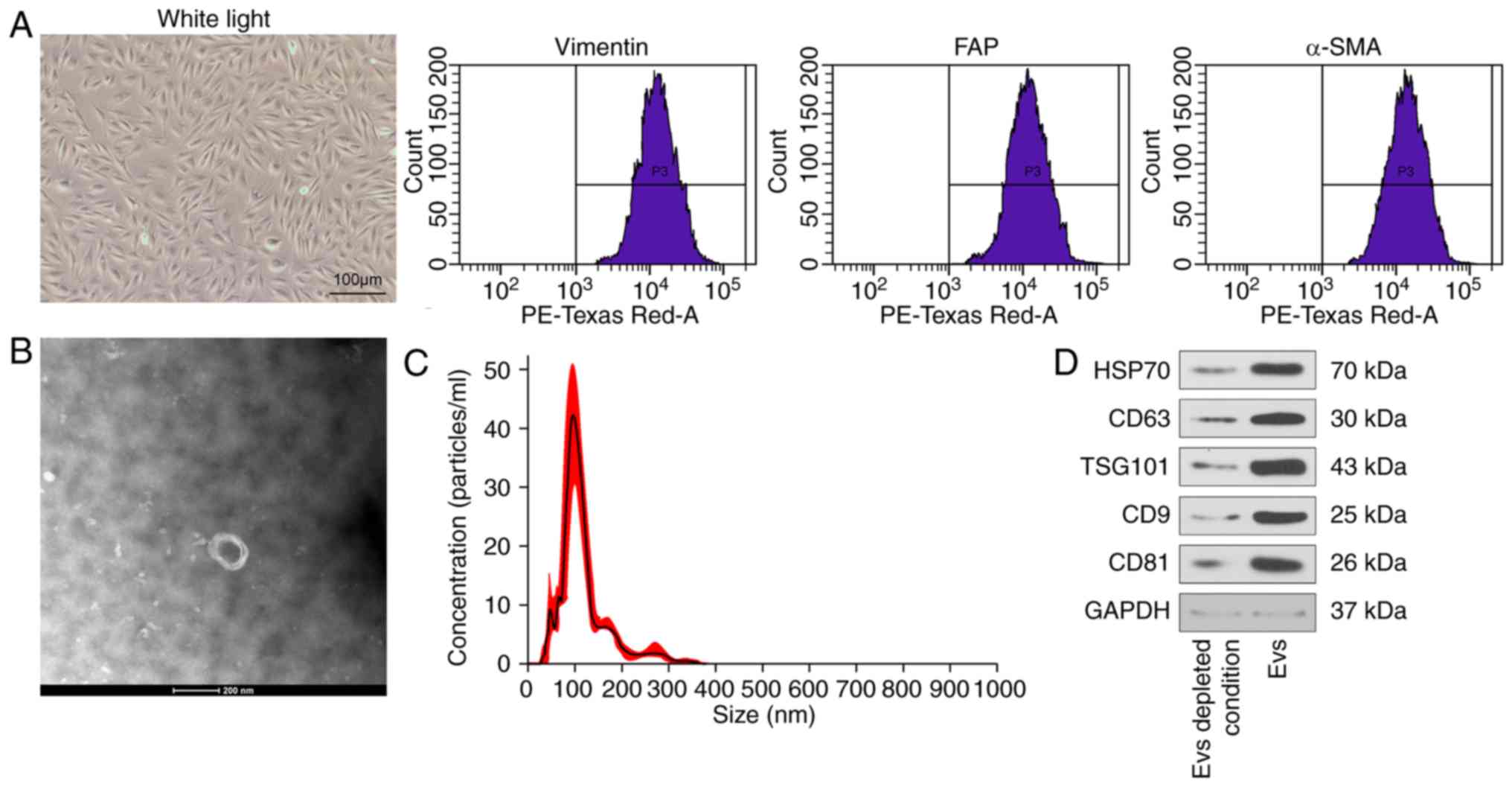
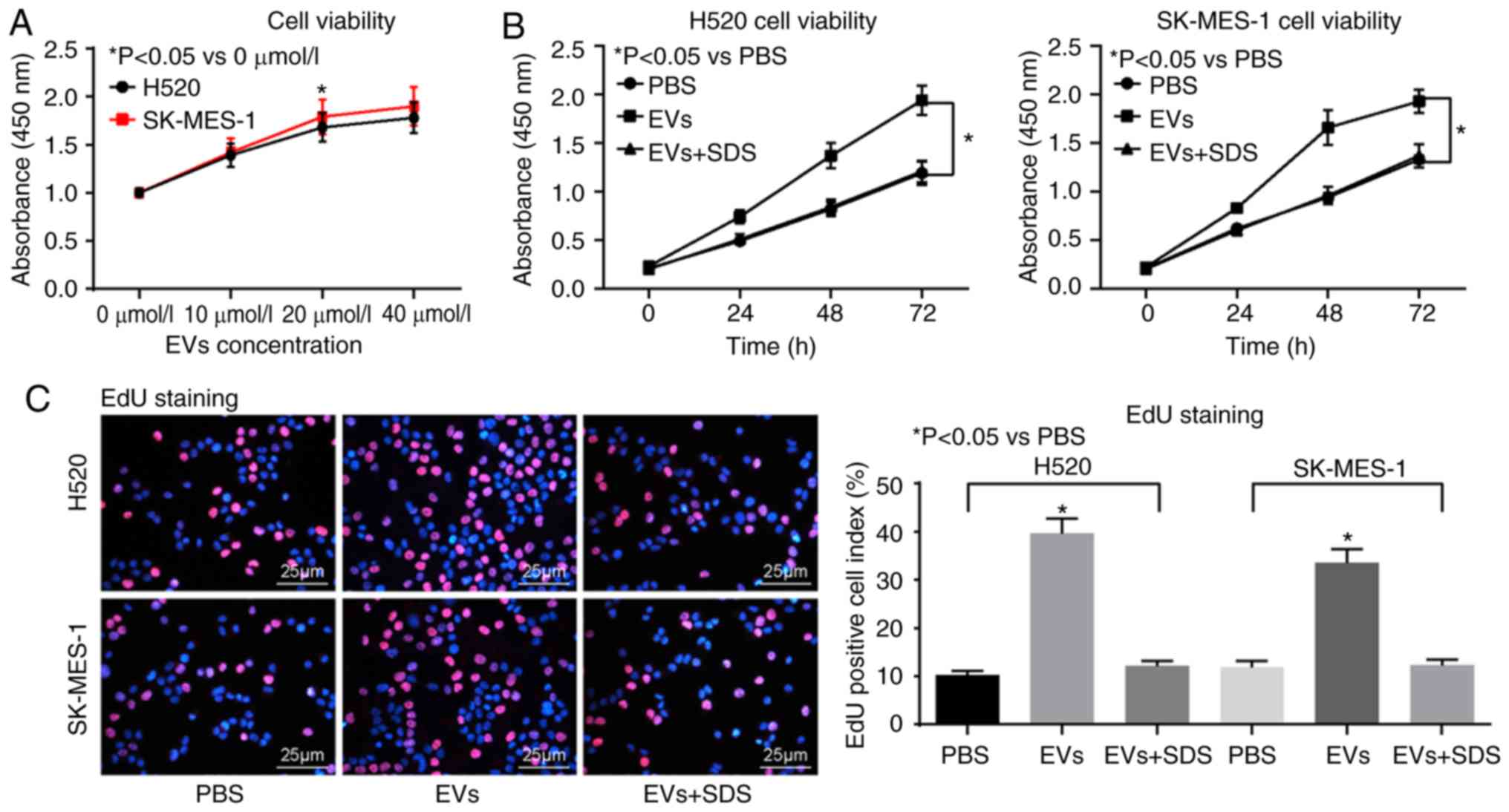
