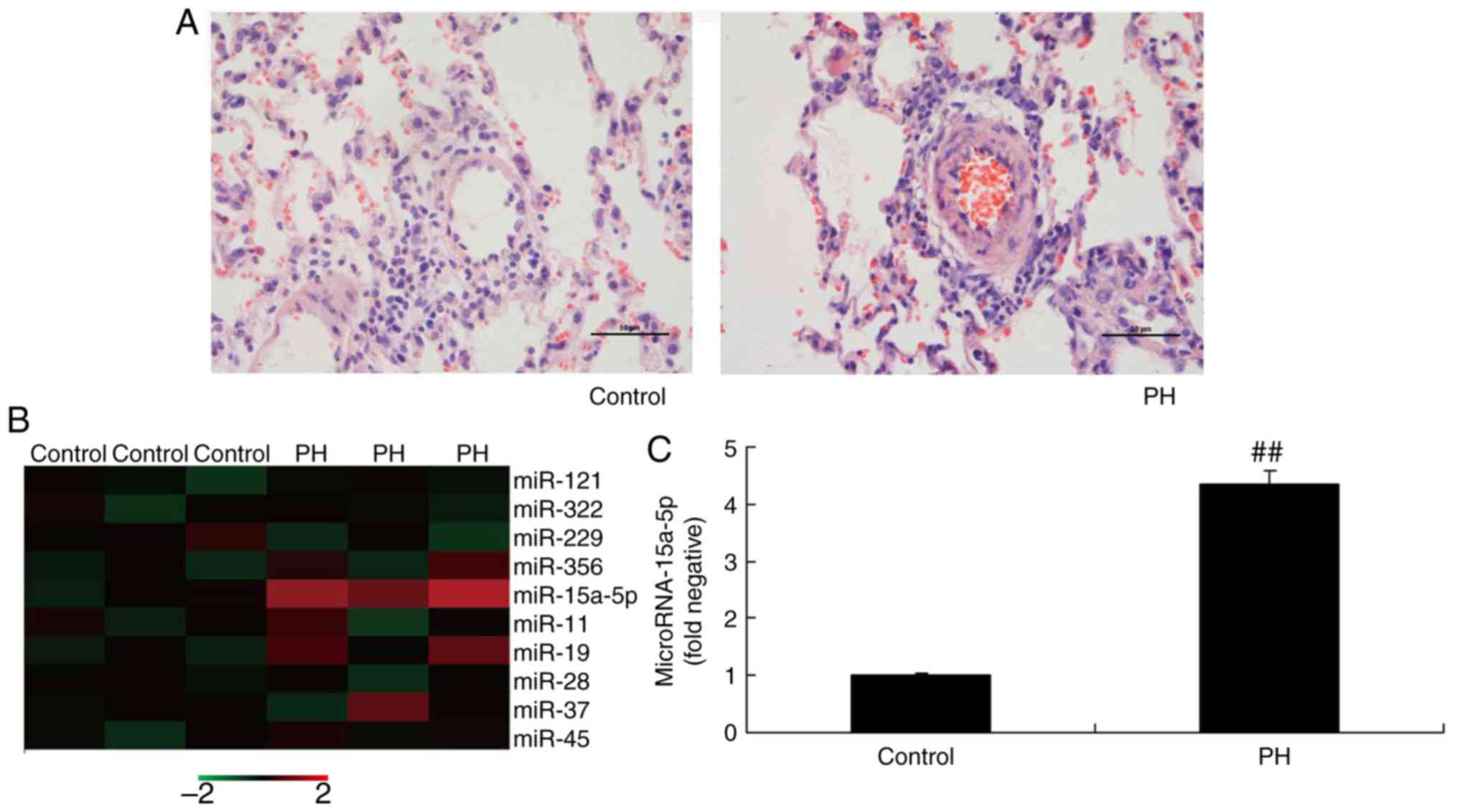
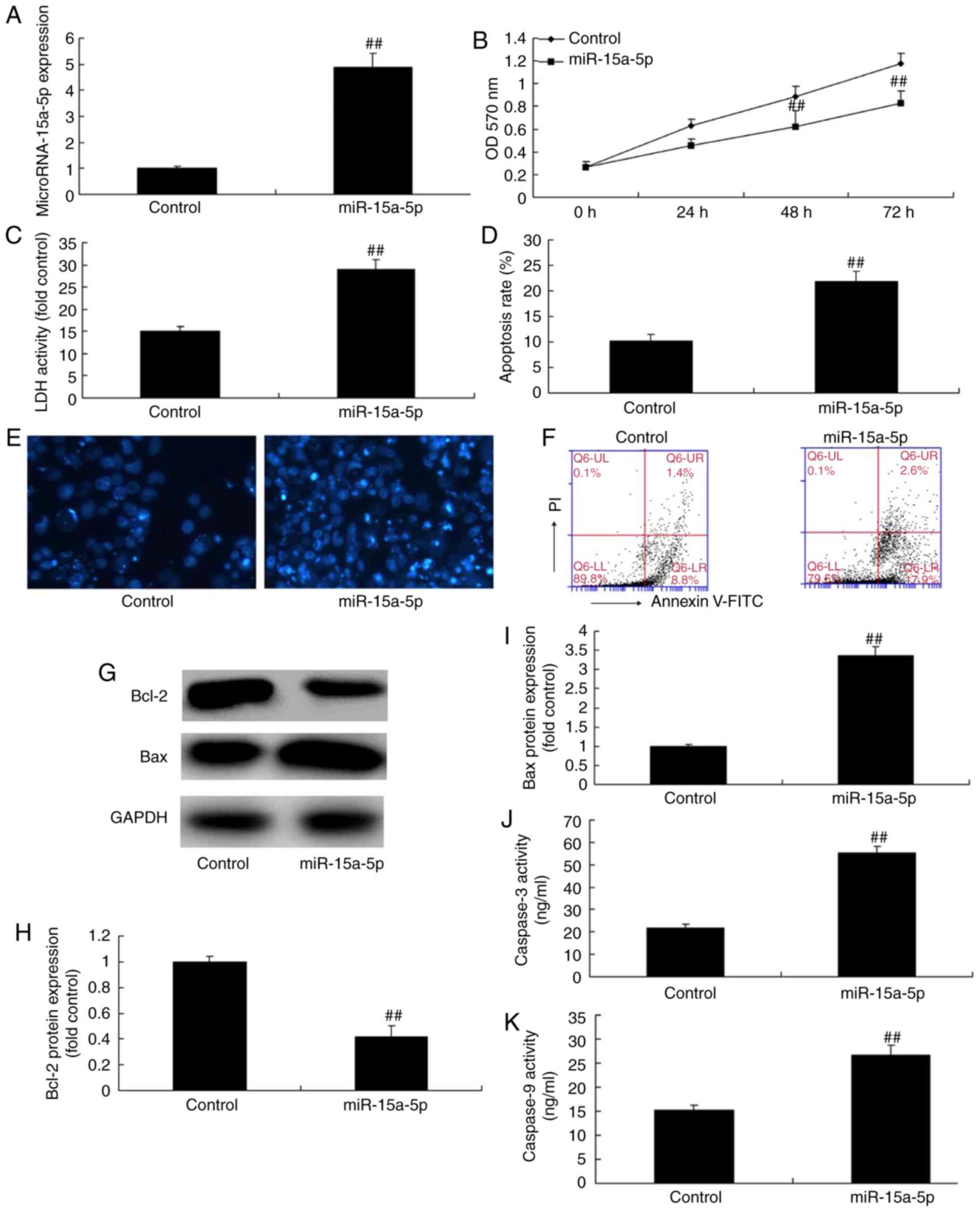
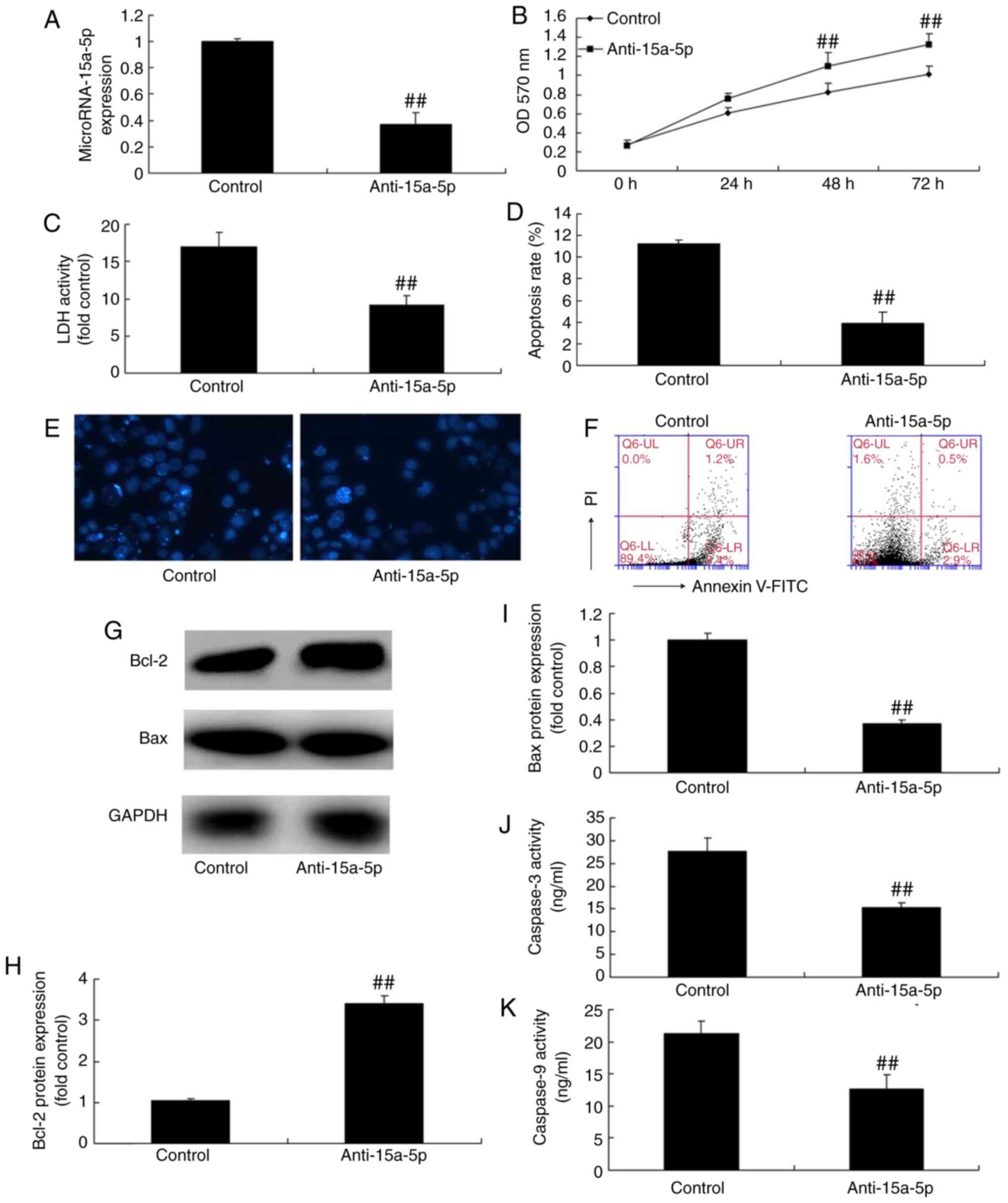
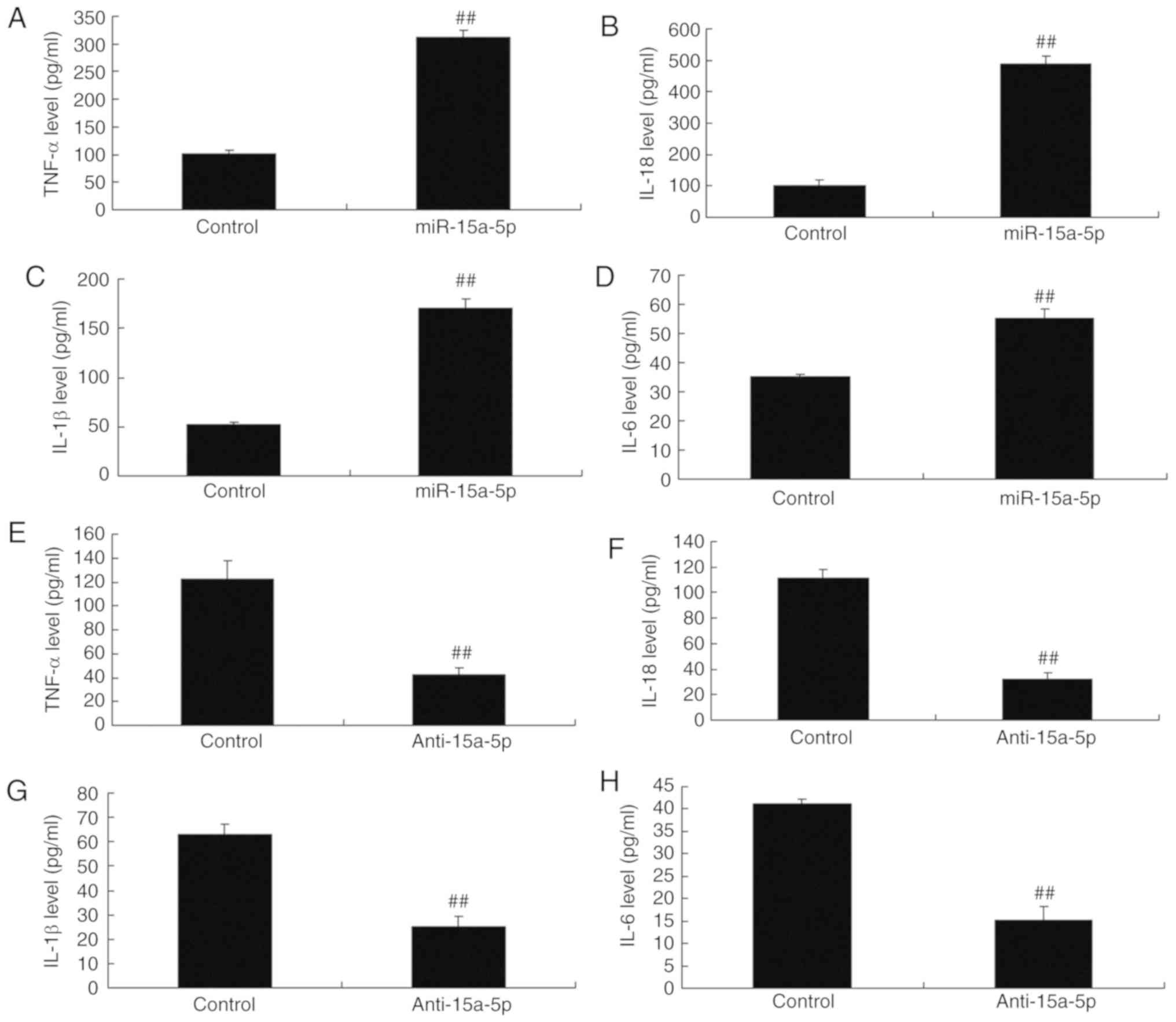
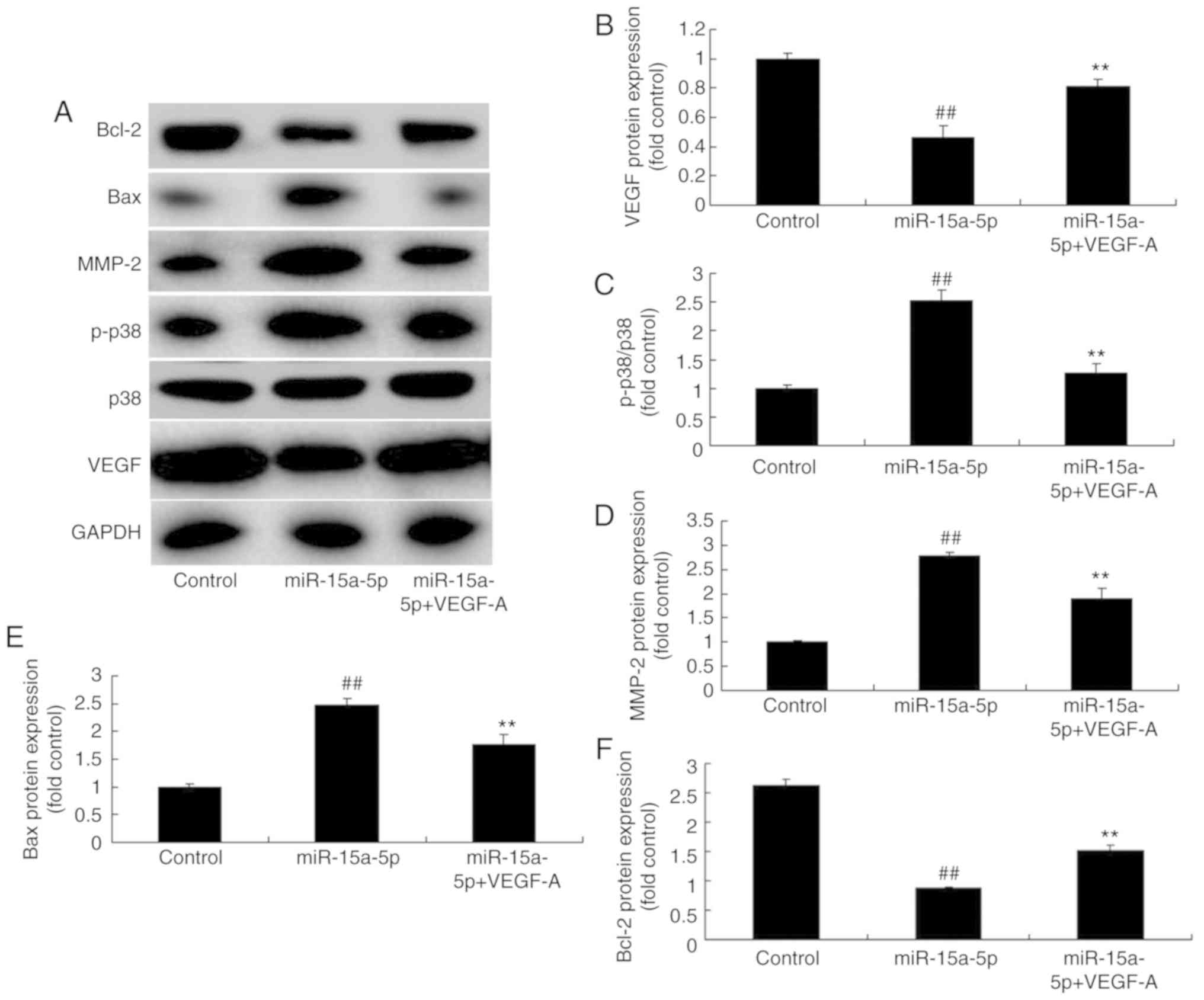
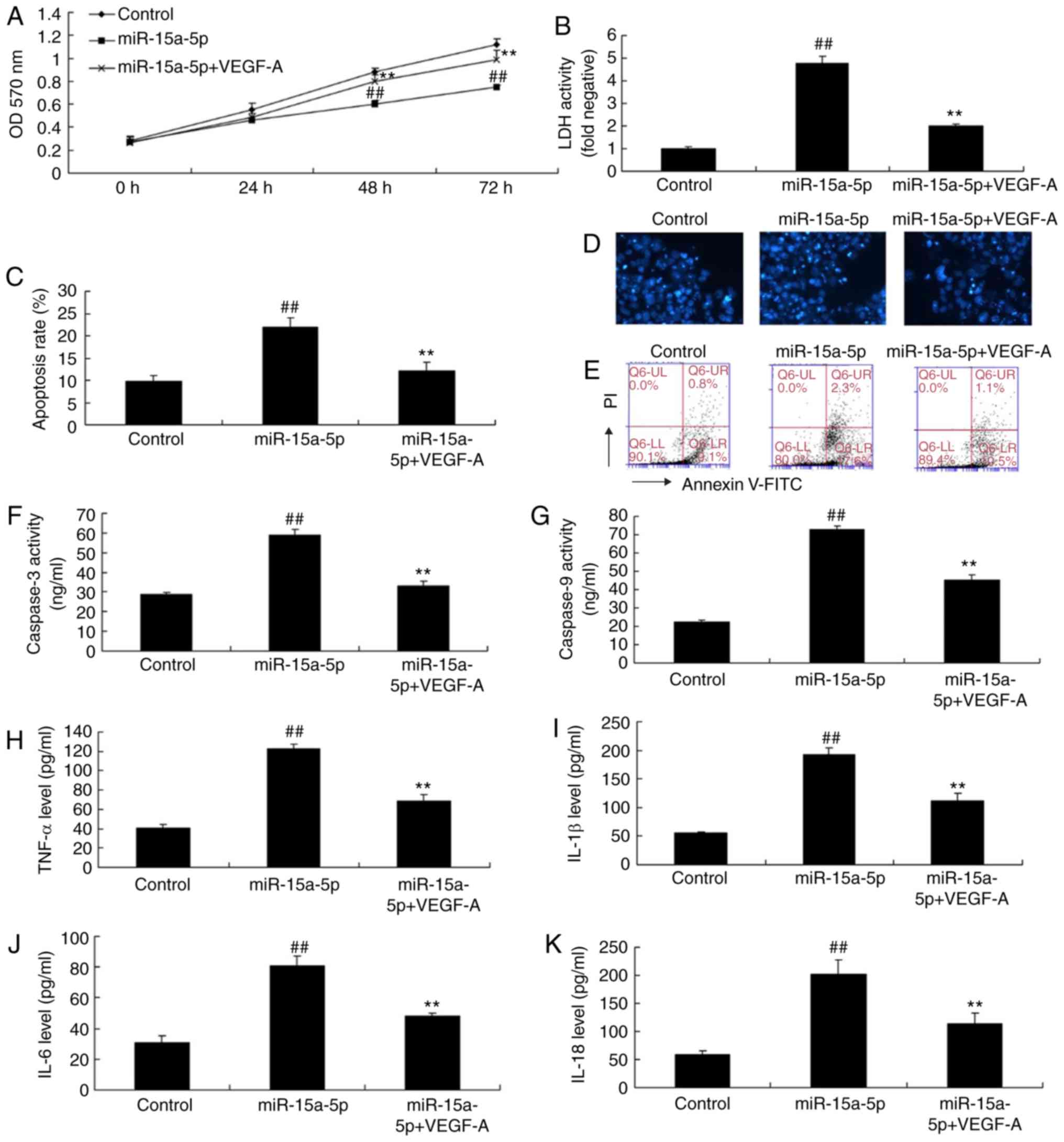
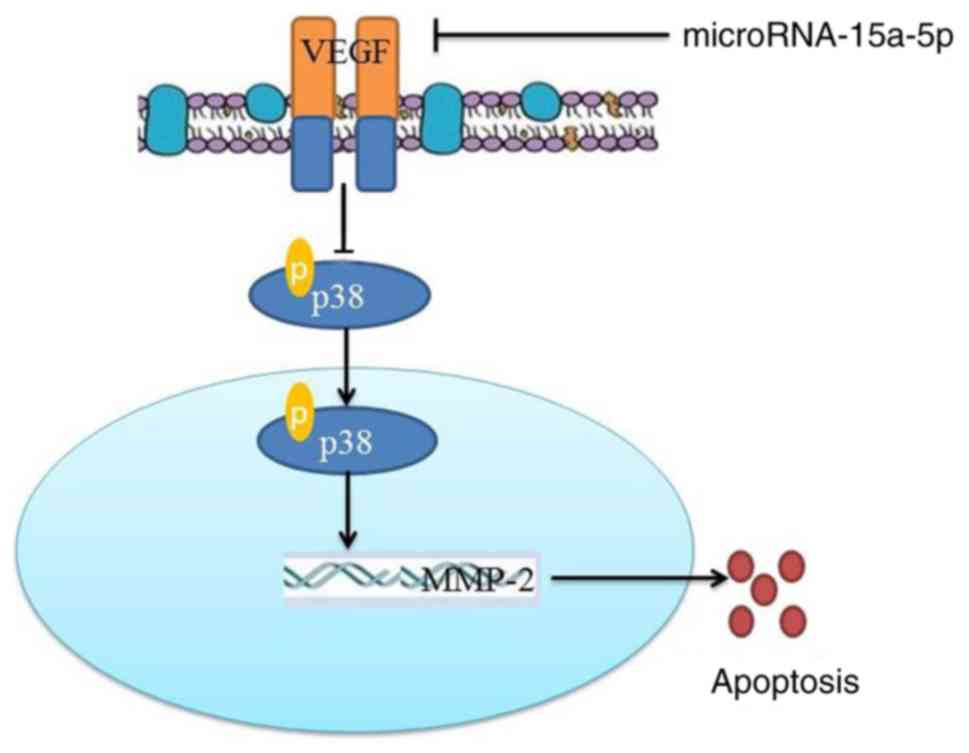
|
1
|
Veeraraghavan S, Koss MN and Sharma OP:
Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 5:310–313.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Prins KW and Thenappan T: World health
organization group I pulmonary hypertension: epidemiology and
pathophysiology. Cardiol Clin. 34:363–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dorfmuller P, Perros F, Balabanian K and
Humbert M: Inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur
Respir J. 22:358–363. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Humbert M, Morrell NW, Archer SL, Stenmark
KR, MacLean MR, Lang IM, Christman BW, Weir EK, Eickelberg O,
Voelkel NF and Rabinovitch M: Cellular and molecular pathobiology
of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 43(12 Suppl
S): pp. 13S–24S. 2004, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Akagi S, Nakamura K, Akagi T, Nakagawa K,
Takaya Y, Sarashina T, Ejiri K and Ito H: Feasibility of repairing
