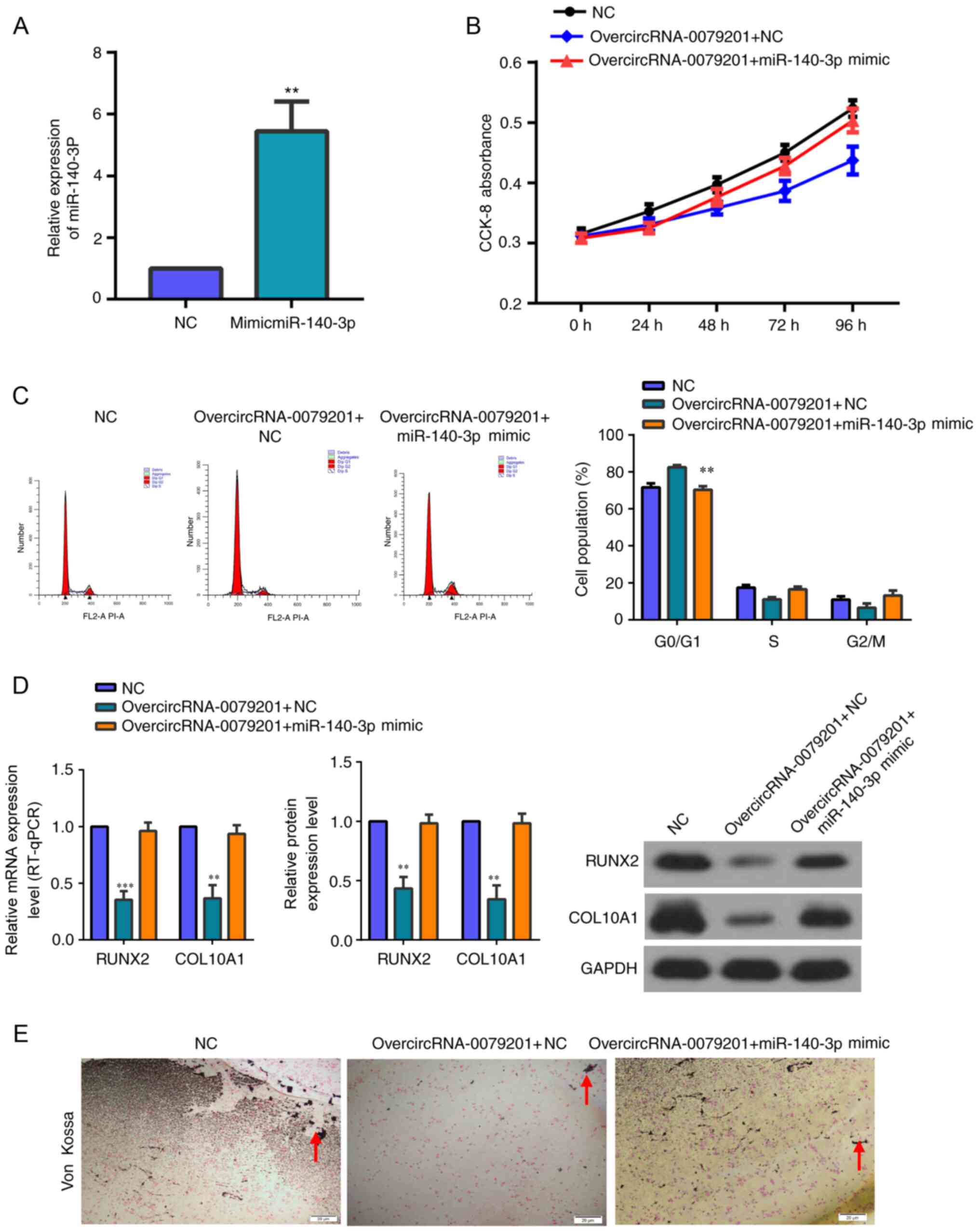
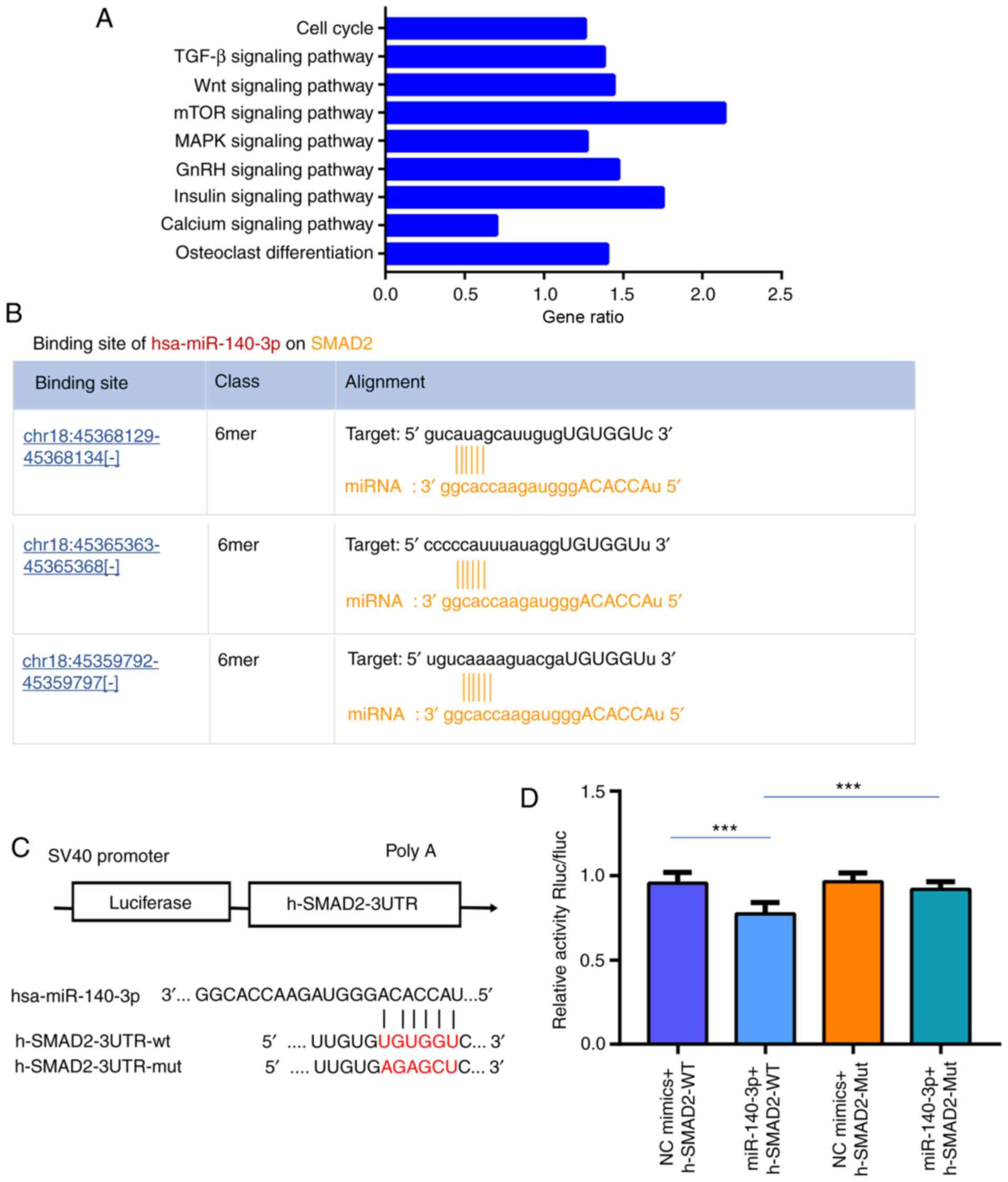
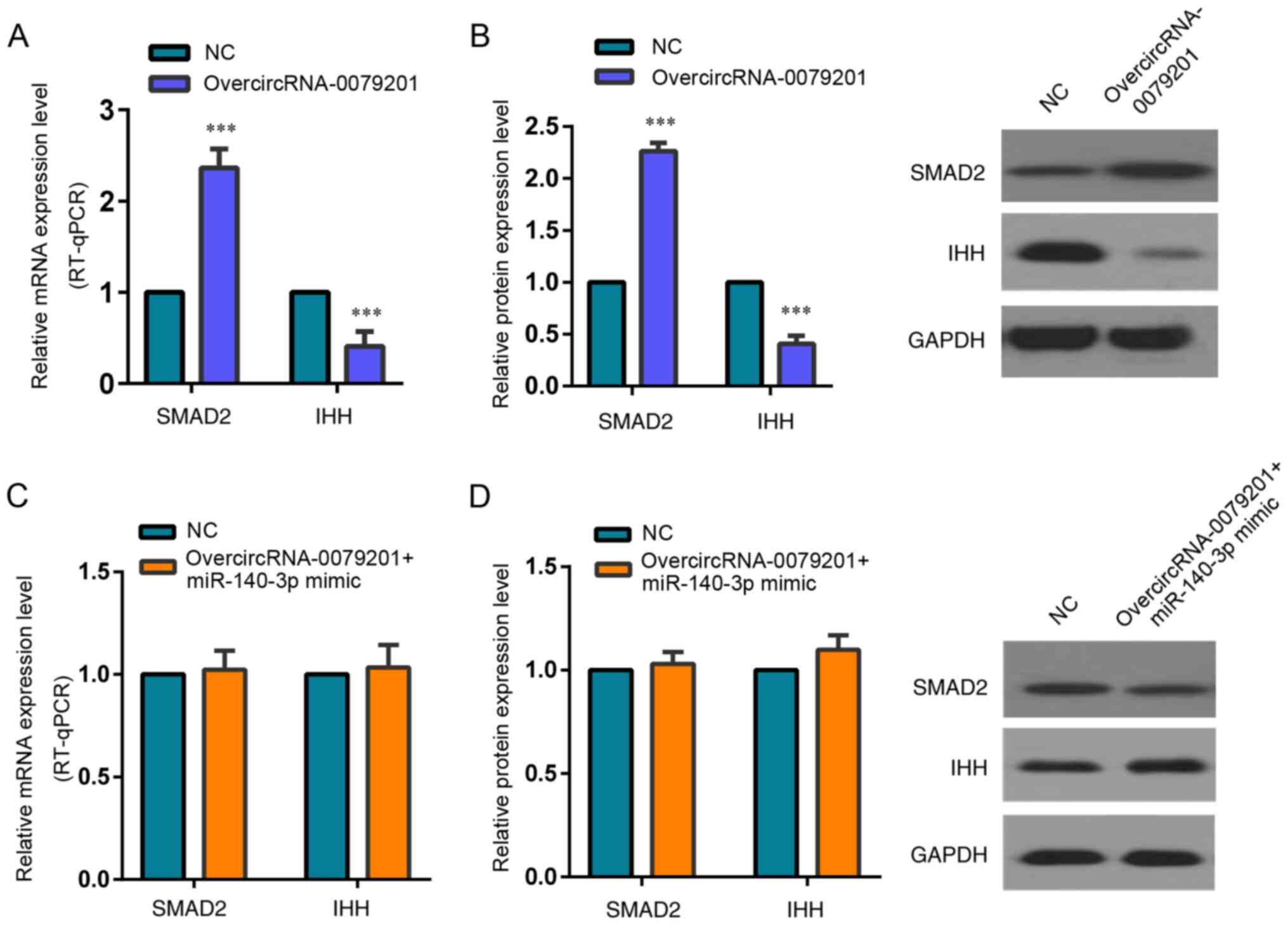
|
1
|
Cohen LE: Idiopathic short stature: A
clinical review. JAMA. 311:1787–1796. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kang MJ: Novel genetic cause of idiopathic
short stature. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 22:153–157. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Montalbano A, Juergensen L, Fukami M,
Thiel CT, Hauer NH, Roeth R, Weiss B, Naiki Y, Ogata T, Hassel D
and Rappold GA: Functional missense and splicing variants in the
retinoic acid catabolizing enzyme CYP26C1 in idiopathic short
stature. Eur J Hum Genet. 26:1113–1120. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dias C, Giordano M, Frechette R, Bellone
S, Polychronakos C, Legault L, Deal CL and Goodyer CG: Genetic
variations at the human growth hormone receptor (GHR) gene locus
are associated with idiopathic short stature. J Cell Mol Med.
