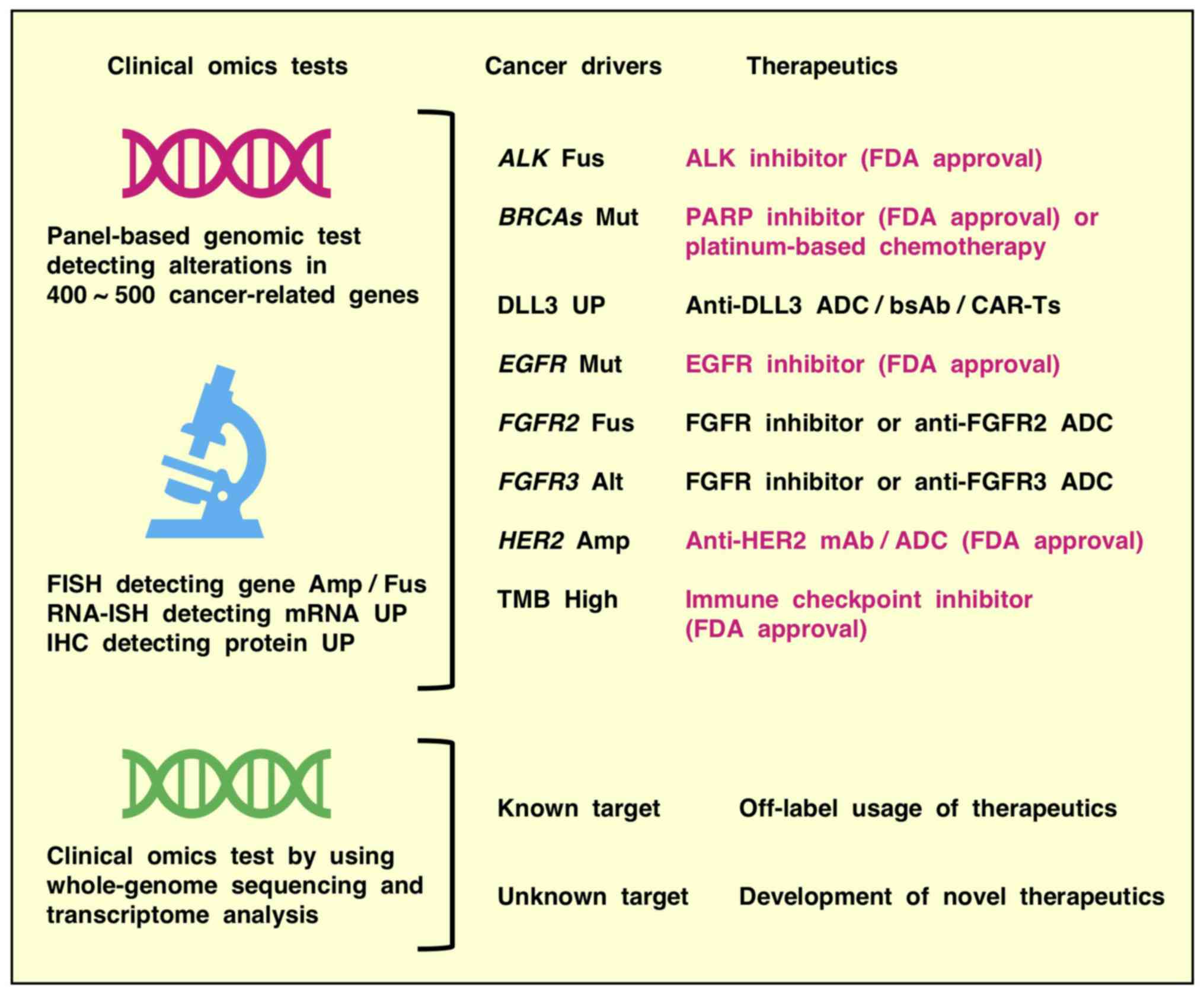
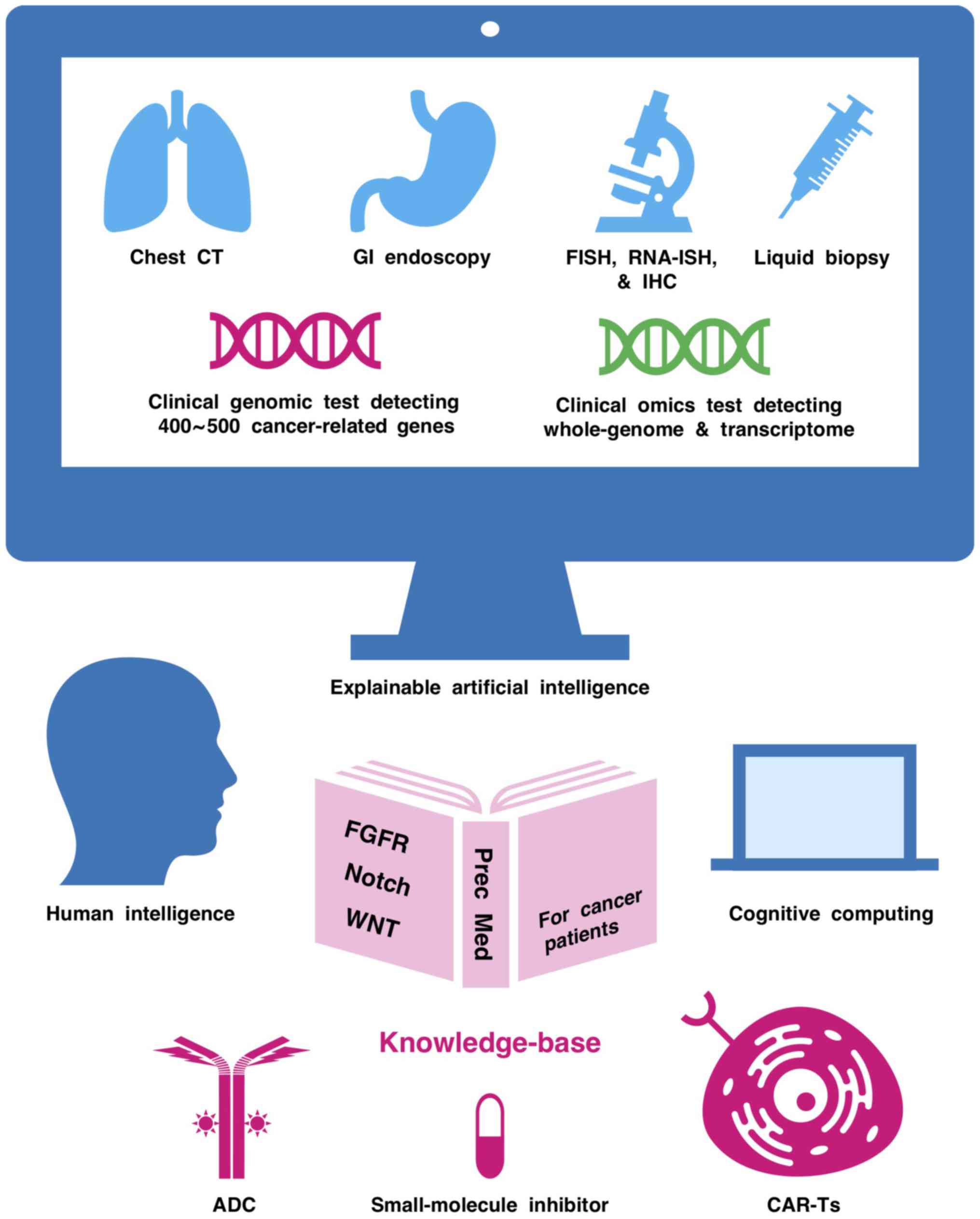
|
1
|
Guruharsha KG, Kankel MW and
Artavanis-Tsakonas S: The Notch signalling system: Recent insights
into the complexity of a conserved pathway. Nat Rev Genet.
13:654–666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray SJ: Notch signalling in context. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:722–735. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meurette O and Mehlen P: Notch signaling
in the tumor micro-environment. Cancer Cell. 34:536–548. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siebel C and Lendahl U: Notch signaling in
development, tissue homeostasis, and disease. Physiol Rev.
97:1235–1294. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wimmer RA, Leopoldi A, Aichinger M, Wick
N, Hantusch B, Novatchkova M, Taubenschmid J, Hämmerle M, Esk C,
Bagley JA, et al: Human blood vessel organoids as a model of
diabetic vasculopathy. Nature. 565:505–510. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ranganathan P, Weaver KL and Capobianco
AJ: Notch signalling in solid tumours: A little bit of everything
but not all the time. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:338–351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ntziachristos P, Lim JS, Sage J and
Aifantis I: From fly wings to targeted cancer therapies: A
centennial for notch signaling. Cancer Cell. 25:318–334. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aster JC, Pear WS and Blacklow SC: The
varied roles of Notch in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 12:245–275. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nowell CS and Radtke F: Notch as a tumour
suppressor. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:145–159. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Espinoza I and Miele L: Notch inhibitors
for cancer treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 139:95–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takebe N, Miele L, Harris PJ, Jeong W,
Bando H, Kahn M, Yang SX and Ivy SP: Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and
Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical update. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 12:445–464. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Owen DH, Giffin MJ, Bailis JM, Smit MD,
Carbone DP and He K: DLL3: An emerging target in small cell lung
cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 12:612019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
D'Souza B, Miyamoto A and Weinmaster G:
The many facets of Notch ligands. Oncogene. 27:5148–5167. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kangsamaksin T, Murtomaki A, Kofler NM,
Cuervo H, Chaudhri RA, Tattersall IW, Rosenstiel PE, Shawber C and
Kitajewski J: NOTCH decoys that selectively block DLL/NOTCH or
JAG/NOTCH disrupt angiogenesis by unique mechanisms to inhibit
tumor growth. Cancer Discov. 5:182–197. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kakuda S and Haltiwanger RS: Deciphering
the Fringe-mediated Notch code: Identification of activating and
inhibiting sites allowing discrimination between ligands. Dev Cell.