defects followed by treatment with pulmonary hypertension-specific
drugs (Repair and Treat) in patients with pulmonary hypertension
associated with atrial septal defect: Study protocol for
interventional trial. Acta Med Okayama. 70:397–400. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Portt L, Norman G, Clapp C, Greenwood M
and Greenwood MT: Anti-apoptosis and cell survival: A review.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:238–359. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Courboulin A, Barrier M, Perreault T,
Bonnet P, Tremblay VL, Paulin R, Tremblay E, Lambert C, Jacob MH,
Bonnet SN, et al: Plumbagin reverses proliferation and resistance
to apoptosis in experimental PAH. Eur Respir J. 40:618–629. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mohr AM and Mott JL: Overview of microRNA
biology. Semin Liver Dis. 35:3–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fischer SEJ: RNA interference and
MicroRNA-mediated silencing. Curr Protoc Mol Biol.
112:26.1.1–26.1.5. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Naveed A, Ur-Rahman S, Abdullah S and
Naveed MA: A concise review of MicroRNA exploring the insights of
MicroRNA regulations in bacterial, viral and metabolic diseases.
Mol Biotechnol. 59:518–529. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yun EJ, Lorizio W, Seedorf G, Abman SH and
Vu TH: VEGF and endothelium-derived retinoic acid regulate lung
vascular and alveolar development. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 310:L287–L298. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Muratore CS, Nguyen HT, Ziegler MM and
Wilson JM: Stretch-induced upregulation of VEGF gene expression in
murine pulmonary culture: A role for angiogenesis in lung
development. J Pediatr Surg. 35:906–912. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Partovian C, Adnot S, Eddahibi S, Teiger
E, Levame M, Dreyfus P, Raffestin B and Frelin C: Heart and lung
VEGF mRNA expression in rats with monocrotaline- or hypoxia-induced
pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol. 275:H1948–H1956.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tuder RM, Flook BE and Voelkel NF:
Increased gene expression for VEGF and the VEGF receptors KDR/Flk
and Flt in lungs exposed to acute or to chronic hypoxia. Modulation
of gene expression by nitric oxide. J Clin Invest. 95:1798–1807.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
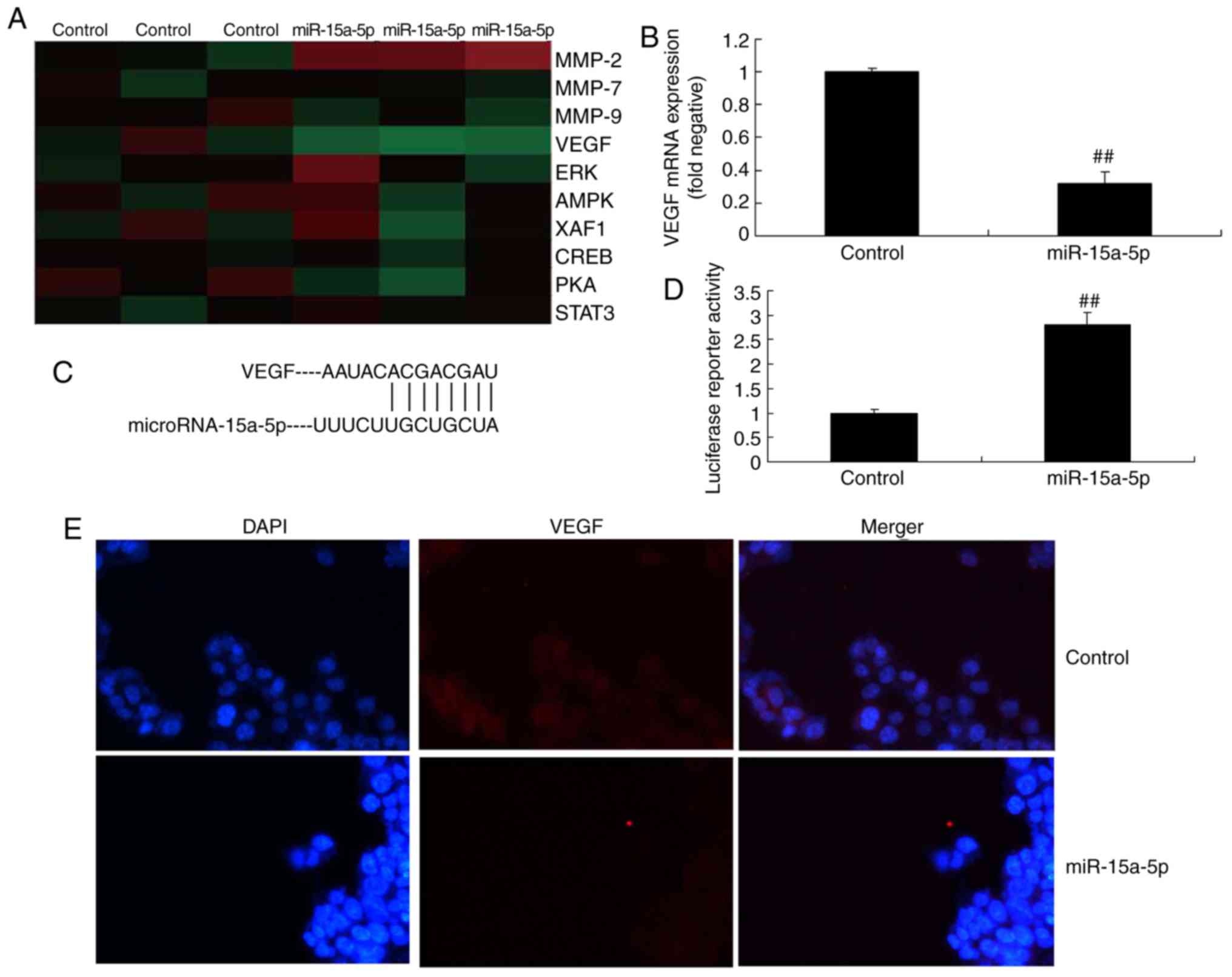
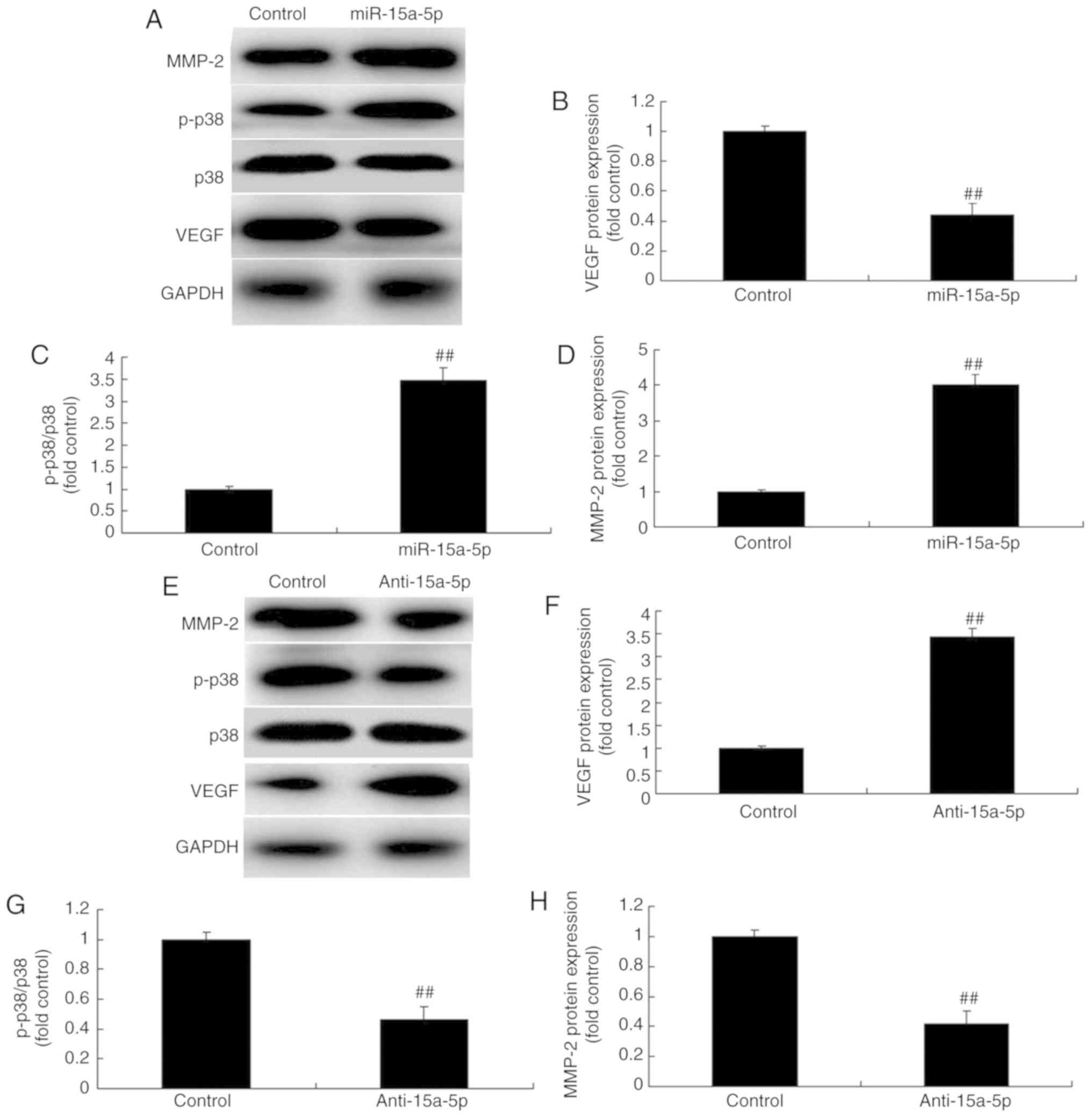
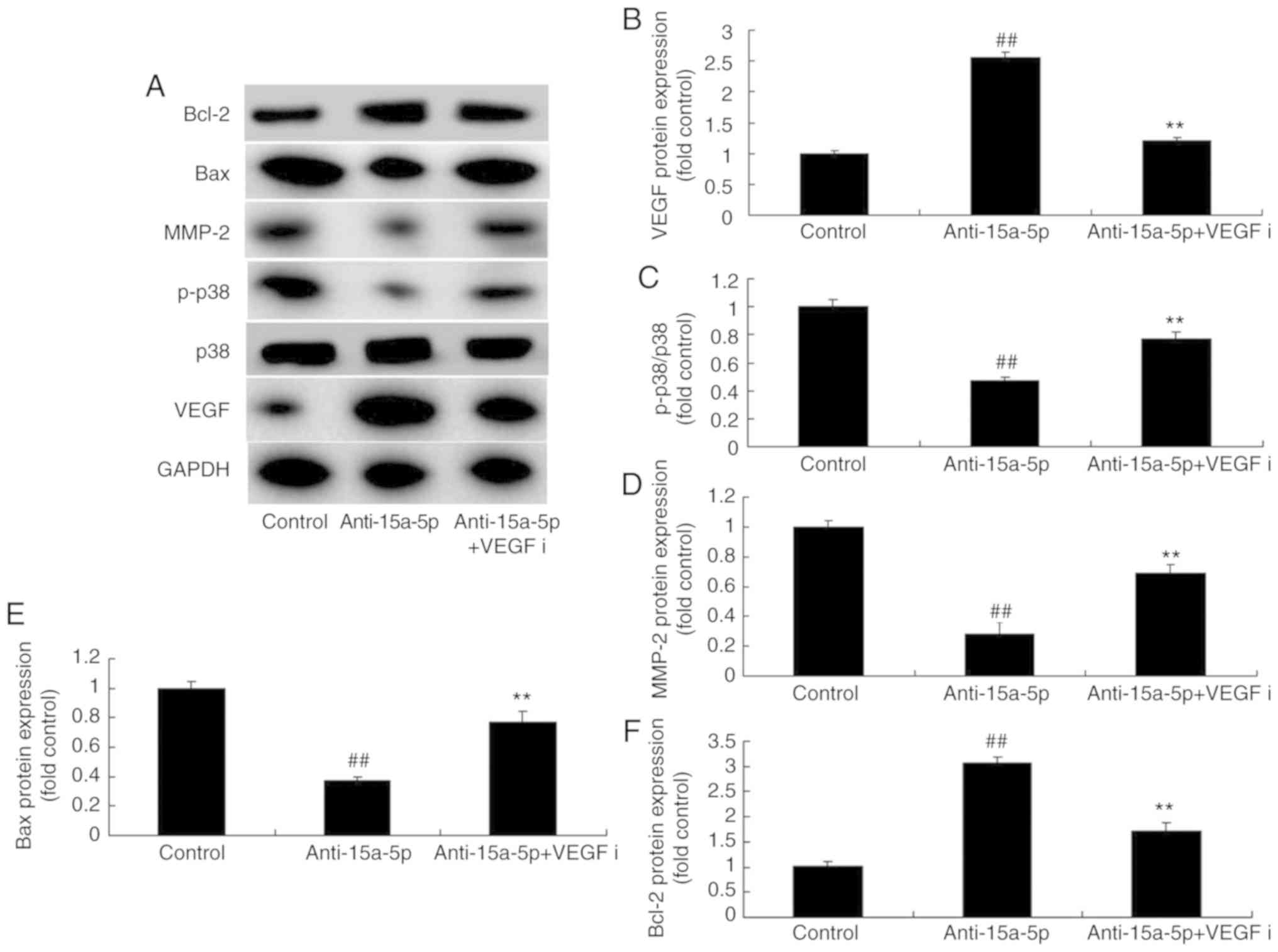
