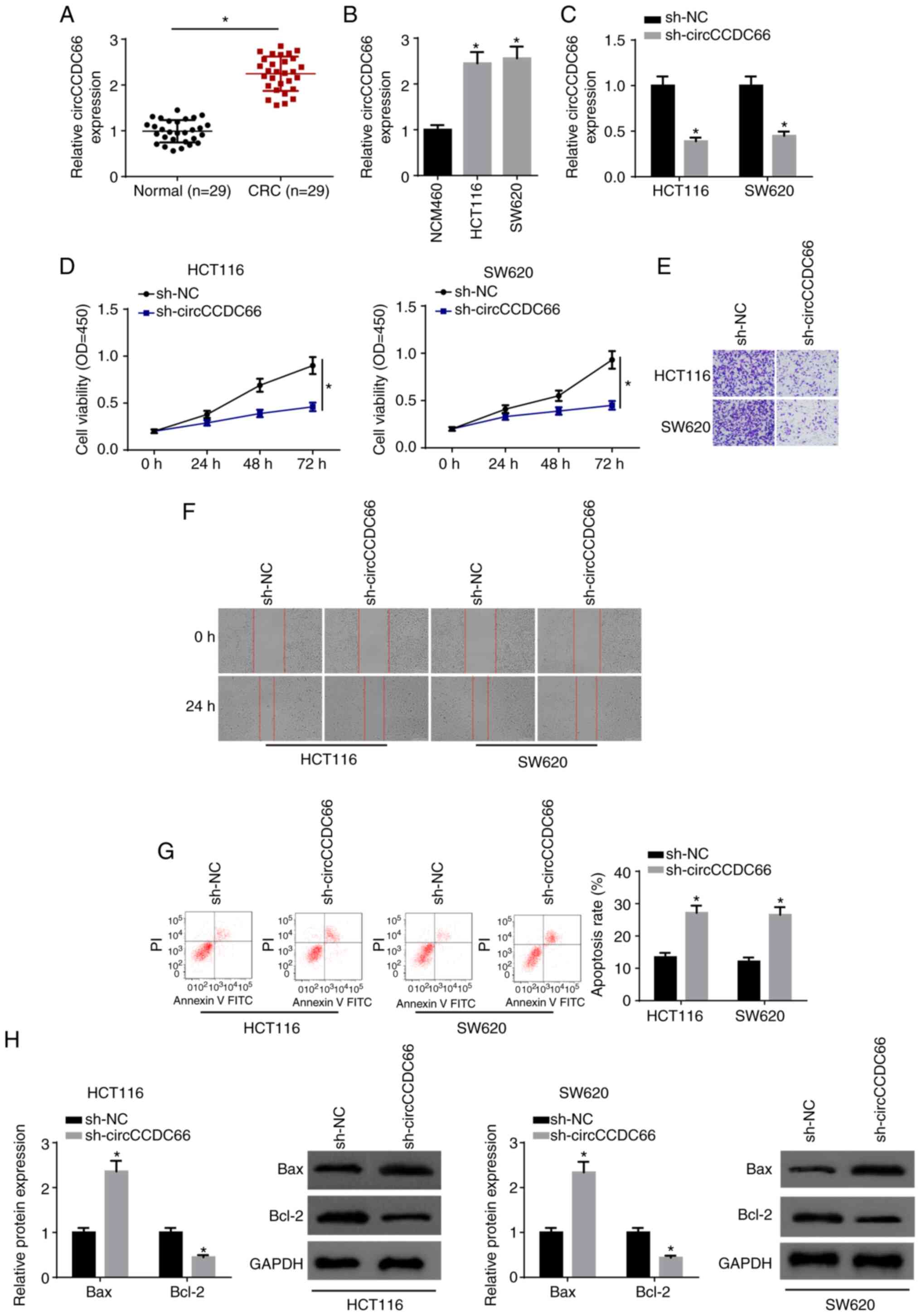
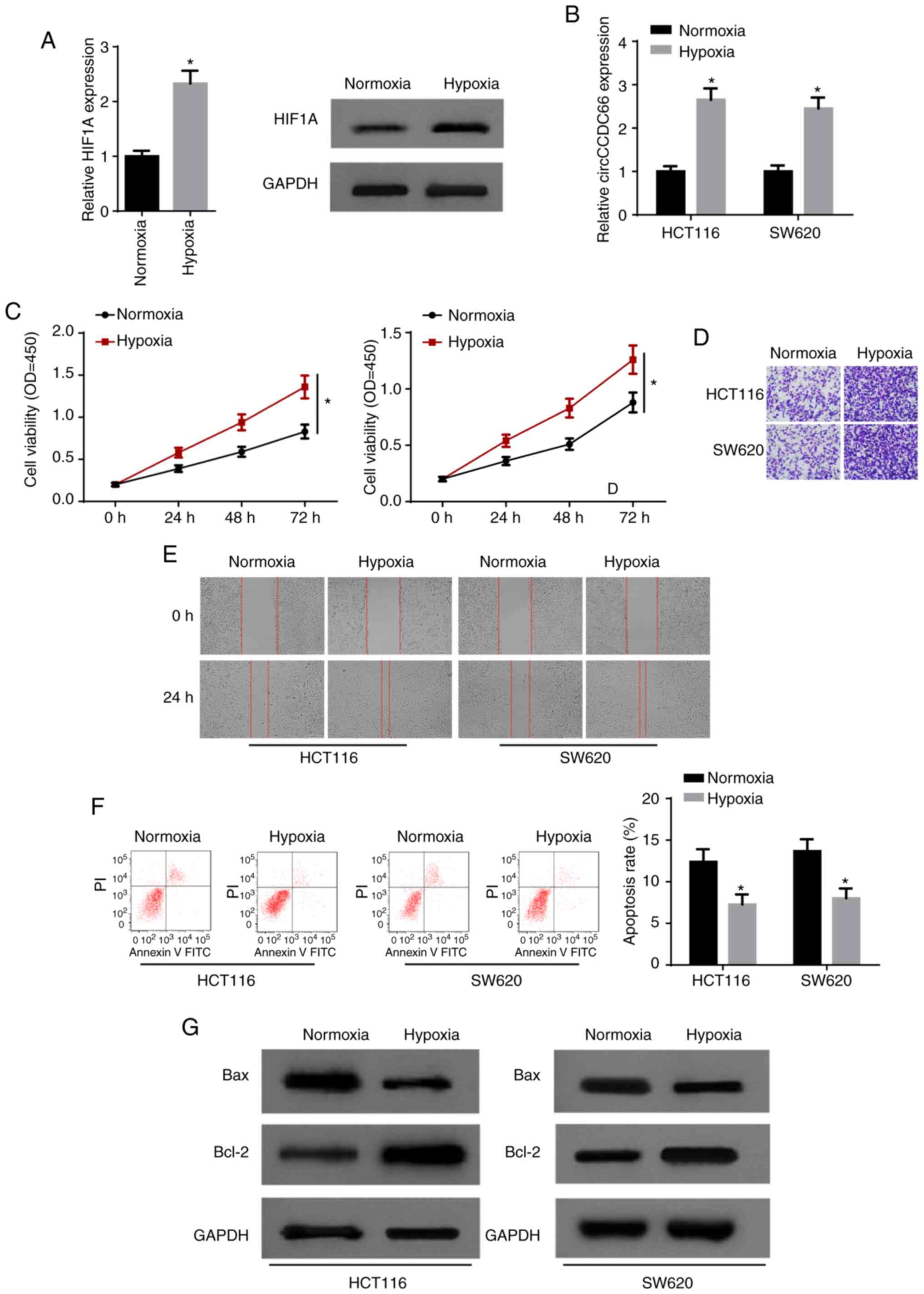
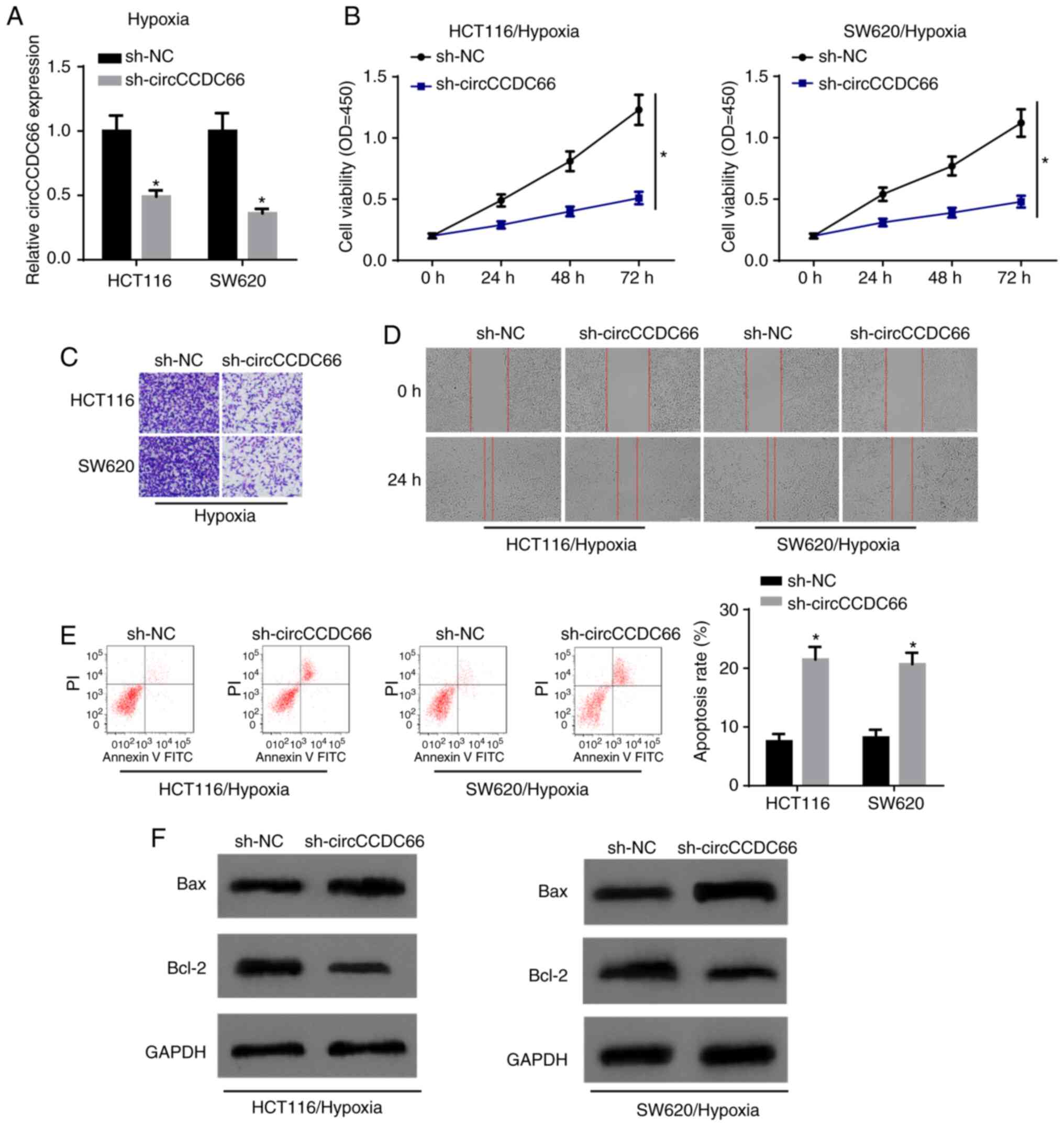
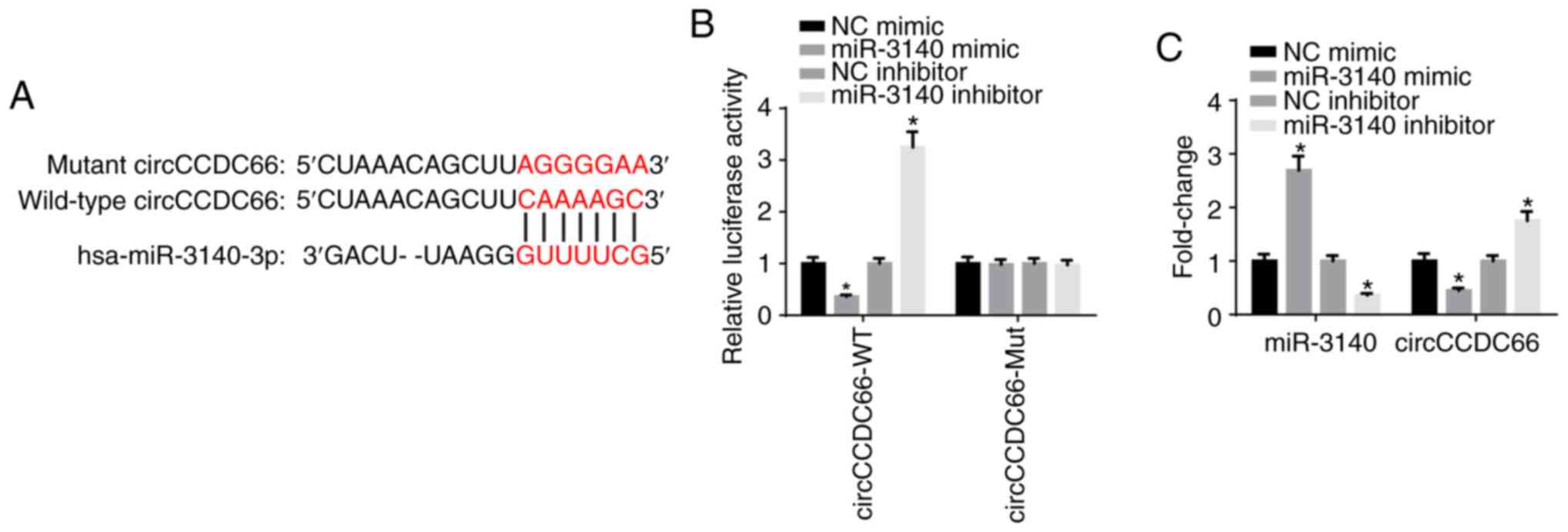
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bruera G and Ricevuto E: Intensive
chemotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer: Weighing between
safety and clinical efficacy: Evaluation of Masi G, Loupakis F,
Salvatore L, et al: Bevacizumab with FOLFOXIRI (irinotecan,
oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and folinate) as first-line treatment
for metastatic colorectal cancer: A phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol.
11:845–852. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
Expert Opin Biol Ther. 11:821–814. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Petrelli F and Barni S: Correlation of
progression-free and post-progression survival with overall
