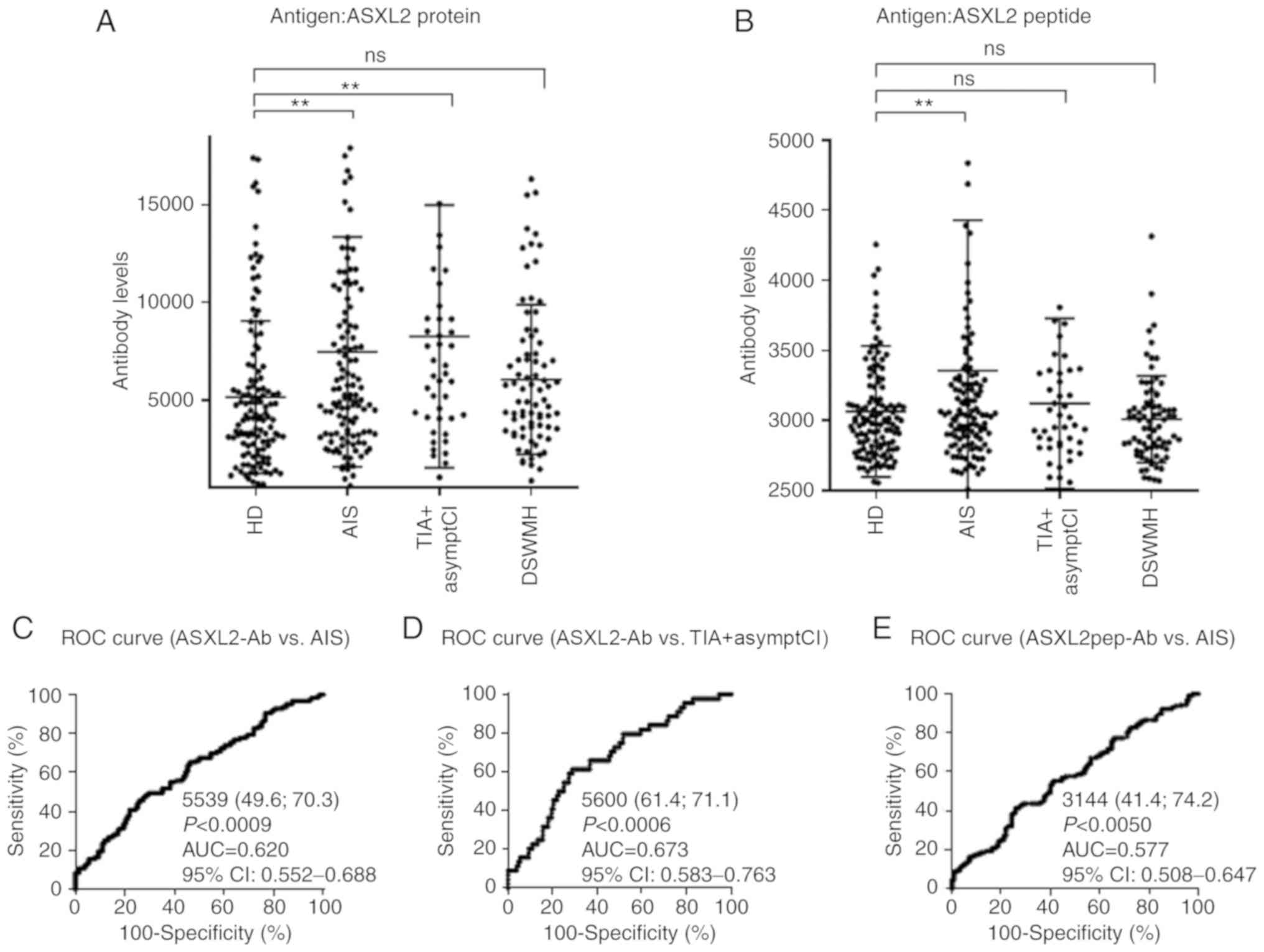
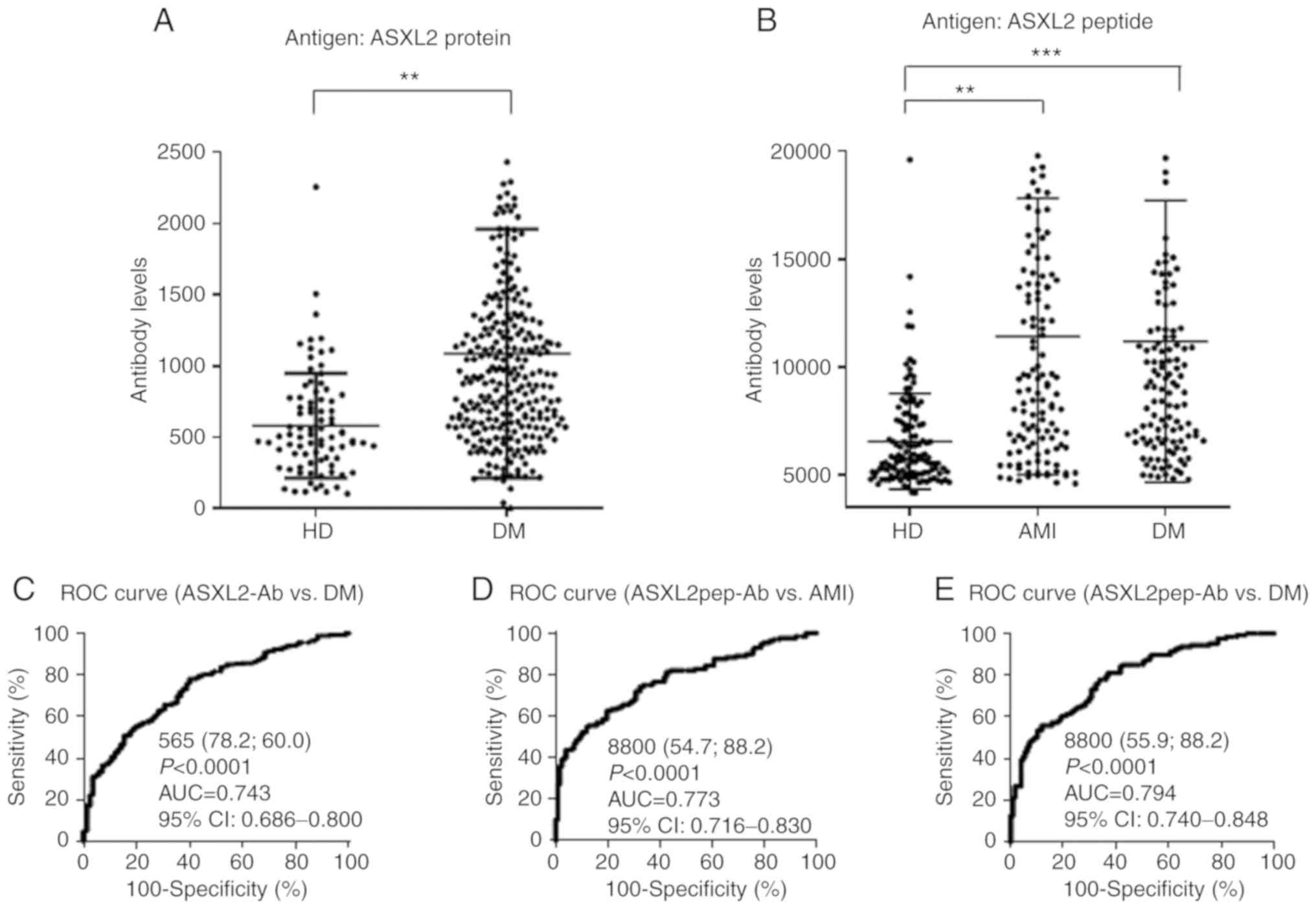
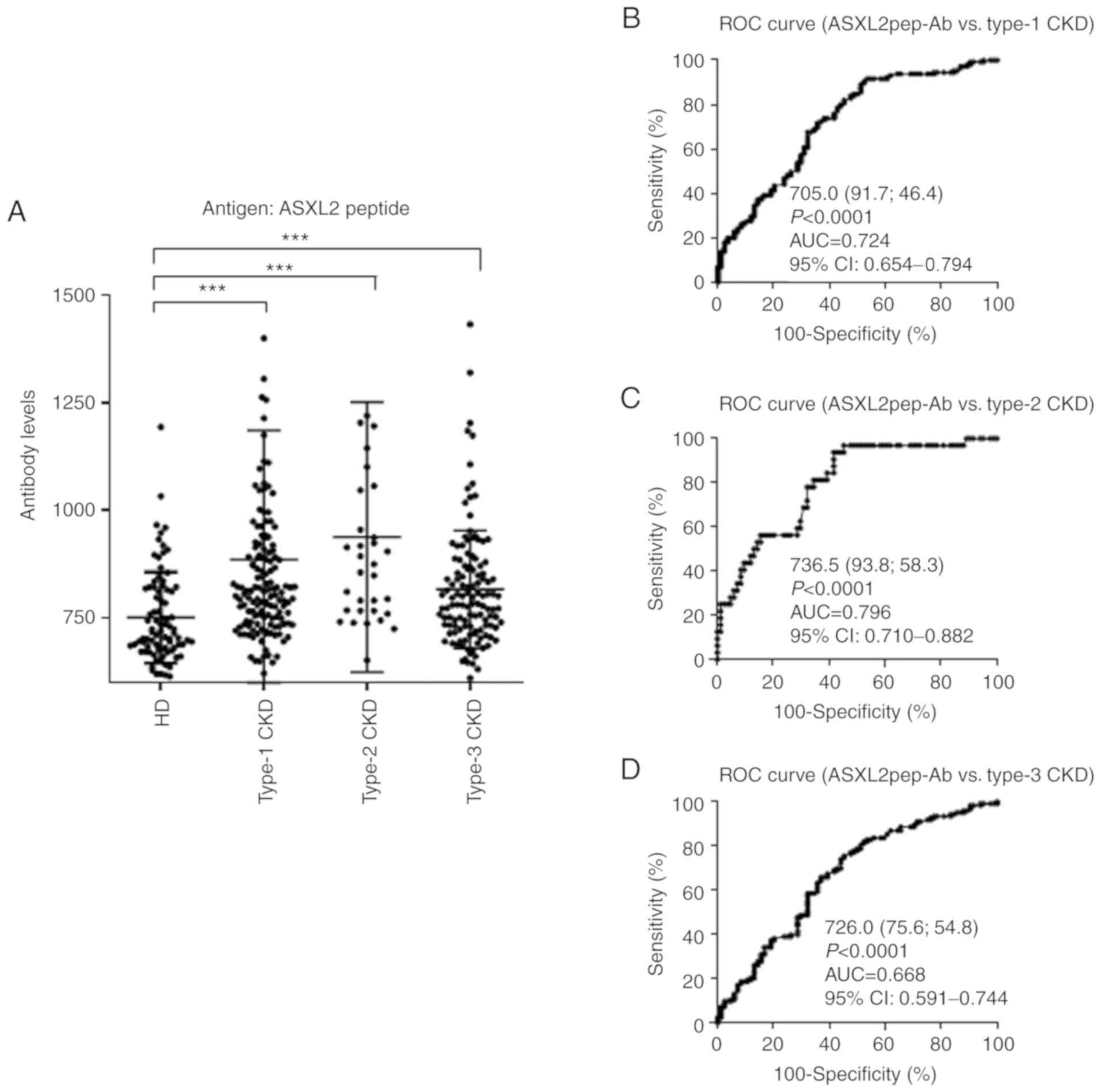
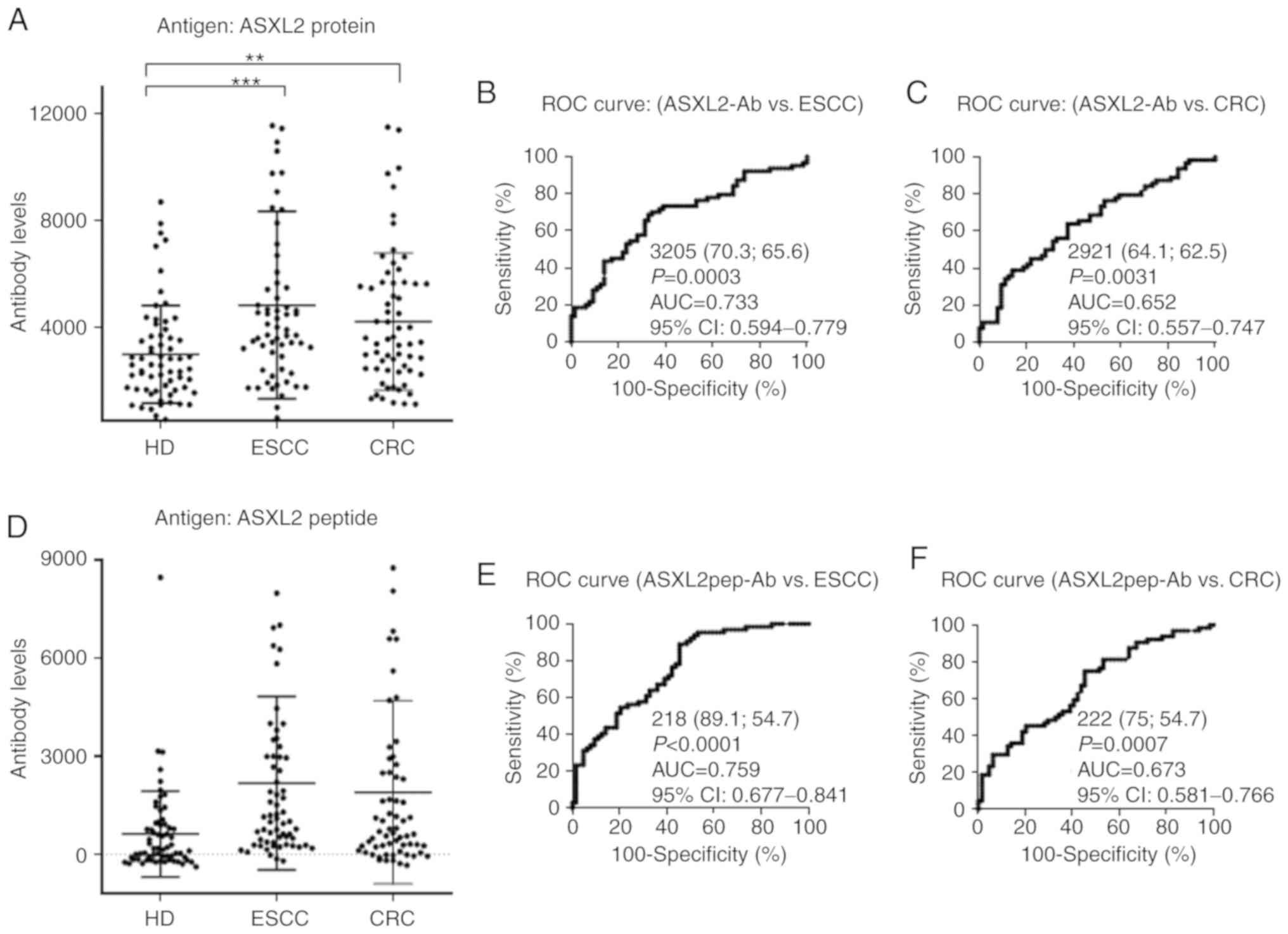
|
1
|
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S,
Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, et
al: Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20
age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the global
burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 380:2095–2128. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meschia JF and Brott T: Ischaemic stroke.
Eur J Neurol. 25:35–40. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Writing Group Members; Mozaffarian D,
Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de
Ferranti S, Després JP, et al: Executive summary: Heart disease and
stroke statistics-2016 update: A report from the American Heart
Association. Circulation. 133:447–454. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
French BR, Boddepalli RS and Govindarajan
R: Acute ischemic stroke: Current status and future directions. Mol
Med. 113:480–486. 2016.
|
|
5
|
Deb P, Sharma S and Hassan KM:
Pathophysiologic mechanisms of acute ischemic stroke: An overview
with emphasis on therapeutic significance beyond thrombolysis.
