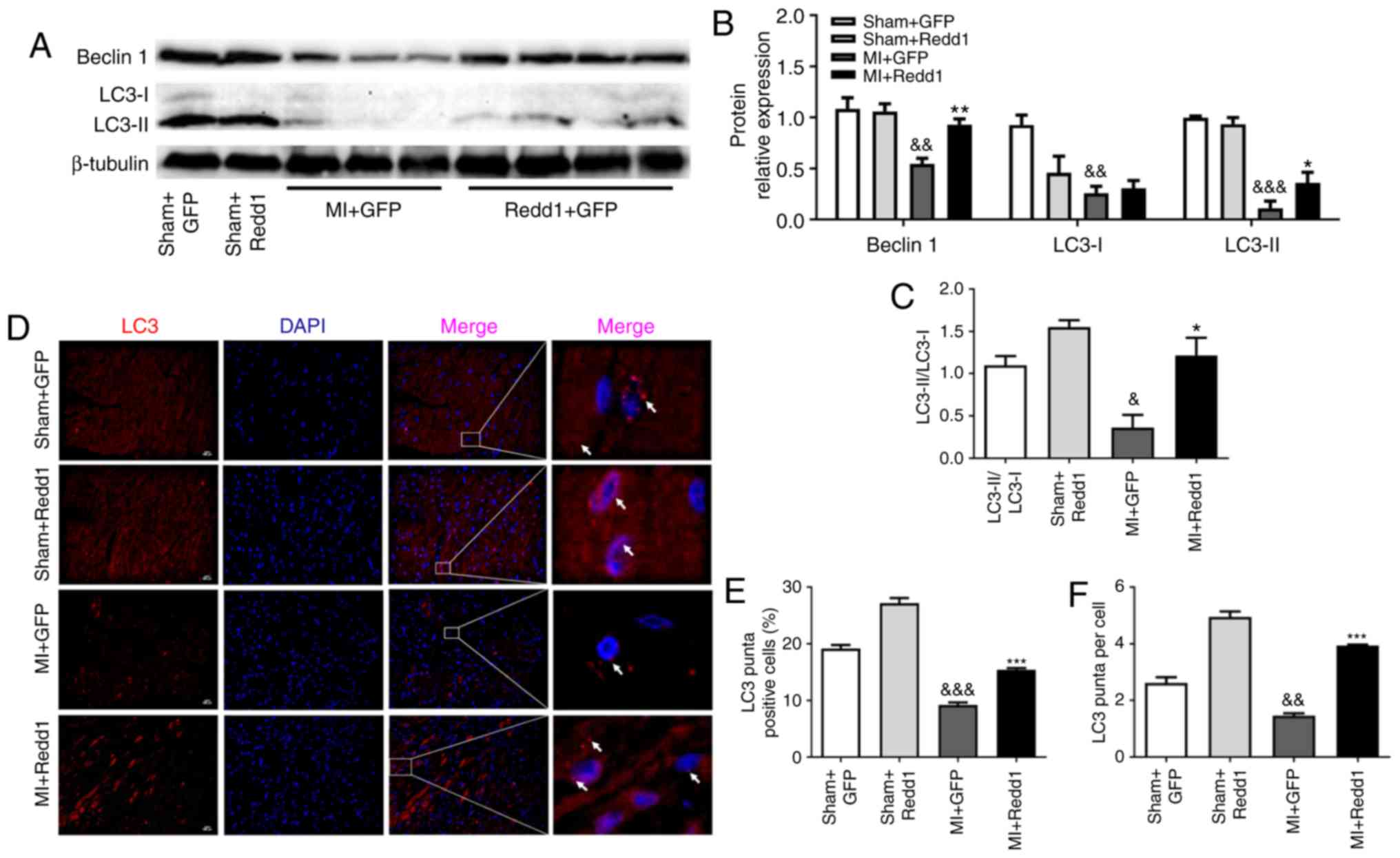
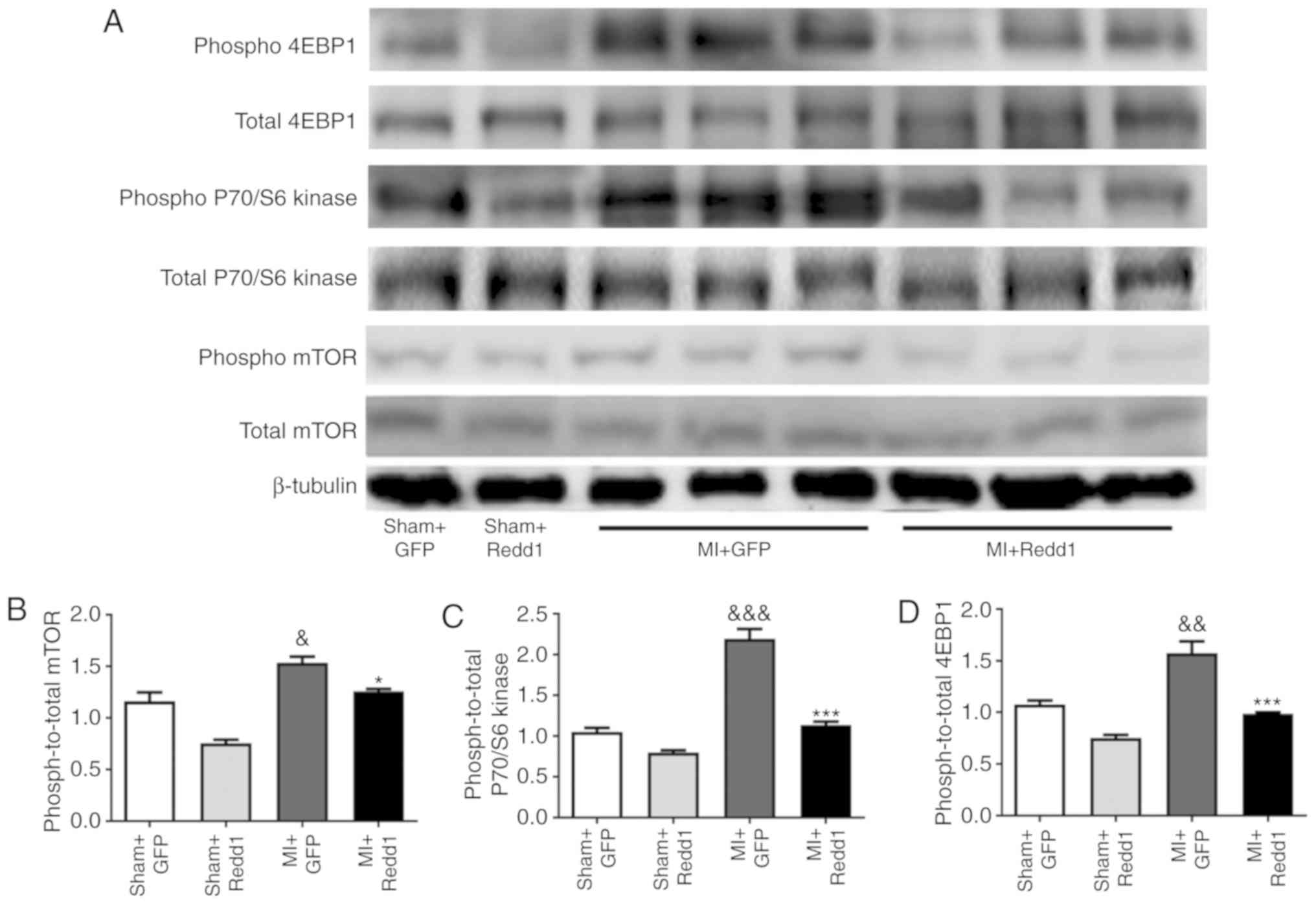
|
1
|
Michaud CM: Murray CJ and Bloom BR: Burden
of disease-implications for future research. JAMA. 285:535–539.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Deedwania PC: The key to unraveling the
mystery of mortality in heart failure: An integrated approach.
Circulation. 107:1719–1721. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
White HD, Norris RM, Brown MA, Brandt PW,
Whitlock RM and Wild CJ: Left ventricular end-systolic volume as
the major determinant of survival after recovery from myocardial
infarction. Circulation. 76:44–51. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gajarsa JJ and Kloner RA: Left ventricular
remodeling in the post-infarction heart: A review of cellular,
molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic modalities. Heart Fail Rev.
