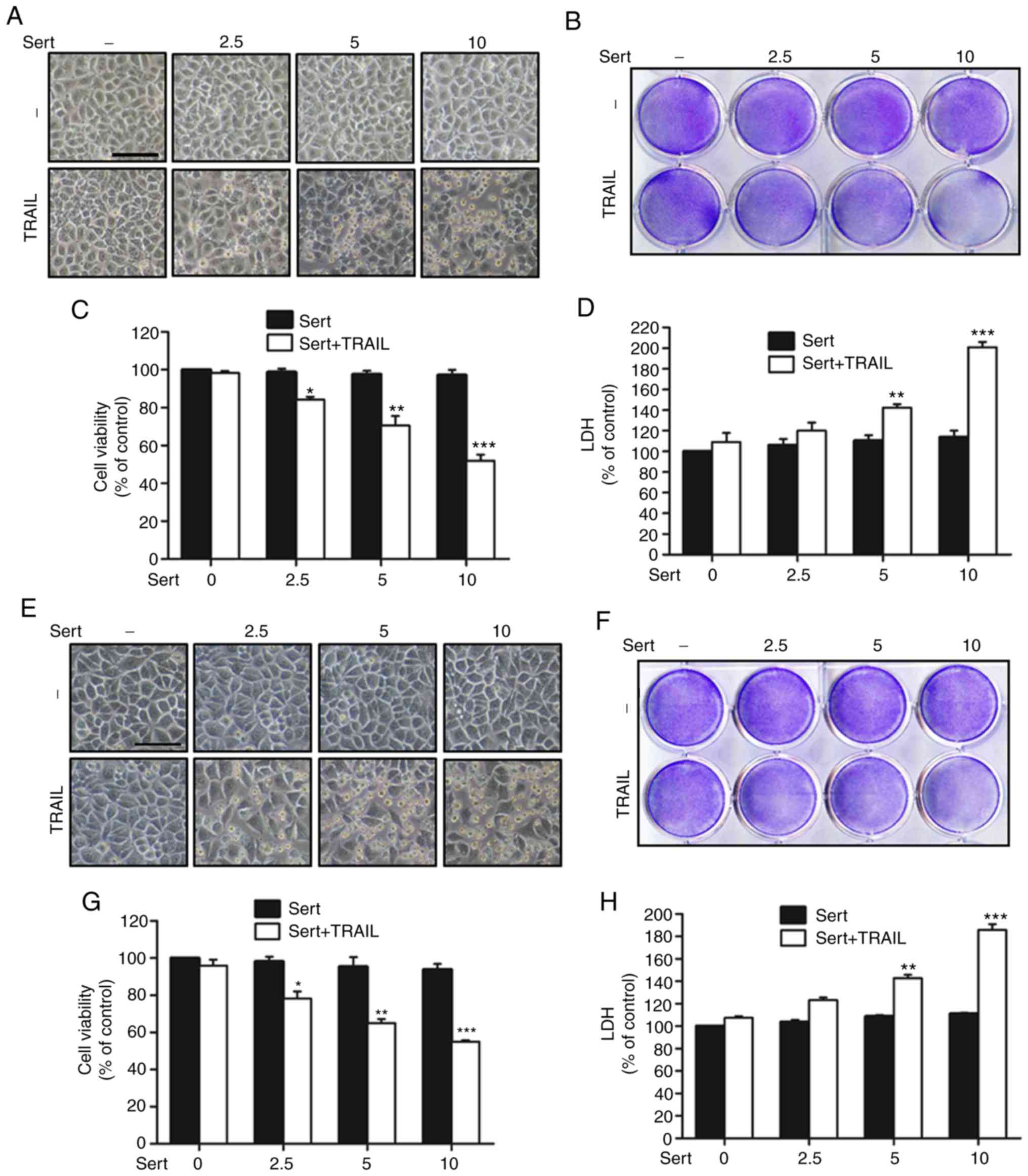
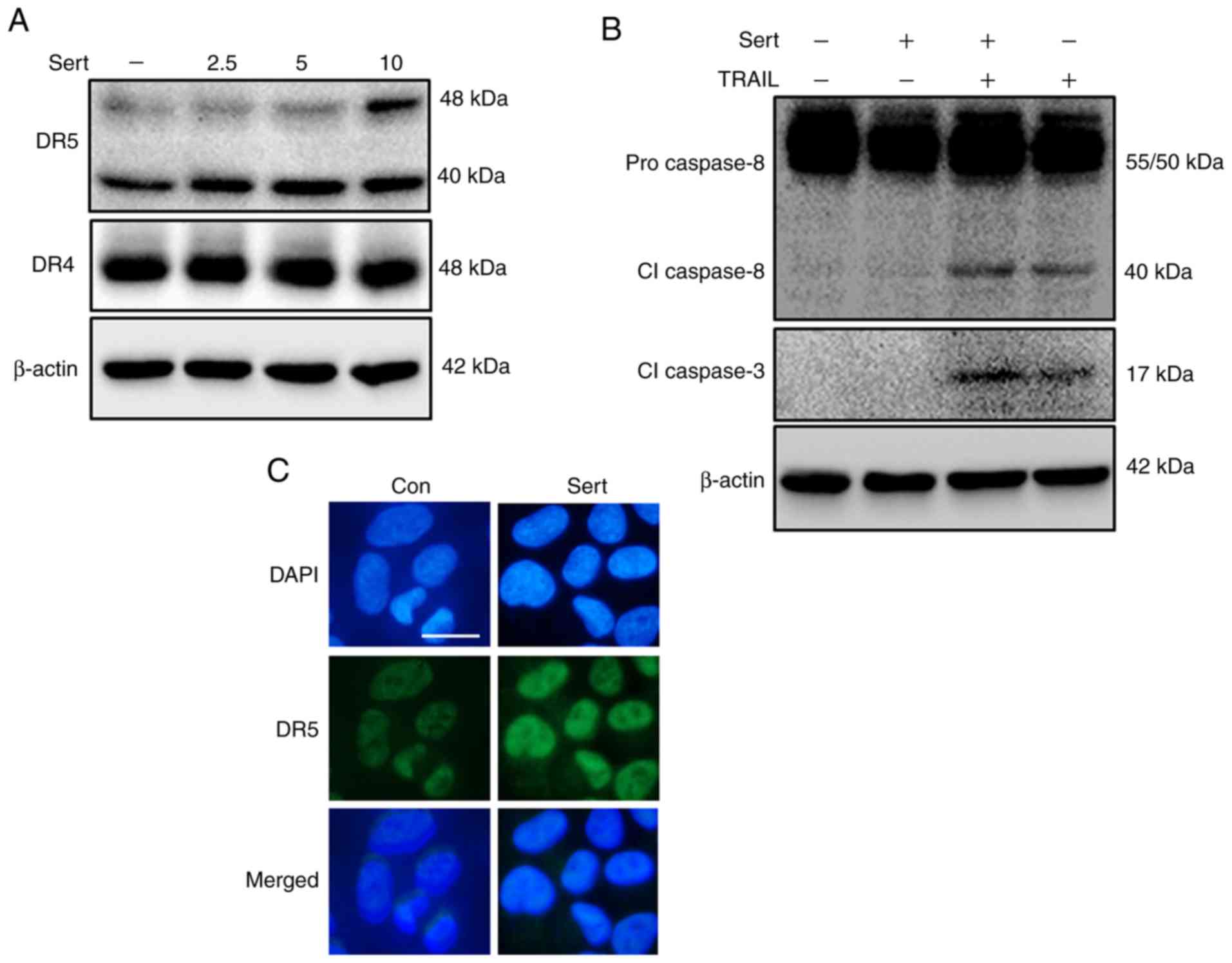
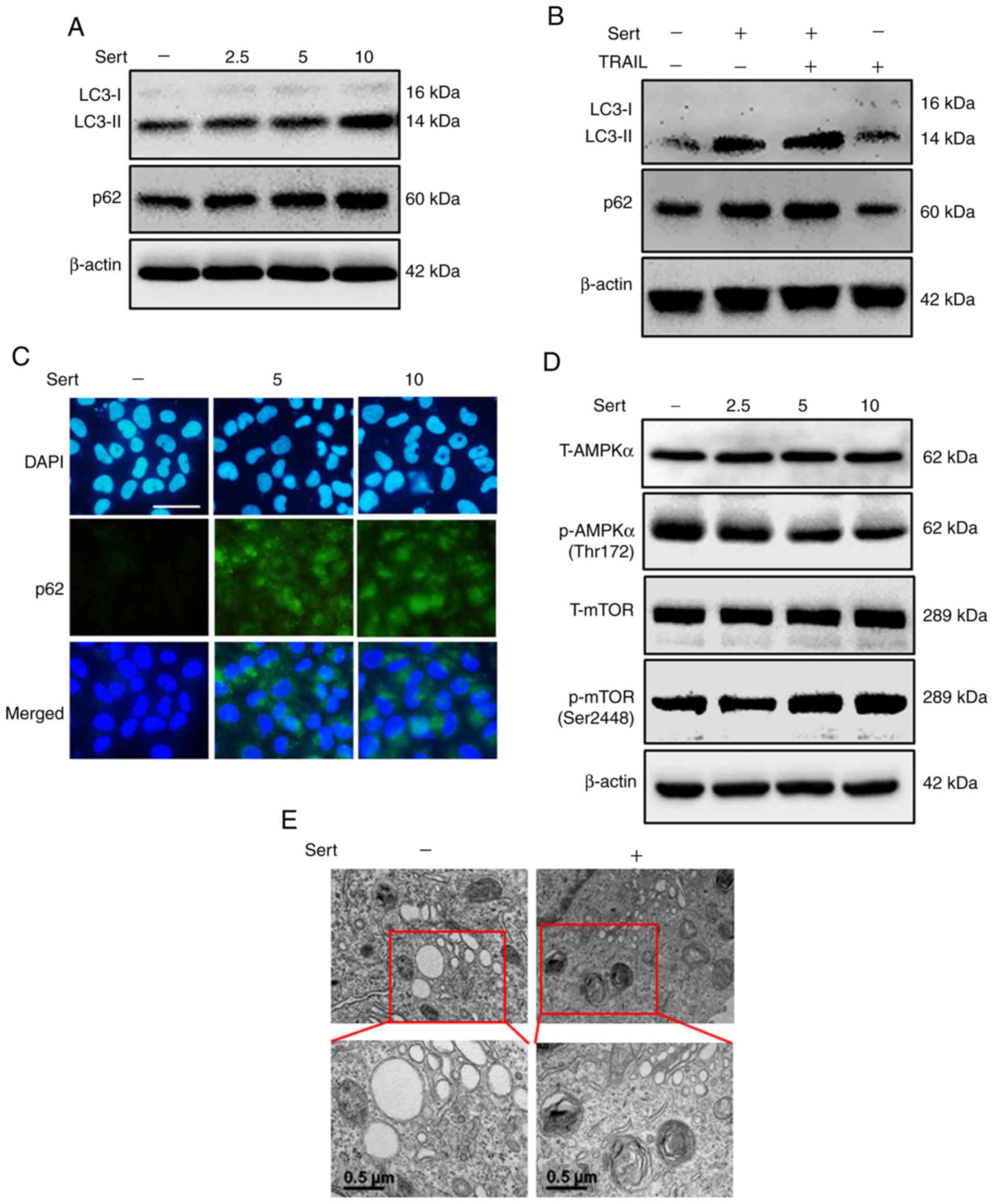
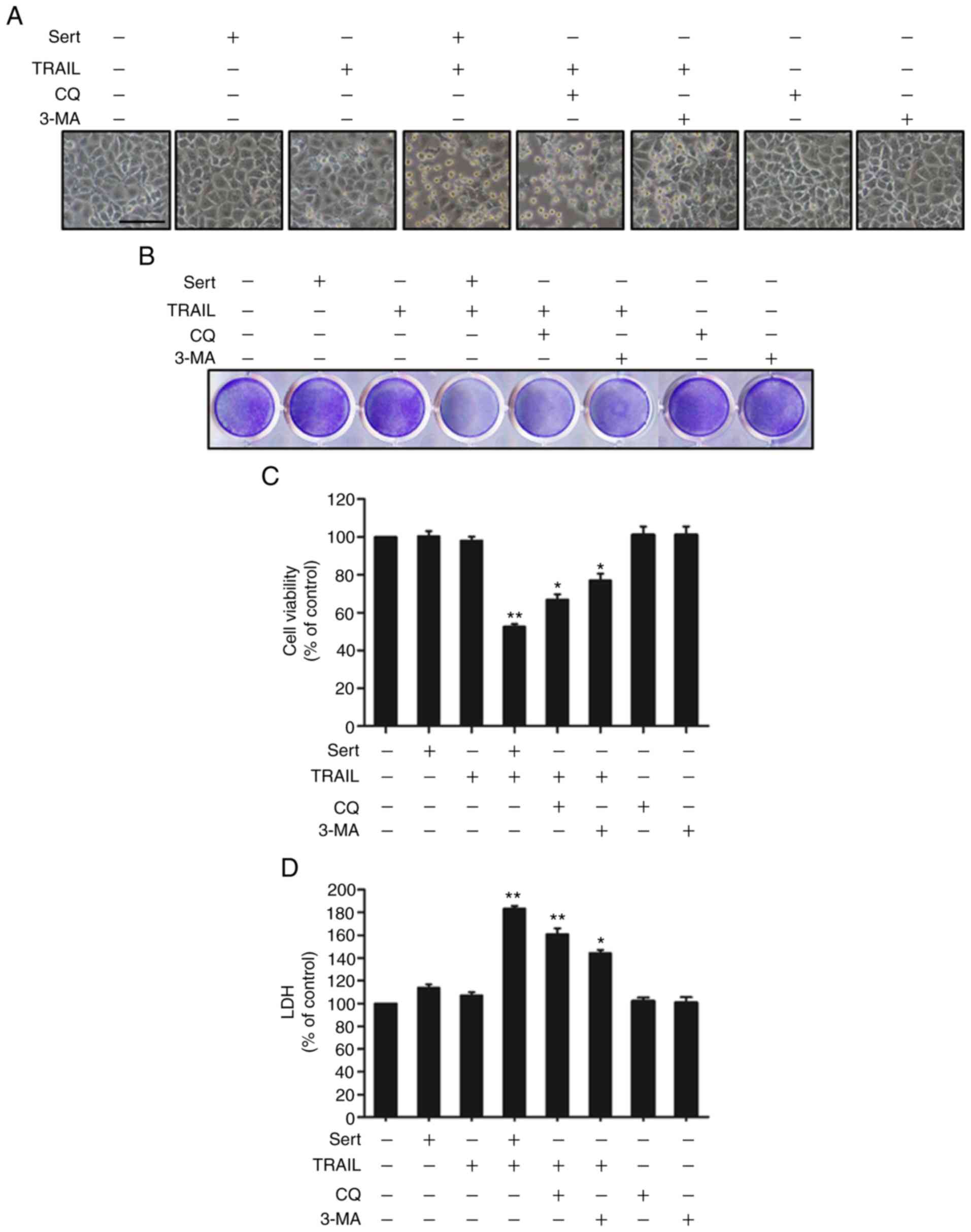
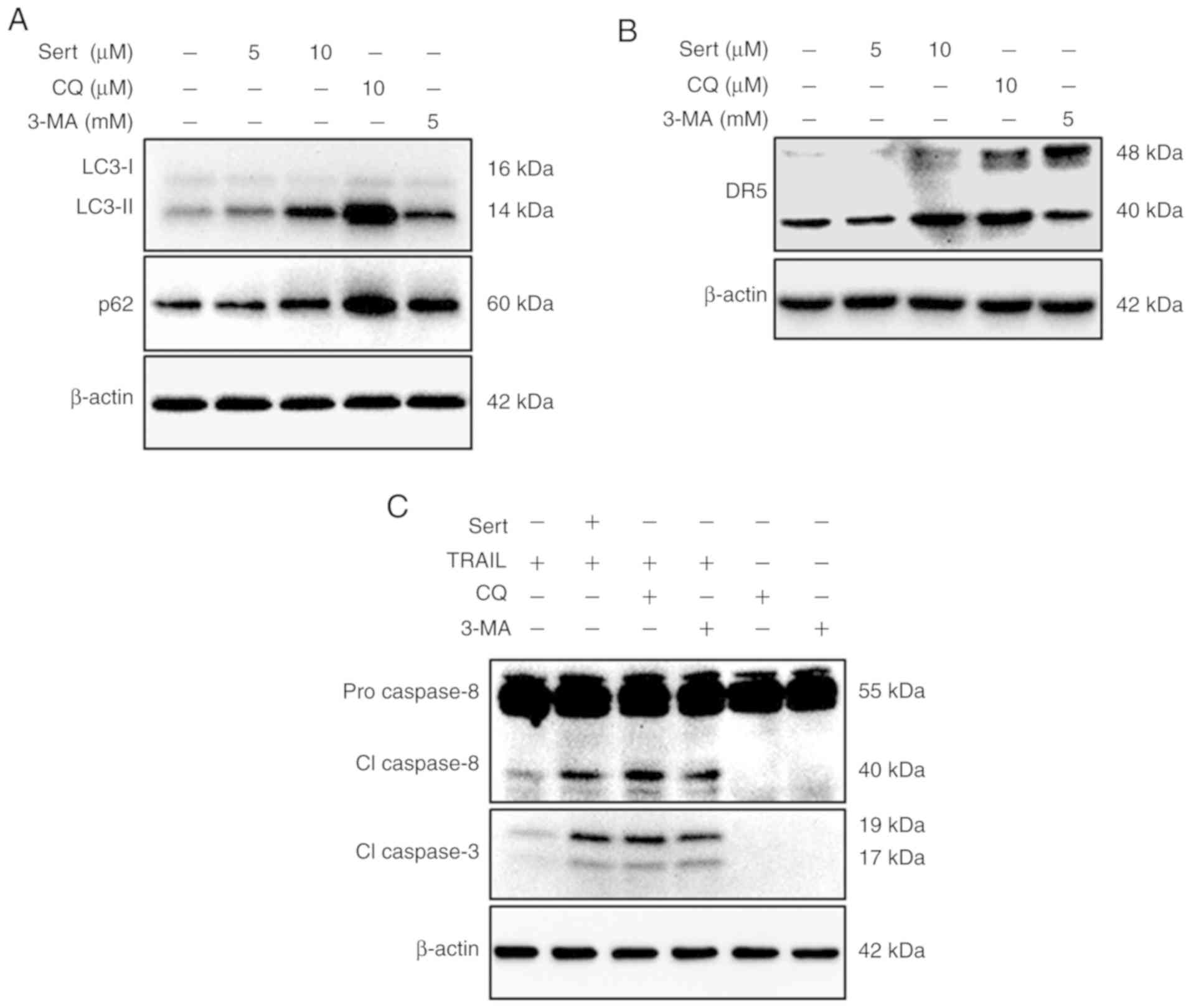
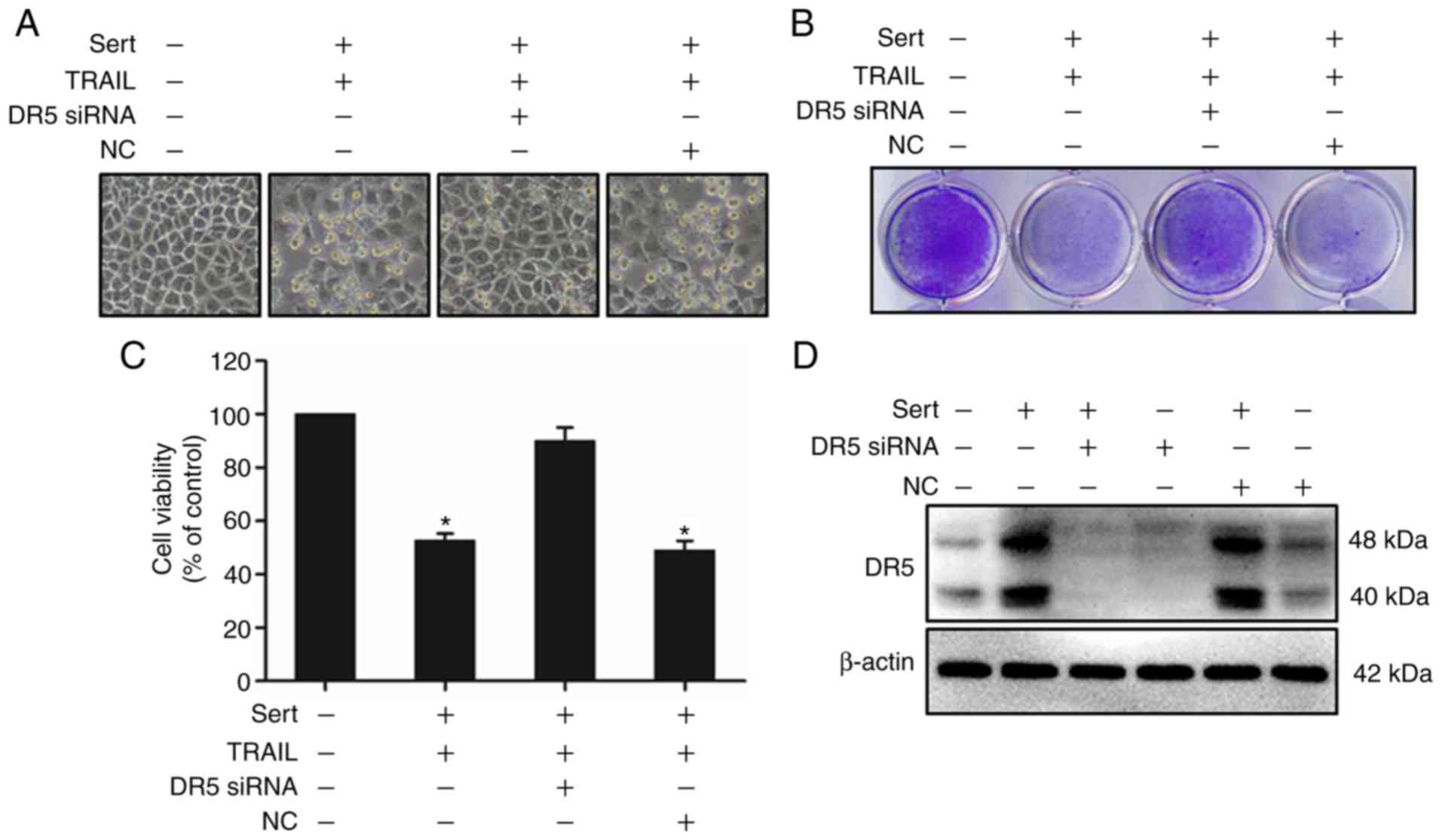
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zingone A, Brown D, Bowman ED, Vidal O,
Sage J, Neal J and Ryan BM: Relationship between anti-depressant
