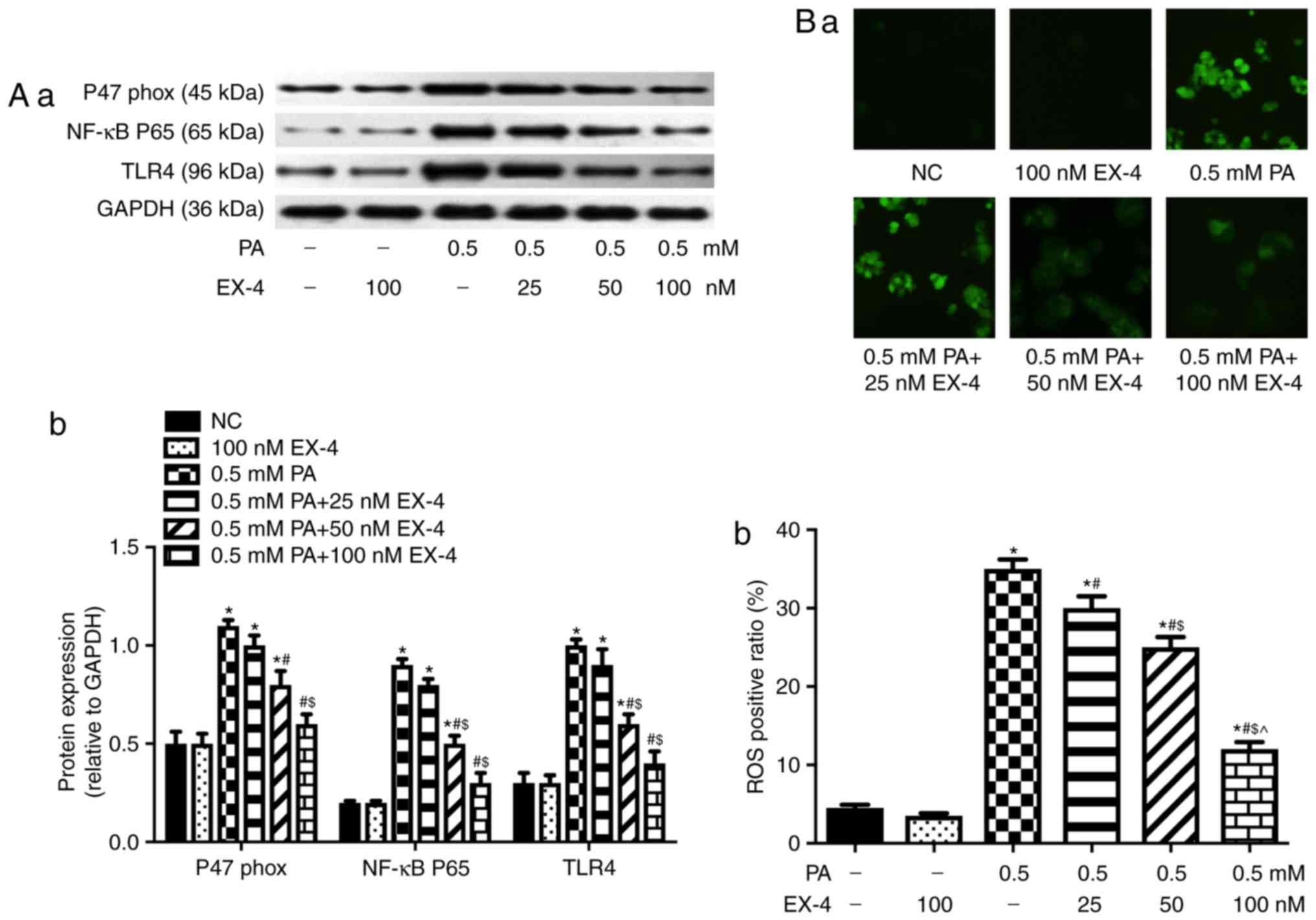
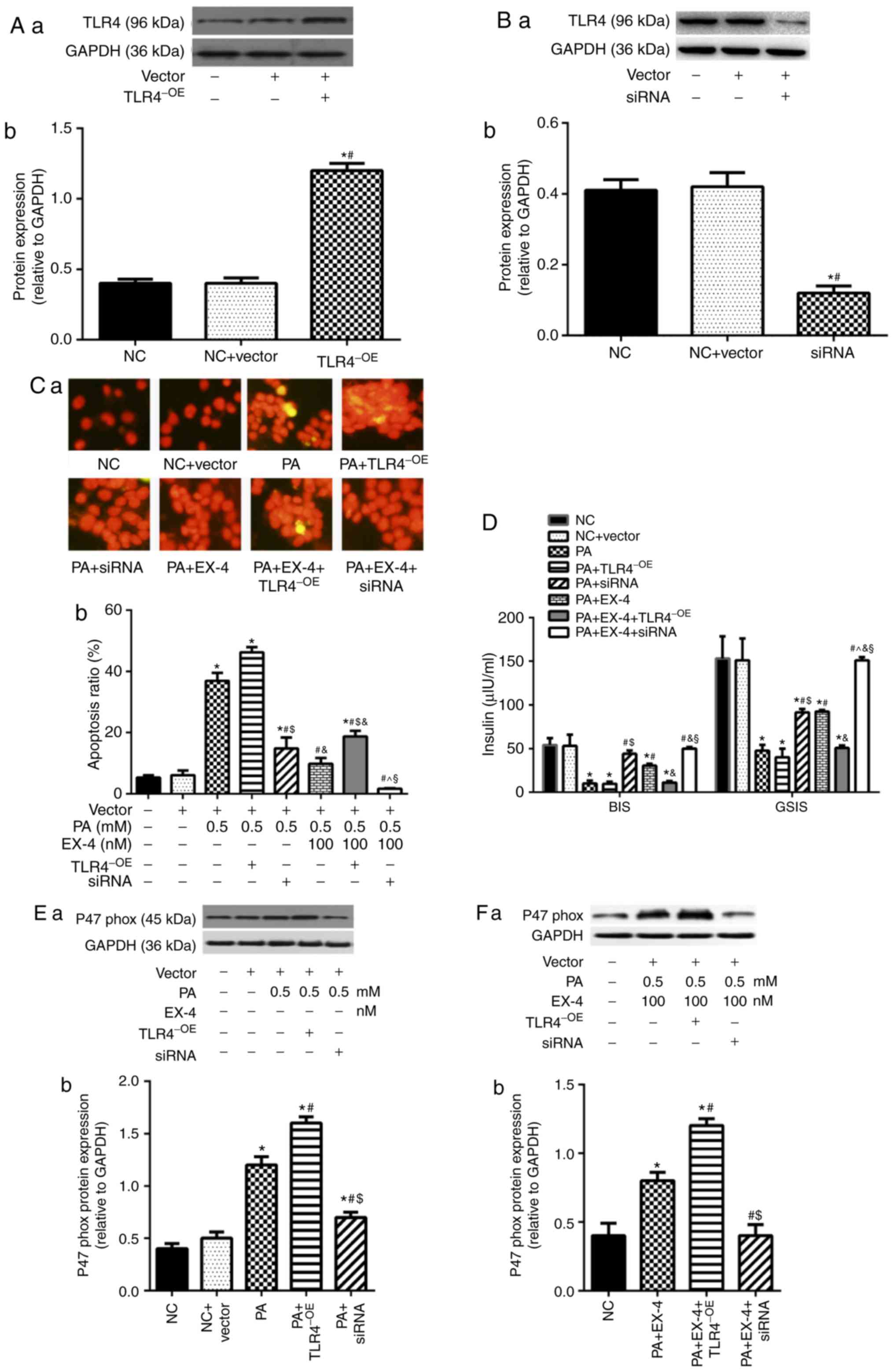
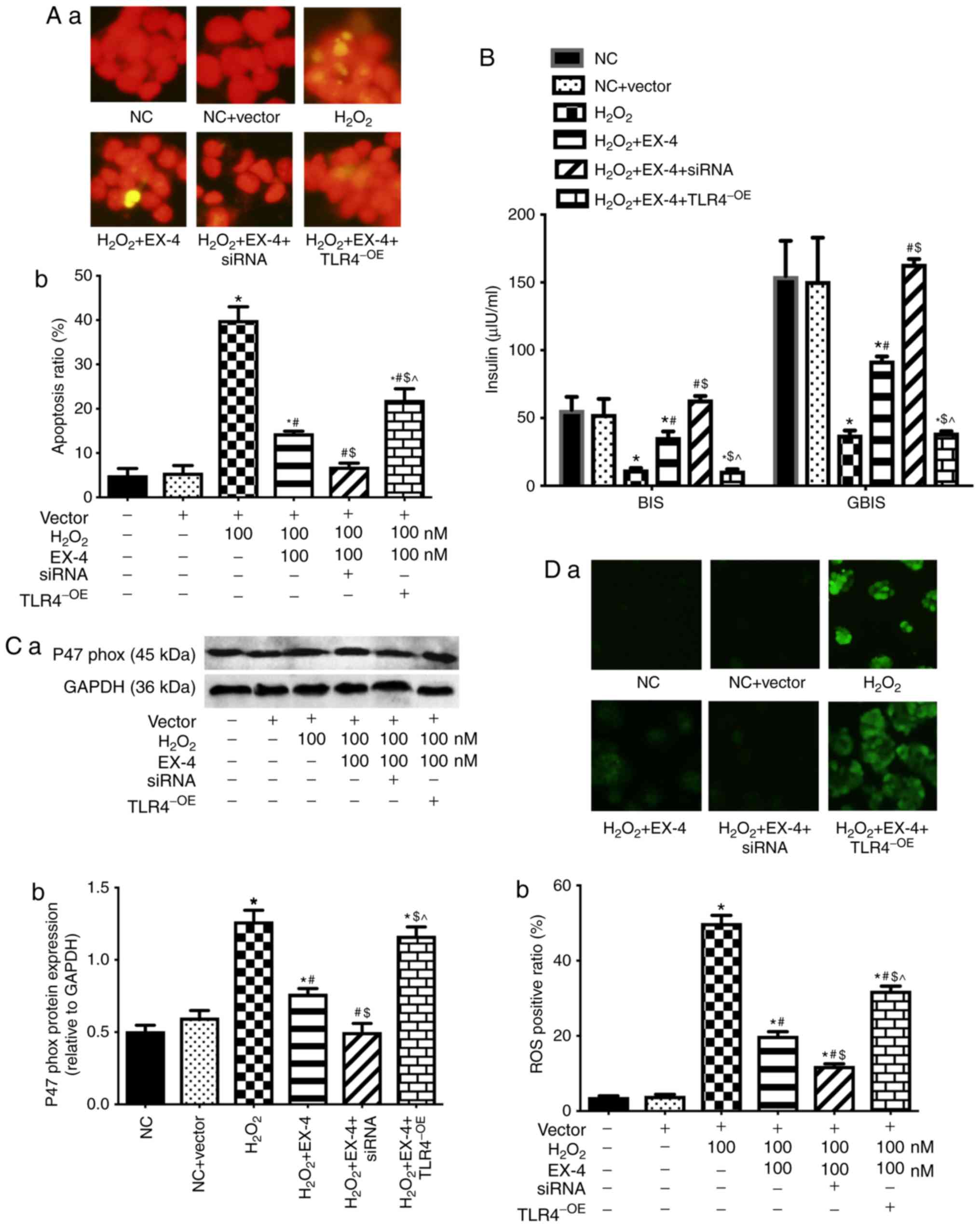
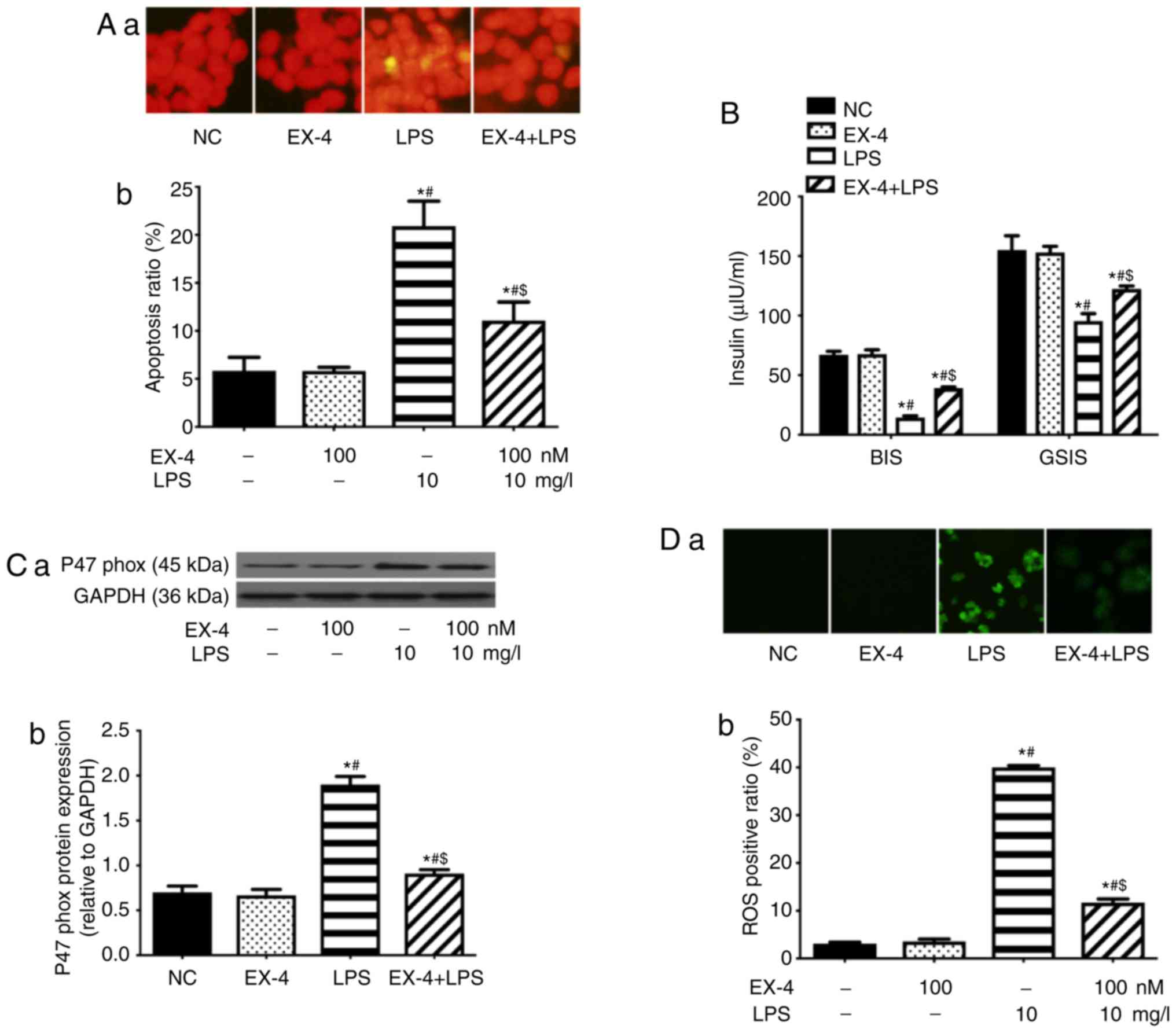
|
1
|
Hirota Y, Matsuda T, Nakajima S, Takabe M,
Hashimoto N, Nakamura T, Okada Y, Sakaguchi K and Ogawa W: Effects
of exenatide and liraglutide on postchallenge glucose disposal in
individuals with normal glucose tolerance. Endocrine. 64:43–47.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gu J, Wei Q, Zheng H, Meng X, Zhang J and
Wang D: Exendin-4 promotes survival of mouse pancreatic beta-cell
line in lipotoxic conditions, through the extracellular
signal-related kinase 1/2 pathway. J Diabetes Res.
2016:52940252016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Natalicchio A, Labarbuta R, Tortosa F,
Biondi G, Marrano N, Peschechera A, Carchia E, Orlando MR,
Leonardini A, Cignarelli A, et al: Exendin-4 protects pancreatic
beta cells from palmitate-induced apoptosis by interfering with
GPR40 and the MKK4/7 stress kinase signalling pathway.
