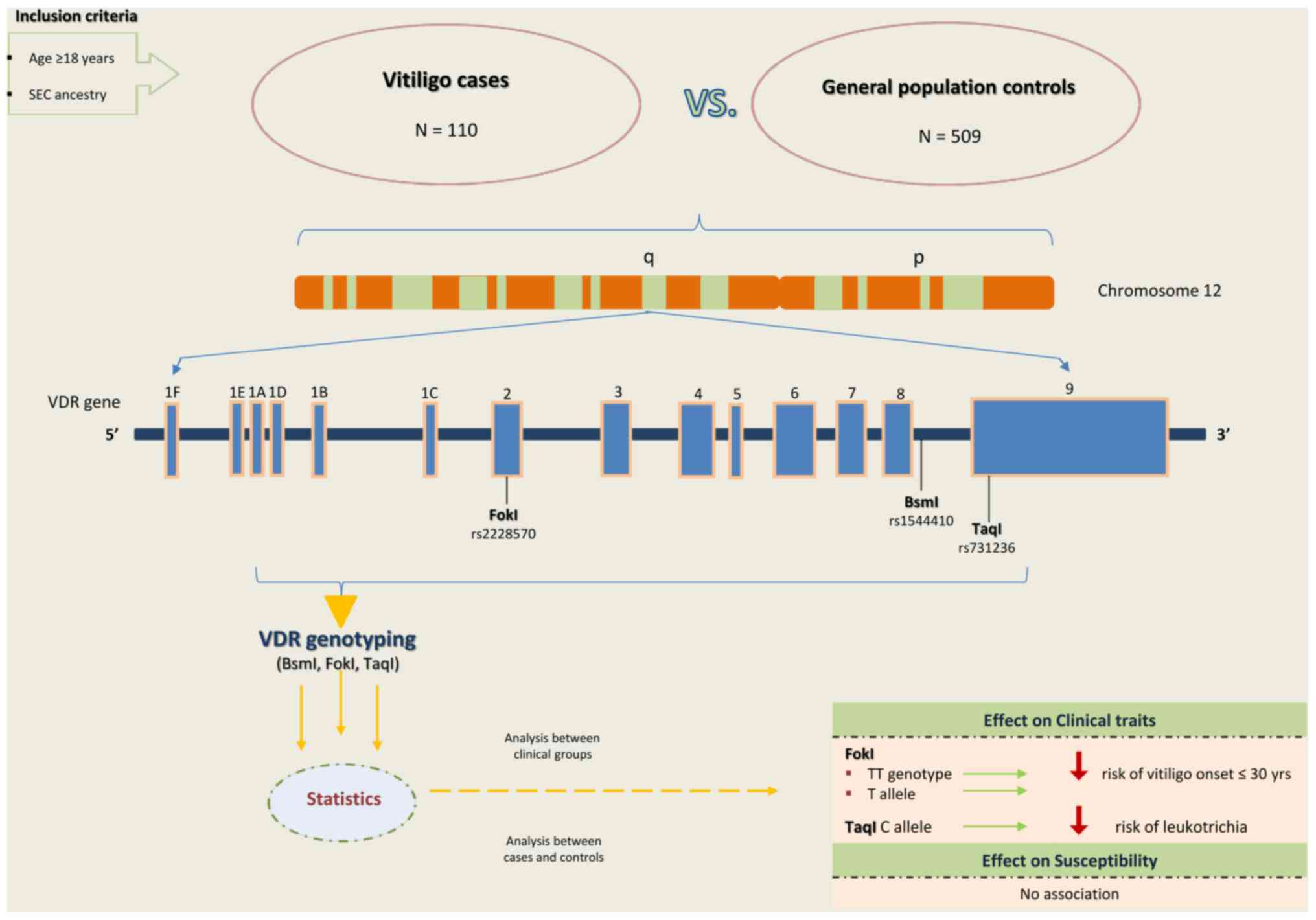
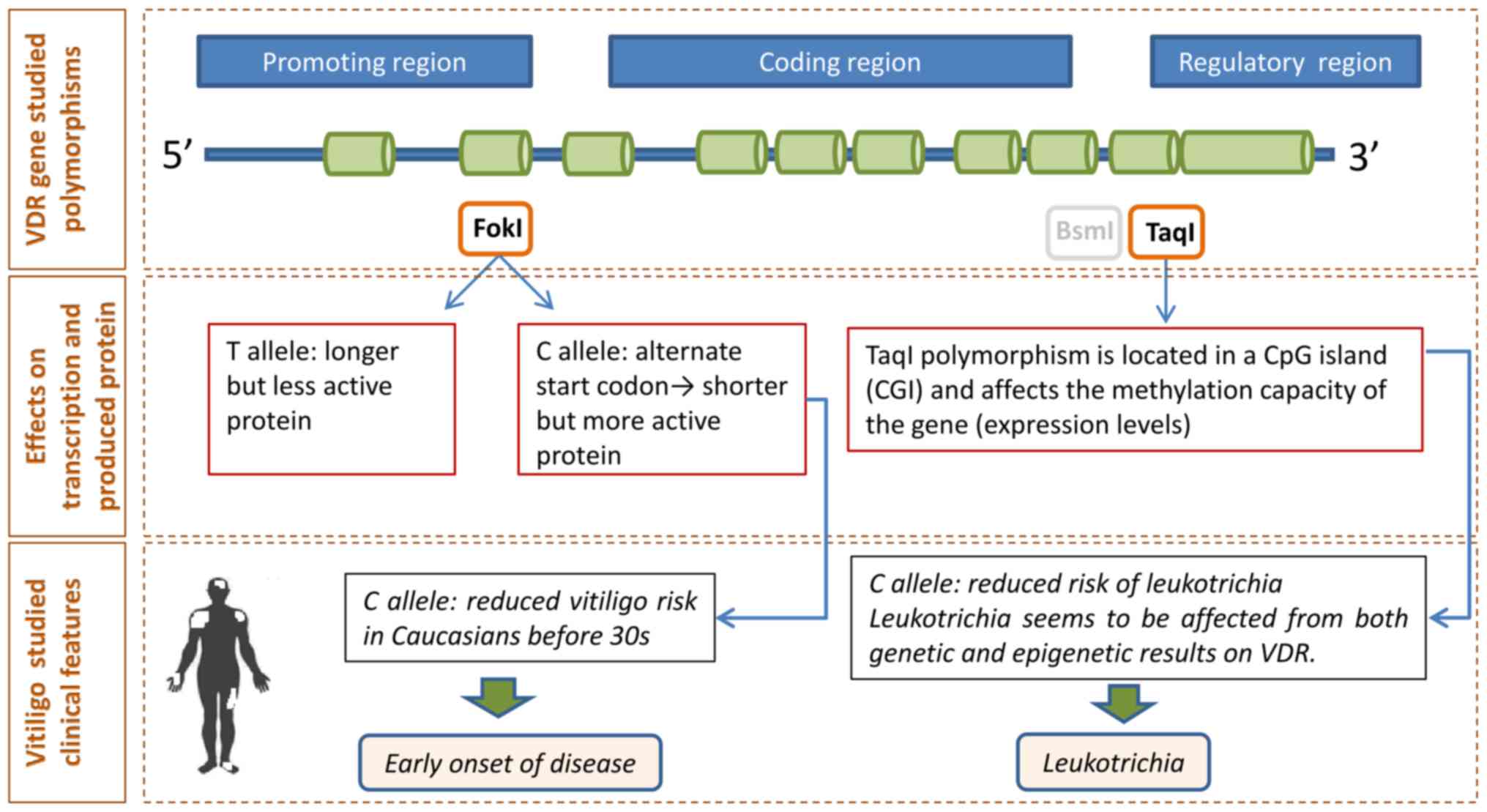
|
1
|
Ezzedine K, Eleftheriadou V, Whitton M and
van Geel N: Vitiligo. Lancet. 386:74–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Roberts GHL, Santorico SA and Spritz RA:
The genetic architecture of vitiligo. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res.
