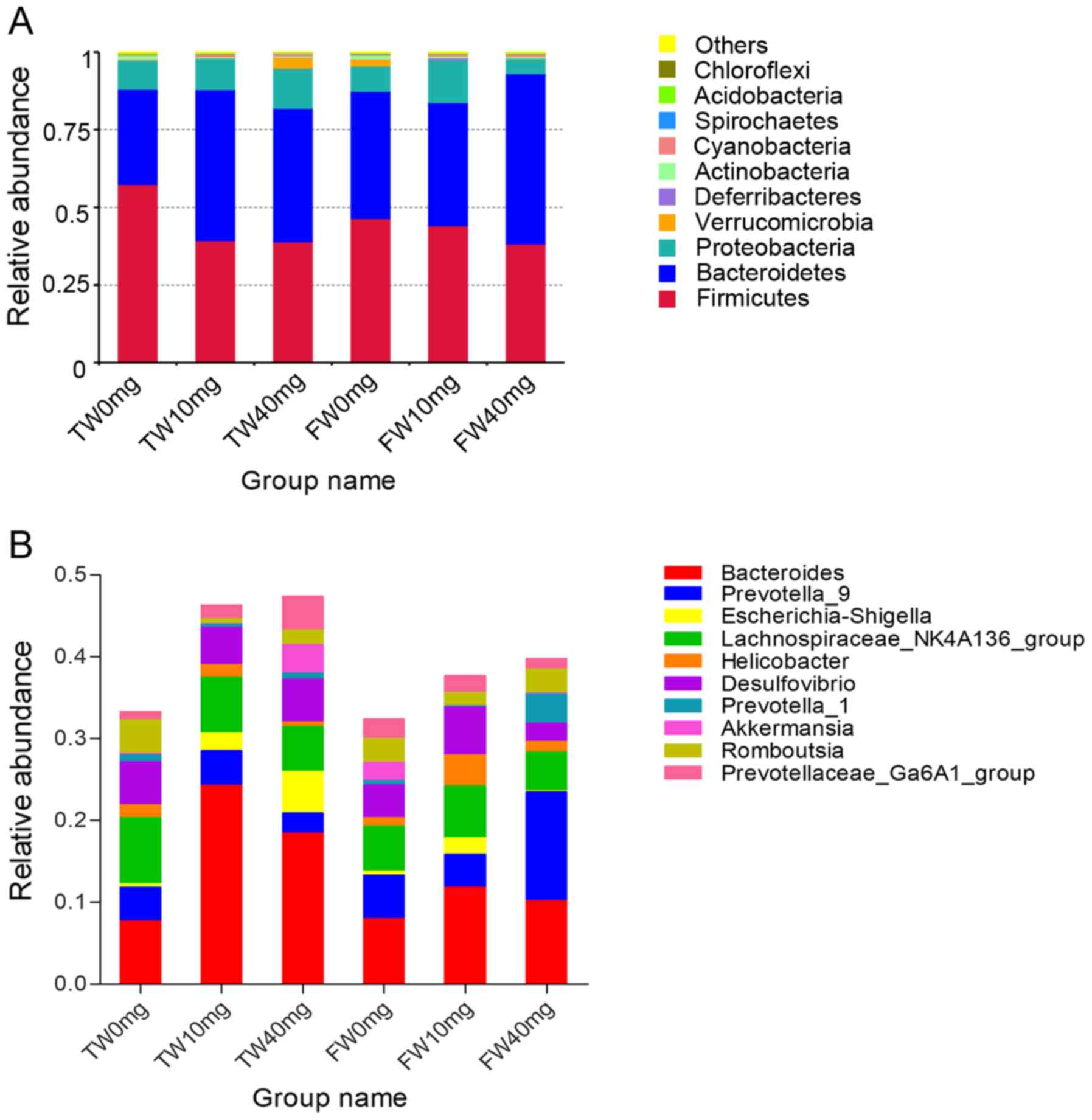
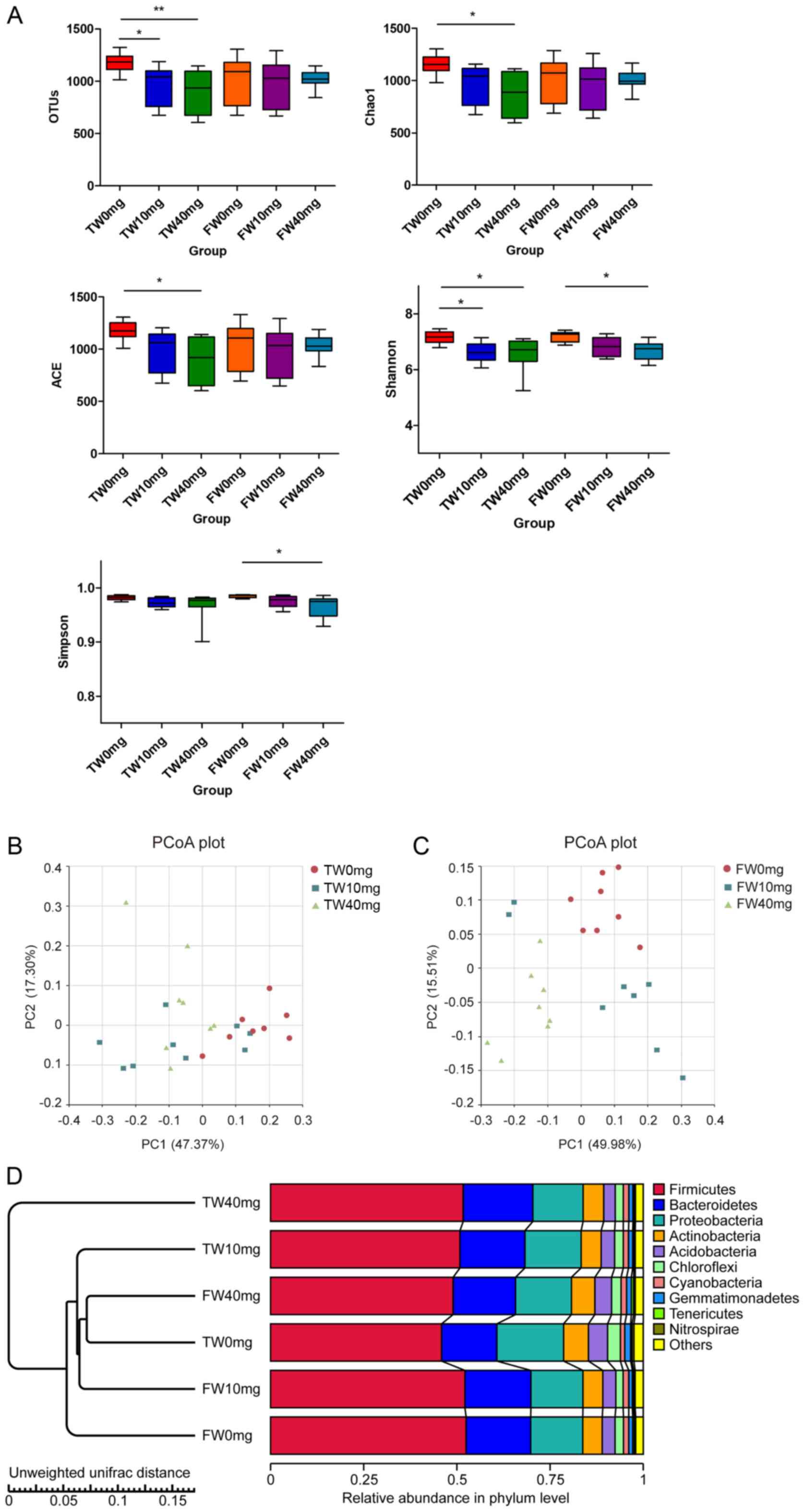
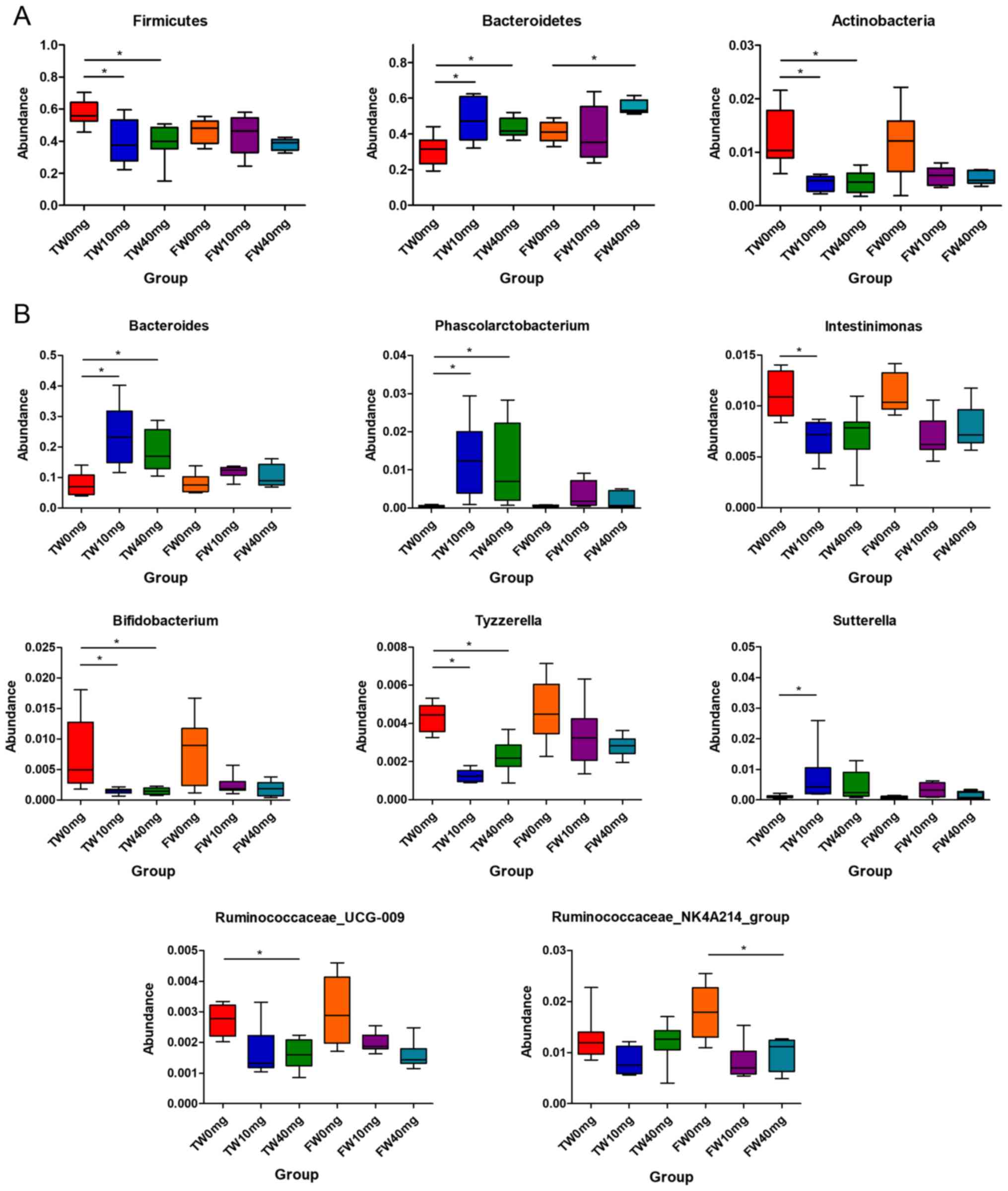
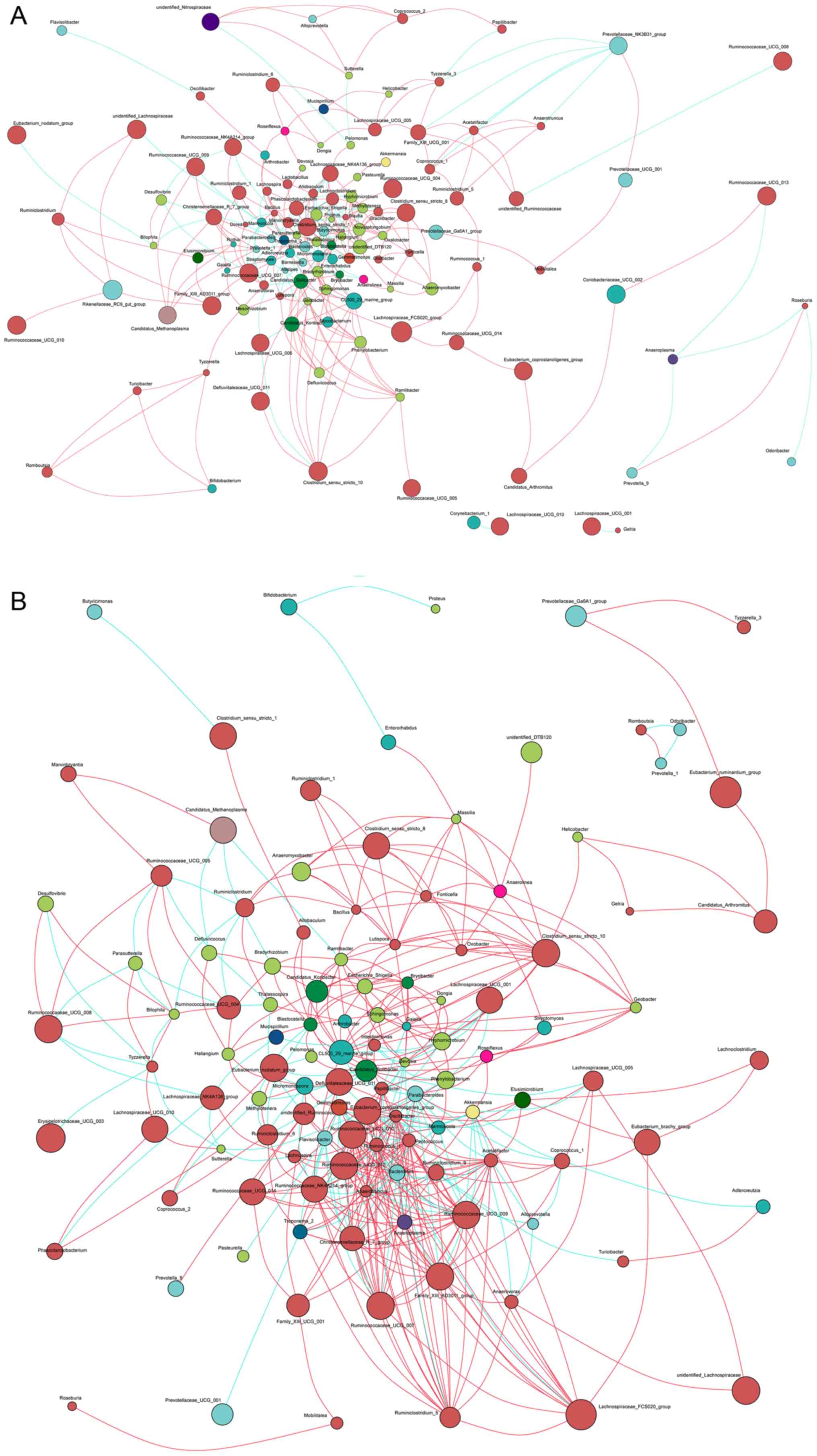
|
1
|
Jain KS, Kathiravan MK, Somani RS and
Shishoo CJ: The biology and chemistry of hyperlipidemia. Bioorg Med
Chem. 15:4674–4699. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Farnier M and Davignon J: Current and
future treatment of hyperlipidemia: The role of statins. Am J
Cardiol. 82:3J–10J. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fazio S and Linton MF: The role of
fibrates in managing hyperlipidemia: Mechanisms of action and
clinical efficacy. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 6:148–157. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vickers S, Duncan CA, Chen IW, Rosegay A
and Duggan DE: Metabolic disposition studies on simvastatin, a
cholesterol-lowering prodrug. Drug Metab Dispos. 18:138–145.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pedersen TR, Kjekshus J, Berg K, Haghfelt
