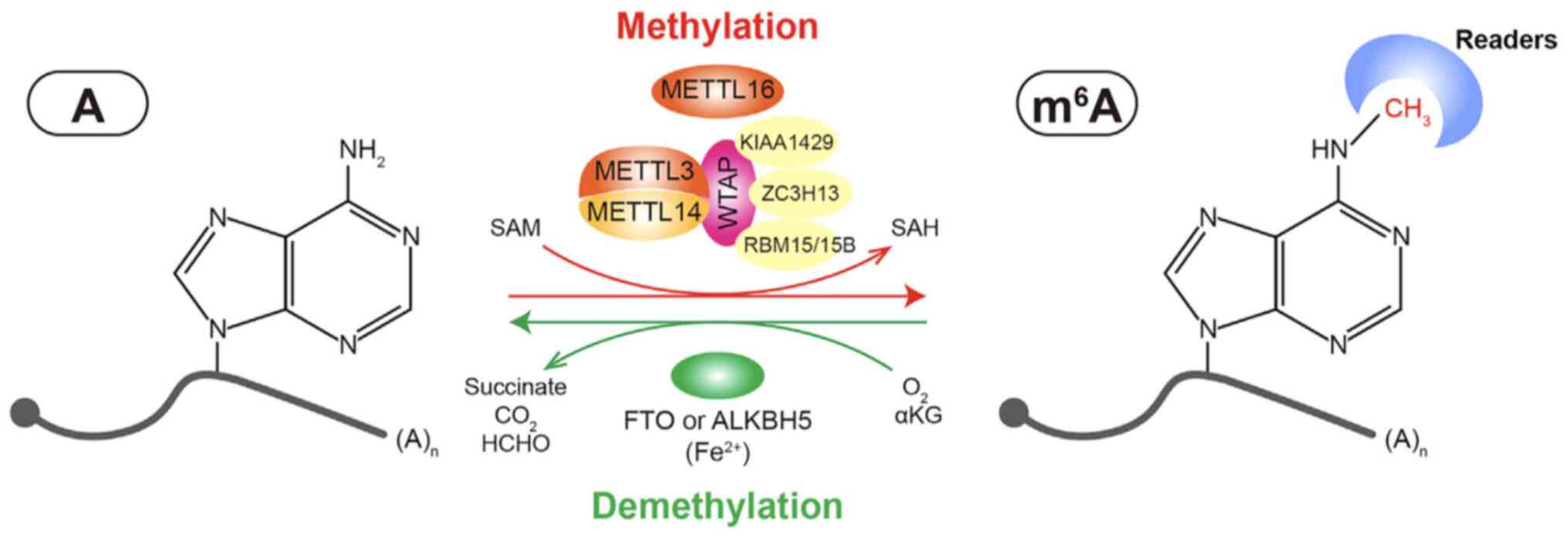
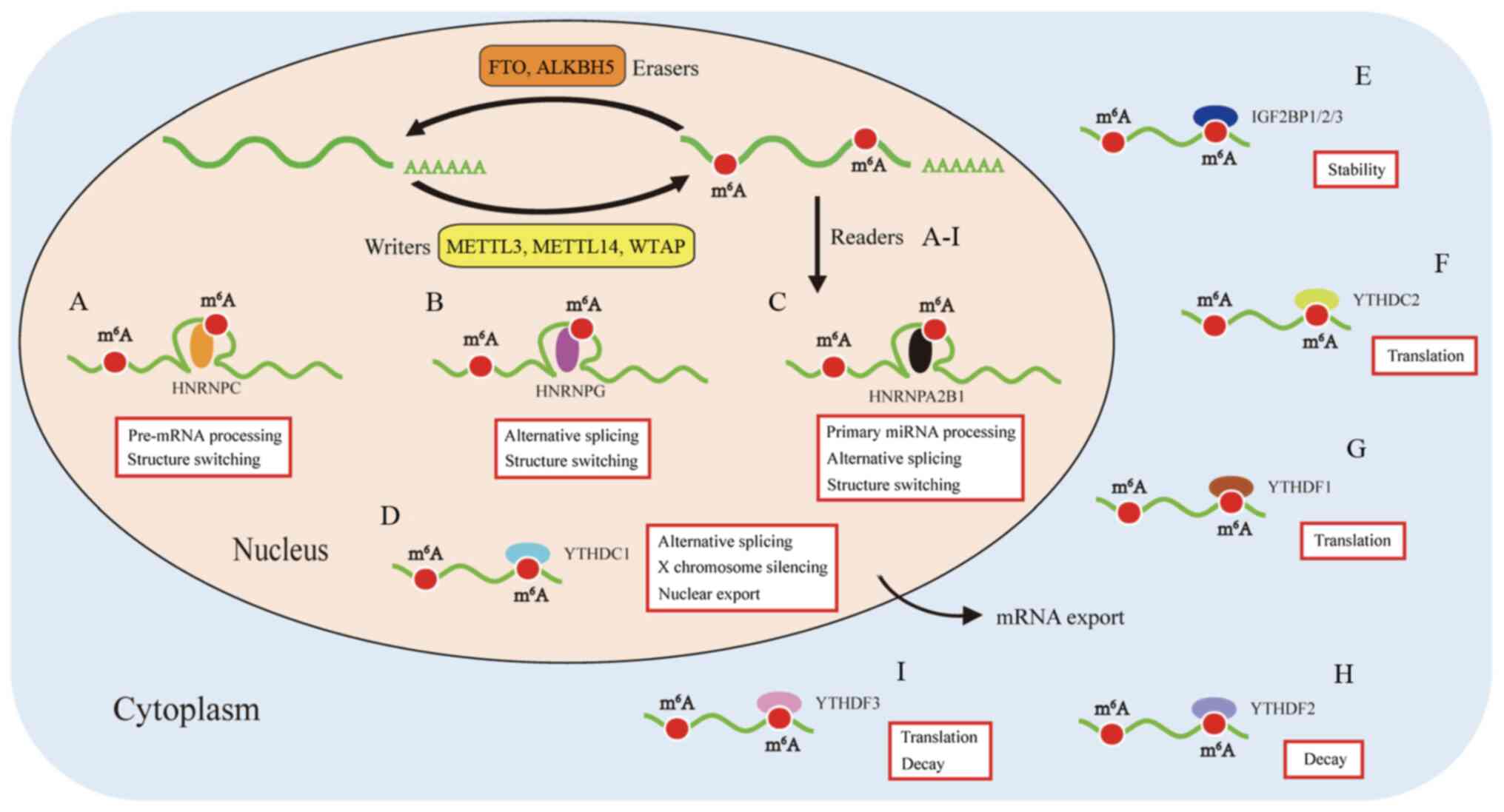
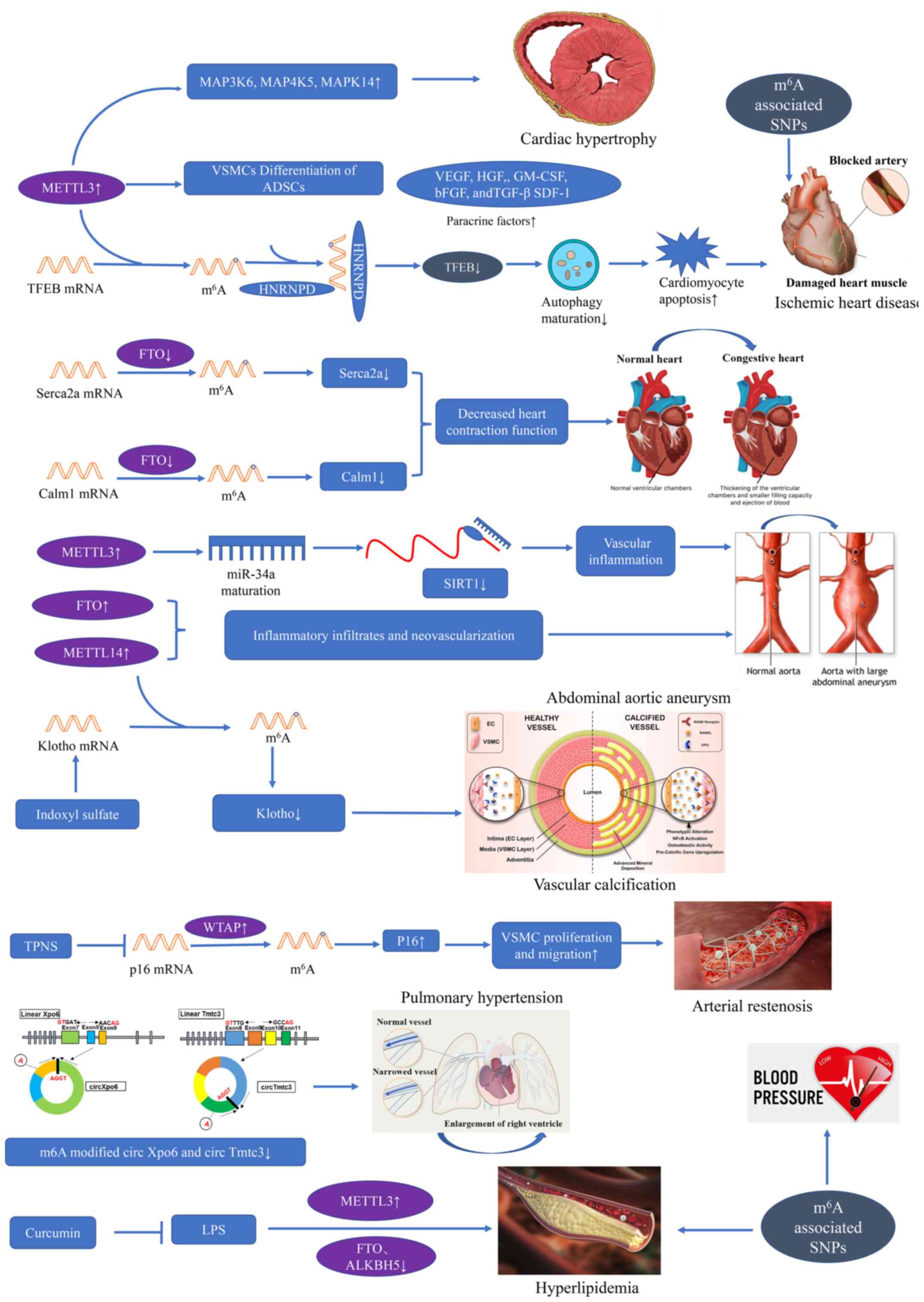
|
1
|
Stellos K: The rise of epitranscriptomic
era: Implications for cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res.