40:193–201. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nandagopal N, Santat LA, LeBon L, Sprinzak
D, Bronner ME and Elowitz MB: Dynamic ligand discrimination in the
Notch signaling pathway. Cell. 172:869–880.e19. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sjöqvist M and Andersson ER: Do as I say,
Not(ch) as I do: Lateral control of cell fate. Dev Biol. 447:58–70.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lambrecht BN, Vanderkerken M and Hammad H:
The emerging role of ADAM metalloproteinases in immunity. Nat Rev
Immunol. 18:745–758. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang G, Zhou R, Zhou Q, Guo X, Yan C, Ke
M, Lei J and Shi Y: Structural basis of Notch recognition by human
γ-secretase. Nature. 565:192–197. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kopan R and Ilagan MX: The canonical Notch
signaling pathway: Unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell.
137:216–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vilimas T, Mascarenhas J, Palomero T,
Mandal M, Buonamici S, Meng F, Thompson B, Spaulding C, Macaroun S,
Alegre ML, et al: Targeting the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in
Notch1-induced T-cell leukemia. Nat Med. 13:70–77. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Vermezovic J, Adamowicz M, Santarpia L,
Rustighi A, Forcato M, Lucano C, Massimiliano L, Costanzo V,
Bicciato S, Del Sal G and d'Adda di Fagagna F: Notch is a direct
negative regulator of the DNA-damage response. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
22:417–424. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Polacheck WJ, Kutys ML, Yang J, Eyckmans
J, Wu Y, Vasavada H, Hirschi KK and Chen CS: A non-canonical Notch
complex regulates adherens junctions and vascular barrier function.
Nature. 552:258–262. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
O'Neil J, Grim J, Strack P, Rao S,
Tibbitts D, Winter C, Hardwick J, Welcker M, Meijerink JP, Pieters
R, et al: FBW7 mutations in leukemic cells mediate NOTCH pathway
activation and resistance to γ-secretase inhibitors. J Exp Med.
204:1813–1824. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Liu P, Inuzuka H and Wei W: Roles
of F-box proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:233–247. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shan H, Li X, Xiao X, Dai Y, Huang J, Song
J, Liu M, Yang L, Lei H, Tong Y, et al: USP7 deubiquitinates and
stabilizes NOTCH1 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 3:292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
LaFoya B, Munroe JA, Pu X and Albig AR:
Src kinase phosphorylates Notch1 to inhibit MAML binding. Sci Rep.
8:155152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ramakrishnan G, Davaakhuu G, Chung WC, Zhu
H, Rana A, Filipovic A, Green AR, Atfi A, Pannuti A, Miele L and
Tzivion G: AKT and 143-3 regulate Notch4 nuclear localization. Sci
Rep. 5:87822015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sun Y, Klauzinska M, Lake RJ, Lee JM,
Santopietro S, Raafat A, Salomon D, Callahan R and
Artavanis-Tsakonas S: Trp53 regulates Notch 4 signaling through
Mdm2. J Cell Sci. 124:1067–1076. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
McGill MA and McGlade CJ: Mammalian Numb
proteins promote Notch1 receptor ubiquitination and degradation of
the Notch1 intracellular domain. J Biol Chem. 278:23196–23203.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pettersson S, Sczaniecka M, McLaren L,
Russell F, Gladstone K, Hupp T and Wallace M: Non-degradative
ubiquitination of the Notch1 receptor by the E3 ligase MDM2
activates the Notch signalling pathway. Biochem J. 450:523–536.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bhardwaj A, Yang Y, Ueberheide B and Smith
S: Whole proteome analysis of human tankyrase knockout cells
reveals targets of tankyrase-mediated degradation. Nat Commun.
8:22142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schaller MA, Logue H, Mukherjee S, Lindell
DM, Coelho AL, Lincoln P, Carson WF IV, Ito T, Cavassani KA,
Chensue SW, et al: Delta-like 4 differentially regulates murine CD4
T cell expansion via BMI1. PLoS One. 5:e121722010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
López-Arribillaga E, Rodilla V,
Pellegrinet L, Guiu J, Iglesias M, Roman AC, Gutarra S, González S,
Muñoz-Cánoves P, Fernández- Salguero P, et al: Bmi1 regulates
murine intestinal stem cell proliferation and self-renewal
downstream of Notch. Development. 142:41–50. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ronchini C and Capobianco AJ: Induction of
cyclin D1 transcription and CDK2 activity by Notch(ic): Implication
for cell cycle disruption in transformation by Notch(ic). Mol Cell
Biol. 21:5925–5934. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tanis KQ, Podtelezhnikov AA, Blackman SC,
Hing J, Railkar RA, Lunceford J, Klappenbach JA, Wei B, Harman A,
Camargo LM, et al: An accessible pharmacodynamic transcriptional
biomarker for Notch target engagement. Clin Pharmacol Ther.
99:370–380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
García-Peydró M, Fuentes P, Mosquera M,
García-León MJ, Alcain J, Rodríguez A, García de Miguel P, Menéndez
P, Weijer K, Spits H, et al: The NOTCH1/CD44 axis drives
pathogenesis in a T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia model. J Clin
Invest. 128:2802–2818. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rangarajan A, Talora C, Okuyama R, Nicolas
M, Mammucari C, Oh H, Aster JC, Krishna S, Metzger D, Chambon P, et
al: Notch signaling is a direct determinant of keratinocyte growth
arrest and entry into differentiation. EMBO J. 20:3427–3436. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Procopio MG, Laszlo C, Al Labban D, Kim
DE, Bordignon P, Jo SH, Goruppi S, Menietti E, Ostano P, Ala U, et
al: Combined CSL and p53 downregulation promotes cancer-associated
fibroblast activation. Nat Cell Biol. 17:1193–1204. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jarriault S, Le Bail O, Hirsinger E,
Pourquié O, Logeat F, Strong CF, Brou C, Seidah NG and Isra l A:
Delta-1 activation of Notch-1 signaling results in HES-1
transactivation. Mol Cell Biol. 18:7423–7431. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lim JS, Ibaseta A, Fischer MM, Cancilla B,
O'Young G, Cristea S, Luca VC, Yang D, Jahchan NS, Hamard C, et al:
Intratumoural heterogeneity generated by Notch signalling promotes
small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 545:360–364. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Stoeck A, Lejnine S, Truong A, Pan L, Wang
H, Zang C, Yuan J, Ware C, MacLean J, Garrett-Engele PW, et al:
Discovery of biomarkers predictive of GSI response in
triple-negative breast cancer and adenoid cystic carcinoma. Cancer
Discov. 4:1154–1167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Maier MM and Gessler M: Comparative
analysis of the human and mouse Hey1 promoter: Hey genes are new
Notch target genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 275:652–660. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Weng AP, Millholland JM, Yashiro-Ohtani Y,
Arcangeli ML, Lau A, Wai C, Del Bianco C, Rodriguez CG, Sai H,
Tobias J, et al: c-Myc is an important direct target of Notch1 in
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Genes Dev.
20:2096–2109. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gekas C, D'Altri T, Aligué R, González J,
Espinosa L and Bigas A: β-Catenin is required for T-cell leukemia
initiation and MYC transcription downstream of Notch1. Leukemia.
30:2002–2010. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tottone L, Zhdanovskaya N, Carmona Pestaña
Á, Zampieri M, Simeoni F, Lazzari S, Ruocco V, Pelullo M, Caiafa P,
Felli MP, et al: Histone modifications drive aberrant Notch3
expression/activity and growth in T-ALL. Front Oncol. 9:1982019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pirot P, van Grunsven LA, Marine JC,
Huylebroeck D and Bellefroid EJ: Direct regulation of the Nrarp
gene promoter by the Notch signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 322:526–534. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wakabayashi N, Skoko JJ, Chartoumpekis DV,
Kimura S, Slocum SL, Noda K, Palliyaguru DL, Fujimuro M, Boley PA,
Tanaka Y, et al: Notch-Nrf2 axis: Regulation of Nrf2 gene
expression and cytoprotection by Notch signaling. Mol Cell Biol.
