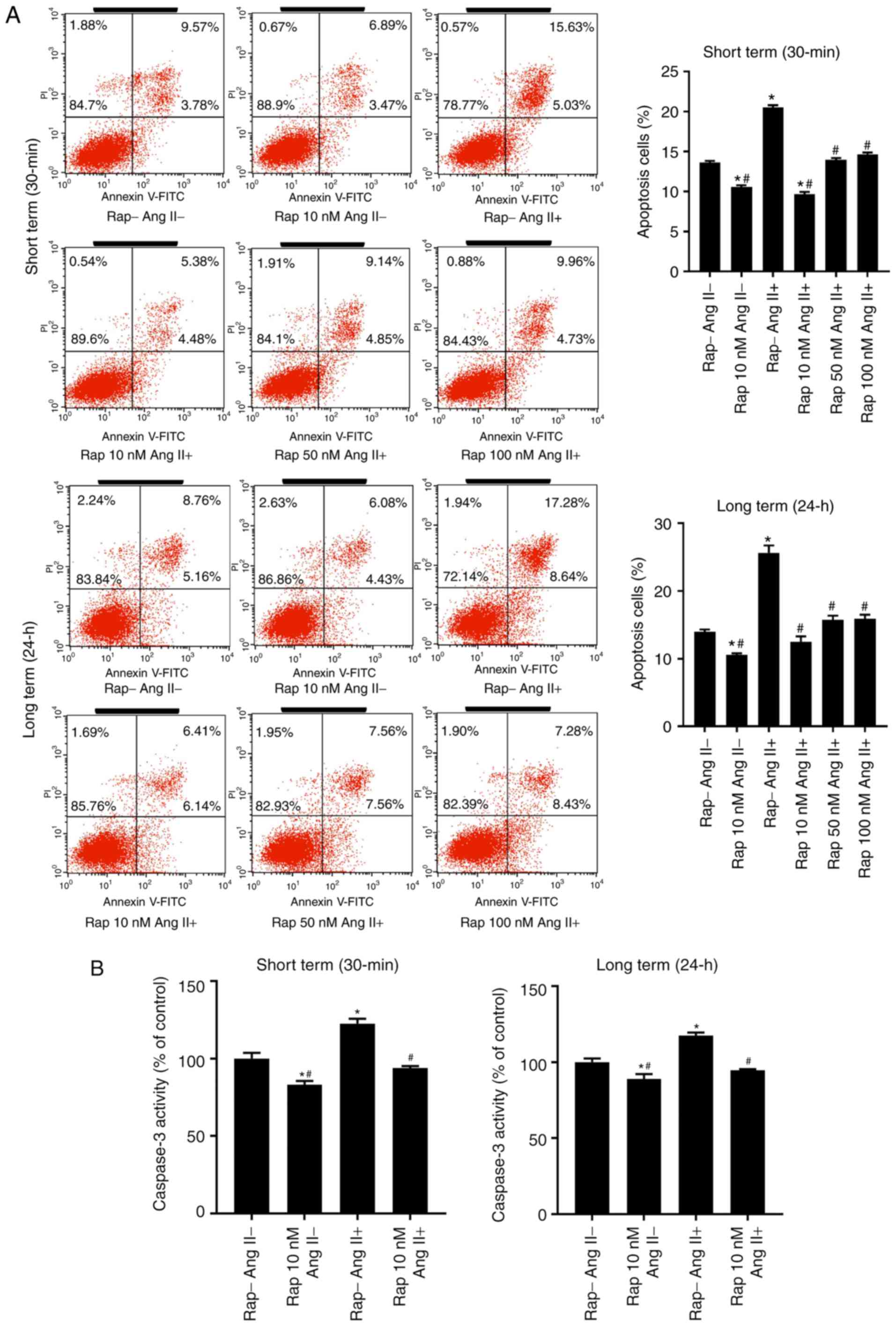
