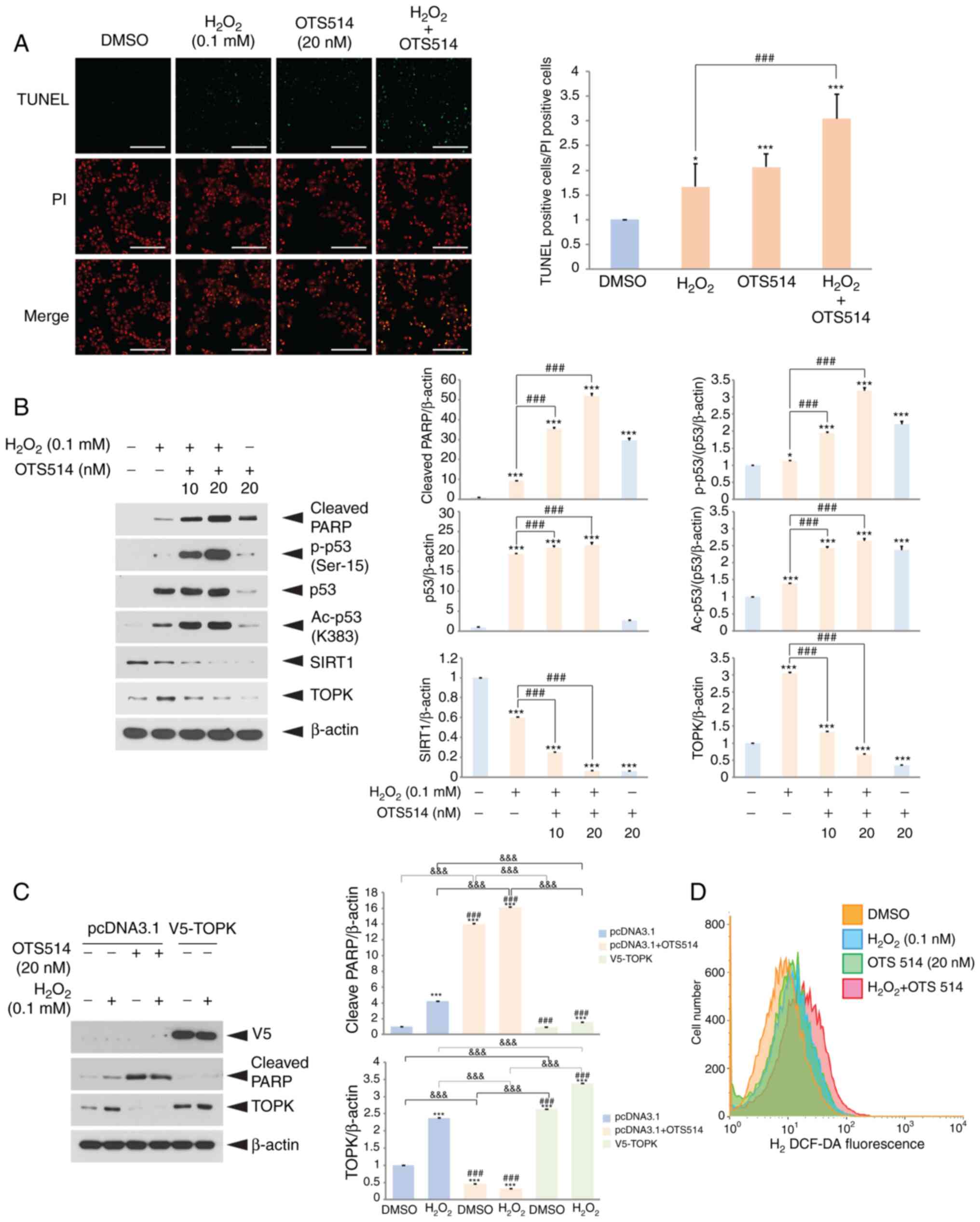
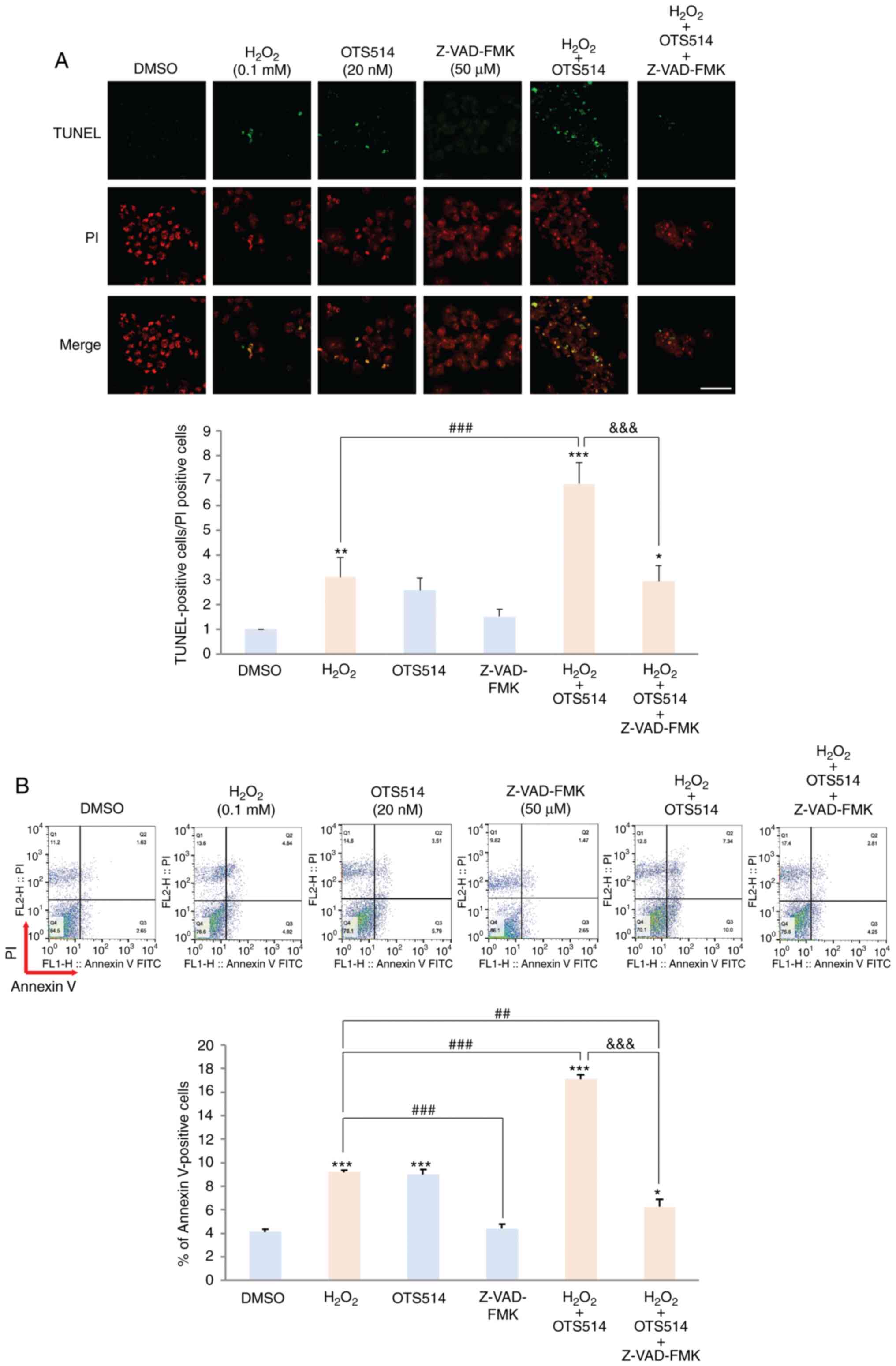
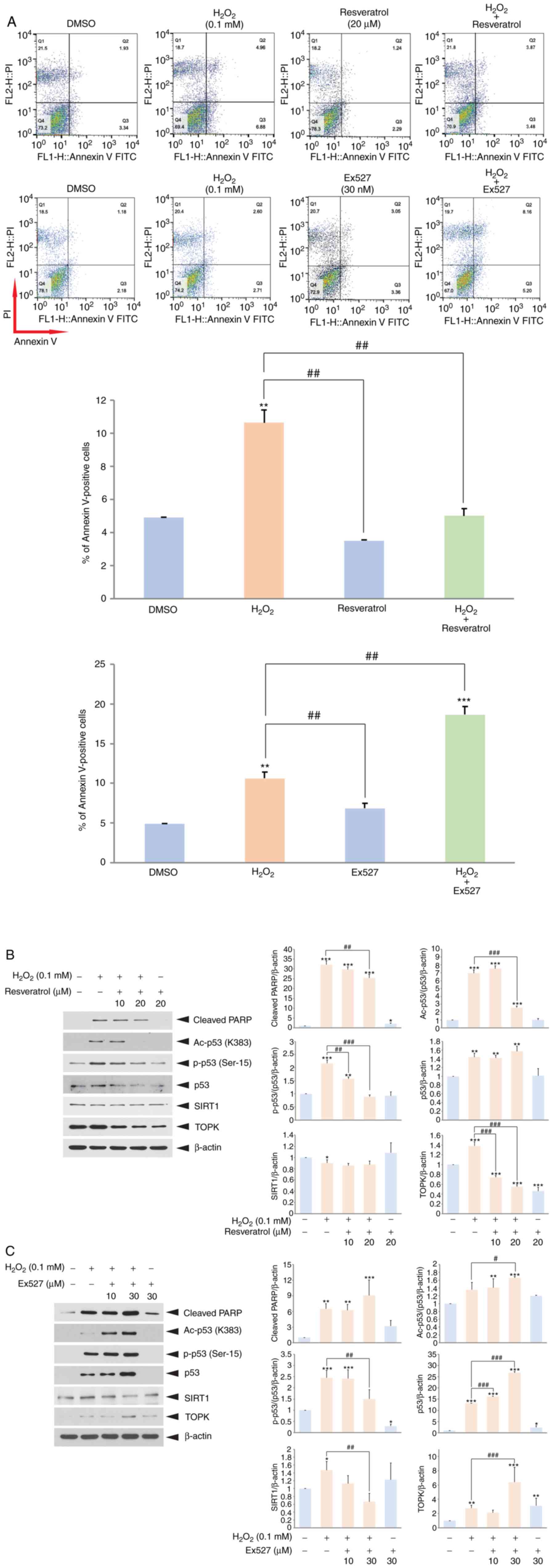
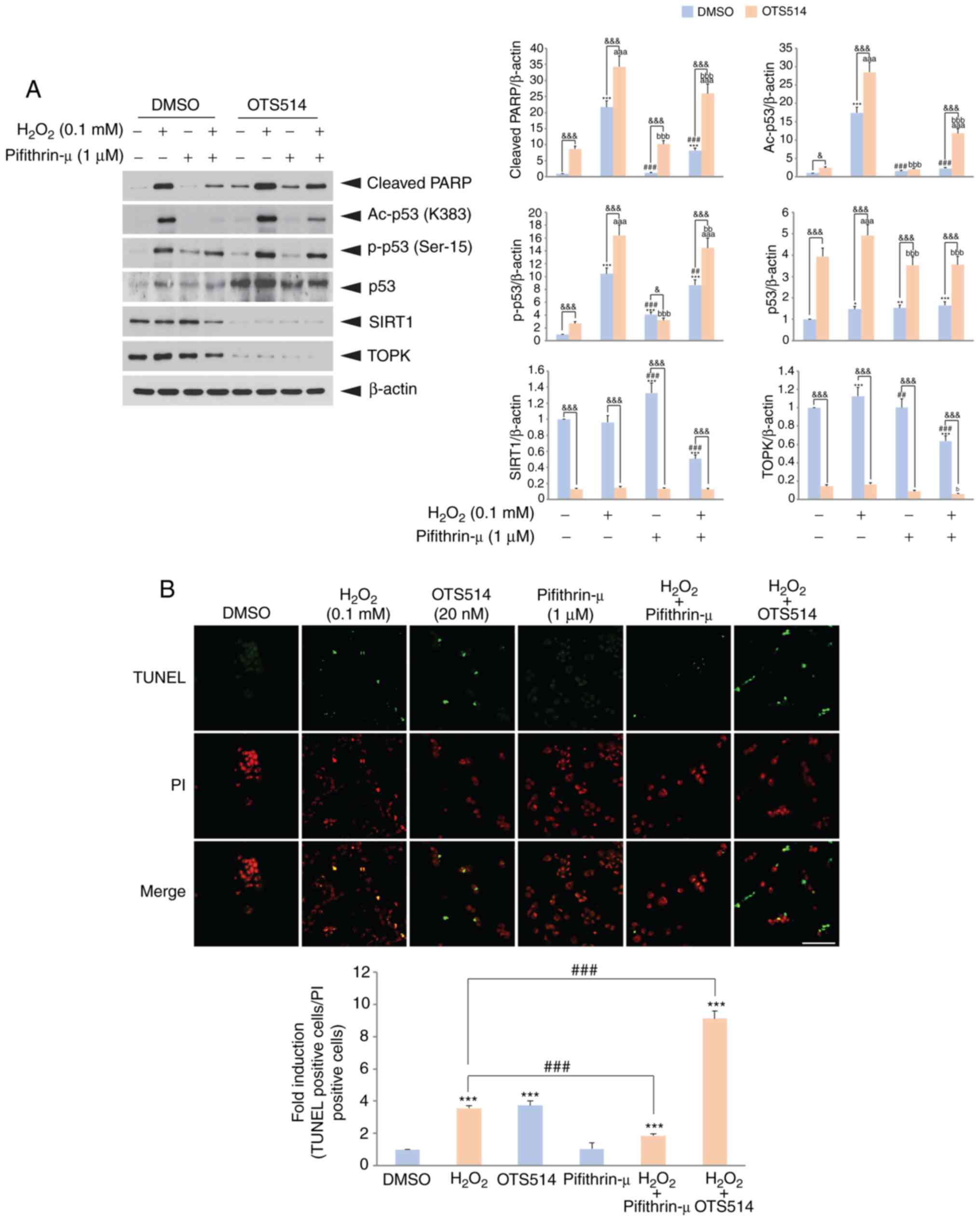
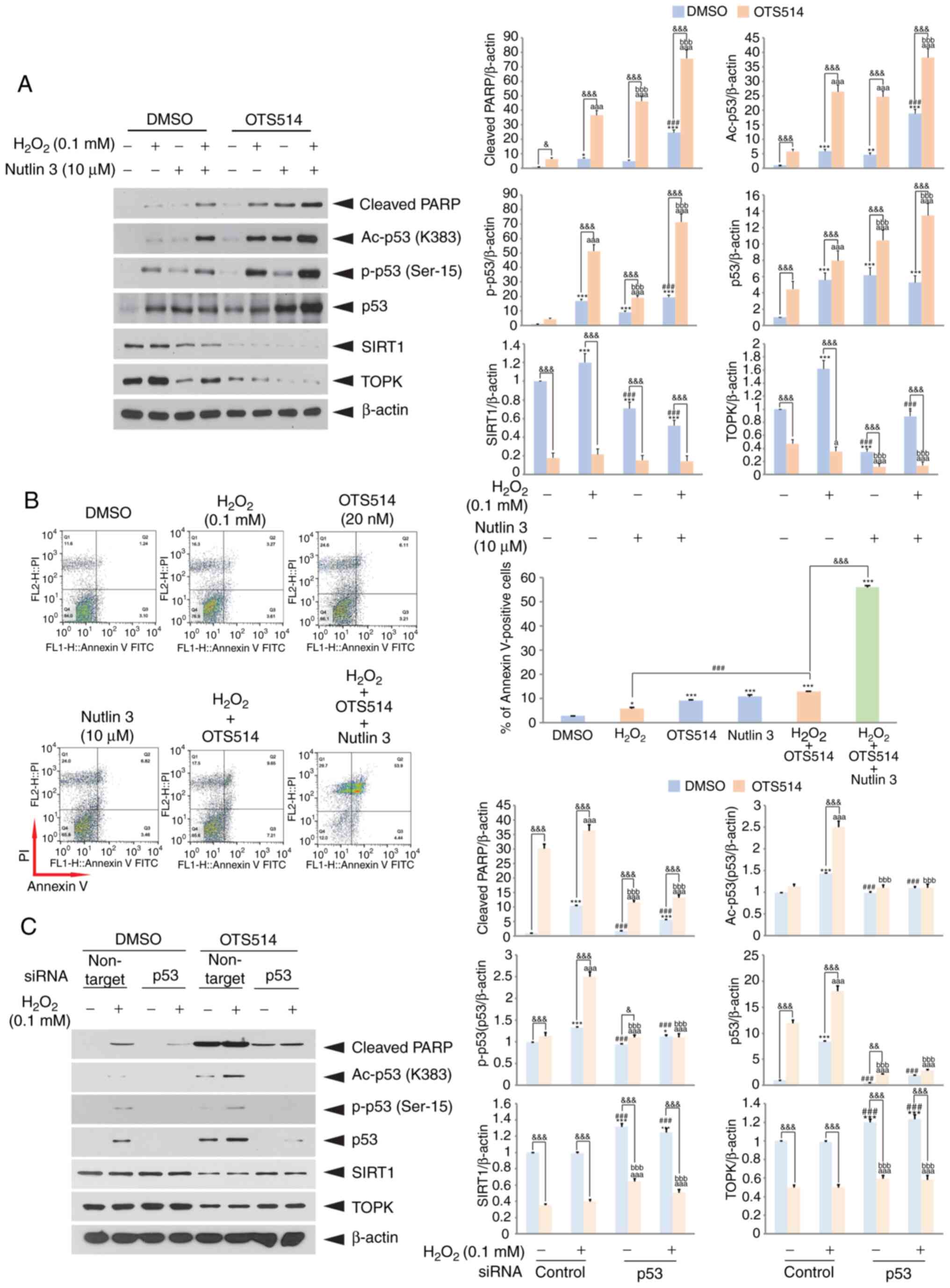
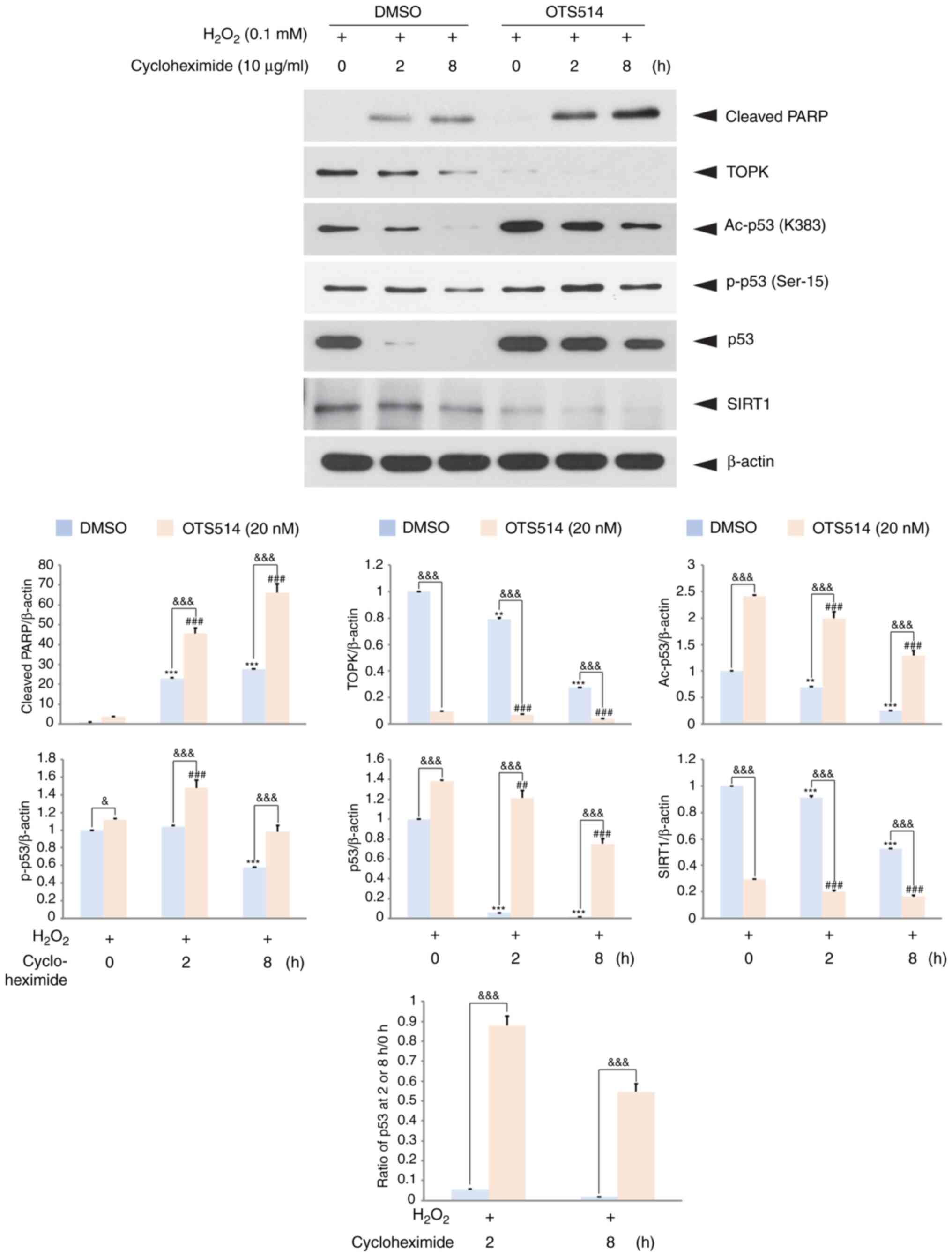
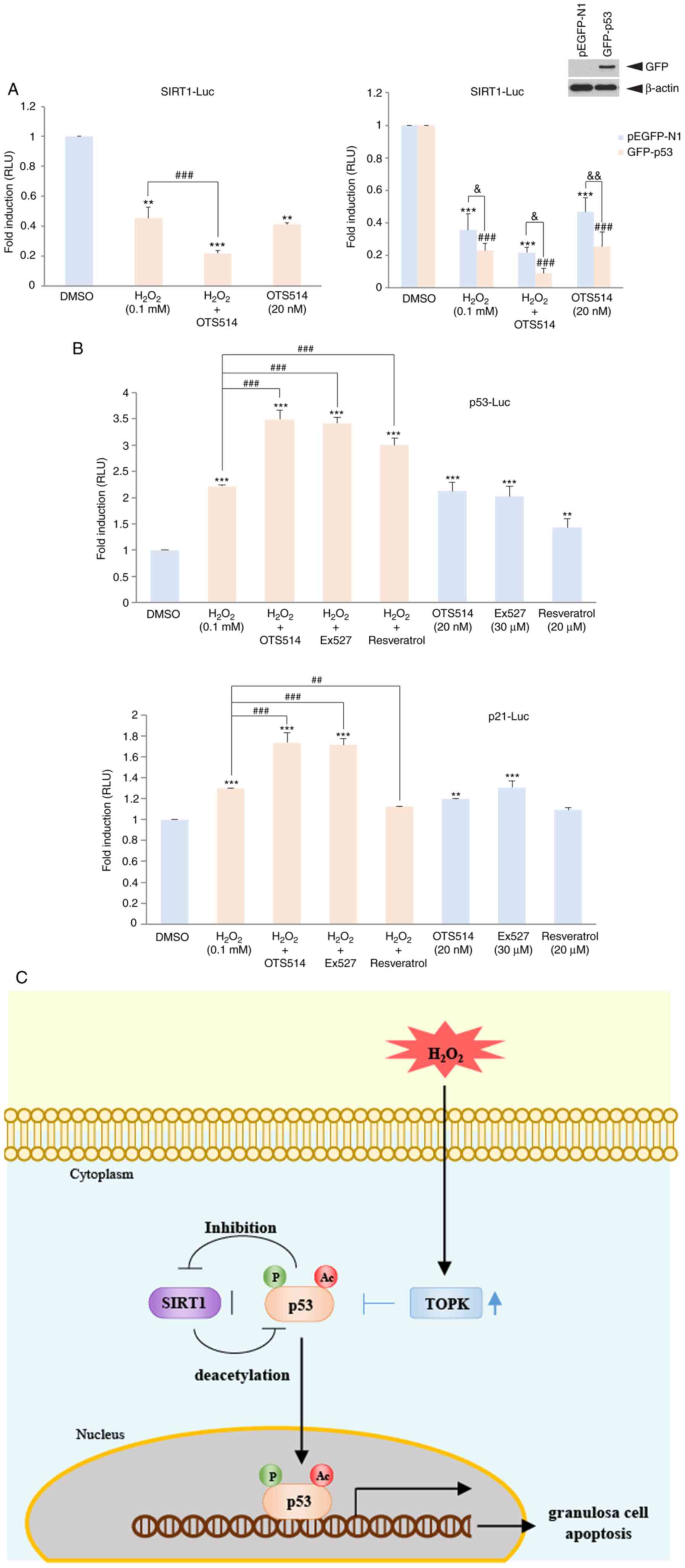
|
1
|
Adeldust H, Zeinoaldini S, Kohram H, Amiri
Roudbar M and Daliri Joupari M: In vitro maturation of ovine oocyte
in a modified granulosa cells co-culture system and
alpha-tocopherol supplementation: Effects on nuclear maturation and
cleavage. J Anim Sci Technol. 57:272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tripathi A, Shrivastav TG and Chaube SK:
An increase of granu-losa cell apoptosis mediates aqueous neem
(Azadirachta indica) leaf extract-induced oocyte apoptosis in rat.
Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 3:27–36. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Devine PJ, Perreault SD and Luderer U:
Roles of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in ovarian
toxicity. Biol Reprod. 86:272012.
|
|
4
|
Tatone C, Di Emidio G, Vitti M, Di Carlo
M, Santini S, D'Alessandro AM, Falone S and Amicarelli F: Sirtuin
functions in female fertility: Possible role in oxidative stress
and aging. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:6596872015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang H, Yan B, Liao D, Huang S and Qiu Y:
Acetylation of HDAC1 and degradation of SIRT1 form a positive
feedback loop to regulate p53 acetylation during heat-shock stress.
