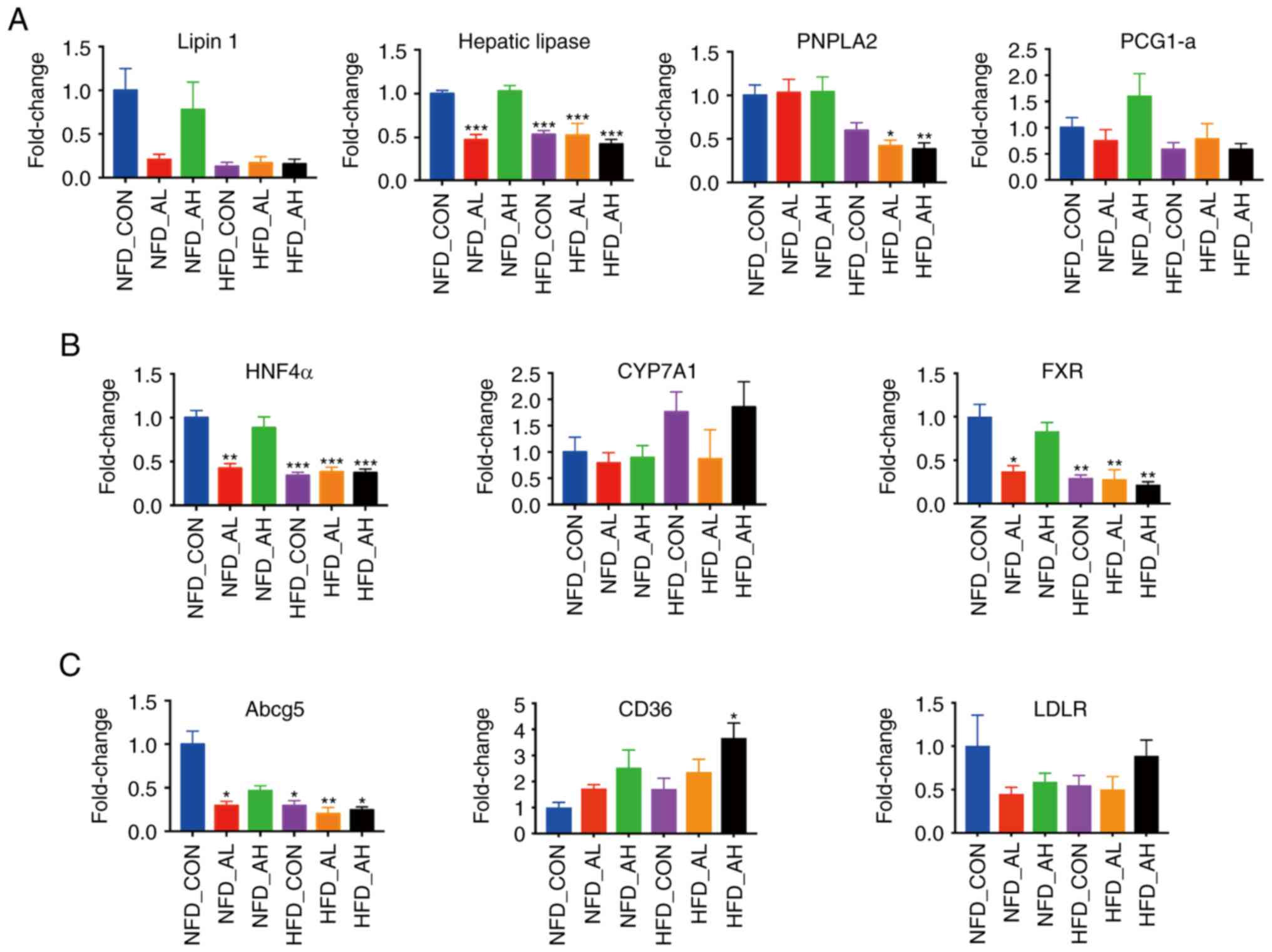
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
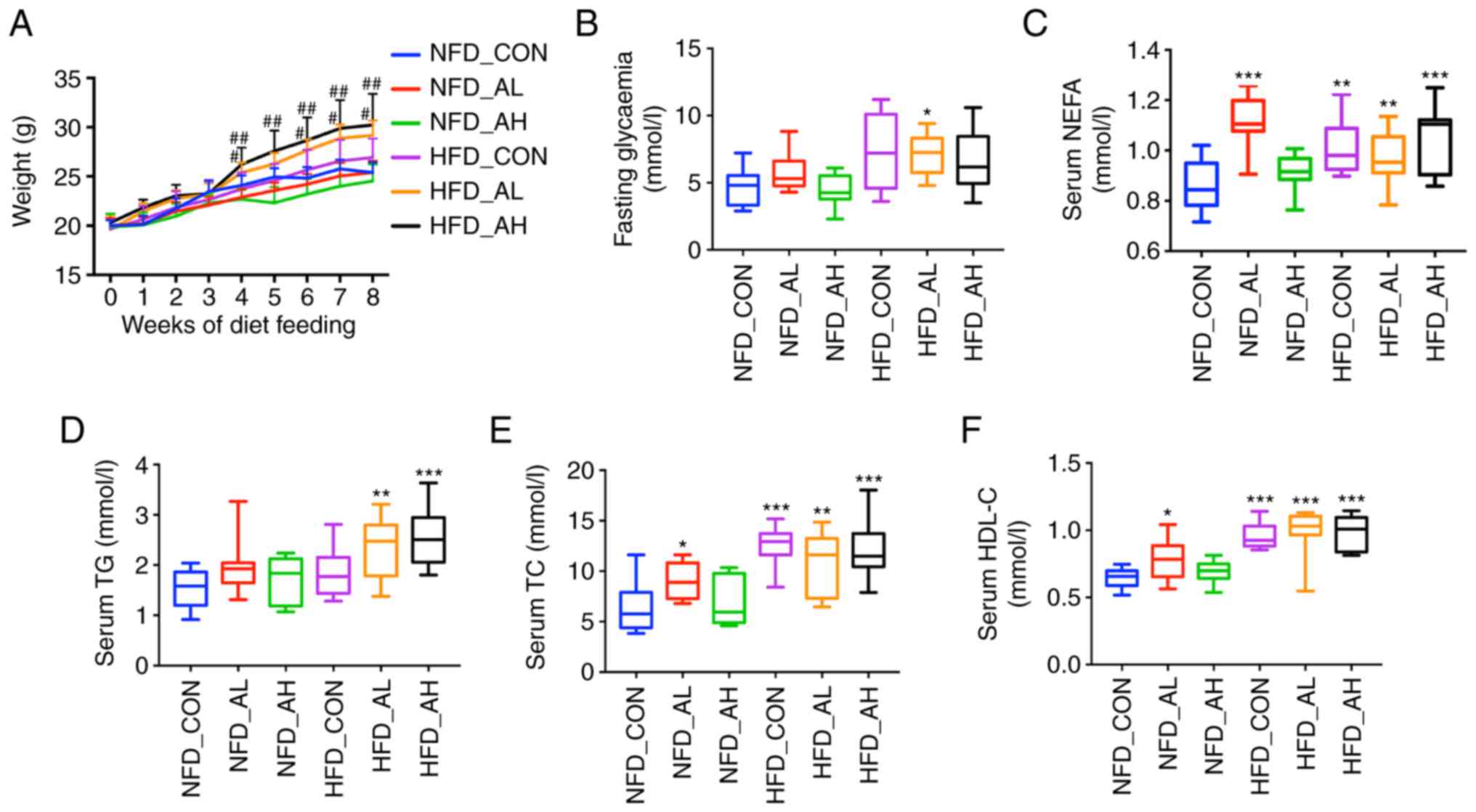
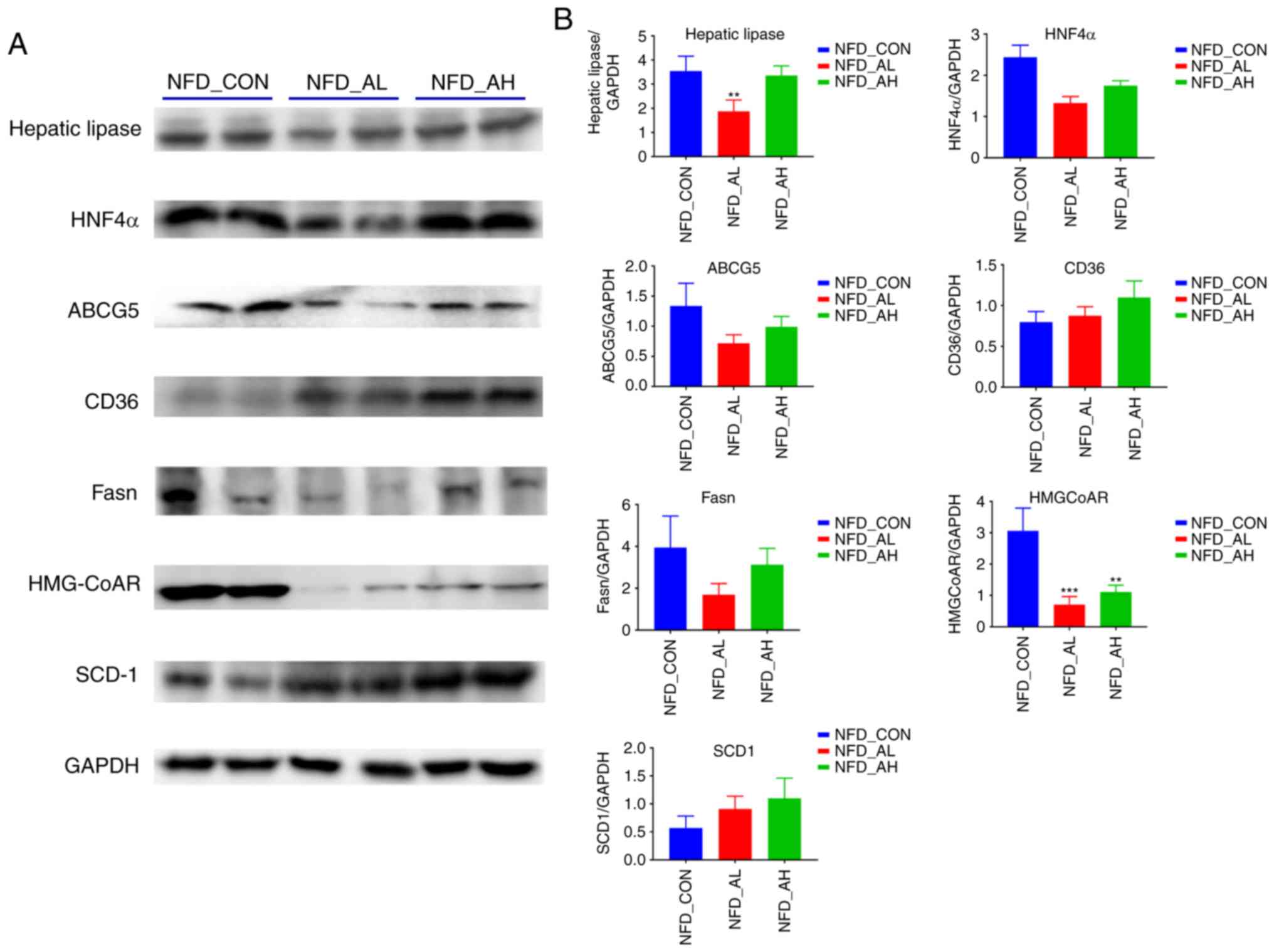
|
5
|
Das B and Sinha D: Diallyl disulphide
suppresses the cannonical Wnt signaling pathway and reverses the
fibronectin-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition of A549 lung
cancer cells. Food Funct. 10:191–202. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Su B, Su J, Zeng Y, Ding E, Liu F, Tan T,
Xia H, Wu YH, Zeng X, Ling H, et al: Diallyl disulfide inhibits
TGF-β1-induced upregulation of Rac1 and β-catenin in
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor growth of gastric
cancer. Oncol Rep. 39:2797–2806. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Wang Z, Li J and Sang X: Diallyl
disulfide suppresses FOXM1-mediated proliferation and invasion in
osteosarcoma by upregulating miR-134. J Cell Biochem. Nov 1. pp.
2018Epub ahead of print.
|
|
8
|
Ko JW, Jeong SH, Kwon HJ, Shin NR, Seo YS,
Kim JC, Shin IS and Kim JS: Preventive effect of garlic oil and its
organosulfur component diallyl-disulfide on cigarette smoke-induced
airway inflammation in mice. Nutrients. 10:E16592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Singh AK, Bishayee A and Pandey AK:
Targeting histone deacetylases with natural and synthetic agents:
An emerging anticancer strategy. Nutrients. 10:E7312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang Y, Chi Z, Gao R and Lei Z: The roles
of natural compounds in epigenetics. Nat Product Commun.