use and lung cancer survival. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 10:33–39.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schelhaas S, Held A, Wachsmuth L, Hermann
S, Honess DJ, Heinzmann K, Smith DM, Griffiths JR, Faber C and
Jacobs AH: Gemcitabine mechanism of action confounds early
assessment of treatment response by
3′-Deoxy-3′-[18F]Fluorothymidine in preclinical models of lung
cancer. Cancer Res. 76:7096–7105. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garcia G and Odaimi M: Systemic
combination chemotherapy in elderly pancreatic cancer: A review. J
Gastrointest Cancer. 48:121–128. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun W, Sanderson PE and Zheng W: Drug
combination therapy increases successful drug repositioning. Drug
Discov Today. 21:1189–1195. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uchibori K, Inase N, Araki M, Kamada M,
Sato S, Okuno Y, Fujita N and Katayama R: Brigatinib combined with
anti-EGFR antibody overcomes osimertinib resistance in EGFR-mutated
non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Commun. 8:147682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aggarwal BB: Signalling pathways of the
TNF superfamily: A double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:745–756.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mellier G, Huang S, Shenoy K and Pervaiz
S: TRAILing death in cancer. Mol Aspects Med. 31:93–112. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nazim UM, Rasheduzzaman M, Lee YJ, Seol DW
and Park SY: Enhancement of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by
5-fluorouracil requires activating Bax and p53 pathways in
TRAIL-resistant lung cancers. Oncotarget. 8:18095–18105. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O'Leary L, van der Sloot AM, Reis CR,
Deegan S, Ryan AE, Dhami SPS, Murillo LS, Cool RH, Sampaio PC,
Thompson K, et al: Decoy receptors block TRAIL sensitivity at a
supracellular level: The role of stromal cells in controlling
tumour TRAIL sensitivity. Oncogene. 35:1261–1270. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang S and El-Deiry WS: TRAIL and
apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene.
