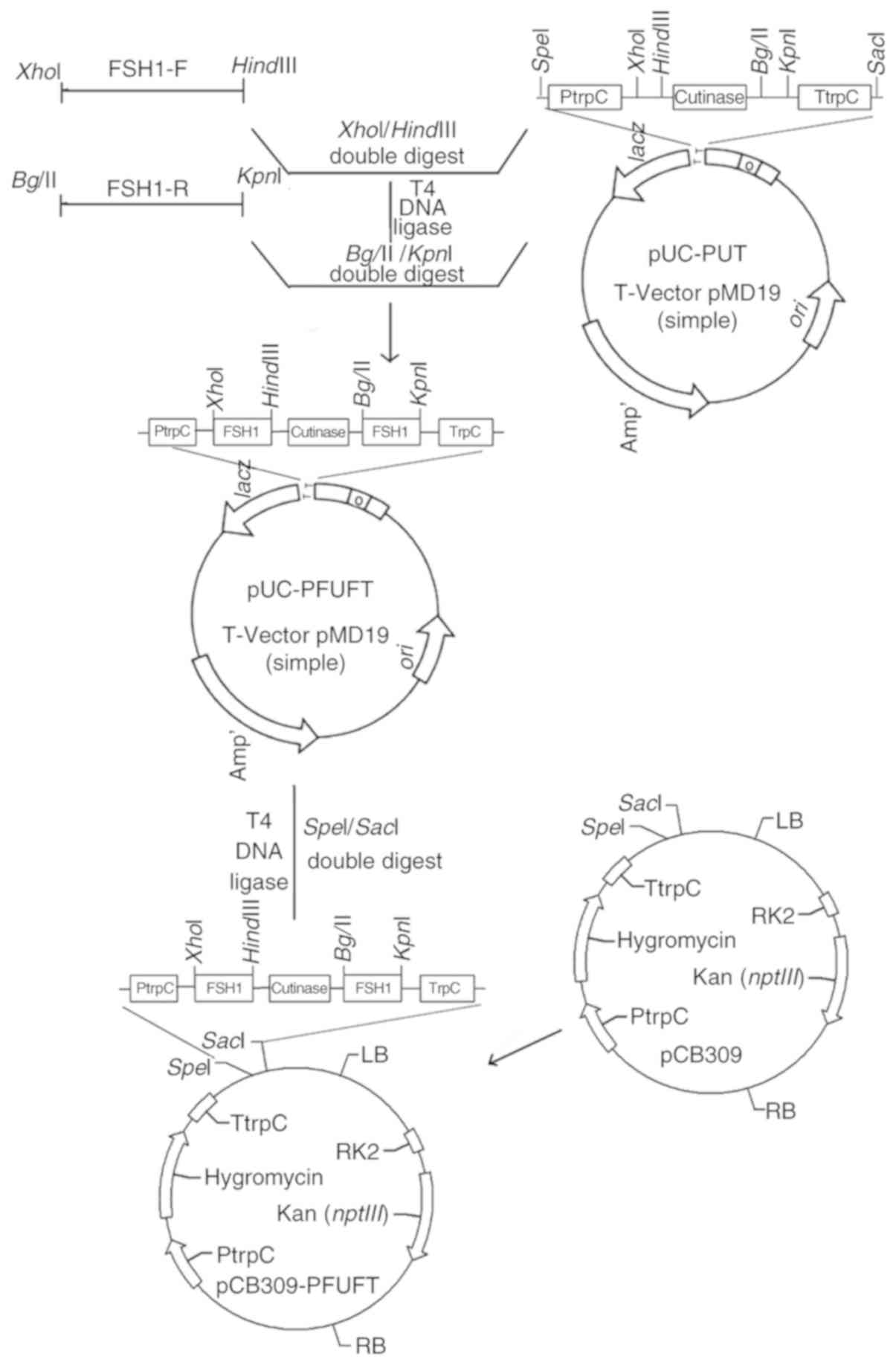
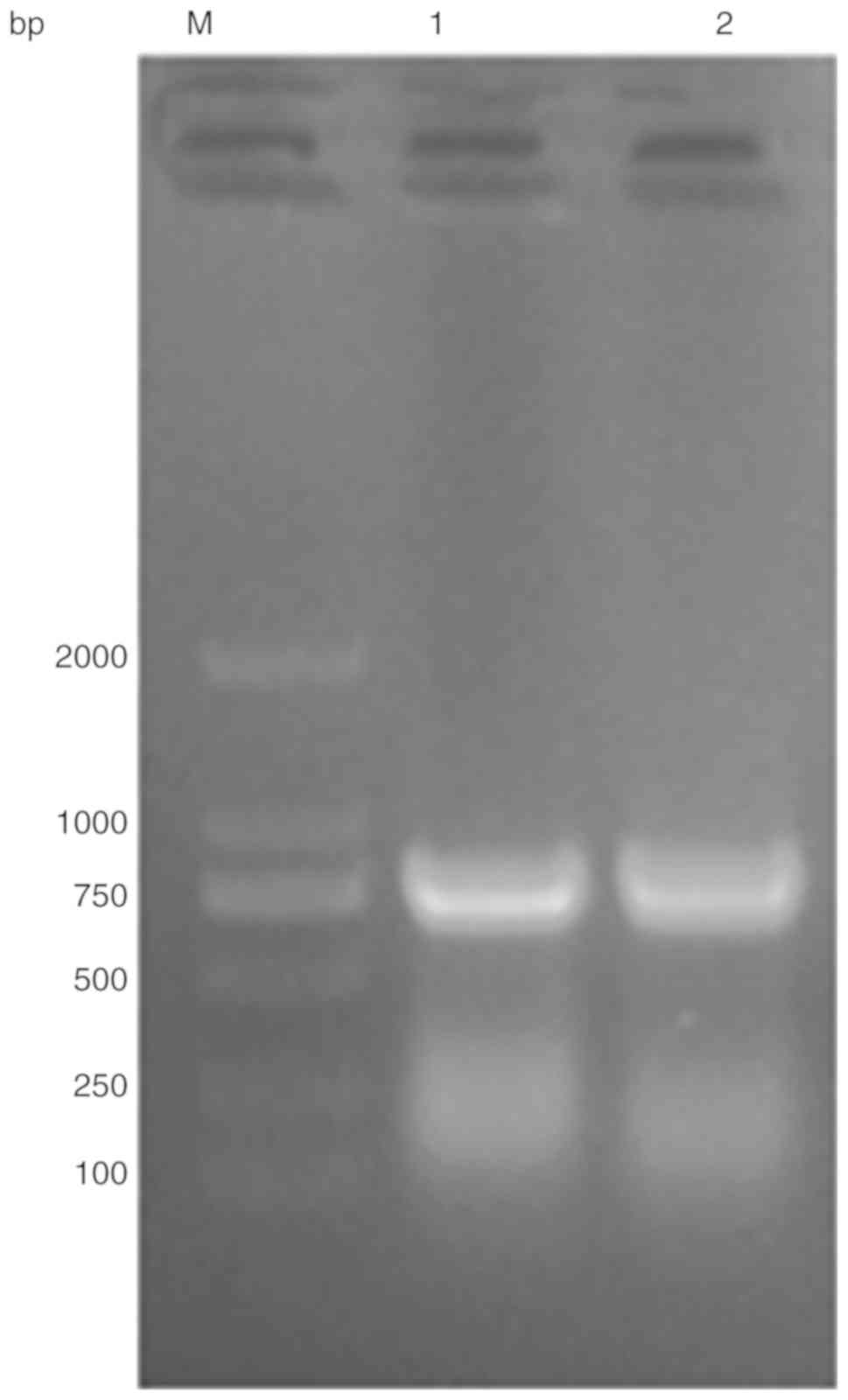
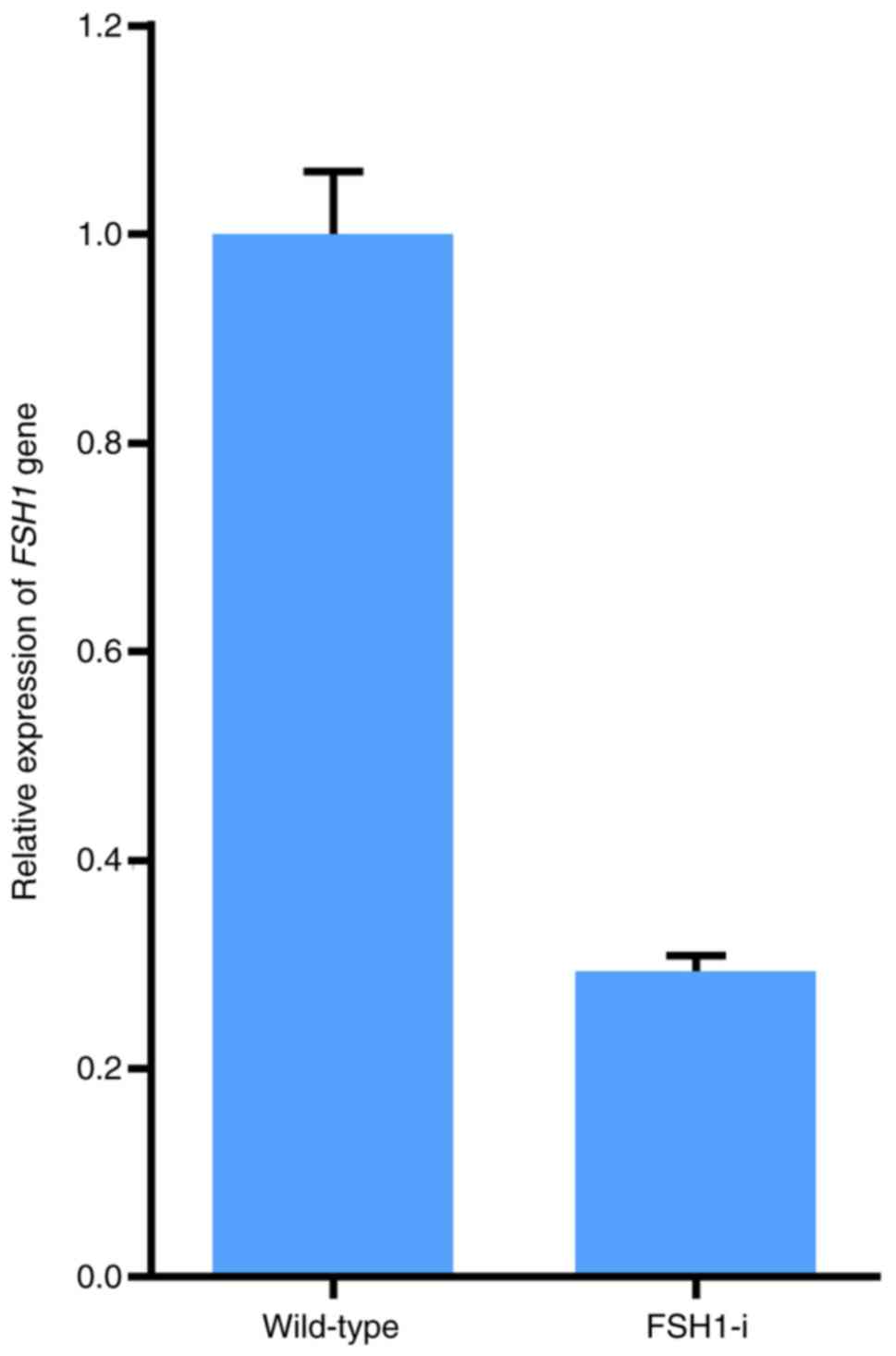
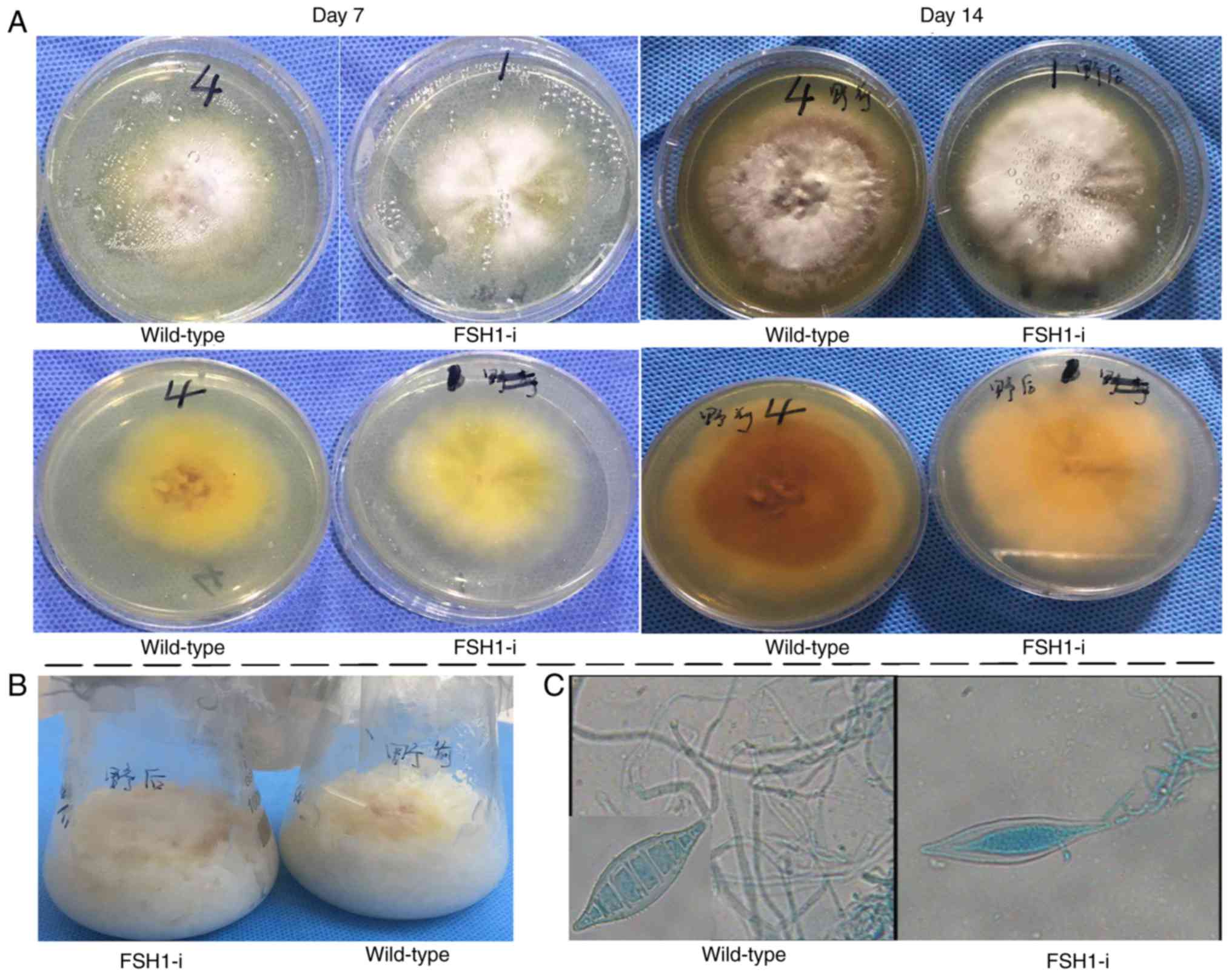
|
1
|
Mao L, Zhang L, Li H, Chen W, Wang H, Wu
S, Guo C, Lu A, Yang G, An L, et al: Pathogenic fungus Microsporum
canis activates the NLRP3 inflammasome. Infect Immun. 82:882–892.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yu J, Wan Z, Chen W, Wang W and Li R:
Molecular typing study of the Microsporum canis strains isolated
from an outbreak of tinea capitis in a school. Mycopathologia.
157:37–41. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vermout S, Baldo A, Tabart J, Losson B and
Mignon B: Secreted dipeptidyl peptidases as potential virulence
factors for Microsporum canis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol.