13:1067–1072. 2018.
|
|
11
|
Schroeder BO and Bäckhed F: Signals from
the gut microbiota to distant organs in physiology and disease. Nat
Med. 22:1079–1089. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gart E, Souto Lima E, Schuren F, de Ruiter
CGF, Attema J, Verschuren L, Keijer J, Salic K, Morrison MC and
Kleemann R: Diet-independent correlations between bacteria and
dysfunction of gut, adipose tissue, and liver: A comprehensive
microbiota analysis in feces and mucosa of the ileum and colon in
obese mice with NAFLD. Int J Mol Sci. 20:E12018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hrncir T, Hrncirova L, Kverka M and
Tlaskalova-Hogenova H: The role of gut microbiota in intestinal and
liver diseases. Lab Anim. 53:271–280. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Filocamo A, Nueno-Palop C, Bisignano C,
Mandalari G and Narbad A: Effect of garlic powder on the growth of
commensal bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract. Phytomedicine.
19:707–711. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Guan M, Zhao X and Li X: Effects
of garlic polysaccha-ride on alcoholic liver fibrosis and
intestinal microflora in mice. Pharm Biol. 56:325–332. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nair AB and Jacob S: A simple practice
guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin
Pharm. 7:27–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lai YS, Chen WC, Ho CT, Lu KH, Lin SH,
Tseng HC, Lin SY and Sheen LY: Garlic essential oil protects
against obesity-triggered nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through
modulation of lipid metabolism and oxidative stress. J Agric Food
Chem. 62:5897–5906. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang YH, Lei ZL, Huang L, Yang F, Zhang N,
Yuan J, Li K, Chen J and Zhang J: Antitumor ability of berberine
accompanied by modulation of gut microbiome in sarcoma-180
tumor-bearing mice. Int J Pharmacol. 14:460–470. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J,
Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich
JK, Gordon JI, et al: QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput
community sequencing data. Nat Methods. 7:335–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Edgar RC: UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU
sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods. 10:996–998.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM and Cole JR:
Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences
into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol.
73:5261–5267. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kemp PF and Aller JY: Bacterial diversity
in aquatic and other environments: What 16S rDNA libraries can tell
us. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 47:161–177. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Frosini BV: Descriptive measures of
ecological diversity. Environmetrics, in Encyclopedia of Life
Support Systems (EOLSS). Developed under the Auspices of the UNESCO
Eolss Publishers; Oxford: 2004, http://www.eolss.net/ebooks/sample%20chapters/c02/e4-26-01-01.pdf
|
|
24
|
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D,
Miropolsky L, Garrett WS and Huttenhower C: Metagenomic biomarker
discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 12:R602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bae J, Kumazoe M, Fujimura Y and Tachibana
H: Diallyl disulfide potentiates anti-obesity effect of green tea
in high-fat/high-sucrose diet-induced obesity. J Nutr Biochem.
64:152–161. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ryu JH and Kang D: Physicochemical
properties, biological activity, health benefits, and general
limitations of aged black garlic: A review. Molecules. 22:E9192017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hosseini A and Hosseinzadeh H: A review on
the effects of Allium sativum (Garlic) in metabolic syndrome. J
Endocrinol Invest. 38:1147–1157. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Elkayam A, Mirelman D, Peleg E, Wilchek M,
Miron T, Rabinkov A, Oron-Herman M and Rosenthal T: The effects of
allicin on weight in fructose-induced hyperinsulinemic,
hyper-lipidemic, hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens.
16:1053–1056
|
|
29
|
Lee CG, Rhee DK, Kim BO, Um SH and Pyo S:
Allicin induces beige-like adipocytes via KLF15 signal cascade. J
Nutr Biochem. 64:13–24. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Shi Q, Hornsby PJ, Meng Q, Vandeberg JF
and Vandeberg JL: Longitudinal analysis of short-term high-fat diet
on endothelial senescence in baboons. Am J Cardiovasc Dis.
3:107–119. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
You M, Jogasuria A, Lee K, Wu J, Zhang Y,
Lee YK and Sadana P: Signal transduction mechanisms of alcoholic
fatty liver disease: Emerging role of Lipin-1. Curr Mol Pharmacol.
10:226–236. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen Y, Rui BB, Tang LY and Hu CM: Lipin
family proteins-key regulators in lipid metabolism. Ann Nutr Metab.
