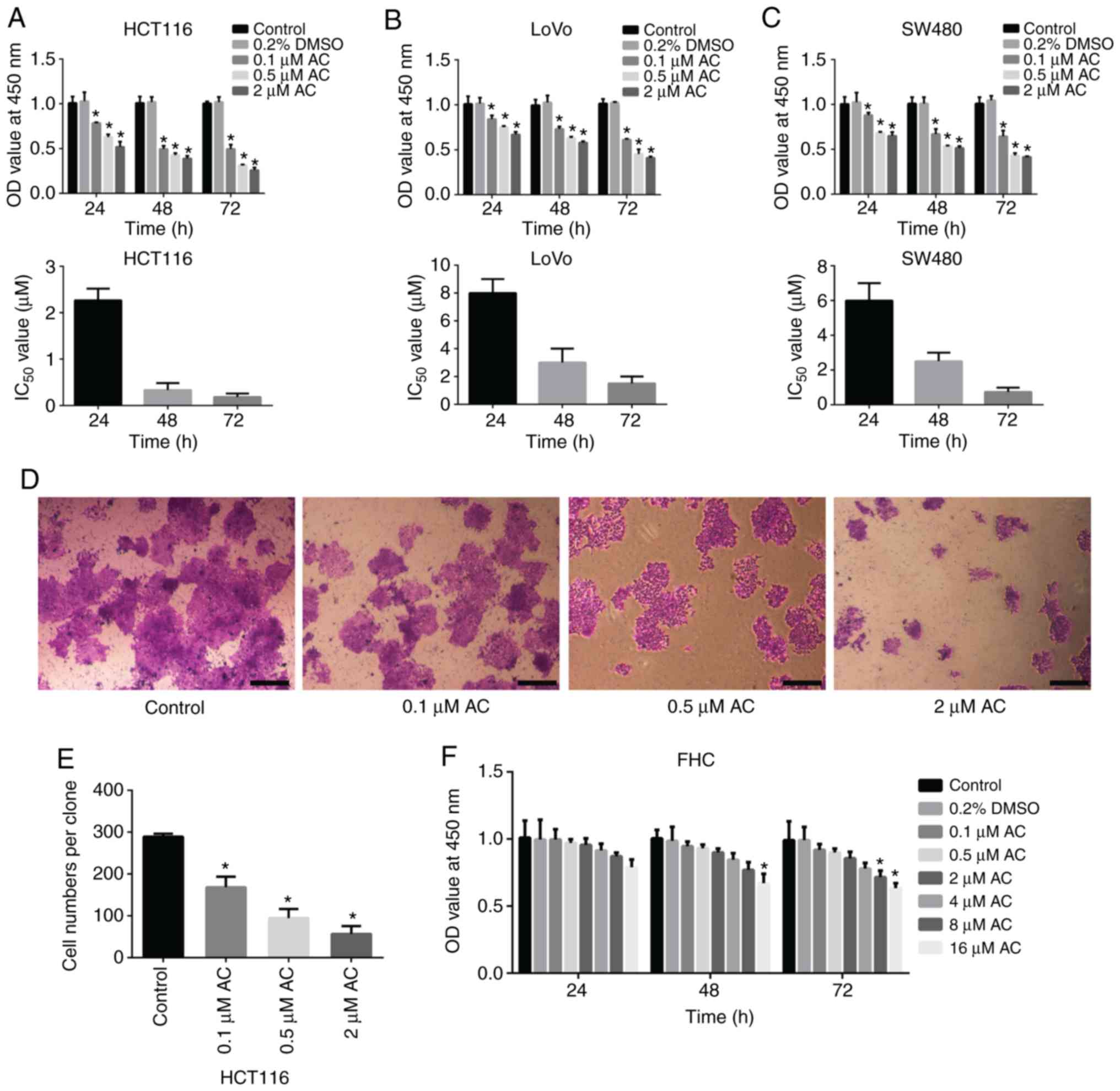
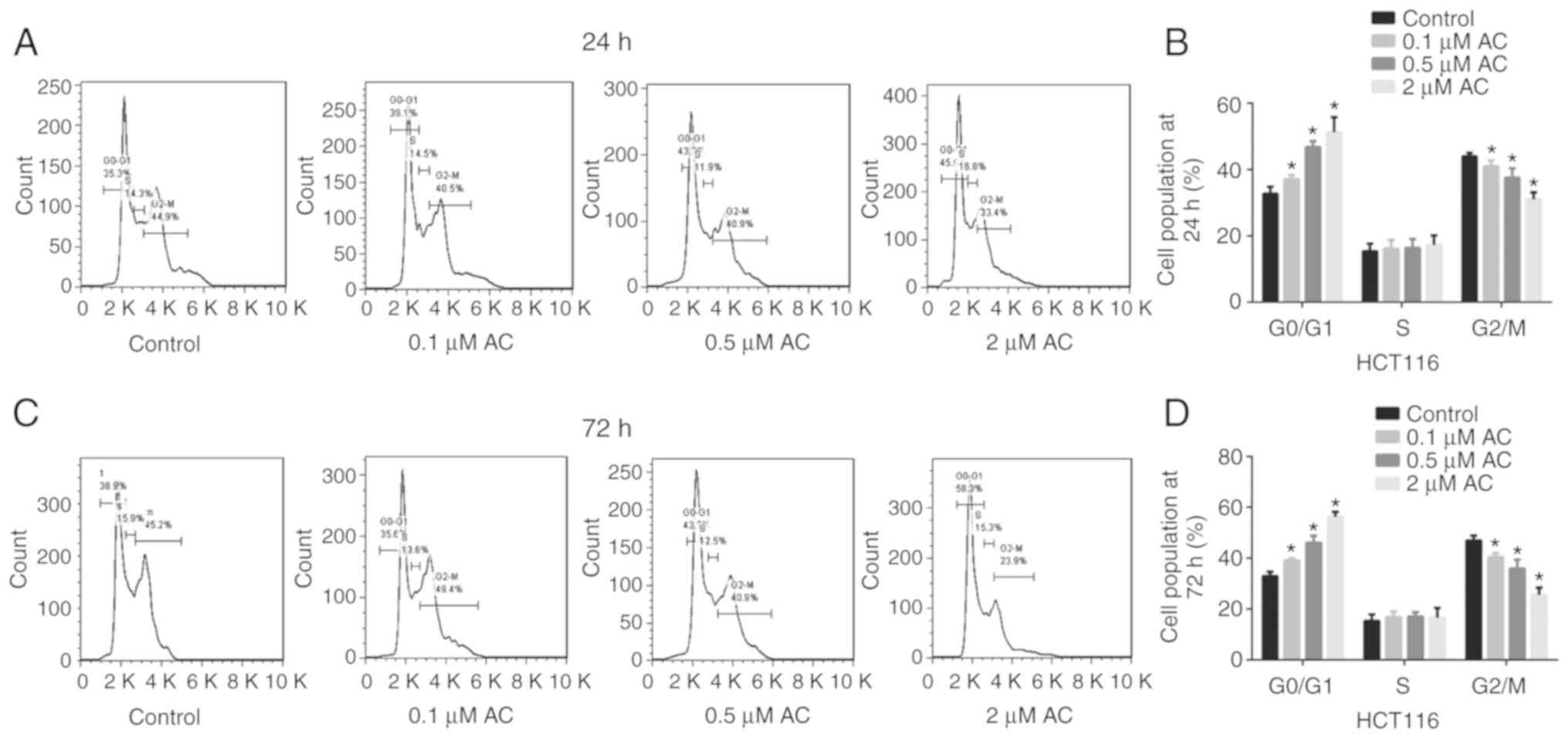
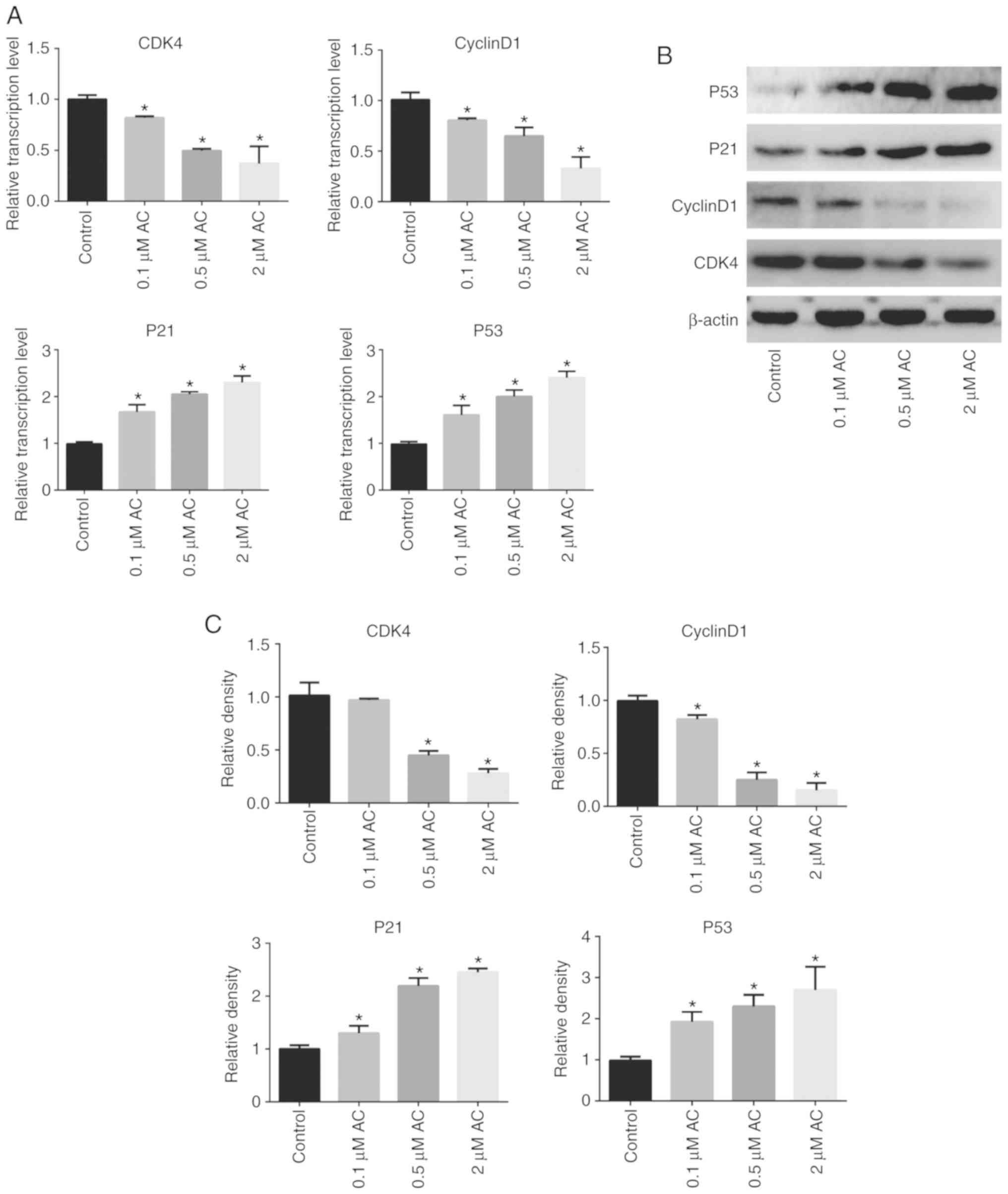
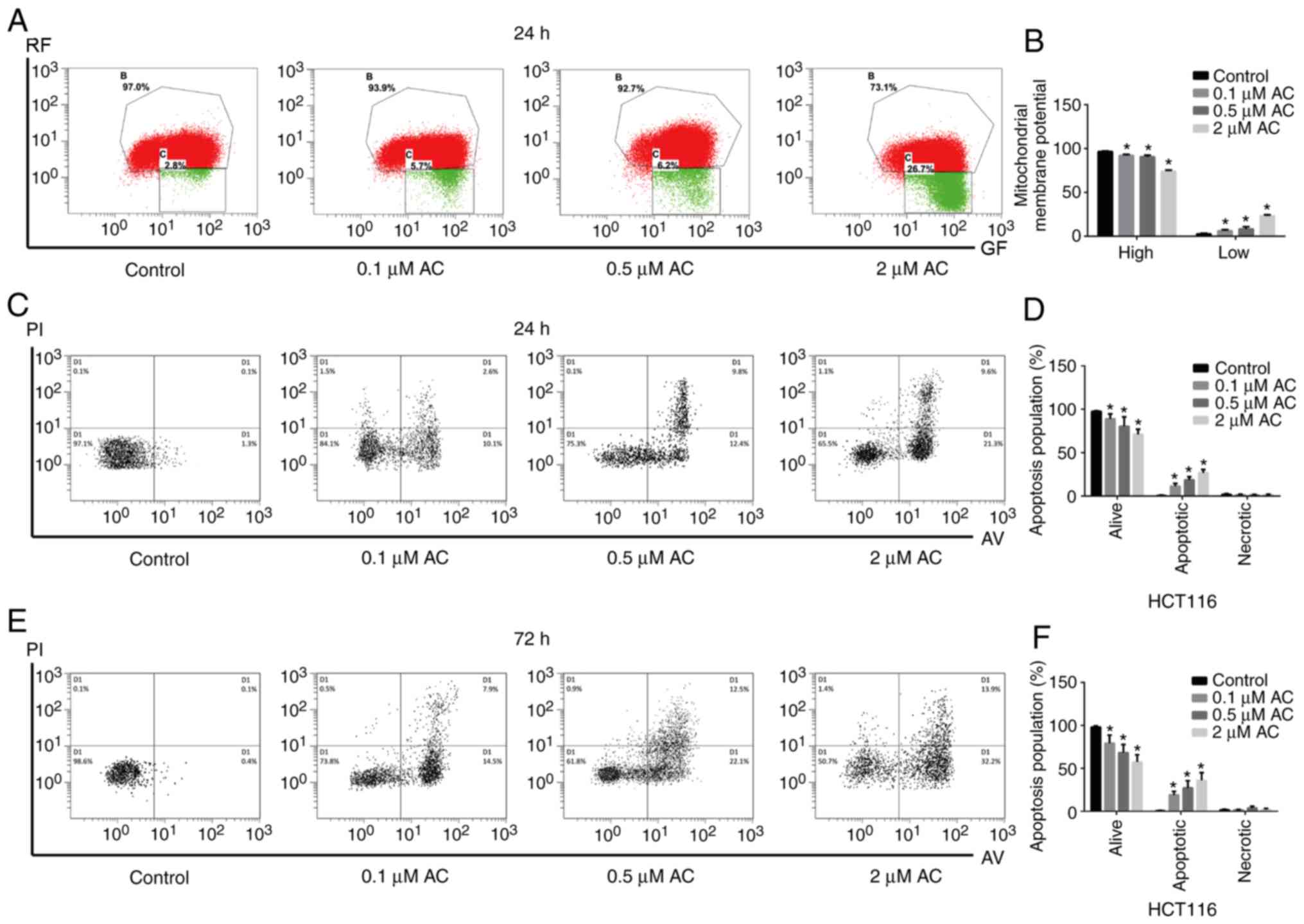
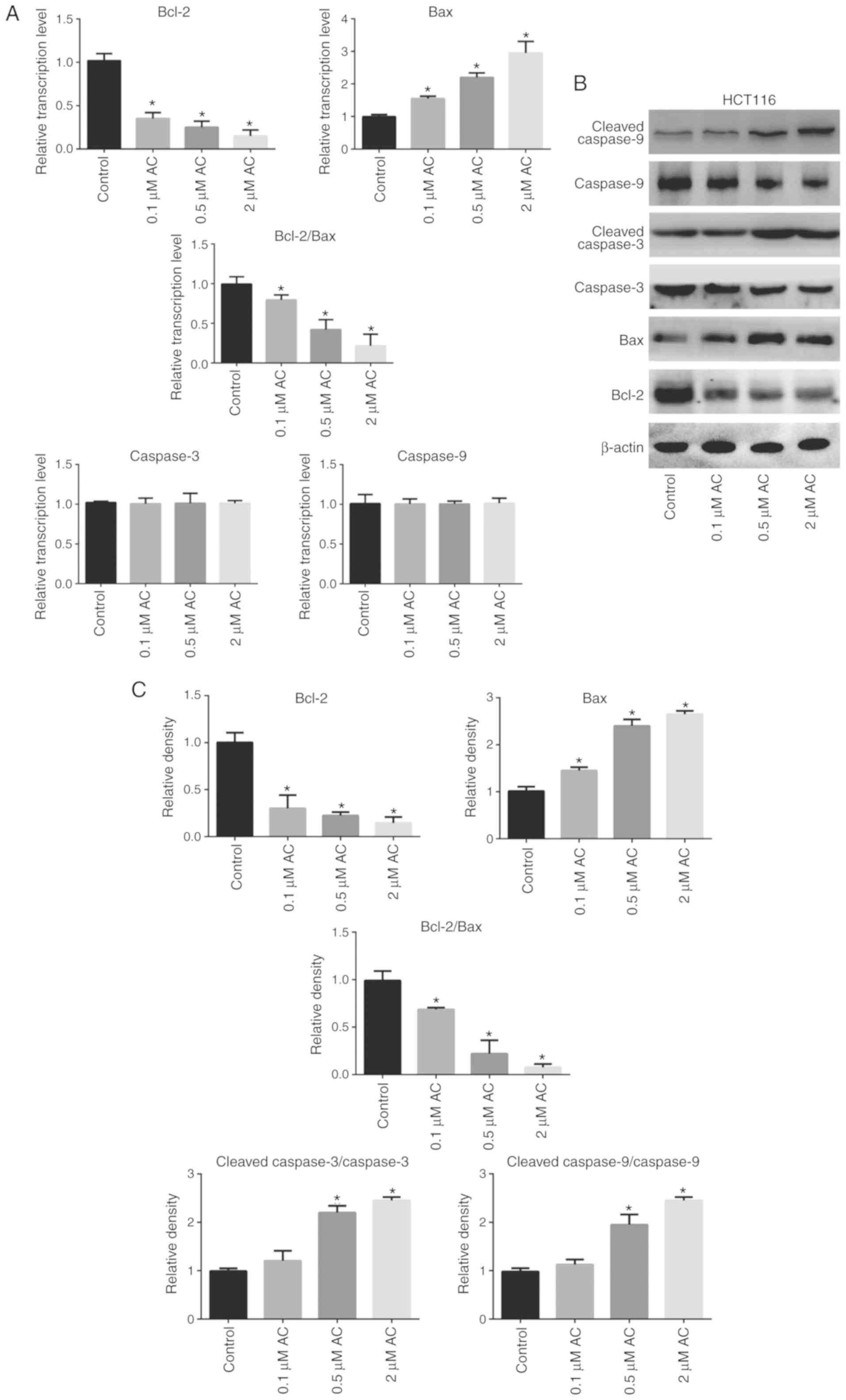
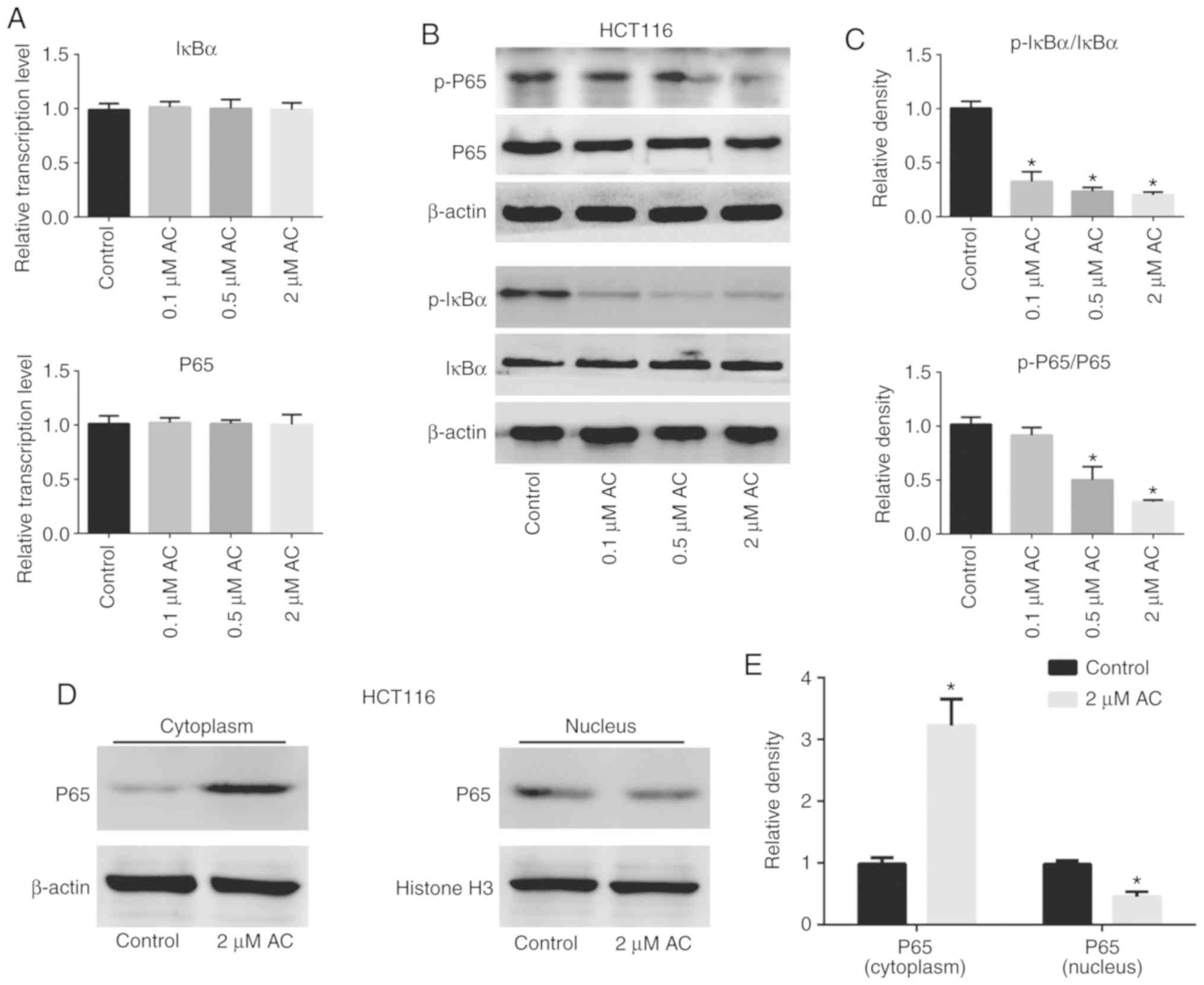
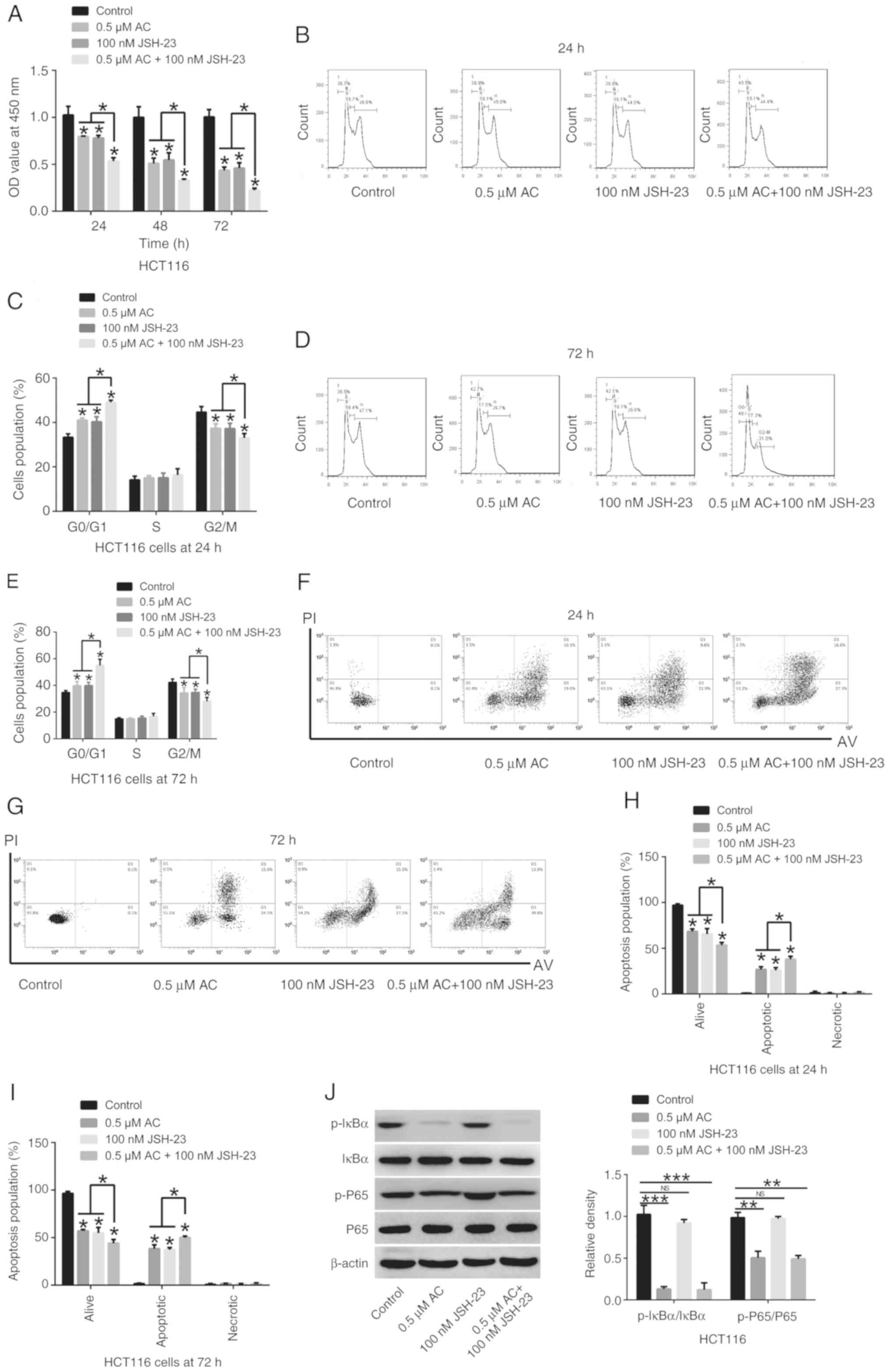
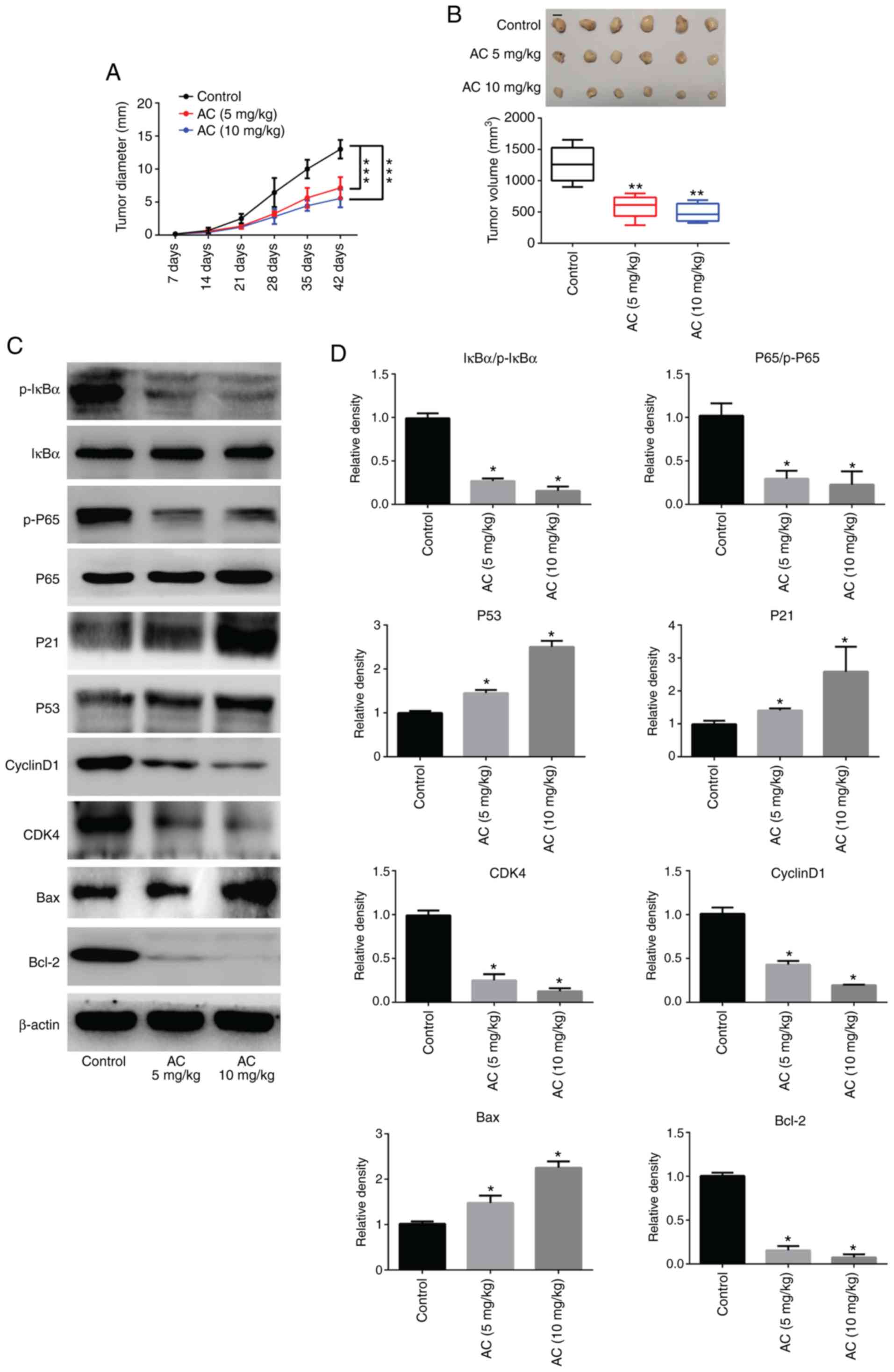
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB,
Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL and Siegel
RL: Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J
Clin. 69:363–385. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Van der Jeught K, Xu HC, Li YJ, Lu XB and
Ji G: Drug resistance and new therapies in colorectal cancer. World
J Gastroenterol. 24:3834–3848. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bahrami A, Amerizadeh F, Hassanian SM,