survival in advanced colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 24:186–192.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zheng H, Wu Y, Guo T, Liu F, Xu Y and Cai
S: Hypoxia induces growth differentiation factor 15 to promote the
metastasis of colorectal cancer via PERK-eIF2α signaling. Biomed
Res Int. 2020:59582722020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Choi BJ, Park SA, Lee SY, Cha YN and Surh
YJ: Hypoxia induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal
cancer cells through ubiquitin-specific protease 47-mediated
stabilization of Snail: A potential role of Sox9. Sci Rep.
7:159182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H and Bartel DP:
Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular
RNAs. Genome Biol. 15:4092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barrett SP, Wang PL and Salzman J:
Circular RNA biogenesis can proceed through an exon-containing
lariat precursor. Elife. 4:e075402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang H, Huang H, Li Y, Lu Y and Ye T:
CircRNA_0058063 functions as a ceRNA in bladder cancer progression
via targeting miR-486-3p/FOXP4 axis. Biosci Rep.
40:BSR201934842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu K, Qin X, Shao Y, Zhou Y, Ye G and Xu
S: Circular RNA MTO1 suppresses tumorigenesis of gastric carcinoma
by sponging miR-200-5p and targeting PEBP1. Mol Cell Probes.
52:1015622020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bian L, Zhi X, Ma L, Zhang J, Chen P, Sun
S, Li J, Sun Y and Qin J: Hsa_circRNA_103809 regulated the cell
proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer via
miR-532-3p/FOXO4 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 505:346–352.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zeng K, Chen X, Xu M, Liu X, Hu X, Xu T,
Sun H, Pan Y, He B and Wang S: CircHIPK3 promotes colorectal cancer
growth and metastasis by sponging miR-7. Cell Death Dis. 9:4172018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hsiao KY, Lin YC, Gupta SK, Chang N, Yen
L, Sun HS and Tsai SJ: Noncoding effects of circular RNA CCDC66
promote colon cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Res.
77:2339–2350. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wei Y, Zhang Y, Meng Q, Cui L and Xu C:
Hypoxia-induced circular RNA has_circRNA_403658 promotes bladder
cancer cell growth through activation of LDHA. Am J Transl Res.
11:6838–6849. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren S, Liu J, Feng Y, Li Z, He L, Li L,
Cao X, Wang Z and Zhang Y: Knockdown of circDENND4C inhibits
glycolysis, migration and invasion by up-regulating miR-200b/c in
breast cancer under hypoxia. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3882019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Turchinovich A, Weiz L and Burwinkel B:
Extracellular miRNAs: The mystery of their origin and function.
