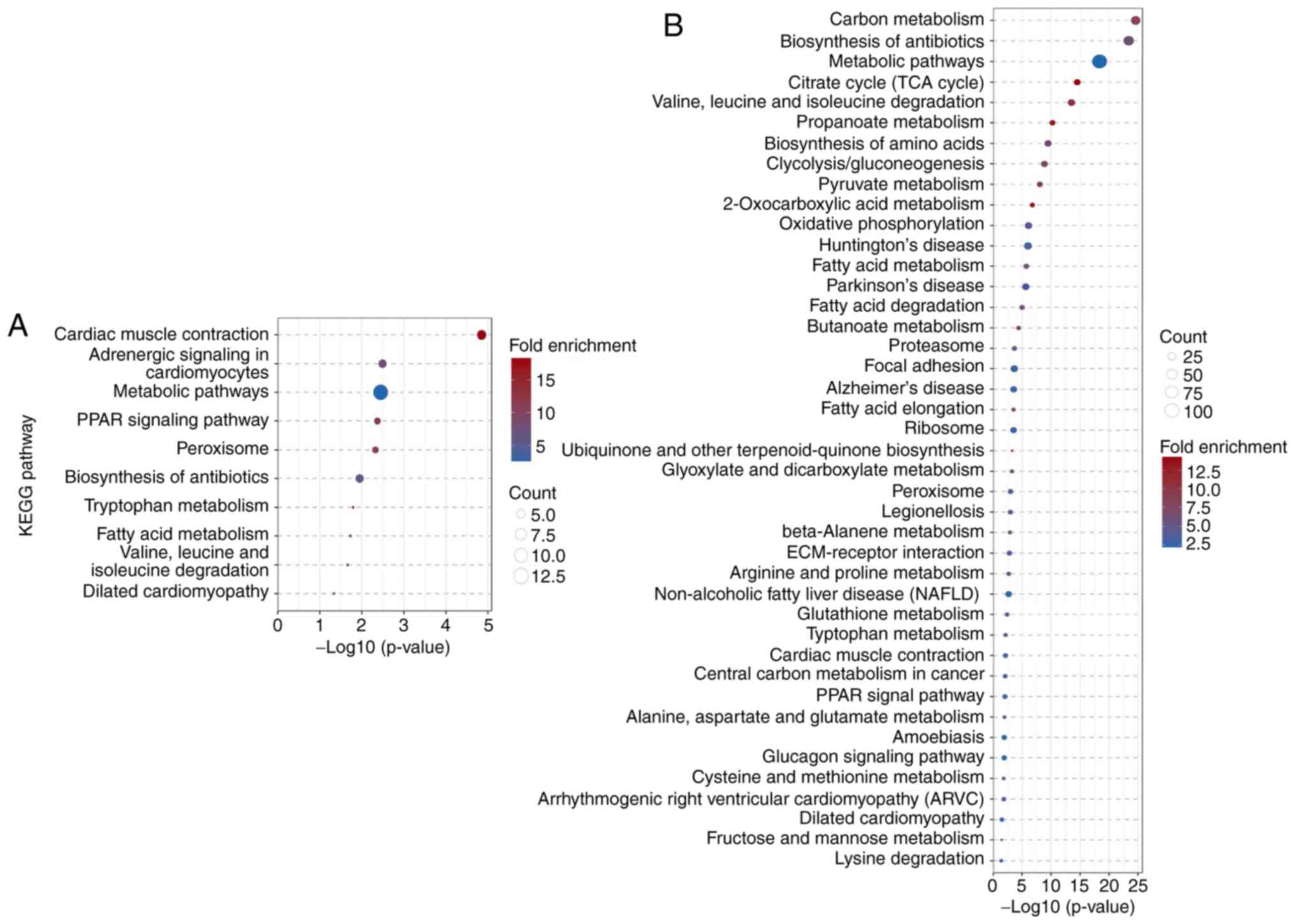
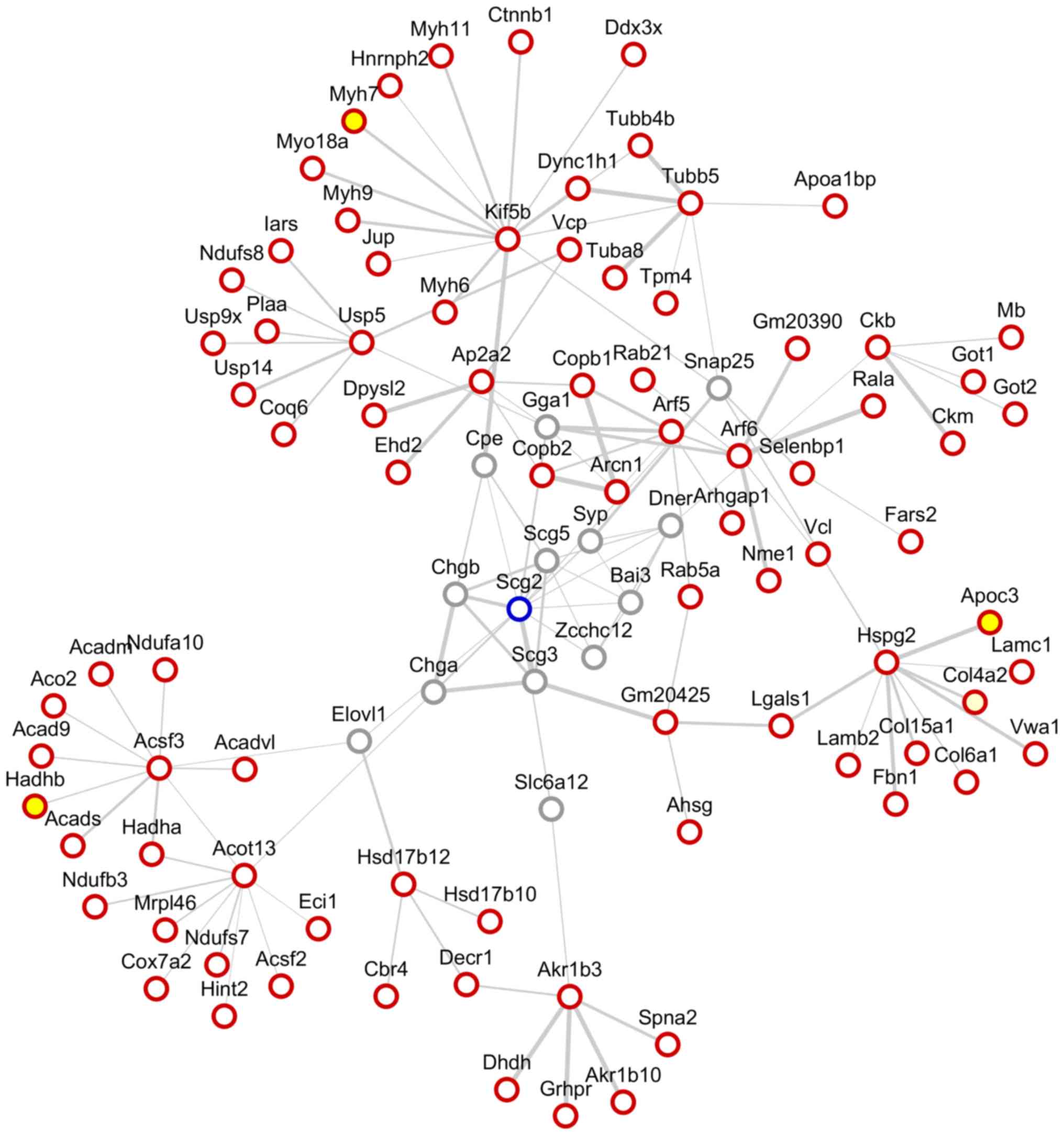
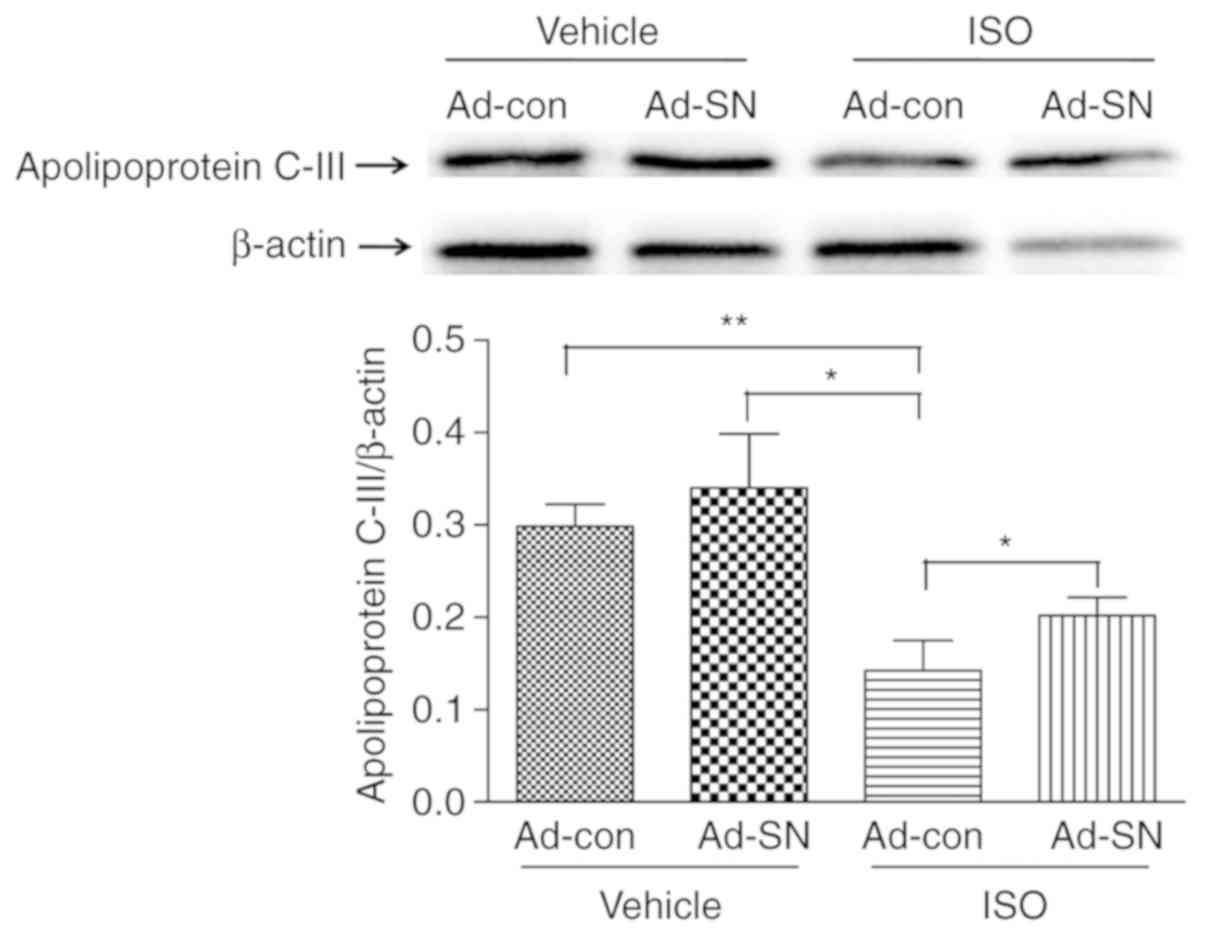
|
1
|
Frey N and Olson EN: Cardiac hypertrophy:
The good, the bad, and the ugly. Annu Rev Physiol. 65:45–79. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oparil S: Pathogenesis of ventricular
hypertrophy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 5:57B–65B. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cingolani HE, Ennis IL, Aiello EA and
Perez NG: Role of auto-crine/paracrine mechanisms in response to
myocardial strain. Pflugers Arch. 462:29–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Doroudgar S and Glembotski CC: The
cardiokine story unfolds: Ischemic stress-induced protein secretion
