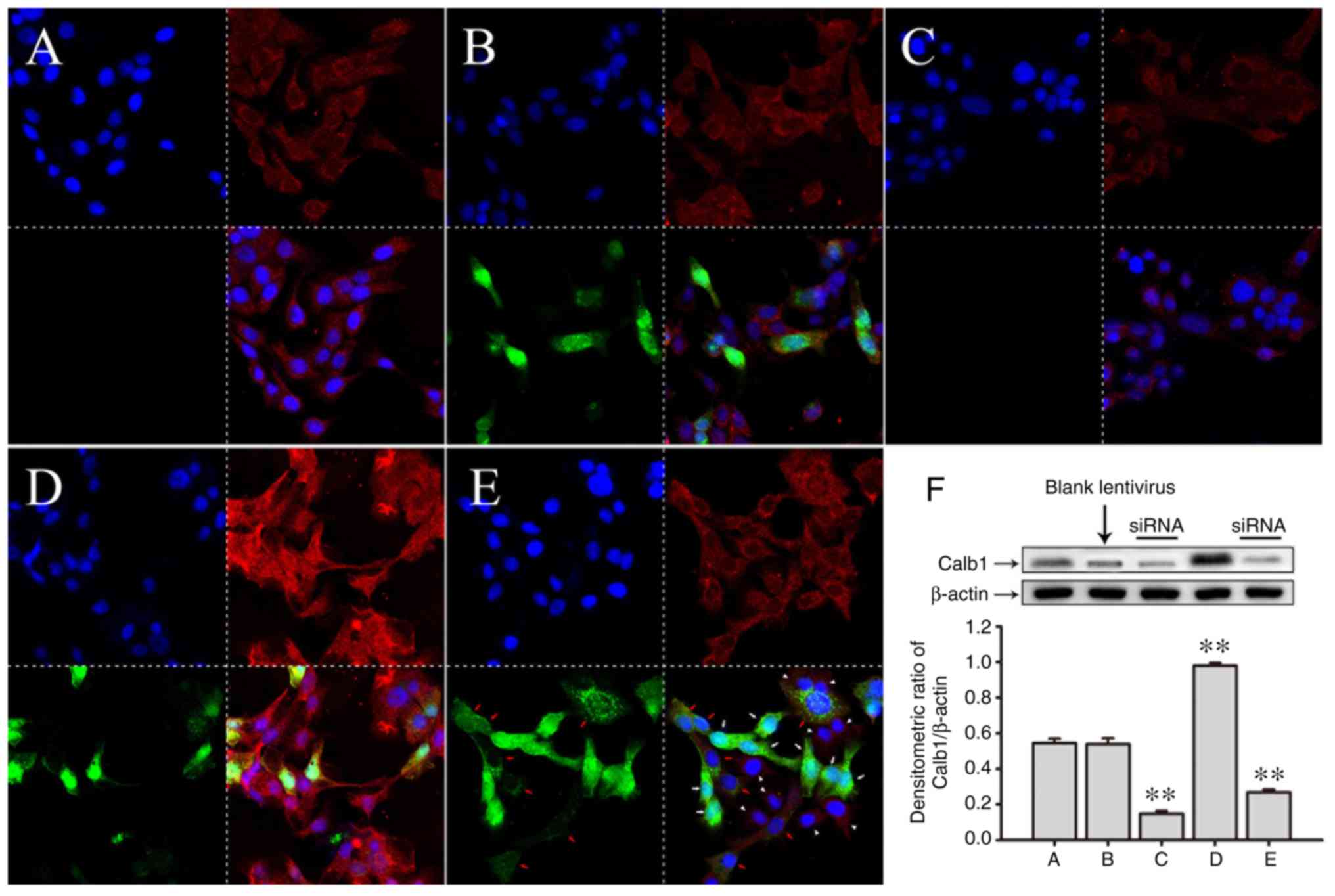
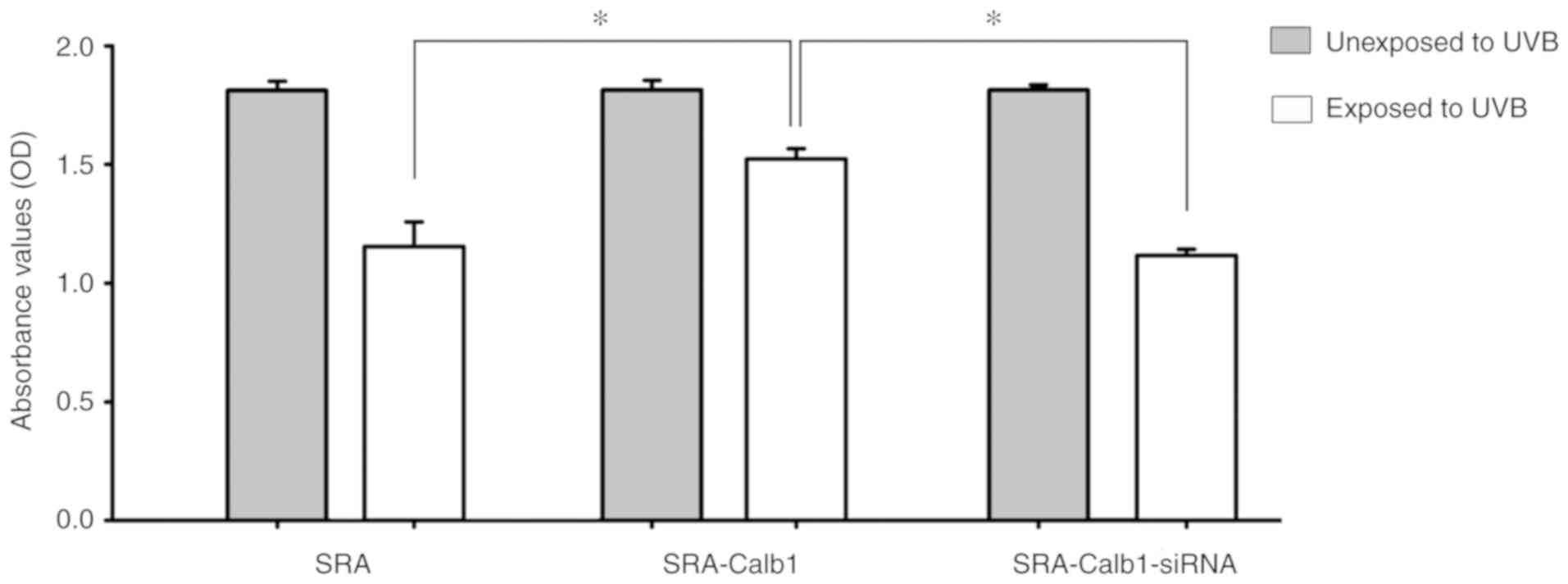
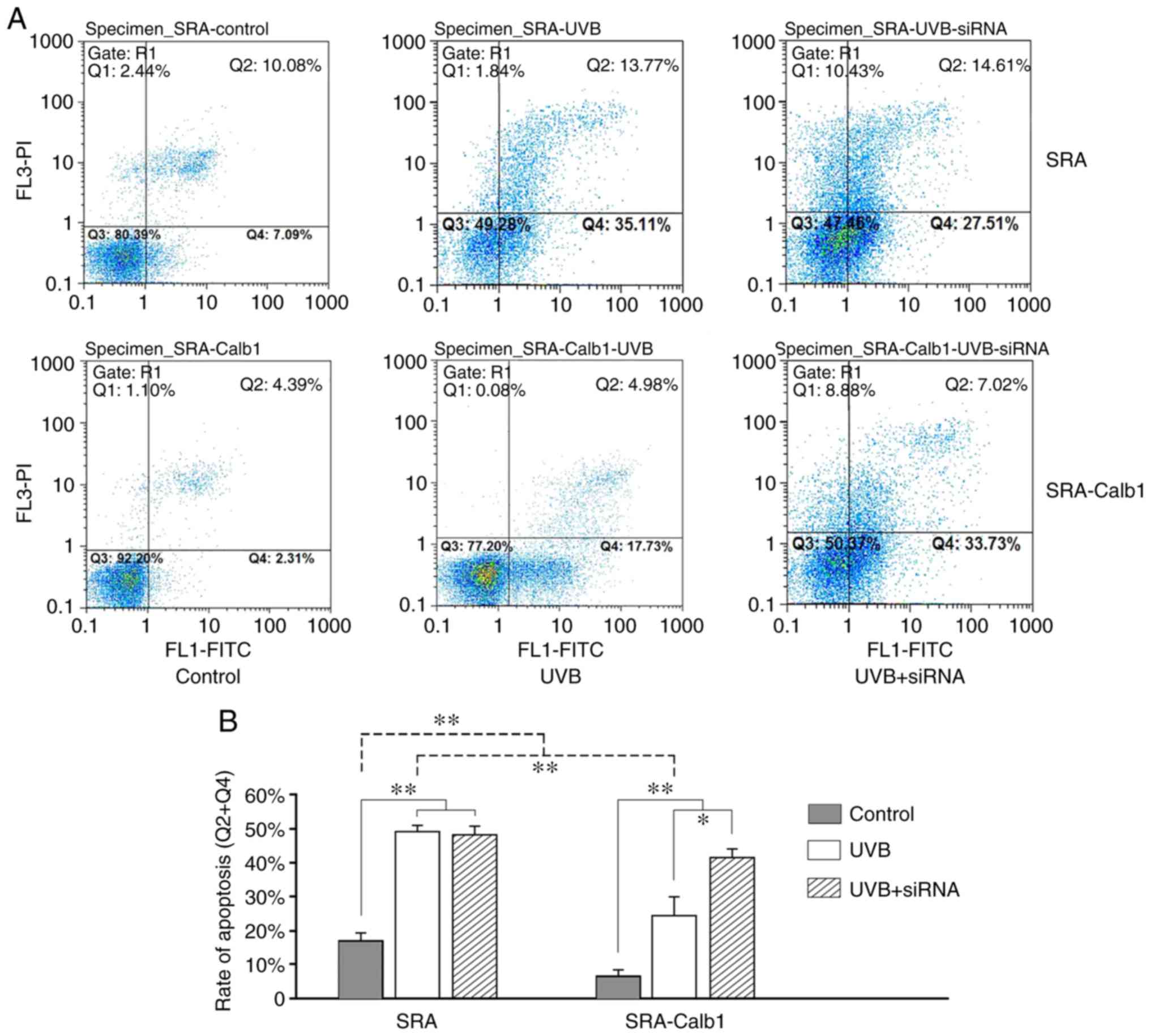
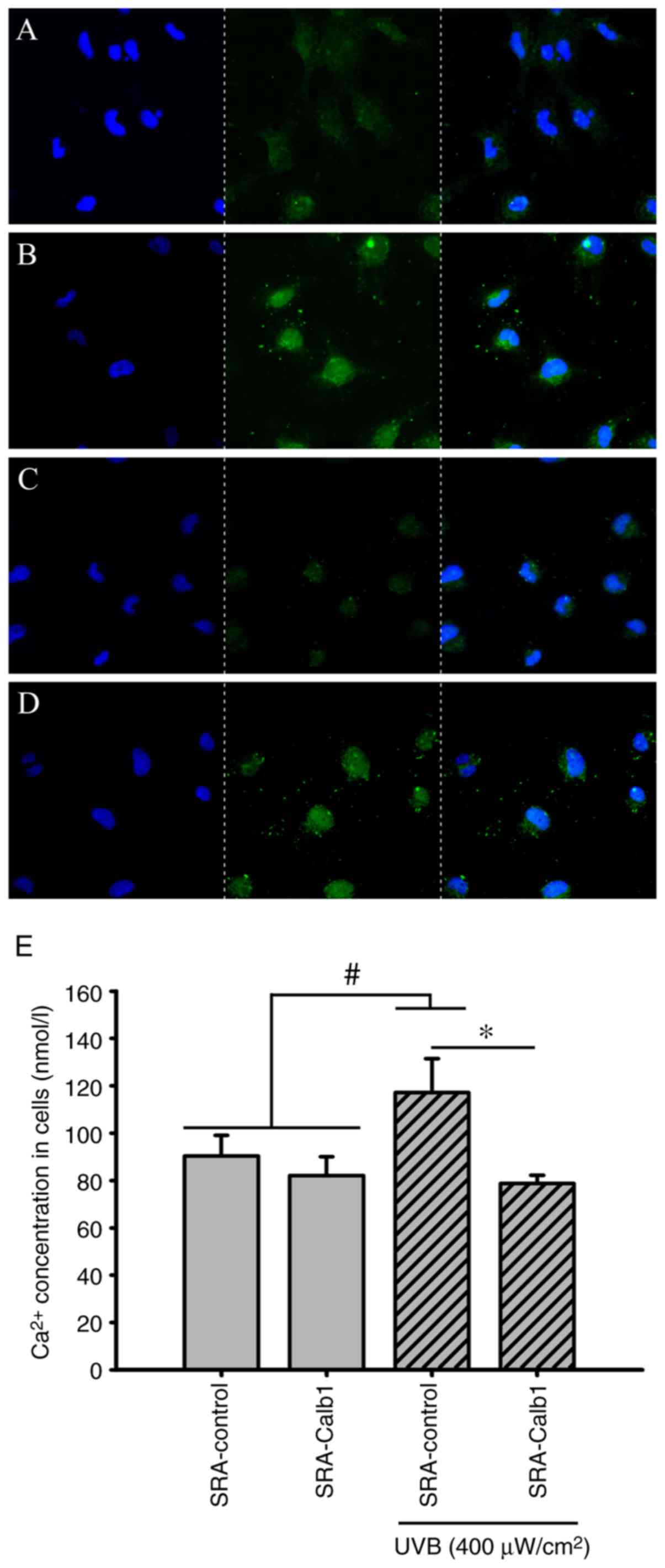
|
1
|
Jia S, Shi J, Chen X and Tang L:
Ultraviolet radiation-induced apoptosis in human lens epithelial
cells and its effect on Bcl-2 and Bax. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi
Xue Ban. 37:730–736. 2012.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McCarty CA and Taylor HR: A review of the
epidemiologic evidence linking ultraviolet radiation and cataracts.
Dev Ophthalmol. 35:21–31. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li WC, Kuszak JR, Dunn K, Wang RR, Ma W,
Wang GM, Spector A, Leib M, Cotliar AM and Weiss M: Lens epithelial
cell apoptosis appears to be a common cellular basis for
non-congenital cataract development in humans and animals. J Cell
Biol. 130:169–181. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Andley UP, Walsh A, Kochevar IE and Reddan
JR: Effect of ultraviolet-B radiation on protein synthesis in
cultured lens epithelial cells. Curr Eye Res. 9:1099–1106. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Andley UP, Malone JP and Townsend RR:
Inhibition of lens photodamage by UV-absorbing contact lenses.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:8330–8341. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee DH, Cho KS, Park SG, Kim EK and Joo
CK: Cellular death mediated by nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB)
translocation in cultured human lens epithelial cells after