T, Faergeman O, Faergeman G, Pyörälä K, Miettinen T, Wilhelmsen L,
Olsson AG, et al: Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444
patients with coronary heart disease: The scandinavian simvastatin
survival study (4S). 1994. Atheroscler Suppl. 5:81–87. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Parks BW, Nam E, Org E, Kostem E, Norheim
F, Hui ST, Pan C, Civelek M, Rau CD, Bennett BJ, et al: Genetic
control of obesity and gut microbiota composition in response to
high-fat, high-sucrose diet in mice. Cell Metab. 17:141–152. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wikoff WR, Anfora AT, Liu J, Schultz PG,
Lesley SA, Peters EC and Siuzdak G: Metabolomics analysis reveals
large effects of gut microflora on mammalian blood metabolites.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:3698–3703. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gill SR, Pop M, Deboy RT, Eckburg PB,
Turnbaugh PJ, Samuel BS, Gordon JI, Relman DA, Fraser-Liggett CM
and Nelson KE: Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut
microbiome. Science. 312:1355–1359. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hooper LV, Littman DR and Macpherson AJ:
Interactions between the microbiota and the immune system. Science.
336:1268–1273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu H, Esteve E, Tremaroli V, Khan MT,
Caesar R, Mannerås-Holm L, Ståhlman M, Olsson LM, Serino M,
Planas-Fèlix M, et al: Metformin alters the gut microbiome of
individuals with treatment-naive type 2 diabetes, contributing to
the therapeutic effects of the drug. Nat Med. 23:850–858. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gopalakrishnan V, Spencer CN, Nezi L,
Reuben A, Andrews MC, Karpinets TV, Prieto PA, Vicente D, Hoffman
K, Wei SC, et al: Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1
immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science. 359:97–103. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jia W, Li H, Zhao L and Nicholson JK: Gut
microbiota: A potential new territory for drug targeting. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 7:123–129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zimmermann M, Zimmermann-Kogadeeva M,
