|
1
|
Liu J: Pharmacology of oleanolic acid and
ursolic acid. J Ethnopharmacol. 49:57–68. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Somova LO, Nadar A, Rammanan P and Shode
FO: Cardiovascular, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effects of
oleanolic and ursolic acids in experimental hypertension.
Phytomedicine. 10:115–121. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsai SJ and Yin MC: Antioxidative and
anti-inflammatory protection of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in
PC12 cells. J Food Sci. 73:H174–H178. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jesus JA, Lago JH, Laurenti MD, Yamamoto
ES and Passero LF: Antimicrobial activity of oleanolic and ursolic
acids: An update. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2015:6204722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rohilla S and Bhatt DC: Significance of
hepatoprotective liver specific targeted drug delivery: A review on
novel herbal and formulation approaches in the management of
hepatotoxicity. Curr Drug Targets. 19:1519–1549. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Potočnjak I, Šimić L, Vukelić I and
Domitrović R: Oleanolic acid attenuates cisplatin-induced
nephrotoxicity in mice and chemo-sensitizes human cervical cancer
cells to cisplatin cytotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol. 132:1106762019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Raphael TJ and Kuttan G: Effect of
naturally occurring triterpenoids glycyrrhizic acid, ursolic acid,
oleanolic acid and nomilin on the immune system. Phytomedicine.
10:483–489. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Somova LI, Shode FO and Mipando M:
Cardiotonic and antidys-rhythmic effects of oleanolic and ursolic
acids, methyl maslinate and uvaol. Phytomedicine. 11:121–129. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bachhav SS, Bhutada MS, Patil SP, Sharma
KS and Patil SD: Oleanolic acid prevents increase in blood pressure
and nephrotoxicity in nitric oxide dependent type of hypertension
in rats. Pharmacognosy Res. 7:385–392. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu R, Yang W, Qi D, Gong L, Li C, Li Y and
Jiang H: Targeted neurotransmitter metabolomics profiling of
oleanolic acid in the treatment of spontaneously hypertensive rats.
RSC Adv. 9:23276–23288. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
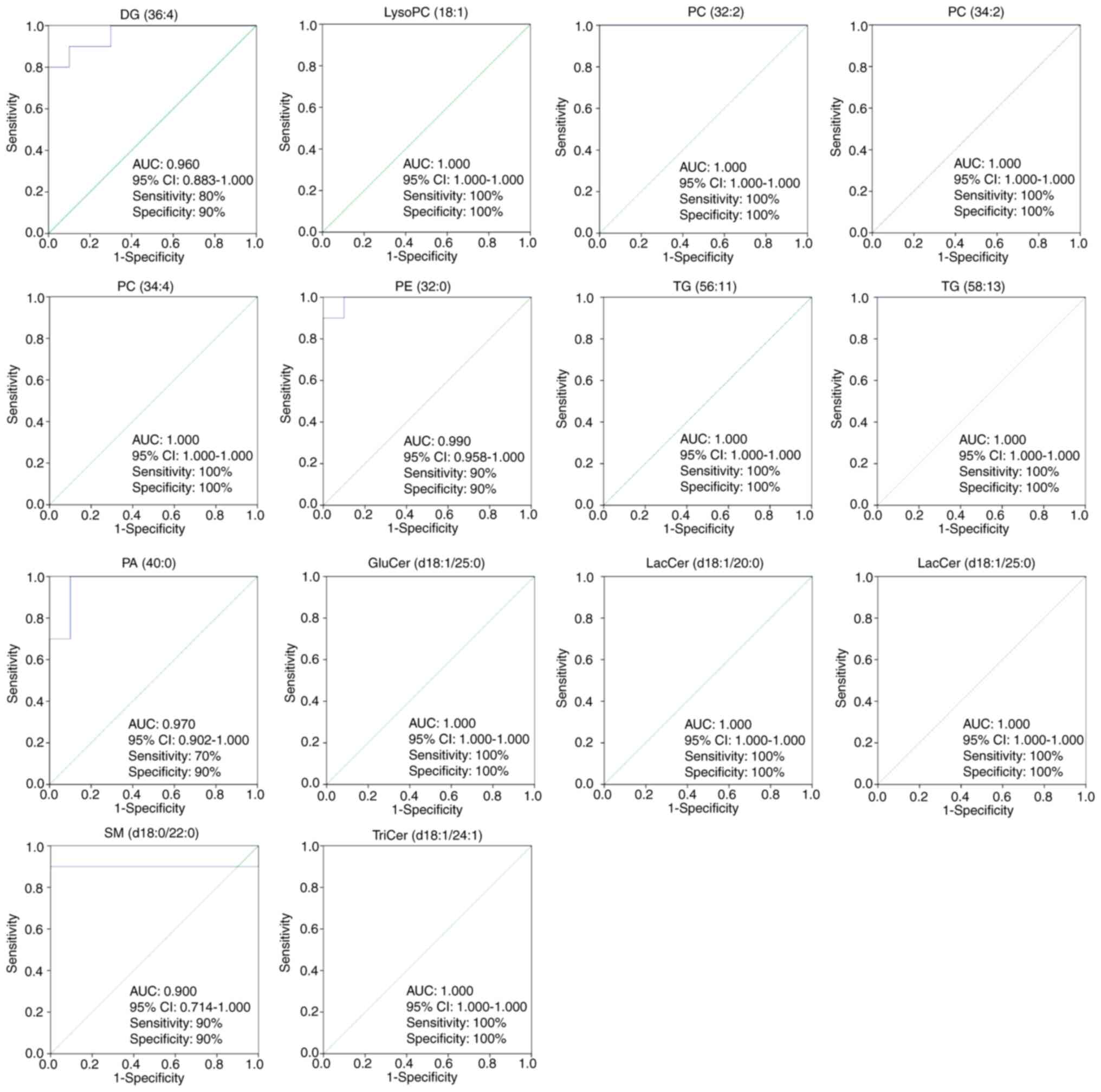
|
|
11
|
Bachhav SS, Patil SD, Bhutada MS and
Surana SJ: Oleanolic acid prevents glucocorticoid-induced
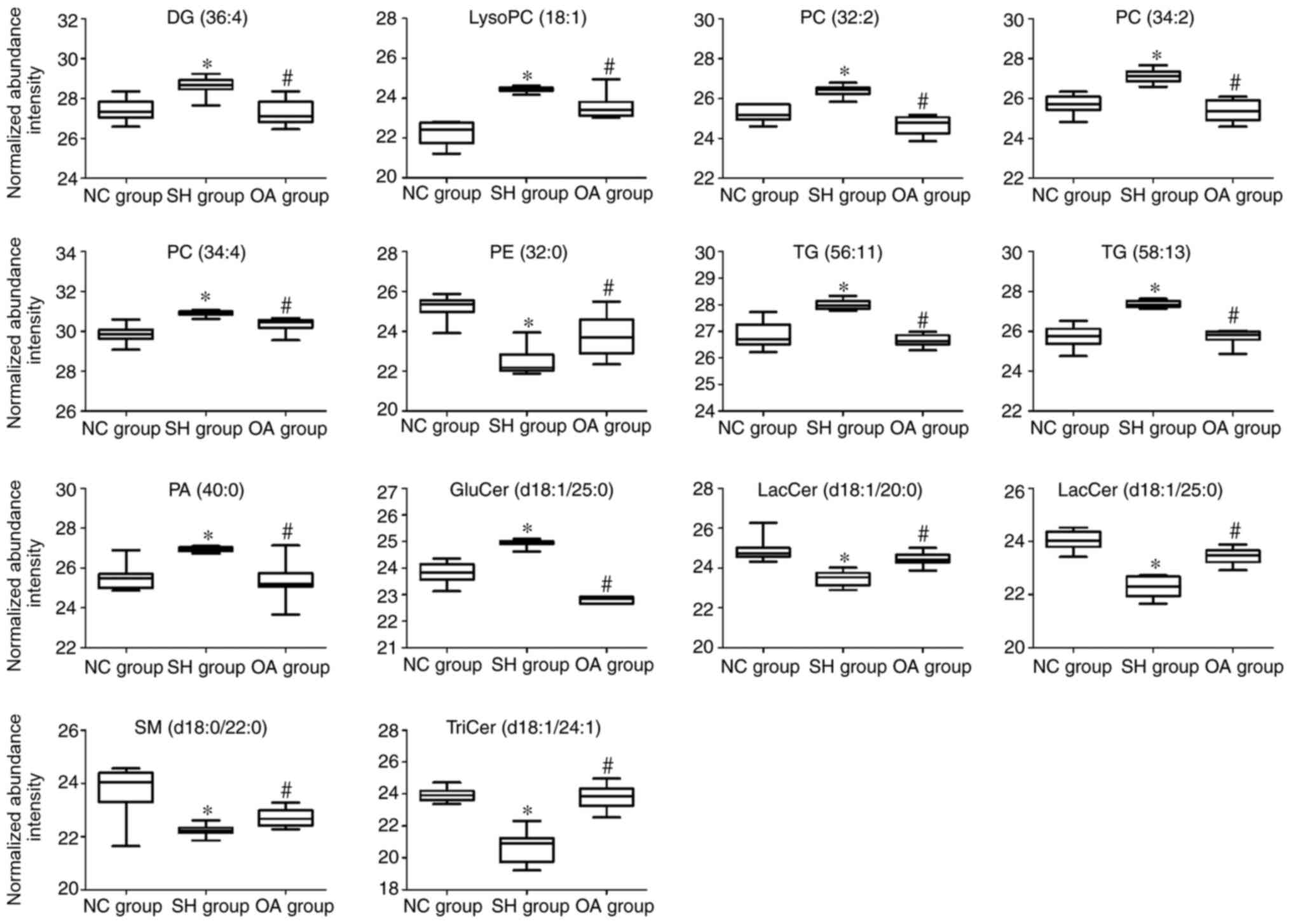
hypertension in rats. Phyther Res. 25:1435–1439. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Madlala HP, Van Heerden FR, Mubagwa K and
Musabayane CT: Changes in renal function and oxidative status
associated with the hypotensive effects of oleanolic acid and
related synthetic derivatives in experimental animals. PLoS One.
