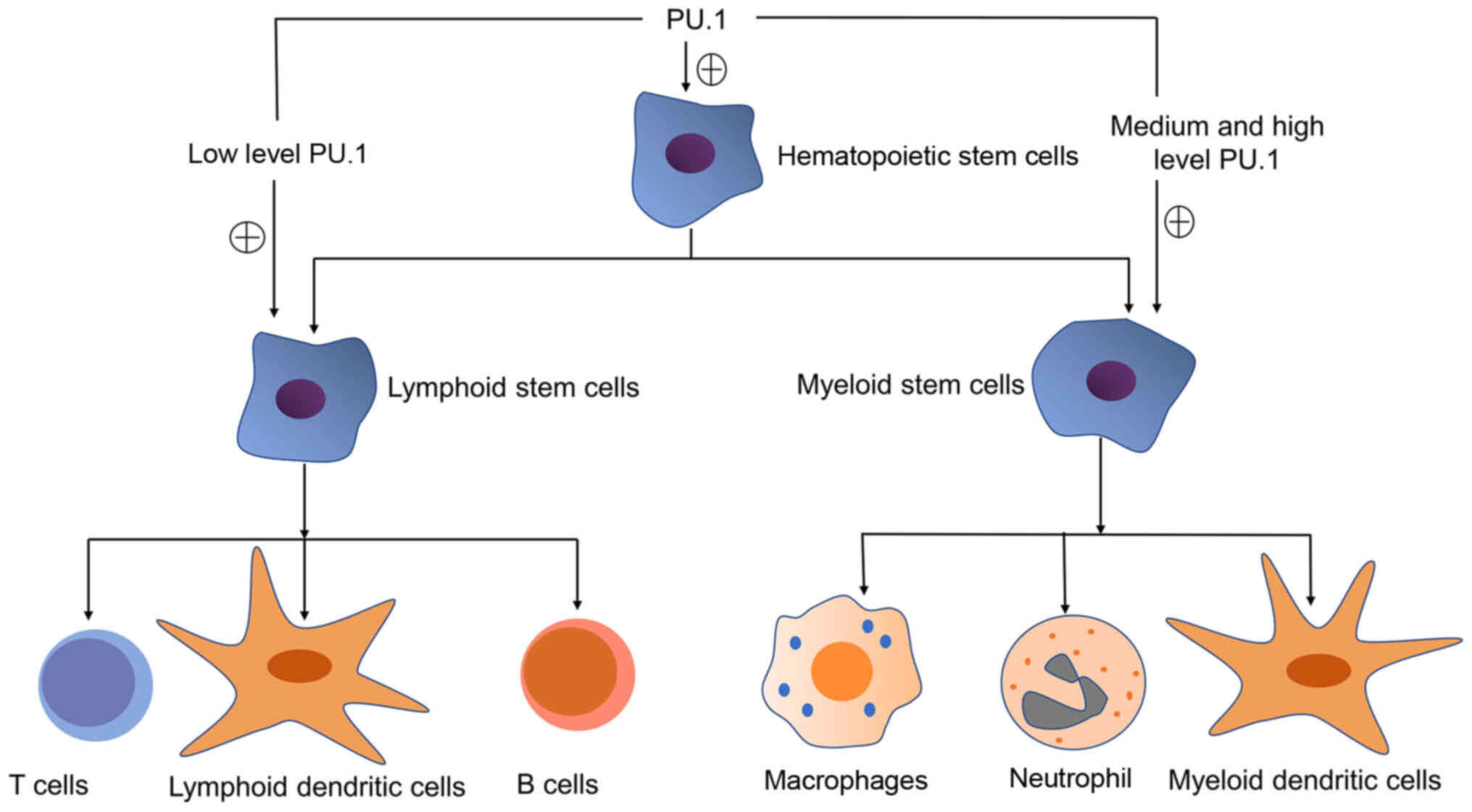
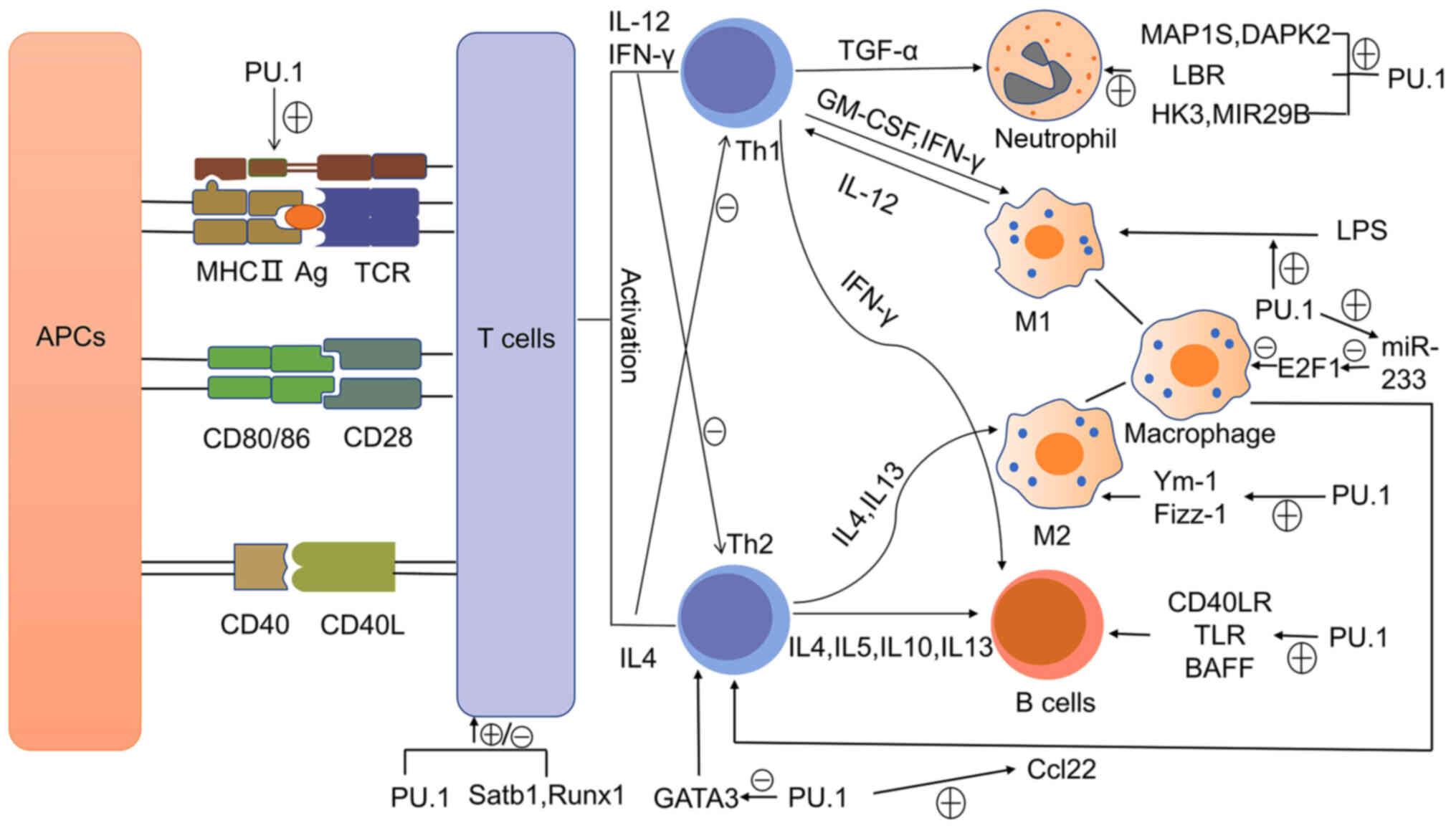
|
1
|
Karim FD, Urness LD, Thummel CS, Klemsz
MJ, McKercher SR, Celada A, Van Beveren C, Maki RA, Gunther CV, Nye
JA, et al: The ETS-domain: A new DNA-binding motif that recognizes
a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 4:1451–1453. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moreau-Gachelin F, Tavitian A and
Tambourin P: Spi1 is a putative oncogene in virally induced murine
erythroleukaemias. Nature. 331:277–280. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gupta P, Gurudutta GU, Saluja D and
Tripathi RP: PU.1 and partners: Regulation of haematopoietic stem
cell fate in normal and malignant haematopoiesis. J Cell Mol Med.