34:653–663. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
VanDussen KL, Carulli AJ, Keeley TM, Patel
SR, Puthoff BJ, Magness ST, Tran IT, Maillard I, Siebel C, Kolterud
Å, et al: Notch signaling modulates proliferation and
differentiation of intestinal crypt base columnar stem cells.
Development. 139:488–497. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Weber BN, Chi AW, Chavez A, Yashiro-Ohtani
Y, Yang Q, Shestova O and Bhandoola A: A critical role for TCF-1 in
T-lineage specification and differentiation. Nature. 476:63–68.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Germar K, Dose M, Konstantinou T, Zhang J,
Wang H, Lobry C, Arnett KL, Blacklow SC, Aifantis I, Aster JC and
Gounari F: T-cell factor 1 is a gatekeeper for T-cell specification
in response to Notch signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:20060–20065. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bray SJ and Gomez-Lamarca M: Notch after
cleavage. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 51:103–109. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen B, Jiang L, Zhong ML, Li JF, Li BS,
Peng LJ, Dai YT, Cui BW, Yan TQ, Zhang WN, et al: Identification of
fusion genes and characterization of transcriptome features in
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
115:373–378. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sanchez-Vega F, Mina M, Armenia J, Chatila
WK, Luna A, La KC, Dimitriadoy S, Liu DL, Kantheti HS, Saghafinia
S, et al: Oncogenic signaling pathways in The Cancer Genome Atlas.
Cell. 173:321–337.e10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Weng AP, Ferrando AA, Lee W, Morris JP IV,
Silverman LB, Sanchez-Irizarry C, Blacklow SC, Look AT and Aster
JC: Activating mutations of NOTCH1 in human T cell acute
lympho-blastic leukemia. Science. 306:269–271. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Palomero T, Barnes KC, Real PJ, Glade
Bender JL, Sulis ML, Murty VV, Colovai AI, Balbin M and Ferrando
AA: CUTLL1, a novel human T-cell lymphoma cell line with t(7;9)
rearrangement, aberrant NOTCH1 activation and high sensitivity to
gamma-secretase inhibitors. Leukemia. 20:1279–1287. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bie De J, Demeyer S, Alberti-Servera L,
Geerdens E, Segers H, Broux M, De Keersmaecker K, Michaux L,
Vandenberghe P, Voet T, et al: Single-cell sequencing reveals the
origin and the order of mutation acquisition in T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 32:1358–1369. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Puente XS, Pinyol M, Quesada V, Conde L,
Ordóñez GR, Villamor N, Escaramis G, Jares P, Beà S, González-Díaz
M, et al: Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in
chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature. 475:101–105. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fabbri G and Dalla-Favera R: The molecular
pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer.
16:145–162. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Karube K, Enjuanes A, Dlouhy I, Jares P,
Martin-Garcia D, Nadeu F, Ordóñez GR, Rovira J, Clot G, Royo C, et
al: Integrating genomic alterations in diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma identifies new relevant pathways and potential therapeutic
targets. Leukemia. 32:675–684. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
61
|
González-Rincón J, Méndez M, Gómez S,
García JF, Martín P, Bellas C, Pedrosa L, Rodríguez-Pinilla SM,
Camacho FI, Quero C, et al: Unraveling transformation of follicular
lymphoma to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. PLoS One.
14:e02128132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kridel R, Meissner B, Rogic S, Boyle M,
Telenius A, Woolcock B, Gunawardana J, Jenkins C, Cochrane C,
Ben-Neriah S, et al: Whole transcriptome sequencing reveals
recurrent NOTCH1 mutations in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood.
119:1963–1971. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Robinson DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Wu YM,
Shankar S, Cao X, Ateeq B, Asangani IA, Iyer M, Maher CA, Grasso
CS, et al: Functionally recurrent rearrangements of the MAST kinase
and Notch gene families in breast cancer. Nat Med. 17:1646–1651.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang K, Zhang Q, Li D, Ching K, Zhang C,
Zheng X, Ozeck M, Shi S, Li X, Wang H, et al: PEST domain mutations
in Notch receptors comprise an oncogenic driver segment in
triple-negative breast cancer sensitive to a γ-secretase inhibitor.
Clin Cancer Res. 21:1487–1496. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Robinson DR, Wu YM, Lonigro RJ, Vats P,
Cobain E, Everett J, Cao X, Rabban E, Kumar-Sinha C, Raymond V, et
al: Integrative clinical genomics of metastatic cancer. Nature.
548:297–303. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Westhoff B, Colaluca IN, D'Ario G,
Donzelli M, Tosoni D, Volorio S, Pelosi G, Spaggiari L, Mazzarol G,
Viale G, et al: Alterations of the Notch pathway in lung cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:22293–22298. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang NJ, Sanborn Z, Arnett KL, Bayston LJ,
Liao W, Proby CM, Leigh IM, Collisson EA, Gordon PB, Jakkula L, et
al: Loss-of-function mutations in Notch receptors in cutaneous and
lung squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:17761–17766. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Agrawal N, Frederick MJ, Pickering CR,
Bettegowda C, Chang K, Li RJ, Fakhry C, Xie TX, Zhang J, Wang J, et
al: Exome sequencing of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
reveals inactivating mutations in NOTCH1. Science. 333:1154–1157.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Stransky N, Egloff AM, Tward AD, Kostic
AD, Cibulskis K, Sivachenko A, Kryukov GV, Lawrence MS, Sougnez C,
McKenna A, et al: The mutational landscape of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Science. 333:1157–1160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Song Y, Li L, Ou Y, Gao Z, Li E, Li X,
Zhang W, Wang J, Xu L, Zhou Y, et al: Identification of genomic
alterations in oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Nature. 509:91–95.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Martincorena I, Fowler JC, Wabik A, Lawson
ARJ, Abascal F, Hall MWJ, Cagan A, Murai K, Mahbubani K, Stratton
MR, et al: Somatic mutant clones colonize the human esophagus with
age. Science. 362:911–917. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
George J, Lim JS, Jang SJ, Cun Y, Ozretić
L, Kong G, Leenders F, Lu X, Fernández-Cuesta L, Bosco G, et al:
Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature.
524:47–53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ali SA, Justilien V, Jamieson L, Murray NR
and Fields AP: Protein kinase Cι drives a NOTCH3-dependent
stem-like phenotype in mutant KRAS lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer
Cell. 29:367–378. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bhagat TD, Zou Y, Huang S, Park J, Palmer
MB, Hu C, Li W, Shenoy N, Giricz O, Choudhary G, et al: Notch
pathway is activated via genetic and epigenetic alterations and is
a therapeutic target in clear cell renal cancer. J Biol Chem.
292:837–846. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
75
|
van Groningen T, Akogul N, Westerhout EM,
Chan A, Hasselt NE, Zwijnenburg DA, Broekmans M, Stroeken P,
Haneveld F, Hooijer GKJ, et al: A NOTCH feed-forward loop drives
reprogramming from adrenergic to mesenchymal state in
neuroblastoma. Nat Commun. 10:15302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ban J, Bennani-Baiti IM, Kauer M, Schaefer
KL, Poremba C, Jug G, Schwentner R, Smrzka O, Muehlbacher K, Aryee
DN and Kovar H: EWS-FLI1 suppresses NOTCH-activated p53 in Ewing's
sarcoma. Cancer Res. 68:7100–7109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Augert A, Eastwood E, Ibrahim AH, Wu N,
Grunblatt E, Basom R, Liggitt D, Eaton KD, Martins R, Poirier JT,
et al: Targeting NOTCH activation in small cell lung cancer through
LSD1 inhibition. Sci Signal. 12:pii: eaau2922. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Song Y, Zhang Y, Jiang H, Zhu Y, Liu L,
Feng W, Yang L, Wang Y and Li M: Activation of Notch3 promotes
pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells proliferation via
Hes1/p27Kip1 signaling pathway. FEBS Open Bio. 5:656–660. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Maraver A, Fernández-Marcos PJ, Herranz D,
Muñoz-Martin M, Gomez-Lopez G, Cañamero M, Mulero F, Megías D,
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Shen J, et al: Therapeutic effect of γ-secretase
inhibition in KrasG12V-driven non-small cell lung carcinoma by
derepression of DUSP1 and inhibition of ERK. Cancer Cell.
22:222–234. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Palomero T, Sulis ML, Cortina M, Real PJ,
Barnes K, Ciofani M, Caparros E, Buteau J, Brown K, Perkins SL, et
al: Mutational loss of PTEN induces resistance to NOTCH1 inhibition
in T-cell leukemia. Nat Med. 13:1203–1210. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhou X, Smith AJ, Waterhouse A, Blin G,
Malaguti M, Lin CY, Osorno R, Chambers I and Lowell S: Hes1
desynchronizes differentiation of pluripotent cells by modulating
STAT3 activity. Stem Cells. 31:1511–1122. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Weng MT, Tsao PN, Lin HL, Tung CC, Change
MC, Chang YT, Wong JM and Wei SC: Hes1 increases the invasion
ability of colorectal cancer cells via the STAT3-MMP14 pathway.