ShahidSales S, Khazaei M, Maftouh M, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Ferns GA
and Avan A: Genetic variants as potential predictive biomarkers in
advanced colorectal cancer patients treated with oxaliplatin-based
chemotherapy. J Cell Physiol. 233:2193–2201. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bylka W, Znajdek-Awiżeń P,
Studzińska-Sroka E, Dańczak-Pazdrowska A and Brzezińska M: Centella
asiatica in dermatology: An overview. Phytother Res. 28:1117–1124.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chandrika UG, Prasad Kumarab and Peramune
AAS: Gotu Kola (Centella asiatica): Nutritional properties and
plausible health benefits. Adv Food Nutr Res. 76:125–157. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
da Rocha PBR, Santos Souza BD, Andrade LM,
Marreto RN, Lima EM and Taveira SF: Development of a
high-performance liquid chromatographic method for asiaticoside
quantification in different skin layers after topical application
of a Centella asiatica extract. Planta Med. 83:1431–1437. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nowwarote N, Osathanon T, Jitjaturunt P,
Manopattanasoontorn S and Pavasant P: Asiaticoside induces type I
collagen synthesis and osteogenic differentiation in human
periodontal ligament cells. Phytother Res. 27:457–462. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lee J, Jung E, Kim Y, Park J, Park J, Hong
S, Kim J, Hyun C, Kim YS and Park D: Asiaticoside induces human