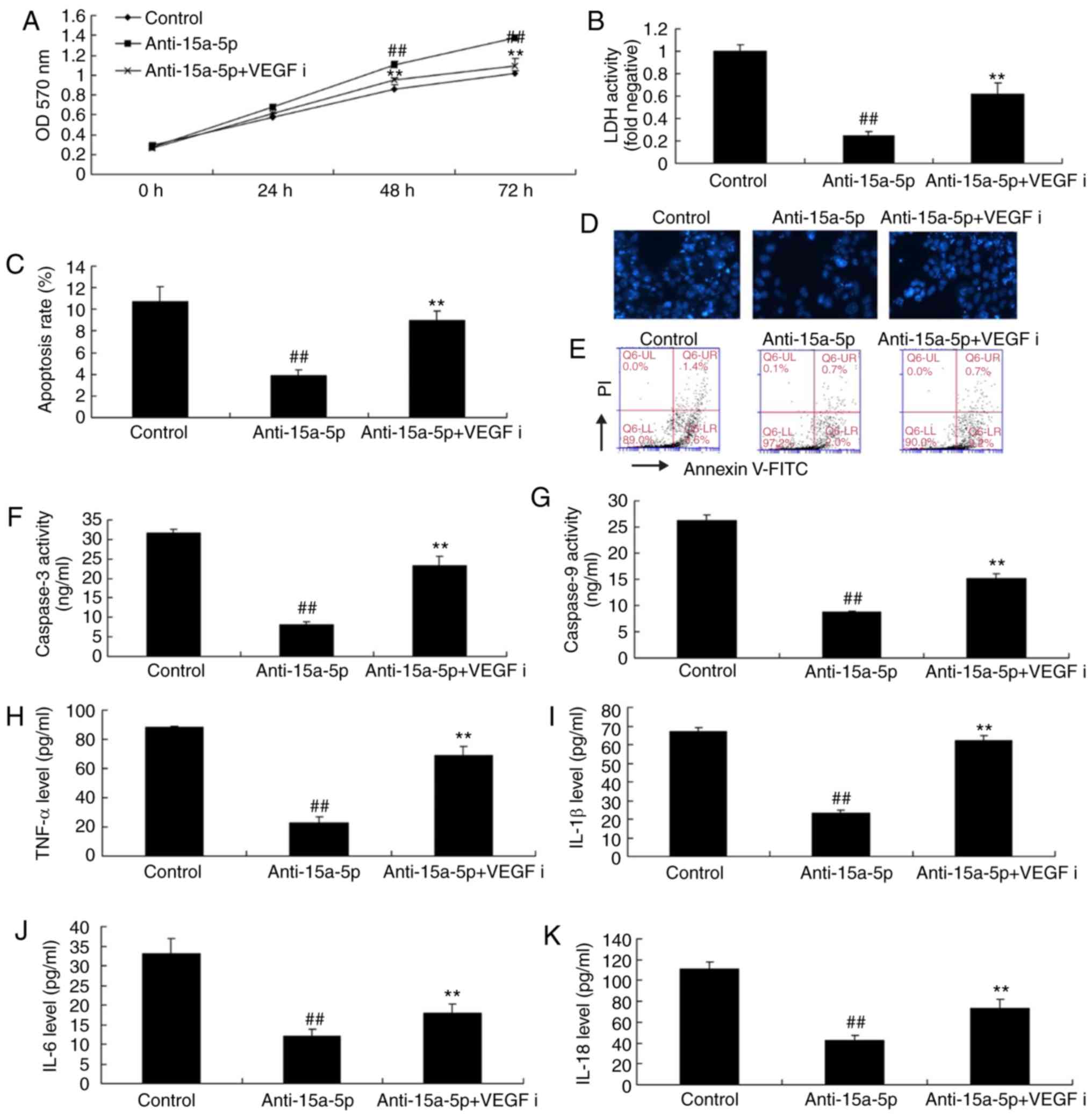
Chen H and Tian Y: MiR-15a-5p regulates
viability and matrix degradation of human osteoarthritis
chondrocytes via targeting VEGFA. Biosci Trends. 10:482–488. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shang J, He Q, Chen Y, Yu D, Sun L, Cheng
G, Liu D, Xiao J and Zhao Z: miR-15a-5p suppresses inflammation and
fibrosis of peritoneal mesothelial cells induced by peritoneal
dialysis via targeting VEGFA. J Cell Physiol. 234:9746–9755. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-timequantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Woik N and Kroll J: Regulation of lung
development and regeneration by the vascular system. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 72:2709–2718. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Voelkel NF and Gomez-Arroyo J: The role of
vascular endothelial growth factor in pulmonary arterial
hypertension. The angiogenesis paradox. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
51:474–484. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sergi C: EPAS 1, congenital heart disease,
and high altitude: Disclosures by genetics, bioinformatics, and
experimental embryology. Biosci Rep. 39:pii: BSR20182197. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Papaioannou AI, Zakynthinos E, Kostikas K,
