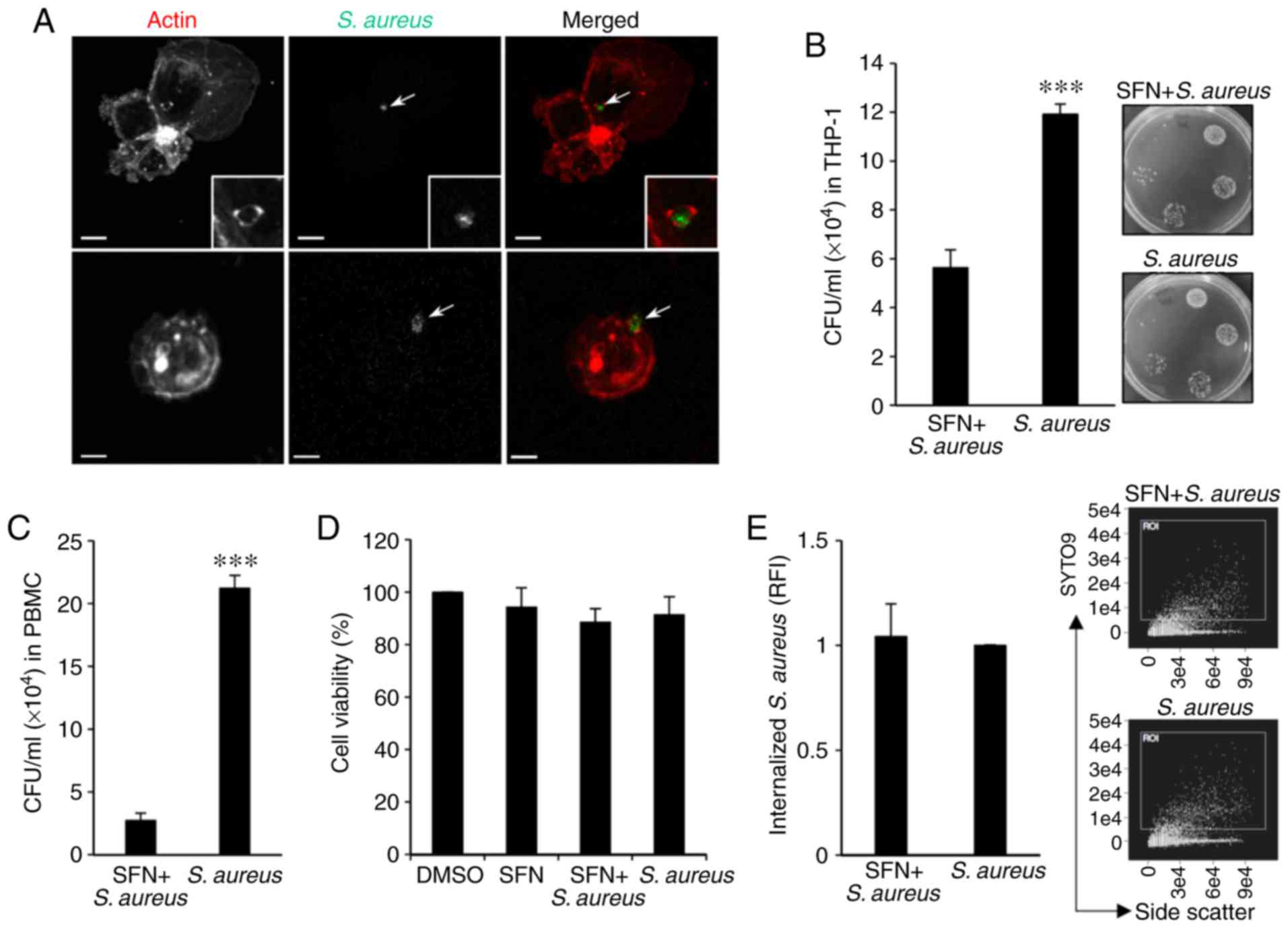
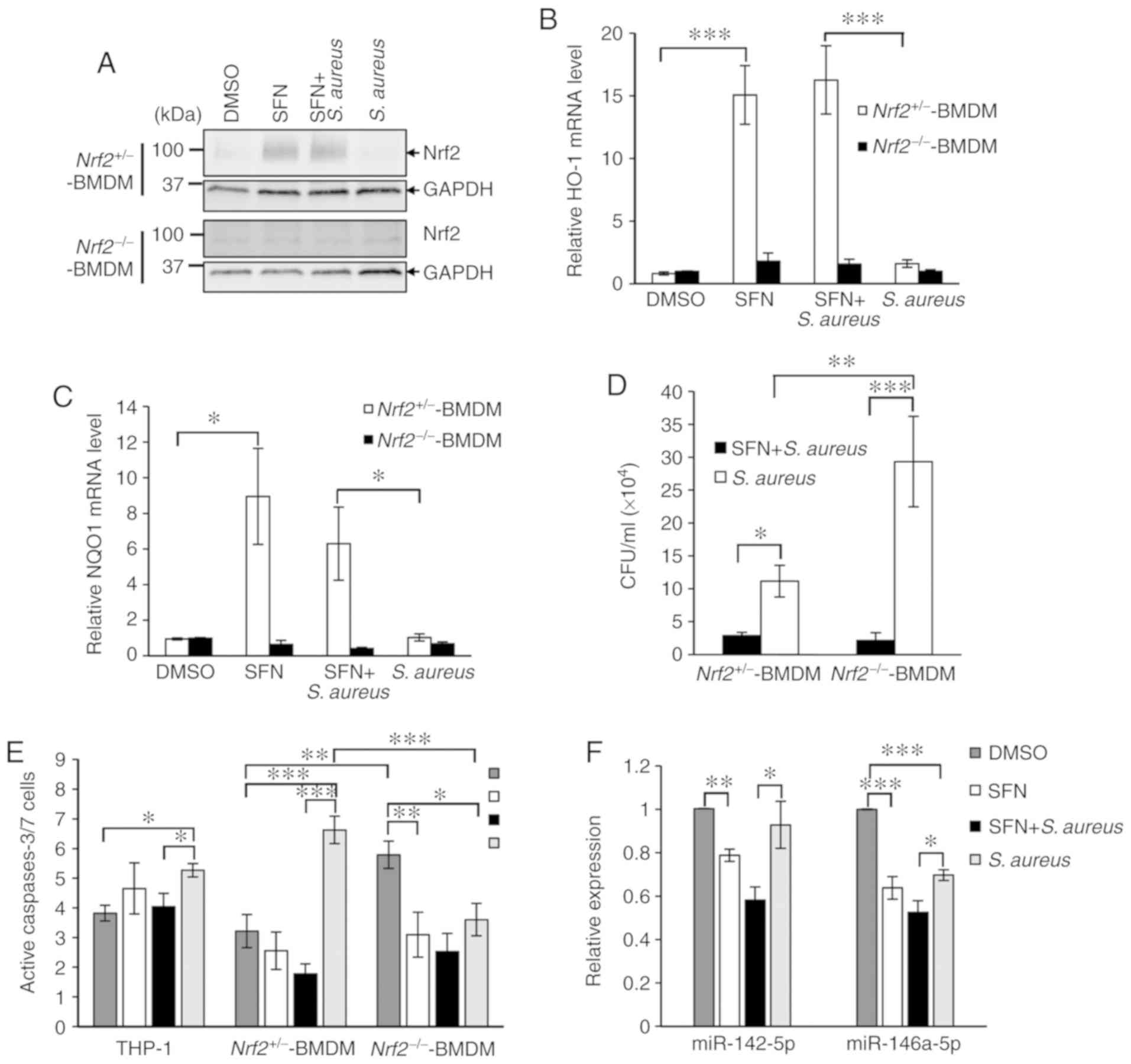
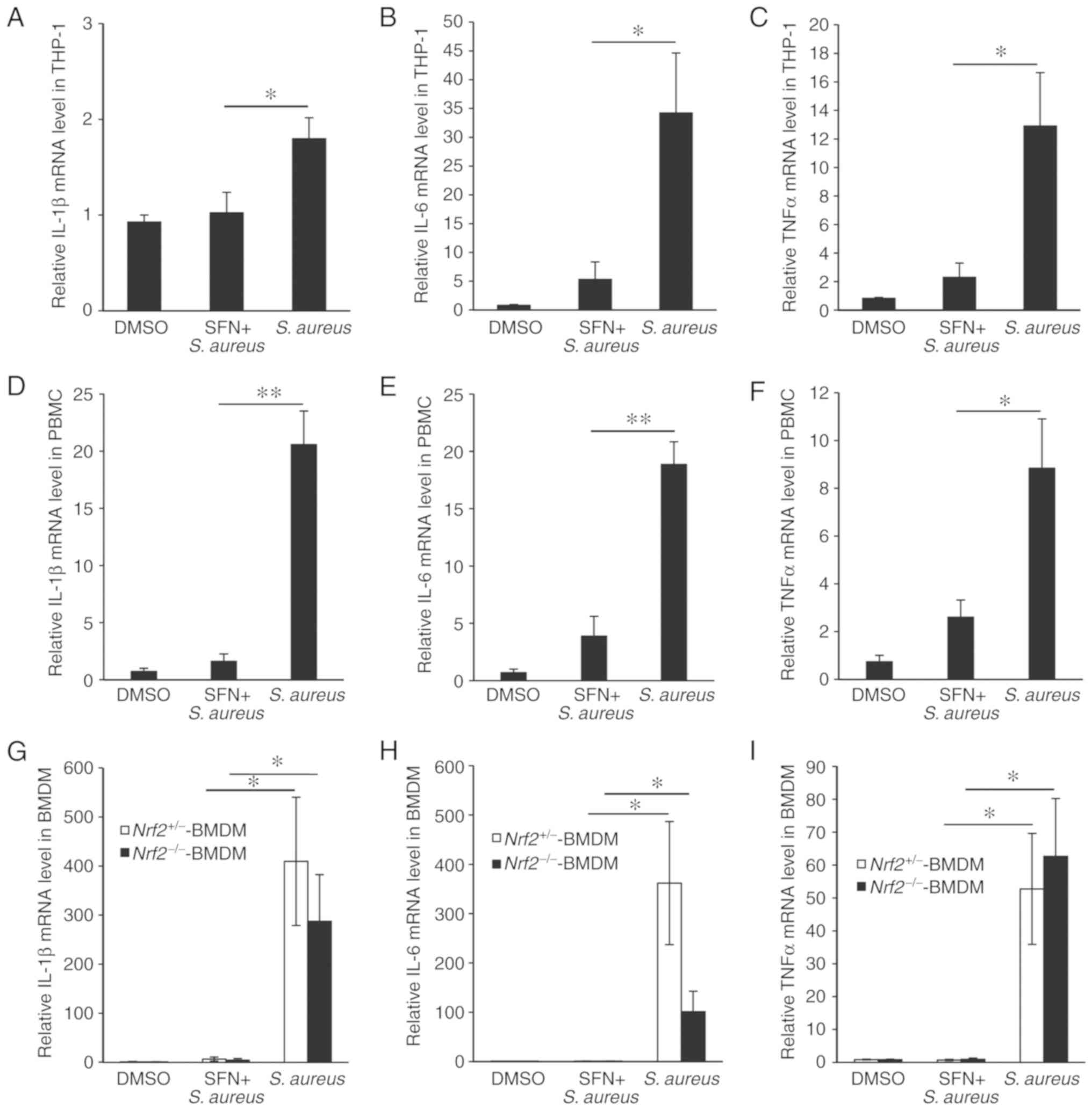
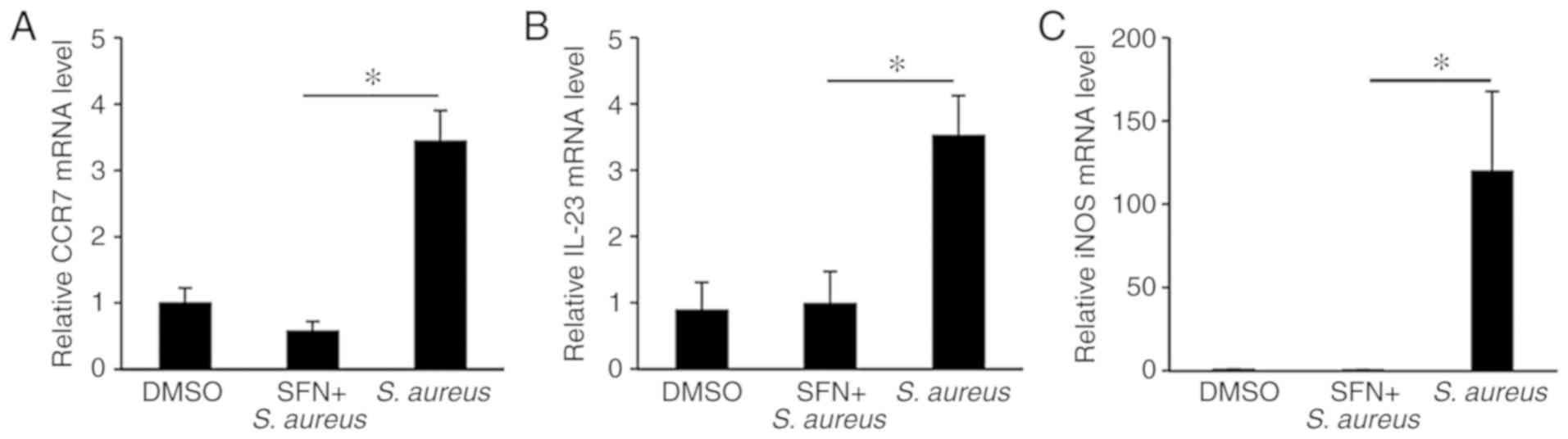
|
1
|
Arango Duque G and Descoteaux A:
Macrophage cytokines: Involvement in immunity and infectious
diseases. Front Immunol. 5:4912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arthur JS and Ley SC: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:679–692.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen GY and Nunez G: Sterile inflammation:
Sensing and reacting to damage. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:826–837. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Iwasaki A and Medzhitov R: Regulation of
adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Science.
327:291–295. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Murray PJ and Wynn TA: Protective and
pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:723–737. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gomez MI, Lee A, Reddy B, Muir A, Soong G,
Pitt A, Cheung A and Prince A: Staphylococcus aureus protein A
induces airway epithelial inflammatory responses by activating
TNFR1. Nat Med. 10:842–848. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kujime K, Hashimoto S, Gon Y, Shimizu K
and Horie T: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and
c-jun-NH2-terminal kinase regulate RANTES production by influenza
virus-infected human bronchial epithelial cells. J Immunol.
164:3222–3228. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
DeLeo FR, Otto M, Kreiswirth BN and
Chambers HF: Community-associated meticillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 375:1557–1568. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Parker D, Ahn D, Cohen T and Prince A:
Innate immune signaling activated by MDR bacteria in the airway.
Physiol Rev. 96:19–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Fraunholz M and Sinha B: Intracellular
Staphylococcus aureus: Live-in and let die. Front Cell Infect
Microbiol. 2:432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fahey JW, Haristoy X, Dolan PM, Kensler
TW, Scholtus I, Stephenson KK, Talalay P and Lozniewski A:
Sulforaphane inhibits extracellular, intracellular, and
antibiotic-resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori and prevents
benzo[a] pyrene-induced stomach tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:7610–7615. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Romeo L, Iori R, Rollin P, Bramanti P and
Mazzon E: Isothiocyanates: An overview of their antimicrobial
activity against human infections. Molecules. 23:E6242018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sita G, Hrelia P, Graziosi A and Morroni
F: Sulforaphane from cruciferous vegetables: Recent advances to
improve glioblastoma treatment. Nutrients. 10:E17552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Johansson NL, Pavia CS and Chiao JW:
Growth inhibition of a spectrum of bacterial and fungal pathogens
by sulforaphane, an isothiocyanate product found in broccoli and
other cruciferous vegetables. Planta Med. 74:747–750. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Furuya AK, Sharifi HJ, Jellinger RM,
Cristofano P, Shi B and de Noronha CM: Sulforaphane Inhibits HIV
Infection of Macrophages through Nrf2. PLoS Pathog.