Wegmann R and Goodman AL: Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism
by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 570:462–467. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nicholson JK, Elaine H and Wilson ID: Gut
microorganisms, mammalian metabolism and personalized health care.
Nat Rev Microbiol. 3:431–438. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Simon JA, Lin F, Hulley SB, Blanche PJ,
Waters D, Shiboski S, Rotter JI, Nickerson DA, Yang H, Saad M and
Krauss RM: Phenotypic predictors of response to simvastatin therapy
among African-Americans and caucasians: The cholesterol and
pharmacogenetics (CAP) study. Am J Cardiol. 97:843–850. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Trupp M, Zhu H, Wikoff WR, Baillie RA,
Zeng ZB, Karp PD, Fiehn O, Krauss RM and Kaddurah-Daouk R:
Metabolomics reveals amino acids contribute to variation in
response to simvastatin treatment. PLoS One. 7:e383862012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kaddurah-Daouk R, Baillie RA, Zhu H, Zeng
ZB, Wiest MM, Nguyen UT, Watkins SM and Krauss RM: Lipidomic
analysis of variation in response to simvastatin in the cholesterol
and pharmacogenetics study. Metabolomics. 6:191–201. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaddurah-Daouk R, Baillie RA, Zhu H, Zeng
ZB, Wiest MM, Nguyen UT, Wojnoonski K, Watkins SM, Trupp M and
Krauss RM: Enteric microbiome metabolites correlate with response
to simvastatin treatment. PLoS One. 6:e254822011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Aura AM, Mattila I, Hyötyläinen T,
Gopalacharyulu P, Bounsaythip C, Orešič M and Oksman-Caldentey KM:
Drug metabolome of the simvastatin formed by human intestinal
microbiota in vitro. Mol Biosyst. 7:437–446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rodriguez AL, Wojcik BM, Wrobleski SK,
Myers DD Jr, Wakefield TW and Diaz JA: Statins, inflammation and
deep vein thrombosis: A systematic review. J Thromb Thrombolysis.