Pathophysiology. 17:197–218. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen YT, Scanlan MJ, Sahin U, Türeci O,
Gure AO, Tsang S, Williamson B, Stockert E, Pfreundschuh M and Old
LJ: A testicular antigen aberrantly expressed in human cancers
detected by autologous antibody screening. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:1914–1918. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gnjatic S, Nishikawa H, Jungbluth AA, Güre
AO, Ritter G, Jäger E, Knuth A, Chen YT and Old LJ: NY-ESO-1:
Review of an immunogenic tumor antigen. Adv Cancer Res. 95:1–30.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shimada H, Nakajima K, Ochiai T, Koide Y,
Okazumi S, Matsubara H, Takeda A, Miyazawa Y, Arima M and Isono K:
Detection of serum p53 antibodies in patients with esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma: Correlation with clinicopathologic
features and tumor markers. Oncol Rep. 5:871–874. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shimada H: p53 molecular approach to
diagnosis and treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann
Gastroenterol Surg. 2:266–273. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qin JJ, Wang XR, Wang P, Ren PF, Shi JX,
Zhang HF, Xia JF, Wang KJ, Song CH, Dai LP, et al: Mini-array of
multiple tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) in the immunodiagnosis of
esophageal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:2635–2640. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakashima K, Shimada H, Ochiai T,
Kuboshima M, Kuroiwa N, Okazumi S, Matsubara H, Nomura F, Takiguchi
M and Takaki H: Serological identification of TROP2 by recombinant
cDNA expression cloning using sera of patients with esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 112:1029–1035. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuboshima M, Shimada H, Liu TL, Nakashima
K, Nomura F, Takiguchi M, Hiwasa T and Ochiai T: Identification of
a novel SEREX antigen, SLC2A1/GLUT1, in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 28:463–468. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kuboshima M, Shimada H, Liu TL, Nomura F,
Takiguchi M, Hiwasa T and Ochiai T: Presence of serum tripartite
motif-containing 21 antibodies in patients with esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 97:380–386. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shimada H, Kuboshima M, Shiratori T,
Nabeya Y, Takeuchi A, Takagi H, Nomura F, Takiguchi M, Ochiai T and
Hiwasa T: Serum anti-myomegalin antibodies in patients with
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 30:97–103.
2007.
|
|
15
|
Shimada H, Shiratori T, Yasuraok M, Kagaya
A, Kuboshima M, Nomura F, Takiguchi M, Ochiai T, Matsubara H and
Hiwasa T: Identification of Makorin 1 as a novel SEREX antigen of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 9:2322009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kagaya A, Shimada H, Shiratori T,
Kuboshima M, Nakashima-Fujita K, Yasuraoka M, Nishimori T, Kurei S,
Hachiya T, Murakami A, et al: Identification of a novel SEREX
antigen family, ECSA, in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Proteome Sci. 9:312011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shimada H, Ito M, Kagaya A, Shiratori T,
Kuboshima M, Suzuki M, Liu TL, Nabeya Y, Matsubara H, Matsushita K,
et al: Elevated serum antibody levels against cyclin L2 in patients
with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Sci Ther.
7:60–66. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Kobayashi S, Hoshino T, Hiwasa T, Satoh M,
Rahmutulla B, Tsuchida S, Komukai Y, Tanaka T, Matsubara H, Shimada
H, et al: Anti-FIRs (PUF60) auto-antibodies are detected in the
sera of early-stage colon cancer patients. Oncotarget.
7:82493–82503. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matsutani T, Hiwasa T, Takiguchi M, Oide
T, Kunimatsu M, Saeki N and Iwadate Y: Autologous antibody to
src-homology 3-domain GRB2-like 1 specifically increases in the
sera of patients with low-grade gliomas. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
31:852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Adachi-Hayama M, Adachi A, Shinozaki N,
Matsutani T, Hiwasa T, Takiguchi M, Saeki N and Iwadate Y:
Circulating anti-filamin C antibody as a potential serum biomarker
for low-grade gliomas. BMC Cancer. 14:4522014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hontani K, Tsuchikawa T, Hiwasa T,
Nakamura T, Ueno T, Kushibiki T, Takahashi M, Inoko K, Takano H,
Takeuchi S, et al: Identification of novel serum autoantibodies
against EID3 in non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
Oncotarget. 8:106206–106221. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Machida T, Kubota M, Kobayashi E, Iwadate
Y, Saeki N, Yamaura A, Nomura F, Takiguchi M and Hiwasa T:
Identification of stroke-associated-antigens via screening of
recombinant proteins from the human expression cDNA library
(SEREX). J Translat Med. 13:712015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Goto KI, Sugiyama T, Matsumura R, Zhang
XM, Kimura R, Taira A, Arita E, Iwase K, Kobayashi E, Iwadate Y, et
al: Identification of cerebral infarction-specific antibody markers
from autoantibodies detected in patients with systemic lupus
erythematosus. J Mol Biomark Diagn. 6:2192015.