33:8–15. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wu J, Zhou M, Wan Y and Xu A:
CD8+ T cells from vitiligo perilesional margins induce
autologous melanocyte apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 7:237–241. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Spritz RA and Andersen GH: Genetics of
Vitiligo. Dermatol Clin. 35:245–255. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Krasanakis T, Nikolouzakis TK, Sgantzos M,
Mariolis-Sapsakos T, Souglakos J, Spandidos DA, Tsitsimpikou C,
Tsatsakis A and Tsiaoussis J: Role of anabolic agents in colorectal
carcinogenesis: Myths and realities (Review). Oncol Rep.
42:2228–2244. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Barbu CG, Arsene AL, Florea S, Albu A,
Sirbu A, Martin S, Nicolae AC, Burcea-Dragomiroiu GTA, Popa DE,
Velescu BS, et al: Cardiovascular risk assessment in osteo-porotic
patients using osteoprotegerin as a reliable predictive biochemical
marker. Mol Med Rep. 16:6059–6067. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Murdaca G, Tonacci A, Negrini S, Greco M,
Borro M, Puppo F and Gangemi S: Emerging role of vitamin D in
autoimmune diseases: An update on evidence and therapeutic
implications. Autoimmun Rev. 18:1023502019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kechichian E and Ezzedine K: Vitamin D and
the skin: an update for dermatologists. Am J Clin Dermatol.
19:223–235. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Upala S and Sanguankeo A: Low
25-hydroxyvitamin D levels are associated with vitiligo: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol
Photomed. 32:181–190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Birlea SA, Costin GE and Norris DA: New
insights on therapy with vitamin D analogs targeting the
intracellular pathways that control repigmentation in human
vitiligo. Med Res Rev. 29:514–546. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Parsad D and Kanwar AJ: Topical vitamin D
analogues in the treatment of vitiligo. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res.
22:487–488. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Siokas V, Aslanidou P, Aloizou AM,
Peristeri E, Stamati P, Liampas I, Arseniou S, Drakoulis N, Aschner
M, Tsatsakis A, et al: Does the CD33 rs3865444 polymorphism confer
susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease? J Mol Neurosci. 70:851–860.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dardiotis E, Aloizou AM, Siokas V, Tsouris
Z, Rikos D, Marogianni C, Aschner M, Kovatsi L, Bogdanos DP and
Tsatsakis A: Paraoxonase-1 genetic polymorphisms in
organo-phosphate metabolism. Toxicology. 411:24–31. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Anbar TS, Hegazy RA, Picardo M and Taieb
A: Beyond vitiligo guidelines: Combined stratified/personalized
approaches for the vitiligo patient. Exp Dermatol. 23:219–223.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nejentsev S, Godfrey L, Snook H, Rance HS,
Walker NM, Lam AC, Guja C, Ionescu-Tirgoviste C, Undlien DE, et al:
Comparative high-resolution analysis of linkage disequilibrium and
tag single nucleotide polymorphisms between populations in the
vitamin D receptor gene. Hum Mol Genet. 13:1633–1639. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li L, Wu Y, Li L, Cai YF, Geng L, Gao XH
and Chen HD: Association of ApaI and BsmI polymorphisms with
vitiligo risk: A meta-analysis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 40:794–803.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Uitterlinden AG, Fang Y, Van Meurs JB,
Pols HA and Van Leeuwen JP: Genetics and biology of vitamin D
receptor polymorphisms. Gene. 338:143–156. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang JZ, Wang M, Ding Y, Gao F, Feng YY,
Yakeya B, Wang P, Wu XJ, Hu FX, Xian J, et al: Vitamin D receptor
gene polymorphism, serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, and risk of
vitiligo: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 97:e115062018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee YH: Vitamin D receptor ApaI, TaqI,
BsmI, and FokI polymorphisms and psoriasis susceptibility: An
updated meta-analysis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 44:498–505. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Heine G, Hoefer N, Franke A, Nöthling U,