collagen I synthesis through TGFbeta receptor I kinase (TbetaRI
kinase)-independent Smad signaling. Planta Med. 72:324–328. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Phaechamud T, Yodkhum K, Charoenteeraboon
J and Tabata Y: Chitosan-aluminum monostearate composite sponge
dressing containing asiaticoside for wound healing and angiogenesis
promotion in chronic wound. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.
50:210–225. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang J, Zhou X, Shen Y, Li H, Zhou G,
Zhang W, Zhang Y and Liu W: Asiaticoside loading into
polylactic-co-glycolic acid electrospun nanofibers attenuates host
inflammatory response and promotes M2 macrophage polarization. J
Biomed Mater Res A. 108:69–80. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang CZ, Niu J, Chong YS, Huang YF, Chu
Y, Xie SY, Jiang ZH and Peng LH: Porous microspheres as promising
vehicles for the topical delivery of poorly soluble asiaticoside
accelerate wound healing and inhibit scar formation in vitro &
in vivo. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 109:1–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qi SH, Xie JL, Pan S, Xu YB, Li TZ, Tang
JM, Liu XS, Shu B and Liu P: Effects of asiaticoside on the
expression of Smad protein by normal skin fibroblasts and
hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Clin Exp Dermatol. 33:171–175. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qiu J, Yu L, Zhang X, Wu Q, Wang D, Wang