in the heart. Trends Mol Med. 17:207–214. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Finckenberg P and Mervaala E: The
cardiokine story unfolds: Ischemic stress-induced protein secretion
in the heart. J Hypertens. 28(Suppl): S33–S38. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Albrecht-Schgoer K, Schgoer W, Holfeld J,
Theurl M, Wiedemann D, Steger C, Gupta R, Semsroth S,
Fischer-Colbrie R, Beer AG, et al: The angiogenic factor
secretoneurin induces coronary angiogenesis in a model of
myocardial infarction by stimulation of vascular endothelial growth
factor signaling in endothelial cells. Circulation. 126:2491–2501.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pertl C, Kaufmann W, Amann R, Heinemann A,
Ebeleseder K, Polansky R, Saria A and Kim S: Secretoneurin, a novel
neuropeptide, in the human dental pulp. Arch Oral Biol. 43:361–365.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ceconi C, Ferrari R, Bachetti T, Opasich
C, Volterrani M, Colombo B, Parrinello G and Corti A: Chromogranin
A in heart failure; a novel neurohumoral factor and a predictor for
mortality. Eur Heart J. 23:967–974. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rosjo H, Masson S, Latini R, Flyvbjerg A,
Milani V, La Rovere MT, Revera M, Mezzani A, Tognoni G, Tavazzi L,
et al: Prognostic value of chromogranin A in chronic heart failure:
Data from the GISSI-Heart Failure trial. Eur J Heart Fail.