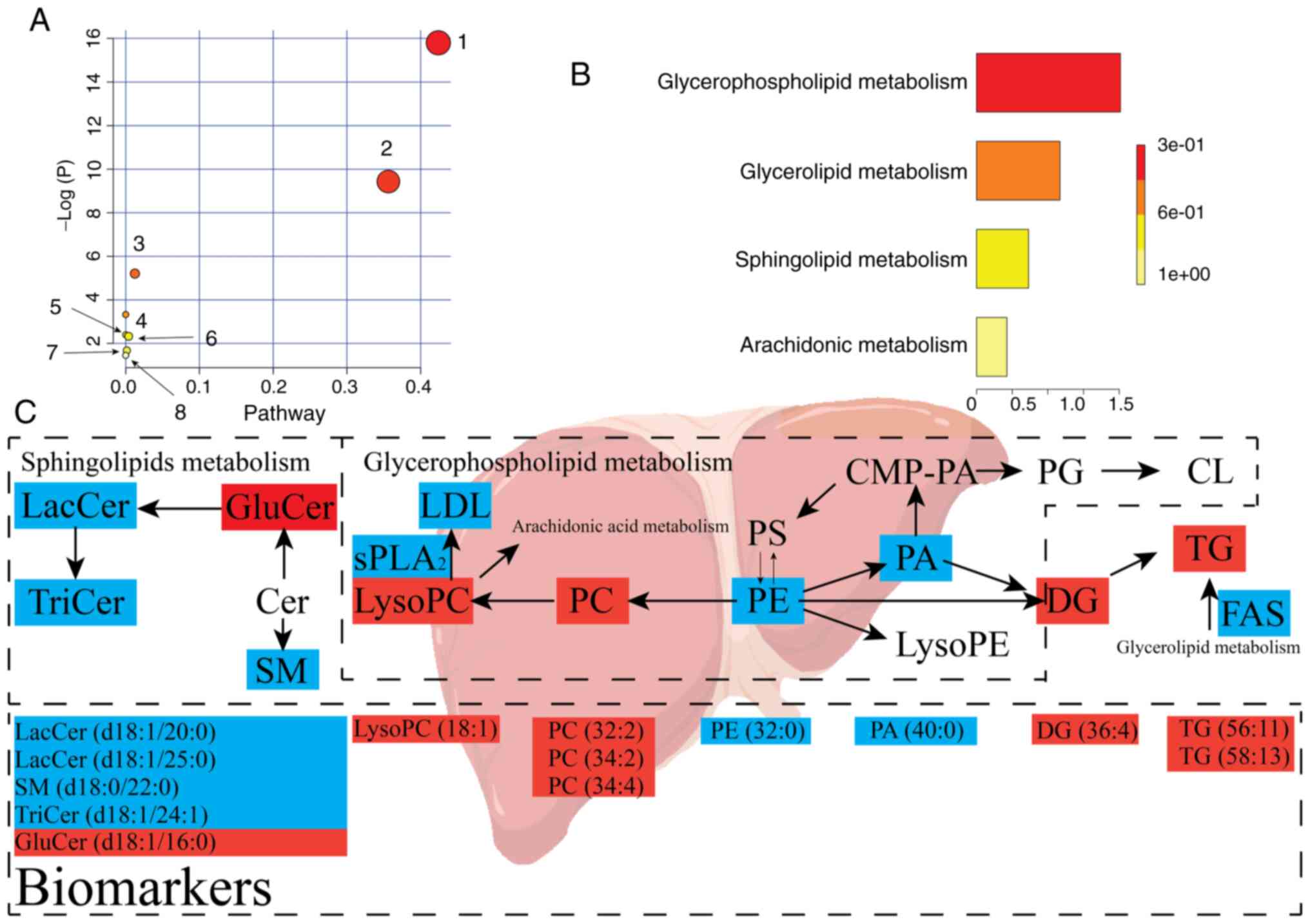
10:e01281922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Somova LI, Shode FO, Ramnanan P and Nadar
A: Antihypertensive, antiatherosclerotic and antioxidant activity
of triterpenoids isolated from Olea europaea, subspecies africana