Kiropoulos T, Koutsokera A, Ziogas A, Koutroumpas A, Sakkas L,
Gourgoulianis KI and Daniil ZD: Serum VEGF levels are related to
the presence of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic
sclerosis. BMC Pulm Med. 9:182009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Saleby J, Bouzina H, Lundgren J and
Radegran G: Angiogenic and inflammatory biomarkers in the
differentiation of pulmonary hypertension. Scand Cardiovasc J.
51:261–270. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kasahara Y, Tuder RM,
Taraseviciene-Stewart L, Le Cras TD, Abman S, Hirth PK,
Waltenberger J and Voelkel NF: Inhibition of VEGF receptors causes
lung cell apoptosis and emphysema. J Clin Invest. 106:1311–1319.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chaudhary KR, Deng Y, Suen CM, Taha M,
Petersen TH, Mei SHJ and Stewart DJ: Efficacy of treprostinil in
the SU5416-hypoxia model of severe pulmonary arterial hypertension:
Haemodynamic benefits are not associated with improvements in
arterial remodelling. Br J Pharmacol. 175:3976–3989. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ye EA, Liu L and Steinle JJ: miR-15a/16
inhibits TGF-beta3/VEGF signaling and increases retinal endothelial
cell barrier proteins. Vision Res. 139:23–29. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schermuly RT, Ghofrani HA, Wilkins MR and
Grimminger F: Mechanisms of disease: Pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Nat Rev Cardiol. 8:443–455. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rabinovitch M, Guignabert C, Humbert M and
Nicolls MR: Inflammation and immunity in the pathogenesis of
pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ Res. 115:165–175. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu Y, Liu LY, Jia Y, Sun YY and Ma FZ:
Role of microRNA-15a-5p in the atherosclerotic inflammatory
response and arterial injury improvement of diabetic by targeting
FASN. Biosci Rep. 39:pii: BSR2018. 18522019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jia X, Hu X, Han S, Miao X, Liu H, Li X,
Lin Z, Wang Z and Gong W: Increased M1 macrophages in young
miR-15a/16−/− mice with tumour grafts or dextran
sulphate sodium-induced colitis. Scand J Immunol. 8:e127032018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Davidovich P, Kearney CJ and Martin SJ:
Inflammatory outcomes of apoptosis, necrosis and necroptosis. Biol
Chem. 395:1163–1171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Pathological roles of
MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1802:396–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ferrari G, Terushkin V, Wolff MJ, Zhang X,
Valacca C, Poggio P, Pintucci G and Mignatti P: TGF-β1 induces
endothelial cell apoptosis by shifting VEGF activation of p38(MAPK)
from the prosurvival p38β to proapoptotic p38α. Mol Cancer Res.
10:605–614. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shi C, Huang F, Gu X, Zhang M, Wen J, Wang
X, You L, Cui X, Ji C and Guo X: Adipogenic miRNA and
meta-signature miRNAs involved in human adipocyte differentiation
and obesity. Oncotarget. 7:40830–40845. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Thenappan T, Chan SY and Weir EK: Role of
extracellular matrix in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 315:H1322–H1331.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bihlet AR, Karsdal MA, Sand JM, Leeming
DJ, Roberts M, White W and Bowler R: Biomarkers of extracellular
matrix turnover are associated with emphysema and
eosinophilic-bronchitis in COPD. Respir Res. 18:222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jablonska-Trypuc A, Matejczyk M and
Rosochacki S: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), the main
extracellular matrix (ECM) enzymes in collagen degradation, as a
target for anticancer drugs. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 31(Sup 1):
S177–S183. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Si-Tayeb K, Monvoisin A, Mazzocco C,
Lepreux S, Decossas M, Cubel G, Taras D, Blanc JF, Robinson DR and
Rosenbaum J: Matrix metalloproteinase 3 is present in the cell
nucleus and is involved in apoptosis. Am J Pathol. 169:1390–1401.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mukherjee A, Adhikari N and Jha T: A
pentanoic acid derivative targeting matrix metalloproteinase-2
(MMP-2) induces apoptosis in a chronic myeloid leukemia cell line.
Eur J Med Chem. 141:37–50. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu H, Zhong Q, Xia Y, Li E, Wang S and Ren
R: MicroRNA-2861 targets STAT3 and MMP2 to regulate the
proliferation and apoptosis of ectopic endometrial cells in
endometriosis. Pharmazie. 74:243–249. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1508452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen D, Wu D, Shao K, Ye B, Huang J and
Gao Y: MiR-15a-5p negatively regulates cell survival and metastasis
by targeting CXCL10 in chronic myeloid leukemia. Am J Transl Res.
9:4308–4316. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|