ultraviolet-B irradiation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 31:614–619.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yao J, Liu Y, Wang X, Shen Y, Yuan S, Wan
Y and Jiang Q: UVB radiation induces human lens epithelial cell
migration via NADPH oxidase-mediated generation of reactive oxygen
species and up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Int J Mol
Med. 24:153–159. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miyashita H, Hatsusaka N, Shibuya E, Mita
N, Yamazaki M, Shibata T, Ishida H, Ukai Y, Kubo E and Sasaki H:
Association between ultraviolet radiation exposure dose and
cataract in Han people living in China and Taiwan: A
cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 14:e02153382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lofgren S: Solar ultraviolet radiation
cataract. Exp Eye Res. 156:112–116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Galichanin K, Lofgren S and Soderberg P:
Cataract after repeated daily in vivo exposure to ultraviolet
radiation. Health Phys. 107:523–529. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang J, Yan H, Lofgren S, Tian X and Lou
MF: Ultraviolet radiation-induced cataract in mice: The effect of
age and the potential biochemical mechanism. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 53:7276–7285. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mody VC Jr, Kakar M, Elfving A, Soderberg
PG and Lofgren S: Ultraviolet radiation-B-induced cataract in
albino rats: Maximum tolerable dose and ascorbate consumption. Acta
Ophthalmol Scand. 84:390–395. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
West SK, Longstreth JD, Munoz BE, Pitcher
HM and Duncan DD: Model of risk of cortical cataract in the US
population with exposure to increased ultraviolet radiation due to
stratospheric ozone depletion. Am J Epidemiol. 162:1080–1088. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Midelfart A: Ultraviolet radiation and
cataract. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 83:642–644. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jing L, Kumari S, Mendelev N and Li PA:
Coenzyme q10 ameliorates ultraviolet B irradiation induced cell
death through inhibition of mitochondrial intrinsic cell death
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 12:8302–8315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shui YB, Sasaki H, Pan JH, Hata I, Kojima
M, Yamada Y, Hirai KI, Takahashia N and Sasaki K: Morphological
observation on cell death and phagocytosis induced by ultraviolet
irradiation in a cultured human lens epithelial cell line. Exp Eye
Res. 71:609–618. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mendelev N, Witherspoon S and Li PA:
Overexpression of human selenoprotein H in neuronal cells
ameliorates ultraviolet irradiation-induced damage by modulating
cell signaling path-ways. Exp Neurol. 220:328–334. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ricci JE, Gottlieb RA and Green DR:
Caspase-Mediated loss of mitochondrial function and generation of