33:371–382. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Greenwood J, Steinman L and Zamvil SS:
Statin therapy and autoimmune disease: From protein prenylation to
immunomodulation. Nat Rev Immunol. 6:358–370. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hennessy E, Adams C, Reen FJ and O’Gara F:
Is there potential for repurposing Statins as novel antimicrobials?
Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 60:5111–5121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhang Q, Wang GJ, A JY, Wu D, Zhu LL, Ma B
and Du Y: Application of GC/MS-based metabonomic profiling in
studying the lipid-regulating effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on
diet-induced hyperlipidemia in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
30:1674–1687. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu QY, Liu YH, Zhang Q, Ma B, Yang ZD, Liu
L, Yao D, Cui GB, Sun JJ and Wu ZM: Metabolomic analysis of
simvastatin and fenofibrate intervention in high-lipid diet-induced
hyperlipidemia rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:1265–1273. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ozansoy G, Guven C, Ceylan A, Can B, Aktan
F, Oz E and Gönül B: Effects of simvastatin treatment on
oxidant/antioxidant state and ultrastructure of
streptozotocin-diabetic rat lung. Cell Biochem Funct. 23:421–426.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
He Q, Qin S, Ma K, Luo S and Zhang X:
Effects of simvastatin on angiogenesis and the expression of Ang1
after myocardial infarction in rats. Heart. 96:A142010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bracht L, Barbosa CP, Caparroz-Assef SM,
Cuman RK, Ishii-Iwamoto EL, Bracht A and Bersani-Amado CA: Effects
of simvastatin, atorvastatin, ezetimibe, and ezetimibe+simvastatin
combination on the inflammatory process and on the liver metabolic
changes of arthritic rats. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 26:722–734. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Magoč T and Salzberg SL: FLASH: Fast
length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies.
Bioinformatics. 27:2957–2963. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ,
Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R, Mills DA and Caporaso JG:
Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina
amplicon sequencing. Nat Methods. 10:57–59. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J,
Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich
JK, Gordon JI, et al: QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput
community sequencing data. Nat Methods. 7:335–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C
and Knight R: UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera
detection. Bioinformatics. 27:2194–2200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Haas BJ, Gevers D, Earl AM, Feldgarden M,
Ward DV, Giannoukos G, Ciulla D, Tabbaa D, Highlander SK, Sodergren
E, et al: Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in
sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res. 21:494–504.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM and Cole JR:
Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences
into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol.
73:5261–5267. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J,
Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J and Glöckner FO: The SILVA ribosomal
RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based
tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:D590–D596. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
White JR, Nagarajan N and Pop M:
Statistical methods for detecting differentially abundant features
in clinical metagenomic samples. PLoS Comput Biol. 5:e10003522009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J Royal Statist Soc. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
37
|
Jiao S, Liu Z, Lin Y, Yang J, Chen W and
Wei G: Bacterial communities in oil contaminated soils:
Biogeography and co-occurrence patterns. Soil Biol Biochem.
98:64–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F,
Liang S, Zhang W, Guan Y, Shen D, et al: A metagenome-wide
association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature.