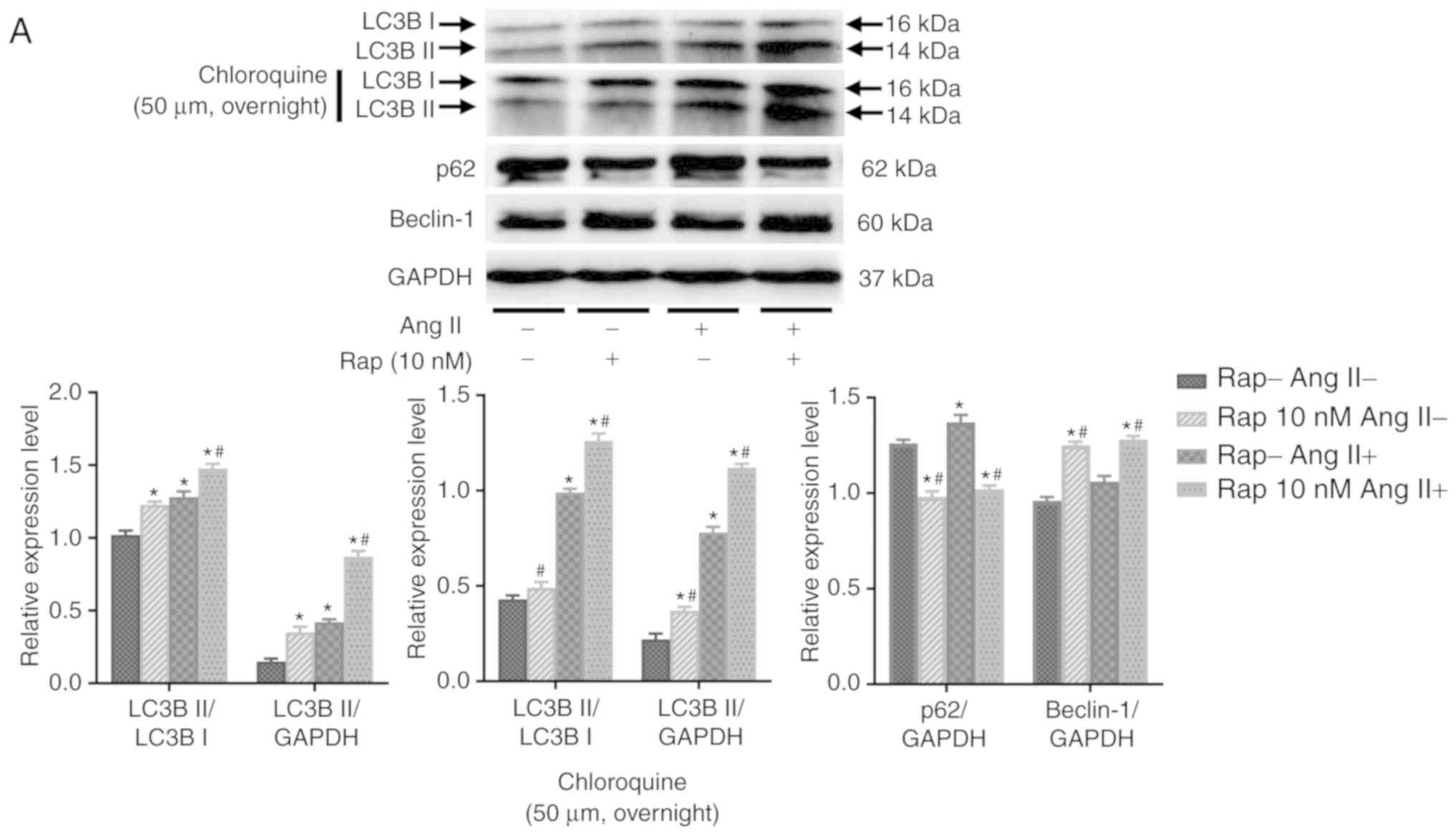
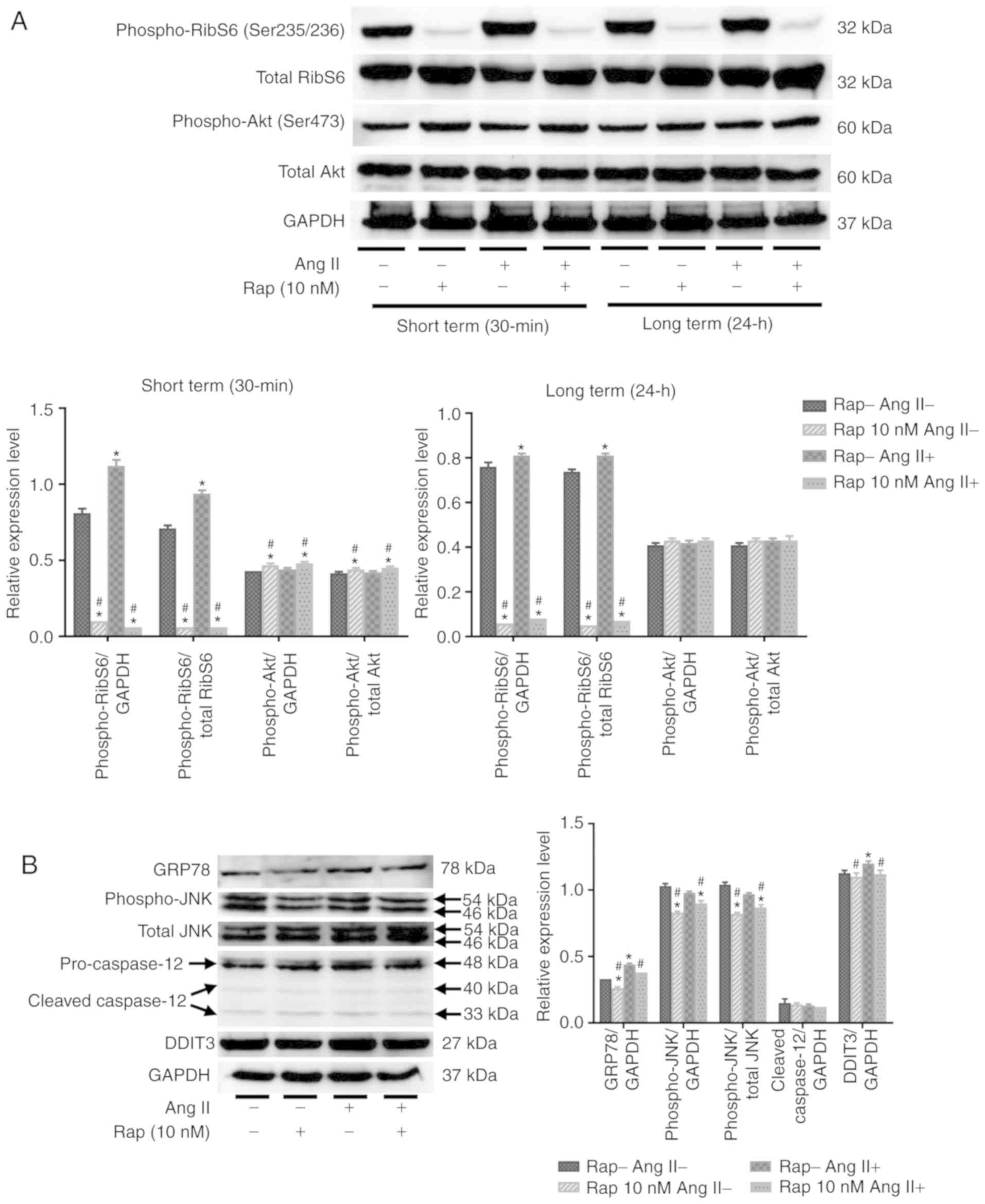
|
1
|
Metra M and Teerlink JR: Heart failure.