113:e2–e3. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang H, Weng H and Chen J: m6A
modification in coding and non-coding RNAs: Roles and therapeutic
implications in cancer. Cancer Cell. 37:270–288. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Desrosiers R, Friderici K and Rottman F:
Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from
Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 71:3971–3975.
1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wei CM, Gershowitz A and Moss B:
Methylated nucleotides block 5′ terminus of HeLa cell messenger
RNA. Cell. 4:379–386. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee M, Kim B and Kim VN: Emerging roles of
RNA modification: m(6)A and U-tail. Cell. 158:980–987. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bhat SS, Bielewicz D, Jarmolowski A and
Szweykowska- Kulinska Z: N6-methyladenosine
(m6A): Revisiting the old with focus on new, an
arabidopsis thaliana centered review. Genes (Basel). 9:5962018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhao W, Qi X, Liu L, Ma S, Liu J and Wu J:
Epigenetic regulation of m6A modifications in human
cancer. Mol Ther. 19:405–412. 2020.
|
|
8
|
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S,
Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, Cesarkas K,
Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Kupiec M, et al: Topology of the human
and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature.
485:201–206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Molinie B, Wang J, Lim KS, Hillebrand R,
Lu ZX, Van Wittenberghe N, Howard BD, Daneshvar K, Mullen AC, Dedon
P, et al: m(6)A-LAIC-seq reveals the census and complexity of the
m(6)A epitranscriptome. Nat Methods. 13:692–698. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fustin JM, Doi M, Yamaguchi Y, Hida H,
Nishimura S, Yoshida M, Isagawa T, Morioka MS, Kakeya H, Manabe I
and Okamura H: RNA-methylation-dependent RNA processing controls
the speed of the circadian clock. Cell. 155:793–806. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han
D, Fu Y, Parisien M, Dai Q, Jia G, et al:
N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability.
Nature. 505:117–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Meyer KD, Patil DP, Zhou J, Zinoviev A,
Skabkin MA, Elemento O, Pestova TV, Qian SB and Jaffrey SR: 5′ UTR
m(6) A promotes cap-independent translation. Cell. 163:999–1010.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Alarcón CR, Lee H, Goodarzi H, Halberg N
and Tavazoie SF: N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for
processing. Nature. 519:482–485. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen XY, Zhang J and Zhu JS: The role of
m6A RNA methylation in human cancer. Mol Cancer.
18:1032019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Edupuganti RR, Geiger S, Lindeboom RGH,
Shi H, Hsu PJ, Lu Z, Wang SY, Baltissen MPA, Jansen PWTC, Rossa M,
et al: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) recruits and
repels proteins to regulate mRNA homeostasis. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
24:870–878. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Visvanathan A and Somasundaram K: mRNA
traffic control reviewed: N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) takes
the driver's seat. Bioessays. Dec 4–2017.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Meyer KD and Jaffrey SR: The dynamic
epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:313–326. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fu Y, Dominissini D, Rechavi G and He C:
Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible
m6A RNA methylation. Nat Rev Genet. 15:293–306. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tong J, Flavell RA and Li HB: RNA
m6A modification and its function in diseases. Front
Med. 12:481–489. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen K, Lu Z, Wang X, Fu Y, Luo GZ, Liu N,
Han D, Dominissini D, Dai Q, Pan T and He C: High-resolution N(6)-
methyladenosine (m(6) A) map using photo-crosslinking-assisted m(6)
A sequencing. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 54:1587–1590. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhou J, Wan J, Gao X, Zhang X, Jaffrey SR
and Qian SB: Dynamic m(6)A mRNA methylation directs translational
control of heat shock response. Nature. 526:591–594. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barbieri I, Tzelepis K, Pandolfini L, Shi
J, Millán-Zambrano G, Robson SC, Aspris D, Migliori V, Bannister
AJ, Han N, et al: Promoter-bound METTL3 maintains myeloid leukaemia
by m6A-dependent translation control. Nature.
552:126–131. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X and He C: Dynamic RNA modifications
in posttranscriptional regulation. Mol Cell. 56:5–12. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi H, Wang X, Lu Z, Zhao BS, Ma H, Hsu
PJ, Liu C and He C: YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of
N-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 27:315–328. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S,
Lu Z, Chen Y, Sulman EP, Xie K, Bögler O, et al: m6A
demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma
stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell
proliferation program. Cancer Cell. 31:591–606.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhu S, Wang JZ, Chen D, He YT, Meng N,
Chen M, Lu RX, Chen XH, Zhang XL and Yan GR: An oncopeptide
regulates m6A recognition by the m6A reader
IGF2BP1 and tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 11:16852020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu Y, Yang X, Chen Z, Tian L, Jiang G,
Chen F, Li J, An P, Lu L, Luo N, et al: m6A-induced
lncRNA RP11 triggers the dissemi-nation of colorectal cancer cells
via upregulation of Zeb1. Mol Cancer. 18:872019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hess ME, Hess S, Meyer KD, Verhagen LA,
Koch L, Brönneke HS, Dietrich MO, Jordan SD, Saletore Y, Elemento
O, et al: The fat mass and obesity associated gene (Fto) regulates
activity of the dopaminergic midbrain circuitry. Nat Neurosci.