Diabetologia. 56:2456–2466. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Oh YS, Lee YJ, Kang Y, Han J, Lim OK and
Jun HS: Exendin-4 inhibits glucolipotoxic ER stress in pancreatic β
cells via regulation of SREBP1c and C/EBPβ transcription factors. J
Endocrinol. 216:343–352. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wu X, Liang W, Guan H, Liu J, Liu L, Li H,
He X, Zheng J, Chen J, Cao X and Li Y: Exendin-4 promotes
pancreatic β-cell proliferation via inhibiting the expression of
Wnt5a. Endocrine. 55:398–409. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Natalicchio A, Biondi G, Marrano N,
Labarbuta R, Tortosa F, Spagnuolo R, D'Oria R, Carchia E,
Leonardini A, Cignarelli A, et al: Long-term exposure of pancreatic
β-cells to palmitate results in SREBP-1C-dependent decreases in
GLP-1 receptor signaling via CREB and AKT and insulin secretory
response. Endocrinology. 157:2243–2258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang Y, Choi PP, Smith WW, Xu W, Ma D,
Cordner ZA, Liang NC and Moran TH: Exendin-4 reduces food intake
via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in the hypothalamus. Sci Rep.
7:69362017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Iwasaki S, Hamada T, Chisaki I, Andou T,
Sano N, Furuta A and Amano N: Mechanism-based
pharmacokinetic/pharmacody-namic modeling of the glucagon-like
peptide-1 receptor agonist exenatide to characterize its
antiobesity effects in diet-induced obese mice. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 362:441–449. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dandona P, Ghanim H, Abuaysheh S, Green K,
Dhindsa S, Makdissi A, Batra M, Kuhadiya ND and Chaudhuri A:
Exenatide increases IL-1RA concentration and induces
Nrf-2Keap-1regulated antioxidant enzymes: Relevance to β-cell
function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 103:1180–1187. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Varin EM, Wojtusciszyn A, Broca C, Muller
D, Ravier MA, Ceppo F, Renard E, Tanti JF and Dalle S: Inhibition
of the MAP3 kinase Tpl2 protects rodent and human β-cells from
apoptosis and dysfunction induced by cytokines and enhances
anti-inflammatory actions of exendin-4. Cell Death Dis.
7:e20652016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chang G, Liu J, Qin S, Jiang Y, Zhang P,
Yu H, Lu K, Zhang N, Cao L, Wang Y, et al: Cardioprotection by
exenatide: A novel mechanism via improving mitochondrial function
involving the GLP-1 receptor/cAMP/PKA pathway. Int J Mol Med.
41:1693–1703. 2018.
|
|
12
|
Kawaguchi T, Itou M, Taniguchi E and Sata
M: Exendin4, a glucagonlike peptide1 receptor agonist, modulates
hepatic fatty acid composition and Δ-5desaturase index in a murine
model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Int J Mol Med. 34:782–787.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee SM, Choi SE, Lee JH, Lee JJ, Jung IR,
Lee SJ, Lee KW and Kang Y: Involvement of the TLR4 (Toll-like
receptor4) signaling pathway in palmitate-induced INS-1 beta cell
death. Mol Cell Biochem. 354:207–217. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Eguchi K, Manabe I, Oishi-Tanaka Y, Ohsugi
M, Kono N, Ogata F, Yagi N, Ohto U, Kimoto M, Miyake K, et al:
Saturated fatty acid and TLR signaling link β cell dysfunction and
islet inflammation. Cell Metab. 15:518–533. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang X, Ge QM, Bian F, Dong Y and Huang
CM: Inhibition of TLR4 protects rat islets against
lipopolysaccharide-induced dysfunction. Mol Med Rep. 15:805–812.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shen X, Yang L, Yan S, Zheng H, Liang L,
Cai X and Liao M: Fetuin A promotes lipotoxicity in β cells through
the TLR4 signaling pathway and the role of pioglitazone in
anti-lipotoxicity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 412:1–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma C, Jiang Y, Zhang X, Chen X, Liu Z and
Tian X: Isoquercetin ameliorates myocardial infarction through
anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis factor and regulating
TLR4-NF-kB signal pathway. Mol Med Rep. 17:6675–6680.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou Y, Ding YL, Zhang JL, Zhang P, Wang
JQ and Li ZH: Alpinetin improved high fat diet-induced
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through improving
oxidative stress, inflammatory response and lipid metabolism.