leaves. J Ethnopharmacol. 84:299–305. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
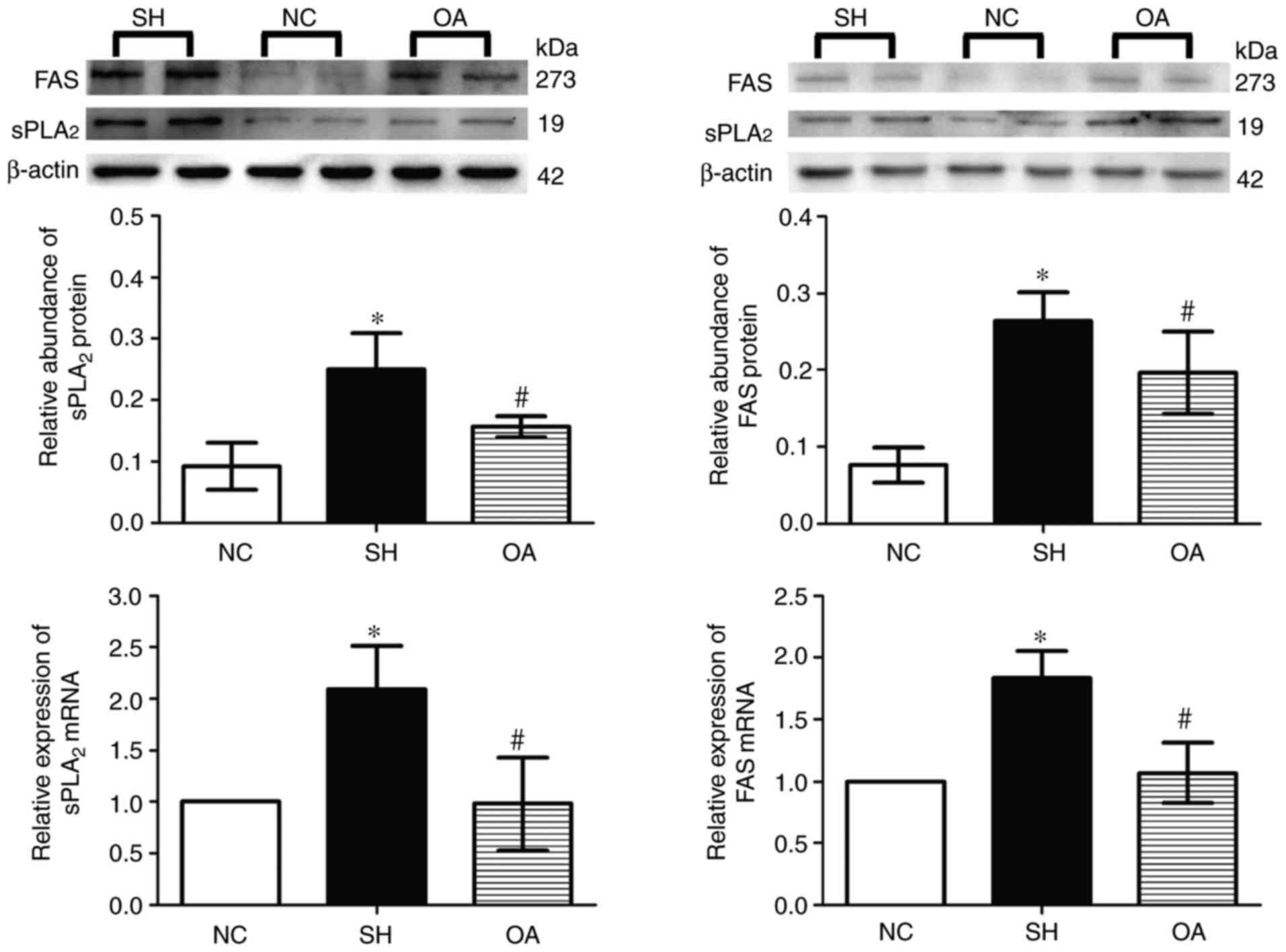
Liao HH, Zhang N, Feng H, Zhang N, Ma ZG,
Yang Z, Yuan Y, Bian ZY and Tang QZ: Oleanolic acid alleviated
pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling. Mol Cell Biochem.