reactive oxygen species during apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 160:65–75.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Celio MR: Calbindin D-28k and parvalbumin
in the rat nervous system. Neuroscience. 35:375–475. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Persechini A, Moncrief ND and Kretsinger
RH: The EF-hand family of calcium-modulated proteins. Trends
Neurosci. 12:462–467. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hemmingsen C: Regulation of renal
calbindin-D28k. Pharmacol Toxicol. 87(Suppl 3): S5–S30. 2000.
|
|
22
|
Duncan MJ and Franklin KM: Expression of
5-HT7 receptor mRNA in the hamster brain: Effect of aging and
association with calbindin-D28K expression. Brain Res. 1143:70–77.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Iacopino AM, Rhoten WB and Christakos S:
Calcium binding protein (calbindin-D28k) gene expression in the
developing and aging mouse cerebellum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res.
8:283–290. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hall AK and Norman AW: Acute actions of
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 upon chick pancreatic calbindin-D28K.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 176:1057–1061. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Margolis DS, Kim D, Szivek JA, Lai LW and
Lien YH: Functionally improved bone in calbindin-D28k knockout
mice. Bone. 39:477–484. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Faucheux C, Bareille R and Amedee J:
Synthesis of calbi-ndin-D28K during mineralization in human bone
marrow stromal cells. Biochemical J. 333:817–823. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Baimbridge KG, Celio MR and Rogers JH:
Calcium-Binding proteins in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci.
15:303–308. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Geng Y, Lin HT, Chen W, Liu ZC, Xiang W
and Chen WR: Age-Related reduction in calbindin-D28K expression in
the spraguedawley rat lens. Mol Med Rep. 11:422–426. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ahmadian SS, Rezvanian A, Peterson M,
Weintraub S, Bigio EH, Mesulam MM and Geula C: Loss of
calbindin-D28K is associated with the full range of tangle
pathology within basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer's
disease. Neurobiol Aging. 36:3163–3170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang C, Jiang C, Yuan H, Xiao C and Gao D:
Role of calbi-ndin-D28K in estrogen treatment for Parkinson's
disease. Neural Regen Res. 8:702–707. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ferrante RJ, Kowall NW and Richardson EP
Jr: Proliferative and degenerative changes in striatal spiny
neurons in Huntington's disease: A combined study using the
sectiongolgi method and calbindin D28k immunocytochemistry. J
Neurosci. 11:3877–3887. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kiyama H, Seto-Ohshima A and Emson PC:
Calbindin D28K as a marker for the degeneration of the
striatonigral pathway in Huntington's disease. Brain Res.
