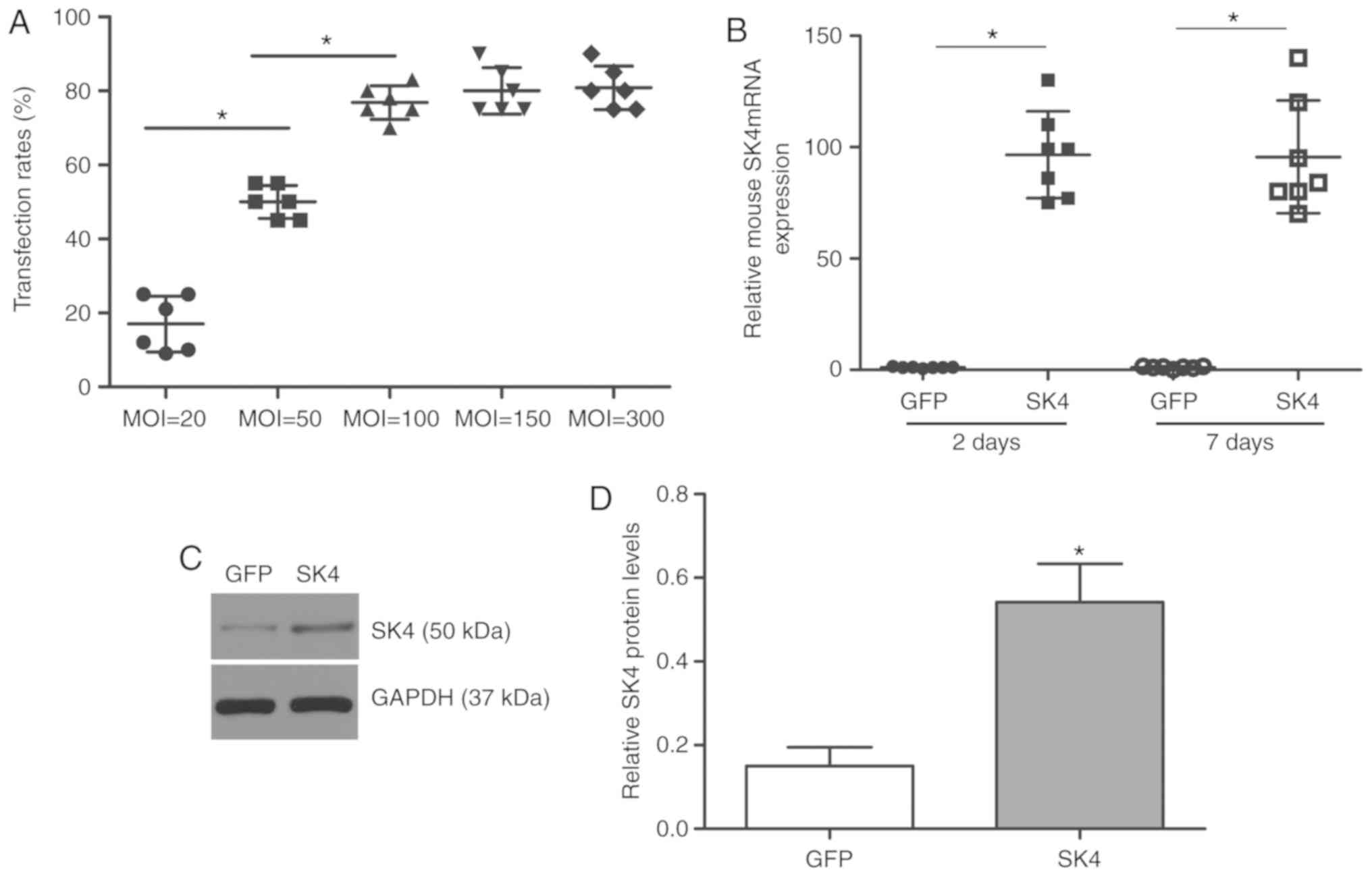
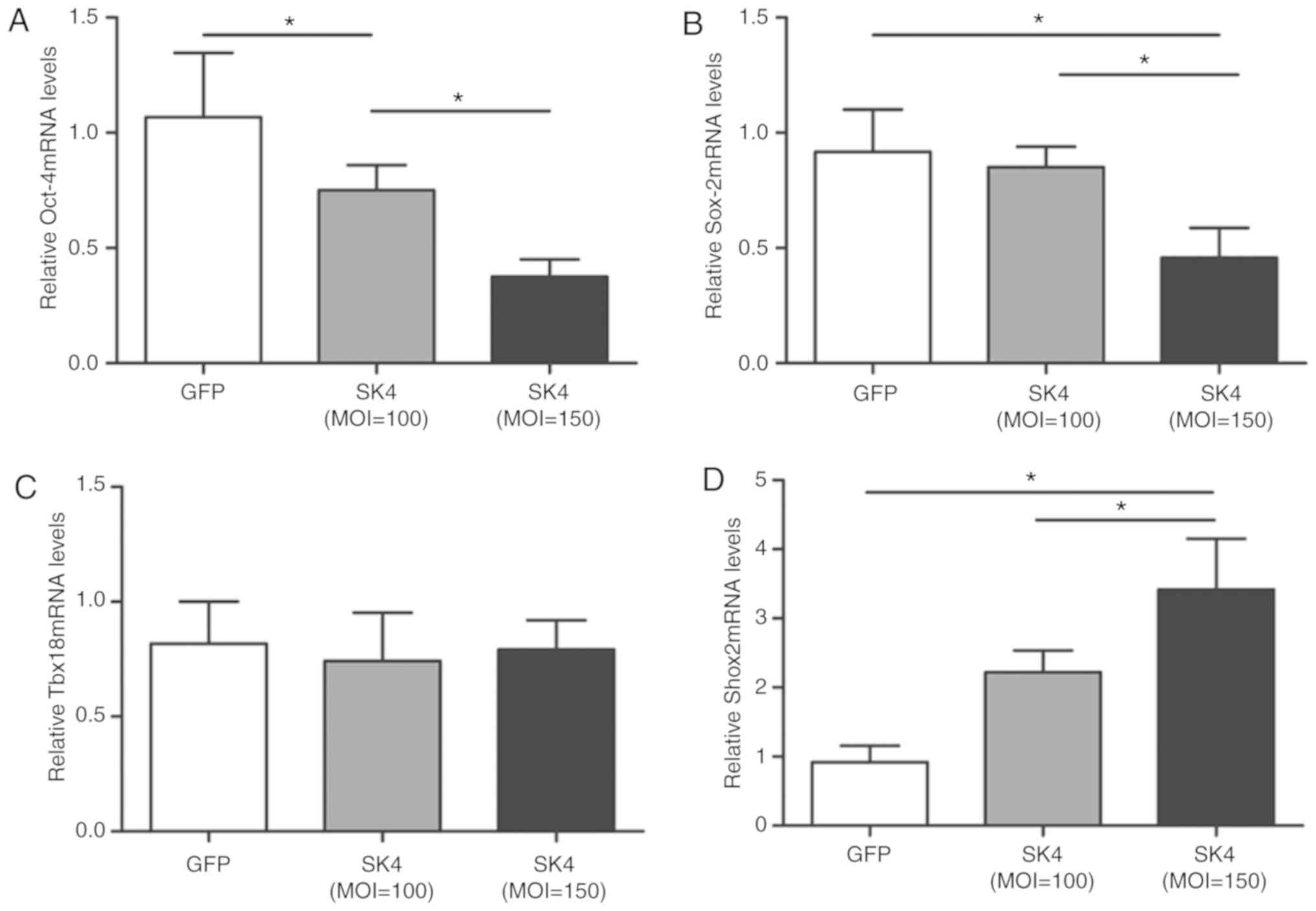
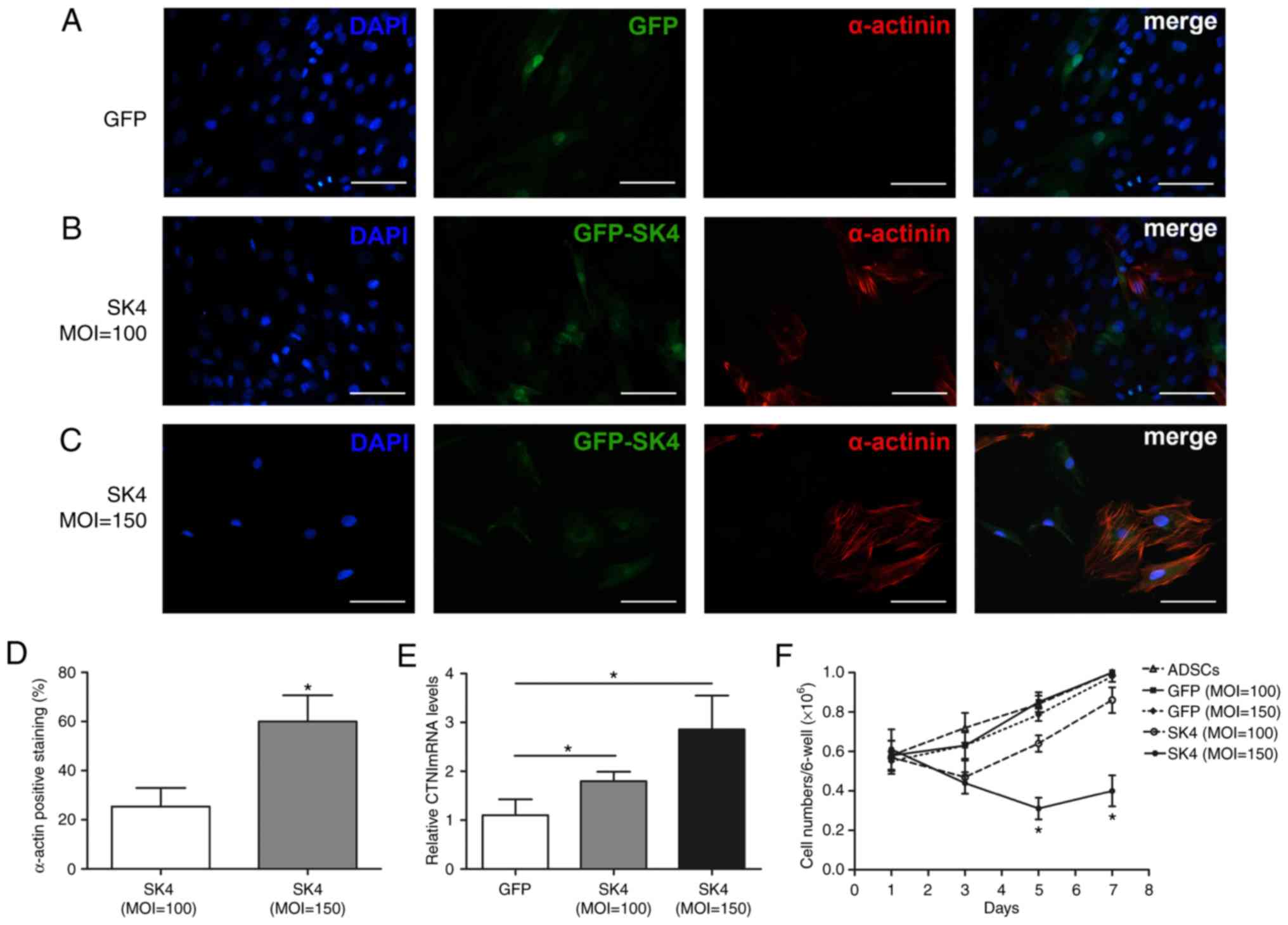
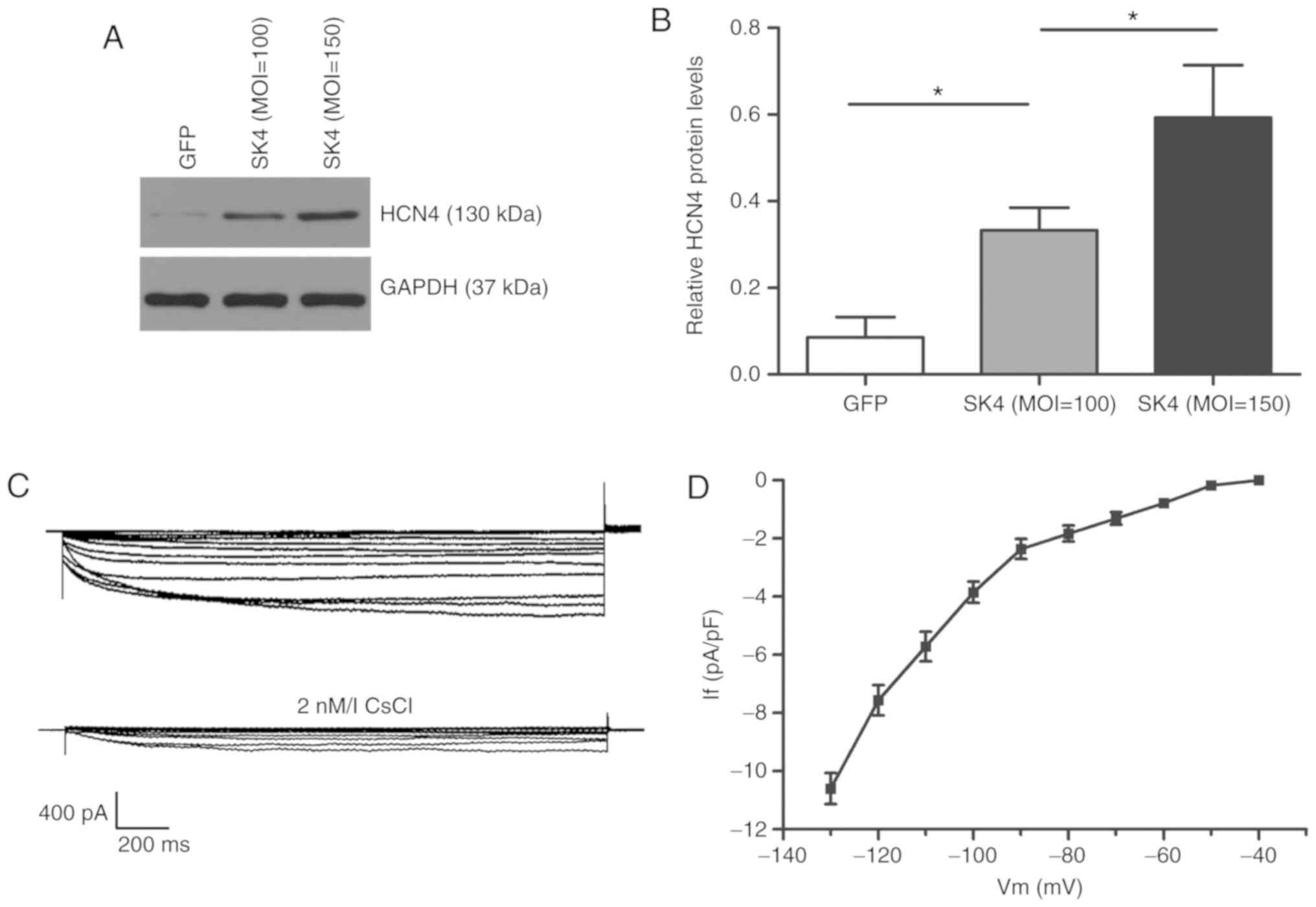
|
1
|
Horsthuis T, Buermans HP, Brons JF,
Verkerk AO, Bakker ML, Wakker V, Clout DE, Moorman AF, 't Hoen PA
and Christoffels VM: Gene expression profiling of the forming
atrioventricular node using a novel tbx3-based node-specific
transgenic reporter. Circ Res. 105:61–69. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mangoni ME and Nargeot J: Properties of
the hyperpolarization-activated current (I(f)) in isolated mouse
sino-atrial cells. Cardiovasc Res. 52:51–64. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vinogradova TM, Zhou YY, Bogdanov KY, Yang
D, Kuschel M, Cheng H and Xiao RP: Sinoatrial node pacemaker
activity requires Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
activation. Circ Res. 87:760–767. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang Q, Timofeyev V, Lu L, Li N,
Singapuri A, Long MK, Bond CT, Adelman JP and Chiamvimonvat N:
Functional roles of a Ca2+-activated K+
