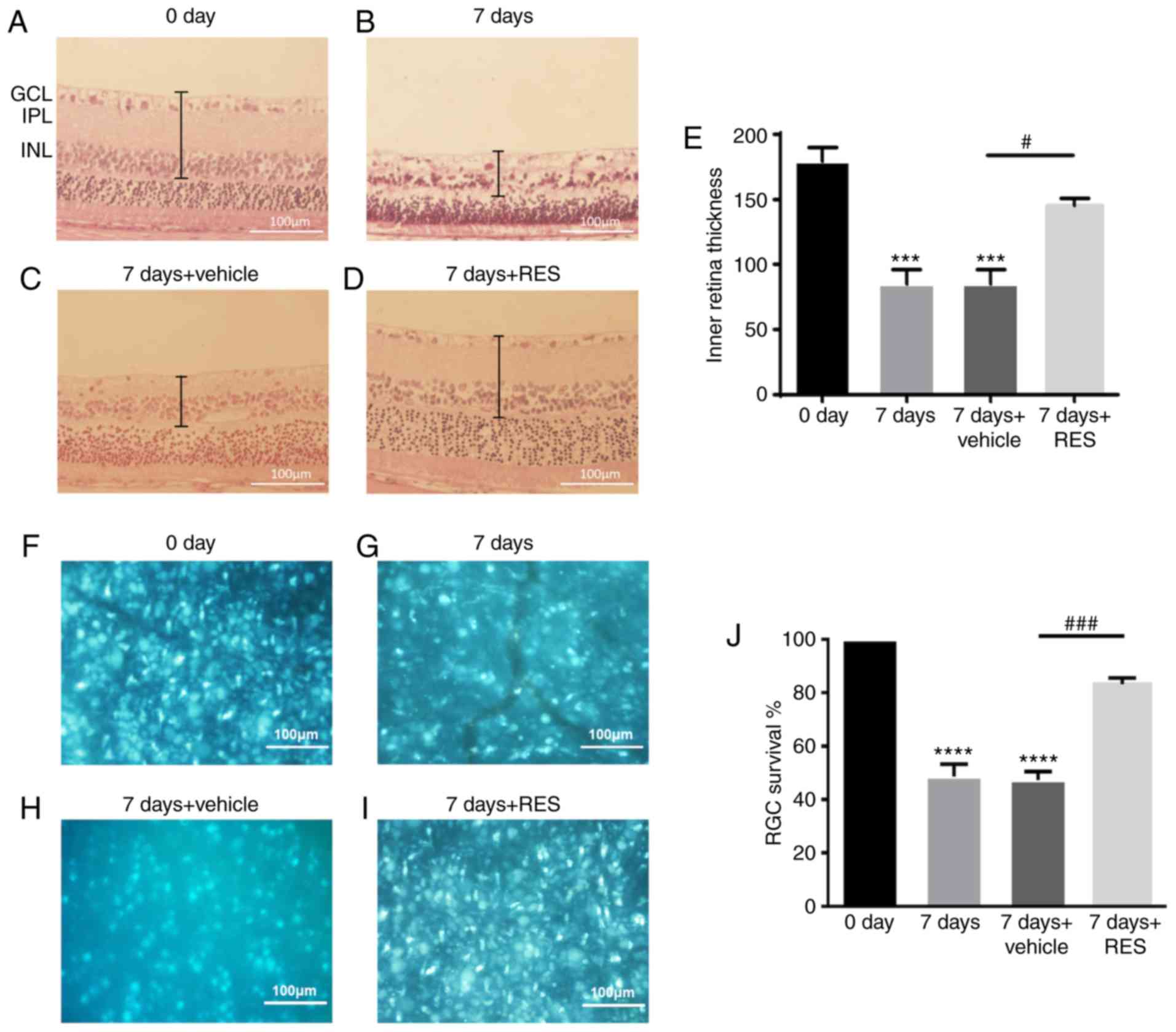
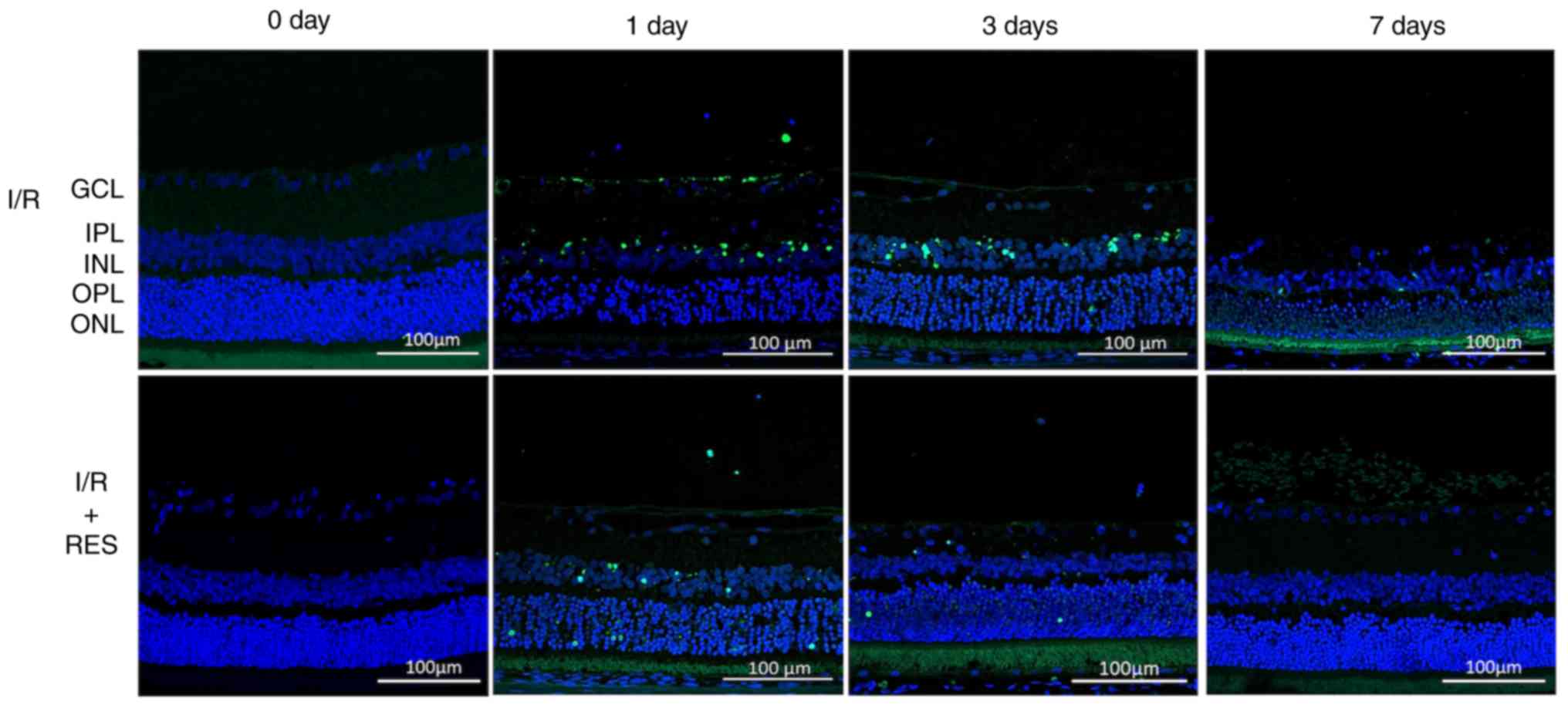
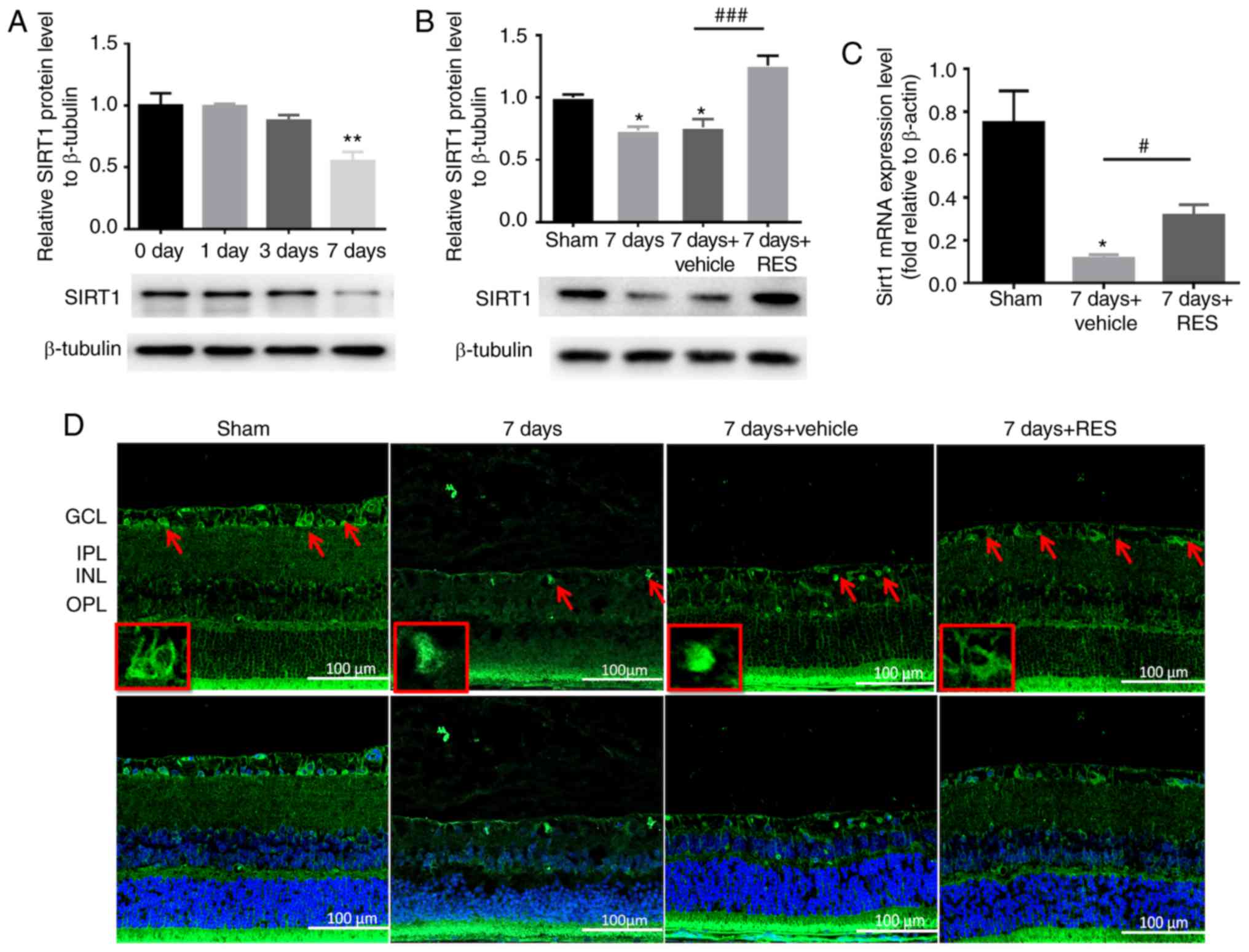
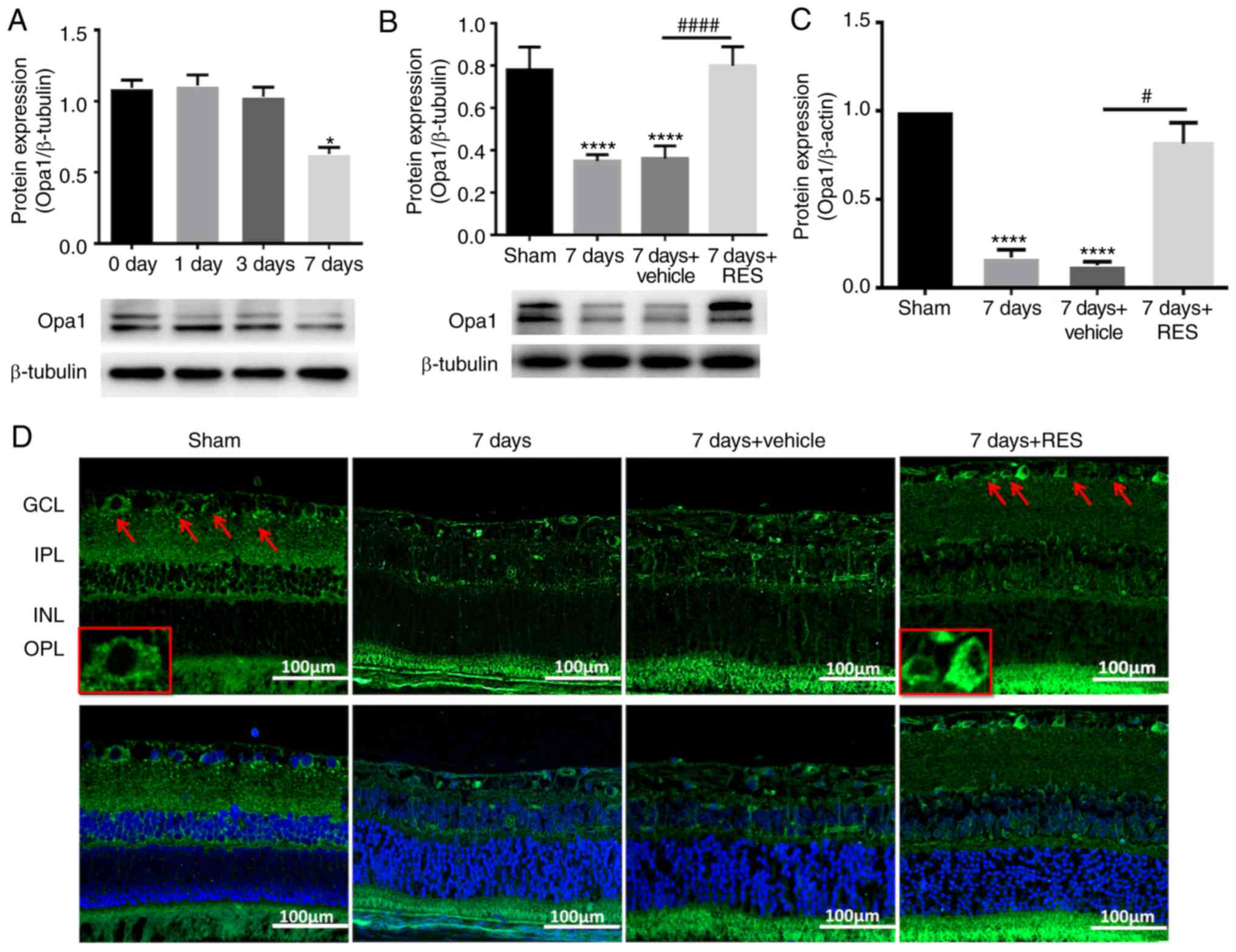
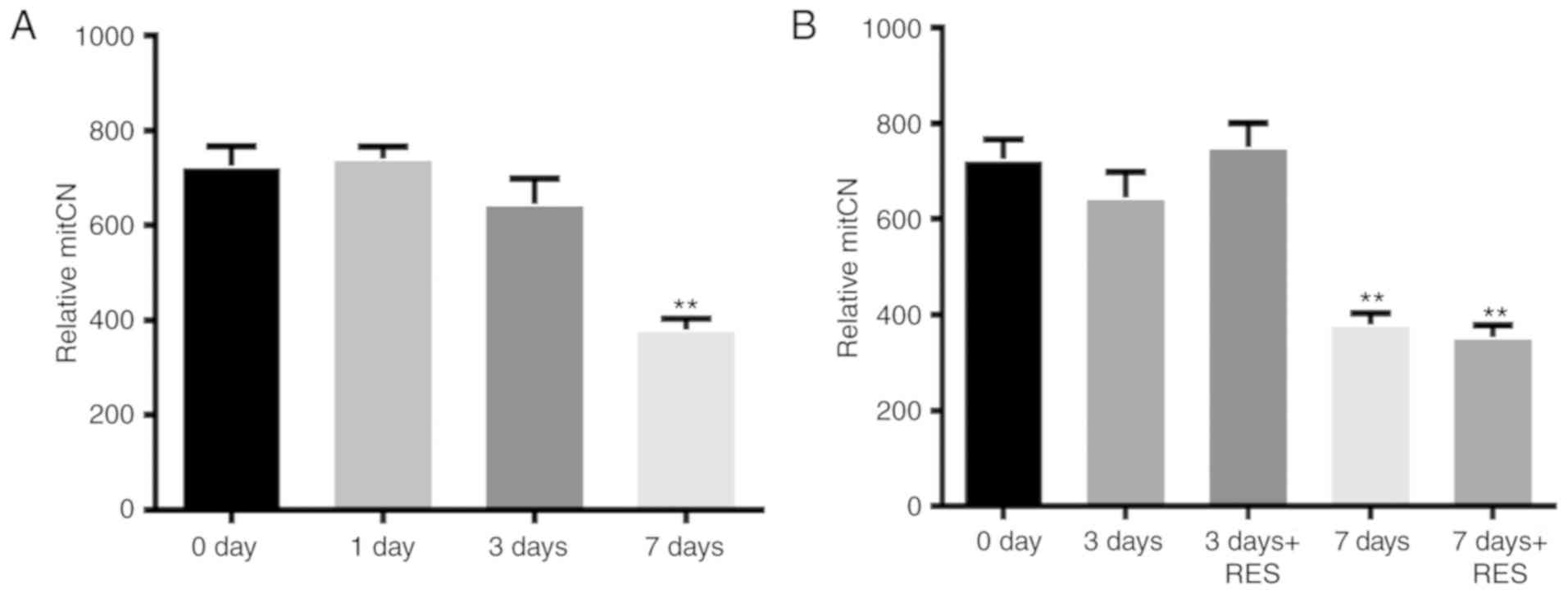
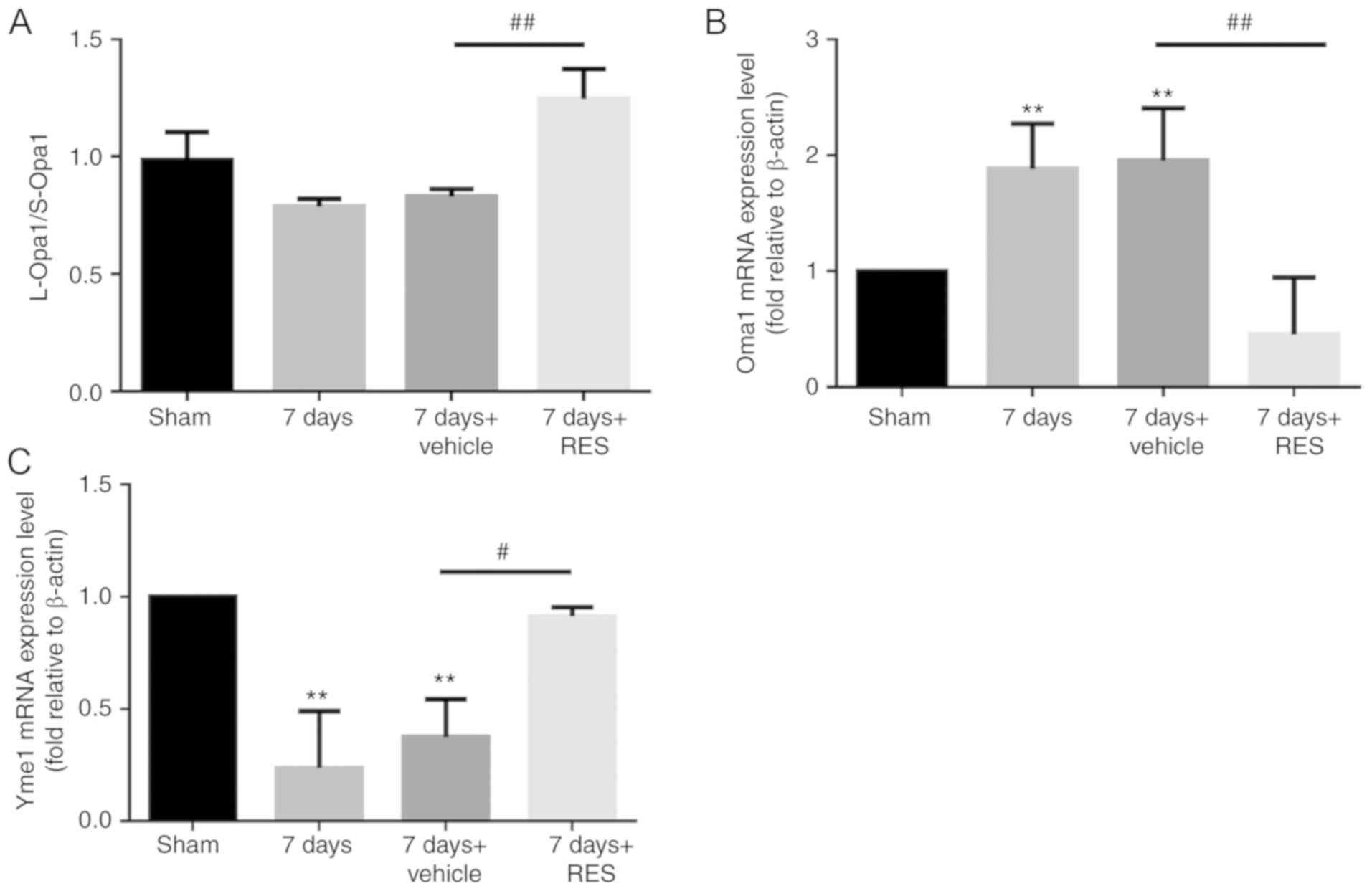
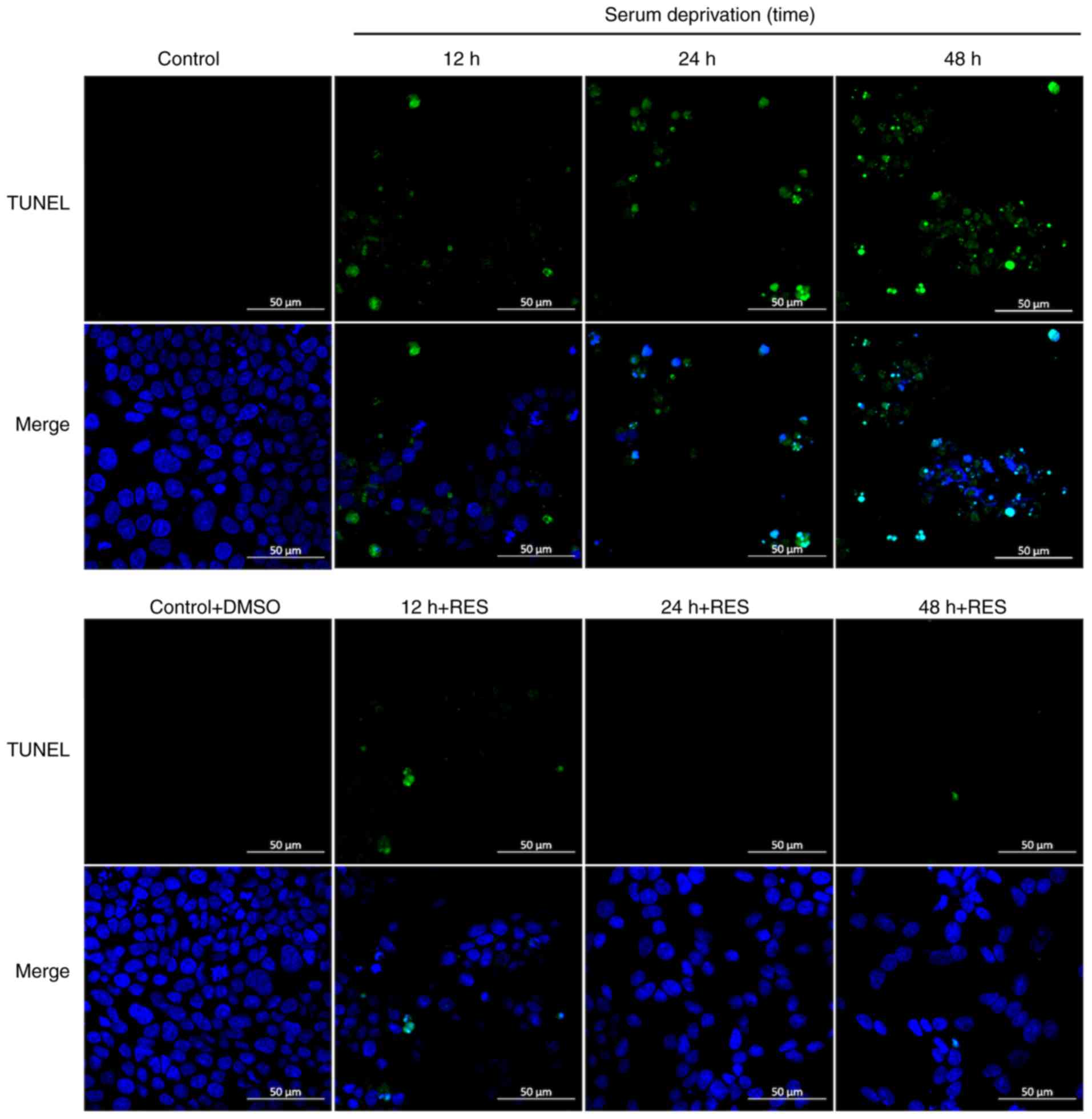
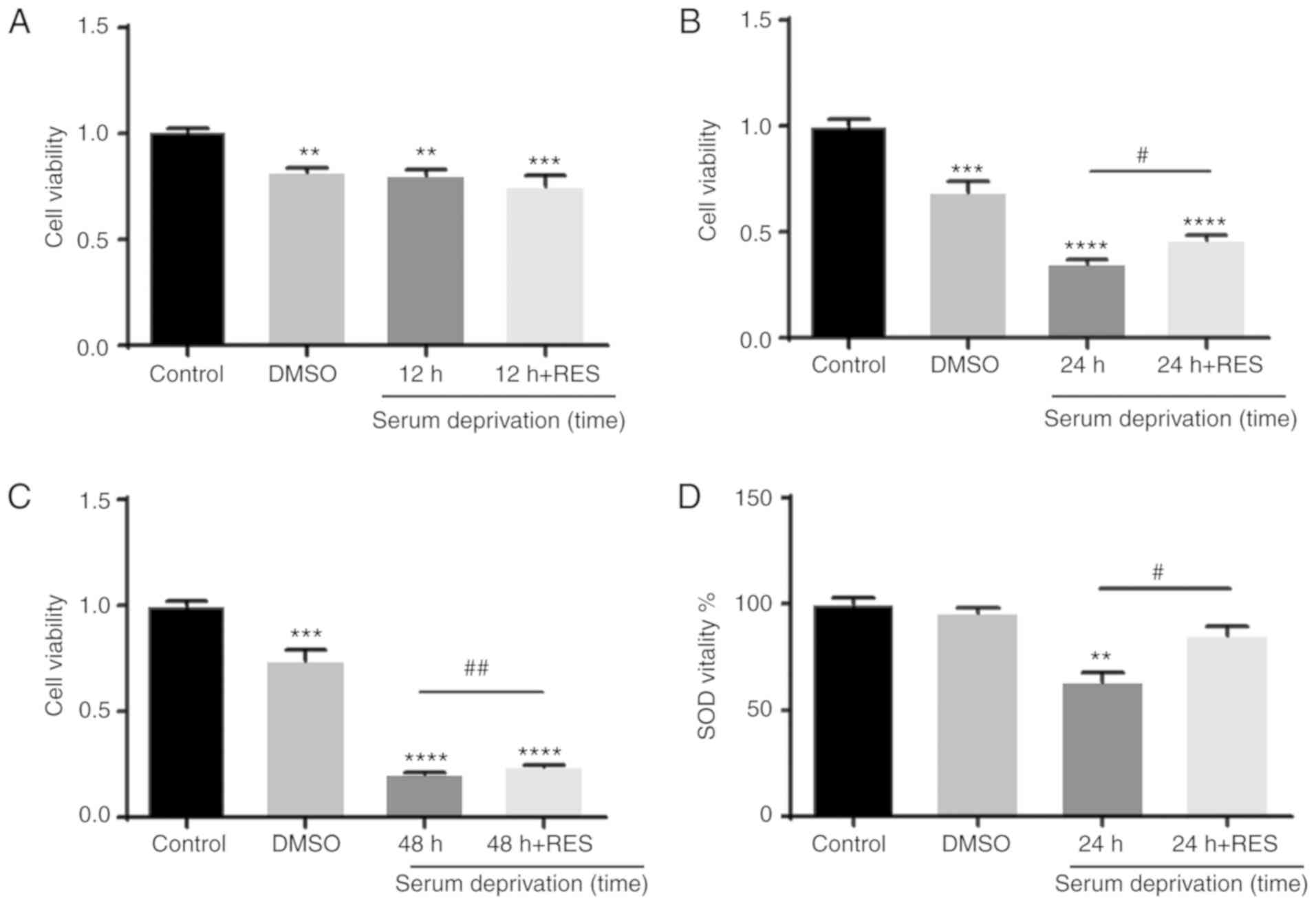
|
1
|
Bonomi L: Epidemiology of angle-closure
glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol Scand Suppl. 236:11–13. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Garcia-Valenzuela E, Shareef S, Walsh J
and Sharma SC: Programmed cell death of retinal ganglion cells
during experimental glaucoma. Exp Eye Res. 61:33–44. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Quigley HA, Nickells RW, Kerrigan LA,
Pease ME, Thibault DJ and Zack DJ: Retinal ganglion cell death in
experimental glaucoma and after axotomy occurs by apoptosis. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 36:774–786. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Almasieh M, Wilson AM, Morquette B, Cueva
Vargas JL and Di Polo A: The molecular basis of retinal ganglion
cell death in glaucoma. Prog Retin Eye Res. 31:152–181. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Williams PA, Harder JM, Foxworth NE,
Cochran KE, Philip VM, Porciatti V, Smithies O and John SW: Vitamin
B3 modulates mitochondrial vulnerability and prevents
glaucoma in aged mice. Science. 355:756–760. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang C, Zhang P, Wang W, Xu Y, Wang M,
Chen X and Dong X: Long-term blue light exposure induces RGC-5 cell
death in vitro: Involvement of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis,
oxidative stress, and MAPK signaling pathways. Apoptosis.