16:1042–1048. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Du K, Zhang L, Lee T and Sun T: m(6)A RNA
methylation controls neural development and is involved in human
diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 56:1596–1606. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wu Y, Xie L, Wang M, Xiong Q, Guo Y, Liang
Y, Li J, Sheng R, Deng P, Wang Y, et al: Mettl3-mediated
m6A RNA methylation regulates the fate of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells and osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 9:47722018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kane SE and Beemon K: Precise localization
of m6A in Rous sarcoma virus RNA reveals clustering of methylation
sites: Implications for RNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 5:2298–2306.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Roignant JY and Soller M: m6A
in mRNA: An ancient mechanism for fine-tuning gene expression.
Trends Genet. 33:380–390. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao Y, Shi Y, Shen H and Xie W:
m6A-binding proteins: The emerging crucial performers in
epigenetics. J Hematol Oncol. 13:352020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang
Y, Yi C, Lindahl T, Pan T, Yang YG and He C: N6-methyladenosine in
nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat
Chem Biol. 7:885–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yao QJ, Sang L, Lin M, Yin X, Dong W, Gong
Y and Zhou BO: Mettl3-Mettl14 methyltransferase complex regulates
the quiescence of adult hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Res.
28:952–954. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P,
Huang CM, Li CJ, Vågbø CB, Shi Y, Wang WL, Song SH, et al: ALKBH5
is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and
mouse fertility. Mol Cell. 49:18–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Ping XL, Sun BF, Wang L, Xiao W, Yang X,
Wang WJ, Adhikari S, Shi Y, Lv Y, Chen YS, et al: Mammalian WTAP is
a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine
methyltrans-ferase. Cell Res. 24:177–189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Slobodin B, Han R, Calderone V, Vrielink
JAFO, Loayza-Puch F, Elkon R and Agami R: Transcription impacts the
efficiency of mRNA translation via co-transcriptional N6-adenosine
methylation. Cell. 169:326–337.e12. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han
D, Ma H, Weng X, Chen K, Shi H and He C: N(6)-methyladenosine
modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell.
161:1388–1399. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Choi J, Ieong KW, Demirci H, Chen J,
Petrov A, Prabhakar A, O'Leary SE, Dominissini D, Rechavi G, Soltis
SM, et al: N(6)-methyladenosine in mRNA disrupts tRNA selection and
translation-elongation dynamics. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 23:110–115.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bujnicki JM, Feder M, Radlinska M and
Blumenthal RM: Structure prediction and phylogenetic analysis of a
functionally diverse family of proteins homologous to the MT-A70
subunit of the human mRNA:m(6)A methyltransferase. J Mol Evol.
55:431–444. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Śledź P and Jinek M: Structural insights
into the molecular mechanism of the m(6)A writer complex. Elife.
5:e184342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang P, Doxtader KA and Nam Y: Structural
basis for cooperative function of Mettl3 and Mettl14
methyltransferases. Mol Cell. 63:306–317. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schöller E, Weichmann F, Treiber T, Ringle
S, Treiber N, Flatley A, Feederle R, Bruckmann A and Meister G:
Interactions, localization, and phosphorylation of the
m6A generating METTL3-METTL14-WTAP complex. RNA.
24:499–512. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yue Y, Liu J and He C: RNA
N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene
expression regulation. Genes Dev. 29:1343–1355. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu J, Yue Y, Han D, Wang X, Fu Y, Zhang
L, Jia G, Yu M, Lu Z, Deng X, et al: A METTL3-METTL14 complex
mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem
Biol. 10:93–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Schwartz S, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Wang
T, Maciag K, Bushkin GG, Mertins P, Ter-Ovanesyan D, Habib N,
Cacchiarelli D, et al: Perturbation of m6A writers reveals two
distinct classes of mRNA methylation at internal and 5′ sites. Cell
Rep. 8:284–296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Patil DP, Chen CK, Pickering BF, Chow A,
Jackson C, Guttman M and Jaffrey SR: m(6)A RNA methylation promotes
XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 537:369–373.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yue Y, Liu J, Cui X, Cao J, Luo G, Zhang
Z, Cheng T, Gao M, Shu X, Ma H, et al: VIRMA mediates preferential
m6A mRNA methylation in 3′UTR and near stop codon and
associates with alternative polyadenylation. Cell Discov. 4:102018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Knuckles P, Lence T, Haussmann IU, Jacob
D, Kreim N, Carl SH, Masiello I, Hares T, Villaseñor R, Hess D, et
al: Zc3h13/Flacc is required for adenosine methylation by bridging
the mRNA-binding factor Rbm15/Spenito to the m6A
machinery component Wtap/Fl(2)d. Genes Dev. 32:415–429. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tang C, Klukovich R, Peng H, Wang Z, Yu T,
Zhang Y, Zheng H, Klungland A and Yan W: ALKBH5-dependent m6A
demethylation controls splicing and stability of long 3′-UTR mRNAs
in male germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:E325–E333. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Boissel S, Reish O, Proulx K,
Kawagoe-Takaki H, Sedgwick B, Yeo GS, Meyre D, Golzio C, Molinari
F, Kadhom N, et al: Loss-of-function mutation in the
dioxygenase-encoding FTO gene causes severe growth retardation and
multiple malformations. Am J Hum Genet. 85:106–111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Su R, Dong L, Li C, Nachtergaele S,
Wunderlich M, Qing Y, Deng X, Wang Y, Weng X, Hu C, et al: R-2HG
exhibits anti-tumor activity by targeting
FTO/m6A/MYC/CEBPA signaling. Cell. 172:90–105.e23. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
A Alemu E, He C and Klungland A:
ALKBHs-facilitated RNA modifications and de-modifications. DNA
Repair (Amst). 44:87–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Alarcón CR, Goodarzi H, Lee H, Liu X,
Tavazoie S and Tavazoie SF: HNRNPA2B1 is a mediator of
m(6)A-dependent nuclear RNA processing events. Cell. 162:1299–1308.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, Qin X, Shi H, Wu
H, Zhao BS, Mesquita A, Liu C, Yuan CL, et al: Recognition of RNA
N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA
stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol. 20:285–295. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang Z, Theler D, Kaminska KH, Hiller M,
de la Grange P, Pudimat R, Rafalska I, Heinrich B, Bujnicki JM,
Allain FH and Stamm S: The YTH domain is a novel RNA binding
domain. J Biol Chem. 285:14701–14710. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Stoilov P, Rafalska I and Stamm S: YTH: A
new domain in nuclear proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 27:495–497.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liao S, Sun H and Xu C: YTH domain: A
family of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) readers.
Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 16:99–107. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Du H, Zhao Y, He J, Zhang Y, Xi H, Liu M,
Ma J and Wu L: YTHDF2 destabilizes m(6)A-containing RNA through
direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat Commun.
7:126262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Xiao W, Adhikari S, Dahal U, Chen YS, Hao
YJ, Sun BF, Sun HY, Li A, Ping XL, Lai WY, et al: Nuclear m(6)A
reader YTHDC1 regulates mRNA splicing. Mol Cell. 61:507–519. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Roundtree IA, Luo GZ, Zhang Z, Wang X,
Zhou T, Cui Y, Sha J, Huang X, Guerrero L, Xie P, et al: YTHDC1
mediates nuclear export of N6-methyladenosine methylated
mRNAs. Elife. 6:e313112017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Kretschmer J, Rao H, Hackert P, Sloan KE,
Höbartner C and Bohnsack MT: The m6A reader protein
YTHDC2 interacts with the small ribosomal subunit and the 5′-3′
exoribonuclease XRN1. RNA. 24:1339–1350. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hsu PJ, Zhu Y, Ma H, Guo Y, Shi X, Liu Y,
Qi M, Lu Z, Shi H, Wang J, et al: Ythdc2 is an
N6-methyladenosine binding protein that regulates
mammalian spermatogenesis. Cell Res. 27:1115–1127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zarnack K, König J, Tajnik M, Martincorena
I, Eustermann S, Stévant I, Reyes A, Anders S, Luscombe NM and Ule
J: Direct competition between hnRNP C and U2AF65 protects the
transcriptome from the exonization of Alu elements. Cell.
152:453–466. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Liu N, Zhou KI, Parisien M, Dai Q,
Diatchenko L and Pan T: N6-methyladenosine alters RNA structure to
regulate binding of a low-complexity protein. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:6051–6063. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bell JL, Wächter K, Mühleck B, Pazaitis N,
Köhn M, Lederer M and Hüttelmaier S: Insulin-like growth factor 2
mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs): Post-transcriptional drivers of
cancer progression? Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:2657–2675. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
68
|
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O,
Mason CE and Jaffrey SR: Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation
reveals enrichment in 3′ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell.
149:1635–1646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
You X, Vlatkovic I, Babic A, Will T,
Epstein I, Tushev G, Akbalik G, Wang M, Glock C, Quedenau C, et al:
Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated
by development and plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 18:603–610. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Linder B, Grozhik AV, Olarerin-George AO,
Meydan C, Mason CE and Jaffrey SR: Single-nucleotide-resolution
mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat Methods.
12:767–772. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ke S, Alemu EA, Mertens C, Gantman EC, Fak
JJ, Mele A, Haripal B, Zucker-Scharff I, Moore MJ, Park CY, et al:
A majority of m6A residues are in the last exons, allowing the
potential for 3′ UTR regulation. Genes Dev. 29:2037–2053. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu N, Parisien M, Dai Q, Zheng G, He C
and Pan T: Probing N6-methyladenosine RNA modification status at
single nucleo-tide resolution in mRNA and long noncoding RNA. RNA.
19:1848–1856. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Garcia-Campos MA, Edelheit S, Toth U,
Safra M, Shachar R, Viukov S, Winkler R, Nir R, Lasman L, Brandis
A, et al: Deciphering the 'm6A Code' via
antibody-independent quantitative profiling. Cell. 178:731–747.e16.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Liu Q and Gregory RI: RNAmod: An
integrated system for the annotation of mRNA modifications. Nucleic
Acids Res. 47:W548–W555. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhang SY, Zhang SW, Fan XN, Zhang T, Meng
J and Huang Y: FunDMDeep-m6A: Identification and prioritization of
functional differential m6A methylation genes. Bioinformatics.
35:i90–i98. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhang Z, Chen LQ, Zhao YL, Yang CG,
Roundtree IA, Zhang Z, Ren J, Xie W, He C and Luo GZ: Single-base
mapping of mA by an antibody-independent method. Sci Adv.
5:eaax02502019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Lin J, Zhu Q, Huang J, Cai R and Kuang Y:
Hypoxia promotes vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) differentiation
of adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC) by regulating Mettl3 and
paracrine factors. Stem Cells Int. 2020:28305652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Cohn JN, Ferrari R and Sharpe N: Cardiac
remodeling-concepts and clinical implications: A consensus paper
from an international forum on cardiac remodeling. Behalf of an
International Forum on Cardiac Remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol.