|
|
24
|
Yoshida Y, Wang H, Hiwasa T, Machida T,
Kobayashi E, Mine S, Tomiyoshi G, Nakamura R, Shinmen N, Kuroda H,
et al: Elevation of autoantibody level against PDCD11 in patients
with transient ischemic attack. Oncotarget. 9:8836–8848. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang H, Zhang XM, Tomiyoshi G, Nakamura R,
Shinmen N, Kuroda H, Kimura R, Mine S, Kamitsukasa I, Wada T, et
al: Association of serum levels of antibodies against MMP1 CBX1,
and CBX5 with transient ischemic attack and cerebral infarction.
Oncotarget. 9:5600–5613. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Linke AT, Marchant B, Marsh P, Frampton G,
Murphy J and Rose ML: Screening of a HUVEC cDNA library with
transplant-associated coronary artery disease sera identifies RPL7
as a candidate autoantigen associated with this disease. Clin Exp
Immunol. 126:173–179. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hiwasa T, Machida T, Zhang XM, Kimura R,
Wang H, Iwase K, Ashino H, Taira A, Arita E, Mine S, et al:
Elevated levels of autoantibodies against ATP2B4 and BMP-1 in sera
of patients with atherosclerosis-related diseases. Immunome Res.
11:0972015.
|
|
28
|
Hiwasa T, Tomiyoshi G, Nakamura R, Shinmen
N, Kuroda H, Kunimatsu M, Mine S, Machida T, Sato E, Takemoto M, et
al: Serum SH3BP5-specific antibody level is a biomarker of
athero-sclerosis. Immunome Res. 13:1322017.
|
|
29
|
Nakamura R, Tomiyoshi G, Shinmen N, Kuroda
H, Kudo T, Doi H, Mine S, Machida T, Kamitsukasa I, Wada T, et al:
An anti-deoxyhypusine synthase antibody as a marker of
atherosclerosis-related cerebral infarction myocardial infarction
diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. SM Atheroscler J.
1:10012017.
|
|
30
|
Chen PM, Ohno M, Hiwasa T, Nishi K, Saijo
S, Sakamoto J, Morita Y, Matsuda S, Watanabe S, Kuwabara Y, et al:
Nardilysin is a promising biomarker for the early diagnosis of
acute coro-nary syndrome. Int J Cardiol. 243:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hiwasa T, Zhang XM, Kimura R, Machida T,
Kitamura K, Yamazoe R, Kunimatsu M, Mine S, Kobayashi E, Iwadate Y,
et al: Association of serum antibody levels against TUBB2C with
diabetes and cerebral infarction. Gratis J Biomed Sci. 1:49–63.
2015.
|
|
32
|
Palmer JP, Asplin CM, Clemons P, Lyen K,
Tatpati O, Raghu PK and Paquette TL: Insulin antibodies in
insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science.
222:1337–1339. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Baekkeskov S, Aanstoot HJ, Christgau S,
Reetz A, Solimena M, Cascalho M, Folli F, Richter-Olesen H and De
Camilli P: Identification of the 64K autoantigen in
insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic
acid decarboxylase. Nature. 347:151–156. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hiwasa T, Zhang XM, Kimura R, Ohno M, Chen
PM, Nishi E, Ono K, Kimura T, Kamitsukasa I, Wada T, et al:
Elevated adiponectin antibody levels in sera of patients with
atherosclerosis-related coronary artery disease cerebral infarction
and diabetes mellitus. J Circ Biomark. 5:82016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sugimoto K, Tomiyoshi G, Mori M, Kuwabara
S, Hirano S, Sawai S, Beppu M, Muto M, Uzawa A, Kitamura K, et al:
Identification of serum anti-GADD34 antibody as a common marker of
diabetes mellitus and Parkinson disease. J Alzheimers Dis
Parkinsonism. 7:3582017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhu H, Li Z, Lv J and Zhao R: Effects of
cerebral small vessel disease on the outcome of patients with
ischemic stroke caused by large artery atherosclerosis. Neurol Res.
