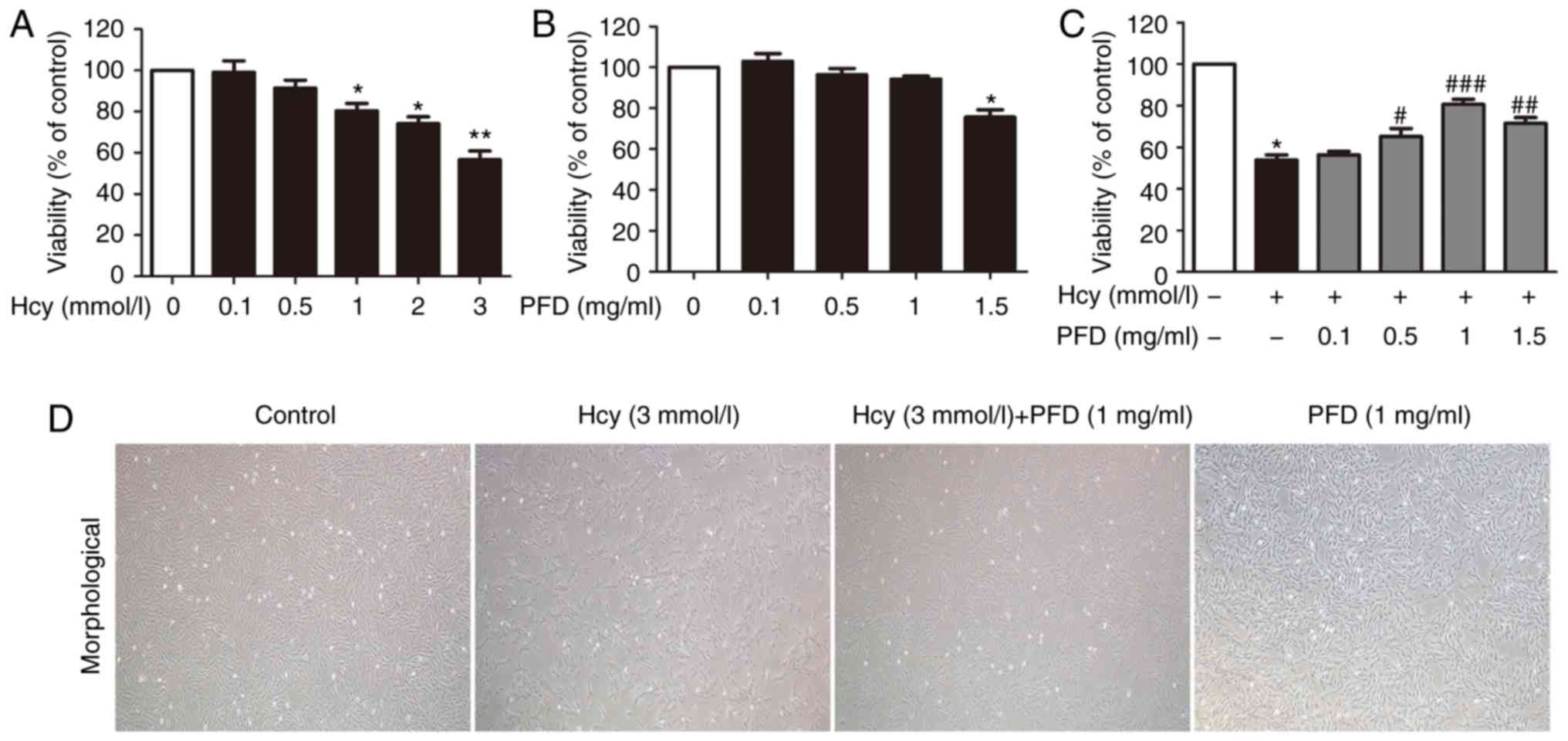
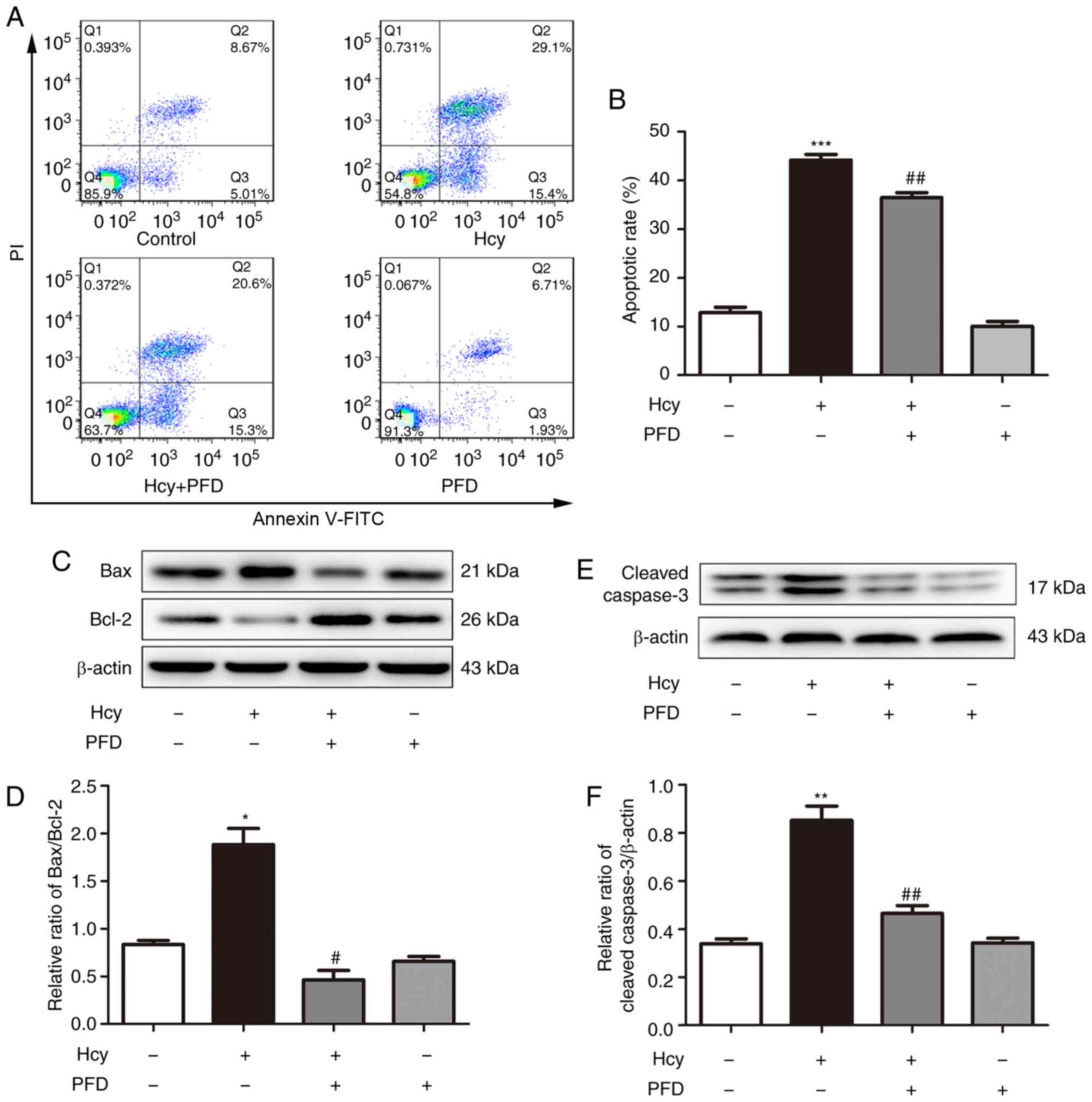
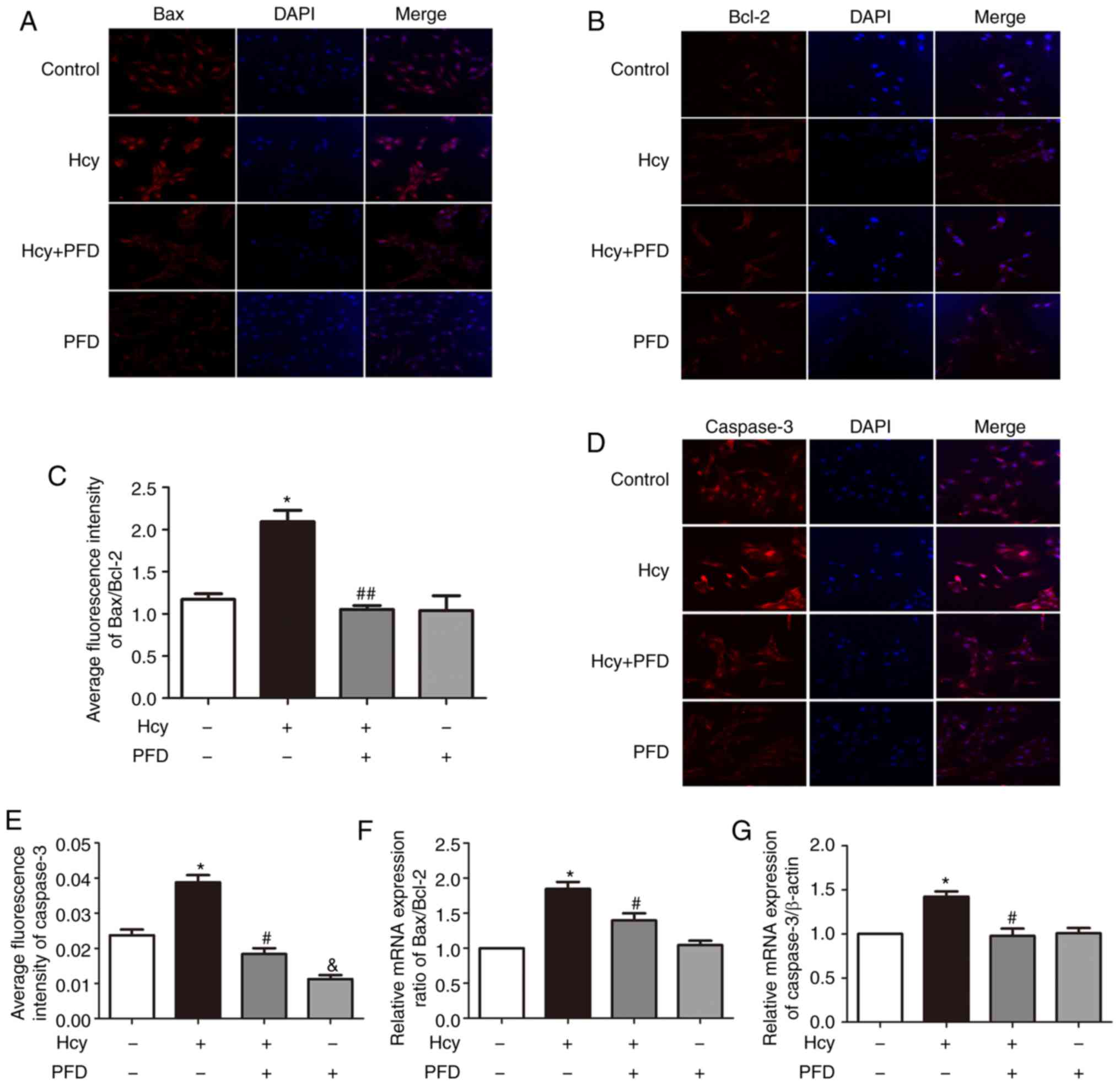
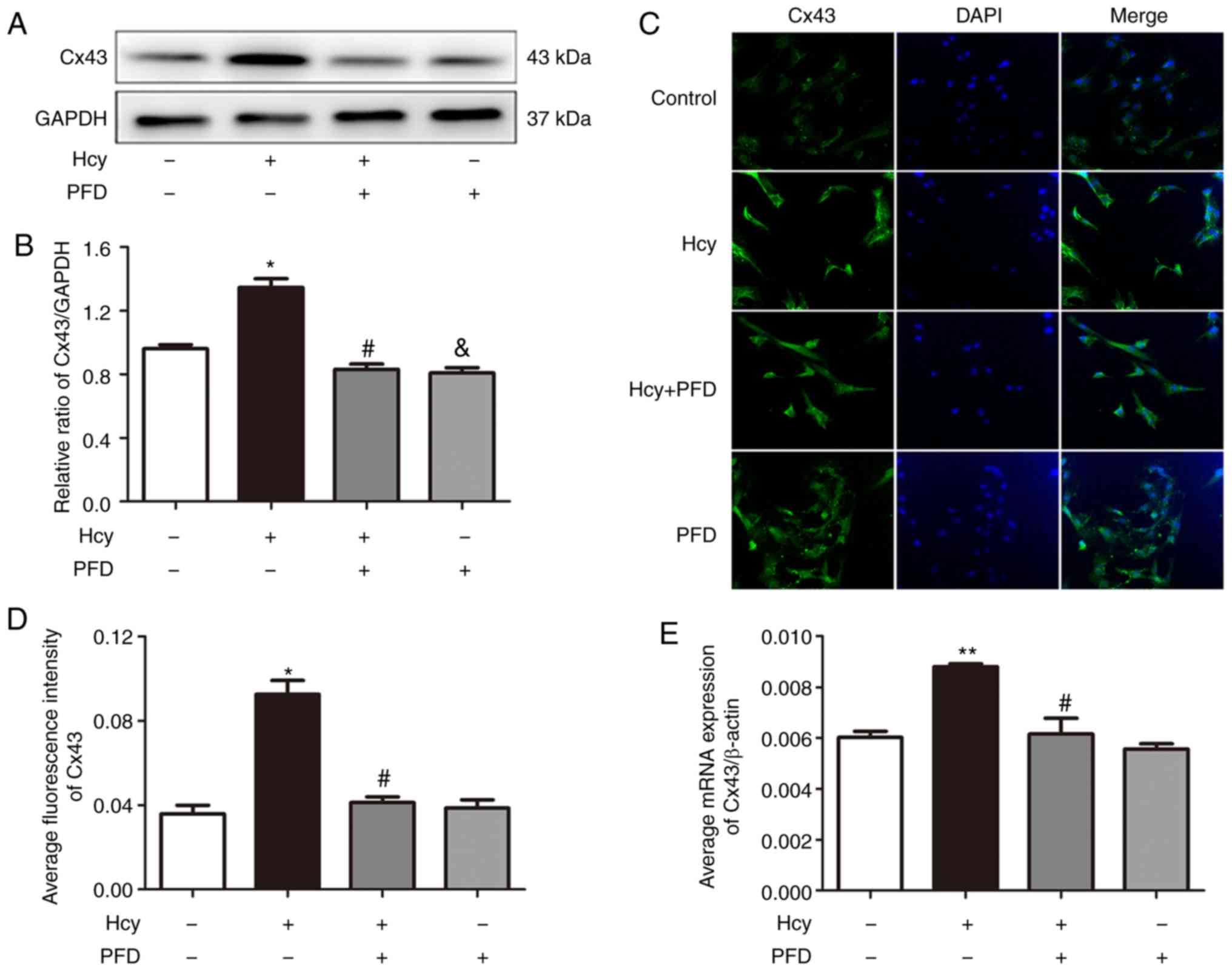
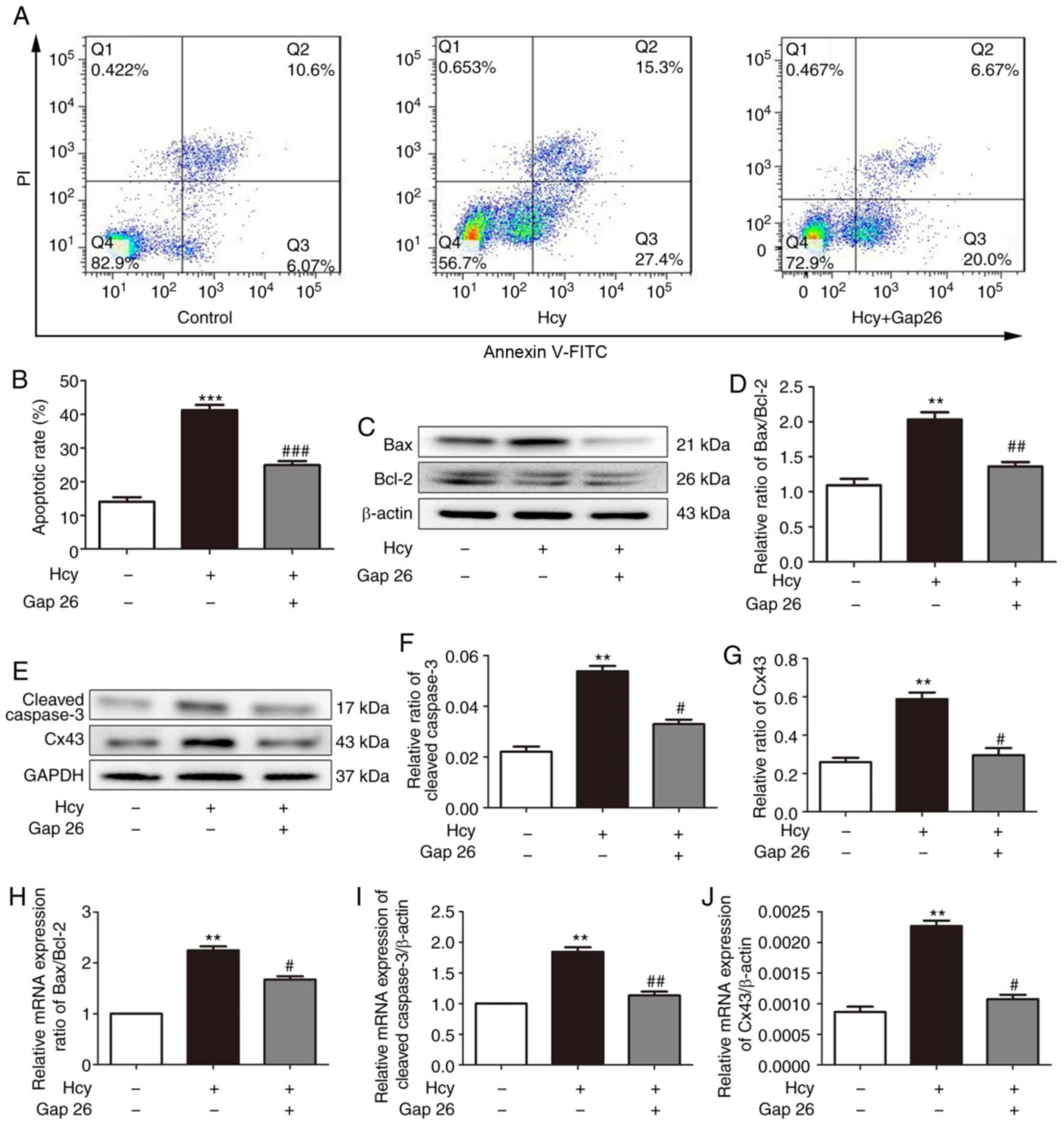
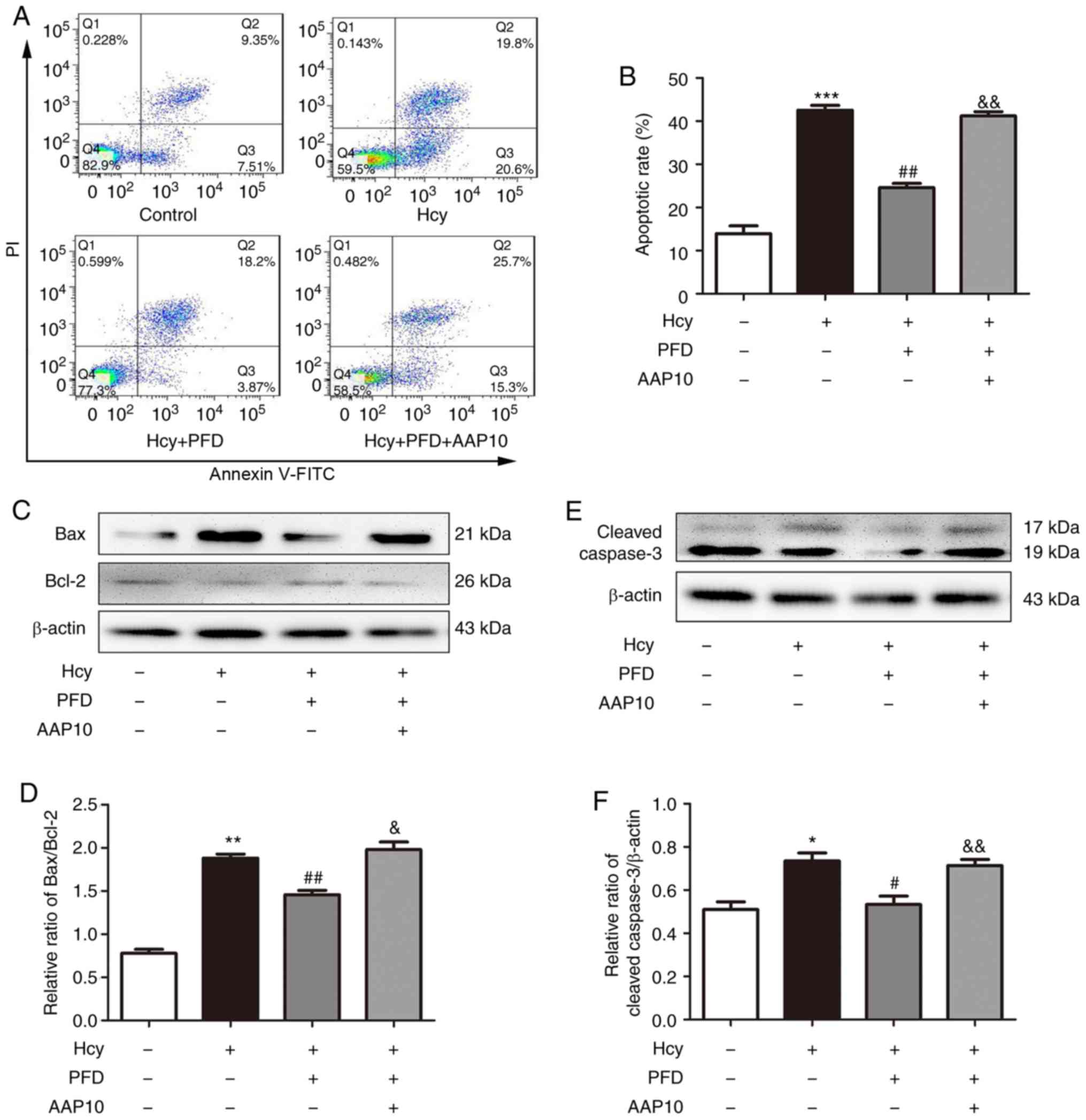
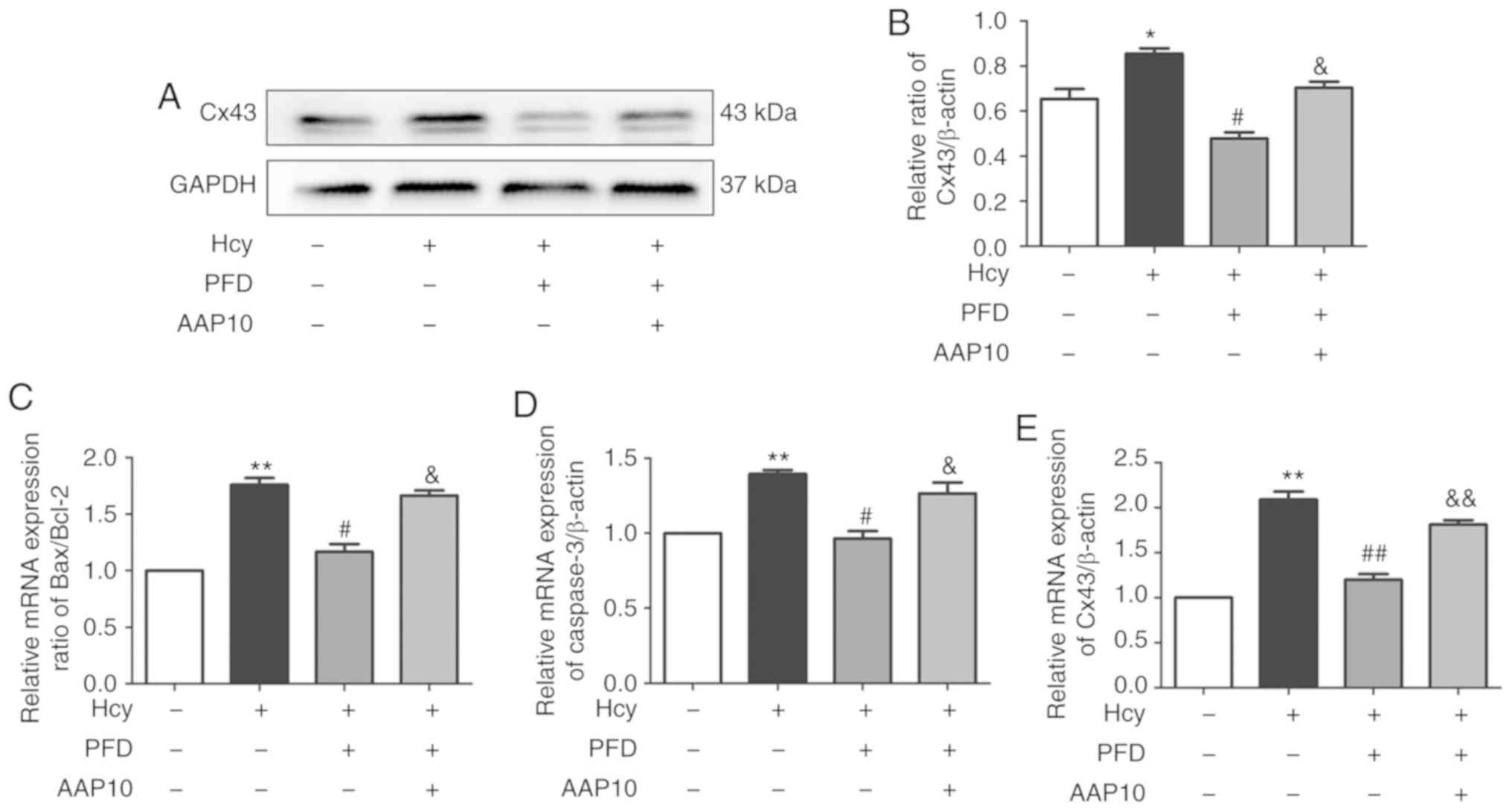
|
1
|
Shekhar A, Heeger P, Reutelingsperger C,
Arbustini E, Narula N, Hofstra L, Bax JJ and Narula J: Targeted
imaging for cell death in cardiovascular disorders. JACC Cardiovasc
Imaging. 11:476–493. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Madonna R, Balistreri CR, De Rosa S,
Muscoli S, Selvaggio S, Selvaggio G, Ferdinandy P and De Caterina
