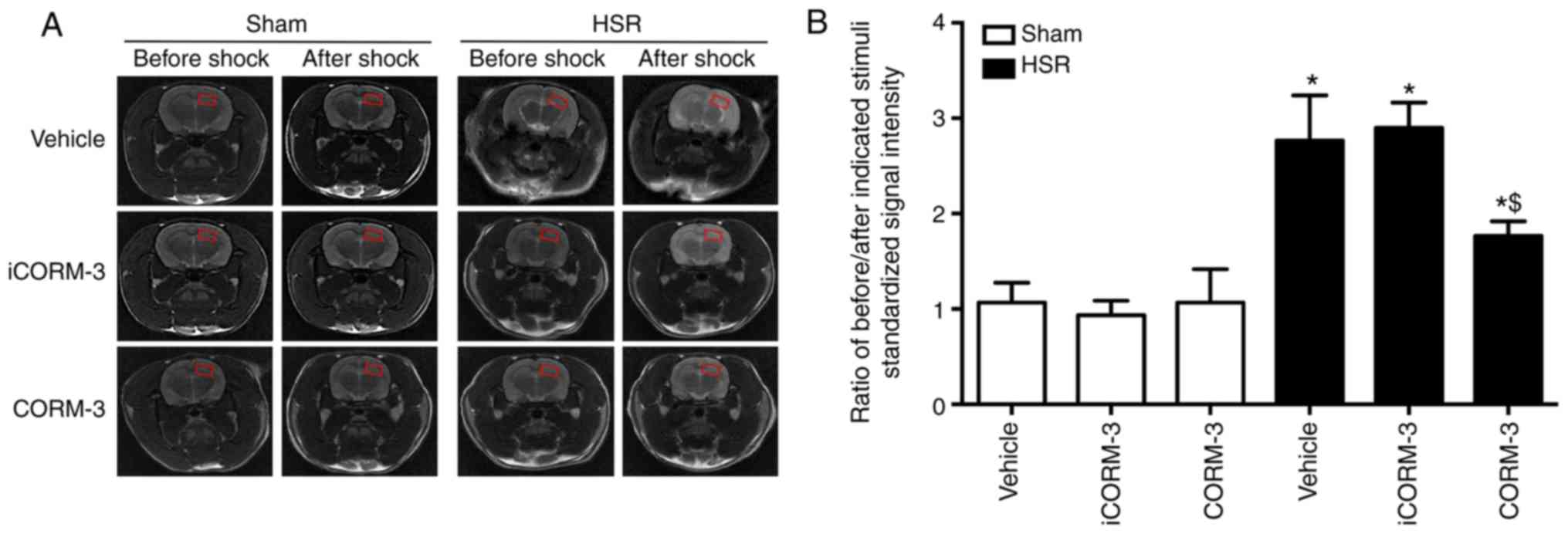
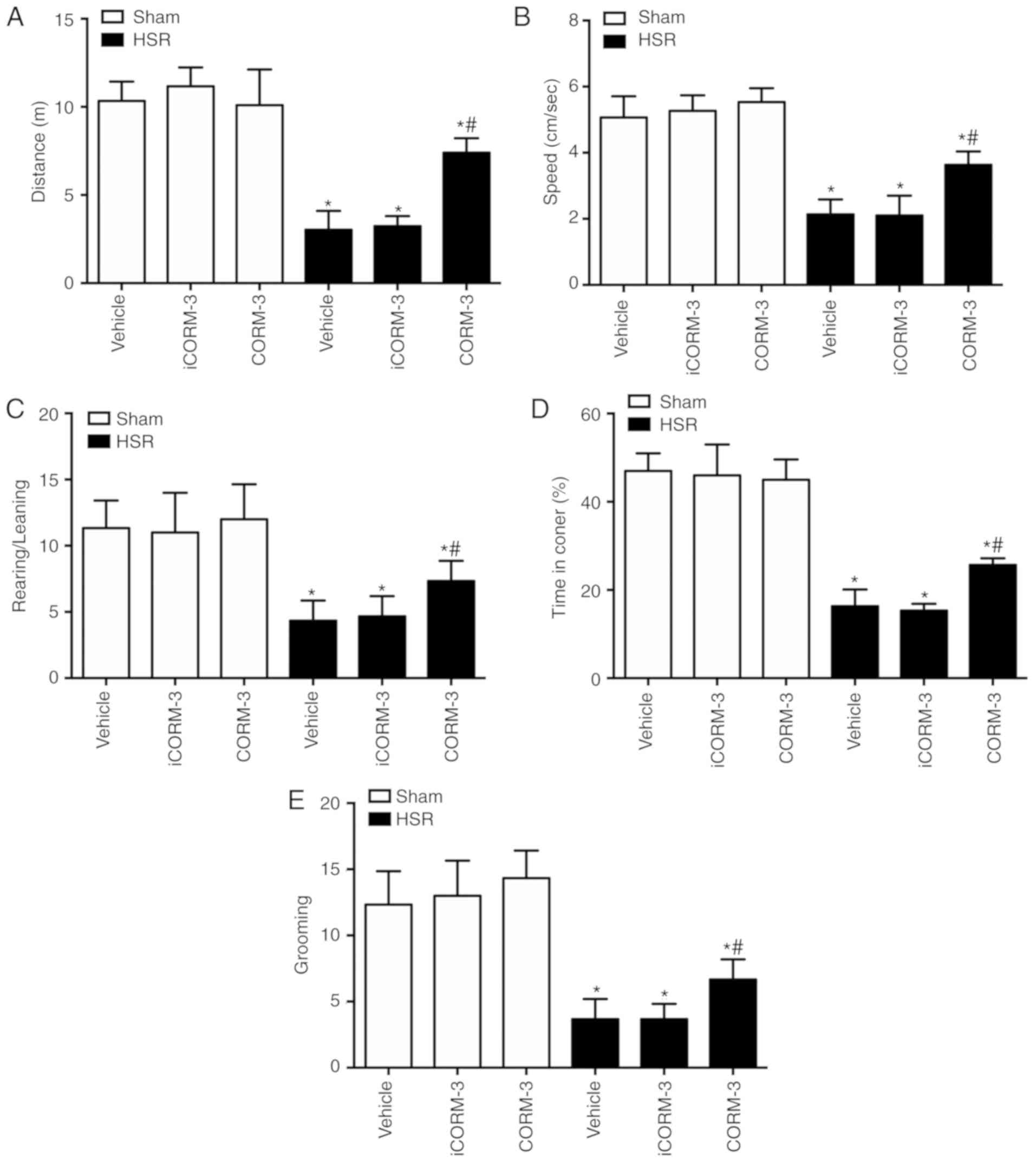
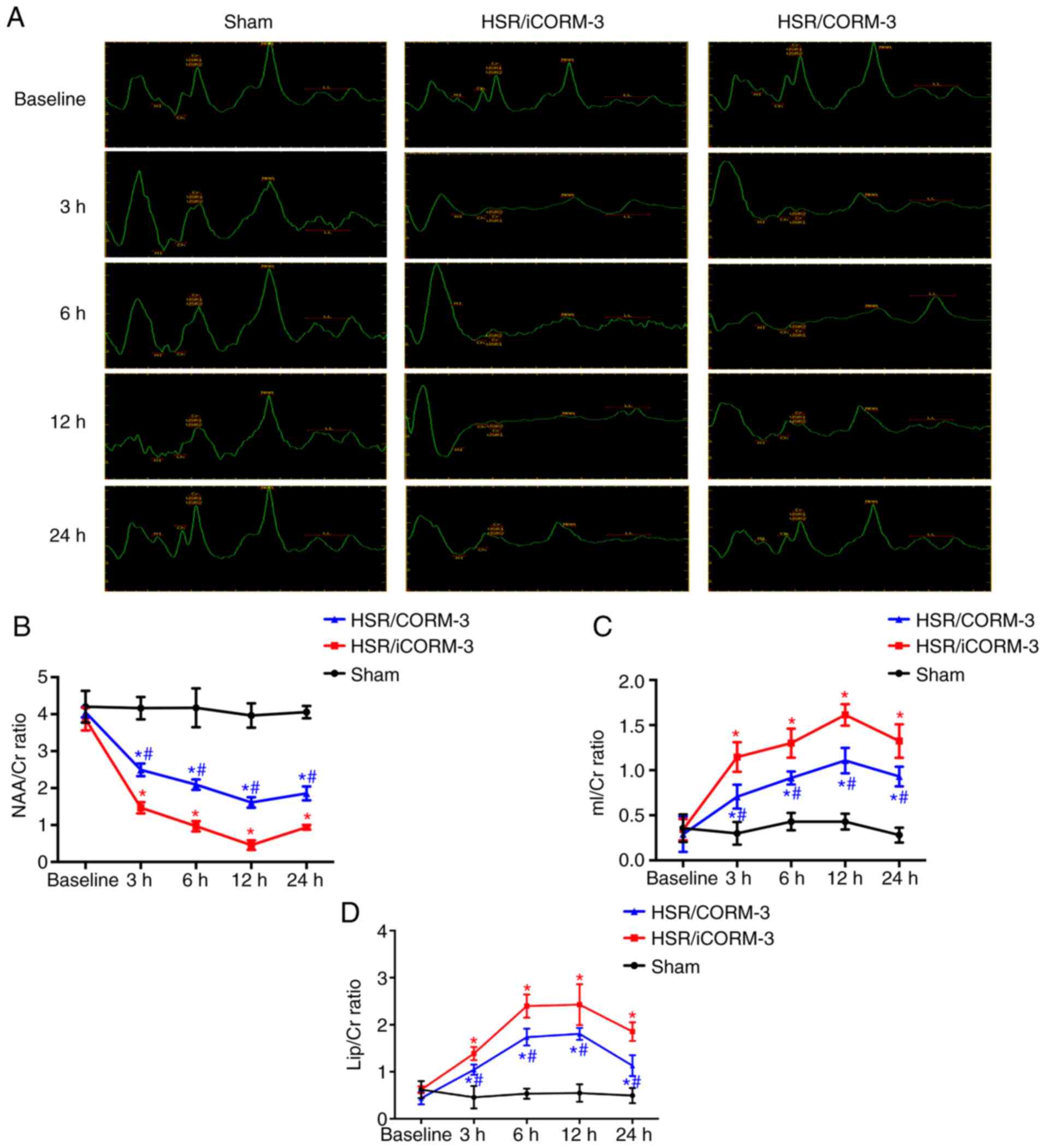
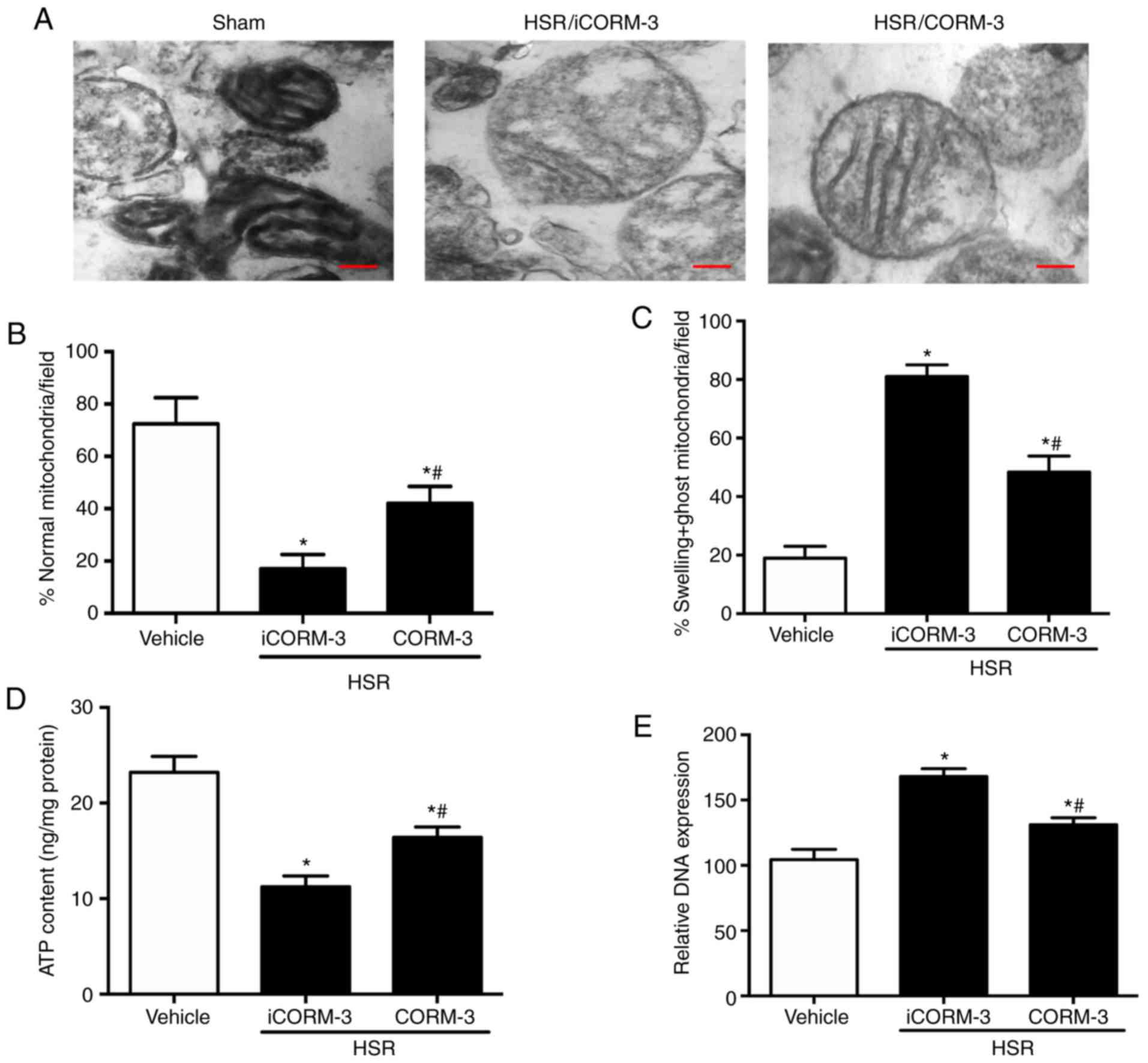
|
1
|
Demuro JP, Simmons S, Jax J and Gianelli
SM: Application of the shock index to the prediction of need for
hemostasis intervention. Am J Emerg Med. 31:1260–1263. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Singhal AK, Abrams JD, Mohara J, Hasz RD,
Nathan HM, Fisher CA, Furukawa S and Goldman BI: Potential
suitability for transplantation of hearts from human
non-heart-beating donors: Data review from the gift of life donor
program. J Heart Lung Transplant. 24:1657–1664. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dexter F, Hindman BJ, Cutkomp J and Smith
T: Blood warms as it flows retrograde from a femoral cannulation
site to the carotid artery during cardiopulmonary bypass.
Perfusion. 9:393–397. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yoshioka M, Itoh Y, Mori K, Ueno K,
Matsumoto M and Togashi H: Effects of an interleukin-1beta analogue
[Lys-D-Pro-Thr], on incomplete cerebral ischemia-induced inhibition
of long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal neurons in vivo.