40:381–390. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Khyzha N, Alizada A, Wilson MD and Fish
JE: Epigenetics of atherosclerosis: Emerging mechanisms and
methods. Trends Mol Med. 23:332–347. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Valdivielso JM, Rodríguez-Puyol D, Pascual
J, Barrios C, Bermúdez-López M, Sánchez-Niño MD, Pérez-Fernández M
and Ortiz A: Atherosclerosis in chronic kidney disease: More, less,
or just different? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 39:1938–1966.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Goldstein LB, Bushnell CD, Adams RJ, Appel
LJ, Braun LT, Chaturvedi S, Creager MA, Culebras A, Eckel RH, Hart
RG, et al: Guidelines for the primary prevention of stroke: A
guideline for healthcare professionals from the American heart
association/American stroke association. Stroke. 42:517–584. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Alloubani A, Saleh A and Abdelhafiz I:
Hypertension and diabetes mellitus as a predictive risk factors for
stroke. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 12:577–584. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shao C, Wang J, Tian J and Tang YD:
Coronary artery disease: From mechanism to clinical practice. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 1177:1–36. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nishiura R, Fujimoto S, Sato Y, Yamada K,
Hisanaga S, Hara S, Nakao H and Kitamura K: Elevated
osteoprotegerin levels predict cardiovascular events in new
hemodialysis patients. Am J Nephrol. 29:257–263. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Komatsu H, Fujimoto S, Hara S, Fukuda A,
Fukudome K, Yamada K, Sato Y and Kitamura K: Recent therapeutic
strategies improve renal outcome in patients with IgA nephropathy.
Am J Nephrol. 30:19–25. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use soft-ware 'EZR' for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Identification and
characterization of ASXL2 gene in silico. Int J Oncol. 23:845–850.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Park UH, Yoon SK, Park T, Kim EJ and Um
SJ: Additional sex comb-like (ASXL) proteins 1 and 2 play opposite
roles in adipogenesis via reciprocal regulation of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor {gamma}. J Biol Chem.
286:1354–1363. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Della-Morte D, Palmirotta R, Rehni AK,
Pastore D, Capuani B, Pacifici F, De Marchis ML, Dave KR, Bellia A,
Fogliame G, et al: Pharmacogenomics and pharmacogenetics of
thiazolidinediones: Role in diabetes and cardiovascular risk
factors. Pharmacogenomics. 15:2063–2082. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lehrke M and Lazar MA: The many faces of
PPARgamma. Cell. 123:993–999. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Evans RM, Barish GD and Wang YX: PPARs and
the complex journey to obesity. Nat Med. 10:355–361. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Poulsen LI, Siersbaek M and Mandrup S:
PPARs: Fatty acid sensors controlling metabolism. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 23:631–639. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Watkins SM, Reifsnyder PR, Pan HJ, German
JB and Leiter EH: Lipid metabolome-wide effects of the PPARgamma
agonist rosiglitazone. J Lipid Res. 43:1809–1817. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Salomone S and Drago F: Effects of PPARγ
ligands on vascular tone. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 5:282–291. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Marx N, Kehrle B, Kohlhammer K, Grub M,
Koenig W, Hombach V, Libby P and Plutzky J: PPAR activators as
antiin-flammatory mediators in human T lymphocytes: Implications
for atherosclerosis and transplantation-associated
arteriosclerosis. Circ Res. 90:703–710. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Venkitaraman AR: Cancer susceptibility and
the functions of BRCA1 and BRCA2. Cell. 108:171–182. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tarsounas M and Sung P: The
antitumorigenic roles of BRCA1-BARD1 in DNA repair and replication.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:284–299. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mallery DL, Vandenberg CJ and Hiom K:
Activation of the E3 ligase function of the BRCA1/BARD1 complex by
polyubiquitin chains. EMBO J. 21:6755–6762. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Nishikawa H, Wu W, Koike A, Kojima R, Gomi
H, Fukuda M and Ohta T: BRCA1-associated protein 1 interferes with
BRCA1/BARD1 RING heterodimer activity. Cancer Res. 69:111–119.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Greenberg RA, Sobhian B, Pathania S,
Cantor SB, Nakatani Y and Livingston DM: Multifactorial
contributions to an acute DNA damage response by
BRCA1/BARD1-containing complexes. Genes Dev. 20:34–46. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Peng H, Prokop J, Karar J, Park K, Cao L,
Harbour JW, Bowcock AM, Malkowicz SB, Cheung M, Testa JR and
Rauscher FJ III: Familial and somatic BAP1 mutations inactivate
ASXL1/2-mediated allosteric regulation of BAP1 deubiquitinase by
targeting multiple independent domains. Cancer Res. 78:1200–1213.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
60
|
Park UH, Kang MR, Kim EJ, Kwon YS, Hur W,
Yoon SK, Song BJ, Park JH, Hwang JT, Jeong JC and Um SJ: ASXL2
promotes proliferation of breast cancer cells by linking ERα to
histone methylation. Oncogene. 35:3742–3752. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Martinet W, Knaapen MW, De Meyer GR,
Herman AG and Kockx MM: Elevated levels of oxidative DNA damage and
DNA repair enzymes in human atherosclerotic plaques. Circulation.