12:e10055812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, Ishii T,
Igarashi K, Katoh Y, Oyake T, Hayashi N, Satoh K, Hatayama I, et
al: An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase
II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 236:313–322. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Itoh K, Mochizuki M, Ishii Y, Ishii T,
Shibata T, Kawamoto Y, Kelly V, Sekizawa K, Uchida K and Yamamoto
M: Transcription factor Nrf2 regulates inflammation by mediating
the effect of 15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)-prostaglandin j(2). Mol Cell
Biol. 24:36–45. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Ishii Y, Itoh K, Morishima Y, Kimura T,
Kiwamoto T, Iizuka T, Hegab AE, Hosoya T, Nomura A, Sakamoto T, et
al: Transcription factor Nrf2 plays a pivotal role in protection
against elastase-induced pulmonary inflammation and emphysema. J
Immunol. 175:6968–6975. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kobayashi EH, Suzuki T, Funayama R,
Nagashima T, Hayashi M, Sekine H, Tanaka N, Moriguchi T, Motohashi
H, Nakayama K and Yamamoto M: Nrf2 suppresses macrophage
inflammatory response by blocking proinflammatory cytokine
transcription. Nat Commun. 7:116242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou X, Li X and Wu M: miRNAs reshape
immunity and inflammatory responses in bacterial infection. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 3:142018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Selbach M, Schwanhausser B, Thierfelder N,
Fang Z, Khanin R and Rajewsky N: Widespread changes in protein
synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. 455:58–63. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fuentes F, Paredes-Gonzalez X and Kong AN:
Dietary glucosinolates sulforaphane, phenethyl isothiocyanate,
indole-3-carbinol/3,3′-diin-dolylmethane: Anti-oxidative
stress/inflammation, Nrf2, epigenetics/epigenomics and in vivo
cancer chemopreventive efficacy. Curr Pharmacol Rep. 1:179–196.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bonay M, Roux AL, Floquet J, Retory Y,
Herrmann JL, Lofaso F and Deramaudt TB: Caspase-independent
apoptosis in infected macrophages triggered by sulforaphane via
Nrf2/p38 signaling pathways. Cell death Discov. 1:150222015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jorgensen I, Rayamajhi M and Miao EA:
Programmed cell death as a defence against infection. Nat Rev
Immunol. 17:151–164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheng D, Li J, Zhang L and Hu L:
miR-142-5p suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis of human
osteosarcoma cell line, HOS, by targeting PLA2G16 through the
ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 17:1363–1371. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shu L, Zhang W, Huang G, Huang C, Zhu X,
Su G and Xu J: Troxerutin attenuates myocardial cell apoptosis
following myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition
of miR-146a-5p expression. J Cell Physiol. 234:9274–9282. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Atri C, Guerfali FZ and Laouini D: Role of
human macrophage polarization in inflammation during infectious
diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 19:E18012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sendi P and Proctor RA: Staphylococcus
aureus as an intracellular pathogen: The role of small colony
variants. Trends Microbiol. 17:54–58. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hamza T and Li B: Differential responses
of osteoblasts and macrophages upon Staphylococcus aureus
infection. BMC Microbiol. 14:2072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Reddick LE and Alto NM: Bacteria fighting
back: How pathogens target and subvert the host innate immune
system. Mol Cell. 54:321–328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Meduri GU, Kanangat S, Stefan J, Tolley E
and Schaberg D: Cytokines IL-1beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha enhance in
vitro growth of bacteria. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 160:961–967.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Di Domenico EG, Cavallo I, Bordignon V,
Prignano G, Sperduti I, Gurtner A, Trento E, Toma L, Pimpinelli F,
Capitanio B and Ensoli F: Inflammatory cytokines and biofilm
production sustain Staphylococcus aureus outgrowth and persistence:
A pivotal interplay in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Sci
Rep. 8:95732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ma J, Gulbins E, Edwards MJ, Caldwell CC,
Fraunholz M and Becker KA: Staphylococcus aureus α-toxin induces
inflammatory cytokines via lysosomal acid sphingomyelinase and
ceramides. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:2170–2184. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Klemm C, Bruchhagen C, van Kruchten A,
Niemann S, Löffler B, Peters G, Ludwig S and Ehrhardt C:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) regulate IL-6
over-production during concomitant influenza virus and
Staphylococcus aureus infection. Sci Rep. 7:424732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cohen P: Targeting protein kinases for the
development of anti-inflammatory drugs. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
21:317–324. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gao XJ, Wang TC, Zhang ZC, Cao YG, Zhang
NS and Guo MY: Brazilin plays an anti-inflammatory role with
regulating Toll-like receptor 2 and TLR 2 downstream pathways in
Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 27:130–137. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bi CL, Wang H, Wang YJ, Sun J, Dong JS,
Meng X and Li JJ: Selenium inhibits Staphylococcus aureus-induced
inflammation by suppressing the activation of the NF-κB and MAPK
signalling pathways in RAW264.7 macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol.