19:922–932. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Das A, Bell CM, Berlinicke CA,
Marsh-Armstrong N and Zack DJ: Programmed switch in the
mitochondrial degradation pathways during human retinal ganglion
cell differentiation from stem cells is critical for RGC survival.
Redox Biol. 34:1014652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Giacomello M, Pyakurel A, Glytsou C and
Scorrano L: The cell biology of mitochondrial membrane dynamics.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:204–224. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee S, Van Bergen NJ, Kong GY,
Chrysostomou V, Waugh HS, O'Neill EC, Crowston JG and Trounce IA:
Mitochondrial dysfunction in glaucoma and emerging bioenergetic
therapies. Exp Eye Res. 93:204–212. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Schober MS, Chidlow G, Wood JP and Casson
RJ: Bioenergetic-based neuroprotection and glaucoma. Clin Exp
Ophthalmol. 36:377–385. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dhingra A, Jayas R, Afshar P, Guberman M,
Maddaford G, Gerstein J, Lieberman B, Nepon H, Margulets V, Dhingra
R and Kirshenbaum LA: Ellagic acid antagonizes Bnip3-mediated
mitochondrial injury and necrotic cell death of cardiac myocytes.
Free Radic Biol Med. 112:411–422. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Geng J, Wei M, Yuan X, Liu Z, Wang X,
Zhang D, Luo L, Wu J, Guo W and Qin ZH: TIGAR regulates
mitochondrial functions through SIRT1-PGC1 α pathway and
translocation of TIGAR into mitochondria in skeletal muscle. FASEB
J. 33:6082–6098. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun Y, Xue W, Song Z, Huang K and Zheng L:
Restoration of Opa1-long isoform inhibits retinal injury-induced
neurodegeneration. J Mol Med (Berl). 94:335–346. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Youle RJ and van der Bliek AM:
Mitochondrial fission, fusion, and stress. Science. 337:1062–1065.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Frezza C, Cipolat S, Martins de Brito O,
Micaroni M, Beznoussenko GV, Rudka T, Bartoli D, Polishuck RS,
Danial NN, De Strooper B and Scorrano L: OPA1 controls apoptotic
cristae remodeling independently from mitochondrial fusion. Cell.
126:177–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baur JA and Sinclair DA: Therapeutic
potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 5:493–506. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chong ZZ, Shang YC, Wang S and Maiese K:
SIRT1: new avenues of discovery for disorders of oxidative stress.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:167–178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ahmed T, Javed S, Javed S, Tariq A, Šamec
D, Tejada S, Nabavi SF, Braidy N and Nabavi SM: Resveratrol and
Alzheimer's disease: Mechanistic insights. Mol Neurobiol.
54:2622–2635. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pandey AK, Bhattacharya P, Shukla SC, Paul
S and Patnaik R: Resveratrol inhibits matrix metalloproteinases to
attenuate neuronal damage in cerebral ischemia: A molecular docking
study exploring possible neuroprotection. Neural Regen Res.