409:145–154. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ahn YM, Choi YH, Yoon JJ, Lee YJ, Cho KW,
Kang DG and Lee HS: Oleanolic acid modulates the renin-angiotensin
system and cardiac natriuretic hormone concomitantly with volume
and pressure balance in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 809:231–241. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Madlala HP, Metzinger T, Van Heerden FR,
Musabayane CT, Mubagwa K and Dessy C: Vascular
endothelium-dependent and independent actions of oleanolic acid and
its synthetic oleanane derivatives as possible mechanisms for
hypotensive effects. PLoS One. 11:e01473952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marteau JB, Zaiou M, Siest G and
Visvikis-Siest S: Genetic determinants of blood pressure
regulation. J Hypertens. 23:2127–2143. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bacon SL, Sherwood A, Hinderliter A and
Blumenthal JA: Effects of exercise, diet and weight loss on high
blood pressure. Sports Med. 34:307–316. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hinterwirth H, Stegemann C and Mayr M:
Lipidomics Quest for molecular lipid biomarkers in cardiovascular
disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 7:941–954. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tian Y, Jiang F, Li Y, Jiang H, Chu Y, Zhu
L and Guo W: Evaluation of the anti-hypertensive effect of Tengfu
Jiangya tablet by combination of UPLC-Q-exactive-MS-based
metabolomics and iTRAQ-based proteomics technology. Biomed
Pharmacother. 100:324–334. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tian Z, Zhang S, Wang H, Chen Z, Sun M,
Sun L, Gong L, Li Y and Jiang H: Intervention of uncaria and its
components on liver lipid metabolism in spontaneously hypertensive
rats. Front Pharmacol. 11:9102020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Kerage D, Brindley DN and Hemmings DG:
Review: Novel insights into the regulation of vascular tone by
sphingosine 1-phosphate. Placenta. 35(Suppl): S86–S92. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cogolludo A, Villamor E, Perez-Vizcaino F
and Moreno L: Ceramide and regulation of vascular tone. Int J Mol
Sci. 20:4112019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Spijkers LJ, van den Akker RF, Janssen BJ,
Debets JJ, De Mey JG, Stroes ES, van den Born BJ, Wijesinghe DS,
Chalfant CE, MacAleese L, et al: Hypertension is associated with
marked alterations in sphingolipid biology: A potential role for
ceramide. PLoS One. 6:e218172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Graessler J, Schwudke D, Schwarz PE,
Herzog R, Shevchenko A and Bornstein SR: Top-down lipidomics
reveals ether lipid deficiency in blood plasma of hypertensive
patients. PLoS One. 4:e62612009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu A, Chu YJ, Wang X, Yu R, Jiang H, Li
Y, Zhou H, Gong LL, Yang WQ and Ju J: Serum metabolomics study
based on LC-MS and antihypertensive effect of uncaria on
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Evidence-based Complement Altern
Med. 2018:92819462018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hu C, Kong H, Qu F, Li Y, Yu Z, Gao P,
Peng S and Xu G: Application of plasma lipidomics in studying the
response of patients with essential hypertension to
antihypertensive drug therapy. Mol Biosyst. 7:3271–3279. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pyttel S, Zschörnig K, Nimptsch A, Paasch
U and Schiller J: Enhanced lysophosphatidylcholine and
sphingomyelin contents are characteristic of spermatozoa from obese
men-A MALDI mass spectrometric study. Chem Phys Lipids.
165:861–865. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Law SH, Chan ML, Marathe GK, Parveen F,
Chen CH and Ke LY: An updated review of lysophosphatidylcholine
metabolism in human diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 20:11492019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Sun GY, Shelat PB, Jensen MB, He Y, Sun AY
and Simonyi A: Phospholipases A2 and inflammatory responses in the
central nervous system. Neuromolecular Med. 12:133–148. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lara-Castro C and Garvey WT: Intracellular
lipid accumulation in liver and muscle and the insulin resistance
syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 37:841–856. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Erion DM and Shulman GI:
Diacylglycerol-mediated insulin resistance. Nat Med. 16:400–402.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ke C, Zhu X, Zhang Y and Shen Y:
Metabolomic characterization of hypertension and dyslipidemia.
Metabolomics. 14:1172018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kawamoto R, Tabara Y, Kohara K, Kusunoki
T, Abe M and Miki T: Interaction between serum uric acid and
triglycerides in relation to prehypertension in community-dwelling
Japanese adults. Clin Exp Hypertens. 36:64–69. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shimizu Y, Sato S, Koyamatsu J, Yamanashi
H, Nagayoshi M, Kadota K, Kawashiri SY, Inoue K, Nagata Y and Maeda
T: Platelets and circulating CD34-positive cells as an indicator of
the activity of the vicious cycle between hypertension and
endothelial dysfunction in elderly Japanese men. Atherosclerosis.
259:26–31. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Borghi C, Dormi A, Veronesi M, Sangiorgi Z
and Gaddi A; Brisighella Heart Study Working Party: Association
between different lipid-lowering treatment strategies and blood
pressure control in the Brisighella heart study. Am Heart J.