Schumann RR, Hamann L and Worm M: Association of vitamin D receptor
gene polymorphisms with severe atopic dermatitis in adults. Br J
Dermatol. 168:855–858. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ezzedine K, Lim HW, Suzuki T, Katayama I,
Hamzavi I, Lan CCE, Goh BK, Anbar T, Silva de Castro C, Lee AY, et
al: Vitiligo Global Issue Consensus Conference Panelists: Revised
classification/nomenclature of vitiligo and related issues: The
Vitiligo Global Issues Consensus Conference. Pigment Cell Melanoma
Res. 25:E1–E13. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aydıngöz IE, Bingül I, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S,
Vural P and Uysal M: Analysis of vitamin D receptor gene
polymorphisms in vitiligo. Dermatology. 224:361–368. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Birlea S, Birlea M, Cimponeriu D, Apostol
P, Cosgarea R, Gavrila L, Tigan S, Costin G and Das P: Autoimmune
diseases and vitamin D receptor Apa-I polymorphism are associated
with vitiligo in a small inbred Romanian community. Acta Derm
Venereol. 86:209–214. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hassan I, Bhat YJ, Majid S, Sajad P,
Rasool F, Malik RA and Ul Haq I: Association of vitamin D receptor
gene polymorphisms and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in vitiligo
- a case-control study. Indian Dermatol Online J. 10:131–138.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li K, Shi Q, Yang L, Li X, Liu L, Wang L,
Li Q, Wang G, Li CY and Gao TW: The association of vitamin D
receptor gene polymorphisms and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels
with generalized vitiligo. Br J Dermatol. 167:815–821. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ochoa-Ramírez LA, Díaz-Camacho SP,
Becerra-Loaiza DS, Verdugo-Nieto L, Muñoz-Estrada VF,
Servín-Vázquez LA, Osuna-Ramírez I, Rodríguez-Millán J and
Velarde-Félix JS: Catalase but not vitamin D receptor gene
polymorphisms are associated with nonsegmental vitiligo in
Northwestern Mexicans. Int J Dermatol. 58:1264–1269. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sobeih S, Mashaly HM, Gawdat H, Amr K,
Hamid MF and Shaalan E: Evaluation of the correlation between serum
levels of vitamin D and vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in an
Egyptian population. Int J Dermatol. 55:1329–1335. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee DY, Kim CR, Park JH and Lee JH: The
incidence of leukotrichia in segmental vitiligo: Implication of
poor response to medical treatment. Int J Dermatol. 50:925–927.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
van Geel N, Grine L, De Wispelaere P,
Mertens D, Prinsen CAC and Speeckaert R: Clinical visible signs of
disease activity in vitiligo: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 33:1667–1675. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saccone D, Asani F and Bornman L:
Regulation of the vitamin D receptor gene by environment, genetics
and epigenetics. Gene. 561:171–180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang D, Xu X, Ma H, Yue X, Li C and Zhu W:
Optimization of the method for the culture of melanocyte precursors
from hair follicles and their activation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin
D3. Exp Ther Med. 6:967–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Katsarou MS, Karathanasopoulou A,
Andrianopoulou A, Desiniotis V, Tzinis E, Dimitrakis E, Lagiou M,
Charmandari E, Aschner M, Tsatsakis AM, et al: Beta 1, Beta 2 and
Beta 3 adrenergic receptor gene polymorphisms in a Southeastern
European population. Front Genet. 9:5602018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Katsarou MS, Papasavva M, Latsi R, Toliza
I, Gkaros AP, Papakonstantinou S, Gatzonis S, Mitsikostas DD,
Kovatsi L, Izotov BN, et al: Population-based analysis of cluster
headache-associated genetic polymorphisms. J Mol Neurosci.
65:367–376. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Katsarou MS, Latsi R, Papasavva M,
Demertzis N, Kalogridis T, Tsatsakis AM, Spandidos DA and Drakoulis
N: Population-based analysis of the frequency of HFE gene
polymorphisms: Correlation with the susceptibility to develop
hereditary hemochromatosis. Mol Med Rep. 14:630–636. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|