R: Impact of sex differences and diabetes on coronary
atherosclerosis and ischemic heart disease. J Clin Med. 8:pii: E98.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Luo F, Das A, Chen J, Wu P, Li X and Fang
Z: Metformin in patients with and without diabetes: A paradigm
shift in cardiovascular disease management. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
18:542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aminzadeh A and Mehrzadi S:
Cardioprotective effect of levosimendan against
homocysteine-induced mitochondrial stress and apoptotic cell death
in H9C2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 507:395–399. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fan CD, Sun JY, Fu XT, Hou YJ, Li Y, Yang
MF, Fu XY and Sun BL: Astaxanthin attenuates homocysteine-induced
cardiotoxicity in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting mitochondrial
dysfunction and oxidative damage. Front Physiol. 8:10412017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang Z, Zhao L, Zhou Y, Lu X, Wang Z,
Wang J and Li W: Taurine ameliorated homocysteine-induced H9C2
cardiomyocyte apoptosis by modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Apoptosis. 22:647–661. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ostrakhovitch EA and Tabibzadeh S:
Homocysteine and age-associated disorders. Ageing Res Rev.
49:144–164. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yang Y, Yan X, Xue J, Zheng Y, Chen M, Sun
Z, Liu T, Wang C, You H and Luo D: Connexin43 dephosphorylation at
serine 282 is associated with connexin43-mediated cardiomyocyte
apop-tosis. Cell Death Differ. 26:1332–1345. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vozzi C, Dupont E, Coppen SR, Yeh HI and
Severs NJ: Chamber-related differences in connexin expression in
the human heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 31:991–1003. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li H, Brodsky S, Kumari S, Valiunas V,