13:4349–4363. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ueno N, Nishimura N, Ueno S, Endo S,
Tatetsu H, Hirata S, Hata H, Matsuoka M, Mitsuya H and Okuno Y:
PU.1 acts as tumor suppressor for myeloma cells through direct
transcriptional repression of IRF4. Oncogene. 36:4481–4497. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tenen DG, Hromas R, Licht JD and Zhang DE:
Transcription factors, normal myeloid development, and leukemia.
Blood. 90:489–519. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Batista CR, Lim M, Laramée AS,
Abu-Sardanah F, Xu LS, Hossain R, Bell GL, Hess DA and DeKoter RP:
Driver mutations in Janus kinases in a mouse model of B-cell
leukemia induced by deletion of PU.1 and Spi-B. Blood Adv.
2:2798–2810. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dozmorov MG, Wren JD and Alarcón-Riquelme
ME: Epigenomic elements enriched in the promoters of autoimmunity
susceptibility genes. Epigenetics. 9:276–285. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Alivernini S, Kurowska-Stolarska M,
Tolusso B, Benvenuto R, Elmesmari A, Canestri S, Petricca L,
Mangoni A, Fedele AL, Di Mario C, et al: MicroRNA-155 influences
B-cell function through PU.1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun.
7:129702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Turkistany SA and DeKoter RP: The
transcription factor PU.1 is a critical regulator of cellular
communication in the immune system. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz).
59:431–440. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pospíšil V, Krsmanovic P, Chramostová K,
Vokurka K, Laslo P and Stopka T: Graded PU.1 levels activate
granulocyte vs macrophage genes via multiple(super) enhancer
elements. Exp Hematol. 76(Suppl): S822019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nutt SL, Metcalf D, D'Amico A, Polli M and
Wu L: Dynamic regulation of PU.1 expression in multipotent
hematopoietic progenitors. Exp Med. 201:221–231. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yashiro T, Takeuchi H, Kasakura K and
Nishiyama C: PU.1 regulates Ccr7 gene expression by binding to its
promoter in naïve CD4+ T cells. FEBS Open Bio.
10:1115–1121. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anderson MK, Weiss AH, Hernandez-Hoyos G,
Dionne CJ and Rothenberg EV: Constitutive expression of PU.1 in
fetal hematopoietic progenitors blocks T cell development at the
pro-T cell stage. Immunity. 16:285–296. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yashiro T, Nakano S, Nomura K, Uchida Y,
Kasakura K and Nishiyama C: A transcription factor PU.1 is critical
for Ccl22 gene expression in dendritic cells and macrophages. Sci
Rep. 9:11612019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lloberas J, Soler C and Celada A: The key
role of PU.1/SPI-1 in B cells, myeloid cells and macrophages.
Immunol Today. 20:184–189. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Petrovick MS, Hiebert SW, Friedman AD,
Hetherington CJ, Tenen DG and Zhang DE: Multiple functional domains
of AML1: PU.1 and C/EBPalpha synergize with different regions of
AML1. Mol Cell Biol. 18:3915–3925. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marecki S and Fenton MJ: PU.1/interferon
regulatory factor interactions: Mechanisms of transcriptional
regulation. Cell Biochem Biophys. 33:127–148. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Behre G, Whitmarsh AJ, Coghlan MP, Hoang
T, Carpenter CL, Zhang DE, Davis RJ and Tenen DG: c-Jun is a
JNK-independent coactivator of the PU.1 transcription factor. J
Biol Chem. 274:4939–4946. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang P, Zhang X, Iwama A, Yu C, Smith KA,
Mueller BU, Narravula S, Torbett BE, Orkin SH and Tenen DG: PU.1
inhibits GATA-1 function and erythroid differentiation by blocking
GATA-1 DNA binding. Blood. 96:2641–2648. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rekhtman N, Choe KS, Matushansky I, Murray
S, Stopka T and Skoultchi AI: PU.1 and pRB interact and cooperate
to repress GATA-1 and block erythroid differentiation. Mol Cell
Biol. 23:7460–7474. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stopka T, Amanatullah DF, Papetti M and
Skoultchi AI: PU.1 inhibits the erythroid program by binding to
GATA-1 on DNA and creating a repressive chromatin structure. EMBO
J. 24:3712–3723. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Burda P, Laslo P and Stopka T: The role of
PU.1 and GATA-1 transcription factors during normal and
leukemogenic hematopoiesis. Leukemia. 24:1249–1257. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
O'Neill LA and Pearce EJ: Immunometabolism
governs dendritic cell and macrophage function. J Exp Med.