Cell Death Dis. 6:e17472015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Han Y, Luo H, Wang H, Cai J and Zhang Y:
SIRT1 induces resistance to apoptosis in human granulosa cells by
activating the ERK pathway and inhibiting NF-κB signaling with
anti-inflammatory functions. Apoptosis. 22:1260–1272.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Abdolvahabi Z, Nourbakhsh M, Hosseinkhani
S, Hesari Z, Alipour M, Jafarzadeh M, Ghorbanhosseini SS, Seiri P,
Yousefi Z, Yarahmadi S and Golpou P: MicroRNA-590-3P suppresses
cell survival and triggers breast cancer cell apoptosis via
targeting sirtuin-1 and deacetylation of p53. J Cell Biochem.
120:9356–9368. 2019.
|
|
8
|
Yu X, Zhang S, Zhao D, Zhang X, Xia C,
Wang T, Zhang M, Liu T, Huang W and Wu B: SIRT1 inhibits apoptosis
in in vivo and in vitro models of spinal cord injury via
microRNA-494. Int J Mol Med. 43:1758–1768. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han MK, Song EK, Guo Y, Ou X, Mantel C and
Broxmeyer HE: SIRT1 regulates apoptosis and Nanog expression in
mouse embryonic stem cells by controlling p53 subcellular
localization. Cell Stem Cell. 2:241–251. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kume S, Haneda M, Kanasaki K, Sugimoto T,
Araki SI, Isono M, Isshiki K, Uzu T, Kashiwagi A and Koya D: Silent
information regulator 2 (SIRT1) attenuates oxidative stress-induced
mesangial cell apoptosis via p53 deacetylation. Free Radic Biol
Med. 40:2175–2182. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yuan F, Liu L, Lei Y and Tang P: P53
inhibits the upregulation of sirtuin 1 expression induced by c-Myc.
Oncol Lett. 14:4396–4402. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zlobec I, Molinari F, Kovac M, Bihl MP,
Altermatt HJ, Diebold J, Frick H, Germer M, Horcic M, Montani M, et
al: Prognostic and predictive value of TOPK stratified by KRAS and
BRAF gene alterations in sporadic, hereditary and metastatic
colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 102:151–161. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Zykova TA, Zhu F, Wang L, Li H, Bai R, Lim
DY, Yao K, Bode AM and Dong Z: The T-LAK cell-originated protein
kinase signal pathway promotes colorectal cancer metastasis.
EBioMedicine. 18:73–82. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Su TC, Chen CY, Tsai WC, Hsu HT, Yen HH,
Sung WW and Chen CJ: Cytoplasmic, nuclear, and total PBK/TOPK
expression is associated with prognosis in colorectal cancer
patients: A retrospective analysis based on immunohistochemistry
stain of tissue microarrays. PLoS One. 13:e02048662018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shih MC, Chen JY, Wu YC, Jan YH, Yang BM,
Lu PJ, Cheng HC, Huang MS, Yang CJ, Hsiao M and Lai JM: TOPK/PBK
promotes cell migration via modulation of the PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathway
and is associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer. Oncogene.
31:2389–2400. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lei B, Qi W, Zhao Y, Li Y, Liu S, Xu X,
Zhi C, Wan L and Shen H: PBK/TOPK expression correlates with mutant
p53 and affects patients' prognosis and cell proliferation and
viability in lung adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 46:217–224. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ohashi T, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Miyamae
M, Okajima W, Imamura T, Kiuchi J, Kosuga T, Konishi H, Shiozaki A,
et al: Overexpression of PBK/TOPK relates to tumour malignant
potential and poor outcome of gastric carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
116:218–226. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Sun H, Zhang L, Shi C, Hu P, Yan W, Wang
Z, Duan Q, Lu F, Qin L, Lu T, et al: TOPK is highly expressed in
circulating tumor cells, enabling metastasis of prostate cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:12392–12404. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pirovano G, Ashton TM, Herbert KJ, Bryant
RJ, Verrill CL, Cerundolo L, Buffa FM, Prevo R, Harrap I, Ryan AJ,
et al: TOPK modulates tumour-specific radiosensitivity and
correlates with recurrence after prostate radiotherapy. Br J
Cancer. 117:503–512. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ikeda Y, Park JH, Miyamoto T, Takamatsu N,
Kato T, Iwasa A, Okabe S, Imai Y, Fujiwara K, Nakamura Y, et al:
T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK) as a prognostic factor
and a potential therapeutic target in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 22:6110–6117. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang MY, Lin ZR, Cao Y, Zheng LS, Peng LX,
Sun R, Meng DF, Xie P, Yang JP, Cao L, et al: PDZ binding kinase
(PBK) is a theranostic target for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Driving
tumor growth via ROS signaling and correlating with patient
survival. Oncotarget. 7:26604–26616. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ohashi T, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Miyamae
M, Okajima W, Imamura T, Kiuchi J, Nishibeppu K, Kosuga T, Konishi
H, et al: Overexpression of PBK/TOPK contributes to tumor
development and poor outcome of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 36:6457–6466. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Abe Y, Matsumoto S, Kito K and Ueda N:
Cloning and expression of a novel MAPKK-like protein kinase,
lymphokine- activated killer T-cell-originated protein kinase,
specifically expressed in the testis and activated lymphoid cells.
