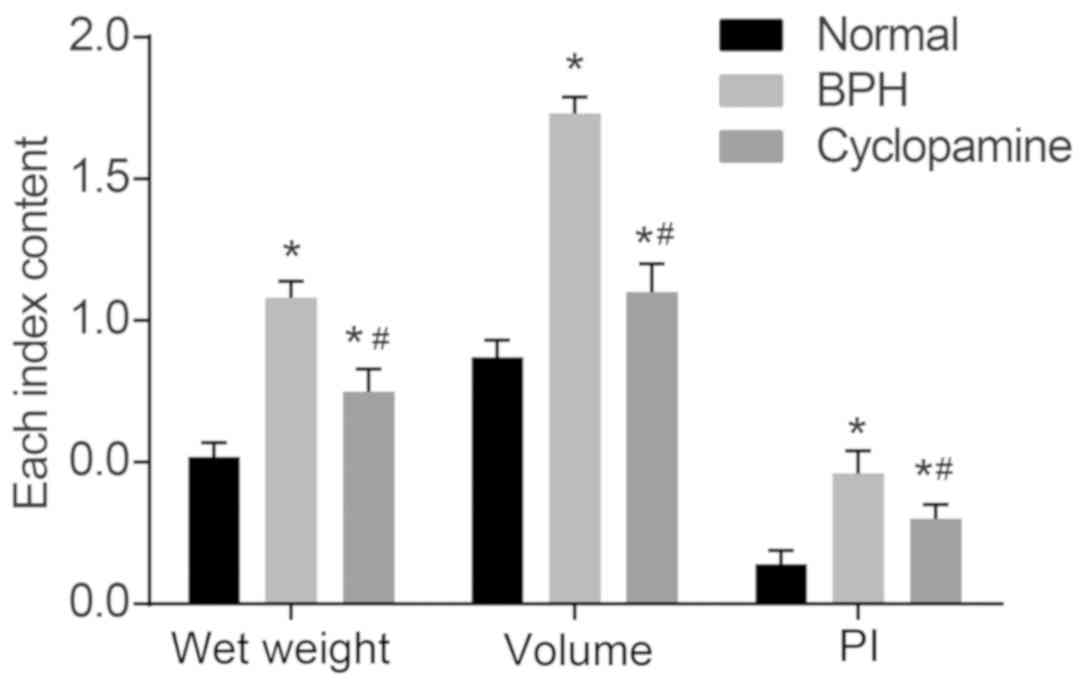
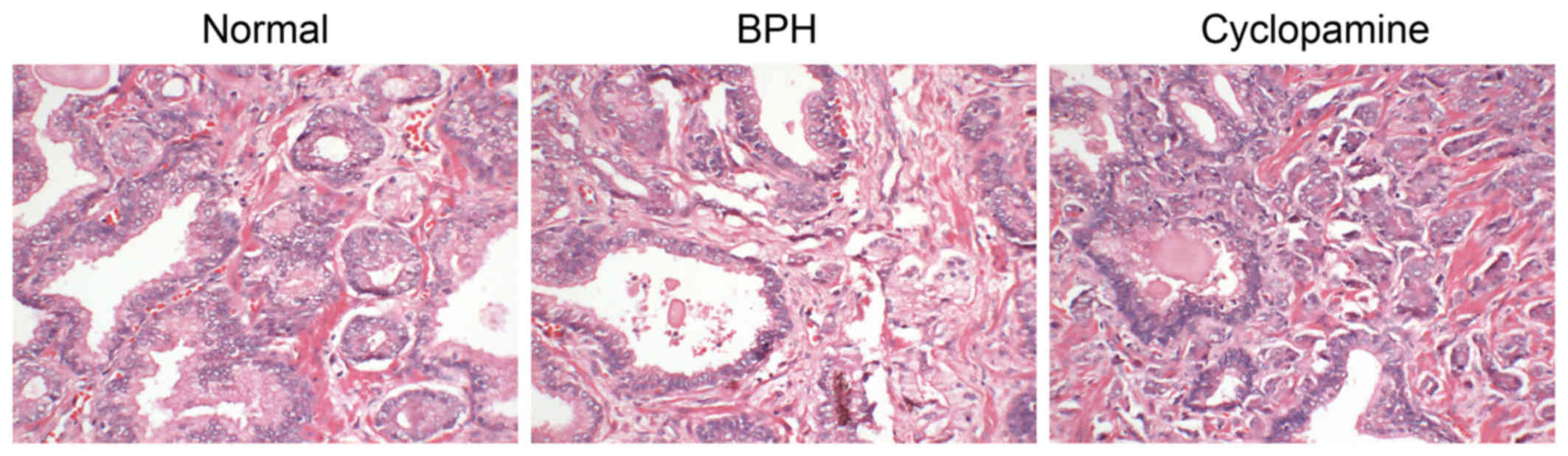
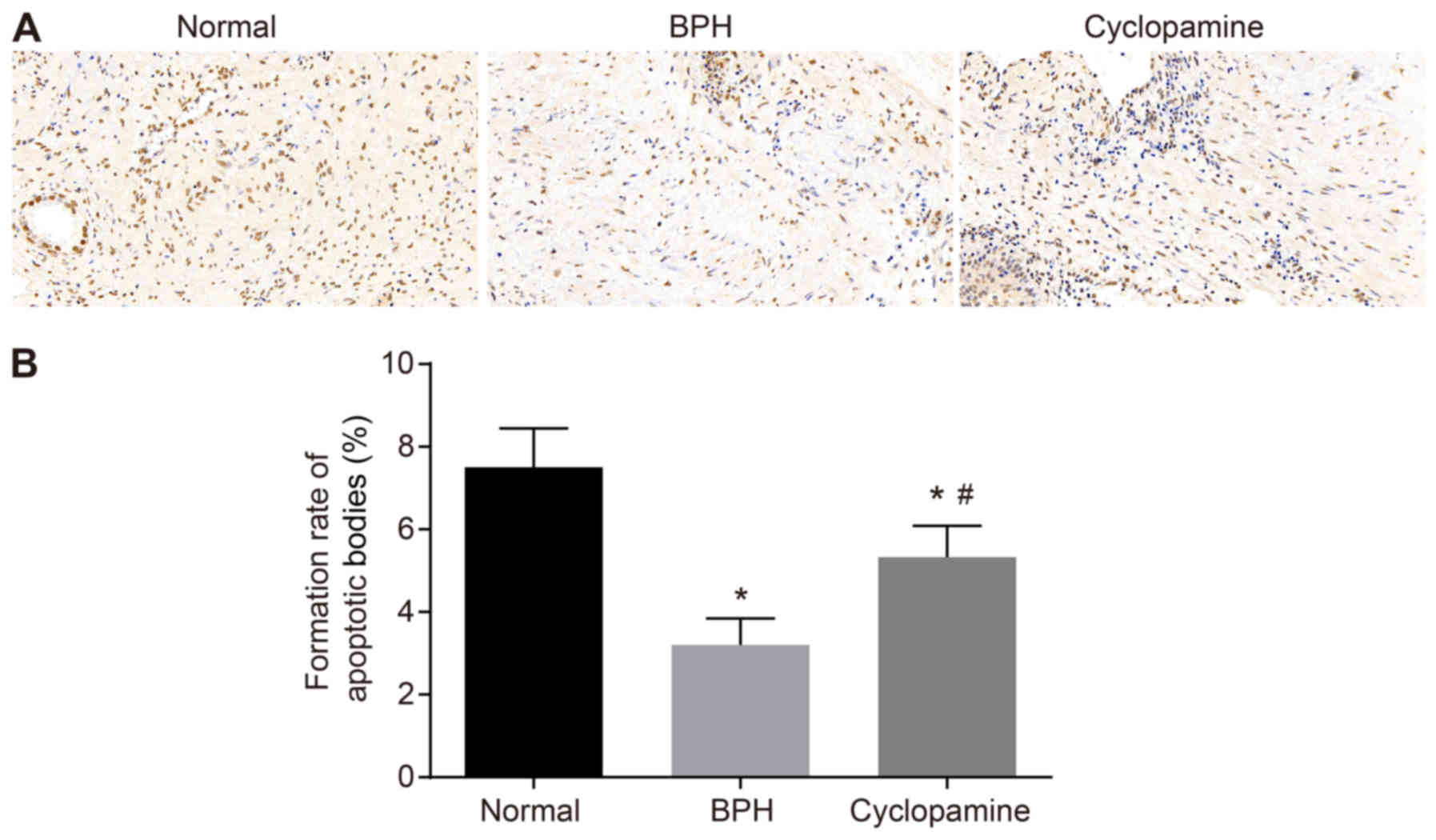
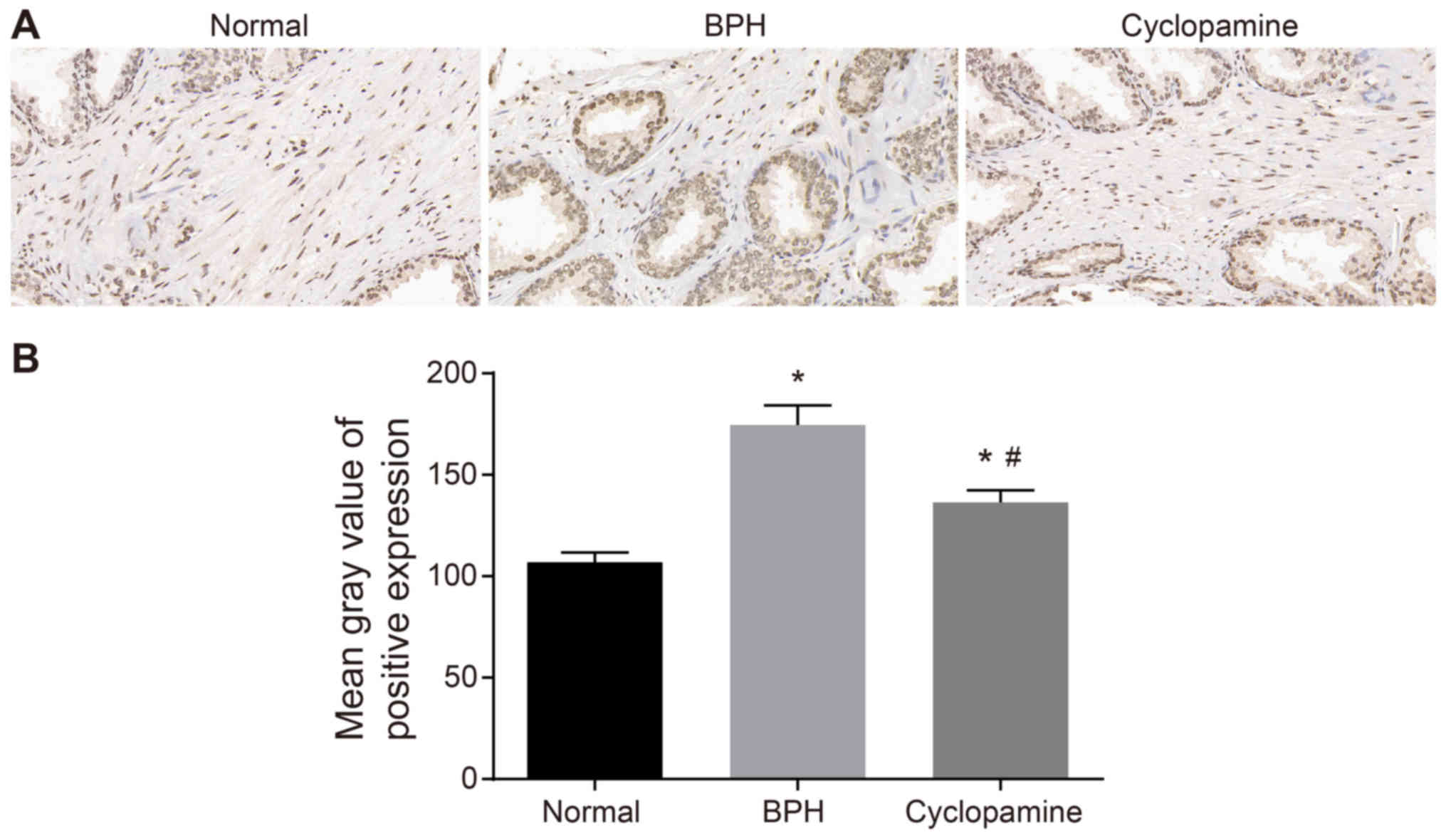
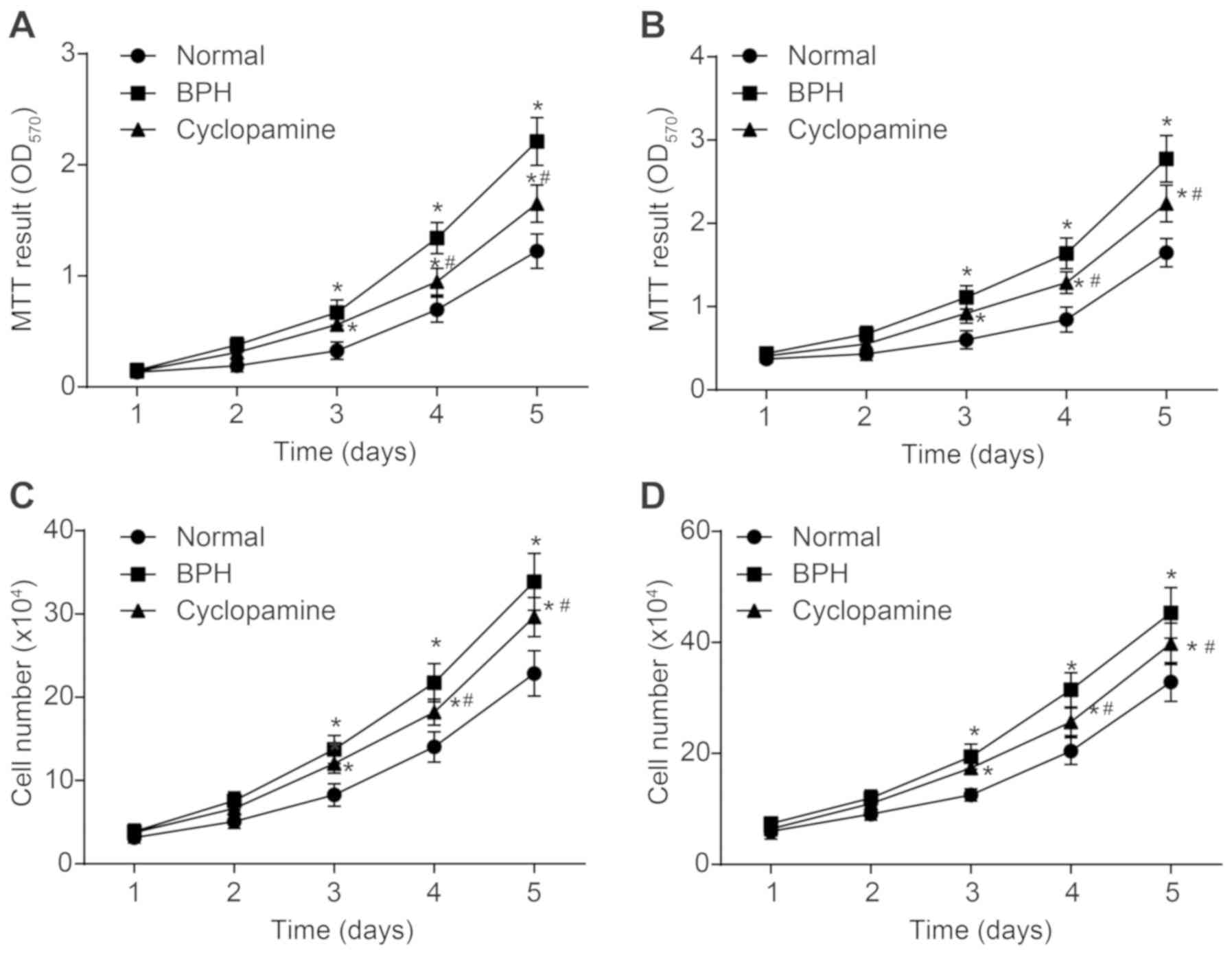
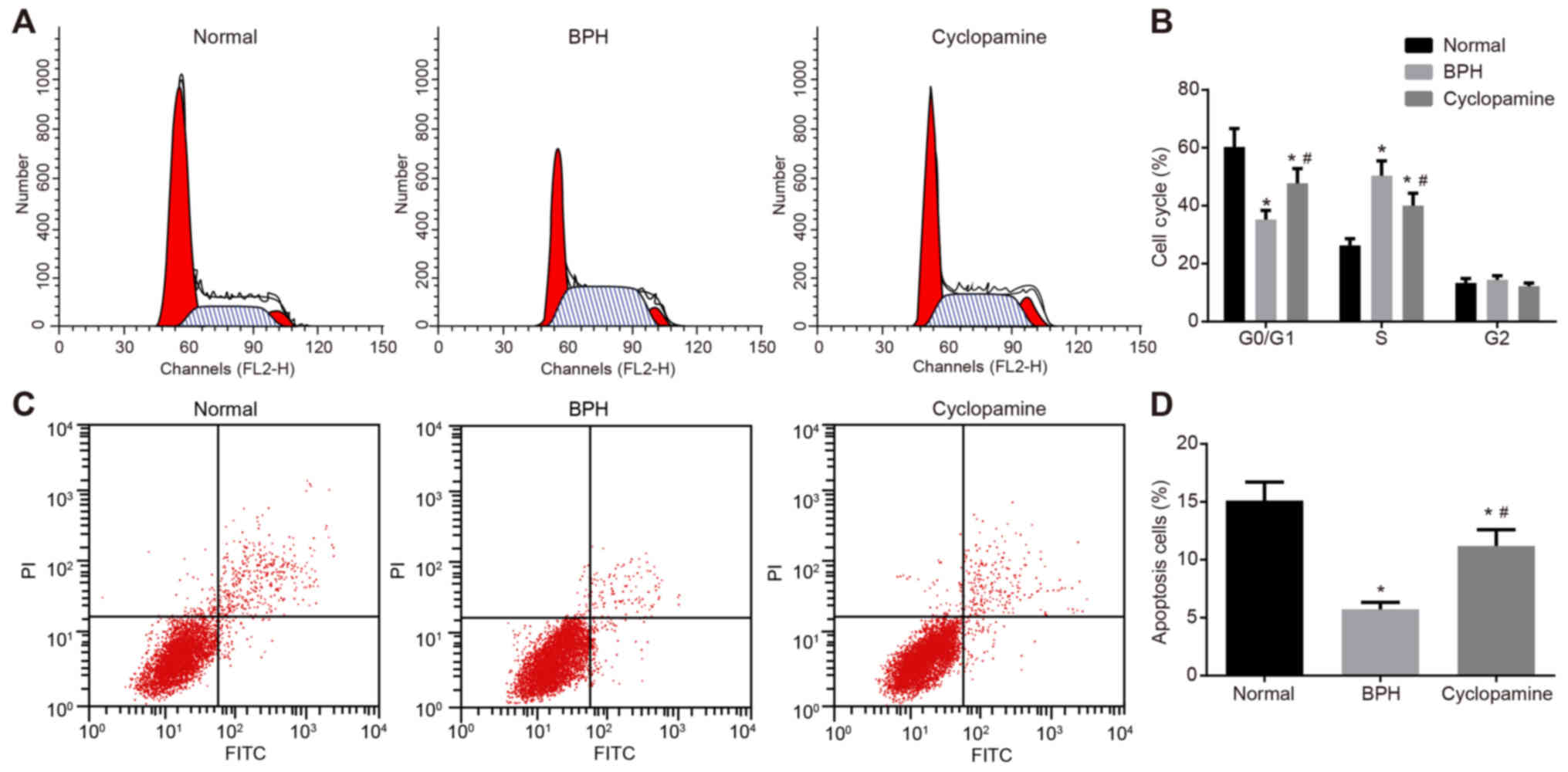
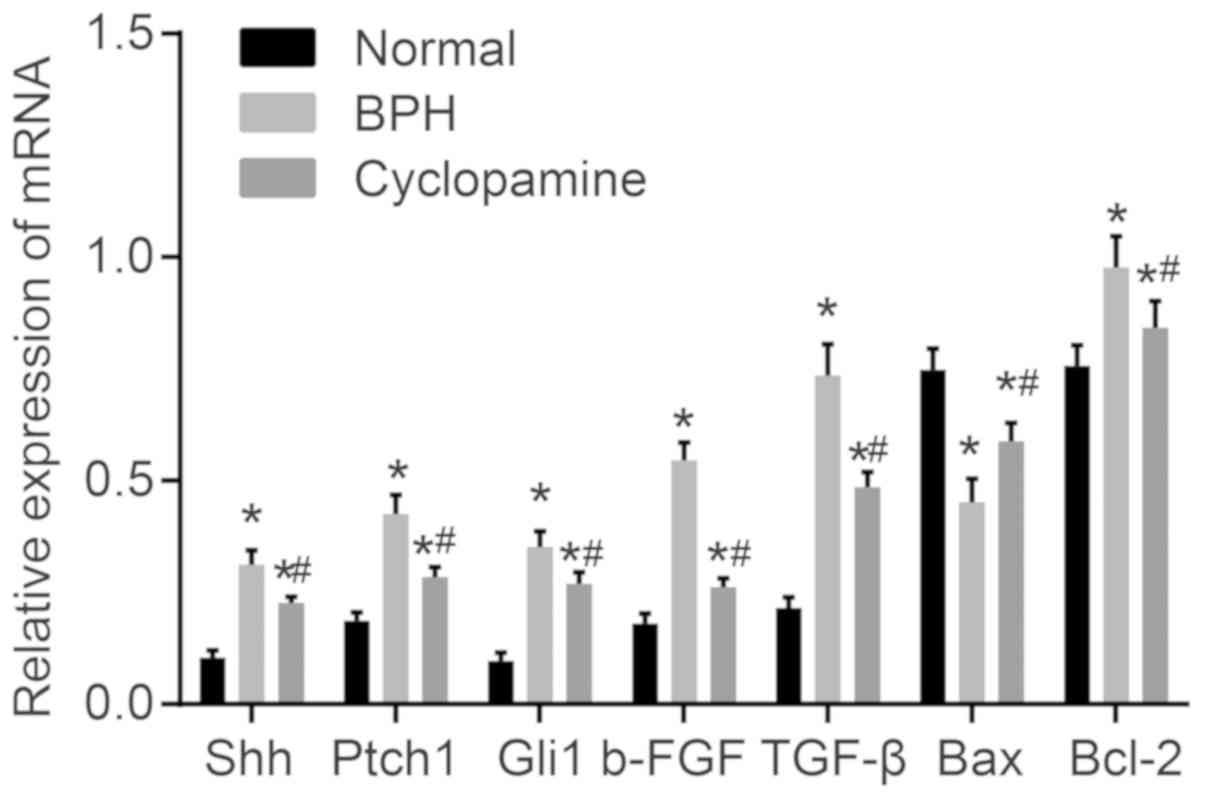
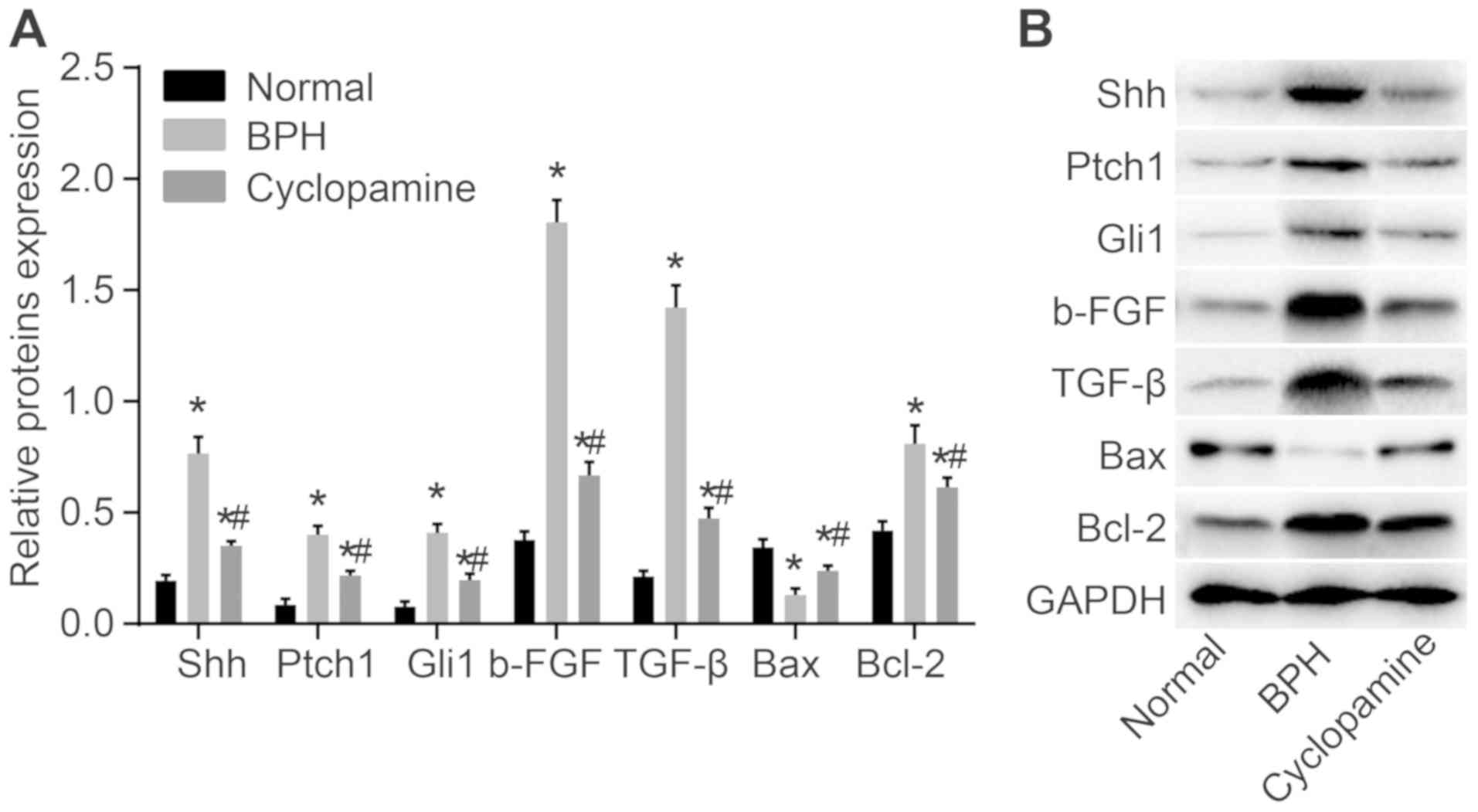
|
1
|
Kristal AR, Arnold KB, Schenk JM,
Neuhouser ML, Goodman P, Penson DF and Thompson IM: Dietary
patterns, supplement use, and the risk of symptomatic benign
prostatic hyperplasia: Results from the prostate cancer prevention
trial. Am J Epidemiol. 167:925–934. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
De Nunzio C, Kramer G, Marberger M,
Montironi R, Nelson W, Schröder F, Sciarra A and Tubaro A: The