Neurosci Lett. 261:171–174. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bergsbaken T1, Fink SL, den Hartigh AB,
Loomis WP and Cookson BT: Coordinated host responses during
pyroptosis: caspase-1-dependent lysosome exocytosis and
inflammatory cytokine maturation. J Immunol. 187:2748–2754. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sekerdag E, Solaroglu I and Gursoyozdemir
Y: Cell death mechanisms in stroke and novel molecular and cellular
treatment options. Curr Neuropharmacol. 16:1396–1415. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang JR, Yao FH, Zhang JG, Ji ZY, Li KL,
Zhan J, Tong YN, Lin LR and He YN: Ischemia-reperfusion induces
renal tubule pyroptosis via the CHOP-caspase-11 pathway. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 306:F75–F84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Xia P, Pan Y, Zhang F, Wang N, Wang E, Guo
Q and Ye Z: Pioglitazone confers neuroprotection against
ischemia-induced pyroptosis due to its inhibitory effects on
HMGB-1/RAGE and Rac1/ROS pathway by activating PPAR-γ. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 45:2351–2368. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Schallner N, Fuchs M, Schwer CI, Loop T,
Buerkle H, Lagrèze WA, van Oterendorp C, Biermann J and Goebel U:
Postconditioning with inhaled carbon monoxide counteracts apoptosis
and neuroinflammation in the ischemic rat retina. PLoS One.
7:e464792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
R Oliveira S, Queiroga CS and Vieira HL:
Mitochondria and carbon monoxide: Cytoprotection and control of
cell metabolism-a role for Ca(2+) ? J Physiol. 594:4131–4138. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Choi EY, Choe SH, Hyeon JY, Choi JI, Choi
IS and Kim SJ: Carbon monoxide-releasing molecule-3 suppresses
Prevotella intermedia lipopolysaccharide-induced production of
nitric oxide and interleukin-1β in murine macrophages. Eur J
Pharmacol. 764:22–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee DW, Shin HY, Jeong JH, Han J, Ryu S,
Nakahira K and Moon JS: Carbon monoxide regulates
glycolysis-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 493:957–963. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang W, Tao A, Lan T, Cepinskas G, Kao R,
Martin CM and Rui T: Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-3 improves
myocardial function in mice with sepsis by inhibiting NLRP3
inflammasome activation in cardiac fibroblasts. Basic Res Cardiol.
112:162017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Latz E, Xiao TS and Stutz A: Activation
and regulation of the inflammasomes. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:397–411.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang LM, Zhang DX, Fu L, Li Y, Wang XP,
Qi MM, Li CC, Song PP, Wang XD and Kong XJ: Carbon
monoxide-releasing molecule-3 protects against cortical pyroptosis
induced by hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation via mitochondrial
regulation. Free Radic Biol Med. 141:299–309. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang LM and Zhang DX: The dual
neuroprotective-neurotoxic effects of sevoflurane after hemorrhagic
shock injury. J Surg Res. 235:591–599. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ampawong S, Isarangkul D and Aramwit P:
Sericin ameliorated dysmorphic mitochondria in high-cholesterol
diet/streptozotocin rat by antioxidative property. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 242:411–421. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mariappan N, Soorappan RN, Haque M,
Sriramula S and Francis J: TNF-α-induced mitochondrial oxidative
stress and cardiac dysfunction: Restoration by superoxide dismutase
mimetic Tempol. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 293:H2726–H2737.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hao P, Liang Z, Piao H, Ji X, Wang Y, Liu
Y, Liu R and Liu J: Conditioned medium of human adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells mediates protection in neurons following
glutamate excitotoxicity by regulating energy metabolism and GAP-43
expression. Metab Brain Dis. 29:193–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang DX, Zhang LM, Zhao XC and Sun W:
Neuroprotective effects of erythropoietin against
sevoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis in primary rat cortical
neurons involving the EPOR-Erk1/2-Nrf2/Bach1 signal pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 87:332–341. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kawanishi S, Takahashi T, Morimatsu H,
Shimizu H, Omori E, Sato K, Matsumi M, Maeda S, Nakao A and Morita
K: Inhalation of carbon monoxide following resuscitation
ameliorates hemorrhagic shock-induced lung injury. Mol Med Rep.