Lancet. 390:1981–1995. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cahill TJ, Choudhury RP and Riley PR:
Heart regeneration and repair after myocardial infarction:
Translational opportunities for novel therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 16:699–717. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Teringova E and Tousek P: Apoptosis in
ischemic heart disease. J Transl Med. 15:872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Whelan RS, Kaplinskiy V and Kitsis RN:
Cell death in the pathogenesis of heart disease: Mechanisms and
significance. Annu Rev Physiol. 72:19–44. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tham YK, Bernardo BC, Ooi JY, Weeks KL and
McMullen JR: Pathophysiology of cardiac hypertrophy and heart
failure: Signaling pathways and novel therapeutic targets. Arch
Toxicol. 89:1401–1438. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ziaeian B and Fonarow GC: Epidemiology and
aetiology of heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. 13:368–378. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Narula J, Haider N, Virmani R, DiSalvo TG,
Kolodgie FD, Hajjar RJ, Schmidt U, Semigran MJ, Dec GW and Khaw BA:
Apoptosis in myocytes in end-stage heart failure. N Engl J Med.
335:1182–1189. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hein S, Arnon E, Kostin S, Schönburg M,
Elsässer A, Polyakova V, Bauer EP, Klövekorn WP and Schaper J:
Progression from compensated hypertrophy to failure in the
pressure-overloaded human heart: Structural deterioration and
compensatory mechanisms. Circulation. 107:984–991. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wencker D, Chandra M, Nguyen K, Miao W,
Garantziotis S, Factor SM, Shirani J, Armstrong RC and Kitsis RN: A
mechanistic role for cardiac myocyte apoptosis in heart failure. J
Clin Invest. 111:1497–1504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abbate A, Biondi-Zoccai GG and Baldi A:
Pathophysiologic role of myocardial apoptosis in post-infarction
left ventricular remodeling. J Cell Physiol. 193:145–153. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Olivetti G, Abbi R, Quaini F, Kajstura J,
Cheng W, Nitahara JA, Quaini E, Di Loreto C, Beltrami CA, Krajewski
S, et al: Apoptosis in the failing human heart. N Engl J Med.
336:1131–1141. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kostin S, Pool L, Elsässer A, Hein S,
Drexler HC, Arnon E, Hayakawa Y, Zimmermann R, Bauer E, Klövekorn
WP and Schaper J: Myocytes die by multiple mechanisms in failing
human hearts. Circ Res. 92:715–724. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dickhout JG, Carlisle RE and Austin RC:
Interrelationship between cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, and
chronic kidney disease: Endoplasmic reticulum stress as a mediator
of pathogenesis. Circ Res. 108:629–642. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kolwicz SC Jr, Purohit S and Tian R:
Cardiac metabolism and its interactions with contraction, growth,
and survival of cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 113:603–616. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Minamino T, Komuro I and Kitakaze M:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress as a therapeutic target in
cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 107:1071–1082. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim I, Xu W and Reed JC: Cell death and
endoplasmic reticulum stress: Disease relevance and therapeutic
opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:1013–1030. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Okada K, Minamino T, Tsukamoto Y, Liao Y,
Tsukamoto O, Takashima S, Hirata A, Fujita M, Nagamachi Y, Nakatani
T, et al: Prolonged endoplasmic reticulum stress in hypertrophic
and failing heart after aortic constriction: Possible contribution
of endoplasmic reticulum stress to cardiac myocyte apoptosis.