54:299–308. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brosh-Nissimov T, Ben-Ami R, Astman N,
Malin A, Baruch Y and Galor I: An outbreak of Microsporum canis
infection at a military base associated with stray cat exposure and
person-to-person transmission. Mycoses. 61:472–476. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hermoso de Mendoza M, Hermoso de Mendoza
J, Alonso JM, Rey JM, Sanchez S, Martin R, Bermejo F, Cortes M,
Benitez JM, Garcia WL and Garcia-Sanchez A: A zoonotic ringworm
outbreak caused by a dysgonic strain of Microsporum canis from
stray cats. Rev Iberoam Micol. 27:62–65. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Binder B, Lackner HK, Poessl BD, Propst E,
Weger W, Smolle J and Ginter Hanselmayer G: Prevalence of tinea
capitis in southeastern Austria between 1985 and 2008: Up-to-date
picture of the current situation. Mycoses. 54:243–247. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Del Boz J, Crespo V, Rivas-Ruiz F and de
Troya M: A 30-year survey of paediatric tinea capitis in southern
Spain. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 25:170–174. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Costa M, Passos XS, Hasimoto e Souza LK,
Miranda AT, Lemos Jde A, Oliveira JG Jr and Silva Mdo R:
Epidemiology and etiology of dermatophytosis in Goiânia, GO,
Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 35:19–22. 2002.In Portuguese.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Doss RW, El-Rifaie AA, Radi N and
El-Sherif AY: Antimicrobial susceptibility of tinea capitis in
children from Egypt. Indian J Dermatol. 63:155–159. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu M, Li L, Wang J, Zhang C, Kang K and
Zhang Q: Tinea capitis in southeastern China: A 16-year survey.
Mycopathologia. 169:235–239. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li C and Liu W: Epidemiology of tinea
capitis among children in China in recent years: A retrospective
analysis. Chin J Mycol. 6:77–82. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Yin B, Xiao Y, Ran Y, Kang D, Dai Y and
Lama J: Microsporum canis infection in three familial cases with
tinea capitis and tinea corporis. Mycopathologia. 176:259–265.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Berg JC, Hamacher KL and Roberts GD:
Pseudomycetoma caused by Microsporum canis in an immunosuppressed
patient: A case report and review of the literature. J Cutan
Pathol. 34:431–434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Anemüller W, Baumgartner S and Brasch J:
Atypical Microsporum canis variant in an immunosuppressed child. J
Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 6:473–475. 2008.In English and German.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Brillowska-Dabrowska A, Michalek E, Saunte
DM, Nielsen SS and Arendrup MC: PCR test for Microsporum canis
identification. Med Mycol. 51:576–579. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sharma R, de Hoog S, Presber W and Gräser
Y: A virulent genotype of Microsporum canis is responsible for the
majority of human infections. J Med Microbiol. 56:1377–1385. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ayanbimpe GM, Taghir H, Diya A and Wapwera
S: Tinea capitis among primary school children in some parts of
central nigeria. Mycoses. 51:336–340. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Patel GA and Schwartz RA: Tinea capitis:
Still an unsolved problem? Mycoses. 54:183–188. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Baldo A, Mathy A, Tabart J, Camponova P,
Vermout S, Massart L, Maréchal F, Galleni M and Mignon B: Secreted
subtilisin Sub3 from Microsporum canis is required for adherence to
but not for invasion of the epidermis. Br J Dermatol. 162:990–997.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Băguţ ET, Baldo A, Mathy A, Cambier L,
Antoine N, Cozma V and Mignon B: Subtilisin Sub3 is involved in
adherence of Microsporum canis to human and animal epidermis. Vet
Microbiol. 160:413–419. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Baldo A, Chevigné A, Dumez ME, Mathy A,
Power P, Tabart J, Cambier L, Galleni M and Mignon B: Inhibition of
the kerati-nolytic subtilisin protease Sub3 from Microsporum canis
by its propeptide (proSub3) and evaluation of the capacity of
proSub3 to inhibit fungal adherence to feline epidermis. Vet
Microbiol. 159:479–484. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi Y, Niu Q, Yu X, Jia X, Wang J, Lin D
and Jin Y: Assessment of the function of SUB6 in the pathogenic
dermatophyte. Trichophyton mentagrophytes Med Mycol. 54:59–71.
2016.
