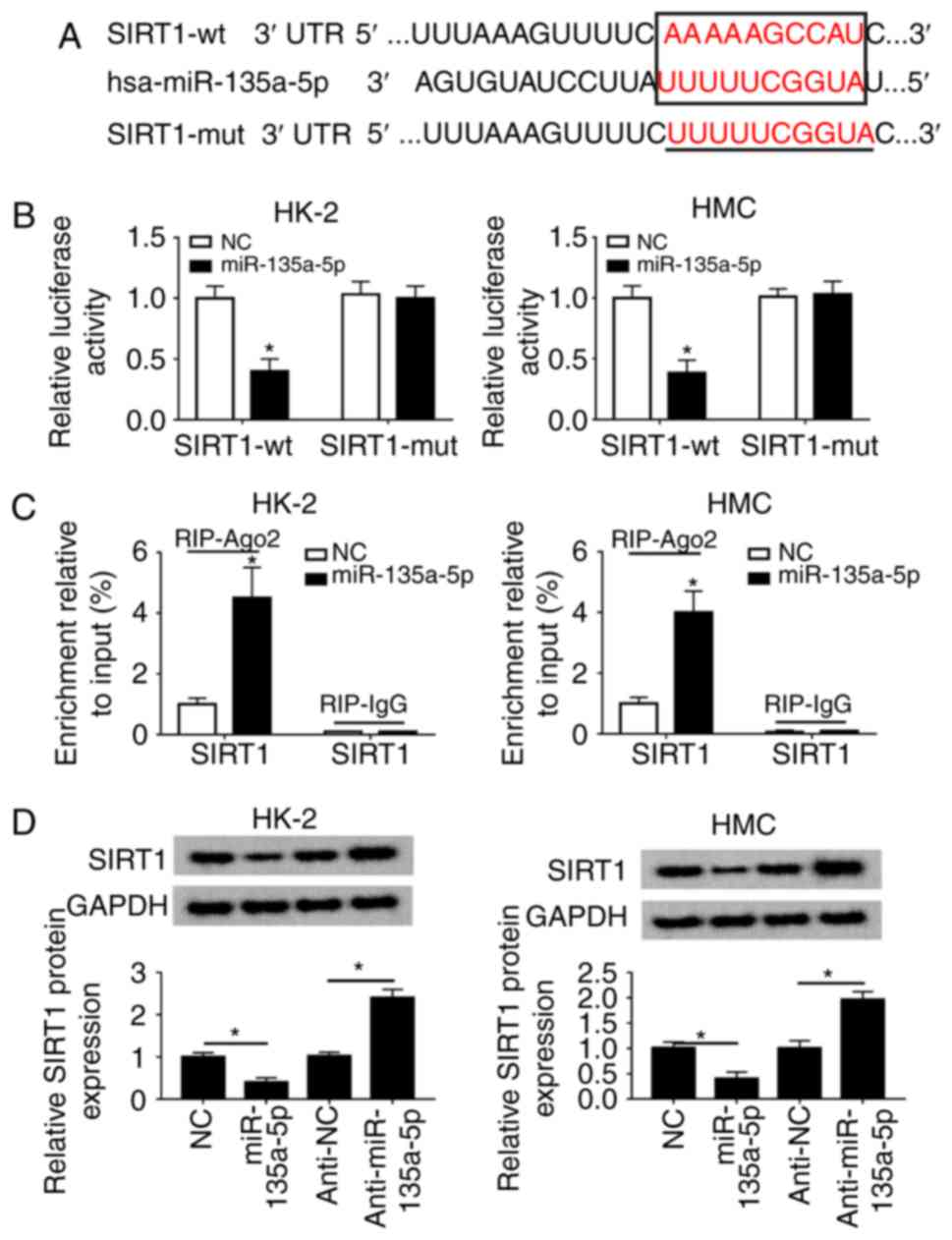
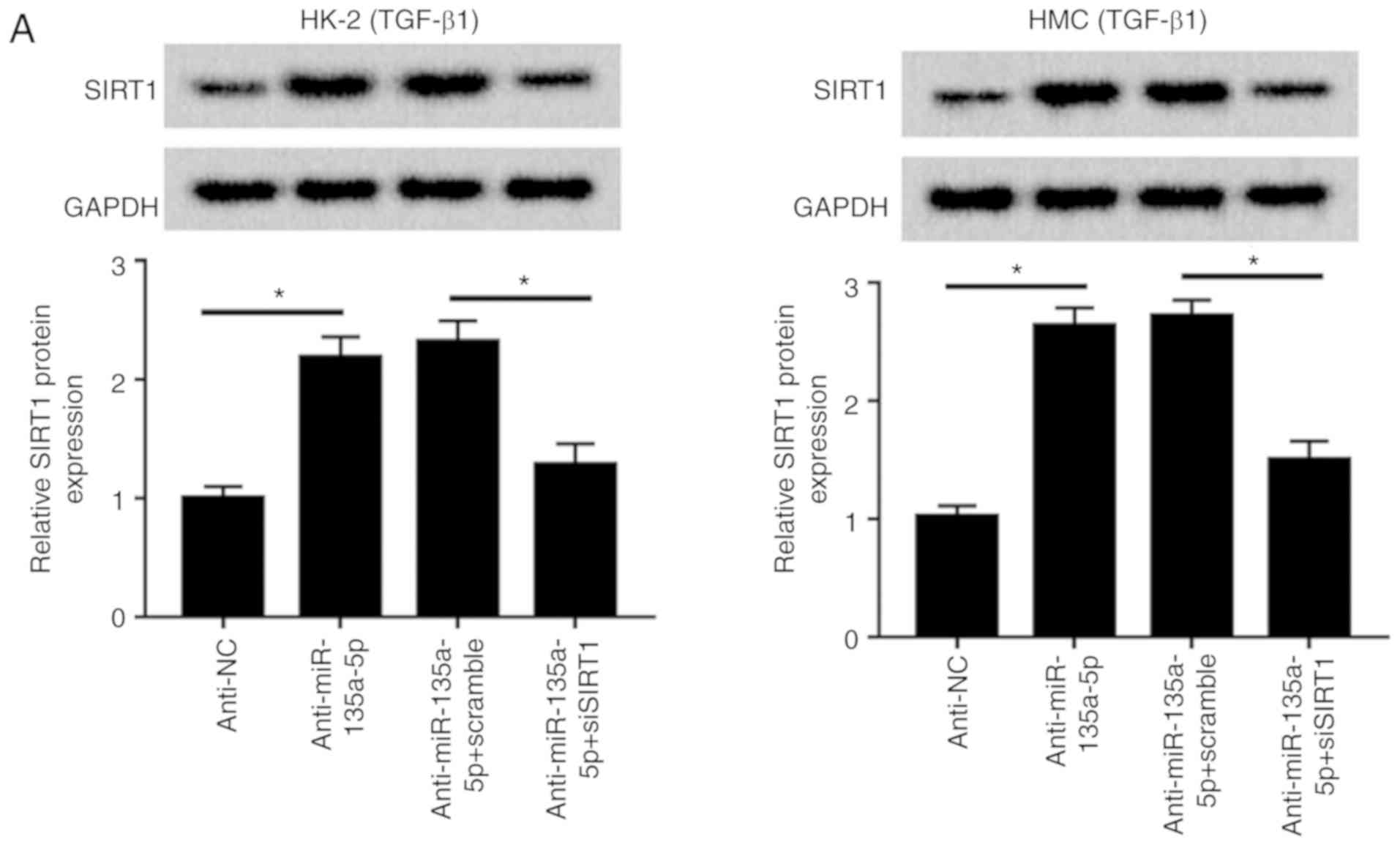
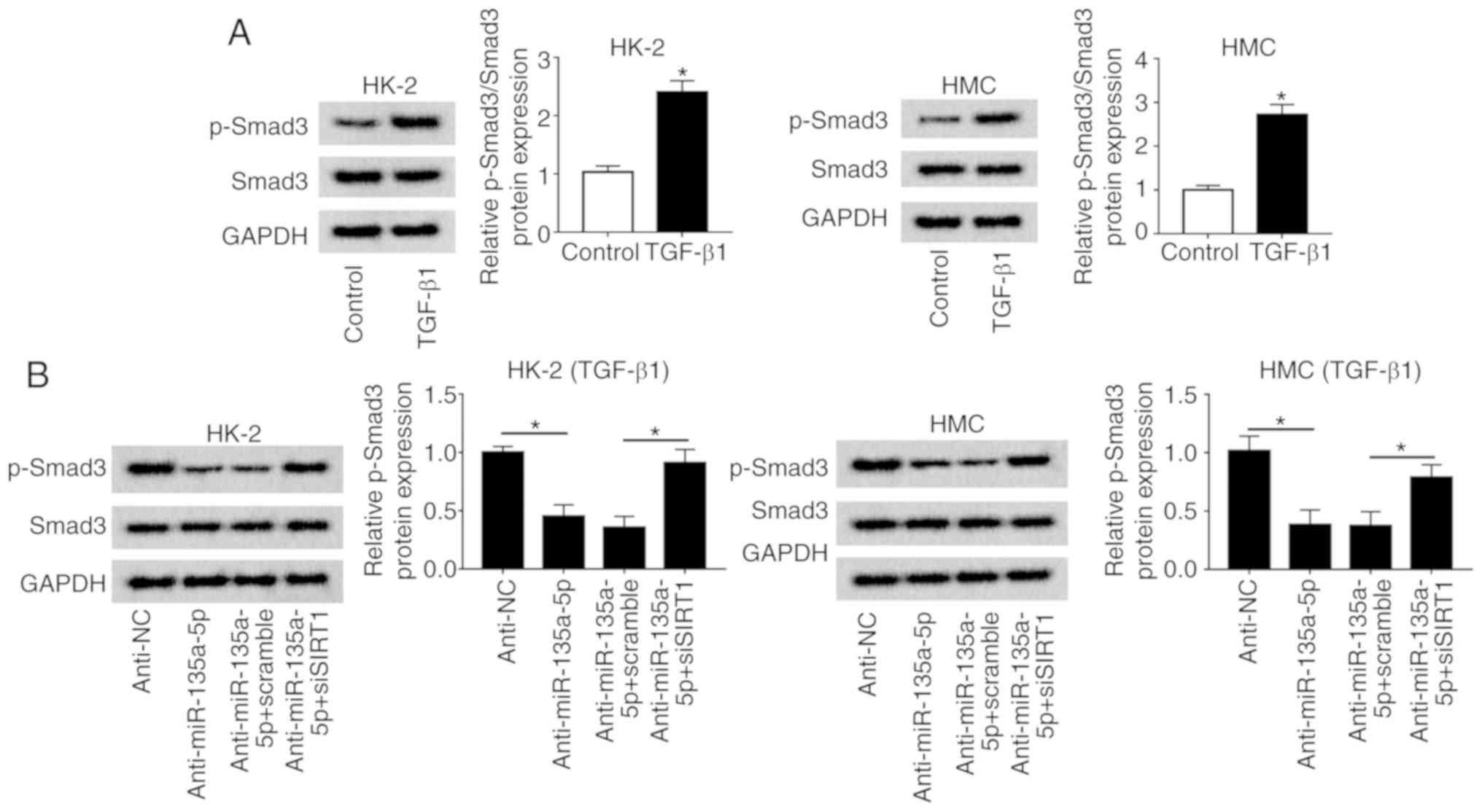
|
1
|
Liu ZH: Nephrology in China. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 9:523–528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Coimbra TM, Janssen U, Gröne HJ, Ostendorf
T, Kunter U, Schmidt H, Brabant G and Floege J: Early events
leading to renal injury in obese Zucker (fatty) rats with type II
diabetes. Kidney Int. 57:167–182. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kanwar YS, Sun L, Xie P, Liu FY and Chen
S: A glimpse of various pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic
nephropathy. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:395–423. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gilbert RE and Cooper ME: The
tubulointerstitium in progressive diabetic kidney disease: More
than an aftermath of glomerular injury? Kidney Int. 56:1627–1637.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Steffes MW, Osterby R, Chavers B and Mauer
SM: Mesangial expansion as a central mechanism for loss of kidney
function in diabetic patients. Diabetes. 38:1077–1081. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang S, Yang Z, Xiong F, Chen C, Chao X,
Huang J and Huang H: Betulinic acid ameliorates experimental
diabetic-induced renal inflammation and fibrosis via inhibiting the
activation of NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
434:135–143. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mason RM and Wahab NA: Extracellular
matrix metabolism in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
14:1358–1373. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song KH, Park J, Park JH, Natarajan R and
Ha H: Fractalkine and its receptor mediate extracellular matrix
accumulation in diabetic nephropathy in mice. Diabetologia.