10:568–575. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Richard T, Pawlus AD, Iglésias ML, Pedrot
E, Waffo-Teguo P, Mérillon JM and Monti JP: Neuroprotective
properties of resveratrol and derivatives. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1215:103–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Abu-Amero KK, Kondkar AA and Chalam KV:
Resveratrol and ophthalmic diseases. Nutrients. 8:2002016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zuo L, Khan RS, Lee V, Dine K, Wu W and
Shindler KS: SIRT1 promotes RGC survival and delays loss of
function following optic nerve crush. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
54:5097–5102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Krishnamoorthy RR, Agarwal P, Prasanna G,
Vopat K, Lambert W, Sheedlo HJ, Pang IH, Shade D, Wordinger RJ,
Yorio T, et al: Characterization of a transformed rat retinal
ganglion cell line. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 86:1–12. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu B, Chen H, Johns TG and Neufeld AH:
Epidermal growth factor receptor activation: An upstream signal for
transition of quiescent astrocytes into reactive astrocytes after
neural injury. J Neurosci. 26:7532–7540. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bennet D and Kim S: Effects of agmatine
and resveratrol on RGC-5 cell behavior under light stimulation.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 38:84–97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chintala SK, Zhang X, Austin JS and Fini
ME: Deficiency in matrix metalloproteinase gelatinase B (MMP-9)
protects against retinal ganglion cell death after optic nerve
ligation. J Biol Chem. 277:47461–47468. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z,
Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P,
Elliott P, et al: Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and
protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and
PGC-1alpha. Cell. 127:1109–1122. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Anderson CJ, Kahl A, Fruitman H, Qian L,
Zhou P, Manfredi G and Iadecola C: Prohibitin levels regulate OMA1
activity and turnover in neurons. Cell Death Differ. 27:1896–1906.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Griparic L, Kanazawa T and van der Bliek
AM: Regulation of the mitochondrial dynamin-like protein Opa1 by
proteolytic cleavage. J Cell Biol. 178:757–764. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Osborne NN, Casson RJ, Wood JP, Chidlow G,
Graham M and Melena J: Retinal ischemia: Mechanisms of damage and
potential therapeutic strategies. Prog Retin Eye Res. 23:91–147.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao H, Zhang HL, Shou J, Chen L, Shen Y,
Tang Q, Huang J and Zhu J: Towards retinal ganglion cell
regeneration. Regen Med. 7:865–875. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Semba RD, Ferrucci L, Bartali B,
Urpí-Sarda M, Zamora-Ros R, Sun K, Cherubini A, Bandinelli S and
Andres-Lacueva C: Resveratrol levels and all-cause mortality in
older community-dwelling adults. JAMA Intern Med. 174:1077–1084.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang X, Feng Y, Wang Y, Wang J, Xiang D,
Niu W and Yuan F: Resveratrol ameliorates disorders of
mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics in a rat chronic ocular
hypertension model. Life Sci. 207:234–245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lindsey JD, Duong-Polk KX, Hammond D,
Leung CK and Weinreb RN: Protection of injured retinal ganglion
cell dendrites and unfolded protein response resolution after
long-term dietary resveratrol. Neurobiol Aging. 36:1969–1981. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Szabo ME, Droy-Lefaix MT, Doly M and
Braquet P: Free radical-mediated effects in reperfusion injury: A
histologic study with superoxide dismutase and EGB 761 in rat
retina. Ophthalmic Res. 23:225–234. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Belforte N, Sande PH, de Zavalia N,
Fernandez DC, Silberman DM, Chianelli MS and Rosenstein RE:
Ischemic tolerance protects the rat retina from glaucomatous
damage. PLoS One. 6:e237632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Seigel GM: Review: R28 retinal precursor
cells: The first 20 years. Mol Vis. 20:301–306. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Charles I, Khalyfa A, Kumar DM,
Krishnamoorthy RR, Roque RS, Cooper N and Agarwal N: Serum
deprivation induces apoptotic cell death of transformed rat retinal
ganglion cells via mitochondrial signaling pathways. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:1330–1338. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee SB, Kim JJ, Kim TW, Kim BS, Lee MS and
Yoo YD: Serum deprivation-induced reactive oxygen species
production is mediated by Romo1. Apoptosis. 15:204–218. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu Q, Ju WK, Crowston JG, Xie F, Perry G,
Smith MA, Lindsey JD and Weinreb RN: Oxidative stress is an early
event in hydrostatic pressure induced retinal ganglion cell damage.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 48:4580–4589. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kang KD, Andrade da Costa BL and Osborne
NN: Stimulation of prostaglandin EP2 receptors on RGC-5 cells in
culture blunts the negative effect of serum withdrawal. Neurochem
Res. 35:820–829. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kvanta A, Seregard S, Sejersen S, Kull B
and Fredholm BB: Localization of adenosine receptor messenger. RNAs
in the rat eye Exp Eye Res. 65:595–602. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Grillo SL, McDevitt DS, Voas MG, Khan AS,
Grillo MA and Stella SJ Jr: Adenosine receptor expression in the
adult zebrafish retina. Purinergic Signal. 15:327–342. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Castillo A, Tolón MR, Fernández-Ruiz J,
Romero J and Martinez-Orgado J: The neuroprotective effect of
cannabidiol in an in vitro model of newborn hypoxic-ischemic brain
damage in mice is mediated by CB(2) and adenosine receptors.
Neurobiol Dis. 37:434–440. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Dai SS, Zhou YG, Li W, An JH, Li P, Yang
N, Chen XY, Xiong RP, Liu P, Zhao Y, et al: Local glutamate level
dictates adenosine A2A receptor regulation of neuroinflammation and
traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci. 30:5802–5810. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Von Lubitz DK, Lin RC, Popik P, Carter MF
and Jacobson KA: Adenosine A3 receptor stimulation and cerebral
ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol. 263:59–67. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kressel M and Groscurth P: Distinction of
apoptotic and necrotic cell death by in situ labelling of
fragmented DNA. Cell Tissue Res. 278:549–556. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hass DT and Barnstable CJ: Mitochondrial
uncoupling protein 2 knock-out promotes mitophagy to decrease
retinal ganglion cell death in a mouse model of glaucoma. J
Neurosci. 39:3582–3596. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Olichon A, Guillou E, Delettre C, Landes
T, Arnauné-Pelloquin L, Emorine LJ, Mils V, Daloyau M, Hamel C,
Amati-Bonneau P, et al: Mitochondrial dynamics and disease OPA1.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1763:500–509. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shalaeva DN, Dibrova DV, Galperin MY and
Mulkidjanian AY: Modeling of interaction between cytochrome c and
the WD domains of Apaf-1: Bifurcated salt bridges underlying
apopto-some assembly. Biol Direct. 10:292015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Olichon A, Baricault L, Gas N, Guillou E,
Valette A, Belenguer P and Lenaers G: Loss of OPA1 perturbates the
mitochondrial inner membrane structure and integrity, leading to
cytochrome c release and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 278:7743–7746.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Varanita T, Soriano ME, Romanello V,
Zaglia T, Quintana-Cabrera R, Semenzato M, Menabò R, Costa V,
Civiletto G, Pesce P, et al: The OPA1-dependent mitochondrial
cristae remodeling pathway controls atrophic, apoptotic, and
ischemic tissue damage. Cell Metab. 21:834–844. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang L, He Z, Zhang Q, Wu Y, Yang X, Niu
W, Hu Y and Jia J: Exercise pretreatment promotes mitochondrial
dynamic protein OPA1 expression after cerebral ischemia in rats.