106:927–932. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Andreassi MG and Botto N: DNA damage as a
new emerging risk factor in atherosclerosis. Trends Cardiovasc Med.
13:270–275. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Shukla PC, Singh KK, Quan A, Al-Omran M,
Teoh H, Lovren F, Cao L, Rovira II, Pan Y, Brezden-Masley C, et al:
BRCA1 is an essential regulator of heart function and survival
following myocardial infarction. Nat Commun. 2:5932011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wold MS: Replication protein A: A
heterotrimeric, single-stranded DNA-binding protein required for
eukaryotic DNA metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 66:61–92. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Erdile LF, Wold MS and Kelly TJ: The
primary structure of the 32-kDa subunit of human replication
protein A. J Biol Chem. 265:3177–3182. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Atabek ME, Akyürek N, Eklioglu BS and Alp
H: Impaired systolic blood dipping and nocturnal hypertension: An
independent predictor of carotid intima-media thickness in type 1
diabetic patients. J Diabetes Complicat. 28:51–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Dans T,
Avezum A, Lanas F, McQueen M, Budaj A, Pais P, Varigos J, et al:
Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with
myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study):
Case-control study. Lancet. 364:937–952. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
O'Donnell MJ, Xavier D, Liu L, Zhang H,
Chin SL, Rao-Melacini P, Rangarajan S, Islam S, Pais P, McQueen MJ,
et al: Risk factors for ischaemic and intracerebral haemorrhagic
stroke in 22 countries (the INTERSTROKE study): A case-control
study. Lancet. 376:112–123. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Lindgren AM, Nissinen AM, Tuomilehto JO
and Pukkala E: Cancer pattern among hypertensive patients in North
Karelia, Finland. J Hum Hypertens. 19:373–379. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Sanfilippo KM, McTigue KM, Fidler CJ,
Neaton JD, Chang Y, Fried LF, Liu S and Kuller LH: Hypertension and
obesity and the risk of kidney cancer in 2 large cohorts of US men
and women. Hypertension. 63:934–941. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Sun LM, Kuo HT, Jeng LB, Lin CL, Liang JA
and Kao CH: Hypertension and subsequent genitourinary and
gynecologic cancers risk: A population-based cohort study. Medicine
(Baltimore). 94:e7532015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Han H, Guo W, Shi W, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Ye X
and He J: Hypertension and breast cancer risk: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 7:448772017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Schmid U1, Stopper H, Schweda F, Queisser
N and Schupp N: Angiotensin II induces DNA damage in the kidney.
Cancer Res. 68:9239–9246. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Naito A, Hiwasa T, Tanabe N, Sanada TJ,
Sugiura T, Shigeta A, Terada J, Takizawa H, Kashiwado K, Sakao S
and Tatsumi K: Elevated levels of autoantibodies against EXD2 and
PHAX in the sera of patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary
hypertension. PLoS One. 14:e02113772019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Rothwell PM and Warlow CP: Timing of TIAs
preceding stroke: Time window for prevention is very short.
Neurology. 64:817–820. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hill MD, Yiannakoulias N, Jeerakathil T,
Tu JV, Svenson LW and Schopflocher DP: The high risk of stroke
immediately after transient ischemic attack: A population-based
study. Neurology. 62:2015–2020. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|