213:15–23. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Tarique AA, Logan J, Thomas E, Holt PG,
Sly PD and Fantino E: Phenotypic, functional, and plasticity
features of classical and alternatively activated human
macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 53:676–688. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nair MG, Gallagher IJ, Taylor MD, Loke P,
Coulson PS, Wilson RA, Maizels RM and Allen JE: Chitinase and Fizz
family members are a generalized feature of nematode infection with
selective upregulation of Ym1 and Fizz1 by antigen-presenting
cells. Infect Immun. 73:385–394. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Wang N, Liang H and Zen K: Molecular
mechanisms that influence the macrophage m1-m2 polarization
balance. Front Immunol. 5:6142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Juhas U, Ryba-Stanisławowska M, Szargiej P
and Myśliwska J: Different pathways of macrophage activation and
polarization. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 69:496–502. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Karpurapu M, Wang X, Deng J, Park H, Xiao
L, Sadikot RT, Frey RS, Maus UA, Park GY, Scott EW and Christman
JW: Functional PU.1 in macrophages has a pivotal role in NF-κB
activation and neutrophilic lung inflammation during endotoxemia.
Blood. 118:5255–5266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qian F, Deng J, Lee YG, Zhu J, Karpurapu
M, Chung S, Zheng JN, Xiao L, Park GY and Christman JW: The
transcription factor PU.1 promotes alternative macrophage
polarization and asthmatic airway inflammation. J Mol Cell Biol.
7:557–567. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tagore M, McAndrew MJ, Gjidoda A and Floer
M: The lineage-specific transcription factor PU.1 prevents
polycomb-mediated heterochromatin formation at macrophage-specific
genes. Mol Cell Biol. 35:2610–2625. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
van Oevelen C, Collombet S, Vicent G,
Hoogenkamp M, Lepoivre C, Badeaux A, Bussmann L, Sardina JL,
Thieffry D, Beato M, et al: C/EBPα activates pre-existing and de
novo macrophage enhancers during induced Pre-B cell
transdifferentiation and myelopoiesis. Stem Cell Reports.
5:232–247. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Solomon LA, Podder S, He J,
Jackson-Chornenki NL, Gibson K, Ziliotto RG, Rhee J and DeKoter RP:
Coordination of myeloid differentiation with reduced cell cycle
progression by PU.1 induction of MicroRNAs targeting cell cycle
regulators and lipid anabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 37:e00013–17. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Denechaud PD, Lopez-Mejia IC, Giralt A,
Lai Q, Blanchet E, Delacuisine B, Nicolay BN, Dyson NJ, Bonner C,
Pattou F, et al: E2F1 mediates sustained lipogenesis and
contributes to hepatic steatosis. J Clin Invest. 126:137–150. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Eguchi J, Kong X, Tenta M, Wang X, Kang S
and Rosen ED: Interferon regulatory factor 4 regulates
obesity-induced inflammation through regulation of adipose tissue
macrophage polarization. Diabetes. 62:3394–3403. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shen C, Chen MT, Zhang XH, Yin XL, Ning
HM, Su R, Lin HS, Song L, Wang F, Ma YN, et al: The PU.1-modulated
MicroRNA-22 is a regulator of monocyte/macrophage differentiation
and acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS Genet. 12:e10062592016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Shakerian L, Ghorbani S, Talebi F and
Noorbakhsh F: MicroRNA-150 targets PU.1 and regulates macrophage
differentiation and function in experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 323:167–174. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kruger P, Saffarzadeh M, Weber AN, Rieber
N, Radsak M, von Bernuth H, Benarafa C, Roos D, Skokowa J and Hartl
D: Neutrophils: Between host defence, immune modulation, and tissue
injury. PLoS Pathog. 11:e10046512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mantovani A, Cassatella MA, Costantini C
and Jaillon S: Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of
innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:519–531. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Haimovici A, Brigger D, Torbett BE, Fey MF
and Tschan MP: Induction of the autophagy-associated gene MAP1S via
PU.1 supports APL differentiation. Leuk Res. 38:1041–1047. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Humbert M, Federzoni EA, Britschgi A,
Schläfli AM, Valk PJ, Kaufmann T, Haferlach T, Behre G, Simon HU,
Torbett BE, et al: The tumor suppressor gene DAPK2 is induced by
the myeloid transcription factors PU.1 and C/EBPα during
granulocytic differentiation but repressed by PML-RARα in APL. J
Leukoc Biol. 95:83–93. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Bialik S and Kimchi A: The
death-associated protein kinases: Structure, function, and beyond.