PLoS One. 10:e01443222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Jin S, Mutvei AP, Chivukula IV, Andersson
ER, Ramsköld D, Sandberg R, Lee KL, Kronqvist P, Mamaeva V, Ostling
P, et al: Non-canonical Notch signaling activates IL-6/JAK/STAT
signaling in breast tumor cells and is controlled by p53 and
IKKα/IKKβ. Oncogene. 32:4892–4902. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Schreck KC, Taylor P, Marchionni L,
Gopalakrishnan V, Bar EE, Gaiano N and Eberhart CG: The Notch
target Hes1 directly modulates Gli1 expression and Hedgehog
signaling: A potential mechanism of therapeutic resistance. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:6060–6070. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Bonyadi Rad E, Hammerlindl H, Wels C,
Popper U, Ravindran Menon D, Breiteneder H, Kitzwoegerer M, Hafner
C, Herlyn M, Bergler H and Schaider H: Notch4 signaling induces a
mesenchymal-epithelial-like transition in melanoma cells to
suppress malignant behaviors. Cancer Res. 76:1690–1697. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wang D, Xu J, Liu B, He X, Zhou L, Hu X,
Qiao F, Zhang A, Xu X, Zhang H, et al: IL6 blockade potentiates the
anti-tumor effects of γ-secretase inhibitors in Notch3-expressing
breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 25:330–339. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Hartman BH, Reh TA and Bermingham-McDonogh
O: Notch signaling specifies prosensory domains via lateral
induction in the developing mammalian inner ear. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 107:15792–15797. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Petrovic J, Formosa-Jordan P,
Luna-Escalante JC, Abelló G, Ibañes M, Neves J and Giraldez F:
Ligand-dependent Notch signaling strength orchestrates lateral
induction and lateral inhibition in the developing inner ear.
Development. 141:2313–2324. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sun W, Gaykalova DA, Ochs MF, Mambo E,
Arnaoutakis D, Liu Y, Loyo M, Agrawal N, Howard J, Li R, et al:
Activation of the NOTCH pathway in head and neck cancer. Cancer
Res. 74:1091–1104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
90
|
Turley SJ, Cremasco V and Astarita JL:
Immunological hallmarks of stromal cells in the tumour
microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol. 15:669–682. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Valkenburg KC, de Groot AE and Pienta KJ:
Targeting the tumour stroma to improve cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 15:366–381. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Östman A and Corvigno S: Microvascular
mural cells in cancer. Trends Cancer. 4:838–848. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Lambrechts D, Wauters E, Boeckx B, Aibar
S, Nittner D, Burton O, Bassez A, Decaluwé H, Pircher A, Van den
Eynde K, et al: Phenotype molding of stromal cells in the lung
tumor microenvironment. Nat Med. 24:1277–1289. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Bartoschek M, Oskolkov N, Bocci M, Lövrot
J, Larsson C, Sommarin M, Madsen CD, Lindgren D, Pekar G, Karlsson
G, et al: Spatially and functionally distinct subclasses of breast
cancer-associated fibroblasts revealed by single cell RNA
sequencing. Nat Commun. 9:51502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kalluri R: The biology and function of
fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:582–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Altorki NK, Markowitz GJ, Gao D, Port JL,
Saxena A, Stiles B, McGraw T and Mittal V: The lung
microenvironment: An important regulator of tumour growth and
metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:9–31. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
97
|
Wang Z and Zöller M: Exosomes, metastases,
and the miracle of cancer stem cell markers. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
38:259–295. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Katoh M: Canonical and non-canonical WNT
signaling in cancer stem cells and their niches: Cellular
heterogeneity, omics reprogramming, targeted therapy and tumor
plasticity (Review). Int J Oncol. 51:1357–1369. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Dotto GP: Multifocal epithelial tumors and
field cancerization: Stroma as a primary determinant. J Clin
Invest. 124:1446–1453. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Shibue T and Weinberg RA: EMT, CSCs, and
drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:611–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Schreiber RD, Old LJ and Smyth MJ: Cancer
immunoediting: Integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression
and promotion. Science. 331:1565–1570. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Fukumura D, Kloepper J, Amoozgar Z, Duda
DG and Jain RK: Enhancing cancer immunotherapy using
antiangiogenics: Opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
15:325–340. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Robbins J, Blondel BJ, Gallahan D and
Callahan R: Mouse mammary tumor gene int-3: A member of the Notch
gene family transforms mammary epithelial cells. J Virol.
66:2594–2599. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Peters G, Lee AE and Dickson C: Concerted
activation of two potential proto-oncogenes in carcinomas induced
by mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 320:628–631. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Shackleford GM, MacArthur CA, Kwan HC and
Varmus HE: Mouse mammary tumor virus infection accelerates mammary
carcinogenesis in Wnt-1 transgenic mice by insertional activation
of int-2/Fgf-3 and hst/Fgf-4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:740–744.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Katoh M: WNT and FGF gene clusters
(review). Int J Oncol. 21:1269–1273. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Lowther W, Wiley K, Smith GH and Callahan
R: A new common integration site, Int7, for the mouse mammary tumor
virus in mouse mammary tumors identifies a gene whose product has
furin-like and thrombospondin-like sequences. J Virol.
79:10093–10096. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Theodorou V, Kimm MA, Boer M, Wessels L,
Theelen W, Jonkers J and Hilkens J: MMTV insertional mutagenesis
identifies genes, gene families and pathways involved in mammary
cancer. Nat Genet. 39:759–769. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zhan T, Rindtorff N and Boutros M: Wnt
signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 36:1461–1473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
110
|
Morgan RG, Mortensson E and Williams AC:
Targeting LGR5 in colorectal cancer: Therapeutic gold or too
plastic. Br J Cancer. 118:1410–1418. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Estrach S, Ambler CA, Lo Celso C, Hozumi K
and Watt FM: Jagged 1 is a beta-catenin target gene required for
ectopic hair follicle formation in adult epidermis. Development.
133:4427–4438. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ma L, Wang Y, Hui Y, Du Y, Chen Z, Feng H,
Zhang S, Li N, Song J, Fang Y, et al: WNT/NOTCH pathway is
essential for the maintenance and expansion of human MGE
progenitors. Stem Cell Reports. 12:934–949. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Boulter L, Govaere O, Bird TG, Radulescu
S, Ramachandran P, Pellicoro A, Ridgway RA, Seo SS, Spee B, Van
Rooijen N, et al: Macrophage-derived Wnt opposes Notch signaling to
specify hepatic progenitor cell fate in chronic liver disease. Nat
Med. 18:572–579. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Högström J, Heino S, Kallio P, Lähde M,
Leppänen VM, Balboa D, Wiener Z and Alitalo K: Transcription factor
PROX1 suppresses Notch pathway activation via the nucleosome
remod-eling and deacetylase complex in colorectal cancer stem-like
cells. Cancer Res. 78:5820–5832. 2018.
|
|
115
|
Phng LK, Potente M, Leslie JD, Babbage J,
Nyqvist D, Lobov I, Ondr JK, Rao S, Lang RA, Thurston G and
Gerhardt H: Nrarp coordinates endothelial Notch and Wnt signaling
to control vessel density in angiogenesis. Dev Cell. 16:70–82.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Liu W, Li H, Hong SH, Piszczek GP, Chen W
and Rodgers GP: Olfactomedin 4 deletion induces colon
adenocarcinoma in ApcMin/+ mice. Oncogene. 35:5237–5247.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Giancotti FG: Mechanisms governing
metastatic dormancy and reactivation. Cell. 155:750–764. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Katoh M: Multi-layered prevention and
treatment of chronic inflammation, organ fibrosis and cancer
associated with canonical WNT/β-catenin signaling activation
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 42:713–725. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Dimri GP, Martinez JL, Jacobs JJ, Keblusek
P, Itahana K, Van Lohuizen M, Campisi J, Wazer DE and Band V: The
Bmi-1 oncogene induces telomerase activity and immortalizes human
mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 62:4736–4745. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
De Jaime-Soguero A, Aulicino F, Ertaylan
G, Griego A, Cerrato A, Tallam A, Del Sol A, Cosma MP and Lluis F:
Wnt/Tcf1 pathway restricts embryonic stem cell cycle through
activation of the Ink4/Arf locus. PLoS Genet. 13:e10066822017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Srinivasan T, Walters J, Bu P, Than EB,
Tung KL, Chen KY, Panarelli N, Milsom J, Augenlicht L, Lipkin SM
and Shen X: NOTCH signaling regulates asymmetric cell fate of fast-
and slow-cycling colon cancer-initiating cells. Cancer Res.
76:3411–3421. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Germann M, Xu H, Malaterre J, Sampurno S,
Huyghe M, Cheasley D, Fre S and Ramsay RG: Tripartite interactions
between Wnt signaling, Notch and Myb for stem/progenitor cell
functions during intestinal tumorigenesis. Stem Cell Res.