Brink P, Kaide J, Nasjletti A and Goligorsky MS: Paradoxical
overexpression and translocation of connexin43 in
homocysteine-treated endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 282:H2124–H2133. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Komiya C, Tanaka M, Tsuchiya K, Shimazu N,
Mori K, Furuke S, Miyachi Y, Shiba K, Yamaguchi S, Ikeda K, et al:
Antifibrotic effect of pirfenidone in a mouse model of human
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci Rep. 7:447542017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stahnke T, Kowtharapu BS, Stachs O,
Schmitz KP, Wurm J, Wree A, Guthoff RF and Hovakimyan M:
Suppression of TGF-β pathway by pirfenidone decreases extracellular
matrix deposition in ocular fibroblasts in vitro. PLoS One.
12:e01725922017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen JF, Liu H, Ni HF, Lv LL, Zhang MH,
Zhang AH, Tang RN, Chen PS and Liu BC: Improved mitochondrial
function underlies the protective effect of pirfenidone against
tubulointerstitial fibrosis in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. PLoS One.
8:e835932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He X, Li L, Tang M, Zeng Y, Li H and Yu X:
Biomimetic electrical stimulation induces rat bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into cardiomyocyte-like
cells via TGF-beta 1 in vitro. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 148:47–53.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fan XD, Zheng HB, Fan XS and Lu S:
Increase of SOX9 promotes hepatic ischemia/reperfusion (IR) injury
by activating TGF-β1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 503:215–221.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCq method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Decrock E, Vinken M, De Vuyst E, Krysko
DV, D'Herde K, Vanhaecke T, Vandenabeele P, Rogiers V and Leybaert
L: Connexin-related signaling in cell death: To live or let die?