controversial relationship between benign prostatic hyperplasia and
prostate cancer: The role of inflammation. Eur Urol. 60:106–117.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McVary KT, Roehrborn CG, Avins AL, Barry
MJ, Bruskewitz RC, Donnell RF, Foster HE Jr, Gonzalez CM, Kaplan
SA, Penson DF, et al: Update on AUA guideline on the management of
benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 185:1793–1803. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Neuhouser ML, Schenk J, Song YJ, Tangen
CM, Goodman PJ, Pollak M, Penson DF, Thompson IM and Kristal AR:
Insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor binding
protein-3 and risk of benign prostate hyperplasia in the prostate
cancer prevention trial. Prostate. 68:1477–1486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaplan SA, Walmsley K and Te AE:
Tolterodine extended release attenuates lower urinary tract
symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol.
174:2273–2275; discussion 2275-2276. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Keehn A, Taylor J and Lowe FC:
Phytotherapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Curr Urol Rep.
17:532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ok CY, Singh RR and Vega F: Aberrant
activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway in malignant
hematological neoplasms. Am J Pathol. 180:2–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Yoo YA, Kang MH, Kim JS and Oh SC: Sonic
hedgehog signaling promotes motility and invasiveness of gastric
cancer cells through TGF-beta-mediated activation of the ALK5-Smad
3 pathway. Carcinogenesis. 29:480–490. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen Q, Gao G and Luo S: Hedgehog
signaling pathway and ovarian cancer. Chin J Cancer Res.
25:346–353. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taylor R, Long J, Yoon JW, Childs R,
Sylvestersen KB, Nielsen ML, Leong KF, Iannaccone S, Walterhouse
DO, Robbins DJ and Iannaccone P: Regulation of GLI1 by cis DNA
elements and epigenetic marks. DNA Repair (Amst). 79:10–21. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Skoda AM, Simovic D, Karin V, Kardum V,
Vranic S and Serman L: The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway
in cancer: A comprehensive review. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 18:8–20.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Bar EE, Chaudhry A, Lin A, Fan X, Schreck
K, Matsui W, Piccirillo S, Vescovi AL, DiMeco F, Olivi A and
Eberhart CG: Cyclopamine-mediated hedgehog pathway inhibition
depletes stem-like cancer cells in glioblastoma. Stem Cells.
25:2524–2533. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kumar SK, Roy I, Anchoori RK, Fazli S,
Maitra A, Beachy PA and Khan SR: Targeted inhibition of hedgehog
signaling by cyclopamine prodrugs for advanced prostate cancer.
Bioorg Med Chem. 16:2764–2768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Atkins D, Reiffen KA, Tegtmeier CL,
Winther H, Bonato MS and Störkel S: Immunohistochemical detection
of EGFR in paraffin-embedded tumor tissues: Variation in staining
intensity due to choice of fixative and storage time of tissue
sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 52:893–901. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang X, Harrington N, Moraes RC, Wu MF,
Hilsenbeck SG and Lewis MT: Cyclopamine inhibition of human breast
cancer cell growth independent of Smoothened (Smo). Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 115:505–521. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Slusarz A, Shenouda NS, Sakla MS,
Drenkhahn SK, Narula AS, MacDonald RS, Besch-Williford CL and
Lubahn DB: Common botanical compounds inhibit the hedgehog
signaling pathway in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 70:3382–3390.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen JK, Taipale J, Cooper MK and Beachy
PA: Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of
cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev. 16:2743–2748. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Palumbo A, Casanova LM, Corrêa MFP, Da
Costa NM, Nasciutti LE and Costa SS: Potential therapeutic effects
of underground parts of Kalanchoe gastonis-bonnieri on benign
prostatic hyperplasia. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2019:63407572019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Kogan-Sakin I, Cohen M, Paland N, Madar S,
Solomon H, Molchadsky A, Brosh R, Buganim Y, Goldfinger N, Klocker
H, et al: Prostate stromal cells produce CXCL-1, CXCL-2, CXCL-3 and
IL-8 in response to epithelia-secreted IL-1. Carcinogenesis.