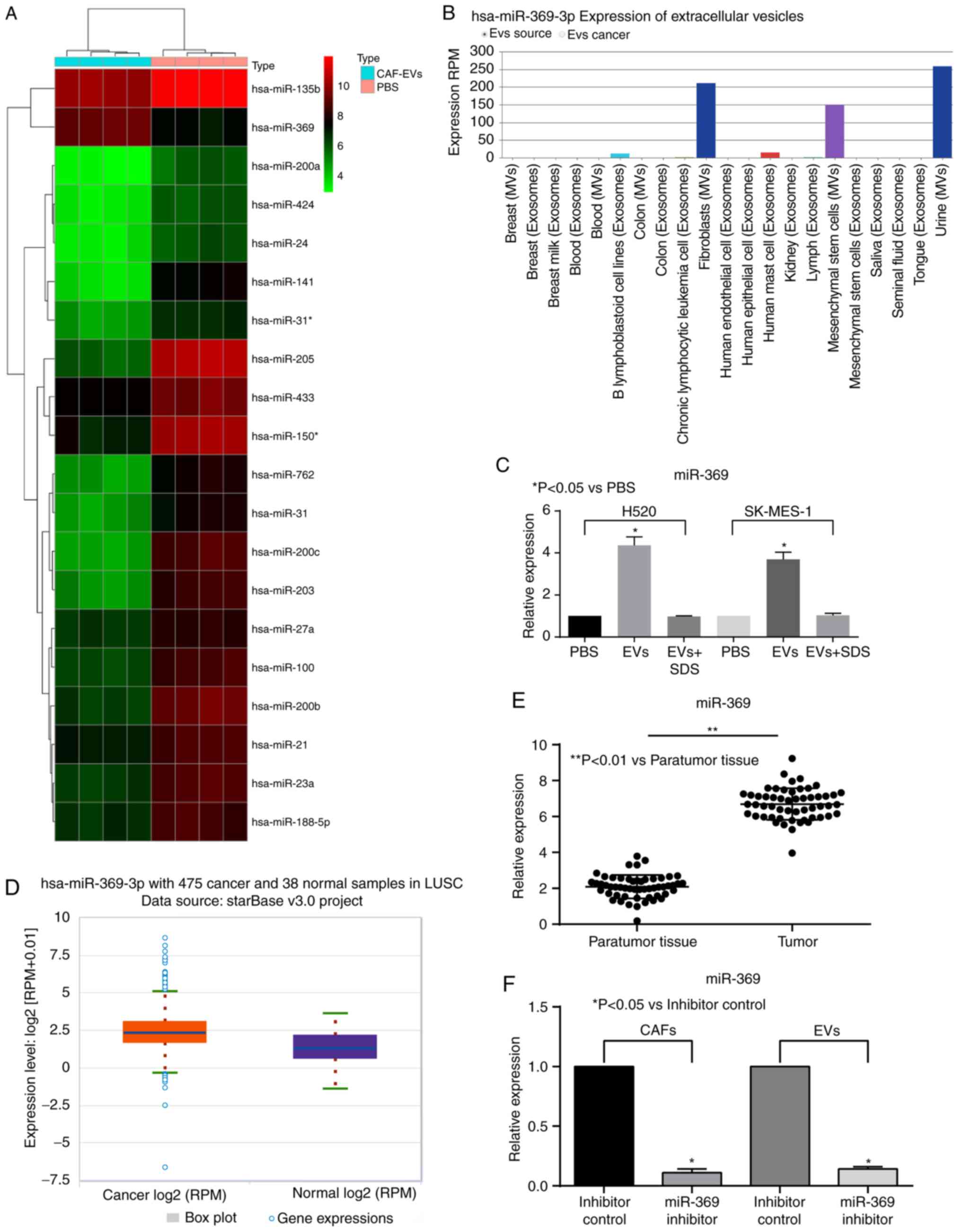
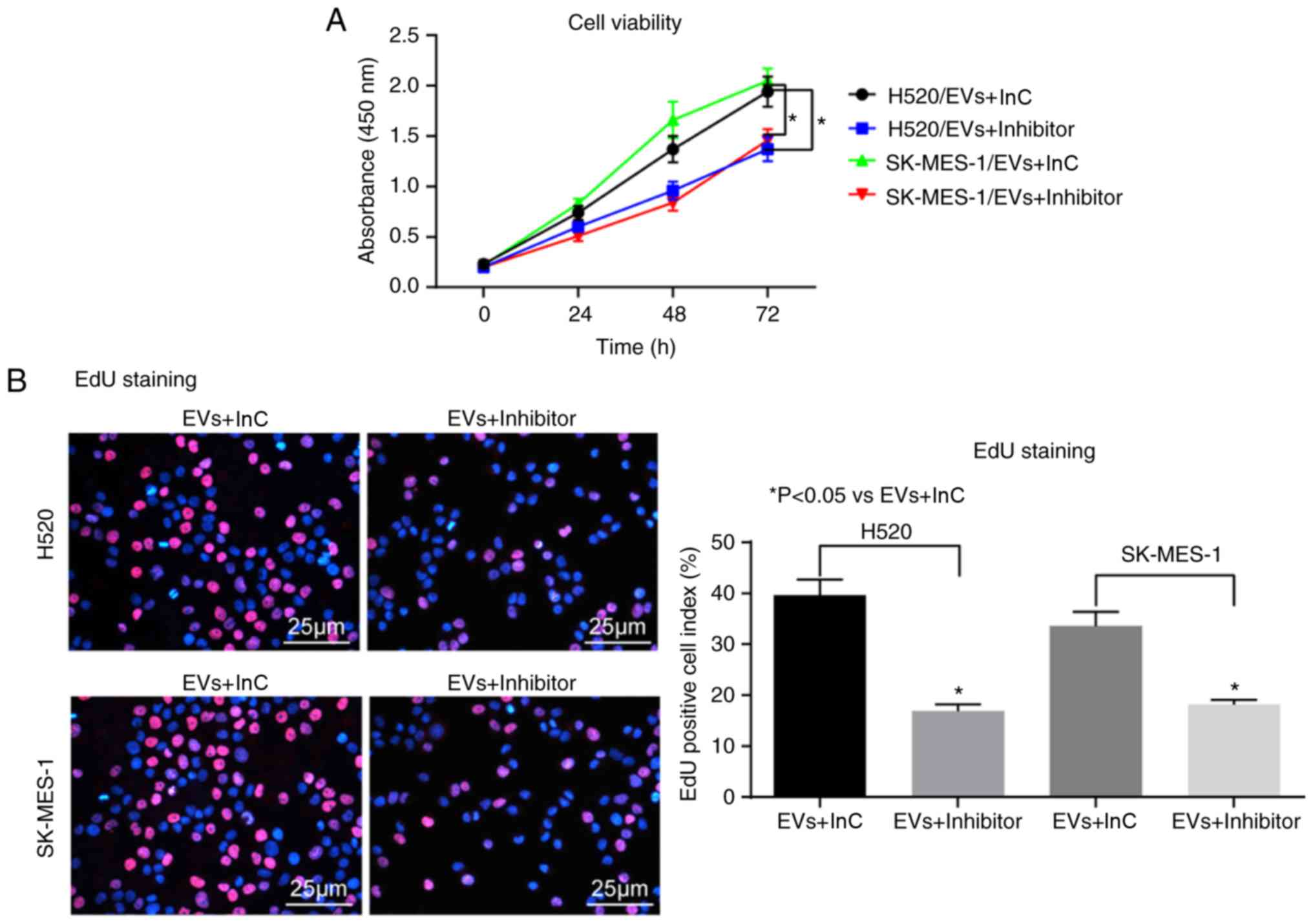
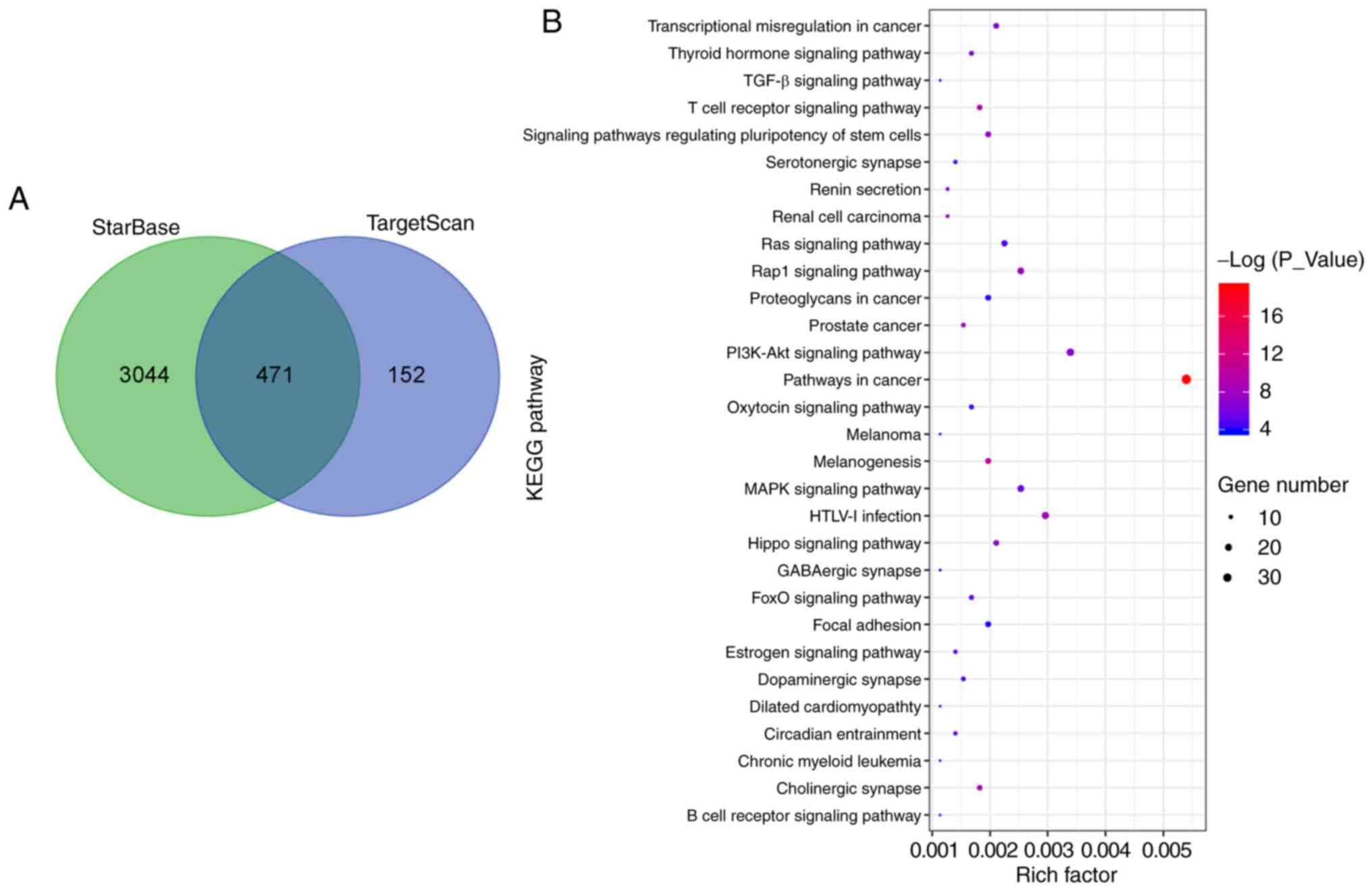
