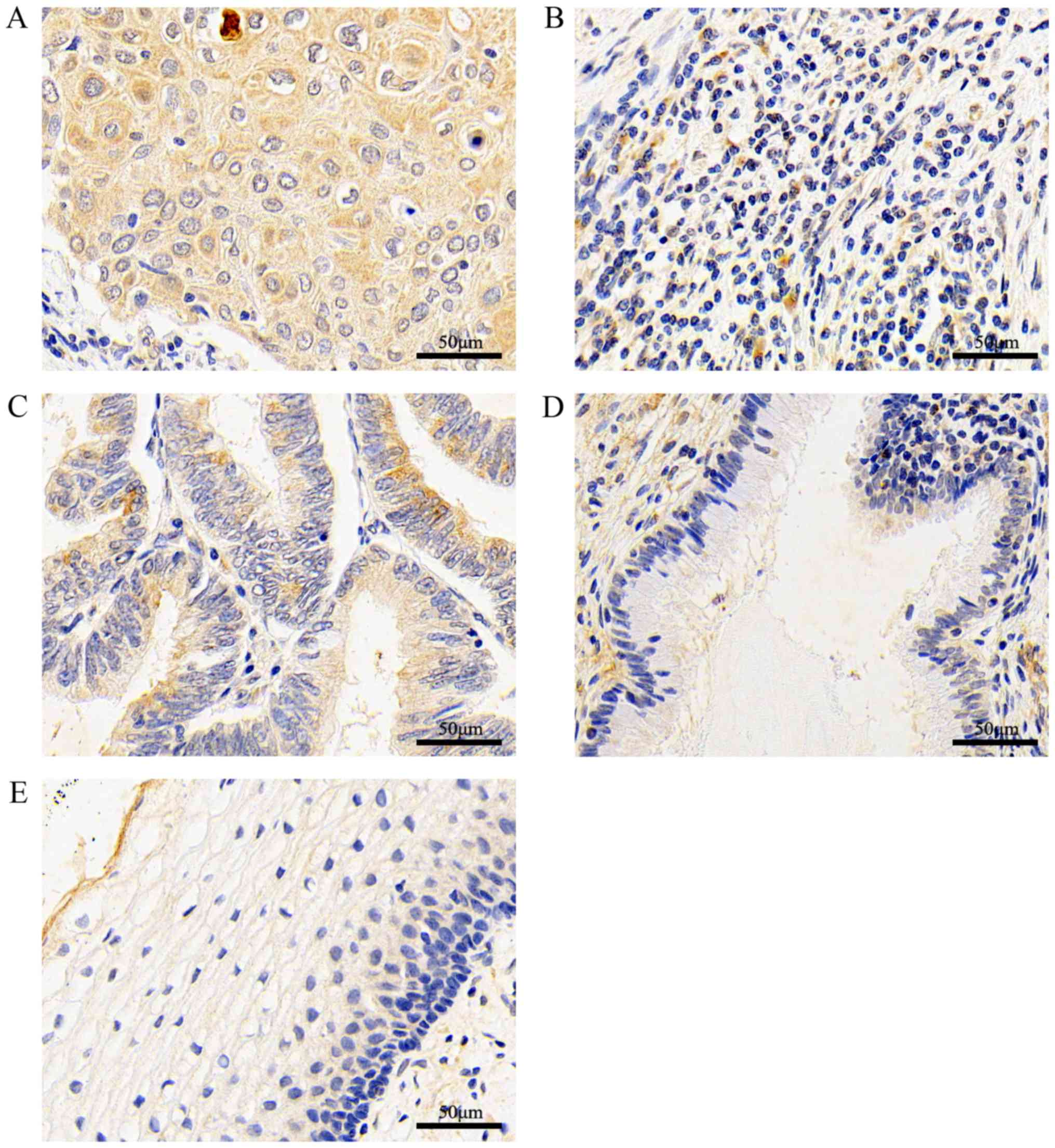
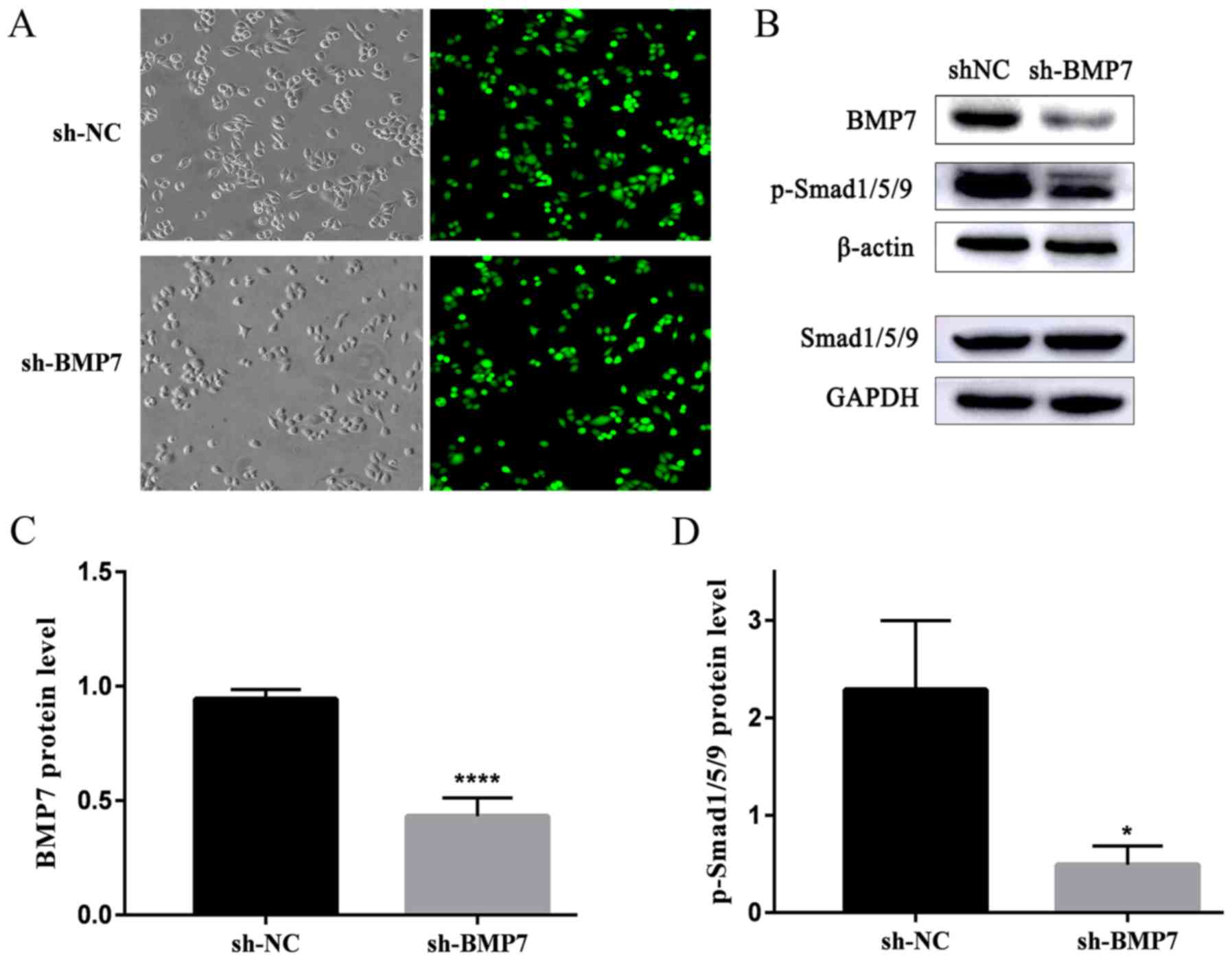
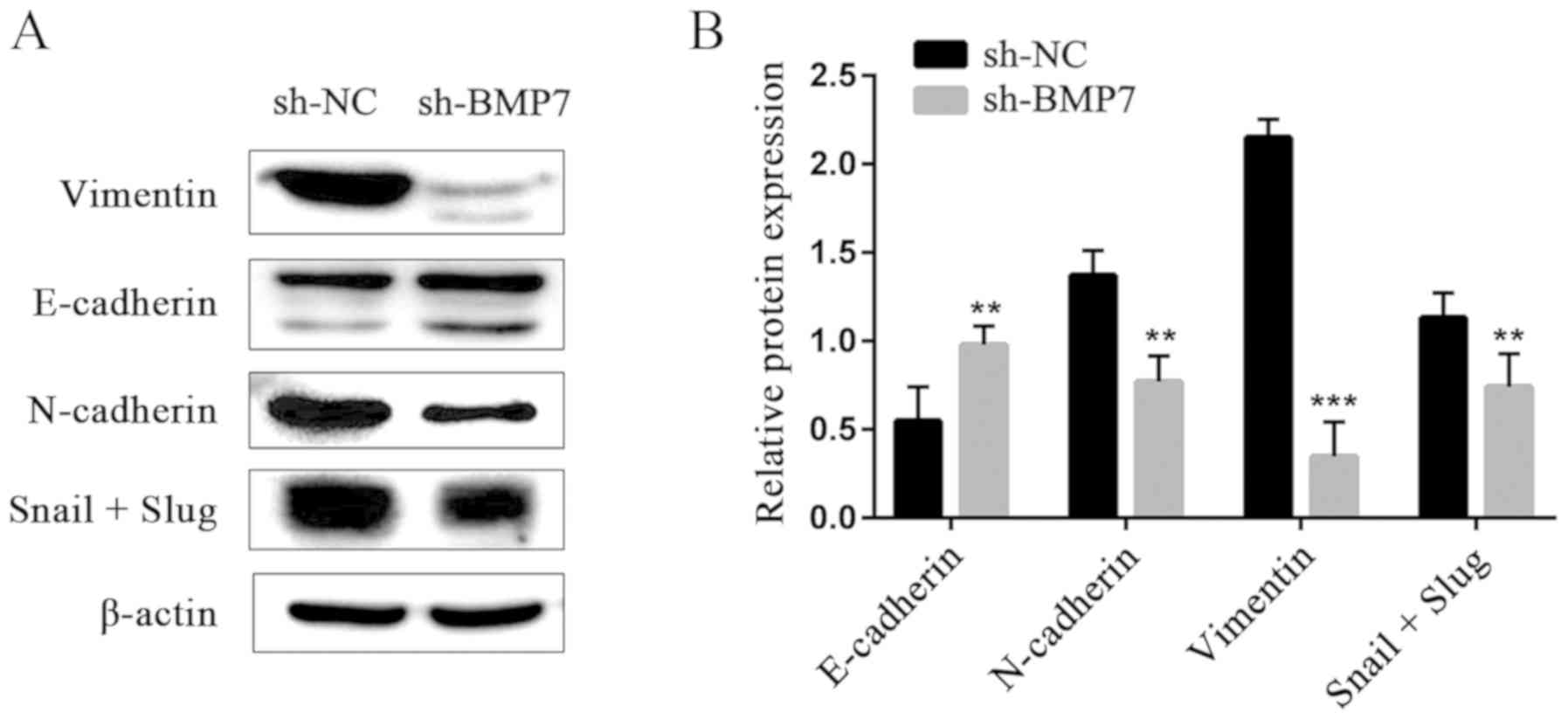