22:8628–8633. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang S: The promise of cancer therapeutics
targeting the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and TRAIL
receptor pathway. Oncogene. 27:6207–6215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu GS: TRAIL as a target in anti-cancer
therapy. Cancer Lett. 285:1–5. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin CY, Park C, Hwang HJ, Kim GY, Choi BT,
Kim WJ and Choi YH: Naringenin up-regulates the expression of death
receptor 5 and enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human lung
cancer A549 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:300–309. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dai X, Zhang J, Arfuso F, Chinnathambi A,
Zayed ME, Alharbi SA, Kumar AP, Ahn KS and Sethi G: Targeting
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor by natural
products as a potential therapeutic approach for cancer therapy.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 240:760–773. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ding J, Polier G, Köhler R, Giaisi M,
Krammer PH and Li-Weber M: Wogonin and related natural flavones
overcome tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
(TRAIL) protein resistance of tumors by down-regulation of c-FLIP
protein and up-regulation of TRAIL receptor 2 expression. J Biol
Chem. 287:641–649. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tanida I, Minematsu-Ikeguchi N, Ueno T and
Kominami E: Lysosomal turnover, but not a cellular level, of
endogenous LC3 is a marker for autophagy. Autophagy. 1:84–91. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gómez-Sánchez R, Yakhine-Diop SMS,
Rodríguez-Arribas M, Pedro JMB, Martínez-Chacón G, Uribe-Carretero
E, de Castro DCJ, Pizarro-Estrella E, Fuentes JM and González-Polo
RA: mRNA and protein dataset of autophagy markers (LC3 and p62) in
several cell lines. Data Brief. 7:641–647. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boya P, González-Polo R, Casares N,
Perfettini J, Dessen P, Larochette N, Métivier D, Meley D, Souquere
S, Yoshimori T, et al: Inhibition of macroautophagy triggers
apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 25:1025–1040. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mauthe M, Orhon I, Rocchi C, Zhou X, Luhr
M, Hijlkema K, Coppes RP, Engedal N, Mari M and Reggiori F:
Chloroquine inhibits autophagic flux by decreasing
autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Autophagy. 14:1435–1455. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Heckmann BL, Yang X, Zhang X and Liu J:
The autophagic inhibitor 3-methyladenine potently stimulates
PKA-dependent lipolysis in adipocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 168:163–171.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D and Hardie
DG: AMP-activated protein kinase: Ancient energy gauge provides
clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 1:15–25.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou C, Gu J, Zhang G, Dong D, Yang Q,
Chen M and Xu D: AMPK-autophagy inhibition sensitizes
icaritin-induced anti-colorectal cancer cell activity. Oncotarget.
8:14736–14747. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cho SW, Na W, Choi M, Kang SJ, Lee S and
Choi CY: Autophagy inhibits cell death induced by the anti-cancer
drug morusin. Am J Cancer Res. 7:518–530. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Laoutidis ZG and Mathiak K:
Antidepressants in the treatment of depression/depressive symptoms
in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC
Psychiatry. 13:1402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Serafin MB, Bottega A, da Rosa TF, Machado
CS, Foletto VS, Coelho SS, da Mota AD and Hörner R: Drug
repositioning in oncology. Am J Ther. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xia D, Zhang Y, Xu G, Yan W, Pan X and
Tong J: Sertraline exerts its antitumor functions through both
apoptosis and autophagy pathways in acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Leuk Lymphoma. 58:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S and
Stork B: Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy:
Cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol. 32:2–11. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Di Rosso ME, Sterle HA, Cremaschi GA and
Genaro AM: Beneficial effect of fluoxetine and sertraline on
chronic stress-induced tumor growth and cell dissemination in a
mouse model of lymphoma: Crucial role of antitumor immunity. Front
Immunol. 9:13412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dhabhar FS, Saul AN, Holmes TH, Daugherty
C, Neri E, Tillie JM, Kusewitt D and Oberyszyn TM: High-anxious
individuals show increased chronic stress burden, decreased
protective immunity, and increased cancer progression in a mouse
model of squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e330692012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thaker PH, Han LY, Kamat AA, Arevalo JM,
Takahashi R, Lu C, Jennings NB, Armaiz-Pena G, Bankson JA, Ravoori
M, et al: Chronic stress promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in
a mouse model of ovarian carcinoma. Nat Med. 12:939–944. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim-Fuchs C, Le CP, Pimentel MA,
Shackleford D, Ferrari D, Angst E, Hollande F and Sloan EK: Chronic
stress accelerates pancreatic cancer growth and invasion: A
critical role for beta-adrenergic signaling in the pancreatic
microenvironment. Brain Behav Immun. 40:40–47. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hassan S, Karpova Y, Baiz D, Yancey D,
Pullikuth A, Flores A, Register T, Cline JM, D'Agostino Jr, Danial
N, et al: Behavioral stress accelerates prostate cancer development
in mice. J Clin Invest. 123:874–886. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sloan EK, Priceman SJ, Cox BF, Yu S,
Pimentel MA, Tangkanangnukul V, Arevalo JMG, Morizono K,
Karanikolas BDW, Wu L, et al: The sympathetic nervous system
induces a metastatic switch in primary breast cancer. Cancer Res.