525:209–214. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hong SM, Chung SY, Park MS, Huh YB, Park
MS and Yeo SG: Immunoreactivity of calcium-binding proteins in the
central auditory nervous system of aged rats. J Korean Neurosurg
Soc. 45:231–235. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fan Y, Shi L, Gu Y, Zhao Y, Xie J, Qiao J,
Yang GY, Wang Y and Lu CZ: Pretreatment with PTD-calbindin D 28k
alleviates rat brain injury induced by ischemia and reperfusion. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 27:719–728. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
D'Orlando C, Celio MR and Schwaller B:
Calretinin and calbindin D-28k, but not parvalbumin protect against
glutamate-induced delayed excitotoxicity in transfected N18-RE 105
neuroblastomaretina hybrid cells. Brain Res. 945:181–190. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Meier TJ, Ho DY, Park TS and Sapolsky RM:
Gene transfer of calbindin D28k cDNA via herpes simplex virus
amplicon vector decreases cytoplasmic calcium ion response and
enhances neuronal survival following glutamatergic challenge but
not following cyanide. J Neurochem. 71:1013–1023. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bellido T, Huening M, Raval-Pandya M,
Manolagas SC and Christakos S: Calbindin-D28k is expressed in
osteoblastic cells and suppresses their apoptosis by inhibiting
caspase-3 activity. J Biol Chem. 275:26328–26332. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Youn HY, McCanna DJ, Sivak JG and Jones
LW: In vitro ultraviolet-induced damage in human corneal, lens, and
retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol Vis. 17:237–246.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Okuno T: Ultraviolet action spectrum for
cell killing in a human lens epithelial cell line. Ind Health.
45:137–142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Teng H, Huang LY, Tian F, Dong LJ and
Zhang H: Effects of SMP-30 overexpression on apoptosis of human
lens epithelial cells induced by ultraviolet B irradiation.
Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 53:835–841. 2017.In Chinese; Abstract
available in Chinese from the publisher. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li WC and Spector A: Lens epithelial cell
apoptosis is an early event in the development of UVB-induced
cataract. Free Radic Biol Med. 20:301–311. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sun X, Zou W and Zhao C: Expression of P53
during lens epithe-lial cell apoptosis induced by ultraviolet. J
Tongji Med Univ. 21:263–264. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Andley UP, Lewis RM, Reddan JR and
Kochevar IE: Action spectrum for cytotoxicity in the UVA- and
UVB-wavelength region in cultured lens epithelial cells. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 35:367–373. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Marian MJ, Li H, Borchman D and Paterson
CA: Plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase expression in the human lens. Exp
Eye Res. 81:57–64. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Marian MJ, Mukhopadhyay P, Borchman D,
Tang D and Paterson CA: Regulation of sarco/endoplasmic and plasma
membrane calcium ATPase gene expression by calcium in cultured
human lens epithelial cells. Cell Calcium. 41:87–95. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wu Q, Guo D, Bi H, Wang D and Du Y: UVB
irradiation-induced dysregulation of plasma membrane calcium
ATPase1 and intra-cellular calcium homeostasis in human lens
epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 382:263–272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Williams MR, Duncan G, Riach RA and Webb
SF: Acetylcholine receptors are coupled to mobilization of
intracellular calcium cultured human lens cells. Exp Eye Res.
57:381–384. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Riach RA, Duncan G, Williams MR and Webb
SF: Histamine and ATP mobilize calcium by activation of H1 and P2u
receptors in human lens epithelial cells. J Physiol. 486:273–282.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Masaki H, Izutsu Y, Yahagi S and Okano Y:
Reactive oxygen species in HaCaT keratinocytes after UVB
irradiation are triggered by intracellular Ca(2+) levels. J
Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 14:50–52. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ding BX and Wang CB: Inhibitory effect of
polypeptides from chlamys farreri on UVB-induced apoptosis and DNA
damage in normal human dermal fibroblasts in vitro. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 24:1006–1010. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wackernagel W, Ettinger K, Weitgasser U,
Bakir BG, Schmut O, Goessler W and Faschinger C: Opacification of a
silicone intra-ocular lens caused by calcium deposits on the optic.