channel in atrioventricular nodes. Circ Res. 102:465–471. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Attali B, Weisbrod D, Bueno H, Behar J,
Haron-Khun S and Yadin D: SK4 Ca2+-activated
K+ channels regulate sinoatrial node firing rate and
cardiac pacing in vivo. Biophys J. 112:35a2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Haron-Khun S, Weisbrod D, Bueno H, Yadin
D, Behar J, Peretz A, Binah O, Hochhauser E, Eldar M, Yaniv Y, et
al: SK4 K+ channels are therapeutic targets for the
treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. EMBO Mol Med. 9:415–429. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oliván-Viguera A, Valero MS, Coleman N,
Brown BM, Laría C, Murillo MD, Gálvez JA, Díaz-de-Villegas MD,
Wulff H, Badorrey R and Köhler R: A novel pan-negative-gating
modulator of KCa2/3 channels, fluoro-di-benzoate, RA-2, inhibits
endothelium-derived hyperpolarization-type relaxation in coronary
artery and produces bradycardia in vivo. Mol Pharmacol. 87:338–348.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kharche S, Yu J, Lei M and Zhang H: A
mathematical model of action potentials of mouse sinoatrial node
cells with molecular bases. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
301:H945–H963. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weisbrod D, Peretz A, Ziskind A, Menaker
N, Oz S, Barad L, Eliyahu S, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Dascal N,
Khananshvili D, et al: SK4 Ca2+ activated K+
channel is a critical player in cardiac pacemaker derived from
human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:E1685–E1694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Devor DC, Singh AK, Frizzell RA and
Bridges RJ: Modulation of Cl- secretion by benzimidazolones. I.
Direct activation of a Ca(2+)-dependent K+. channel Am J
Physiol. 271:L775–L784. 1996.
|
|
11
|
Kleger A, Seufferlein T, Malan D,
Tischendorf M, Storch A, Wolheim A, Latz S, Protze S, Porzner M,
Proepper C, et al: Modulation of calcium-activated potassium
channels induces cardiogenesis of pluripotent stem cells and
enrichment of pacemaker-like cells. Circulation. 122:1823–1836.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Müller M, Stockmann M, Malan D, Wolheim A,