|
|
23
|
Grumbt M, Monod M, Yamada T, Hertweck C,
Kunert J and Staib P: Keratin degradation by dermatophytes relies
on cysteine dioxygenase and a sulfite efflux pump. J Invest
Dermatol. 133:1550–1555. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mathy A, Baldo A, Schoofs L, Cambier L,
Defaweux V, Tabart J, Maréchal F, Symoens F and Mignon B:
Fungalysin and dipeptidyl-peptidase gene transcription in
Microsporum canis strains isolated from symptomatic and
asymptomatic cats. Vet Microbiol. 146:179–182. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakayashiki H: RNA silencing in fungi:
Mechanisms and applications. FEBS Lett. 579:5950–5957. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang FR, Zhang Y, Zhang ZY, Yang GL, Jing
LJ and Bai YG: Analysis of the differentially expressed genes in
Microsporum canis in inducing smooth skin and scalp tissue
conditions. Clin Exp Dermatol. 36:896–902. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gräser Y, EI Fari M, Vilgalys R, Kuijpers
AF, De Hoog GS, Presber W and Tietz H: Phylogeny and taxonomy of
the family arthrodermataceae (dermatophytes) using sequence
analysis of the ribosomal ITS region. Med Mycol. 37:105–114. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jackson CJ, Barton RC and Evans EG:
Species identification and strain differentiation of dermatophyte
fungi by analysis of ribosomal-DNA intergenic spacer regions. J
Clin Microbiol. 37:931–936. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Z, Hou B, Wu YZ, Wang Y, Liu X and
Han S: Two component histidine kinase DRK1 is required for
pathogenesis in sporothrix schenckii. Mol Med Rep. 17:721–728.
2018.
|
|
30
|
Zhang P, Xu B, Wang Y, Li Y, Qian Z, Tang
S, Huan S and Ren S: Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated
transformation as a tool for insertional mutagenesis in the fungus
penicillium marneffei. Mycol Res. 112:943–949. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Basma AA, Zuraini Z and Sasidharan SA:
Transmission electron microscopy study of the diversity of Candida
albicans cells induced by Euphorbia hirta L. Leaf extract in vitro
Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 1:20–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang F, Tao J, Qian Z, You S, Dong H, Shen
H, Chen X, Tang S and Ren S: A histidine kinase PmHHK1 regulates
polar growth, sporulation and cell wall composition in the
dimorphic fungus Penicillium marneffei. Mycol Res. 113:915–923.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jin XJ, Wang AP, Qiao JJ, Liu W, Wan J,
Wang XH, Wu LS and Li RY: Establishment of an animal model of
dermatophytosis and evaluation of the antifungal efficacy on
dermatophytosis with this model. Chin J Dermatol. 42:125–128.
2009.In Chinese.
|
|
35
|
Silverman J and Muir WW III: A review of
laboratory animal anesthesia with chloral hydrate and chloralose.
Lab Anim Sci. 43:210–216. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Olszewski J: Guinea pig as often object to
otoneurological experimental examinations. Otolaryngol Pol.
61:838–841. 2007.In Polish. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mao N, Gao Q, Hu H, Zhu T and Hao L: BPA
disrupts the cardio-protection by 17β-oestradiol against
ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated guinea pig hearts.
Steroids. 146:50–56. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou Y, Song J, Wang YP, Zhang AM, Tan CY,
Liu YH, Zhang ZP, Wang Y, Ma KT, Li L and Si JQ: Age-associated
variation in the expression and function of TMEM16A
calcium-activated chloride channels in the cochlear stria
vascularis of guinea pigs. Mol Med Rep. 20:1593–1604.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vermout S, Tabart J, Baldo A, Monod M,
Losson B and Mignon B: RNA silencing in the dermatophyte
Microsporum canis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 275:38–45. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Quevillon-Cheruel S, Leulliot N, Graille
M, Hervouet N, Coste F, Bénédetti H, Zelwer C, Janin J and Van
Tilbeurgh H: Crystal structure of yeast YHR049W/FSH1, a member of
the serine hydrolase family. Protein Sci. 14:1350–1356. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Baxter SM, Rosenblum JS, Knutson S, Nelson
MR, Montimurro JS, Di Gennaro JA, Speir JA, Burbaum JJ and Fetrow
JS: Synergistic computational and experimental proteomics
approaches for more accurate detection of active serine hydrolases
in yeast. Mol Cell Proteomics. 3:209–225. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gang L, Wei C, Yuqing T, Huarong T, Chater
KF and Buttner MJ: A novel gene: sawD related to the
differentiation of streptomyces ansochromogenes. Chin J Biotechnol.
15:195–202. 1999.
|
|
43
|
Greenberg JH, King RD, Krebs S and Field
R: A quantitative dermatophyte infection model in the guinea pig-a
parallel to the quantitated human infection model. J Invest
Dermatol. 67:704–708. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang X, Wang Y, Chi W, Shi Y, Chen S, Lin
D and Jin Y: Metalloprotease genes of Trichophyton mentagrophytes
are important for pathogenicity. Med Mycol. 52:36–45. 2014.
|