J Cataract Refract Surg. 30:517–520. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Truscott RJ, Marcantonio JM, Tomlinson J
and Duncan G: Calcium-induced opacification and proteolysis in the
intact rat lens. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 31:2405–2411.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hightower KR, Duncan G, Dawson A,
Wormstone IM, Reddan J and Dziedizc D: Ultraviolet irradiation
(UVB) interrupts calcium cell signaling in lens epithelial cells.
Photochem Photobiol. 69:595–598. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Dolmetsch RE, Lewis RS, Goodnow CC and
Healy JI: Differential activation of transcription factors induced
by Ca2+ response amplitude and duration. Nature. 386:855–858. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Richter C and Kass GE: Oxidative stress in
mitochondria: Its relationship to cellular Ca2+ homeostasis, cell
death, proliferation, and differentiation. Chem Biol Interact.
77:1–23. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Martikainen P, Kyprianou N, Tucker RW and
Isaacs JT: Programmed death of nonproliferating
androgen-independent prostatic cancer cells. Cancer Res.
51:4693–4700. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lynch K, Fernandez G, Pappalardo A and
Peluso JJ: Basic fibroblast growth factor inhibits apoptosis of
spontaneously immortalized granulosa cells by regulating
intracellular free calcium levels through a protein kinase
Cdelta-dependent pathway. Endocrinology. 141:4209–4217. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Huang Y, Li X, Wang Y, Wang H, Huang C and
Li J: Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced hepatic stellate cell
apoptosis through calcium-mediated JNK/P38 MAPK and
Calpain/Caspase-12 pathways. Mol Cell Biochem. 394:1–12. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li L, Cao Z, Jia P and Wang Z: Calcium
signals and caspase-12 participated in paraoxon-induced apoptosis
in EL4 cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 24:728–736. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Jiang L, Liu Y, Ma MM, Tang YB, Zhou JG
and Guan YY: Mitochondria dependent pathway is involved in the
protective effect of bestrophin-3 on hydrogen peroxide-induced
apoptosis in basilar artery smooth muscle cells. Apoptosis.
18:556–565. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Min SK, Lee SK, Park JS, Lee J, Paeng JY,
Lee SI, Lee HJ, Kim Y, Pae HO, Lee SK and Kim EC: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress is involved in hydrogen peroxide induced apoptosis
in immortalized and malignant human oral keratinocytes. J Oral
Pathol Med. 37:490–498. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hoenderop JG, Hartog A, Stuiver M, Doucet
A, Willems PH and Bindels RJ: Localization of the epithelial Ca(2+)
channel in rabbit kidney and intestine. J Am Soc Nephrol.
11:1171–1178. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sun S, Li F, Gao X, Zhu Y, Chen J, Zhu X,
Yuan H and Gao D: Calbindin-D28K inhibits apoptosis in dopaminergic
neurons by activation of the PI3-kinase-Akt signaling pathway.
Neuroscience. 199:359–367. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Verdes JM, Morana JA, Battes D, Gutiérrez
F, Guerrero F, Goicoa A, Fidalgo LE, Barbeito CG, Zanuzzi CN,
Portiansky EL and Gimeno EJ: Calbindin D28k expression and the
absence of apoptosis in the cerebellum of solanum bonariense
L-intoxicated bovines. Vet Pathol. 47:569–572. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Guo Q, Christakos S, Robinson N and
Mattson MP: Calbindin D28k blocks the proapoptotic actions of
mutant presenilin 1: Reduced oxidative stress and preserved
mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:3227–3232. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Turner PR, Mefford S, Christakos S and
Nissenson RA: Apoptosis mediated by activation of the G
protein-coupled receptor for parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related
protein (PTHrP). Mol Endocrinol. 14:241–254. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|