35:569–582. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Kehat I and Molkentin JD: Molecular
pathways underlying cardiac remodeling during pathophysiological
stimulation. Circulation. 122:2727–2735. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Maier T, Guell M and Serrano L:
Correlation of mRNA and protein in complex biological samples. FEBS
Lett. 583:3966–3973. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Dorn LE, Lasman L, Chen J, Xu X, Hund TJ,
Medvedovic M, Hanna JH, van Berlo JH and Accornero F: The
N6-Methyladenosine mRNA methylase METTL3 controls
cardiac homeostasis and hypertrophy. Circulation. 139:533–545.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays
for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Song H, Pu J, Wang L, Wu L, Xiao J, Liu Q,
Chen J, Zhang M, Liu Y, Ni M, et al: ATG16L1 phosphorylation is
oppositely regulated by CSNK2/casein kinase 2 and PPP1/protein
phos-phatase 1 which determines the fate of cardiomyocytes during
hypoxia/reoxygenation. Autophagy. 11:1308–1325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Pastore N, Brady OA, Diab HI, Martina JA,
Sun L, Huynh T, Lim JA, Zare H, Raben N, Ballabio A and Puertollano
R: TFEB and TFE3 cooperate in the regulation of the innate immune
response in activated macrophages. Autophagy. 12:1240–1258. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zhao E and Czaja MJ: Transcription factor
EB: A central regulator of both the autophagosome and lysosome.
Hepatology. 55:1632–1634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Song H, Feng X, Zhang H, Luo Y, Huang J,
Lin M, Jin J, Ding X, Wu S, Huang H, et al: METTL3 and ALKBH5
oppositely regu-late m6A modification of TFEB mRNA,
which dictates the fate of hypoxia/reoxygenation-treated
cardiomyocytes. Autophagy. 15:1419–1437. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Misquitta CM, Iyer VR, Werstiuk ES and
Grover AK: The role of 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) mediated
mRNA stability in cardiovascular pathophysiology. Mol Cell Biochem.
224:53–67. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Gratacós FM and Brewer G: The role of AUF1
in regulated mRNA decay. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 1:457–473.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Su YR, Chiusa M, Brittain E, Hemnes AR,
Absi TS, Lim CC and Di Salvo TG: Right ventricular protein
expression profile in end-stage heart failure. Pulm Circ.
5:481–497. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Mathiyalagan P, Adamiak M, Mayourian J,
Sassi Y, Liang Y, Agarwal N, Jha D, Zhang S, Kohlbrenner E,
Chepurko E, et al: FTO-Dependent N6-Methyladenosine
regulates cardiac function during remodeling and repair.
Circulation. 139:518–532. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
91
|
Wang Y, Li Y, Toth JI, Petroski MD, Zhang
Z and Zhao JC: N6-methyladenosine modification destabilizes
developmental regulators in embryonic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol.
16:191–198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Berulava T, Buchholz E, Elerdashvili V,
Pena T, Islam MR, Lbik D, Mohamed BA, Renner A, von Lewinski D,
Sacherer M, et al: Changes in m6A RNA methylation contribute to
heart failure progression by modulating translation. Eur J Heart
Fail. 22:54–66. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Kmietczyk V, Riechert E, Kalinski L,
Boileau E, Malovrh E, Malone B, Gorska A, Hofmann C, Varma E,
Jürgensen L, et al: m6A-mRNA methylation regulates
cardiac gene expression and cellular growth. Life Sci Alliance.
2:e2018002332019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Hirsch AT, Haskal ZJ, Hertzer NR, Bakal
CW, Creager MA, Halperin JL, Hiratzka LF, Murphy WR, Olin JW,
Puschett JB, et al: ACC/AHA 2005 Practice Guidelines for the
management of patients with peripheral arterial disease (lower
extremity, renal, mesenteric, and abdominal aortic): A
collaborative report from the American Association for Vascular
Surgery/Society for Vascular Surgery, Society for Cardiovascular
Angiography and Interventions, Society for Vascular Medicine and
Biology, Society of Interventional Radiology, and the ACC/AHA Task
Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Develop
Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Peripheral Arterial
Disease): Endorsed by the American Association of Cardiovascular
and Pulmonary Rehabilitation; National Heart, Lung, and Blood
Institute; Society for Vascular Nursing; TransAtlantic
Inter-Society Consensus; and Vascular Disease Foundation.
Circulation. 113:e463–e654. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Reeps C, Pelisek J, Seidl S, Schuster T,
Zimmermann A, Kuehnl A and Eckstein HH: Inflammatory infiltrates
and neovessels are relevant sources of MMPs in abdominal aortic
aneurysm wall. Pathobiology. 76:243–252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
He Y, Xing J, Wang S, Xin S, Han Y and
Zhang J: Increased m6A methylation level is associated with the
progression of human abdominal aortic aneurysm. Ann Transl Med.