21:2985–2999. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hattori A, Katoh-Fukui Y, Nakamura A,
Matsubara K, Kamimaki T, Tanaka H, Dateki S, Adachi M, Muroya K,
Yoshida S, et al: Next generation sequencing-based mutation
screening of 86 patients with idiopathic short stature. Endocr J.
64:947–954. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim J, Suh BK, Ko CW, Lee KH, Shin CH,
Hwang JS, Kim HS, Chung WY, Kim CJ, Han HS, et al: Recombinant
growth hormone therapy for prepubertal children with idiopathic
short stature in Korea: A phase III randomized trial. J Endocrinol
Invest. 41:475–483. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Heo SH, Choi JH, Kim YM, Jung CW, Lee J,
Jin HY, Kim GH, Lee BH, Shin CH and Yoo HW: Comparative proteomic
analysis in children with idiopathic short stature (ISS) before and
after short-term recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) therapy.
Proteomics. 13:1211–1219. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
van Gool SA, Kamp GA, Odink RJ, de Muinck
Keizer-Schrama SM, Delemarre-van de Waal HA, Oostdijk W and Wit JM:
High-dose GH treatment limited to the prepubertal period in young
children with idiopathic short stature does not increase adult
height. Eur J Endocrinol. 162:653–660. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cutfield WS and Albert BB: Growth hormone
treatment for idiopathic short stature. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev.
16(Suppl 1): S113–S122. 2018.
|
|
10
|
Ying YQ, Hou L, Liang Y, Wu W and Luo XP:
Efficacy and safety of recombinant human growth hormone in treating
Chinese children with idiopathic short stature. Growth Horm IGF
Res. 42-43:80–85. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Michigami T: Regulatory mechanisms for the
development of growth plate cartilage. Cell Mol Life Sci.
70:4213–4221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee DS, Roh SY, Choi H and Park JC: NFI-C
is required for epiphyseal chondrocyte proliferation during
postnatal cartilage development. Mol Cells. 43:739–748.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen J and Long F: mTORC1 signaling
controls mammalian skeletal growth through stimulation of protein
synthesis. Development. 141:2848–2854. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Beermann J, Piccoli MT, Viereck J and Thum
T: Non-coding RNAs in development and disease: Background,
mechanisms, and therapeutic approaches. Physiol Rev. 96:1297–1325.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu X, She Y, Wu H, Zhong D and Zhang J:
Long non-coding RNA Gas5 regulates proliferation and apoptosis in
HCS-2/8 cells and growth plate chondrocytes by controlling FGF1
expression via miR-21 regulation. J Biomed Sci. 25:182018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jee YH, Wang J, Yue S, Jennings M, Clokie
SJ, Nilsson O, Lui JC and Baron J: mir-374-5p mir-379-5p and
mir-503-5p regulate proliferation and hypertrophic differentiation
of growth plate chondrocytes in male rats. Endocrinology.
159:1469–1478. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miyaki S, Sato T, Inoue A, Otsuki S, Ito
Y, Yokoyama S, Kato Y, Takemoto F, Nakasa T, Yamashita S, et al:
MicroRNA-140 plays dual roles in both cartilage development and
homeostasis. Genes Dev. 24:1173–1185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun J, Wei X, Li S, Sun C, Wang C, Li P,
Wei DL and Wei L: The effects of Indian hedgehog deletion on
mesenchyme cells: Inducing intermediate cartilage scaffold
ossification to cause growth plate and phalange joint absence,
short limb, and dwarfish phenotypes. Stem Cells Dev. 27:1412–1425.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Y, Li C, Tan C and Liu X: Circular
RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human diseases. J Med Genet.