13:355–366. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Mourao L, Jacquemin G, Huyghe M, Nawrocki
WJ, Menssouri N, Servant N and Fre S: Lineage tracing of
Notch1-expressing cells in intestinal tumours reveals a distinct
population of cancer stem cells. Sci Rep. 9:8882019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Jain RK: Normalizing tumor
microenvironment to treat cancer: Bench to bedside to biomarkers. J
Clin Oncol. 31:2205–2218. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
De Palma M, Biziato D and Petrova TV:
Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 17:457–474. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Yunus M, Jansson PJ, Kovacevic Z,
Kalinowski DS and Richardson DR: Tumor-induced neoangiogenesis and
receptor tyrosine kinases-Mechanisms and strategies for acquired
resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1863:1217–1225. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Potente M, Gerhardt H and Carmeliet P:
Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell. 146:873–887.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Goel HL and Mercurio AM: VEGF targets the
tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:871–882. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Bridges E, Oon CE and Harris A: Notch
regulation of tumor angiogenesis. Future Oncol. 7:569–588. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Simons M, Gordon E and Claesson-Welsh L:
Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:611–625. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Wieland E, Rodriguez-Vita J, Liebler SS,
Mogler C, Moll I, Herberich SE, Espinet E, Herpel E, Menuchin A,
Chang-Claude J, et al: Endothelial Notch1 activity facilitates
metastasis. Cancer Cell. 31:355–367. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Wohlfeil SA, Häfele V, Dietsch B,
Schledzewski K, Winkler M, Zierow J, Leibing T, Mohammadi MM,
Heineke J, Sticht C, et al: Hepatic endothelial Notch activation
protects against liver metastasis by regulating endothelial-tumor
cell adhesion independent of angiocrine signaling. Cancer Res.
79:598–610. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Radtke F, MacDonald HR and
Tacchini-Cottier F: Regulation of innate and adaptive immunity by
Notch. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:427–437. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Lobry C, Oh P, Mansour MR, Look AT and
Aifantis I: Notch signaling: Switching an oncogene to a tumor
suppressor. Blood. 123:2451–2459. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Amsen D, Helbig C and Backer RA: Notch in
T cell differentiation: all things considered. Trends Immunol.
36:802–814. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Charbonnier LM, Wang S, Georgiev P, Sefik
E and Chatila TA: Control of peripheral tolerance by regulatory T
cell-intrinsic Notch signaling. Nat Immunol. 16:1162–1173. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Wang YC, He F, Feng F, Liu XW, Dong GY,
Qin HY, Hu XB, Zheng MH, Liang L, Feng L, et al: Notch signaling
determines the M1 versus M2 polarization of macrophages in
antitumor immune responses. Cancer Res. 70:4840–4849. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Liu H, Wang J, Zhang M, Xuan Q, Wang Z,
Lian X and Zhang Q: Jagged1 promotes aromatase inhibitor resistance
by modulating tumor-associated macrophage differentiation in breast
cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 166:95–107. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Rashedi I, Gómez-Aristizábal A, Wang XH,
Viswanathan S and Keating A: TLR3 or TLR4 activation enhances
mesenchymal stromal cell-mediated Treg induction via Notch
signaling. Stem Cells. 35:265–275. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Cahill EF, Tobin LM, Carty F, Mahon BP and
English K: Jagged-1 is required for the expansion of CD4+ CD25+
FoxP3+ regulatory T cells and tolerogenic dendritic cells by murine
mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Kared H, Adle-Biassette H, Foïs E, Masson
A, Bach JF, Chatenoud L, Schneider E and Zavala F:
Jagged2-expressing hematopoietic progenitors promote regulatory T
cell expansion in the periphery through Notch signaling. Immunity.
25:823–834. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Ting HA, de Almeida Nagata D, Rasky AJ,
Malinczak CA, Maillard IP, Schaller MA and Lukacs NW: Notch ligand
Delta-like 4 induces epigenetic regulation of Treg cell
differentiation and function in viral infection. Mucosal Immunol.
11:1524–1536. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Zhang L, Yu X, Zheng L, Zhang Y, Li Y,
Fang Q, Gao R, Kang B, Zhang Q, Huang JY, et al: Lineage tracking
reveals dynamic relationships of T cells in colorectal cancer.
Nature. 564:268–272. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Gustafsson MV, Zheng X, Pereira T, Gradin
K, Jin S, Lundkvist J, Ruas JL, Poellinger L, Lendahl U and
Bondesson M: Hypoxia requires Notch signaling to maintain the
undifferentiated cell state. Dev Cell. 9:617–628. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Katoh M: FGFR inhibitors: Effects on
cancer cells, tumor microenvironment and whole-body homeostasis
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 38:3–15. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Grazioli P, Felli MP, Screpanti I and
Campese AF: The mazy case of Notch and immunoregulatory cells. J
Leukoc Biol. 102:361–368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Katoh M: Genomic testing, tumor
microenvironment and targeted therapy of Hedgehog-related human
cancers. Clin Sci (Lond). 133:953–970. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Yang Z, Qi Y, Lai N, Zhang J, Chen Z, Liu
M, Zhang W, Luo R and Kang S: Notch1 signaling in melanoma cells
promoted tumor-induced immunosuppression via upregulation of
TGF-β1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:12018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Mao L, Zhao ZL, Yu GT, Wu L, Deng WW, Li
YC, Liu JF, Bu LL, Liu B, Kulkarni AB, et al: γ-Secretase inhibitor
reduces immunosuppressive cells and enhances tumour immunity in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 142:999–1009.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
El-Khoueiry AB, Desai J, Iyer SP, Gadgeel
SM, Ramalingam SS, Horn L, LoRusso P, Bajaj G, Kollia G, Qi Z, et
al: A phase I study of AL101, a pan-NOTCH inhibitor, in patients
(pts) with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors. J Clin
Oncol. 36(15 Suppl): S25152018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Massard C, Azaro A, Soria JC, Lassen U, Le
Tourneau C, Sarker D, Smith C, Ohnmacht U, Oakley G, Patel BKR, et
al: First-in-human study of LY3039478, an oral Notch signaling
inhibitor in advanced or metastatic cancer. Ann Oncol.
29:1911–1917. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Habets RA, de Bock CE, Serneels L,
Lodewijckx I, Verbeke D, Nittner D, Narlawar R, Demeyer S, Dooley
J, Liston A, et al: Safe targeting of T cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia by pathology-specific NOTCH inhibition. Sci Transl Med.
11:pii: eaau6246. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Messersmith WA, Shapiro GI, Cleary JM,
Jimeno A, Dasari A, Huang B, Shaik MN, Cesari R, Zheng X, Reynolds
JM, et al: A phase I, dose-finding study in patients with advanced
solid malignancies of the oral γ-secretase inhibitor PF-03084014.
Clin Cancer Res. 21:60–67. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Kummar S, O'Sullivan Coyne G, Do KT,
Turkbey B, Meltzer PS, Polley E, Choyke PL, Meehan R, Vilimas R,
Horneffer Y, et al: Clinical activity of the γ-secretase inhibitor
PF-03084014 in adults with desmoid tumors (aggressive
fibromatosis). J Clin Oncol. 35:1561–1569. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Tolcher AW, Messersmith WA, Mikulski SM,
Papadopoulos KP, Kwak EL, Gibbon DG, Patnaik A, Falchook GS, Dasari
A, Shapiro GI, et al: Phase I study of RO4929097, a gamma
secre-tase inhibitor of Notch signaling, in patients with
refractory metastatic or locally advanced solid tumors. J Clin
Oncol. 30:2348–2353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Strosberg JR, Yeatman T, Weber J, Coppola
D, Schell MJ, Han G, Almhanna K, Kim R, Valone T, Jump H and
Sullivan D: A phase II study of RO4929097 in metastatic colorectal
cancer. Eur J Cancer. 48:997–1003. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Jordan NV, Bardia A, Wittner BS, Benes C,
Ligorio M, Zheng Y, Yu M, Sundaresan TK, Licausi JA, Desai R, et
al: HER2 expression identifies dynamic functional states within
circulating breast cancer cells. Nature. 537:102–106. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Diluvio G, Del Gaudio F, Giuli MV,
Franciosa G, Giuliani E, Palermo R, Besharat ZM, Pignataro MG,
Vacca A, d'Amati G, et al: NOTCH3 inactivation increases triple
negative breast cancer sensitivity to gefitinib by promoting EGFR
tyrosine dephosphorylation and its intracellular arrest.
Oncogenesis. 7:422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Yao J, Qian C, Shu T, Zhang X, Zhao Z and
Liang Y: Combination treatment of PD98059 and DAPT in gastric
cancer through induction of apoptosis and downregulation of
WNT/β-catenin. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:833–839. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Smith DC, Eisenberg PD, Manikhas G, Chugh
R, Gubens MA, Stagg RJ, Kapoun AM, Xu L, Dupont J and Sikic B: A
phase I dose escalation and expansion study of the anticancer stem
cell agent demcizumab (anti-DLL4) in patients with previously
treated solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 20:6295–6303. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Chiorean EG, LoRusso P, Strother RM,
Diamond JR, Younger A, Messersmith WA, Adriaens L, Liu L, Kao RJ,
DiCioccio AT, et al: A phase I first-in-human study of enoticumab
(REGN421), a fully human Delta-like ligand 4 (DLL4) monoclonal
antibody, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
21:2695–2703. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Falchook GS, Dowlati A, Naing A, Gribbin
MJ, Jenkins DW, Chang LL, Lai DW and Smith DC: Phase I study of
MEDI0639 in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol.