X, Xia C and Feng H: Asiaticoside attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via down-regulation of
NF-kB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 26:181–187. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Luo Y, Fu C, Wang Z, Zhang Z, Wang H and
Liu Y: Asiaticoside attenuates the effects of spinal cord injury
through antioxidant and antiinflammatory effects, and inhibition of
the p38MAPK mechanism. Mol Med Rep. 12:8294–8300. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fitri AR, Pavasant P, Chamni S and
Sumrejkanchanakij P: Asiaticoside induces osteogenic
differentiation of human peri-odontal ligament cells through the
Wnt pathway. J Periodontol. 89:596–605. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Al-Saeedi FJ, Bitar M and Pariyani S:
Effect of asiaticoside on 99mTc-tetrofosmin and 99mTc-sestamibi
uptake in MCF-7 cells. J Nucl Med Technol. 39:279–283. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yingchun L, Huihan W, Rong Z, Guojun Z,
Ying Y and Zhuogang L: Antitumor activity of asiaticoside against
multiple myeloma drug-resistant cancer cells is mediated by
autophagy induction, activation of effector caspases, and
inhibition of cell migration, invasion, and STAT-3 signaling
pathway. Med Sci Monit. 25:1355–1361. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang YH, Zhang SH, Zhen RX, Xu XD and
Zhen YS: Asiaticoside inducing apoptosis of tumor cells and
enhancing anti-tumor activity of vincristine. Ai Zheng.