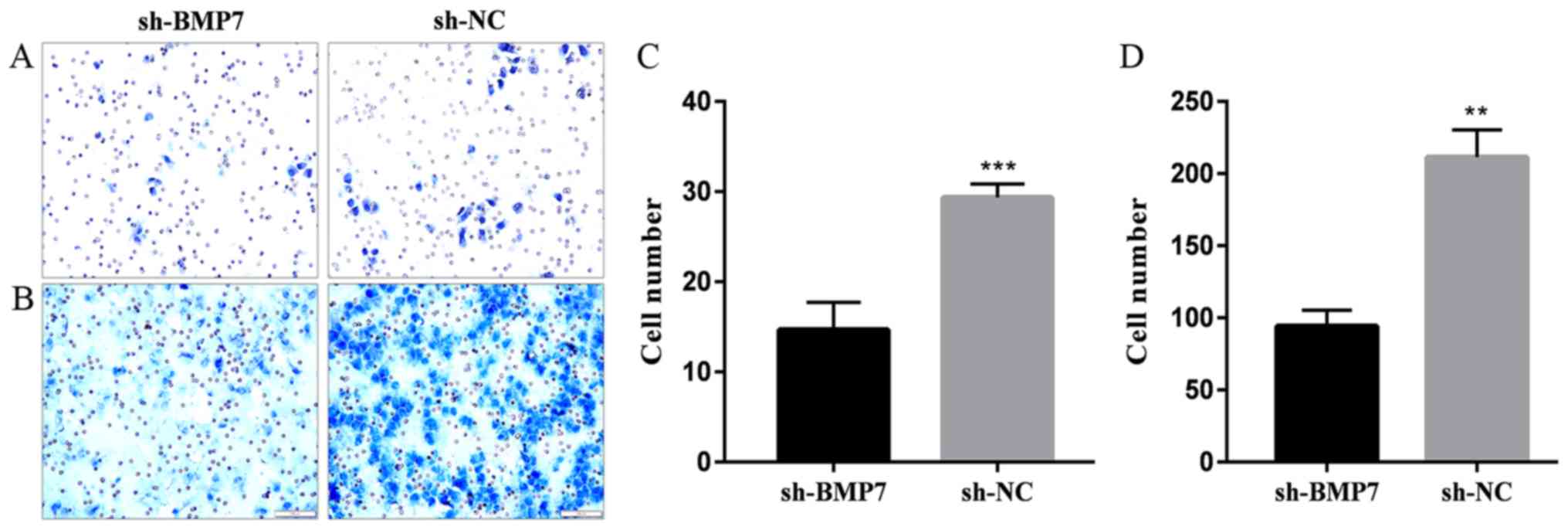
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu P: Big data evaluation of the clinical
epidemiology of cervical cancer in mainland China. Chin J Pract
Gynecol Obstet. 34:41–45. 2018.