53:359–365. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Greene J, Baird AM, Brady L, Lim M, Gray
SG, McDermott R and Finn SP: Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, function
and role in human diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 4:382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ebbesen KK, Kjems J and Hansen TB:
Circular RNAs: Identification, biogenesis and function. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1859:163–168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Haque S and Harries LW: Circular RNAs
(circRNAs) in health and disease. Genes (Basel). 8:3532017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yu CX and Sun S: An emerging role for
circular RNAs in osteoarthritis. Yonsei Med J. 59:349–355. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Mo Y, Gong Z, Yang X, Yang M,
Zhang S, Xiong F, Xiang B, Zhou M, Liao Q, et al: Circular RNAs in
human cancer. Mol Cancer. 16:252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aufiero S, Reckman YJ, Pinto YM and
Creemers EE: Circular RNAs open a new chapter in cardiovascular
biology. Nat Rev Cardiol. 16:503–514. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lui JC: Regulation of body growth by
microRNAs. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 456:2–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kozhemyakina E, Lassar AB and Zelzer E: A
pathway to bone: Signaling molecules and transcription factors
involved in chondrocyte development and maturation. Development.
142:817–831. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
van der Kraan PM, Goumans MJ, Blaney
Davidson E and ten Dijke P: Age-dependent alteration of TGF-β
signalling in osteoarthritis. Cell Tissue Res. 347:257–265. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang W, Song B, Anbarchian T, Shirazyan A,
Sadik JE and Lyons KM: Smad2 and Smad3 regulate chondrocyte
proliferation and differentiation in the growth plate. PLoS Genet.
12:e10063522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang L, Zhang C, Wang W, Wang J, Xiao Y,
Lu W, Ma X, Chen L, Ni J, Wang D, et al: Pathogenic gene screening
in 91 Chinese patients with short stature of unknown etiology with
a targeted next-generation sequencing panel. BMC Med Genet.
19:2122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Blair JC and Savage MO: The GH-IGF-I axis
in children with idiopathic short stature. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
13:325–330. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Z, Yang T and Xiao J: Circular RNAs:
Promising biomarkers for human diseases. EBioMedicine. 34:267–274.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Arnaiz E, Sole C, Manterola L,
Iparraguirre L, Otaegui D and Lawrie CH: CircRNAs and cancer:
Biomarkers and master regulators. Semin Cancer Biol. 58:90–99.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xiong S, Peng H, Ding X, Wang X, Wang L,
Wu C, Wang S, Xu H and Liu Y: Circular RNA expression profiling and
the potential role of hsa_circ_0089172 in Hashimoto's thyroiditis
via sponging miR125a-3p. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 17:38–48. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao T, Zheng Y, Hao D, Jin X, Luo Q, Guo
Y, Li D, Xi W, Xu Y, Chen Y, et al: Blood circRNAs as biomarkers
for the diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia. J Cell Biochem.
120:16483–16494. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qian Z, Liu H, Li M, Shi J, Li N, Zhang Y,
Zhang X, Lv J, Xie X, Bai Y, et al: Potential diagnostic power of
blood circular RNA expression in active pulmonary tuberculosis.
EBioMedicine. 27:18–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Wang Y, Li SF, Dang YJ, Shi XM, Chen L,
Wang N, Cai Y and Zhao YY: Differentially expressed circular RNAs
in maternal and neonatal umbilical cord plasma from SGA compared
with AGA. J Cell Biochem. 121:713–722. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Deng A, Zhang H, Hu M, Liu S, Wang Y, Gao
Q and Guo C: The inhibitory roles of Ihh downregulation on
chondrocyte growth and differentiation. Exp Ther Med. 15:789–794.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Karp SJ, Schipani E, St-Jacques B,
Hunzelman J, Kronenberg H and McMahon AP: Indian hedgehog
coordinates endochondral bone growth and morphogenesis via
parathyroid hormone related-protein-dependent and -independent
pathways. Development. 127:543–548. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|