780:159–165. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
He W, Ma J, Chen Y, Jiang X, Wang Y, Shi
T, Zhang Q, Yang Y, Jiang X, Yin S, et al: Ephedrine hydrochloride
protects mice from Staphylococcus aureus-induced peritonitis. Am J
Transl Res. 10:670–683. 2018.
|
|
40
|
Watanabe I, Ichiki M, Shiratsuchi A and
Nakanishi Y: TLR2-mediated survival of Staphylococcus aureus in
macrophages: A novel bacterial strategy against host innate
immunity. J Immunol. 178:4917–4925. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Youn HS, Kim YS, Park ZY, Kim SY, Choi NY,
Joung SM, Seo JA, Lim KM, Kwak MK, Hwang DH and Lee JY:
Sulforaphane suppresses oligomerization of TLR4 in a
thiol-dependent manner. J Immunol. 184:411–419. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Takeuchi O, Hoshino K and Akira S: Cutting
edge: TLR2-deficient and MyD88-deficient mice are highly
susceptible to Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Immunol.
165:5392–5396. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hruz P, Zinkernagel AS, Jenikova G, Botwin
GJ, Hugot JP, Karin M, Nizet V and Eckmann L: NOD2 contributes to
cutaneous defense against Staphylococcus aureus through
alpha-toxin-dependent innate immune activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 106:12873–12878. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Muller-Anstett MA, Muller P, Albrecht T,
Nega M, Wagener J, Gao Q, Kaesler S, Schaller M, Biedermann T and
Götz F: Staphylococcal peptidoglycan co-localizes with Nod2 and
TLR2 and activates innate immune response via both receptors in
primary murine keratinocytes. PLoS One. 5:e131532010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Villamon E, Gozalbo D, Roig P, O'Connor
JE, Fradelizi D and Gil ML: Toll-like receptor-2 is essential in
murine defenses against Candida albicans infections. Microbes
infect. 6:1–7. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kong X, Thimmulappa R, Kombairaju P and
Biswal S: NADPH oxidase-dependent reactive oxygen species mediate
amplified TLR4 signaling and sepsis-induced mortality in
Nrf2-deficient mice. J Immunol. 185:569–577. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tanaka K, Kim SE, Yano H, Matsumoto G,
Ohuchida R, Ishikura Y, Araki M, Araki K, Park S, Komatsu T, et al:
MiR-142 is required for staphylococcus aureus clearance at skin
wound sites via small GTPase-mediated regulation of the neutrophil
actin cytoskeleton. J Invest Dermatol. 137:931–940. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lambert KA, Roff AN, Panganiban RP,
Douglas S and Ishmael FT: MicroRNA-146a is induced by inflammatory
stimuli in airway epithelial cells and augments the
anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. PLoS One.
13:e02054342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Roos J, Enlund E, Funcke JB, Tews D,
Holzmann K, Debatin KM, Wabitsch M and Fischer-Posovszky P:
miR-146a-mediated suppression of the inflammatory response in human
adipocytes. Sci Rep. 6:383392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|