Biomed Pharmacother. 97:1397–1408. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xu MX, Wang M and Yang WW: Gold-quercetin
nanoparticles prevent metabolic endotoxemia-induced kidney injury
by regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling and Nrf2 pathway in high fat
diet fed mice. Int J Nanomedicine. 12:327–345. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Xiang JN, Chen DL and Yang LY: Effect of
PANDER in βTC6-cell lipoapoptosis and the protective role of
exendin-4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421:701–706. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kondo M, Tanabe K, Amo-Shiinoki K,
Hatanaka M, Morii T, Takahashi H, Seino S, Yamada Y and Tanizawa Y:
Activation of GLP-1 receptor signalling alleviates cellular
stresses and improves beta cell function in a mouse model of
Wolfram syndrome. Diabetologia. 61:2189–2201. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang G, Lei Y, Inoue A, Piao L, Hu L,
Jiang H, Sasaki T, Wu H, Xu W, Yu C, et al: Exenatide mitigated
diet-induced vascular aging and atherosclerotic plaque growth in
ApoE-deficient mice under chronic stress. Atherosclerosis.
264:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ke J, Wei R, Yu F, Zhang J and Hong T:
Liraglutide restores angiogenesis in palmitate-impaired human
endothelial cells through PI3K/Akt-Foxo1-GTPCH1 pathway. Peptides.
86:95–101. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shen X, Yang L, Yan S, Wei W, Liang L,
Zheng H and Cai X: The effect of FFAR1 on pioglitazone-mediated
attenuation of palmitic acid-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis
in βTC6 cells. Metabolism. 63:335–351. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Seo JH, Lim JW and Kim H: Differential
role of ERK and p38 on NF-κB activation in helicobacter
pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. J Cancer Prev.
18:346–350. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lu Z, Shen SX, Zhi DJ and Luo FH: The
establishment of 'two-step sequential filtration method' on the
yield rate of purified islets in rats. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za
Zhi. 15:572–576. 2013.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kassem M, Niazi ZR, Abbas M, El Habhab A,
Kreutter G, Khemais-Benkhiat S, Auger C, Antal MC, Schini-Kerth VB,
Toti F and Kessler L: Senescence of pancreas in middle-aged rats
with normal vascular function. Ann Transplant. 22:177–186. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen DL, Xiang JN and Yang LY: Role of
ERp46 in β-cell lipoapoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress
pathway as well as the protective effect of exendin-4. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 426:324–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Q, Lin Y, Wang S, Zhang L and Guo L:
GLP-1 inhibits high-glucose-induced oxidative injury of vascular
endothelial cells. Sci Rep. 7:80082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schiapaccassa A, Maranhão PA, de Souza
MDGC, Panazzolo DG, Nogueira Neto JF, Bouskela E and Kraemer-Aguiar
LG: 30-days effects of vildagliptin on vascular function, plasma
viscosity, inflammation, oxidative stress, and intestinal peptides
on drug-naive women with diabetes and obesity: A randomized
head-to-head metformin-controlled study. Diabetol Metab Syndr.
11:702019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Steven S, Jurk K, Kopp M, Kröller-Schön S,
Mikhed Y, Schwierczek K, Roohani S, Kashani F, Oelze M, Klein T, et
al: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signalling reduces
micro-vascular thrombosis, nitro-oxidative stress and platelet
activation in endotoxaemic mice. Br J Pharmacol. 174:1620–1632.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Shimoda M, Kanda Y, Hamamoto S, Tawaramoto
K, Hashiramoto M, Matsuki M and Kaku K: The human glucagon-like
peptide-1 analogue liraglutide preserves pancreatic beta cells via
regulation of cell kinetics and suppression of oxidative and
endoplasmic reticulum stress in a mouse model of diabetes.