12:549–556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rosjo H, Husberg C, Dahl MB, Stridsberg M,
Sjaastad I, Finsen AV, Carlson CR, Oie E, Omland T and Christensen
G: Chromogranin B in heart failure: A putative cardiac biomarker
expressed in the failing myocardium. Circ Heart Fail. 3:503–511.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jansson AM, Rosjo H, Omland T, Karlsson T,
Hartford M, Flyvbjerg A and Caidahl K: Prognostic value of
circulating chromogranin A levels in acute coronary syndromes. Eur
Heart J. 30:25–32. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Yuan G, Chen H, Xia C, Gao L and Yu C:
Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of secretoneurin based on
Pb(2+)-decorated reduced graphene oxide-tetraethylene pentamine as
a label. Biosens Bioelectron. 69:95–99. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rosjo H, Stridsberg M, Florholmen G,
Stenslokken KO, Ottesen AH, Sjaastad I, Husberg C, Dahl MB, Oie E,
Louch WE, et al: Secretogranin II; a protein increased in the
myocardium and circulation in heart failure with cardioprotective
properties. PLoS One. 7:e374012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen HL, Liu Y, Jiang W, Wang XX, Yuan GL,
Zhao YL and Yu C: Secretoneurin suppresses cardiac hypertrophy
through suppression of oxidant stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 822:13–24.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zieske LR: A perspective on the use of
iTRAQ reagent technology for protein complex and profiling studies.
J Exp Bot. 57:1501–1508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han X, Shao W, Liu Z, Fan S, Yu J, Chen J,
Qiao R, Zhou J and Xie P: iTRAQ-based quantitative analysis of
hippocampal postsynaptic density-associated proteins in a rat
chronic mild stress model of depression. Neuroscience. 298:220–292.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sharma R, Gowda H, Chavan S, Advani J,
Kelkar D, Kumar GS, Bhattacharjee M, Chaerkady R, Prasad TS, Pandey
A, et al: Proteomic signature of endothelial dysfunction identified
in the serum of acute ischemic stroke patients by the itraq-based
lc-MS approach. J Proteome Res. 14:2466–2479. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Q, Su X, Jiang X, Dong X, Fan Y,
Zhang J, Yu C, Gao W, Shi S, Jiang J, et al: iTRAQ technology-based
identification of human peripheral serum proteins associated with
depression. Neuroscience. 330:291–325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu DD, Deng DF, Li X, Wei LL, Li YY, Yang
XY, Yu W, Wang C, Jiang TT, Li ZJ, et al: Discovery and
identification of serum potential biomarkers for pulmonary
tuberculosis using iTRAQ-coupled two-dimensional LC-MS/MS.
Proteomics. 14:322–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mohamed BA, Asif AR, Schnelle M, Qasim M,
Khadjeh S, Lbik D, Schott P, Hasenfuss G and Toischer K: Proteomic
analysis of short-term preload-induced eccentric cardiac
hypertrophy. J Transl Med. 14:1492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mitra A, Basak T, Ahmad S, Datta K, Datta
R, Sengupta S and Sarkar S: Comparative proteome profiling during
cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial infarction reveals altered
glucose oxidation by differential activation of pyruvate
dehydrogenase e1 component subunit β. J Mol Biol. 427:2104–2120.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chowdhury D, Tangutur AD, Khatua TN,
Saxena P, Banerjee SK and Bhadra MP: A proteomic view of
isoproterenol induced cardiac hypertrophy: Prohibitin identified as
a potential biomarker in rats. J Transl Med. 11:1302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zamorano-Leon JJ, Modrego J,
Mateos-Caceres PJ, Macaya C, Martin-Fernandez B, Miana M, de las
Heras N, Cachofeiro V, Lahera V and López-Farré AJ: A proteomic
approach to determine changes in proteins involved in the
myocardial metabolism in left ventricles of spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 25:347–358. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mesaros C and Blair IA: Mass
spectrometry-based approaches to targeted quantitative proteomics
in cardiovascular disease. Clin Proteomics. 13:202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Luo J, Deng ZL, Luo X, Tang N, Song WX,
Chen J, Sharff KA, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Kinzler KW, et al: A protocol
for rapid generation of recombinant adenoviruses using the AdEasy
system. Nat Protoc. 2:1236–1247. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lopez-Gordo E, Kohlbrenner E, Katz MG and
Weber T: AAV vectors for efficient gene delivery to rodent hearts.