66:10–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Silbernagel G, Scharnagl H, Kleber ME,
Delgado G, Stojakovic T, Laaksonen R, Erdmann J, Rankinen T,
Bouchard C, Landmesser U, et al: LDL triglycerides, hepatic lipase
activity, and coronary artery disease: An epidemiologic and
Mendelian randomization study. Atherosclerosis. 282:37–44. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Y, Matye D, Nguyen N, Zhang Y and Li
T: HNF4α regulates CSAD to couple hepatic taurine production to
bile acid synthesis in mice. Gene Expr. 18:187–196. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Miquilena-Colina ME, Lima-Cabello E,
Sánchez-Campos S, García-Mediavilla MV, Fernández-Bermejo M,
Lozano-Rodríguez T, Vargas-Castrillón J, Buqué X, Ochoa B,
Aspichueta P, et al: Hepatic fatty acid translocase CD36
upregulation is associated with insulin resistance,
hyperinsulinaemia and increased steatosis in non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis and chronic hepatitis C. Gut. 60:1394–1402. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Seo YJ, Lee K, Song JH, Chei S and Lee BY:
Ishige okamurae extract suppresses obesity and hepatic steatosis in
high fat diet-induced obese mice. Nutrients. 10:E18022018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bozic M, Guzmán C, Benet M, Sánchez-Campos
S, García-Monzón C, Gari E, Gatius S, Valdivielso JM and Jover R:
Hepatocyte vitamin D receptor regulates lipid metabolism and
mediates experimental diet-induced steatosis. J Hepatol.
65:748–757. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang F, Sun W, Chen J, Jiang L, Yang P,
Huang Y, Gong A, Liu S and Ma S: SREBP-2, a new target of
metformin? . Drug Des Devel Ther. 12:4163–4170. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sakr HF, Hussein AM, Eid EA and AlKhateeb
M: Possible mechanisms underlying fatty liver in a rat model of
male hypogonadism: A protective role for testosterone. Steroids.
135:21–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu J, Cinar R, Xiong K, Godlewski G,
Jourdan T, Lin Y, Ntambi JM and Kunos G: Monounsaturated fatty
acids generated via stearoyl CoA desaturase-1 are endogenous
inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:18832–188327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de Fourmestraux V, Neubauer H, Poussin C,
Farmer P, Falquet L, Burcelin R, Delorenzi M and Thorens B:
Transcript profiling suggests that differential metabolic
adaptation of mice to a high fat diet is associated with changes in
liver to muscle lipid fluxes. J Biol Chem. 279:50743–50753. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gallego-Escuredo JM, Gómez-Ambrosi J,
Catalan V, Domingo P, Giralt M, Frühbeck G and Villarroya F:
Opposite alterations in FGF21 and FGF19 levels and disturbed
expression of the receptor machinery for endocrine FGFs in obese
patients. Int J Obes (Lond). 39:121–129. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhang F, Yu L, Lin X, Cheng P, He L, Li X,
Lu X, Tan Y, Yang H, Cai L and Zhang C: Minireview: Roles of
fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in metabolic regulation and
chronic diseases. Mol Endocrinol. 29:1400–1413. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gérard C and Vidal H: Impact of gut
microbiota on host glycemic control. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
10:pp. 292019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Halawa MR, El-Salam MA, Mostafa BM and
Sallout SS: The gut microbiome, lactobacillus acidophilus; relation
with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rev. Feb 6–2019, Epub
ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ai D, Pan H, Han R, Li X, Liu G, Xia LC,
et al: Using decision tree aggregation with random forest model to
identify gut microbes associated with colorectal cancer. Genes
(Basel). 10. pp. E1122019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini
V, Mardis ER and Gordon JI: An obesity-associated gut microbiome
with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 444:1027–1031.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Islam KB, Fukiya S, Hagio M, Fujii N,
Ishizuka S, Ooka T, Ogura Y, Hayashi T and Yokota A: Bile acid is a
host factor that regulates the composition of the cecal microbiota
in rats. Gastroenterology. 141:1773–1781. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zheng X, Huang F, Zhao A, Lei S, Zhang Y,
Xie G, Chen T, Qu C, Rajani C, Dong B, et al: Bile acid is a
significant host factor shaping the gut microbiome of diet-induced
obese mice. BMC Biol. 15:1202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Belizário JE, Faintuch J and
Garay-Malpartida M: Gut micro-biome dysbiosis and immunometabolism:
New frontiers for treatment of metabolic diseases. Mediators
Inflamm. 2018.2037838:2018.
|
|
51
|
Litvak Y, Byndloss MX, Bäumler AJ, et al:
Colonocyte metabolism shapes the gut microbiota. Science. 362:pp.
eaat90762018, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|