490:55–60. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Langille MG, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG,
McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA, Clemente JC, Burkepile DE, Vega
Thurber RL, Knight R, et al: Predictive functional profiling of
microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat
Biotechnol. 31:814–821. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Kawashima M,
Furumichi M and Tanabe M: Data, information, knowledge and
principle: Back to metabolism in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res.
42:D199–D205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Mega JL, Morrow DA, Brown A, Cannon CP and
Sabatine MS: Identification of genetic variants associated with
response to statin therapy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
29:1310–1315. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Barber MJ, Mangravite LM, Hyde CL, Chasman
DI, Smith JD, McCarty CA, Li X, Wilke RA, Rieder MJ, Williams PT,
et al: Genome-wide association of lipid-lowering response to
statins in combined study populations. PLoS One. 5:e97632010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu Y, Song X, Zhou H, Zhou X, Xia Y, Dong
X, Zhong W, Tang S, Wang L, Wen S, et al: Gut microbiome associates
with lipid-lowering effect of rosuvastatin in vivo. Front
Microbiol. 9:5302018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
He X, Zheng N, He J, Liu C, Feng J, Jia W
and Li H: Gut microbiota modulation attenuated the hypolipidemic
effect of simvastatin in high-fat/cholesterol-diet fed mice. J
Proteome Res. 16:1900–1910. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Catry E, Pachikian BD, Salazar N, Neyrinck
AM, Cani PD and Delzenne NM: Ezetimibe and simvastatin modulate gut
microbiota and expression of genes related to cholesterol
metabolism. Life Sci. 132:77–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sun B, Li L and Zhou X: Comparative
analysis of the gut microbiota in distinct statin response patients
in East China. J Microbiol. 56:886–892. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim J, Lee H, An J, Song Y, Lee CK, Kim K
and Kong H: Alterations in gut microbiota by statin therapy and
possible intermediate effects on hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia.
Front Microbiol. 10:19472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S and Gordon
JI: Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity.
Nature. 444:1022–1023. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K,
Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R,
et al: Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial
enterotypes. Science. 334:105–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gentile CL and Weir TL: The gut microbiota
at the intersection of diet and human health. Science. 362:776–780.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Daniel H, Gholami AM, Berry D,
Desmarchelier C, Hahne H, Loh G, Mondot S, Lepage P, Rothballer M,
Walker A, et al: High-fat diet alters gut microbiota physiology in
mice. ISME J. 8:295–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Lin H, An Y, Hao F, Wang Y and Tang H:
Correlations of fecal metabonomic and microbiomic changes induced
by high-fat diet in the pre-obesity state. Sci Rep. 6:216182016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Backhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh
GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF and Gordon JI: The gut microbiota as an
environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 101:15718–15723. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kelly TN, Bazzano LA, Ajami NJ, He H, Zhao
J, Petrosino JF, Correa A and He J: Gut microbiome associates with
lifetime cardiovascular disease risk profile among bogalusa heart
study participants. Circ Res. 119:956–964. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Muñiz Pedrogo DA, Jensen MD, Van Dyke CT,
Murray JA, Woods JA, Chen J, Kashyap PC and Nehra V: Gut microbial
carbohydrate metabolism hinders weight loss in overweight adults
undergoing lifestyle intervention with a volumetric diet. Mayo Clin
Proc. 93:1104–1110. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wu F, Guo X, Zhang J, Zhang M, Ou Z and
Peng Y: Phascolarctobacterium faecium abundant colonization in
human gastrointestinal tract. Exp Ther Med. 14:3122–3126. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Canfora EE, Jocken JW and Blaak EE:
Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin
sensitivity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 11:577–591. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Rodrigues RR, Greer RL, Dong X, Dsouza KN,
Gurung M, Wu JY, Morgun A and Shulzhenko N: Antibiotic-induced
alterations in gut microbiota are associated with changes in
glucose metabolism in healthy mice. Front Microbiol. 8:23062017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gauffin Cano P, Santacruz A, Moya A and
Sanz Y: Bacteroides uniformis CECT 7771 ameliorates metabolic and
immunological dysfunction in mice with high-fat-diet induced
obesity. PLoS One. 7:e410792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kim MS, Hwang SS, Park EJ and Bae JW:
Strict vegetarian diet improves the risk factors associated with
metabolic diseases by modulating gut microbiota and reducing
intestinal inflammation. Environ Microbiol Rep. 5:765–775.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yoshida N, Emoto T, Yamashita T, Watanabe
H, Hayashi T, Tabata T, Hoshi N, Hatano N, Ozawa G, Sasaki N, et
al: Bacteroides vulgatus and bacteroides dorei reduce gut microbial
lipopolysaccharide production and inhibit atherosclerosis.