J Biol Chem. 275:21525–21531. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsumoto S, Abe Y, Fujibuchi T, Takeuchi
T, Kito K, Ueda N, Shigemoto K and Gyo K: Characterization of a
MAPKK-like protein kinase TOPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
325:997–1004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu F, Zykova TA, Kang BS, Wang Z, Ebeling
MC, Abe Y, Ma WY, Bode AM and Dong Z: Bidirectional signals
transduced by TOPK-ERK interaction increase tumorigenesis of HCT116
colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology. 133:219–231. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aksamitiene E, Kholodenko BN, Kolch W,
Hoek JB and Kiyatkin A: PI3K/Akt-Sensitive MEK-independent
compensatory circuit of ERK activation in ER-positive PI3K-mutant
T47D breast cancer cells. Cell Signal. 22:1369–1378. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Oh SM, Zhu F, Cho YY, Ki WL, Bong SK, Kim
HG, Zykova T, Bode AM and Dong Z: T-Lymphokine-activated killer
cell-originated protein kinase functions as a positive regulator of
c-Jun-NH2-kinase 1 signaling and H-ras-induced cell transformation.
Cancer Res. 67:5186–5194. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Seol MA, Park JH, Jeong JH, Lyu J, Han SY
and Oh SM: Role of TOPK in lipopolysaccharide-induced breast cancer
cell migration and invasion. Oncotarget. 8:40190–40203. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nandi AK, Ford T, Fleksher D, Neuman B and
Rapoport AP: Attenuation of DNA damage checkpoint by PBK, a novel
mitotic kinase, involves protein-protein interaction with tumor
suppressor p53. Biochem Biophy Res Commun. 358:181–188. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hu F, Gartenhaus RB, Eichberg D, Liu Z,
Fang HB and Rapoport AP: PBK/TOPK interacts with the DBD domain of
tumor suppressor p53 and modulates expression of transcriptional
targets including p21. Oncogene. 29:5464–5474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park JH, Yoon DS, Choi HJ, Hahm DH and Oh
SM: Phosphorylation of IκBα at serine 32 by T-lymphokine-activated
killer cell-originated protein kinase is essential for
chemoresistance against doxorubicin in cervical cancer cells. J
Biol Chem. 288:3585–3593. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Weng Q, Liu Z, Li B, Liu K, Wu W and Liu
H: Oxidative stress induces mouse follicular granulosa cells
apoptosis via JNK/FoxO1pathway. PLoS One. 11:e01678692016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang H, Xie Y, Yang D and Ren D: Oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis in granulosa cells involves JNK, p53 and
puma. Oncotarget. 8:25310–25322. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang M, Zhang Q, Hu Y, Xu L, Jiang Y,
Zhang C, Ding L, Jiang R, Sun J, Sun H and Yan G: MiR-181a
increases FoxO1 acetylation and promotes granulosa cell apoptosis
via SIRT1 downregulation. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Joel M, Mughal AA, Grieg Z, Murrell W,
Palmero S, Mikkelsen B, Fjerdingstad HB, Sandberg CJ, Behnan J,
Glover JC, et al: Targeting PBK/TOPK decreases growth and survival
of glioma initiating cells in vitro and attenuates tumor growth in
vivo. Mol Cancer. 14:1212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim DJ, Li Y, Reddy K, Lee MH, Kim MO, Cho
YY, Lee SY, Kim JE, Bode AM and Dong Z: Novel TOPK inhibitor
HI-TOPK-032 effectively suppresses colon cancer growth. Cancer Res.
72:3060–3068. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xu M and Xu S: PBK/TOPK overexpression and
survival in solid tumors: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis.
Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e147662019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Keren-Tal I, Suh BS, Dantes A, Lindner S,
Oren M and Amsterdam A: Involvement of p53 expression in
cAMP-mediated apoptosis in immortalized granulosa cells. Exp Cell
Res. 218:283–295. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Heller DT, Cahill DM and Schultz RM:
Biochemical studies of mammalian oogenesis: Metabolic cooperativity
between granu-losa cells and growing mouse oocytes. Dev Biol.
84:455–464. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brower PT and Schultz RM: Intercellular
communication between granulosa cells and mouse oocytes: Existence
and possible nutritional role during oocyte growth. Dev Biol.
90:144–153. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bruzzone R, White TW and Paul DL:
Connections with connexins: The molecular basis of direct
intercellular signaling. Eur J Biochem. 238:1–27. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kumar NM and Gilula NB: The gap junction
communication channel. Cell. 84:381–388. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Grazul-Bilska AT, Reynolds LP and Redmer
DA: Gap junctions in the ovaries. Biol Reprod. 57:947–957. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang HW, Hwang KJ, Kwon HC, Kim HS, Choi
KW and Oh KS: Detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and
apoptosis in human fragmented embryos. Hum Reprod. 13:998–1002.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hensley K, Robinson KA, Gabbita SP,
Salsman S and Floyd RA: Reactive oxygen species, cell signaling,
and cell injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 28:1456–1462. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dröge W: Free radicals in the
physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev. 82:47–95.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Goud AP, Goud PT, Diamond MP, Gonik B and
Abu-Soud HM: Reactive oxygen species and oocyte aging: Role of
superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and hypochlorous acid. Free Radic
Biol Med. 44:1295–1304. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li D, Ueta E, Kimura T, Yamamoto T and
Osaki T: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) control the expression of
Bcl-2 family proteins by regulating their phosphorylation and
ubiquitination. Cancer Sci. 95:644–650. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Alarifi S, Ali H, Alkahtani S and Alessia
MS: Regulation of apoptosis through bcl-2/bax proteins expression
and DNA damage by nano-sized gadolinium oxide. Int J Nanomedicine.