7:7972019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Zhong L, He X, Song H, Sun Y, Chen G, Si
X, Sun J, Chen X, Liao W, Liao Y and Bin J: METTL3 induces AAA
development and progression by modulating
N6-methyladenosine-dependent primary miR34a processing. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 21:394–411. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Thomas B, Matsushita K, Abate KH, Al-Aly
Z, Ärnlöv J, Asayama K, Atkins R, Badawi A, Ballew SH, Banerjee A,
et al: Global Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes of Reduced GFR. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 28:2167–2179. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Fang Y, Ginsberg C, Sugatani T,
Monier-Faugere MC, Malluche H and Hruska KA: Early chronic kidney
disease-mineral bone disorder stimulates vascular calcification.
Kidney Int. 85:142–150. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Cao XS, Chen J, Zou JZ, Zhong YH, Teng J,
Ji J, Chen ZW, Liu ZH, Shen B, Nie YX, et al: Association of
indoxyl sulfate with heart failure among patients on hemodialysis.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 10:111–119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
101
|
Chen J, Ning Y, Zhang H, Song N, Gu Y, Shi
Y, Cai J, Ding X and Zhang X: METTL14-dependent m6A regulates
vascular calcification induced by indoxyl sulfate. Life Sci.
239:1170342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB,
Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, Mathier MA, McGoon MD, Park MH,
Rosenson RS, et al: ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on
pulmonary hypertension a report of the American College of
Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and
the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the
American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society,
Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 53:1573–1619. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S,
Lang I, Torbicki A, Simonneau G, Peacock A, Vonk Noordegraaf A,
Beghetti M, et al: 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and
treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European
Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society
(ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and
Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and
Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 37:67–119. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Weitzenblum E, Sautegeau A, Ehrhart M,
Mammosser M and Pelletier A: Long-term oxygen therapy can reverse
the progression of pulmonary hypertension in patients with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 131:493–498.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Shi Y, Fan S, Wu M, Zuo Z, Li X, Jiang L,
Shen Q, Xu P, Zeng L, Zhou Y, et al: YTHDF1 links hypoxia
adaptation and non-small cell lung cancer progression. Nat commun.
10:48922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zhang C, Samanta D, Lu H, Bullen JW, Zhang
H, Chen I, He X and Semenza GL: Hypoxia induces the breast cancer
stem cell phenotype by HIF-dependent and ALKBH5-mediated
m6A-demethylation of NANOG mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E2047–E2056. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Fry NJ, Law BA, Ilkayeva OR, Holley CL and
Mansfield KD: N6-methyladenosine is required for the
hypoxic stabilization of specific mRNAs. RNA. 23:1444–1455. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Zhou C, Molinie B, Daneshvar K, Pondick
JV, Wang J, Van Wittenberghe N, Xing Y, Giallourakis CC and Mullen
AC: Genome-wide maps of m6A circRNAs identify widespread and
cell-type-specific methylation patterns that are distinct from
mRNAs. Cell Rep. 20:2262–2276. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Wang J, Zhu MC, Kalionis B, Wu JZ, Wang
LL, Ge HY, Chen CC, Tang XD, Song YL, He H and Xia SJ:
Characteristics of circular RNA expression in lung tissues from
mice with hypoxiainduced pulmonary hypertension. Int J Mol Med.
42:1353–1366. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Su H, Wang G, Wu L, Ma X, Ying K and Zhang
R: Transcriptome-wide map of m6A circRNAs identified in
a rat model of hypoxiamediated pulmonary hypertension. BMC
Genomics. 21:392020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Chan JJ and Tay Y: Noncoding RNA: RNA
regulatory networks in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19:2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Baarsma HA and Königshoff M: 'WNT-er is
coming': WNT signalling in chronic lung diseases. Thorax.
72:746–759. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Savai R, Al-Tamari HM, Sedding D,
Kojonazarov B, Muecke C, Teske R, Capecchi MR, Weissmann N,
Grimminger F, Seeger W, et al: Pro-proliferative and inflammatory
signaling converge on FoxO1 transcription factor in pulmonary
hypertension. Nat Med. 20:1289–1300. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Haraksingh RR and Snyder MP: Impacts of
variation in the human genome on gene regulation. J Mol Biol.
425:3970–3977. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Mao F, Xiao L, Li X, Liang J, Teng H, Cai
W and Sun ZS: RBP-Var: A database of functional variants involved
in regulation mediated by RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:D154–D163. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
116
|
Wu X and Hurst LD: Determinants of the
usage of splice-associated cis-Motifs predict the distribution of
human pathogenic SNPs. Mol Biol Evol. 33:518–529. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
117
|
Ramaswami G, Deng P, Zhang R, Anna Carbone
M, Mackay TFC and Billy Li J: Genetic mapping uncovers
cis-regulatory land-scape of RNA editing. Nat Commun. 6:81942015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Zheng Y, Nie P, Peng D, He Z, Liu M, Xie
Y, Miao Y, Zuo Z and Ren J: m6AVar: A database of functional
variants involved in m6A modification. Nucleic Acids Res.
46:D139–D145. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
119
|
Yang N, Ying P, Tian J, Wang X, Mei S, Zou
D, Peng X, Gong Y, Yang Y, Zhu Y, et al: Genetic variants in m6A
modification genes are associated with esophageal squamous-cell
carcinoma in the Chinese population. Carcinogenesis. 41:761–768.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Mo XB, Lei SF, Zhang YH and Zhang H:
Detection of m6A-asso-ciated SNPs as potential
functional variants for coronary artery disease. Epigenomics.