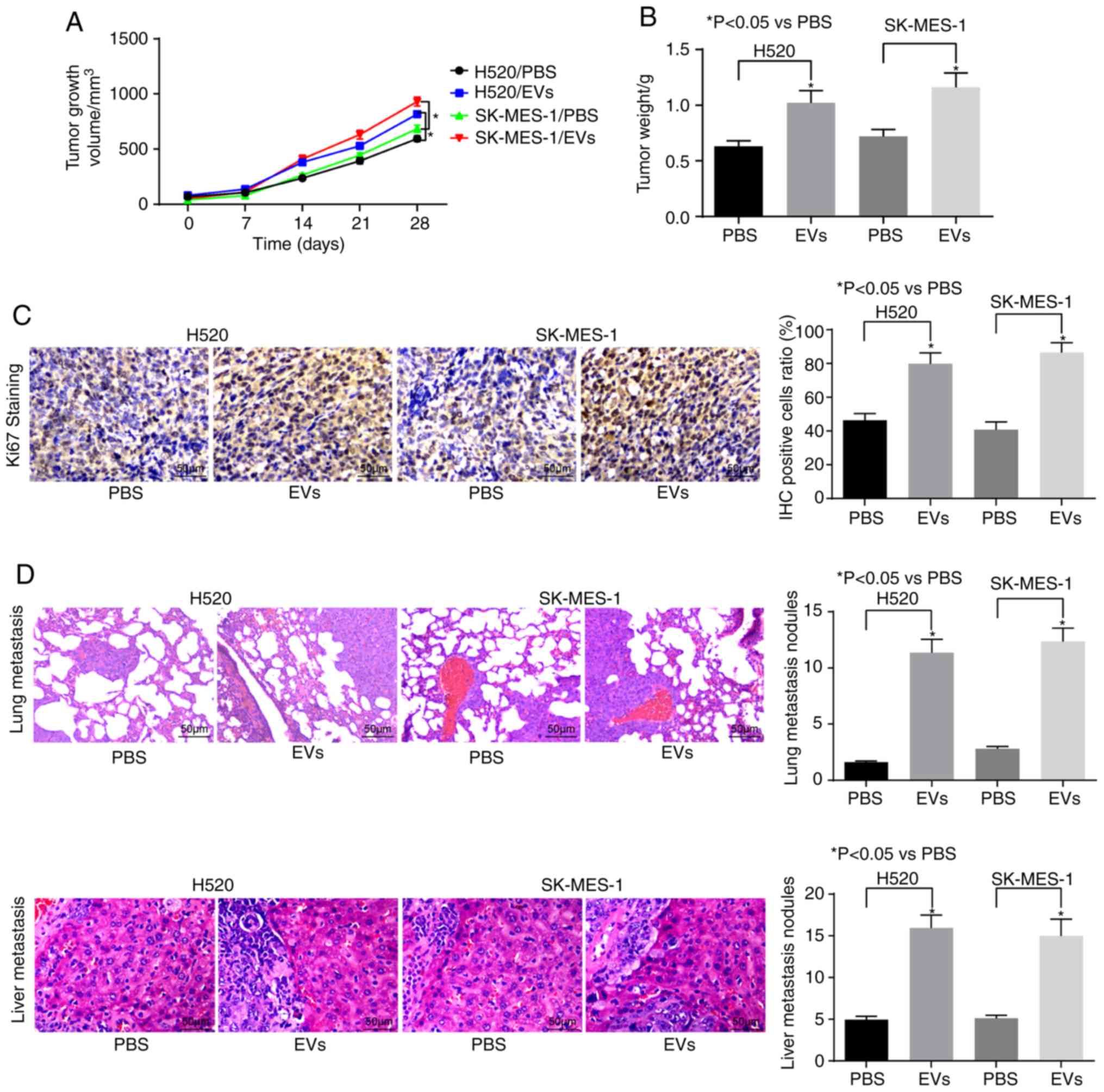
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL and Jemal A: Lung
Cancer Statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 893:1–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xu F, Zhang H, Chen J, Lin L and Chen Y:
Immune signature of T follicular helper cells predicts clinical
prognostic and therapeutic impact in lung squamous cell carcinoma.