Int J Mol Sci. 15:4453–4463. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Williams PA, Morgan JE and Votruba M: Opa1
deficiency in a mouse model of dominant optic atrophy leads to
retinal ganglion cell. dendropathy Brain. 133:2942–2951. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Hu X, Dai Y, Zhang R, Shang K and Sun X:
Overexpression of optic atrophy type 1 protects retinal ganglion
cells and upregu-lates Parkin expression in experimental glaucoma.
Front Mol Neurosci. 11:3502018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Jardim FR, de Rossi FT, Nascimento MX, da
Silva Barros RG, Borges PA, Prescilio IC and de Oliveira MR:
Resveratrol and brain mitochondria:. A review Mol Neurobiol.
55:2085–2101. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
de Oliveira MR, Nabavi SF, Manayi A,
Daglia M, Hajheydari Z and Nabavi SM: Resveratrol and the
mitochondria: From triggering the intrinsic apoptotic pathway to
inducing mitochondrial biogenesis, a mechanistic view. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1860:727–745. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Peng K, Tao Y, Zhang J, Wang J, Ye F, Dan
G, Zhao Y, Cai Y, Zhao J, Wu Q, et al: Resveratrol regulates
mitochondrial biogenesis and fission/fusion to attenuate
rotenone-induced neurotoxicity. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:67056212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lee H, Smith SB, Sheu SS and Yoon Y: The
short variant of optic atrophy 1 (OPA1) improves cell survival
under oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 295:6543–6560. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
MacVicar T and Langer T: OPA1 processing
in cell death and disease-the long and short of it. J Cell Sci.
129:2297–2306. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lang A, Anand R, Altinoluk-Hambüchen S,
Ezzahoini H, Stefanski A, Iram A, Bergmann L, Urbach J, Böhler P,
Hänsel J, et al: SIRT4 interacts with OPA1 and regulates
mitochondrial quality control and mitophagy. Aging (Albany NY).
9:2163–2189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Alavi MV: Targeted OMA1 therapies for
cancer. Int J Cancer. 145:2330–2341. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ishihara N, Fujita Y, Oka T and Mihara K:
Regulation of mitochondrial morphology through proteolytic cleavage
of OPA1. EMBO J. 25:2966–2977. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Song Z, Chen H, Fiket M, Alexander C and
Chan DC: OPA1 processing controls mitochondrial fusion and is
regulated by mRNA splicing, membrane potential, and Yme1L. J Cell
Biol. 178:749–755. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Rainbolt TK, Lebeau J, Puchades C and
Wiseman RL: Reciprocal degradation of YME1L and OMA1 adapts
mitochondrial proteo-lytic activity during stress. Cell Rep.
14:2041–2049. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Stiburek L, Cesnekova J, Kostkova O,
Fornuskova D, Vinsova K, Wenchich L, Houstek J and Zeman J: YME1L
controls the accumulation of respiratory chain subunits and is
required for apoptotic resistance, cristae morphogenesis, and cell
proliferation. Mol Biol Cell. 23:1010–1023. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Rainbolt TK, Saunders JM and Wiseman RL:
YME1L degradation reduces mitochondrial proteolytic capacity during
oxidative stress. EMBO Rep. 16:97–106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
70
|
Singh LN, Crowston JG, Lopez Sanchez MIG,
Van Bergen NJ, Kearns LS, Hewitt AW, Yazar S, Mackey DA, Wallace DC
and Trounce IA: Mitochondrial DNA variation and disease
susceptibility in primary open-angle glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 59:4598–4602. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Kumar M, Tanwar M, Faiq MA, Pani J, Shamsi
MB, Dada T and Dada R: Mitochondrial DNA nucleotide changes in
primary congenital glaucoma patients. Mol Vis. 19:220–230.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Garcia I, Innis-Whitehouse W, Lopez A,
Keniry M and Gilkerson R: Oxidative insults disrupt OPA1-mediated
mitochondrial dynamics in cultured mammalian cells. Redox Rep.
23:160–167. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kondadi AK, Anand R and Reichert AS:
Functional interplay between cristae biogenesis, mitochondrial
dynamics and mitochondrial DNA integrity. Int J Mol Sci.
20:43112019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
74
|
Chen S, Fan Q, Li A, Liao D, Ge J, Laties
AM and Zhang X: Dynamic mobilization of PGC-1α mediates
mitochondrial biogenesis for the protection of RGC-5 cells by
resveratrol during serum deprivation. Apoptosis. 18:786–799. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kim MJ, Chi BH, Yoo JJ, Ju YM, Whang YM
and Chang IH: Structure establishment of three-dimensional (3D)
cell culture printing model for bladder cancer. PLoS One.
14:e2236892019.
|
|
76
|
Liang T, Tao Q, Guan R, Cao G, Shen H, Liu
Z and Xia Q: Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of
cyanidin-3-O-glu-coside (C3G) liposome in Caco-2 cells cultivated
in 2D and 3D cell culture models. J Food Sci. 84:1638–1645. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Burd A, Kwok CH, Hung SC, Chan HS, Gu H,
Lam WK and Huang L: A comparative study of the cytotoxicity of
silver-based dressings in monolayer cell, tissue explant, and
animal models. Wound Repair Regen. 15:94–104. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Li D, Ni S, Miao KS and Zhuang C: PI3K/Akt
and caspase pathways mediate oxidative stress-induced chondrocyte
apoptosis. Cell Stress Chaperones. 24:195–202. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
79
|
Fukai T and Ushio-Fukai M: Superoxide
dismutases: Role in redox signaling, vascular function, and
diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:1583–1606. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen WM, Shaw LH, Chang PJ, Tung SY, Chang
TS, Shen CH, Hsieh YY and Wei KL: Hepatoprotective effect of
resveratrol against ethanol-induced oxidative stress through
induction of superoxide dismutase in vivo and in vitro. Exp Ther
Med. 11:1231–1238. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Tomé-Carneiro J, Larrosa M,
González-Sarrías A, Tomás-Barberán FA, García-Conesa MT and Espín
JC: Resveratrol and clinical trials: The crossroad from in vitro
studies to human evidence. Curr Pharm Des. 19:6064–6093. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|