16:13–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen J, Hsieh AF, Dharmarajan K, Masoudi
FA and Krumholz HM: National trends in heart failure
hospitalization after acute myocardial infarction for medicare
beneficiaries: 1998-2010. Circulation. 128:2577–2584. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maejima Y, Kyoi S, Zhai P, Liu T, Li H,
Ivessa A, Sciarretta S, Del Re DP, Zablocki DK, Hsu CP, et al: Mst1
inhibits autophagy by promoting the interaction between Beclin1 and
Bcl-2. Nat Med. 19:1478–1488. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Konstantinidis K, Whelan RS and Kitsis RN:
Mechanisms of cell death in heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 32:1552–1562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yan L, Sadoshima J, Vatner DE and Vatner
SF: Autophagy: A novel protective mechanism in chronic ischemia.
Cell Cycle. 5:1175–1177. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hou L, Guo J, Xu F, Weng X, Yue W and Ge
J: Cardiomyocyte dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase1
attenuates left-ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial
infarction: Involvement in oxdative stress and apoptosis. Basic Res
Cardiol. 113:282018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu CY, Zhang YH, Li RB, Zhou LY, An T,
Zhang RC, Zhai M, Huang Y, Yan KW, Dong YH, et al: LncRNA CAIF
inhibits autophagy and attenuates myocardial infarction by blocking
p53-mediated myocardin transcription. Nat Commun. 9:292018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Betz C and Hall MN: Where is mTOR and what
is it doing there? J Cell Biol. 203:563–574. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
McMullen JR, Shioi T, Zhang L, Tarnavski
O, Sherwood MC, Kang PM and Izumo S: Phosphoinositide
3-kinase(p110alpha) plays a critical role for the induction of
physiological, but not pathological, cardiac hypertrophy. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 100:12355–12360. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Boluyt MO, Zheng JS, Younes A, Long X,
O'Neill L, Silverman H, Lakatta EG and Crow MT: Rapamycin inhibits
alpha 1-adren-ergic receptor-stimulated cardiac myocyte hypertrophy
but not activation of hypertrophy-associated genes. Evidence for
involvement of p70 S6 kinase Circ Res. 81:176–186. 1997.
|
|
14
|
Mazelin L, Panthu B, Nicot AS, Belotti E,
Tintignac L, Teixeira G, Zhang Q, Risson V, Baas D, Delaune E, et
al: mTOR inactivation in myocardium from infant mice rapidly leads
to dilated cardio-myopathy due to translation defects and
p53/JNK-mediated apoptosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 97:213–225. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McMullen JR, Sherwood MC, Tarnavski O,
Zhang L, Dorfman AL, Shioi T and Izumo S: Inhibition of mTOR
signaling with rapamycin regresses established cardiac hypertrophy
induced by pressure overload. Circulation. 109:3050–3055. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yan L, Guo N, Cao Y, Zeng S, Wang J, Lv F,
Wang Y and Cao X: miRNA145 inhibits myocardial infarctioninduced
apoptosis through autophagy via Akt3/mTOR signaling pathway in
vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Med. 42:1537–1547. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Buss SJ, Muenz S, Riffel JH, Malekar P,
Hagenmueller M, Weiss CS, Bea F, Bekeredjian R, Schinke-Braun M,
Izumo S, et al: Beneficial effects of Mammalian target of rapamycin
inhibition on left ventricular remodeling after myocardial
infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 54:2435–2446. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ellisen LW, Ramsayer KD, Johannessen CM,
Yang A, Beppu H, Minda K, Oliner JD, McKeon F and Haber DA: REDD1,
a developmentally regulated transcriptional target of p63 and p53,
links p63 to regulation of reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell.