7:3–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chamorro V, Pandolfi R, Moreno L, Barreira
B, Martínez-Ramas A, Morales-Cano D, Ruiz-Cabello J, Lorente JA,
Duarte J, Cogolludo Á, et al: Effects of quercetin in a rat model
of hemorrhagic traumatic shock and reperfusion. Molecules. 21:pii:
E1739. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu X, Wang J, Zhang Q, Duan X, Chen Z and
Zhang Y: Postconditioning with sevoflurane ameliorates spatial
learning and memory deficit after hemorrhage shock and
resuscitation in rats. J Surg Res. 206:307–315. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng G, Zhan Y, Wang H, Luo Z, Zheng F,
Zhou Y, Wu Y, Wang S, Wu Y, Xiang G, et al: Carbon monoxide
releasing molecule-3 alleviates neuron death after spinal cord
injury via inflammasome regulation. EBioMedicine. 40:643–654. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jabaut J, Ather JL, Taracanova A, Poynter
ME and Ckless K: Mitochondria-targeted drugs enhance Nlrp3
inflammasome-dependent IL-1β secretion in association with
alterations in cellular redox and energy status. Free Radic Biol
Med. 60:233–245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xi H, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Yang WY, Jiang X, Sha
X, Cheng X, Wang J, Qin X, Yu J, et al: Caspase-1 inflammasome
activation mediates homocysteine-induced pyrop-apoptosis in
endothelial cells. Circ Res. 118:1525–1539. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ahn H, Kim J, Kang SG, Yoon SI, Ko HJ, Kim
PH, Hong EJ, An BS, Lee E and Lee GS: Mercury and arsenic attenuate
canonical and non-canonical NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Sci Rep.
8:136592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kravcukova P, Danielisova V, Nemethova M,
Burda J and Gottlieb M: Transient forebrain ischemia impact on
lymphocyte DNA damage, glutamic acid level, and SOD activity in
blood. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 29:887–894. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lehotský J, Racay P, Pavlíková M,
Tatarková Z, Urban P, Chomová M, Kovalská M and Kaplán P:
Cross-talk of intracellular calcium stores in the response to
neuronal ischemia and ischemic tolerance. Gen Physiol Biophys.
28:F104–F114. 2009.
|
|
30
|
Signoretti S, Marmarou A, Tavazzi B,
Lazzarino G, Beaumont A and Vagnozzi R: N-Acetylaspartate reduction
as a measure of injury severity and mitochondrial dysfunction
following diffuse traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma.
18:977–991. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ory-Lavollée L, Blakely RD and Coyle JT:
Neurochemical and immunocytochemical studies on the distribution of
N-acetyl-aspartylglutamate and N-acetyl-aspartate in rat spinal
cord and some peripheral nervous tissues. J Neurochem. 48:895–899.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chang C and Jang T: Age-dependent
neurotoxicity of striatal lesions produced by aminooxyacetic acid:
Quantitative in vitro 1H NMR spectroscopic studies. J Neurochem.
65:1192–1198. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mierisová S and Ala-Korpela M: MR
spectroscopy quantitation: A review of frequency domain methods.
NMR Biomed. 14:247–259. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Harada K, Honmou O, Liu H, Bando M, Houkin
K and Kocsis JD: Magnetic resonance lactate and lipid signals in
rat brain after middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Brain Res.
1134:206–213. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lavitrano M, Smolenski RT, Musumeci A,
Maccherini M, Slominska E, Di Florio E, Bracco A, Mancini A, Stassi
G, Patti M, et al: Carbon monoxide improves cardiac energetics and
safeguards the heart during reperfusion after cardiopulmonary
bypass in pigs. FASEB J. 18:1093–1095. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Almeida AS, Queiroga CS, Sousa MF, Alves
PM and Vieira HL: Carbon monoxide modulates apoptosis by
reinforcing oxidative metabolism in astrocytes: Role of Bcl-2. J
Biol Chem. 287:10761–10770. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chai H, Schultz G, Aghaie K and Zhou W: In
vivo assessment of the effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on intimal
hyperplasia in ApoE knockout mice. J Surg Res. 162:26–32. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Feng S, Fox D and Man SM: Mechanisms of
gasdermin family members in inflammasome signaling and cell death.
J Mol Biol. 430:3068–3080. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|