Int Immunopharmacol. 81:1059322020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shi Y, Li Y, Yan C, Su H and Ying K:
Identification of key genes and evaluation of clinical outcomes in
lung squamous cell carcinoma using integrated bioinformatics
analysis. Oncol Lett. 18:5859–5870. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Erez N, Truitt M, Olson P, Arron ST and
Hanahan D: Cancer-associated fibroblasts are activated in incipient
neoplasia to orchestrate tumor-promoting inflammation in an
NF-kappaB-dependent manner. Cancer Cell. 17:135–147. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hanley CJ, Mellone M, Ford K, Thirdborough
SM, Mellows T, Frampton SJ, Smith DM, Harden E, Szyndralewiez C,
Bullock M, et al: Targeting the Myofibroblastic Cancer-Associated
Fibroblast Phenotype Through Inhibition of NOX4. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 110:2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Raposo G and Stoorvogel W: Extracellular
vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol.
200:373–383. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang X, Li Y, Zou L and Zhu Z: Role of
exosomes in crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and
cancer cells. Front Oncol. 9:3562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun LP, Xu K, Cui J, Yuan DY, Zou B, Li J,
Liu JL, Li KY, Meng Z and Zhang B: Cancer-associated
fibroblast-derived exosomal miR3825p promotes the migration and
invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 42:1319–1328.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hao GJ, Ding YH, Wen H, Li XF, Zhang W, Su
HY, Liu DM and Xie NL: Attenuation of deregulated miR-369-3p
expression sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin
via modulation of the nucleotide sugar transporter SLC35F5. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 488:501–508. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42(Database issue): D92–D97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tlemsani C, Pecuchet N, Gruber A,
Laurendeau I, Danel C, Riquet M, Le Pimpec-Barthes F, Fabre E,
Mansuet-Lupo A, Damotte D, et al: NF1 mutations identify molecular
and clinical subtypes of lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Med.
8:4330–4337. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brems H, Park C, Maertens O, Pemov A,
Messiaen L, Upadhyaya M, Claes K, Beert E, Peeters K, Mautner V, et
al: Glomus tumors in neurofibromatosis type 1: Genetic, functional,
and clinical evidence of a novel association. Cancer Res.
69:7393–7401. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stites EC, Trampont PC, Haney LB, Walk SF
and Ravichandran KS: Cooperation between Noncanonical Ras Network
Mutations. Cell Rep. 10:307–316. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang X, Min S, Liu H, Wu N, Liu X, Wang T,
Li W, Shen Y, Wang H, Qian Z, et al: Nf1 loss promotes Kras-driven
lung adenocarcinoma and results in Psat1-mediated glutamate
dependence. EMBO Mol Med. 11:e98562019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Redig AJ, Capelletti M, Dahlberg SE, Sholl
LM, Mach S, Fontes C, Shi Y, Chalasani P and Jänne PA: Clinical and
molecular characteristics of NF1-mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 22:3148–3156. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Modak JM, Roy-O'Reilly M, Zhu L, Staff I
and McCullough LD: Differential MicroRibonucleic acid expression in
cardioembolic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 28:121–124. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Morishima
K and Tanabe M: New approach for understanding genome variations in
KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D590–D595. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Guo L, Li Y, Feng GH, Teng F, Li
W and Zhou Q: MicroRNA-494 promotes cancer progression and targets
adenomatous polyposis coli in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer.