148:285–292. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kintscher U, Marx N, Martus P, Stoppelhaar
M, Schimkus J, Schneider A, Walcher D, Kümmel A, Winkler R, Kappert
K, et al: Effect of high-dose valsartan on inflammatory and lipid
parameters in patients with Type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 89:209–215. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sarkar K, Sinha AK and Mehta JL: The role
of statins in endothelial dysfunction in hypertension. Curr Opin
Cardiol. 21:316–321. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jacobson TA and Zimmerman FH: Fibrates in
combination with statins in the management of dyslipidemia. J Clin
Hypertens. 8:35–43. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wierzbicki AS: Lipid lowering: Another
method of reducing blood pressure? J Hum Hypertens. 16:753–760.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kwong E, Li Y, Hylemon PB and Zhou H: Bile
acids and sphin-gosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 in hepatic lipid
metabolism. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:151–157. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen H, Chen L, Liu D, Chen DQ, Vaziri ND,
Yu XY, Zhang L, Su W, Bai X and Zhao YY: Combined clinical
phenotype and lipidomic analysis reveals the impact of chronic
kidney disease on lipid metabolism. J Proteome Res. 16:1566–1578.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Walther A, Cannistraci CV, Simons K, Durán
C, Gerl MJ, Wehrli S and Kirschbaum C: Lipidomics in major
depressive disorder. Front Psychiatry. 9:4592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhuang X, Deng ZB, Mu J, Zhang L, Yan J,
Miller D, Feng W, McClain CJ and Zhang HG: Ginger-derived
nanoparticles protect against alcohol-induced liver damage. J
Extracell Vesicles. 4:287132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nguyen P, Leray V, Diez M, Serisier S, Le
Bloc'h J, Siliart B and Dumon H: Liver lipid metabolism. J Anim
Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 92:272–283. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Xie J, Jiang HQ, Li YL, Nie L, Zhou HL and
Yang WQ: Study on the intervention effects of pinggan prescription
() on spontaneously hypertensive rats based on metabonomic and
pharmacodynamic methods. Chin J Integr Med. 25:348–353. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Biernacki M, Ambrożewicz E, Gęgotek A,
Toczek M and Skrzydlewska E: Long-term administration of fatty acid
amide hydrolase inhibitor (URB597) to rats with spontaneous
hypertension disturbs liver redox balance and phospholipid
metabolism. Adv Med Sci. 64:15–23. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Bourbon NA, Sandirasegarane L and Kester
M: Ceramide-induced inhibition of Akt is mediated through protein
kinase Czeta: Implications for growth arrest. J Biol Chem.
277:3286–3292. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Mulders ACM, Mathy MJ, Meyer zu Heringdorf
D, ter Braak M, Hajji N, Olthof DC, Michel MC, Alewijnse AE and
Peters SL: Activation of sphingosine kinase by muscarinic receptors
enhances NO-mediated and attenuates EDHF-mediated vasorelaxation.
Basic Res Cardiol. 104:50–59. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Mulders ACM, Hendriks-Balk MC, Mathy MJ,
Michel MC, Alewijnse AE and Peters SLM: Sphingosine
kinase-dependent activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by
angiotensin II. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:2043–2048. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Brown WJ, Chambers K and Doody A:
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) enzymes in membrane trafficking: Mediators
of membrane shape and function. Traffic. 4:214–221. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cole LK, Vance JE and Vance DE:
Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and lipoprotein metabolism.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1821:754–761. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Benrezzouk R, Terencio MC, Ferrándiz ML,
San Feliciano A, Gordaliza M, Miguel del Corral JM, de la Puente ML
and Alcaraz MJ: Inhibition of human sPLA2 and 5-lipoxygenase
activities by two neoclerodane diterpenoids. Life Sci.
64:PL205–PL211. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Mallat Z, Lambeau G and Tedgui A:
Lipoprotein-associated and secreted phospholipases A2 in
cardiovascular disease: Roles as biological effectors and
biomarkers. Circulation. 122:2183–2200. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Boekholdt SM, Keller TT, Wareham NJ, Luben
R, Bingham SA, Day NE, Sandhu MS, Jukema JW, Kastelein JJ, Hack CE
and Khaw KT: Serum levels of type II secretory phospholipase A2 and
the risk of future coronary artery disease in apparently healthy
men and women: The EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:839–846. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hurt-Camejo E, Camejo G, Peilot H, Oörni K
and Kovanen P: Phospholipase A(2) in vascular disease. Circ Res.
89:298–304. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Rosengren B, Peilot H, Umaerus M,
Jönsson-Rylander AC, Mattsson-Hultén L, Hallberg C, Cronet P,
Rodriguez-Lee M and Hurt-Camejo E: Secretory phospholipase A2 group
V: Lesion distribution, activation by arterial proteoglycans, and
induction in aorta by a Western diet. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 26:1579–1585. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sonoki K, Iwase M, Sasaki N, Ohdo S,
Higuchi S, Takata Y and Iida M: Secretory PLA2 inhibitor indoxam
suppresses LDL modification and associated inflammatory responses
in TNFalpha-stimulated human endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol.
153:1399–1408. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Guardiola M, Exeter HJ, Perret C,
Folkersen L, Van't Hooft F, Eriksson P, Franco-Cereceda A,
Paulsson-Berne G, Palmen J, Li K, et al: PLA2G10 gene variants,
sPLA2 activity, and coronary heart disease risk. Circ Cardiovasc
Genet. 8:356–362. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kume N and Gimbrone MA Jr:
Lysophosphatidylcholine transcriptionally induces growth factor
gene expression in cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest.