Circulation. 110:705–712. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oyadomari S, Araki E and Mori M:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in pancreatic
beta-cells. Apoptosis. 7:335–345. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Takemura G, Kanamori H, Okada H, Miyazaki
N, Watanabe T, Tsujimoto A, Goto K, Maruyama R, Fujiwara T and
Fujiwara H: Anti-apoptosis in nonmyocytes and pro-autophagy in
cardio-myocytes: Two strategies against postinfarction heart
failure through regulation of cell death-degeneration. Heart Fail
Rev. 23:759–772. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kanamori H, Takemura G, Goto K, Maruyama
R, Ono K, Nagao K, Tsujimoto A, Ogino A, Takeyama T, Kawaguchi T,
et al: Autophagy limits acute myocardial infarction induced by
permanent coronary artery occlusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 300:H2261–H2271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kanamori H, Takemura G, Goto K, Maruyama
R, Tsujimoto A, Ogino A, Takeyama T, Kawaguchi T, Watanabe T,
Fujiwara T, et al: The role of autophagy emerging in postinfarction
cardiac remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 91:330–339. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sciarretta S, Zhai P, Shao D, Maejima Y,
Robbins J, Volpe M, Condorelli G and Sadoshima J: Rheb is a
critical regulator of autophagy during myocardial ischemia:
Pathophysiological implications in obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Circulation. 125:1134–1146. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ghosh R and Pattison JS: Macroautophagy
and chaperone-mediated autophagy in heart failure: The known and
the unknown. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:86020412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang C, Yitzhaki S, Perry CN, Liu W,
Giricz Z, Mentzer RM Jr and Gottlieb RA: Autophagy induced by
ischemic preconditioning is essential for cardioprotection. J
Cardiovasc Transl Res. 3:365–373. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
De Meyer GR and Martinet W: Autophagy in
the cardiovascular system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:1485–1495.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gurusamy N, Lekli I, Gorbunov NV,
Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM and Das DK: Cardioprotection by
adaptation to ischaemia augments autophagy in association with
BAG-1 protein. J Cell Mol Med. 13:373–387. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bhuiyan MS, Pattison JS, Osinska H, James
J, Gulick J, McLendon PM, Hill JA, Sadoshima J and Robbins J:
Enhanced autophagy ameliorates cardiac proteinopathy. J Clin
Invest. 123:5284–5297. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nakai A, Yamaguchi O, Takeda T, Higuchi Y,
Hikoso S, Taniike M, Omiya S, Mizote I, Matsumura Y, Asahi M, et
al: The role of autophagy in cardiomyocytes in the basal state and
in response to hemodynamic stress. Nat Med. 13:619–624. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth control and disease. Cell. 149:274–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sciarretta S, Forte M, Frati G and
Sadoshima J: New insights into the role of mTOR signaling in the
cardiovascular system. Circ Res. 122:489–505. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sadoshima J and Izumo S: Rapamycin
selectively inhibits angiotensin II-induced increase in protein
synthesis in cardiac myocytes in vitro. Potential role of 70-kD S6
kinase in angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res.
77:1040–1052. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Simm A, Schlüter K, Diez C, Piper HM and
Hoppe J: Activation of p70(S6) kinase by beta-adrenoceptor agonists
on adult cardio-myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 30:2059–2067. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Buss SJ, Muenz S, Riffel JH, Malekar P,
Hagenmueller M, Weiss CS, Bea F, Bekeredjian R, Schinke-Braun M,
Izumo S, et al: Beneficial effects of Mammalian target of rapamycin
inhibition on left ventricular remodeling after myocardial
infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 54:2435–2446. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li Q, Xie J, Li R, Shi J, Sun J, Gu R,
Ding L, Wang L and Xu B: Overexpression of microRNA-99a attenuates
heart remodelling and improves cardiac performance after myocardial
infarction. J Cell Mol Med. 18:919–928. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sengupta S, Sheen
JH, Hsu PP, Bagley AF, Markhard AL and Sabatini DM: Prolonged
rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assembly and Akt-PKB. Mol Cell.
22:159–168. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Völkers M, Konstandin MH, Doroudgar S,
Toko H, Quijada P, Din S, Joyo A, Ornelas L, Samse K, Thuerauf DJ,
et al: Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 protects the heart
from ischemic damage. Circulation. 128:2132–2144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Benjamin D, Colombi M, Moroni C and Hall
MN: Rapamycin passes the torch: A new generation of mTOR
inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 10:868–880. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Di R, Wu X, Chang Z, Zhao X, Feng Q, Lu S,
Luan Q, Hemmings BA, Li X and Yang Z: S6K inhibition renders
cardiac protection against myocardial infarction through PDK1
phos-phorylation of Akt. Biochem J. 441:199–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Liu M, Mao C, Li J, Han F and Yang P:
Effects of the Activin A-follistatin system on myocardial cell
apoptosis through the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in heart
failure. Int J Mol Sci. 18:2017.