Tischendorf M, Linta L, Katz SF, Lin Q, Latz S, Brunner C, et al:
Ca2+ activated K channels-new tools to induce cardiac
commitment from pluripotent stem cells in mice and men. Stem Cell
Rev Rep. 8:720–740. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liebau S, Tischendorf M, Ansorge D, Linta
L, Stockmann M, Weidgang C, Iacovino M, Boeckers T, von Wichert G,
Kyba M and Kleger A: An inducible expression system of the
calcium-activated potassium channel 4 to study the differential
impact on embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2011:4568152011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jara-Avaca M, Kempf H, Rückert M,
Robles-Diaz D, Franke A, la Roche J, Fischer M, Malan D, Sasse P,
Solodenko W, et al: EBIO does not induce cardiomyogenesis in human
pluripotent stem cells but modulates cardiac subtype enrichment by
lineage-selective survival. Stem Cell Reports. 8:305–317. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Taha MF and Hedayati V: Isolation,
identification and multipotential differentiation of mouse adipose
tissue-derived stem cells. Tissue Cell. 42:211–216. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Planat-Bénard V, Menard C, André M, Puceat
M, Perez A, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Pénicaud L and Casteilla L:
Spontaneous cardiomyocyte differentiation from adipose tissue
stroma cells. Circ Res. 94:223–229. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yang M, Zhang GG, Wang T, Wang X, Tang YH,
Huang H, Barajas-Martinez H, Hu D and Huang CX: TBX18 gene induces
adipose-derived stem cells to differentiate into pacemaker-like
cells in the myocardial microenvironment. Int J Mol Med.
38:1403–1410. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2 (-Delta Delta C(T) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Reményi A, Lins K, Nissen LJ, Reinbold R,
Schöler HR and Wilmanns M: Crystal structure of a POU/HMG/DNA
ternary complex suggests differential assembly of Oct4 and Sox2 on
two enhancers. Genes Dev. 17:2048–2059. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Izadpanah R, Trygg C, Patel B, Kriedt C,
Dufour J, Gimble JM and Bunnell BA: Biologic properties of
mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow and adipose tissue.