10:995–1005. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tirado-Hurtado I, Fajardo W and Pinto JA:
DNA damage inducible transcript 4 Gene: The switch of the
metabolism as potential target in cancer. Front Oncol. 8:1062018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brugarolas J, Lei K, Hurley RL, Manning
BD, Reiling JH, Hafen E, Witters LA, Ellisen LW and Kaelin WG Jr:
Regulation of mTOR function in response to hypoxia by REDD1 and the
TSC1/TSC2 tumor suppressor complex. Genes Dev. 18:2893–2904. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee DK, Kim JH, Kim J, Choi S, Park M,
Park W, Kim S, Lee KS, Kim T, Jung J, et al: REDD-1 aggravates
endotoxin-induced inflammation via atypical NF-κB activation. FASEB
J. 32:4585–4599. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qiao S, Dennis M, Song X, Vadysirisack DD,
Salunke D, Nash Z, Yang Z, Liesa M, Yoshioka J, Matsuzawa S, et al:
A REDD1/TXNIP pro-oxidant complex regulates ATG4B activity to
control stress-induced autophagy and sustain exercise capacity. Nat
Commun. 6:70142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Canal M, Romani-Aumedes J, Martin-Flores
N, Pérez-Fernández V and Malagelada C: RTP801/REDD1: A stress
coping regulator that turns into a troublemaker in
neurodegen-erative disorders. Front Cell Neurosci. 8:3132014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ben Sahra I, Regazzetti C, Robert G,
Laurent K, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Auberger P, Tanti JF,
Giorgetti-Peraldi S and Bost F: Metformin, independent of AMPK,
induces mTOR inhibition and cell-cycle arrest through REDD1. Cancer
Res. 71:4366–4372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hernandez G, Lal H, Fidalgo M, Guerrero A,
Zalvide J, Force T and Pombo CM: A novel cardioprotective
p38-MAPK/mTOR pathway. Exp Cell Res. 317:2938–2949. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen R, Wang B, Chen L, Cai D, Li B, Chen
C, Huang E, Liu C, Lin Z, Xie WB and Wang H: DNA damage-inducible
transcript 4 (DDIT4) mediates methamphetamine-induced autophagy and
apoptosis through mTOR signaling pathway in cardiomyocytes. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 295:1–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu C, Xue R, Wu D, Wu L, Chen C, Tan W,
Chen Y and Dong Y: REDD1 attenuates cardiac hypertrophy via
enhancing autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 454:215–220. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sciarretta S, Volpe M and Sadoshima J:
Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in cardiac physiology and
disease. Circ Res. 114:549–564. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Volkers M, Konstandin MH, Doroudgar S,
Toko H, Quijada P, Din S, Joyo A, Ornelas L, Samse K, Thuerauf DJ,
et al: Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 protects the heart
from ischemic damage. Circulation. 128:2132–2144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao Y, Xiong X, Jia L and Sun Y:
Targeting Cullin-RING ligases by MLN4924 induces autophagy via
modulating the HIF1-REDD1-TSC1-mTORC1-DEPTOR axis. Cell Death Dis.
3:e3862012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Prasad KM, Xu Y, Yang Z, Acton ST and
French BA: Robust cardiomyocyte-specific gene expression following
systemic injection of AAV: In vivo gene delivery follows a poisson
distribution. Gene Ther. 18:43–52. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang X, Meng H, Chen P, Yang N, Lu X, Wang
ZM, Gao W, Zhou N, Zhang M, Xu Z, et al: Beneficial effects of
muscone on cardiac remodeling in a mouse model of myocardial
infarction. Int J Mol Med. 34:103–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oliveira AC, Melo MB, Motta-Santos D,
Peluso AA, Souza-Neto F, da Silva RF, Almeida JFQ, Canta G, Reis
AM, Goncalves G, et al: Genetic deletion of the alamandine receptor
MRGD leads to dilated cardiomyopathy in mice. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 316:H123–H133. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Jia LX, Qi GM, Liu O, Li TT, Yang M, Cui
W, Zhang WM, Qi YF and Du J: Inhibition of platelet activation by
clopidogrel prevents hypertension-induced cardiac inflammation and
fibrosis. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 27:521–530. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dai W, Hale SL, Martin BJ, Kuang JQ, Dow
JS, Wold LE and Kloner RA: Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell
transplantation in postinfarcted rat myocardium: Short- and
long-term effects. Circulation. 112:214–223. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hochman JS and Choo H: Limitation of
myocardial infarct expansion by reperfusion independent of
myocardial salvage. Circulation. 75:299–306. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lubbe WF, Peisach M, Pretorius R, Bruyneel
KJ and Opie LH: Distribution of myocardial blood flow before and
after coronary artery ligation in the baboon. Relation to early
ventricular fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 8:478–487. 1974.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lee EJ, Park SJ, Kang SK, Kim GH, Kang HJ,
Lee SW, Jeon HB and Kim HS: Spherical bullet formation via
E-cadherin promotes therapeutic potency of mesenchymal stem cells
derived from human umbilical cord blood for myocardial infarction.