|
|
3
|
Bragdon B, Moseychuk O, Saldanha S, King
D, Julian J and Nohe A: Bone morphogenetic proteins: A critical
review. Cell Signal. 23:609–620. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sunde JS, Donninger H, Wu K, Johnson ME,
Pestell RG, Rose GS, Mok SC, Brady J, Bonome T and Birrer MJ:
Expression profiling identifies altered expression of genes that
contribute to the inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta
signaling in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 66:8404–8412. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cheng L, Lu W, Kulkarni B, Pejovic T, Yan
X, Chiang JH, Hood L, Odunsi K and Lin B: Analysis of chemotherapy
response programs in ovarian cancers by the next-generation
sequencing technologies. Gynecol Oncol. 117:159–169. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Megumi K, Ishigami S, Uchikado Y, Kita Y,
Okumura H, Matsumoto M, Uenosono Y, Arigami T, Kijima Y, Kitazono
M, et al: Clinicopathological significance of BMP7 expression in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:2066–2071.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Aoki M, Ishigami S, Uenosono Y, Arigami T,
Uchikado Y, Kita Y, Kurahara H, Matsumoto M, Ueno S and Natsugoe S:
Expression of BMP-7 in human gastric cancer and its clinical
significance. Br J Cancer. 104:714–718. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shen W, Pang H, Xin B, Duan L, Liu L and
Zhang H: Biological effects of BMP7 on small-cell lung cancer cells
and its bone metastasis. Int J Oncol. 53:1354–1362. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Na YR, Seok SH, Kim DJ, Han JH, Kim TH,
Jung H, Lee BH and Park JH: Bone morphogenetic protein 7 induces
mesenchymal to-epithelial transition in melanoma cells, leading to
inhibition of metastasis. Cancer Sci. 100:2218–2225. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ying X, Sun Y and He P: Bone Morphogenetic
Protein-7 inhibits EMT-associated genes in breast cancer. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 37:1271–1278. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kobayashi A, Okuda H, Xing F, Pandey PR,
Watabe M, Hirota S, Pai SK, Liu W, Fukuda K, Chambers C, et al:
Bone morphogenetic protein 7 in dormancy and metastasis of prostate
cancer stem-like cells in bone. J Exp Med. 208:2641–2655. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cassar L, Nicholls C, Pinto AR, Chen R,
Wang L, Li H and Liu JP: TGF-beta receptor mediated telomerase
inhibition, telomere shortening and breast cancer cell senescence.
Protein Cell. 8:39–54. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Sakai H, Furihata M, Matsuda C, Takahashi
M, Miyazaki H, Konakahara T, Imamura T and Okada T: Augmented
autocrine bone morphogenic protein (BMP) 7 signaling increases the
metastatic potential of mouse breast cancer cells. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 29:327–338. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lim M, Chuong CM and Roy-Burman P: PI3K,
Erk signaling in BMP7-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
(EMT) of PC-3 prostate cancer cells in 2- and 3-dimensional
cultures. Horm Cancer. 2:298–309. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Boon MR, van der Horst G, van der Pluijm
G, Tamsma JT, Smit JW and Rensen PC: Bone morphogenetic protein 7:
A broad-spectrum growth factor with multiple target therapeutic
potency. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:221–229. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cassar L, Li H, Pinto AR, Nicholls C,
Bayne S and Liu JP: Bone morphogenetic protein-7 inhibits
telomerase activity, telomere maintenance, and cervical tumor
growth. Cancer Res. 68:9157–9166. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miyazono K, Kusanagi K and Inoue H:
Divergence and convergence of TGF-beta/BMP signaling. J Cell
Physiol. 187:265–276. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Massagué J, Seoane J and Wotton D: Smad
transcription factors. Genes Dev. 19:2783–2810. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ruzinova MB and Benezra R: Id proteins in
development, cell cycle and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 13:410–418.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roschger C and Cabrele C: The Id-protein
family in developmental and cancer-associated pathways. Cell Commun
Signal. 15:72017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie L, Li J, Zhang Y, Liu B, Peng X, Lin
Y, Xu W and Hu L: Inhibitors of differentiation-1 promotes
nitrosopyrrolidine-induced transformation of HPV 16-immortalized
cervical epithelial cell. Cancer Sci. 105:506–511. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45(W1):
W98–W102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Saitoh M: Involvement of partial EMT in
cancer progression. J Biochem. 164:257–264. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Muthukrishnan SD, Yang X, Friesel R and
Oxburgh L: Concurrent BMP7 and FGF9 signalling governs AP-1
function to promote self-renewal of nephron progenitor cells. Nat
Commun. 6:100272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alarmo EL, Pärssinen J, Ketolainen JM,
Savinainen K, Karhu R and Kallioniemi A: BMP7 influences
proliferation, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 275:35–43. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|