30:698–705. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu XY, Liu X, Xu L, Gui B, Yang QY, Yan
JY and Sun ZY: A mathematical model for predicting putative
association between E2/T ratio and the development of benign
prostate hyperplasia in rats. Biol Reprod. 100:133–138. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shaw A and Bushman W: Hedgehog signaling
in the prostate. J Urol. 177:832–838. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang L, Yang JR, Yang LY and Liu ZT:
Chronic inflammation in benign prostatic hyperplasia: Implications
for therapy. Med Hypotheses. 70:1021–1023. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kobayashi S, Tomiyama Y, Tatemichi S,
Hoyano Y, Kobayashi M and Yamazaki Y: Effects of silodosin and
tamsulosin on the urethra and cardiovascular system in young and
old dogs with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur J Pharmacol.
613:135–140. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Adisa JO, Egbujo EC, Ibrahim B, Musa B and
Madukwe J: Expression of some selected cytokeratins and Ki67
protein in prostatic tumor: Can these be used as tumor markers. Pan
Afr Med J. 20:462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Seligson DB, Yu H, Tze S, Said J, Pantuck
AJ, Cohen P and Lee KW: IGFBP-3 nuclear localization predicts human
prostate cancer recurrence. Horm Cancer. 4:12–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Fonseca-Alves CE, Kobayashi PE, Palmieri C
and Laufer-Amorim R: Investigation of c-KIT and Ki67 expression in
normal, preneoplastic and neoplastic canine prostate. BMC Vet Res.
13:3802017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zheng H, Xu W, Lin J, Peng J and Hong Z:
Qianliening capsule treats benign prostatic hyperplasia via
induction of prostatic cell apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 7:848–854.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vezina CM and Bushman AW: Hedgehog
signaling in prostate growth and benign prostate hyperplasia. Curr
Urol Rep. 8:275–280. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang X, Fan G, Wei F, Bu Y and Huang W:
Hyperoside protects rat ovarian granulosa cells against hydrogen
peroxide-induced injury by sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Chem
Biol Interact. 310:1087592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sharma A, De R, Javed S, Srinivasan R, Pal
A and Bhattacharyya S: Sonic hedgehog pathway activation regulates
cervical cancer stem cell characteristics during epithelial to
mesenchymal transition. J Cell Physiol Feb. 4:Epub ahead of
print.
|
|
32
|
Penna G, Fibbi B, Amuchastegui S, Corsiero
E, Laverny G, Silvestrini E, Chavalmane A, Morelli A, Sarchielli E,
Vannelli GB, et al: The vitamin D receptor agonist elocalcitol
inhibits IL-8-dependent benign prostatic hyperplasia stromal cell
proliferation and inflammatory response by targeting the RhoA/Rho
kinase and NF-kappaB pathways. Prostate. 69:480–493. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Oue T, Yoneda A, Uehara S, Yamanaka H and
Fukuzawa M: Increased expression of the hedgehog signaling pathway
in pediatric solid malignancies. J Pediatr Surg. 45:387–392. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin J, Zhou J, Xu W, Hong Z and Peng J:
Qianliening capsule inhibits benign prostatic hyperplasia
angiogenesis via the HIF-1α signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med.
8:118–124. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Iacopino F, Angelucci C, Lama G, Zelano G,
La Torre G, D'Addessi A, Giovannini C, Bertaccini A, Macaluso MP,
Martorana G and Sica G: Apoptosis-related gene expression in benign
prostatic hyperplasia and prostate carcinoma. Anticancer Res.
26:1849–1854. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shariat SF, Ashfaq R, Roehrborn CG, Slawin
KM and Lotan Y: Expression of survivin and apoptotic biomarkers in
benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 174:2046–2050. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shum CF, Lau W and Teo CPC: Medical
therapy for clinical benign prostatic hyperplasia: α-1 antagonists,
5α reductase inhibitors and their combination. Asian J Urol.
4:185–190. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang G, Zhu F, Han G, Li Z, Yu Q, Li Z
and Li J: Silencing of URG11 expression inhibits the proliferation
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in benign prostatic
hyperplasia cells via the RhoA/ROCK1 pathway. Mol Med Rep.
18:391–398. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Z, Xiao X, Ge R, Li J, Johnson CW,
Rassoulian C and Olumi AF: Metformin inhibits the proliferation of
benign prostatic epithelial cells. PLoS One. 12:e01733352017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|