Trends Biochem Sci. 37:460–465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Thomou T, Mori MA, Dreyfuss JM, Konishi M,
Sakaguchi M, Wolfrum C, Rao TN, Winnay JN, Garcia-Martin R,
Grinspoon SK, et al: Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate
gene expression in other tissues. Nature. 542:450–455. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun N, Zhang L, Zhang C and Yuan Y:
miR-144-3p inhibits cell proliferation of colorectal cancer cells
by targeting BCL6 via inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cell
Mol Biol Lett. 25:192020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Weihua Z, Guorong Z, Xiaolong C and
Weizhan L: MiR-33a functions as a tumor suppressor in
triple-negative breast cancer by targeting EZH2. Cancer Cell Int.
20:852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fang QY, Deng QF, Luo J and Zhou CC:
MiRNA-20a-5p accelerates the proliferation and invasion of
non-small cell lung cancer by targeting and downregulating KLF9.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:2548–2556. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tonouchi E, Gen Y, Muramatsu T, Hiramoto
H, Tanimoto K, Inoue J and Inazawa J: miR-3140 suppresses tumor
cell growth by targeting BRD4 via its coding sequence and
downregulates the BRD4-NUT fusion oncoprotein. Sci Rep. 8:44822018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Dong Y, He D, Peng Z, Peng W, Shi W, Wang
J, Li B, Zhang C and Duan C: Circular RNAs in cancer: An emerging
key player. J Hematol Oncol. 10:22017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meng S, Zhou H, Feng Z, Xu Z, Tang Y, Li P
and Wu M: CircRNA: Functions and properties of a novel potential
biomarker for cancer. Mol Cancer. 16:942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Luan W, Shi Y, Zhou Z, Xia Y and Wang J:
CircRNA_0084043 promote malignant melanoma progression via
miR-153-3p/Snail axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 502:22–29. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li H, Jin X, Liu B, Zhang P, Chen W and Li
Q: CircRNA CBL.11 suppresses cell proliferation by sponging
miR-6778-5p in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 19:8262019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim CW, Oh ET, Kim JM, Park JS, Lee DH,
Lee JS, Kim KK and Park HJ: Hypoxia-induced microRNA-590-5p
promotes colorectal cancer progression by modulating matrix
metalloproteinase activity. Cancer Lett. 416:31–41. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ullmann P, Nurmik M, Schmitz M, Rodriguez
F, Weiler J, Qureshi-Baig K, Felten P, Nazarov PV, Nicot N, Zuegel
N, et al: Tumor suppressor miR-215 counteracts hypoxia-induced
colon cancer stem cell activity. Cancer Lett. 450:32–41. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang L, Song X, Chen X, Wang Q, Zheng X,
Wu C and Jiang J: Circular RNA CircCACTIN promotes gastric cancer
progression by sponging MiR-331-3p and regulating TGFBR1
expression. Int J Biol Sci. 15:1091–1103. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wei S, Zheng Y, Jiang Y, Li X, Geng J,
Shen Y, Li Q, Wang X, Zhao C, Chen Y, et al: The circRNA circPTPRA
suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transitioning and metastasis of
NSCLC cells by sponging miR-96-5p. EBioMedicine. 44:182–193. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sumazin P, Yang X, Chiu HS, Chung WJ, Iyer
A, Llobet-Navas D, Rajbhandari P, Bansal M, Guarnieri P, Silva J
and Califano A: An extensive microRNA-mediated network of RNA-RNA
interactions regulates established oncogenic pathways in
glioblastoma. Cell. 147:370–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tu FL, Guo XQ, Wu HX, He ZY, Wang F, Sun
AJ and Dai XD: Circ-0001313/miRNA-510-5p/AKT2 axis promotes the
development and progression of colon cancer. Am J Transl Res.
12:281–291. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
He JH, Han ZP, Luo JG, Jiang JW, Zhou JB,
Chen WM, Lv YB, He ML, Zheng L, Li YG and Zuo JD: Hsa_Circ_0007843
acts as a mIR-518c-5p sponge to regulate the migration and invasion
of colon cancer SW480 cells. Front Genet. 11:92020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qureshi-Baig K, Kuhn D, Viry E, Pozdeev
VI, Schmitz M, Rodriguez F, Ullmann P, Koncina E, Nurmik M,
Frasquilho S, et al: Hypoxia-induced autophagy drives colorectal
cancer initiation and progression by activating the PRKC/PKC-EZR
(ezrin) pathway. Autophagy. Jan 17–2019.Epub ahead of print.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Che J, Wang W, Huang Y, Zhang L, Zhao J,
Zhang P and Yuan X: miR-20a inhibits hypoxia-induced autophagy by
targeting ATG5/FIP200 in colorectal cancer. Mol Carcinog.
58:1234–1247. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|