23:1599–1604. 2004.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Al-Saeedi FJ: Study of the cytotoxicity of
asiaticoside on rats and tumour cells. BMC Cancer. 14:2202014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Perelman A, Wachtel C, Cohen M, Haupt S,
Shapiro H and Tzur A: JC-1: Alternative excitation wavelengths
facilitate mitochondrial membrane potential cytometry. Cell Death
Dis. 3:e4302012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Soleimani A, Rahmani F, Ferns GA, Ryzhikov
M, Avan A and Hassanian SM: Role of the NF-κB signaling pathway in
the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Gene. 726:1441322020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang Q, Lenardo MJ and Baltimore D: 30
Years of NF-κB: A blossoming of relevance to human pathobiology.
Cell. 168:37–57. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
de Castro Barbosa ML, da Conceicao RA,
Fraga AGM, Camarinha BD, de Carvalho Silva GC, Lima AGF, Cardoso
EA, de Oliveira Freitas and Lione V: NF-kappaB signaling pathway
inhibitors as anticancer drug candidates. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 17:483–490. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kocyigit A and Guler EM: Curcumin induce
DNA damage and apoptosis through generation of reactive oxygen
species and reducing mitochondrial membrane potential in melanoma
cancer cells. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 63:97–105. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yun X, Rao W, Xiao C and Huang Q:
Apoptosis of leukemia K562 and Molt-4 cells induced by emamectin
benzoate involving mitochondrial membrane potential loss and
intracellular Ca(2+) modulation. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol.
52:280–287. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang Y, Zong M, Xu W, Zhang Y, Wang B,
Yang M and Tao L: Natural pyrethrins induces apoptosis in human
hepatocyte cells via Bax- and Bcl-2-mediated mitochondrial pathway.
Chem Biol Interact. 262:38–45. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tang S, Hu J, Meng Q, Dong X, Wang K, Qi
Y, Chu C, Zhang X and Hou L: Daidzein induced apoptosis via
down-regulation of Bcl-2/Bax and triggering of the mitochondrial
pathway in BGC-823 cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 65:197–202. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhu J, Chen M, Chen N, Ma A, Zhu C, Zhao
R, Jiang M, Zhou J, Ye L, Fu H and Zhang X: Glycyrrhetinic acid
induces G1-phase cell cycle arrest in human nonsmall cell lung
cancer cells through endo-plasmic reticulum stress pathway. Int J
Oncol. 46:981–988. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bonelli M, Monica SL, Fumarola C and
Alfieri R: Multiple effects of CDK4/6 inhibition in cancer: From
cell cycle arrest to immunomodulation. Biochem Pharmacol.
170:1136762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He L, Hong G, Zhou L, Zhang J, Fang J, He
W, Tickner J, Han X, Zhao L and Xu J: Asiaticoside, a component of
Centella asiatica attenuates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via
NFATc1 and NF-kB signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol. 234:4267–4276.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yin Z, Yu H, Chen S, Ma C, Ma X, Xu L, Ma
Z, Qu R and Ma S: Asiaticoside attenuates diabetes-induced
cognition deficits by regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-kB pathway. Behav
Brain Res. 292:288–299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meshram SN, Paul D, Manne R, Choppara S,
Sankaran G, Agrawal Y and Santra MK: FBXO32 activates NF-kB through
IkBα degradation in inflammatory and genotoxic stress. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 92:134–140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tsuchiya Y, Osaki K, Kanamoto M, Nakao Y,
Takahashi E, Higuchi T and Kamata H: Distinct B subunits of PP2A
regulate the NF-kB signalling pathway through dephosphorylation of
IKKβ, IkBα and RelA. FEBS Lett. 591:4083–4094. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hu J, Haseebuddin M, Young M and Colburn
NH: Suppression of p65 phosphorylation coincides with inhibition of
IkappaBalpha polyubiquitination and degradation. Mol Carcinog.
44:274–284. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Thoms HC, Dunlop MG and Stark LA:
p38-mediated inactivation of cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent kinase 4
stimulates nucleolar translocation of RelA and apoptosis in
colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67:1660–1669. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|