Annu Rev Biochem. 75:189–210. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Malu K, Garhwal R, Pelletier MG, Gotur D,
Halene S, Zwerger M, Yang ZF, Rosmarin AG and Gaines P: Cooperative
activity of GABP with PU.1 or C/EBPε regulates lamin B receptor
gene expression, implicating their roles in granulocyte nuclear
maturation. J Immunol. 197:910–922. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Keightley MC, Carradice DP, Layton JE,
Pase L, Bertrand JY, Wittig JG, Dakic A, Badrock AP, Cole NJ,
Traver D, et al: The Pu.1 target gene Zbtb11 regulates neutrophil
development through its integrase-like HHCC zinc finger. Nat
Commun. 8:149112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Federzoni EA, Valk PJ, Torbett BE,
Haferlach T, Löwenberg B, Fey MF and Tschan MP: PU.1 is linking the
glycolytic enzyme HK3 in neutrophil differentiation and survival of
APL cells. Blood. 119:4963–4970. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Batliner J, Buehrer E, Federzoni EA, Jenal
M, Tobler A, Torbett BE, Fey MF and Tschan MP: Transcriptional
regulation of MIR29B by PU.1 (SPI1) and MYC during neutrophil
differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukaemia cells. Br J
Haematol. 157:270–274. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Fontana MF, Baccarella A, Pancholi N,
Pufall MA, Herbert DR and Kim CC: JUNB is a key transcriptional
modulator of macrophage activation. J Immunol. 194:177–186. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fischer J, Walter C, Tönges A, Aleth H,
Jordão MJC, Leddin M, Gröning V, Erdmann T, Lenz G, Roth J, et al:
Safeguard function of PU.1 shapes the inflammatory epigenome of
neutrophils. Nat Immunol. 20:546–558. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Guilliams M, Ginhoux F, Jakubzick C, Naik
SH, Onai N, Schraml BU, Segura E, Tussiwand R and Yona S: Dendritic
cells, monocytes and macrophages: A unified nomenclature based on
ontogeny. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:571–578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Belz GT and Nutt SL: Transcriptional
programming of the dendritic cell network. Nat Rev Immunol.
12:101–113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Carotta S, Dakic A, D'Amico A, Pang SH,
Greig KT, Nutt SL and Wu L: The transcription factor PU.1 controls
dendritic cell development and Flt3 cytokine receptor expression in
a dose-dependent manner. Immunity. 32:628–641. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lapko N, Zawadka M, Polosak J, Worthen GS,
Danet-Desnoyers G, Puzianowska-Kuźnicka M and Laudanski K:
Long-term monocyte dysfunction after sepsis in humanized mice is
related to persisted activation of macrophage-colony stimulation
factor (M-CSF) and demethylation of PU.1, and it can be reversed by
blocking M-CSF in vitro or by transplanting naïve autologous stem
cells in vivo. Front Immunol. 8:4012017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Hamdorf M, Berger A, Schüle S, Reinhardt J
and Flory E: PKCδ-induced PU.1 phosphorylation promotes
hematopoietic stem cell differentiation to dendritic cells. Stem
Cells. 29:297–306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yashiro T, Kasakura K, Oda Y, Kitamura N,
Inoue A, Nakamura S, Yokoyama H, Fukuyama K, Hara M, Ogawa H, et
al: The hematopoietic cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is
critical for expression of CD11c. Int Immunol. 29:87–94. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhu XJ, Yang ZF, Chen Y, Wang J and
Rosmarin AG: PU.1 is essential for CD11c expression in
CD8(+)/CD8(-) lymphoid and monocyte-derived dendritic cells during
GM-CSF or FLT3L-induced differentiation. PLoS One. 7:e521412017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kanada S, Nishiyama C, Nakano N, Suzuki R,
Maeda K, Hara M, Kitamura N, Ogawa H and Okumura K: Critical role
of transcription factor PU.1 in the expression of CD80 and CD86 on
dendritic cells. Blood. 117:2211–2222. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Yashiro T, Hara M, Ogawa H, Okumura K and
Nishiyama C: Critical role of transcription factor PU.1 in the
function of the OX40L/TNFSF4 promoter in dendritic cells. Sci Rep.