Methods Mol Biol. 1950:311–332. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Garcia-Olloqui P, Rodriguez-Madoz JR, Di
Scala M, Abizanda G, Vales A, Olague C, Iglesias-Garcia O, Larequi
E, Aguado-Alvaro LP, Ruiz-Villalba A, et al: Effect of heart
ischemia and administration route on biodistribution and
transduction efficiency of AAV9 vectors. J Tissue Eng Regen Med.
Nov 1–2019.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
28
|
Tshori S, Gilon D, Beeri R, Nechushtan H,
Kaluzhny D, Pikarsky E and Razin E: Transcription factor MITF
regulates cardiac growth and hypertrophy. J Clin Invest.
116:2673–2681. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen H, Wang X, Tong M, Wu D, Wu S, Chen
J, Wang X, Kang Y, Tang H, Tang C and Jiang W: Intermedin
suppresses pressure overload cardiac hypertrophy through activation
of autophagy. PLoS One. 8:e647572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang XX, Wang XL, Tong MM, Gan L, Chen H,
Wu SS, Chen JX, Li RL, Wu Y, Zhang HY, et al: SIRT6 protects
cardiomyocytes against ischemia/reperfusion injury by augmenting
FoxO3α-dependent antioxidant defense mechanisms. Basic Res Cardiol.
111:132016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kehat I and Molkentin JD: Molecular
pathways underlying cardiac remodeling during pathophysiological
stimulation. Circulation. 122:2727–2735. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zimmer HG: Catecholamine-induced cardiac
hypertrophy: Significance of proto-oncogene expression. J Mol Med
(Berl). 75:849–859. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kamalov G, Bhattacharya SK and Weber KT:
Congestive heart failure: Where homeostasis begets dyshomeostasis.
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 56:320–328. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dunzendorfer S, Schratzberger P, Reinisch
N, Kahler CM and Wiedermann CJ: Secretoneurin, a novel
neuropeptide, is a potent chemoattractant for human eosinophils.
Blood. 91:1527–1532. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kirchmair R, Marksteiner J, Troger J,
Mahata SK, Mahata M, Donnerer J, Amann R, Fischer-Colbrie R,
Winkler H and Saria A: Human and rat primary C-fibre afferents
store and release secre-toneurin, a novel neuropeptide. Eur J
Neurosci. 6:861–868. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schgoer W, Theurl M, Albrecht-Schgoer K,
Jonach V, Koller B, Lener D, Franz WM and Kirchmair R:
Secretoneurin gene therapy improves blood flow in an ischemia model
in type 1 diabetic mice by enhancing therapeutic
neovascularization. PLoS One. 8:e740292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chan CK and Vanhoutte PM: Secretoneurin
facilitates endothelium-dependent relaxations in porcine coronary
arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 300:H1159–H1165. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schgoer W, Theurl M, Jeschke J, Beer AG,
Albrecht K, Gander R, Rong S, Vasiljevic D, Egger M, Wolf AM, et
al: Gene therapy with the angiogenic cytokine secretoneurin induces
therapeutic angiogenesis by a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism.