33(15 Suppl): S30242015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Ferrarotto R, Eckhardt G, Patnaik A,
LoRusso P, Faoro L, Heymach JV, Kapoun AM, Xu L and Munster P: A
phase I dose-escalation and dose-expansion study of brontictuzumab
in subjects with selected solid tumors. Ann Oncol. 29:1561–1568.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Yen WC, Fischer MM, Axelrod F, Bond C,
Cain J, Cancilla B, Henner WR, Meisner R, Sato A, Shah J, et al:
Targeting Notch signaling with a Notch2/Notch3 antagonist
(tarextumab) inhibits tumor growth and decreases tumor-initiating
cell frequency. Clin Cancer Res. 21:2084–2095. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Smith DC, Chugh R, Patnaik A, Papadopoulos
KP, Wang M, Kapoun AM, Xu L, Dupont J, Stagg RJ and Tolcher A: A
phase 1 dose escalation and expansion study of Tarextumab
(OMP-59R5) in patients with solid tumors. Invest New Drugs.
37:722–730. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
166
|
Beck A, Goetsch L, Dumontet C and Corvaïa
N: Strategies and challenges for the next generation of
antibody-drug conjugates. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:315–337. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Lambert JM and Berkenblit A: Antibody-Drug
conjugates for cancer treatment. Annu Rev Med. 69:191–207. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Carter PJ and Lazar GA: Next generation
antibody drugs: Pursuit of the 'high-hanging fruit'. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 17:197–223. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
June CH, O'Connor RS, Kawalekar OU,
Ghassemi S and Milone MC: CAR T cell immunotherapy for human
cancer. Science. 359:1361–1365. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Saunders LR, Bankovich AJ, Anderson WC,
Aujay MA, Bheddah S, Black K, Desai R, Escarpe PA, Hampl J, Laysang
A, et al: A DLL3-targeted antibody-drug conjugate eradicates
high-grade pulmonary neuroendocrine tumor-initiating cells in vivo.
Sci Transl Med. 7:302ra1362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Rudin CM, Pietanza MC, Bauer TM, Ready N,
Morgensztern D, Glisson BS, Byers LA, Johnson ML, Burris HA III,
Robert F, et al: Rovalpituzumab tesirine, a DLL3-targeted
antibody-drug conjugate, in recurrent small-cell lung cancer: A
first-in-human, first-in-class, open-label, phase 1 study. Lancet
Oncol. 18:42–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
172
|
Carbone DP, Morgensztern D, Le Moulec S,
Santana-Davila R, Ready N, Hann CL, Glisson BS, Dowlati A, Rudin
CM, Lally S, et al: Efficacy and safety of rovalpituzumab tesirine
in patients With DLL3-expressing, ≥ 3rd line small cell lung
cancer: Results from the phase 2 TRINITY study. J Clin Oncol. 36(15
Suppl): S85072018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Rosen LS, Wesolowski R, Baffa R, Liao KH,
Hua SY, Gibson BL, Pirie-Shepherd S and Tolcher AW: A phase I,
dose-escalation study of PF-06650808, an anti-Notch3 antibody-drug
conjugate, in patients with breast cancer and other advanced solid
tumors. Invest New Drugs. Mar 18–2019.Epub ahead of print.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Smit MAD, Borghaei H, TOwonikoko TK,
Hummel HD, Johnson ML, Champiat S, Salgia R, Udagawa H, Boyer MJ
and Govindan R: Phase 1 study of AMG 757, a half-life extended
bispecific T cell engager (BiTE) antibody construct targeting DLL3,
in patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC). J Clin Oncol. 37(15
Suppl): TPS85772019.
|
|
175
|
Li Y, Hickson JA, Ambrosi DJ, Haasch DL,
Foster-Duke KD, Eaton LJ, DiGiammarino EL, Panchal SC, Jiang F,
Mudd SR, et al: ABT-165, a dual variable domain immunoglobulin
(DVD-Ig) targeting DLL4 and VEGF, demonstrates superior efficacy
and favorable safety profiles in preclinical models. Mol Cancer
Ther. 17:1039–1050. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Jimeno A, Moore KN, Gordon M, Chugh R,
Diamond JR, Aljumaily R, Mendelson D, Kapoun AM, Xu L, Stagg R and
Smith DC: A first-in-human phase 1a study of the bispecific
anti-DLL4/anti-VEGF antibody navicixizumab (OMP-305B83) in patients
with previously treated solid tumors. Invest New Drugs. 37:461–472.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Hu S, Fu W, Li T, Yuan Q, Wang F, Lv G, Lv
Y, Fan X, Shen Y, Lin F, et al: Antagonism of EGFR and Notch limits
resistance to EGFR inhibitors and radiation by decreasing
tumor-initiating cell frequency. Sci Transl Med. 9:pii: eaag0339.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Fu W, Lei C, Yu Y, Liu S, Li T, Lin F, Fan
X, Shen Y, Ding M, Tang Y, et al: EGFR/Notch antagonists enhance
the response to inhibitors of the PI3K-Akt pathway by decreasing
tumor-initiating cell frequency. Clin Cancer Res. 25:2835–2847.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Byers LA, Chiappori A and Smit MAD: Phase
1 study of AMG 119, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell
therapy targeting DLL3, in patients with relapsed/refractory small
cell lung cancer (SCLC). J Clin Oncol. 37(15 Suppl):
TPS85762019.
|
|
180
|
Puca L, Gavyert K, Sailer V, Conteduca V,
Dardenne E, Sigouros M, Isse K, Kearney M, Vosoughi A, Fernandez L,
et al: Delta-like protein 3 expression and therapeutic targeting in
neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Sci Transl Med. 11:pii: eaav0891.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Locke FL, Ghobadi A, Jacobson CA, Miklos
DB, Lekakis LJ, Oluwole OO, Lin Y, Braunschweig I, Hill BT,
Timmerman JM, et al: Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene
ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A
single-arm, multicentre, phase 12 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:31–42.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, Waller EK,
Borchmann P, McGuirk JP, Jäger U, Jaglowski S, Andreadis C, Westin
JR, et al: Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 380:45–56. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Kantarjian HM, DeAngelo DJ, Stelljes M,
Martinelli G, Liedtke M, Stock W, Gökbuget N, O'Brien S, Wang K,
Wang T, et al: Inotuzumab ozogamicin versus standard therapy for
acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 375:740–753. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Horwitz S, O'Connor OA, Pro B, Illidge T,
Fanale M, Advani R, Bartlett NL, Christensen JH, Morschhauser F,
Domingo-Domenech E, et al: Brentuximab vedotin with chemotherapy
for CD30-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma (ECHELON-2): A global,
double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 393:229–240. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
185
|
Tilly H, Morschhauser F, Bartlett NL,
Mehta A, Salles G, Haioun C, Munoz J, Chen AI, Kolibaba K, Lu D, et
al: Polatuzumab vedotin in combination with immunochemotherapy in
patients with previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma:
An open-label, non-randomised, phase 1b-2 study. Lancet Oncol.
20:998–1010. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Verma S, Miles D, Gianni L, Krop IE,
Welslau M, Baselga J, Pegram M, Oh DY, Diéras V, Guardino E, et al:
Trastuzumab emtansine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. N
Engl J Med. 367:1783–1791. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Doi T, Shitara K, Naito Y, Shimomura A,
Fujiwara Y, Yonemori K, Shimizu C, Shimoi T, Kuboki Y, Matsubara N,
et al: Safety, pharmacokinetics, and antitumour activity of
trastuzumab deruxtecan (DS-8201), a HER2-targeting antibody-drug
conjugate, in patients with advanced breast and gastric or
gastro-oesophageal tumours: A phase 1 dose-escalation study. Lancet
Oncol. 18:1512–1522. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Banerji U, van Herpen CML, Saura C,
Thistlethwaite F, Lord S, Moreno V, Macpherson IR, Boni V, Rolfo C,
de Vries EGE, et al: Trastuzumab duocarmazine in locally advanced
and metastatic solid tumours and HER2-expressing breast cancer: A
phase 1 dose-escalation and dose-expansion study. Lancet Oncol.
20:1124–1135. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Lassman AB, van den Bent MJ, Gan HK,
Reardon DA, Kumthekar P, Butowski N, Lwin Z, Mikkelsen T, Nabors
LB, Papadopoulos KP, et al: Safety and efficacy of depatuxizumab
mafodotin + temozolomide in patients with EGFR-amplified, recurrent
glioblastoma: Results from an international phase I multicenter
trial. Neuro Oncol. 21:106–114. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
190
|
Moore KN, Martin LP, O'Malley DM,
Matulonis UA, Konner JA, Perez RP, Bauer TM, Ruiz-Soto R and Birrer
MJ: Safety and activity of mirvetuximab soravtansine (IMGN853), a
folate receptor alpha-targeting antibody-drug conjugate, in
platinum-resistant ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal
cancer: A phase I expansion study. J Clin Oncol. 35:1112–1118.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
191
|
Challita-Eid PM, Satpayev D, Yang P, An Z,
Morrison K, Shostak Y, Raitano A, Nadell R, Liu W, Lortie DR, et
al: Enfortumab vedotin antibody-drug conjugate targeting Nectin-4
is a highly potent therapeutic agent in multiple preclinical cancer
models. Cancer Res. 76:3003–3013. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Bardia A, Mayer IA, Vahdat LT, Tolaney SM,
Isakoff SJ, Diamond JR, O'Shaughnessy J, Moroose RL, Santin AD,
Abramson VG, et al: Sacituzumab govitecanhziy in refractory
metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med.