Cell Death Differ. 16:524–536. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pollack M, Phaneuf S, Dirks A and
Leeuwenburgh C: The role of apoptosis in the normal aging brain,
skeletal muscle, and heart. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 959:93–107. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li J, Luo M, Xie N, Wang H and Wang J:
Bioinformatics-based analysis of the involvement of AC005550.3,
RP11-415D17.3, and RP1-140K8.5 in homocysteine-induced vascular
endothelial injury. Am J Transl Res. 10:2126–2136. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Majumder S, Ren L, Pushpakumar S and Sen
U: Hydrogen sulphide mitigates homocysteine-induced apoptosis and
matrix remodelling in mesangial cells through Akt/FOXO1 signalling
cascade. Cell Signal. 61:66–77. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Hong Y, Zhang C, Shen Y, Pan YS,
Chen RZ, Zhang Q and Chen YH: Picroside II attenuates
hyperhomocysteinemia-induced endothelial injury by reducing
inflammation, oxidative stress and cell apoptosis. J Cell Mol Med.
23:464–475. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Neri T, Lombardi S, Faìta F, Petrini S,
Balìa C, Scalise V, Pedrinelli R, Paggiaro P and Celi A:
Pirfenidone inhibits p38-mediated generation of procoagulant
microparticles by human alveolar epithelial cells. Pulm Pharmacol
Ther. 39:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li Z, Liu X, Wang B, Nie Y, Wen J, Wang Q
and Gu C: Pirfenidone suppresses MAPK signalling pathway to reverse
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis. Nephrology
(Carlton). 22:589–597. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yamazaki T, Yamashita N, Izumi Y, Nakamura
Y, Shiota M, Hanatani A, Shimada K, Muro T, Iwao H and Yoshiyama M:
The antifibrotic agent pirfenidone inhibits angiotensin II-induced
cardiac hypertrophy in mice. Hypertens Res. 35:34–40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tsuchiya H, Kaibori M, Yanagida H,
Yokoigawa N, Kwon AH, Okumura T and Kamiyama Y: Pirfenidone
prevents endo-toxin-induced liver injury after partial hepatectomy
in rats. J Hepatology. 40:94–101. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tsai CM, Chen JT, Stewart DJ, Chiu CH, Lai
CL, Hsiao SY, Chen YM and Chang KT: Antagonism between gefitinib
and cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer cells why randomized
trials failed? J Thorac Oncol. 6:559–568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shihab FS, Bennett WM, Yi H and Andoh TF:
Effect of pirfeni-done on apoptosis-regulatory genes in chronic
cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Transplantation. 79:419–426. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Scemes E, Spray DC and Meda P: Connexins,
pannexins, innexins: Novel roles of 'hemi-channels'. Pflugers Arch.
457:1207–1226. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cooreman A, Van Campenhout R, Ballet S,
Annaert P, Van Den Bossche B, Colle I, Cogliati B and Vinken M:
Connexin and pannexin (hemi)channels: Emerging targets in the
treatment of liver disease. Hepatology. 69:1317–1323. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang N, De Bock M, Antoons G, Gadicherla
AK, Bol M, Decrock E, Evans WH, Sipido KR, Bukauskas FF and
Leybaert L: Connexin mimetic peptides inhibit Cx43 hemichannel
opening triggered by voltage and intracellular Ca2+ elevation.
Basic Res Cardiol. 107:3042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hagen A, Dietze A and Dhein S: Human
cardiac gap-junction coupling: Effects of antiarrhythmic peptide
AAP10. Cardiovasc Res. 83:405–415. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zou Z, Liu B, Zeng L, Yang X, Huang R, Wu
C, Zhu H, Gao Y, Yuan D and Yu J: Cx43 inhibition attenuates
sepsis-induced intestinal injury via downregulating ROS transfer
and the activation of the JNK1/Sirt1/FoxO3a signaling pathway.
Mediators Inflamm. 2019:78543892019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tellios N, Feng M, Chen N, Liu H, Tellios
V, Wang M, Li X, Chang CA and Hutnik C: Mechanical stretch
upregulates connexin43 in human trabecular meshwork cells. Clin Exp
Ophthalmol. 47:787–794. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|