Diabetologia. 54:1098–1108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rebelato E, Mares-Guia TR, Graciano MF,
Labriola L, Britto LR, Garay-Malpartida HM, Curi R, Sogayar MC and
Carpinelli AR: Expression of NADPH oxidase in human pancreatic
islets. Life Sci. 91:244–249. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu L, Wang K, Wang W, Wen Z, Wang P, Liu L
and Wang DW: Glucagon-like peptide-1 ameliorates cardiac
lipotoxicity in diabetic cardiomyopathy via the PPARα pathway.
Aging Cell. 17:e127632018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Tesauro M, Schinzari F, Adamo A, Rovella
V, Martini F, Mores N, Barini A, Pitocco D, Ghirlanda G, Lauro D,
et al: Effects of GLP-1 on forearm vasodilator function and glucose
disposal during hyperinsulinemia in the metabolic syndrome.
Diabetes Care. 36:683–689. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Ceriello A, Novials A, Canivell S, La Sala
L, Pujadas G, Esposito K, Testa R, Bucciarelli L, Rondinelli M and
Genovese S: Simultaneous GLP-1 and insulin administration acutely
enhances their vasodilatory, antiinflammatory, and antioxidant
action in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 37:1938–1943. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu XH, Wang YP, Wang LX, Chen Z, Liu XY
and Liu LB: Exendin-4 protects murine MIN6 pancreatic β-cells from
interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis via the NF-κB pathway. J
Endocrinol Invest. 36:803–811. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chang G, Zhang D, Yu H, Zhang P, Wang Y,
Zheng A and Qin S: Cardioprotective effects of exenatide against
oxidative stress-induced injury. Int J Mol Med. 32:1011–1020. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gao H, Zeng Z, Zhang H, Zhou X, Guan L,
Deng W and Xu L: The glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue liraglutide
inhibits oxidative stress and inflammatory response in the liver of
rats with diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biol
Pharm Bull. 38:694–702. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tanaka T, Higashijima Y, Wada T and
Nangaku M: The potential for renoprotection with incretin-based
drugs. Kidney Int. 86:701–711. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim MH, Kim EH, Jung HS, Yang D, Park EY
and Jun HS: EX4 stabilizes and activates Nrf2 via PKCδ,
contributing to the prevention of oxidative stress-induced
pancreatic beta cell damage. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 315:60–69.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kanoski SE, Hayes MR and Skibicka KP:
GLP-1 and weight loss: Unraveling the diverse neural circuitry. Am
J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 310:R885–R895. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wolak M, Staszewska T, Juszczak M,
Gałdyszyńska M and Bojanowska E: Anti-inflammatory and pro-healing
impacts of exendin-4 treatment in Zucker diabetic rats: Effects on
skin wound fibroblasts. Eur J Pharmacol. 842:262–269. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Basolo A, Burkholder J, Osgood K, Graham
A, Bundrick S, Frankl J, Piaggi P, Thearle MS and Krakoff J:
Exenatide has a pronounced effect on energy intake but not energy
expenditure in non-diabetic subjects with obesity: A randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Metabolism. 85:116–125.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jorsal T, Rungby J, Knop FK and Vilsbøll
T: GLP-1 and amylin in the treatment of obesity. Curr Diab Rep.
16:12016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Camastra S, Astiarraga B, Tura A,
Frascerra S, Ciociaro D, Mari A, Gastaldelli A and Ferrannini E:
Effect of exenatide on postprandial glucose fluxes, lipolysis, and
β-cell function in non-diabetic, morbidly obese patients. Diabetes
Obes Metab. 19:412–420. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sun XF, Wang Y, Zhao WJ, Wang L, Bao DQ,
Qu GR, Yao MX, Luan J, Wang YG and Yan SL: Effect of liraglutide on
glucagon secretion in obese type 2 diabetic patients. Zhonghua Nei
Ke Za Zhi. 58:33–38. 2019.In Chinese; Abstract available in Chinese
from the publisher. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Opinto G, Natalicchio A and Marchetti P:
Physiology of incretins and loss of incretin effect in type 2
diabetes and obesity. Arch Physiol Biochem. 119:170–178. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|