J Cell Biochem. 99:1285–1297. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu Y, Liu T, Song K, Fan X, Ma X and Cui
Z: Adipose-derived stem cell: A better stem cell than BMSC. Cell
Biochem Funct. 26:664–675. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Christoffels VM, Smits GJ, Kispert A and
Moorman AF: Development of the pacemaker tissues of the heart. Circ
Res. 106:240–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Potapova I, Plotnikov A, Lu Z, Danilo P
Jr, Valiunas V, Qu J, Doronin S, Zuckerman J, Shlapakova IN, Gao J,
et al: Human mesenchymal stem cells as a gene delivery system to
create cardiac pacemakers. Circ Res. 94:952–959. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Plotnikov AN, Shlapakova I, Szabolcs MJ,
Danilo P Jr, Lorell BH, Potapova IA, Lu Z, Rosen AB, Mathias RT,
Brink PR, et al: Xenografted adult human mesenchymal stem cells
provide a platform for sustained biological pacemaker function in
canine heart. Circulation. 116:706–713. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang H, Li S, Qu D, Li B, He B, Wang C
and Xu Z: Autologous biological pacing function with
adrenergic-responsiveness in porcine of complete heart block. Int J
Cardiol. 168:3747–3751. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Li B, Li Z, Zhang J and Zeng M:
Adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells transfected with the gene
of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel
2 differentiated into pacemaker-like cells. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian
Yi Xue Za Zhi. 29:901–904. 9092013.In Chinese.
|
|
27
|
Chauveau S, Brink PR and Cohen IS: Stem
cell-based biological pacemakers from proof of principle to
therapy: A review. Cytotherapy. 16:873–880. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang P, Rushing SN, Kong CW, Fu J, Lieu
DK, Chan CW, Deng W and Li RA: Electrophysiological properties of
human induced pluripotent stem cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
298:C486–C495. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Bai X, Ma J, Pan Z, Song YH, Freyberg S,
Yan Y, Vykoukal D and Alt E: Electrophysiological properties of
human adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
293:C1539–C1550. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi W, Wymore R, Yu H, Wu J, Wymore RT,
Pan Z, Robinson RB, Dixon JE, McKinnon D and Cohen IS: Distribution
and prevalence of hyperpolarization-activated cation channel (HCN)
mRNA expression in cardiac tissues. Circ Res. 85:e1–e6. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stieber J, Herrmann S, Feil S, Löster J,
Feil R, Biel M, Hofmann F and Ludwig A: The
hyperpolarization-activated channel HCN4 is required for the
generation of pacemaker action potentials in the embryonic heart.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:15235–15240. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Yang M, Zhang G, Li L, Ye B, Huang C
and Tang Y: Transcription factor TBX18 promotes adult rat bone
mesen-chymal stem cell differentiation to biological pacemaker
cells. Int J Mol Med. 41:845–851. 2018.
|
|
33
|
Feng Y, Luo S and Song Z: GW24-e3884
Canine bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells modified with Shox2
gene rebuild biological pacemakers in vitro. Heart. 99:A462013.
|
|
34
|
Weisbrod D, Khun SH, Bueno H, Peretz A and
Attali B: Mechanisms underlying the cardiac pacemaker: The role of
SK4 calcium-activated potassium channels. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
37:82–97. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He JQ, Ma Y, Lee Y, Thomson JA and Kamp
TJ: Human embryonic stem cells develop into multiple types of
cardiac myocytes: Action potential characterization. Circ Res.
93:32–39. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang YM, Hartzell C, Narlow M and Dudley
SC Jr: Stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes demonstrate arrhythmic
potential. Circulation. 106:1294–1299. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N and
Zhou HF: Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation,
differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept
Signal Transduct Res. 35:600–604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Roux PP and Blenis J: ERK and p38
MAPK-activated protein kinases: A family of protein kinases with
diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 68:320–344.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu J, Kubota J, Hirayama J, Nagai Y,
Nishina S, Yokoi T, Asaoka Y, Seo J, Shimizu N, Kajiho H, et al:
p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase controls a switch between
cardiomyocyte and neuronal commitment of murine embryonic stem
cells by activating myocyte enhancer factor 2C-dependent bone
morphogenetic protein 2 transcription. Stem Cells Dev.
19:1723–1734. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Eriksson M and Leppä S: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases and activator protein 1 are required for
proliferation and cardiomyocyte differentiation of P19 embryonal
carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 277:15992–16001. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|