56:1661–1669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wynn TA: Common and unique mechanisms
regulate fibrosis in various fibroproliferative diseases. J Clin
Invest. 117:524–529. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hills CE and Squires PE: The role of TGF-β
and epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:131–139. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sutariya B, Jhonsa D and Saraf MN: TGF-β:
The connecting link between nephropathy and fibrosis.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 38:39–49. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chen S, Hong SW, Iglesias-de la Cruz MC,
Isono M, Casaretto A and Ziyadeh FN: The key role of the
transforming growth factor-beta system in the pathogenesis of
diabetic nephropathy. Ren Fail. 23:471–481. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sharma K, Jin Y, Guo J and Ziyadeh FN:
Neutralization of TGF-beta by anti-TGF-beta antibody attenuates
kidney hypertrophy and the enhanced extracellular matrix gene
expression in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Diabetes. 45:522–530.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang XZ, Wen D, Zhang M, Xie Q, Ma L,
Guan Y, Ren Y, Chen J and Hao CM: Sirt1 activation ameliorates
renal fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad3 pathway. J Cell
Biochem. 115:996–1005. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Böttinger EP and Bitzer M: TGF-beta
signaling in renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:2600–2610. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Massagué J and Chen YG: Controlling
TGF-beta signaling. Genes Dev. 14:627–644. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kato M: TGF-β-induced signaling circuit
loops mediated by microRNAs as new therapeutic targets for renal
fibrosis? Kidney Int. 84:1067–1069. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu Z and Wang F: Epigenetic regulations in
diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Res. 2017:78050582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cui C, Cui Y, Fu Y, Ma S and Zhang S:
Microarray analysis reveals gene and microRNA signatures in
diabetic kidney disease. Mol Med Rep. 17:2161–2168. 2018.
|
|
20
|
Rysz J, Gluba-Brzózka A, Franczyk B,
Jabłonowski Z and Ciałkowska-Rysz A: Novel biomarkers in the
diagnosis of chronic kidney disease and the prediction of its
outcome. Int J Mol Sci. 18:17022017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
He F, Peng F, Xia X, Zhao C, Luo Q, Guan
W, Li Z, Yu X and Huang F: MiR-135a promotes renal fibrosis in
diabetic nephrop-athy by regulating TRPC1. Diabetologia.
57:1726–1736. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kume S, Kitada M, Kanasaki K, Maegawa H
and Koya D: Anti-aging molecule, Sirt1: A novel therapeutic target
for diabetic nephropathy. Arch Pharm Res. 36:230–236. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J,
Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, et al: Prevalence of diabetes among
men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 362:1090–1101. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Roglic G, Unwin N, Bennett PH, Mathers C,
Tuomilehto J, Nag S, Connolly V and King H: The burden of mortality
attributable to diabetes: Realistic estimates for the year 2000.
Diabetes Care. 28:2130–2135. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun Z, Ma Y, Chen F, Wang S, Chen B and
Shi J: miR-133b and miR-199b knockdown attenuate TGF-β1-induced
epithelial to mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis by
targeting SIRT1 in diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Pharmacol.
837:96–104. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bai X, Geng J, Zhou Z, Tian J and Li X:
MicroRNA-130b improves renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis via
repression of Snail-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
diabetic nephropathy. Sci Rep. 6:204752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Putta S, Lanting L, Sun G, Lawson G, Kato
M and Natarajan R: Inhibiting microRNA-192 ameliorates renal
fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 23:458–469.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Loeffler I and Wolf G:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy: Fact
or fiction? Cells. 4:631–652. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Simonson MS: Phenotypic transitions and
fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 71:846–854. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao B, Li H, Liu J, Han P, Zhang C, Bai
H, Yuan X, Wang X, Li L, Ma H, et al: MicroRNA-23b targets ras
GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein 2 to alleviate
fibrosis and albuminuria in diabetic Nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
27:2597–2608. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeng YB, Liang XH, Zhang GX, Jiang N,
Zhang T, Huang JY, Zhang L and Zeng XC: miRNA-135a promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by targeting
forkhead box O1. Cancer Cell Int. 16:632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yao S, Tian C, Ding Y, Ye Q, Gao Y, Yang N
and Li Q: Down-regulation of Krüppel-like factor-4 by
microRNA-135a-5p promotes proliferation and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma by transforming growth factor-β1.