12:4541–4551. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Alachkar H, Mutonga M, Malnassy G, Park
JH, Fulton N, Woods A, Meng L, Kline J, Raca G, Odenike O, et al:
T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase presents a novel therapeutic
target in FLT3-ITD mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget.
6:33410–33425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Matsuo Y, Park JH, Miyamoto T, Yamamoto S,
Hisada S, Alachkar H and Nakamura Y: TOPK inhibitor induces
complete tumor regression in xenograft models of human cancer
through inhibition of cytokinesis. Sci Transl Med. 6:259ra1452014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Park JH, Inoue H, Kato T, Zewde M,
Miyamoto T, Matsuo Y, Salgia R and Nakamura Y: TOPK (T-LAK
cell-originated protein kinase) inhibitor exhibits growth
suppressive effect on small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci.
108:488–496. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wierstra I and Alves J: FOXM1c
transactivates the human c-myc promoter directly via the two TATA
boxes P1 and P2. FEBS J. 273:4645–4667. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hu F, Gartenhaus RB, Zhao XF, Fang HB,
Minkove S, Poss DE and Rapoport AP: C-Myc and E2F1 drive PBK/TOPK
expression in high-grade malignant lymphomas. Leukemia Res.
37:447–454. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Leung TW, Lin SS, Tsang AC, Tong CS, Ching
JC, Leung WY, Gimlich R, Wong GG and Yao KM: Over-expression of
foxM1 stimulates cyclin B1 expression. FEBS Lett. 507:59–66. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zykova TA, Zhu F, Vakorina TI, Zhang J,
Higgins LA, Urusova DV, Bode AM and Dong Z: T-LAK cell-originated
protein kinase (TOPK) phosphorylation of prx1 at ser-32 prevents
UVB-induced apoptosis in RPMI7951 melanoma cells through the
regulation of Prx1 peroxidase activity. J Biol Chem.
285:29138–29146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhao H, Wang R, Tao Z, Gao L, Yan F, Gao
Z, Liu X, Ji X and Luo Y: Ischemic postconditioning relieves
cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury through activating T-LAK
cell-originated protein kinase/protein kinase b pathway in rats.
Stroke. 45:2417–2424. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu Y, Liu H, Cao H, Song B and Zhang W
and Zhang W: PBK/TOPK mediates promyelocyte proliferation via
Nrf2-regulated cell cycle progression and apoptosis. Oncol Rep.
34:3288–3296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hsieh TC, Juan G, Darzynkiewicz Z and Wu
JM: Resveratrol increases nitric oxide synthase, induces
accumulation of p53 and p21(WAF1/CIP1), and suppresses cultured
bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cell proliferation by
perturbing progression through S and G2. Cancer Res. 59:2596–2601.
1999.
|
|
60
|
Luo J, Nikolaev AY, Imai S, Chen D, Su F,
Shiloh A, Guarente L and Gu W: Negative control of p53 by Sir2alpha
promotes cell survival under stress. Cell. 107:137–148. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Shieh SY, Ikeda M, Taya Y and Prives C:
DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53 alleviates inhibition by
MDM2. Cell. 91:325–334. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lambert PF, Kashanchi F, Radonovich MF,
Shiekhattar R and Brady JN: Phosphorylation of p53 serine 15
increases interaction with CBP. J Biol Chem. 273:33048–33053. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Marchenko ND and Moll UM: Mitochondrial
death functions of p53. Mol Cell Oncol. 1:e9559952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chen LJ, Gao YQ, Li XJ, Shen DH and Sun
FY: Melatonin protects against MPTP/MPP+ -induced mitochondrial DNA
oxidative damage in vivo and in vitro. J Pineal Res. 39:34–42.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yu W, Zhang X, Liu J, Wang X, Li S, Liu R,
Liao N, Zhang T and Hai C: Cyclosporine A suppressed glucose
oxidase induced P53 mitochondrial translocation and hepatic cell
apoptosis through blocking mitochondrial permeability transition.
Int J Biol Sci. 12:198–209. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wolff S, Erster S, Palacios G and Moll UM:
P53's mitochondrial translocation and MOMP action is independent of
puma and bax and severely disrupts mitochondrial membrane
integrity. Cell Res. 18:733–744. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sykes SM, Mellert HS, Holbert MA, Li K,
Marmorstein R, Lane WS and McMahon SB: Acetylation of the p53
DNA-binding domain regulates apoptosis induction. Mol Cell.
24:841–851. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Brooks CL and Gu W: The impact of
acetylation and deacetylation on the p53 pathway. Protein Cell.
2:456–462. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Islam S, Abiko Y, Uehara O and Chiba I:
Sirtuin 1 and oral cancer. Oncol Lett. 17:729–738. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ong AL and Ramasamy TS: Role of
sirtuin1-p53 regulatory axis in aging, cancer and cellular
reprogramming. Ageing Res Rev. 43:64–80. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
van Leeuwen I and Lain S: Sirtuins and
p53. Adv Cancer Res. 102:171–195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|