70:7042–7052. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hasegawa H and Saiki I: Psychosocial
stress augments tumor development through beta-adrenergic
activation in mice. Jpn J Cancer Res. 93:729–735. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Toh S, Rodríguez LAG and Hernández-Díaz S:
Use of antidepressants and risk of lung cancer. Cancer Causes
Control. 18:1055–1064. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chou CT, He S and Jan CR:
Paroxetine-induced apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells:
Activation of p38 MAP kinase and caspase-3 pathways without
involvement of [Ca2+]i elevation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
218:265–273. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Abdul M, Logothetis CJ and Hoosein NM:
Growth-inhibitory effects of serotonin uptake inhibitors on human
prostate carcinoma cell lines. J Urol. 154:247–250. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Spanová A, Kovárů H, Lisá V, Lukásová E
and Rittich B: Estimation of apoptosis in C6 glioma cells treated
with antidepressants. Physiol Res. 46:161–164. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Amit BH, Gil-Ad I, Taler M, Bar M, Zolokov
A and Weizman A: Proapoptotic and chemosensitizing effects of
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on T cell lymphoma/leukemia
(Jurkat) in vitro. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 19:726–734. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
LeBlanc H, Lawrence D, Varfolomeev E,
Totpal K, Morlan J, Schow P, Fong S, Schwall R, Sinicropi D and
Ashkenazi A: Tumor-cell resistance to death receptor-induced
apoptosis through mutational inactivation of the proapoptotic Bcl-2
homolog Bax. Nat Med. 8:274–281. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Srivastava RK: TRAIL/Apo-2L: Mechanisms
and clinical applications in cancer. Neoplasia. 3:535–546. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Bellail AC, Qi L, Mulligan P, Chhabra V
and Hao C: TRAIL agonists on clinical trials for cancer therapy:
The promises and the challenges. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 4:34–41.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B,
Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, et al:
Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy: From phenomenology
to molecular understanding in less than a decade. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 8:931–937. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta
T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB and Tsujimoto Y: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent
on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol. 6:1221–1228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Park EJ, Min K, Choi KS, Kubatka P,
Kruzliak P, Kim DE and Kwon TK: Chloroquine enhances TRAIL-mediated
apoptosis through up-regulation of DR5 by stabilization of mRNA and
protein in cancer cells. Sci Rep. 6:229212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu X, Chhipa RR, Nakano I and Dasgupta B:
The AMPK inhibitor compound C is a potent AMPK-independent
antiglioma agent. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:596–605. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zinnah KMA and Park SY: Duloxetine
enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis via AMPK-mediated Inhibition of
autophagy flux in lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 39:6621–6633.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yang Y, Hu L, Zheng H, Mao C, Hu W, Xiong
K, Wang F and Liu C: Application and interpretation of current
autophagy inhibitors and activators. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
34:625–635. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hu X, Shi S, Wang H, Yu X, Wang Q, Jiang
S, Ju D, Ye L and Feng M: Blocking autophagy improves the
anti-tumor activity of afatinib in lung adenocarcinoma with
activating EGFR mutations in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep.
7:45592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lin YC, Lin JF, Wen SI, Yang SC, Tsai TF,
Chen HE, Chou KY and Hwang TI: Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine
inhibit bladder cancer cell growth by targeting basal autophagy and
enhancing apoptosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 33:215–223. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|