380:741–751. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Raje N, Berdeja J, Lin Y, Siegel D,
Jagannath S, Madduri D, Liedtke M, Rosenblatt J, Maus MV, Turka A,
et al: Anti-BCMA CAR T-cell therapy bb2121 in relapsed or
refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 380:1726–1737. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Merlino G, Fiascarelli A, Bigioni M,
Bressan A, Carrisi C, Bellarosa D, Salerno M, Bugianesi R, Manno R,
Bernadó Morales C, et al: MEN1309/OBT076, a first-in-class
antibody-drug conjugate targeting CD205 in solid tumors. Mol Cancer
Ther. 18:1533–1543. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Zhan X, Wang B, Li Z, Li J, Wang H, Chen
L, Jiang H, Wu M, Xiao J, Peng X, et al: Phase I trial of Claudin
18.2-specific chimeric antigen receptor T cells for advanced
gastric and pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 37(15 Suppl):
S25092019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
196
|
García-Alonso S, Ocaña A and Pandiella A:
Resistance to antibody-drug conjugates. Cancer Res. 78:2159–2165.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Shah NN and Fry TJ: Mechanisms of
resistance to CAR T cell therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 16:372–385.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Singal G, Miller PG, Agarwala V, Li G,
Kaushik G, Backenroth D, Gossai A, Frampton GM, Torres AZ, Lehnert
EM, et al: Association of patient characteristics and tumor
genomics with clinical outcomes among patients with non-small cell
lung cancer using a clinicogenomic database. JAMA. 321:1391–1399.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Samstein RM, Lee CH, Shoushtari AN,
Hellmann MD, Shen R, Janjigian YY, Barron DA, Zehir A, Jordan EJ,
Omuro A, et al: Tumor mutational load predicts survival after
immunotherapy across multiple cancer types. Nat Genet. 51:202–206.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Rubinstein JC, Nicolson NG and Ahuja N:
Next-generation sequencing in the management of gastric and
esophageal cancers. Surg Clin North Am. 99:511–527. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Hirsch FR, Suda K, Wiens J and Bunn PA Jr:
New and emerging targeted treatments in advanced non-small-cell
lung cancer. Lancet. 388:1012–1024. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Rizvi H, Sanchez-Vega F, La K, Chatila W,
Jonsson P, Halpenny D, Plodkowski A, Long N, Sauter JL, Rekhtman N,
et al: Molecular determinants of response to anti-programmed cell
death (PD)-1 and anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) blockade in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer profiled with targeted
next-generation sequencing. J Clin Oncol. 36:633–641. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Offin M, Rizvi H, Tenet M, Ni A,
Sanchez-Vega F, Li BT, Drilon A, Kris MG, Rudin CM, Schultz N, et
al: Tumor mutation burden and efficacy of EGFR-tyrosine kinase
inhibitors in patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Cancer
Res. 25:1063–1069. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
204
|
Buchhalter I, Rempel E, Endris V, Allgäuer
M, Neumann O, Volckmar AL, Kirchner M, Leichsenring J, Lier A, von
Winterfeld M, et al: Size matters: Dissecting key parameters for
panel-based tumor mutational burden analysis. Int J Cancer.
144:848–858. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
205
|
Schneider G: Automating drug discovery.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 17:97–113. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
206
|
Katoh M: Fibroblast growth factor
receptors as treatment targets in clinical oncology. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 16:105–122. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
207
|
Somashekhar SP, Sepúlveda MJ, Puglielli S,
Norden AD, Shortliffe EH, Rohit Kumar C, Rauthan A, Arun Kumar N,
Patil P, Rhee K, et al: Watson for oncology and breast cancer
treatment recommendations: Agreement with an expert
multidisciplinary tumor board. Ann Oncol. 29:418–423. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Paley S and Karp PD: The MultiOmics
explainer: Explaining omics results in the context of a
pathway/genome database. BMC Bioinformatics. 20:3992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Cheng JZ, Ni D, Chou YH, Qin J, Tiu CM,
Chang YC, Huang CS, Shen D and Chen CM: Computer-aided diagnosis
with deep learning architecture: Applications to breast lesions in
US images and pulmonary nodules in CT scans. Sci Rep. 6:244542016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, Ko J,
Swetter SM, Blau HM and Thrun S: Dermatologist-level classification
of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature. 542:115–118.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Ardila D, Kiraly AP, Bharadwaj S, Choi B,
Reicher JJ, Peng L, Tse D, Etemadi M, Ye W, Corrado G, et al:
End-to-end lung cancer screening with three-dimensional deep
learning on low-dose chest computed tomography. Nat Med.
25:954–961. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Dascalu A and David EO: Skin cancer
detection by deep learning and sound analysis algorithms: A
prospective clinical study of an elementary dermoscope.
EBioMedicine. 43:107–113. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Mori Y, Kudo SE, Misawa M, Saito Y,
Ikematsu H, Hotta K, Ohtsuka K, Urushibara F, Kataoka S, Ogawa Y,
et al: Real-time use of artificial intelligence in identification
of diminutive polyps during colonoscopy: A prospective study. Ann
Intern Med. 169:357–366. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Aboutalib SS, Mohamed AA, Berg WA, Zuley
ML, Sumkin JH and Wu S: Deep learning to distinguish recalled but
benign mammography images in breast cancer screening. Clin Cancer
Res. 24:5902–5909. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Coudray N, Ocampo PS, Sakellaropoulos T,
Narula N, Snuderl M, Fenyö D, Moreira AL, Razavian N and Tsirigos
A: Classification and mutation prediction from non-small cell lung
cancer histopathology images using deep learning. Nat Med.
24:1559–1567. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Kather JN, Pearson AT, Halama N, Jäger D,
Krause J, Loosen SH, Marx A, Boor P, Tacke F, Neumann UP, et al:
Deep learning can predict microsatellite instability directly from
histology in gastrointestinal cancer. Nat Med. 25:1054–1056. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Campanella G, Hanna MG, Geneslaw L,
Miraflor A, Werneck Krauss, Silva V, Busam KJ, Brogi E, Reuter VE,
Klimstra DS and Fuchs TJ: Clinical-grade computational pathology
using weakly supervised deep learning on whole slide images. Nat
Med. 25:1301–1309. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Hekler A, Utikal JS, Enk AH, Solass W,
Schmitt M, Klode J, Schadendorf D, Sondermann W, Franklin C,
Bestvater F, et al: Deep learning outperformed 11 pathologists in
the classification of histopathological melanoma images. Eur J
Cancer. 118:91–96. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Topol EJ: High-performance medicine: The
convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat Med.
25:44–56. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Zheng H, Bae Y, Kasimir-Bauer S, Tang R,
Chen J, Ren G, Yuan M, Esposito M, Li W, Wei Y, et al: Therapeutic
antibody targeting tumor- and osteoblastic niche-derived Jagged1
sensitizes bone metastasis to chemotherapy. Cancer Cell.
32:731–747.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Li DD, Zhao CH, Ding HW, Wu Q, Ren TS,
Wang J, Chen CQ and Zhao QC: A novel inhibitor of ADAM17 sensitizes
colorectal cancer cells to 5-Fluorouracil by reversing Notch and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro and in vivo. Cell
Prolif. 51:e124802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Weber D, Lehal R, Frismantas V, Bourquin
J, Bauer M, Murone M and Radtke F: 411P-Pharmacological activity of
CB-103-an oral pan-NOTCH inhibitor with a novel mode of action. Ann
Oncol. 28(Suppl 5): v122–v141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
223
|
Moellering RE, Cornejo M, Davis TN, Del
Bianco C, Aster JC, Blacklow SC, Kung AL, Gilliland DG, Verdine GL
and Bradner JE: Direct inhibition of the NOTCH transcription factor
complex. Nature. 462:182–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Sano R, Krytska K, Larmour CE, Raman P,
Martinez D, Ligon GF, Lillquist JS, Cucchi U, Orsini P, Rizzi S, et
al: An antibody-drug conjugate directed to the ALK receptor
demonstrates efficacy in preclinical models of neuroblastoma. Sci
Transl Med. 11:pii: eaau9732. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Boshuizen J, Koopman LA, Krijgsman O,
Shahrabi A, van den Heuvel EG, Ligtenberg MA, Vredevoogd DW, Kemper
K, Kuilman T, Song JY, et al: Cooperative targeting of melanoma
heterogeneity with an AXL antibody-drug conjugate and BRAF/MEK
inhibitors. Nat Med. 24:203–212. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Tao Y, Wang R, Lai Q, Wu M, Wang Y, Jiang
X, Zeng L, Zhou S, Li Z, Yang T, et al: Targeting of DDR1 with
antibody-drug conjugates has antitumor effects in a mouse model of
colon carcinoma. Mol Oncol. 13:1855–1873. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Sommer A, Kopitz C, Schatz CA, Nising CF,
Mahlert C, Lerchen HG, Stelte-Ludwig B, Hammer S, Greven S,
Schuhmacher J, et al: Preclinical efficacy of the auristatin-based
antibody-drug conjugate BAY 1187982 for the treatment of
FGFR2-positive solid tumors. Cancer Res. 76:6331–6339. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Surguladze D, Pennello A, Ren X, Mack T,
Rigby A, Balderes P, Navarro E, Amaladas N, Eastman S, Topper M, et
al: LY3076226, a novel anti-FGFR3 antibody drug conjugate exhibits
potent and durable anti-tumor activity in tumor models harboring
FGFR3 mutations or fusions. Cancer Res. 79(13 Suppl):
S48352019.
