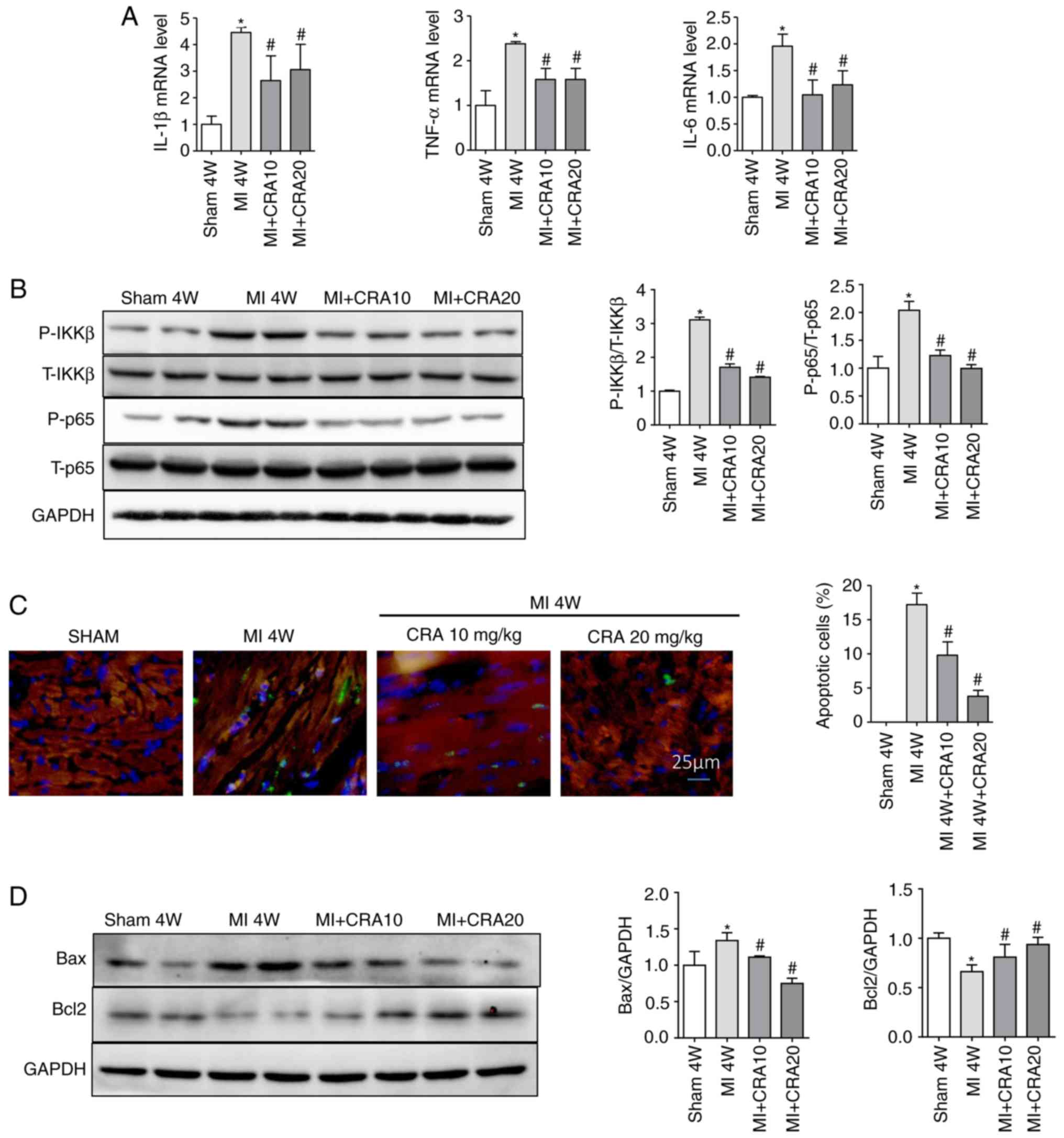
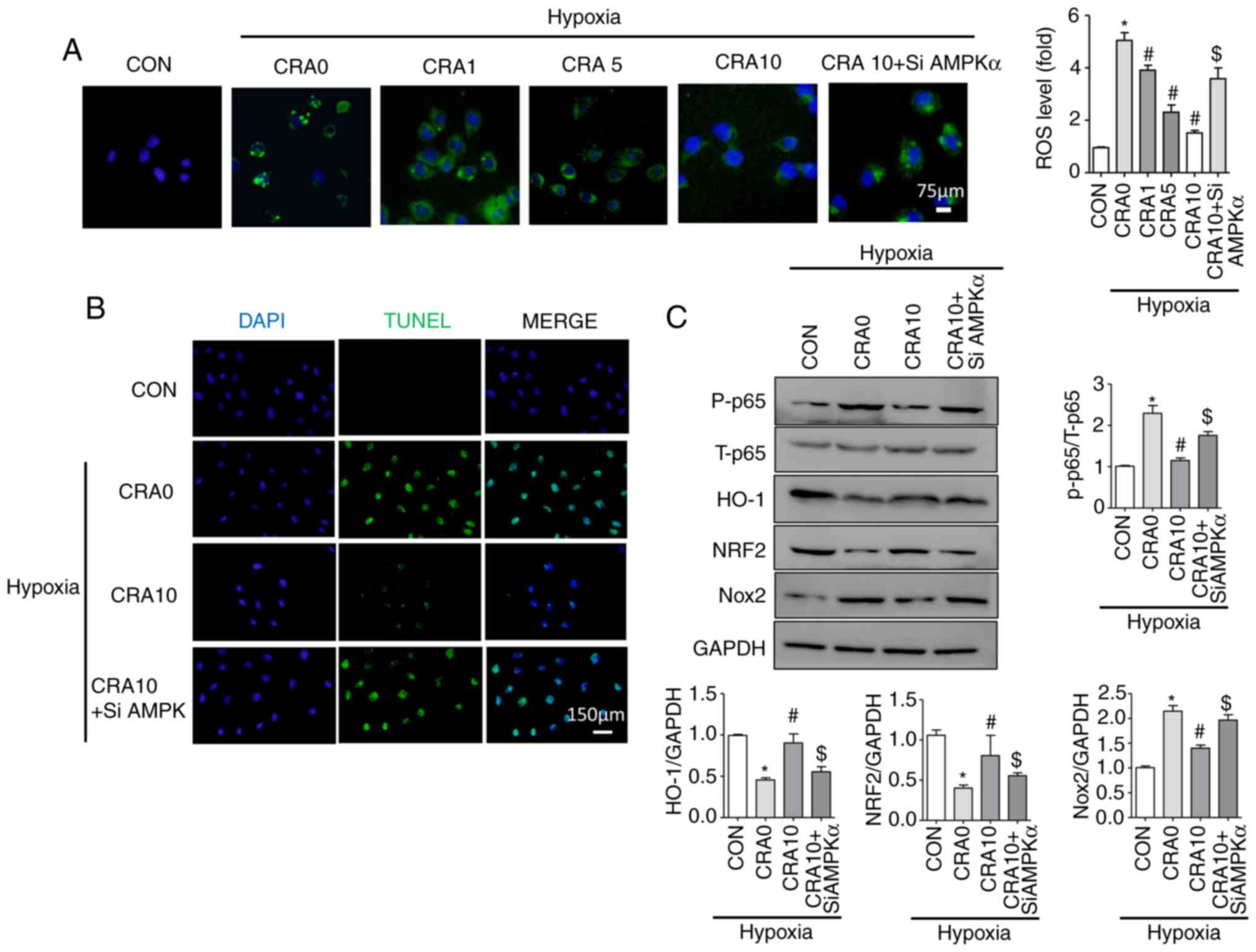
|
1
|
Yang L, Gregorich ZR, Cai W, Zhang P,
Young B, Gu Y, Zhang J and Ge Y: Quantitative proteomics and
immunohistochemistry reveal insights into cellular and molecular
processes in the infarct border zone one month after myocardial
infarction. J Proteome Res. 16:2101–2112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Saxena A, Li N, Sun J, Gupta A,
Lee DW, Tian Q, Dobaczewski M and Frangogiannis NG: Endogenous
IRAK-M attenuates postinfarction remodeling through effects on
macrophages and fibroblasts. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
32:2598–2608. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu X, Wan N, Zhang XJ, Zhao Y, Zhang Y,
Hu G, Wan F, Zhang R, Zhu X, Xia H and Li H: Vinexin-β exacerbates
cardiac dysfunction post-myocardial infarction via mediating
apoptotic and inflammatory responses. Clin Sci (Lond). 128:923–936.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bujak M and Frangogiannis NG: The role of
TGF-beta signaling in myocardial infarction and cardiac remodeling.