Oncotarget. 7:42566–42578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen Y, Zhang J, Wang H, Zhao J, Xu C, Du
Y, Luo X, Zheng F, Liu R, Zhang H and Ma D: miRNA-135a promotes
breast cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting HOXA10. BMC
Cancer. 12:1112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guo LM, Ding GF, Xu W, Ge H, Jiang Y, Chen
XJ and Lu Y: MiR-135a-5p represses proliferation of HNSCC by
targeting HOXA10. Cancer Biol Ther. 19:973–983. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Agarwal P, Srivastava R, Srivastava AK,
Ali S and Datta M: miR-135a targets IRS2 and regulates insulin
signaling and glucose uptake in the diabetic gastrocnemius skeletal
muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:1294–1303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu Y, Liu Y, Pan Y, Lu C, Xu H, Wang X,
Liu T, Feng K and Tang Y: MicroRNA-135a inhibits cardiac fibrosis
induced by isoproterenol via TRPM7 channel. Biomed Pharmacother.
104:252–260. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yuan F, Xie Q, Wu J, Bai Y, Mao B, Dong Y,
Bi W, Ji G, Tao W, Wang Y and Yuan Z: MST1 promotes apoptosis
through regulating Sirt1-dependent p53 deacetylation. J Biol Chem.
286:6940–6945. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Salminen A and Kaarniranta K: NF-kappaB
signaling in the aging process. J Clin Immunol. 29:397–405. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kume S, Haneda M, Kanasaki K, Sugimoto T,
Araki S, Isshiki K, Isono M, Uzu T, Guarente L, Kashiwagi A and
Koya D: SIRT1 inhibits transforming growth factor beta-induced
apoptosis in glomerular mesangial cells via Smad7 deacetylation. J
Biol Chem. 282:151–158. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Xue M, Li Y, Hu F, Jia YJ, Zheng ZJ, Wang
L and Xue YM: High glucose up-regulates microRNA-34a-5p to
aggravate fibrosis by targeting SIRT1 in HK-2 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 498:38–44. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li A, Peng R, Sun Y, Liu H, Peng H and
Zhang Z: LincRNA 1700020I14Rik alleviates cell proliferation and
fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy via miR-34a-5p/Sirt1/HIF-1α
signaling. Cell Death Dis. 9:4612018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Bugyei-Twum A, Ford C, Civitarese R,
Seegobin J, Advani SL, Desjardins JF, Kabir G, Zhang Y, Mitchell M,
Switzer J, et al: Sirtuin 1 activation attenuates cardiac fibrosis
in a rodent pressure overload model by modifying Smad2/3
transactivation. Cardiovasc Res. 114:1629–1641. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang T, Wang J, Pang Y, Dang X, Ren H, Liu
Y, Chen M and Shang D: Emodin suppresses silica-induced lung
fibrosis by promoting Sirt1 signaling via direct contact. Mol Med
Rep. 14:4643–4649. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jiang R, Zhou Y, Wang S, Pang N, Huang Y,
Ye M, Wan T, Qiu Y, Pei L, Jiang X, et al: Nicotinamide riboside
protects against liver fibrosis induced by CCl4 via
regulating the acetylation of Smads signaling pathway. Life Sci.
225:20–28. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li J, Qu X, Ricardo SD, Bertram JF and
Nikolic-Paterson DJ: Resveratrol inhibits renal fibrosis in the
obstructed kidney: Potential role in deacetylation of Smad3. Am J
Pathol. 177:1065–1071. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang Y, Connelly KA, Thai K, Wu X, Kapus
A, Kepecs D and Gilbert RE: Sirtuin 1 activation reduces
transforming growth factor-β1-induced fibrogenesis and affords
organ protection in a model of progressive, experimental kidney and
associated cardiac disease. Am J Pathol. 187:80–90. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|