93:907–911. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Jensen-Urstad APL and Semenkovich CF:
Fatty acid synthase and liver triglyceride metabolism: Housekeeper
or messenger? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1821:747–753. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
62
|
Iizuka K, Miller B and Uyeda K: Deficiency
of carbohydrate-activated transcription factor ChREBP prevents
obesity and improves plasma glucose control in leptin-deficient
(ob/ob) mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 291:E358–E364. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Scott CL: Diagnosis, prevention, and
intervention for the meta-bolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 92:35i–42i.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Berndt J, Kovacs P, Ruschke K, Klöting N,
Fasshauer M, Schön MR, Körner A, Stumvoll M and Blüher M: Fatty
acid synthase gene expression in human adipose tissue: Association
with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 50:1472–1480. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Mayas MD, Ortega FJ, Macías-González M,
Bernal R, Gómez-Huelgas R, Fernández-Real JM and Tinahones FJ:
Inverse relation between FASN expression in human adipose tissue
and the insulin resistance level. Nutr Metab (Lond). 7:32010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Suzuki T, Muramatsu T, Morioka K, Goda T
and Mochizuki K: ChREBP binding and histone modifications modulate
hepatic expression of the Fasn gene in a metabolic syndrome rat
model. Nutrition. 31:877–883. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Nedvedova I, Kolar D, Neckar J, Kalous M,
Pravenec M, Šilhavý J, Korenkova V, Kolar F and Zurmanova JM:
Cardioprotective regimen of adaptation to chronic hypoxia diversely
alters myocardial gene expression in SHR and SHR-mtBN
conplastic rat strains. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:8092019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
German JB, Gillies LA, Smilowitz JT,
Zivkovic AM and Watkins SM: Lipidomics and lipid profiling in
metabolomics. Curr Opin Lipidol. 18:66–71. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yang K and Han X: Lipidomics: Techniques,
applications, and outcomes related to biomedical sciences. Trends
Biochem Sci. 41:954–969. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lapthorn C, Pullen F and Chowdhry BZ: Ion
mobility spec-trometrymass spectrometry (IMS-MS) of small
molecules: Separating and assigning structures to ions. Mass
Spectrom Rev. 32:43–71. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Martano G, Leone M, D'Oro P, Matafora V,
Cattaneo A, Masseroli M and Bachi A: SMfinder: Small molecules
finder for metabolomics and lipidomics analysis. Anal Chem.
92:8874–8882. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press; Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
73
|
Jones KE and Bennett DJ: Motor axon
excitability measures in the rat tail are the same awake or
anaesthetized using sodium pentobarbital. bioRxiv: doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/651927urisimplehttps://doi.org/10.1101/651927.
|
|
74
|
Ma N, Yang Y, Liu X, Kong X, Li S, Qin Z,
Jiao Z and Li J: UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-based metabonomic studies on the
intervention effects of aspirin eugenol ester in atherosclerosis
hamsters. Sci Rep. 7:105442017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
75
|
Iverson SJ, Lang SLC and Cooper MH:
Comparison of the bligh and dyer and folch methods for total lipid
determination in a broad range of marine tissue. Lipids.
36:1283–1287. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Milne S, Ivanova P, Forrester J and Alex
Brown H: Lipidomics: An analysis of cellular lipids by ESI-MS.
Methods. 39:92–103. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Søreide K: Receiver-operating
characteristic curve analysis in diagnostic, prognostic and
predictive biomarker research. J Clin Pathol. 62:1–5. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Blaise BJ, Gouel-Chéron A, Floccard B,
Monneret G and Allaouchiche B: Metabolic phenotyping of traumatized
patients reveals a susceptibility to sepsis. Anal Chem.
85:10850–10855. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Greiner M, Pfeiffer D and Smith RD:
Principles and practical application of the receiver-operating
characteristic analysis for diagnostic tests. Prev Vet Med.
45:23–41. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Miao H, Zhao YH, Vaziri ND, Tang DD, Chen
H, Chen H, Khazaeli M, Tarbiat-Boldaji M, Hatami L and Zhao YY:
Lipidomics biomarkers of diet-induced hyperlipidemia and its
treatment with poria cocos. J Agric Food Chem. 64:969–979. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Xia J, Mandal R, Sinelnikov IV, Broadhurst
D and Wishart DS: MetaboAnalyst 2.0-a comprehensive server for
metabolomic data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 40(Web Server Issue):
W127–W133. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
83
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Zor T and Selinger Z: Linearization of the
Bradford protein assay increases its sensitivity: Theoretical and
experimental studies. Anal Biochem. 236:302–308. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yang C, Yuan W, Yang X, Li P, Wang J, Han
J, Tao J, Li P, Yang H, Lv Q and Zhang W: Circular RNA circ-ITCH
inhibits bladder cancer progression by sponging miR-17/miR-224 and
regulating p21, PTEN expression. Mol Cancer. 17:192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Zhang R, Inagawa H, Kazumura K, Tsuchiya
H, Miwa T, Morishita N, Uchibori S, Hanashiro J, Masaki T, Kobara H
and Soma GI: Evaluation of a hypertensive rat model using
peripheral blood neutrophil activity, phagocytic activity and
oxidized LDL evaluation. Anticancer Res. 38:4289–4294. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Yin J, Xie J, Guo X, Ju L, Li Y and Zhang
Y: Plasma metabolic profiling analysis of cyclophosphamide-induced
cardiotoxicity using metabolomics coupled with UPLC/Q-TOF-MS and
ROC curve. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci.