Cardiovasc Res. 74:184–195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Neri M, Fineschi V, Di Paolo M, Pomara C,
Riezzo I, Turillazzi E and Cerretani D: Cardiac oxidative stress
and inflammatory cytokines response after myocardial infarction.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 13:26–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lambeth JD: NOX enzymes and the biology of
reactive oxygen. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:181–9. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wilson AJ, Gill EK, Abudalo RA, Edgar KS,
Watson CJ and Grieve DJ: Reactive oxygen species signalling in the
diabetic heart: Emerging prospect for therapeutic targeting. Heart.
104:293–299. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Byrne JA, Grieve DJ, Bendall JK, Li JM,
Gove C, Lambeth JD, Cave AC and Shah AM: Contrasting roles of NADPH
oxidase isoforms in pressure-overload versus angiotensin II-induced
cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res. 93:802–805. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Doerries C, Grote K, Hilfiker-Kleiner D,
Luchtefeld M, Schaefer A, Holland SM, Sorrentino S, Manes C,
Schieffer B, Drexler H and Landmesser U: Critical role of the
NAD(P)H oxidase subunit p47phox for left ventricular
remodeling/dysfunction and survival after myocardial infarction.
Circ Res. 100:894–903. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Somanna NK, Valente AJ, Krenz M, Fay WP,
Delafontaine P and Chandrasekar B: The Nox1/4 dual inhibitor
GKT137831 or Nox4 knockdown inhibits angiotensin-II-induced adult
mouse cardiac fibroblast proliferation and migration. AT1
physically associates with Nox4. J Cell Physiol. 231:1130–1141.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Qi Z, Yin F, Lu L, Shen L, Qi S, Lan L,
Luo L and Yin Z: Baicalein reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammation via suppressing JAK/STATs activation and ROS
production. Inflamm Res. 62:845–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao C, Zhang Y, Liu H, Li P, Zhang H and
Cheng G: Fortunellin protects against high fructose-induced
diabetic heart injury in mice by suppressing inflammation and
oxidative stress via AMPK/Nrf-2 pathway regulation. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 490:552–559. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chi PL, Liu CJ, Lee IT, Chen YW, Hsiao LD
and Yang CM: HO-1 induction by CO-RM2 attenuates TNF-α-induced
cytosolic phospholipase A2 expression via inhibition of
PKCα-dependent NADPH oxidase/ROS and NF-kappaB. Mediators Inflamm.
2014:279171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Miura T, Takagi S and Ishida T: Management
of diabetes and its complications with banaba (Lagerstroemia
speciosa L.) and corosolic acid. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2012:871495. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim JH, Kim YH, Song GY, Kim DE, Jeong YJ,
Liu KH, Chung YH and Oh S: Ursolic acid and its natural derivative
corosolic acid suppress the proliferation of APC-mutated colon
cancer cells through promotion of beta-catenin degradation. Food
Chem Toxicol. 67:87–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen H, Yang J, Zhang Q, Chen LH and Wang
Q: Corosolic acid ameliorates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein
E-deficient mice by regulating the nuclear factor-κB signaling
pathway and inhibiting monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
expression. Circ J. 76:995–1003. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kim SJ, Cha JY, Kang HS, Lee JH, Lee JY,
Park JH, Bae JH, Song DK and Im SS: Corosolic acid ameliorates
acute inflammation through inhibition of IRAK-1 phosphorylation in
macrophages. BMB Rep. 49:276–281. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Yamaguchi Y, Yamada K, Yoshikawa N,
Nakamura K, Haginaka J and Kunitomo M: Corosolic acid prevents
oxidative stress, inflammation and hypertension in SHR/NDmcr-cp
rats, a model of metabolic syndrome. Life Sci. 79:2474–2479. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Takagi S, Miura T, Ishibashi C, Kawata T,
Ishihara E, Gu Y and Ishida T: Effect of corosolic acid on the
hydrolysis of disaccharides. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo).