Circulation. 138:2486–2498. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang K, Liao M, Zhou N, Bao L, Ma K, Zheng
Z, Wang Y, Liu C, Wang W, Wang J, et al: Parabacteroides distasonis
alleviates obesity and metabolic dysfunctions via production of
succinate and secondary bile acids. Cell Rep. 26:222–235. e2252019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Balvočiūtė M and Huson DH: SILVA, RDP,
greengenes, NCBI and OTT-how do these taxonomies compare? BMC
Genomics. 18(Suppl 2): 1142017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Gevers D, Kugathasan S, Denson LA,
Vazquez-Baeza Y, Van Treuren W, Ren B, Schwager E, Knights D, Song
SJ, Yassour M, et al: The treatment-naive microbiome in new-onset
crohn’s disease. Cell Host Microbe. 15:382–392. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Douglas GM, Beiko RG and Langille MGI:
Predicting the functional potential of the microbiome from marker
genes using PICRUSt. Methods Mol Biol. 1849:169–177. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Litvak Y, Byndloss MX and Baumler AJ:
Colonocyte metabolism shapes the gut microbiota. Science.
362:eaat9076. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Louis P, Hold GL and Flint HJ: The gut
microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nat Rev
Microbiol. 12:661–672. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Rey FE, Faith JJ, Bain J, Muehlbauer MJ,
Stevens RD, Newgard CB and Gordon JI: Dissecting the in vivo
metabolic potential of two human gut acetogens. J Biol Chem.
285:22082–22090. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Davila AM, Blachier F, Gotteland M,
Andriamihaja M, Benetti PH, Sanz Y and Tomé D: Intestinal luminal
nitrogen metabolism: Role of the gut microbiota and consequences
for the host. Pharmacol Res. 68:95–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Kasubuchi M, Hasegawa S, Hiramatsu T,
Ichimura A and Kimura I: Dietary gut microbial metabolites,
short-chain fatty acids, and host metabolic regulation. Nutrients.
7:2839–2849. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Kimura I, Ozawa K, Inoue D, Imamura T,
Kimura K, Maeda T, Terasawa K, Kashihara D, Hirano K, Tani T, et
al: The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation
via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Nat Commun.
4:18292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhang J, Guo Z, Xue Z, Sun Z, Zhang M,
Wang L, Wang G, Wang F, Xu J, Cao H, et al: A phylo-functional core
of gut microbiota in healthy young chinese cohorts across
lifestyles, geography and ethnicities. ISME J. 9:1979–1990. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Li T and Chiang JY: Bile acid signaling in
metabolic disease and drug therapy. Pharmacol Rev. 66:948–983.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Sayin SI, Wahlström A, Felin J, Jäntti S,
Marschall HU, Bamberg K, Angelin B, Hyötyläinen T, Orešič M and
Bäckhed F: Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by
reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally
occurring FXR antagonist. Cell Metab. 17:225–235. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Long SL, Gahan CGM and Joyce SA:
Interactions between gut bacteria and bile in health and disease.
Mol Aspects Med. 56:54–65. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Parasar B, Zhou H, Xiao X, Shi Q, Brito IL
and Chang PV: Chemoproteomic profiling of gut microbiota-associated
bile salt hydrolase activity. ACS Cent Sci. 5:867–873.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|