|
|
229
|
Rudra-Ganguly N, Challita-Eid PM, Lowe C,
Mattie M, Moon SJ, Mendelsohn BA, Leavitt M, Virata C, A Verlinsky
A, Capo L, et al: AGS62P1, a novel site-specific antibody drug
conjugate targeting FLT3 exhibits potent anti-tumor activity
regardless of FLT3 kinase activation status. Cancer Res. 76(14
Suppl): S5742016.
|
|
230
|
Avilés P, Domínguez JM, Guillén MJ,
Muñoz-Alonso MJ, Mateo C, Rodriguez-Acebes R, Molina-Guijarro JM,
Francesch A, Martínez-Leal JF, Munt S, et al: MI130004, a novel
antibody-drug conjugate combining trastuzumab with a molecule of
marine origin, shows outstanding in iivo activity against
HER2-expressing tumors. Mol Cancer Ther. 17:786–794. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
231
|
Koganemaru S, Kuboki Y, Koga Y, Kojima T,
Yamauchi M, Maeda N, Kagari T, Hirotani K, Yasunaga M, Matsumura Y
and Doi T: U3-1402, a novel HER3-targeting antibody-drug conjugate,
for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
18:2043–2050. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Abrams T, Connor A, Fanton C, Cohen SB,
Huber T, Miller K, Hong EE, Niu X, Kline J, Ison-Dugenny M, et al:
Preclinical antitumor activity of a novel anti-c-KIT antibody-drug
conjugate against mutant and wild-type c-KIT-positive solid tumors.
Clin Cancer Res. 24:4297–4308. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Strickler JH, Weekes CD, Nemunaitis J,
Ramanathan RK, Heist RS, Morgensztern D, Angevin E, Bauer TM, Yue
H, Motwani M, et al: First-in-human phase I, dose-escalation and
-expansion study of telisotuzumab vedotin, an antibody-drug
conjugate targeting c-Met, in patients with advanced solid tumors.
J Clin Oncol. 36:3298–3306. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Sachdev JC, Maitland ML, Sharma M, Moreno
V, Boni V, Kummar S, Stringer-Reasor EM, Forero-Torres A, Lakhani
NJ, Gibson B, et al: PF-06647020 (PF-7020), an antibody-drug
conjugate (ADC) targeting protein tyrosine kinase 7 (PTK7), in
patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors: Results of a phase I
dose escalation and expansion study. J Clin Oncol. 36(15-Suppl):
S55652018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
235
|
Nguyen M, Miyakawa S, Kato J, Mori T, Arai
T, Armanini M, Gelmon K, Yerushalmi R, Leung S, Gao D, et al:
Preclinical efficacy and safety assessment of an antibody-drug
conjugate targeting the c-RET proto-oncogene for breast carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 21:5552–5562. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Yao HP, Feng L, Suthe SR, Chen LH, Weng
TH, Hu CY, Jun ES, Wu ZG, Wang WL, Kim SC, et al: Therapeutic
efficacy, pharmacokinetic profiles, and toxicological activities of
humanized antibody-drug conjugate Zt/g4-MMAE targeting RON receptor
tyrosine kinase for cancer therapy. J Immunother Cancer. 7:752019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Berger C, Sommermeyer D, Hudecek M, Berger
M, Balakrishnan A, Paszkiewicz PJ, Kosasih PL, Rader C and Riddell
SR: Safety of targeting ROR1 in primates with chimeric antigen
receptor-modified T cells. Cancer Immunol Res. 3:206–216. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
238
|
Trudel S, Lendvai N, Popat R, Voorhees PM,
Reeves B, Libby EN, Richardson PG, Hoos A, Gupta I, Bragulat V, et
al: Antibody-drug conjugate, GSK2857916, in relapsed/refractory
multiple myeloma: An update on safety and efficacy from dose
expansion phase I study. Blood Cancer J. 9:372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Godwin CD, Gale RP and Walter RB:
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia.
31:1855–1868. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Socinski MA, Kaye FJ, Spigel DR, Kudrik
FJ, Ponce S, Ellis PM, Majem M, Lorigan P, Gandhi L, Gutierrez ME,
et al: Phase 1/2 study of the CD56-targeting antibody-drug
conjugate lorvotuzumab mertansine (IMGN901) in combination with
carboplatin/etoposide in small-cell lung cancer patients with
extensive-stage disease. Clin Lung Cancer. 18:68–76.e2. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
de Bono JS, Concin N, Hong DS,
Thistlethwaite FC, Machiels JP, Arkenau HT, Plummer R, Jones RH,
Nielsen D, Windfeld K, et al: Tisotumab vedotin in patients with
advanced or metastatic solid tumours (InnovaTV 201): A
first-in-human, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol.
20:383–393. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Dotan E, Cohen SJ, Starodub AN, Lieu CH,
Messersmith WA, Simpson PS, Guarino MJ, Marshall JL, Goldberg RM,
Hecht JR, et al: Phase I/II trial of labetuzumab govitecan
(anti-CEACAM5/SN-38 antibody-drug conjugate) in patients with
refractory or relapsing metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol.
35:3338–3346. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Zhu G, Foletti D, Liu X, Ding S, Melton
Witt J, Hasa-Moreno A, Rickert M, Holz C, Aschenbrenner L, Yang AH,
et al: Targeting CLDN18.2 by CD3 bispecific and ADC modalities for
the treatments of gastric and pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep.
9:84202019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Bhakta S, Crocker LM, Chen Y, Hazen M,
Schutten MM, Li D, Kuijl C, Ohri R, Zhong F, Poon KA, et al: An
anti-GDNF family receptor alpha 1 (GFRA1) antibody-drug conjugate
for the treatment of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Mol
Cancer Ther. 17:638–649. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
245
|
Ott PA, Pavlick AC, Johnson DB, Hart LL,
Infante JR, Luke JJ, Lutzky J, Rothschild NE, Spitler LE, Cowey CL,
et al: A phase 2 study of glembatumumab vedotin, an antibody-drug
conjugate targeting glycoprotein NMB, in patients with advanced
melanoma. Cancer. 125:1113–1123. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Gong X, Azhdarinia A, Ghosh SC, Xiong W,
An Z, Liu Q and Carmon KS: LGR5-targeted antibody-drug conjugate
eradicates gastrointestinal tumors and prevents recurrence. Mol
Cancer Ther. 15:1580–1590. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Purcell JW, Tanlimco SG, Hickson J, Fox M,
Sho M, Durkin L, Uziel T, Powers R, Foster K, McGonigal T, et al:
LRRC15 is a novel mesenchymal protein and stromal target for
antibody-drug conjugates. Cancer Res. 78:4059–4072. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Willuda J, Linden L, Lerchen HG, Kopitz C,
Stelte-Ludwig B, Pena C, Lange C, Golfier S, Kneip C, Carrigan PE,
et al: Preclinical antitumor efficacy of BAY 1129980-a novel
auristatin-based anti-C4.4A (LYPD3) antibody-drug conjugate for the
treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
16:893–904. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Golfier S, Kopitz C, Kahnert A, Heisler I,
Schatz CA, Stelte-Ludwig B, Mayer-Bartschmid A, Unterschemmann K,
Bruder S, Linden L, et al: Anetumab ravtansine: A novel
mesothelin-targeting antibody-drug conjugate cures tumors with
heterogeneous target expression favored by bystander effect. Mol
Cancer Ther. 13:1537–1548. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Banerjee S, Oza AM, Birrer MJ, Hamilton
EP, Hasan J, Leary A, Moore KN, Mackowiak-Matejczyk B, Pikiel J,
Ray-Coquard I, et al: Anti-NaPi2b antibody-drug conjugate
lifastuzumab vedotin (DNIB0600A) compared with pegylated liposomal
doxorubicin in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer in a
randomized, open-label, phase II study. Ann Oncol. 29:917–923.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Sussman D, Smith LM, Anderson ME, Duniho
S, Hunter JH, Kostner H, Miyamoto JB, Nesterova A, Westendorf L,
Van Epps HA, et al: SGN-LIV1A: A novel antibody-drug conjugate
targeting LIV-1 for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Mol
Cancer Ther. 13:2991–3000. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|