54:266–8. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yang J, Leng J, Li JJ, Tang JF, Li Y, Liu
BL and Wen XD: Corosolic acid inhibits adipose tissue inflammation
and ameliorates insulin resistance via AMPK activation in high-fat
fed mice. Phytomedicine. 23:181–190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Leach JP, Heallen T, Zhang M, Rahmani M,
Morikawa Y, Hill MC, Segura A, Willerson JT and Martin JF: Hippo
pathway deficiency reverses systolic heart failure after
infarction. Nature. 550:260–264. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fellahi S, El Harrak M, Kuhn JH, Sebbar G,
Bouaiti el A, Khataby K, Fihri OF, El Houadfi M and Ennaji MM:
Comparison of SYBR green I real-time RT-PCR with conventional
agarose gel-based RT-PCR for the diagnosis of infectious bronchitis
virus infection in chickens in Morocco. BMC Res Notes. 9:2312016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dobaczewski M, Gonzalez-Quesada C and
Frangogiannis NG: The extracellular matrix as a modulator of the
inflammatory and reparative response following myocardial
infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 48:504–511. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Siwik DA, Pagano PJ and Colucci WS:
Oxidative stress regulates collagen synthesis and matrix
metalloproteinase activity in cardiac fibroblasts. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 280:C53–C60. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kunkemoeller B and Kyriakides TR: Redox
signaling in diabetic wound healing regulates extracellular matrix
deposition. Antioxid Redox Signal. 27:823–838. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sirker A, Murdoch CE, Protti A, Sawyer GJ,
Santos CX, Martin D, Zhang X, Brewer AC, Zhang M and Shah AM:
Cell-specific effects of Nox2 on the acute and chronic response to
myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 98:11–17. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kuroda J, Ago T, Nishimura A, Nakamura K,
Matsuo R, Wakisaka Y, Kamouchi M and Kitazono T: Nox4 is a major
source of superoxide production in human brain pericytes. J Vasc
Res. 51:429–438. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ago T, Kuroda J, Pain J, Fu C, Li H and
Sadoshima J: Upregulation of Nox4 by hypertrophic stimuli promotes
apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiac myocytes. Circ
Res. 106:1253–1264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cao J, Tsenovoy PL, Thompson EA, Falck JR,
Touchon R, Sodhi K, Rezzani R, Shapiro JI and Abraham NG: Agonists
of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids reduce infarct size and ameliorate
cardiac dysfunction via activation of HO-1 and Wnt1 canonical
pathway. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 116–117:76–86. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Datla SR, Dusting GJ, Mori TA, Taylor CJ,
Croft KD and Jiang F: Induction of heme oxygenase-1 in vivo
suppresses NADPH oxidase derived oxidative stress. Hypertension.
50:636–642. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qi D and Young LH: AMPK: Energy sensor and
survival mechanism in the ischemic heart. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
26:422–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yan X, Zhang H, Fan Q, Hu J, Tao R, Chen
Q, Iwakura Y, Shen W, Lu L, Zhang Q and Zhang R: Dectin-2
deficiency modulates Th1 differentiation and improves wound healing
after myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 120:1116–1129. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Prabhu SD and Frangogiannis NG: The
biological basis for cardiac repair after myocardial infarction:
From inflammation to fibrosis. Circ Res. 119:91–112. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ullevig S, Zhao Q, Lee CF, Seok Kim H,
Zamora D and Asmis R: NADPH oxidase 4 mediates monocyte priming and
accelerated chemotaxis induced by metabolic stress. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:415–426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Kim MJ, Kadayat T, Um YJ, Jeong TC, Lee ES
and Park PH: Inhibitory effect of
3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-1-(thiophen-2-yl) prop-2-en-1-one, a chalcone
derivative on MCP-1 expression in macrophages via inhibition of ROS
and Akt signaling. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 23:119–127. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Park SY, Jin ML, Yi EH, Kim Y and Park G:
Neochlorogenic acid inhibits against LPS-activated inflammatory
responses through up-regulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and involving AMPK
pathway. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 62:1–10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liao HH, Zhu JX, Feng H, Ni J, Zhang N,
Chen S, Liu HJ, Yang Z, Deng W and Tang QZ: Myricetin possesses
potential protective effects on diabetic cardiomyopathy through
inhibiting IκBα/NFκB and enhancing Nrf2/HO-1. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:8370593. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li M, Ye J, Zhao G, Hong G, Hu X, Cao K,
Wu Y and Lu Z: Gas6 attenuates lipopolysaccharideinduced TNFα
expression and apoptosis in H9C2 cells through NFkappaB and MAPK
inhibition via the Axl/PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med. 44:982–994.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu W, Ru L, Su C, Qi S and Qi X: Serum
levels of inflammatory cytokines and expression of BCL2 and BAX
mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and in patients with
chronic heart failure. Med Sci Monit. 25:2633–2639. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Henstridge DC, Abildgaard J, Lindegaard B
and Febbraio MA: Metabolic control and sex: A focus on
inflammatory-linked mediators. Br J Pharmacol. 176:4193–4207. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Stohs SJ, Miller H and Kaats GR: A review
of the efficacy and safety of banaba (Lagerstroemia speciosa L.)
and corosolic acid. Phytother Res. 26:317–324. 2012.
|