10:1279–1287. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Mo X, Lei S, Zhang Y and Zhang H:
Genome-wide enrichment of m6A-associated
single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the lipid loci. Pharmacogenomics
J. 19:347–357. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Kupper N, Willemsen G, Riese H, Posthuma
D, Boomsma DI and de Geus EJC: Heritability of daytime ambulatory
blood pressure in an extended twin design. Hypertension. 45:80–85.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Evangelou E, Warren HR, Mosen-Ansorena D,
Mifsud B, Pazoki R, Gao H, Ntritsos G, Dimou N, Cabrera CP, Karaman
I, et al: Genetic analysis of over 1 million people identifies 535
new loci associated with blood pressure traits. Nat Genet.
50:1412–1425. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Mo XB, Lei SF, Zhang YH and Zhang H:
Examination of the associations between m6A-associated
single-nucleotide polymorphisms and blood pressure. Hypertens Res.
42:1582–1589. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Lee JY, Lee BS, Shin DJ, Woo Park K, Shin
YA, Joong Kim K, Heo L, Young Lee J, Kyoung Kim Y, Jin Kim Y, et
al: A genome-wide association study of a coronary artery disease
risk variant. J Hum Genet. 58:120–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Gerken T, Girard CA, Tung YC, Webby CJ,
Saudek V, Hewitson KS, Yeo GS, McDonough MA, Cunliffe S, McNeill
LA, et al: The obesity-associated FTO gene encodes a
2-oxoglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science.
318:1469–1472. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Guyenet PG: The sympathetic control of
blood pressure. Nat Rev Neurosci. 7:335–346. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Pausova Z, Syme C, Abrahamowicz M, Xiao Y,
Leonard GT, Perron M, Richer L, Veillette S, Smith GD, Seda O, et
al: A common variant of the FTO gene is associated with not only
increased adiposity but also elevated blood pressure in French
Canadians. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2:260–269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Frayling TM, Timpson NJ, Weedon MN,
Zeggini E, Freathy RM, Lindgren CM, Perry JR, Elliott KS, Lango H,
Rayner NW, et al: A common variant in the FTO gene is associated
with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult
obesity. Science. 316:889–894. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Marcadenti A, Fuchs FD, Matte U, Sperb F,
Moreira LB and Fuchs SC: Effects of FTO RS9939906 and MC4R
RS17782313 on obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus and blood pressure
in patients with hypertension. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 12:1032013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
O'Donnell CJ and Nabel EG: Genomics of
cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 365:2098–2109. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Prospective Studies Collaboration;
Lewington S, Whitlock G, Clarke R, Sherliker P, Emberson J, Halsey
J, Qizilbash N, Peto R and Collins R: Blood cholesterol and
vascular mortality by age, sex, and blood pressure: A meta-analysis
of individual data from 61 prospective studies with 55,000 vascular
deaths. Lancet. 370:1829–1839. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Yadav PK, Rajvanshi PK and Rajasekharan R:
The role of yeast m6A methyltransferase in peroxisomal
fatty acid oxidation. Curr Genet. 64:417–422. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Ma S, Chen C, Ji X, Liu J, Zhou Q, Wang G,
Yuan W, Kan Q and Sun Z: The interplay between m6A RNA methylation
and noncoding RNA in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 12:1212019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Zhang W, Chen G and Deng CQ: Effects and
mechanisms of total Panax notoginseng saponins on proliferation of
vascular smooth muscle cells with plasma pharmacology method. J
Pharm Pharmracol. 64:139–145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Zhu B, Gong Y, Shen L, Li J, Han J, Song
B, Hu L, Wang Q and Wang Z: Total Panax notoginseng saponin
inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration
and intimal hyperplasia by regulating WTAP/p16 signals via
m6A modulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 124:1099352020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Nakarai H, Yamashita A, Nagayasu S,
Iwashita M, Kumamoto S, Ohyama H, Hata M, Soga Y, Kushiyama A,
Asano T, et al: Adipocyte-macrophage interaction may mediate
LPS-induced low-grade inflammation: Potential link with metabolic
complications. Innate Immun. 18:164–170. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Rao DS, Sekhara NC, Satyanarayana MN and
Srinivasan M: Effect of curcumin on serum and liver cholesterol
levels in the rat. J Nutri. 100:1307–1315. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Lu N, Li X, Yu J, Li Y, Wang C, Zhang L,
Wang T and Zhong X: Curcumin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
hepatic lipid metabolism disorder by modification of m6
A RNA methylation in piglets. Lipids. 53:53–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Huang Y, Yan J, Li Q, Li J, Gong S, Zhou
H, Gan J, Jiang H, Jia GF, Luo C and Yang CG: Meclofenamic acid
selectively inhibits FTO demethylation of m6A over ALKBH5. Nucleic
Acids Res. 43:373–384. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
141
|
Li J, Chen Z, Chen F, Xie G, Ling Y, Peng
Y, Lin Y, Luo N, Chiang CM and Wang H: Targeted mRNA demethylation
using an engineered dCas13b-ALKBH5 fusion protein. Nucleic Acids
Res. 48:5684–5694. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Lawson DA, Kessenbrock K, Davis RT,
Pervolarakis N and Werb Z: Tumour heterogeneity and metastasis at
single-cell resolution. Nat Cell Biol. 20:1349–1360. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Paramasivam A, Vijayashree Priyadharsini J
and Raghunandhakumar S: N6-adenosine methylation (m6A): A promising
new molecular target in hypertension and cardiovascular diseases.
Hypertens Res. 43:153–154. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|