17:12018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ji Y, Han Z, Shao L and Zhao Y: Evaluation
of in vivo antitumor effects of low-frequency ultrasound-mediated
miRNA-133a microbubble delivery in breast cancer. Cancer Med.
5:2534–2543. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wei S, Peng L, Yang J, Sang H, Jin D, Li
X, Chen M, Zhang W, Dang Y and Zhang G: Exosomal transfer of
miR-15b-3p enhances tumorigenesis and malignant transformation
through the DYNLT1/Caspase-3/Caspase-9 signaling pathway in gastric
cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang XY, Huang ZL, Huang J, Xu B, Huang
XY, Xu YH, Zhou J and Tang ZY: Exosomal circRNA-100338 promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via enhancing invasiveness and
angiogenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu Y, Liu H, Shi X, Yao Y, Yang W and Song
Y: The long non-coding RNA HNF1A-AS1 regulates proliferation and
metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:9160–9172. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Thery C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ,
Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, Antoniou A, Arab T, Archer F,
Atkin-Smith GK, et al: Minimal information for studies of
extra-cellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of
the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of
the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 7:15357502018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kalluri R: The biology and function of
fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:582–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ab Razak NS, Ab Mutalib NS, Mohtar MA and
Abu N: Impact of chemotherapy on extracellular vesicles:
Understanding the chemo-EVs. Front Oncol. 9:11132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baffa R, Fassan M, Volinia S, O'Hara B,
Liu CG, Palazzo JP, Gardiman M, Rugge M, Gomella LG, Croce CM and
Rosenberg A: MicroRNA expression profiling of human metastatic
cancers identifies cancer gene targets. J Pathol. 219:214–221.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qian B, Wang DM, Gu XS, Zhou K, Wu J,
Zhang CY and He XY: LncRNA H19 serves as a ceRNA and participates
in non-small cell lung cancer development by regulating
microRNA-107. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:5946–5953.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Philpott C, Tovell H, Frayling IM, Cooper
DN and Upadhyaya M: The NF1 somatic mutational landscape in
sporadic human cancers. Hum Genomics. 11:132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rahman MA, Barger JF, Lovat F, Gao M,
Otterson GA and Nana-Sinkam P: Lung cancer exosomes as drivers of
epithelial mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget. 7:54852–54866. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
You J, Li M, Cao LM, Gu QH, Deng PB, Tan Y
and Hu CP: Snail1-dependent cancer-associated fibroblasts induce
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells via
exosomes. QJM. 112:581–590. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
He S, Li Z, Yu Y, Zeng Q, Cheng Y, Ji W,
Xia W and Lu S: Exosomal miR-499a-5p promotes cell proliferation,
migration and EMT via mTOR signaling pathway in lung
adenocarcinoma. Exp Cell Res. 379:203–213. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Verset L, Tommelein J, Moles Lopez X,
Decaestecker C, Boterberg T, De Vlieghere E, Salmon I, Mareel M,
Bracke M, De Wever O and Demetter P: Impact of neoadjuvant therapy
on cancer-associated fibroblasts in rectal cancer. Radiother Oncol.
116:449–454. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wei M, Yang T, Chen X, Wu Y, Deng X, He W,
Yang J and Wang Z: Malignant ascites-derived exosomes promote
proliferation and induce carcinoma-associated fibroblasts
transition in peritoneal mesothelial cells. Oncotarget.
8:42262–42271. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zheng X, Bahr M and Doeppner TR: From
tumor metastasis towards cerebral ischemia-extracellular vesicles
as a general concept of intercellular communication processes. Int
J Mol Sci. 20:E59952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ning X, Zhang H, Wang C and Song X:
Exosomes released by gastric cancer cells induce transition of
pericytes into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Med Sci Monit.
24:2350–2359. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|