Mol Ther. 20:1424–1433. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li Y, Yang R, Guo B, Zhang H and Liu S:
Exosomal miR-301 derived from mesenchymal stem cells protects
myocardial infarction by inhibiting myocardial autophagy. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 514:323–328. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hochman JS, Reynolds HR, Dzavik V, Buller
CE, Ruzyllo W, Sadowski ZP, Maggioni AP, Carvalho AC, Rankin JM,
White HD, et al: Long-term effects of percutaneous coronary
intervention of the totally occluded infarct-related artery in the
subacute phase after myocardial infarction. Circulation.
124:2320–2328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Park KM, Teoh JP, Wang Y, Broskova Z,
Bayoumi AS, Tang Y, Su H, Weintraub NL and Kim IM:
Carvedilol-responsive microRNAs, miR-199a-3p and -214 protect
cardiomyocytes from simulated ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 311:H371–H383. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou Y, Chen Q, Lew KS, Richards AM and
Wang P: Discovery of potential therapeutic miRNA targets in cardiac
ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther.
21:296–309. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Gao C, Wang R, Li B, Guo Y, Yin T, Xia Y,
Zhang F, Lian K, Liu Y, Wang H, et al: TXNIP/Redd1 signalling and
excessive autophagy: A novel mechanism of myocardial
ischaemia/reper-fusion injury in mice. Cardiovasc Res. Jun
26–2019.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hashmi S and Al-Salam S: Acute myocardial
infarction and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: A
comparison. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:8786–8796. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang X, Guo Z, Ding Z and Mehta JL:
Inflammation, autophagy, and apoptosis after myocardial infarction.
J Am Heart Assoc. 7:pii: e008024. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Creemers EE and Pinto YM: Molecular
mechanisms that control interstitial fibrosis in the
pressure-overloaded heart. Cardiovasc Res. 89:265–272. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Berk BC, Fujiwara K and Lehoux S: ECM
remodeling in hypertensive heart disease. J Clin Invest.
117:568–575. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ren J, Zhang S, Kovacs A, Wang Y and
Muslin AJ: Role of p38alpha MAPK in cardiac apoptosis and
remodeling after myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
38:617–623. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Krijnen PA, Nijmeijer R, Meijer CJ, Visser
CA, Hack CE and Niessen HW: Apoptosis in myocardial ischaemia and
infarction. J Clin Pathol. 55:801–811. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Choi AM, Ryter SW and Levine B: Autophagy
in human health and disease. N Engl J Med. 368:1845–1846. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lekli I, Haines DD, Balla G and Tosaki A:
Autophagy: An adaptive physiological countermeasure to cellular
senescence and ischaemia/reperfusion-associated cardiac
arrhythmias. J Cell Mol Med. 21:1058–1072. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Matsui Y, Takagi H, Qu X, Abdellatif M,
Sakoda H, Asano T, Levine B and Sadoshima J: Distinct roles of
autophagy in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion: Roles of
AMP-activated protein kinase and Beclin 1 in mediating autophagy.
Circ Res. 100:914–922. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wu X, He L, Chen F, He X, Cai Y, Zhang G,
Yi Q, He M and Luo J: Impaired autophagy contributes to adverse
cardiac remodeling in acute myocardial infarction. PLoS One.
9:e1128912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nakai A, Yamaguchi O, Takeda T, Higuchi Y,
Hikoso S, Taniike M, Omiya S, Mizote I, Matsumura Y, Asahi M, et
al: The role of autophagy in cardiomyocytes in the basal state and
in response to hemodynamic stress. Nat Med. 13:619–624. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wu P, Yuan X, Li F, Zhang J, Zhu W, Wei M,
Li J and Wang X: Myocardial upregulation of cathepsin D by ischemic
heart disease promotes autophagic flux and protects against cardiac
remodeling and heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. 10:pii: e004044.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jewell JL and Guan KL: Nutrient signaling
to mTOR and cell growth. Trends Biochem Sci. 38:233–242. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Johnson SC, Rabinovitch PS and Kaeberlein
M: MTOR is a key modulator of ageing and age-related disease.
Nature. 493:338–345. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Land SC, Scott CL and Walker D: MTOR
signalling, embryo-genesis and the control of lung development.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 36:68–78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sciarretta S, Forte M, Frati G and
Sadoshima J: New insights into the role of mTOR signaling in the
cardiovascular system. Circ Res. 122:489–505. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|