Circ Res. 105:994–1002. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang K Master's degree, Chen Z Master's
degree, Long L Master's degree, Tao Y Master's degree, Wu Q
Master's degree, Xiang M Master's degree, Liang Y Bachelor's
degree, Xie X Bachelor's degree, Jiang Y Master's degree, Xiao Z
Doctor's degree, et al: iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis
of differentially expressed proteins in chemoresistant
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 19:809–824. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Gupta D, Mohammed M, Mekala LP,
Chintalapati S and Chintalapati VR: iTRAQ-based quantitative
proteomics reveals insights into metabolic and molecular responses
of glucose-grown cells of Rubrivivax benzoatilyticus JA2. J
Proteomics. 194:49–59. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Luo H, Yao L, Zhang Y and Li R: Liquid
chromatography-mass spectrometry-based quantitative proteomics
analysis reveals chondroprotective effects of astragaloside IV in
interleukin-1β-induced SW1353 chondrocyte-like cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 91:796–802. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ren J, Zhao G, Sun X, Liu H, Jiang P, Chen
J, Wu Z, Peng D, Fang Y and Zhang C: Identification of plasma
biomarkers for distinguishing bipolar depression from major
depressive disorder by iTRAQ-coupled LC-MS/MS and bioinformatics
analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 86:17–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li Z, Huang T, Tang M, Cheng B, Peng Y and
Zhang X: iTRAQ-based proteomics reveals key role of
gamma-amino-butyric acid (GABA) in regulating drought tolerance in
perennial creeping bentgrass (Agrostis stolonifera). Plant Physiol
Biochem. 145:216–226. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen C, Hao X, Geng Z and Wang Z:
ITRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis of MG63 in response to
HIF-1α inducers. J Proteomics. 211:1035582019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Tian L, You HZ, Wu H, Wei Y, Zheng M, He
L, Liu JY, Guo SZ, Zhao Y, Zhou RL and Hu X: iTRAQ-based
quantitative proteomic analysis provides insight for molecular
mechanism of neuroticism. Clin Proteomics. 16:382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Diguet N, Trammell SAJ, Tannous C, Deloux
R, Piquereau J, Mougenot N, Gouge A, Gressette M, Manoury B, Blanc
J, et al: Nicotinamide riboside preserves cardiac function in a
mouse model of dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 137:2256–2273.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Huang CY, Lee FL, Peng SF, Lin KH, Chen
RJ, Ho TJ, Tsai FJ, Padma VV and Kuo WW: HSF1 phosphorylation by
ERK/GSK3 suppresses RNF126 to sustain IGF-IIR expression for
hypertension-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Cell Physiol.
233:979–989. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Ding G, May HI, Xu J,
Gillette TG, Wang H and Wang ZV: Temporal dynamics of cardiac
hypertrophic growth in response to pressure overload. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 313:H1119–H1129. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kesidis N, Metaxas TI, Vrabas IS,
Stefanidis P, Vamvakoudis E, Christoulas K, Mandroukas A, Balasas D
and Mandroukas K: Myosin heavy chain isoform distribution in single
fibres of bodybuilders. Eur J Appl Physiol. 103:579–583. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Petropoulou E, Soltani M, Firoozabadi AD,
Namayandeh SM, Crockford J, Maroofian R and Jamshidi Y: Digenic
inheritance of mutations in the cardiac troponin (TNNT2) and
cardiac beta myosin heavy chain (MYH7) as the cause of severe
dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur J Med Genet. 60:485–488. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang L, Zuo L, Hu J, Shao H, Lei C, Qi W,
Liu Y, Miao Y, Ma X, Huang CL, et al: Dual LQT1 and HCM phenotypes
associated with tetrad heterozygous mutations in KCNQ1, MYH7,
MYLK2, and TMEM70 genes in a three-generation Chinese family.
Europace. 18:602–609. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Chugh S, Ouzounian M, Lu Z, Mohamed S, Li
W, Bousette N, Liu PP and Gramolini AO: Pilot study identifying
myosin heavy chain 7, desmin, insulin-like growth factor 7, and
annexin A2 as circulating biomarkers of human heart failure.
Proteomics. 13:2324–2334. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ginsberg HN, Le NA, Goldberg IJ, Gibson
JC, Rubinstein A, Wang-Iverson P, Norum R and Brown WV:
Apolipoprotein B metabolism in subjects with deficiency of
apolipoproteins CIII and AI. Evidence that apolipoprotein CIII
inhibits catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by
lipoprotein lipase in vivo. J Clin Invest. 78:1287–1295. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ooi EM, Barrett PH, Chan DC and Watts GF:
Apolipoprotein C-III: Understanding an emerging cardiovascular risk
factor. Clin Sci (Lond). 114:611–624. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Clavey V, Lestavel-Delattre S, Copin C,
Bard JM and Fruchart JC: Modulation of lipoprotein B binding to the
LDL receptor by exogenous lipids and apolipoproteins CI, CII, CIII,
and E. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 15:963–971. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wyler von Ballmoos MC, Haring B and Sacks
FM: The risk of cardiovascular events with increased apolipoprotein
CIII: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Lipidol.
9:498–510. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jorgensen AB, Frikke-Schmidt R,
Nordestgaard BG and Tybjaerg-Hansen A: Loss-of-function mutations
in APOC3 and risk of ischemic vascular disease. N Engl J Med.
371:32–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Luo M and Peng D: The emerging role of
apolipoprotein C-III: Beyond effects on triglyceride metabolism.
Lipids Health Dis. 15:1842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|