|
|
40
|
Kanamori H, Takemura G, Goto K, Tsujimoto
A, Ogino A, Takeyama T, Kawaguchi T, Watanabe T, Morishita K,
Kawasaki M, et al: Resveratrol reverses remodeling in hearts with
large, old myocardial infarctions through enhanced
autophagy-activating AMP kinase pathway. Am J Pathol. 182:701–713.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ji Y, Luo X, Yang Y, Dai Z, Wu G and Wu Z:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in intestinal
epithelial cells: A feed-back regulation by mechanistic target of
rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 9:382018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Appenzeller-Herzog C and Hall MN:
Bidirectional crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress and
mTOR signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 22:274–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kato H, Nakajima S, Saito Y, Takahashi S,
Katoh R and Kitamura M: mTORC1 serves ER stress-triggered apoptosis
via selective activation of the IRE1-JNK pathway. Cell Death
Differ. 19:310–320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Goldman S and Raya TE: Rat infarct model
of myocardial infarction and heart failure. J Card Fail. 1:169–177.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shioi T, McMullen JR, Tarnavski O,
Converso K, Sherwood MC, Manning WJ and Izumo S: Rapamycin
attenuates load-induced cardiac hypertrophy in mice. Circulation.
107:1664–1670. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bishu K, Ogut O, Kushwaha S, Mohammed SF,
Ohtani T, Xu X, Brozovich FV and Redfield MM: Anti-remodeling
effects of rapamycin in experimental heart failure: Dose response
and interaction with angiotensin receptor blockade. PLoS One.
8:e813252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Schunkert H, Sadoshima J, Cornelius T,
Kagaya Y, Weinberg EO, Izumo S, Riegger G and Lorell BH:
Angiotensin II-induced growth responses in isolated adult rat
hearts. Evidence for load-independent induction of cardiac protein
synthesis by angiotensin II. Circ Res. 76:489–497. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yan M, Yang S, Meng F, Zhao Z, Tian Z and
Yang P: MicroRNA 199a-5p induces apoptosis by targeting JunB. Sci
Rep. 8:66992018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang D, Contu R, Latronico MV, Zhang J,
Rizzi R, Catalucci D, Miyamoto S, Huang K, Ceci M, Gu Y, et al:
MTORC1 regulates cardiac function and myocyte survival through
4E-BP1 inhibition in mice. J Clin Invest. 120:2805–2816. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jung CH, Ro SH, Cao J, Otto NM and Kim DH:
mTOR regulation of autophagy. FEBS Lett. 584:1287–1295. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
McMullen JR, Sherwood MC, Tarnavski O,
Zhang L, Dorfman AL, Shioi T and Izumo S: Inhibition of mTOR
signaling with rapamycin regresses established cardiac hypertrophy
induced by pressure overload. Circulation. 109:3050–3055. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Song X, Kusakari Y, Xiao CY, Kinsella SD,
Rosenberg MA, Scherrer-Crosbie M, Hara K, Rosenzweig A and Matsui
T: mTOR attenuates the inflammatory response in cardiomyocytes and
prevents cardiac dysfunction in pathological hypertrophy. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 299:C1256–C1266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ikeda M, Ide T, Fujino T, Matsuo Y, Arai
S, Saku K, Kakino T, Oga Y, Nishizaki A and Sunagawa K: The
Akt-mTOR axis is a pivotal regulator of eccentric hypertrophy
during volume overload. Sci Rep. 5:158812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Harston RK, McKillop JC, Moschella PC, Van
Laer A, Quinones LS, Baicu CF, Balasubramanian S, Zile MR and
Kuppuswamy D: Rapamycin treatment augments both protein
ubiquitination and Akt activation in pressure-overloaded rat
myocardium. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 300:H1696–H1706. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mori K: Tripartite management of unfolded
proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 101:451–454. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|