1033-1034:428–435. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Kind T, Cho E, Park TD, Deng N, Liu Z, Lee
T, Fiehn O and Kim J: Interstitial cystitis-associated urinary
metabolites identified by mass-spectrometry based metabolomics
analysis. Sci Rep. 6:392272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Girard A, Madani S, Boukortt F,
Cherkaoui-Malki M, Belleville J and Prost J: Fructose-enriched diet
modifies antioxidant status and lipid metabolism in spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Nutrition. 22:758–766. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Dutta M, Joshi M, Srivastava S, Lodh I,
Chakravarty B and Chaudhury K: A metabonomics approach as a means
for identification of potential biomarkers for early diagnosis of
endometriosis. Mol Biosyst. 8:3281–3287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Jiang H, Shen Z, Chu Y, Li Y, Li J, Wang
X, Yang W, Zhang X, Ju J, Xu J and Yang C: Serum metabolomics
research of the anti-hypertensive effects of Tengfu Jiangya tablet
on spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol
Biomed Life Sci. 1002:210–217. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Fenger M, Linneberg A and Jeppesen J:
Network-based analysis of the sphingolipid metabolism in
hypertension. Front Genet. 6:842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Penna C, Tullio F, Moro F, Folino A,
Merlino A and Pagliaro P: Effects of a protocol of ischemic
postconditioning and/or capto-pril in hearts of normotensive and
hypertensive rats. Basic Res Cardiol. 105:181–192. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Lin CH, Lee SY, Zhang CC, Du YF, Hung HC,
Wu HT and Ou HY: Fenretinide inhibits macrophage inflammatory
media-tors and controls hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive
rats via the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 10:3591–3597. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
95
|
Jiang H, Nie L, Li Y and Xie J:
Application of ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with
mass spectrometry to metabonomic study on spontaneously
hypertensive rats and intervention effects of Ping Gan
prescription. J Sep Sci. 35:483–489. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Ye X, Kong W, Zafar MI and Chen LL: Serum
triglycerides as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases in type
2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
prospective studies. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 18:482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Kulkarni H, Meikle PJ, Mamtani M, Weir JM,
Barlow CK, Jowett JB, Bellis C, Dyer TD, Johnson MP, Rainwater DL,
et al: Plasma lipidomic profile signature of hypertension in
mexican american families: Specific role of diacylglycerols.
Hypertension. 62:621–626. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Tokumura A, Fujimoto H, Yoshimoto O,
Nishioka Y, Miyake M and Fukuzawa K: Production of lysophosphatidic
acid by lysophospholipase D in incubated plasma of spontaneously
hypertensive rats and Wistar Kyoto rats. Life Sci. 65:245–253.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Kim J, Choi JN, Choi JH, Cha YS, Muthaiya
MJ and Lee CH: Effect of fermented soybean product (Cheonggukjang)
intake on metabolic parameters in mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 57:1886–1891. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Murugesan G and Fox PL: Role of
lysophosphatidylcholine in the inhibition of endothelial cell
motility by oxidized low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest.
97:2736–2744. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Liu JC, Conklin SM, Manuck SB, Yao JK and
Muldoon MF: Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and blood pressure. Am J
Hypertens. 24:1121–1126. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Hu C, Hoene M, Zhao X, Häring HU,
Schleicher E, Lehmann R, Han X, Xu G and Weigert C: Lipidomics
analysis reveals efficient storage of hepatic triacylglycerides
enriched in unsaturated fatty acids after one bout of exercise in
mice. PLoS One. 5:e133182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Ivandic B, Castellani LW, Wang XP, Qiao
JH, Mehrabian M, Navab M, Fogelman AM, Grass DS, Swanson ME, de
Beer MC, et al: Role of group II secretory phospholipase A2 in
atherosclerosis: 1. Increased atherogenesis and altered
lipoproteins in transgenic mice expressing group IIa phospholipase
A2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 19:1284–1290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Dutra FL, Vieira DP, Coelho FS, Adade CM,
Atella GC, Silva Neto MAC and Lopes AH: Lysophosphatidylcholine
triggers cell differentiation in the protozoan parasite
herpetomonas samuelpessoai through the CK2 pathway. Acta Parasitol.
65:108–117. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Singh N, Shafiq M, Jagavelu K and Hanif K:
Involvement of fatty acid synthase in right ventricle dysfunction
in pulmonary hypertension. Exp Cell Res. 383:1115692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|