6:348252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yashiro T, Yamaguchi M, Watanuki Y,
Kasakura K and Nishiyama C: The transcription factors PU.1 and IRF4
determine dendritic cell-specific expression of RALDH2. J Immunol.
201:3677–3682. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kitamura N, Yokoyama H, Yashiro T, Nakano
N, Nishiyama M, Kanada S, Fukai T, Hara M, Ikeda S, Ogawa H, et al:
Role of PU.1 in MHC class II expression through transcriptional
regulation of class II transactivator pI in dendritic cells. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 129:814–824.e6. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Miura R, Kasakura K, Nakano N, Hara M,
Maeda K, Okumura K, Ogawa H, Yashiro T and Nishiyama C: Role of
PU.1 in MHC class II expression via CIITA transcription in
plasmacytoid dendritic cells. PLoS One. 11:e01540942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yashiro T, Kubo M, Ogawa H, Okumura K and
Nishiyama C: PU.1 suppresses Th2 cytokine expression via silencing
of GATA3 transcription in dendritic cells. PLoS One.
10:e01376992015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nakano N, Nishiyama C, Kanada S, Niwa Y,
Shimokawa N, Ushio H, Nishiyama M, Okumura K and Ogawa H:
Involvement of mast cells in IL-12/23 p40 production is essential
for survival from polymicrobial infections. Blood. 109:4846–4855.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yui MA and Rothenberg EV: Developmental
gene networks: A triathlon on the course to T cell identity. Nat
Rev Immunol. 14:529–545. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Heinz S, Romanoski CE, Benner C, Allison
KA, Kaikkonen MU, Orozco LD and Glass CK: Effect of natural genetic
variation on enhancer selection and function. Nature. 503:487–492.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Natoli G, Ghisletti S and Barozzi I: The
genomic landscapes of inflammation. Genes Dev. 25:101–106. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hosokawa H, Ungerbäck J, Wang X, Matsumoto
M, Nakayama KI, Cohen SM, Tanaka T and Rothenberg EV: Transcription
factor PU.1 represses and activates gene expression in early T
cells by redirecting partner transcription factor binding.
Immunity. 49:7822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Rothenberg EV, Hosokawa H and Ungerbäck J:
Mechanisms of action of hematopoietic transcription factor PU.1 in
initiation of T-cell development. Front Immunol. 10:2282019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ungerbäck J, Hosokawa H, Wang X, Strid T,
Williams BA, Sigvardsson M and Rothenberg EV: Pioneering, chromatin
remodeling, and epigenetic constraint in early T-cell gene
regulation by SPI1 (PU.1). Genome Res. 28:1508–1519. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Champhekar A, Damle SS, Freedman G,
Carotta S, Nutt SL and Rothenberg EV: Regulation of early T-lineage
gene expression and developmental progression by the progenitor
cell transcription factor PU.1. Genes Dev. 29:832–848. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ramming A, Druzd D, Leipe J, Schulze-Koops
H and Skapenko A: Maturation-related histone modifications in the
PU.1 promoter regulate Th9-cell development. Blood. 119:4665–4674.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Goswami R and Kaplan MH: Gcn5 is required
for PU.1-dependent IL-9 induction in Th9 cells. J Immunol.
189:3026–3033. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Rivera Vargas T, Cai Z, Shen Y, Dosset M,
Benoit-Lizon I, Martin T, Roussey A, Flavell RA, Ghiringhelli F and
Apetoh L: Selective degradation of PU.1 during autophagy represses
the differentiation and antitumour activity of TH9 cells. Nat
Commun. 8:5592017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
72
|
Goodnow CC, Vinuesa CG, Randall KL, Mackay
F and Brink R: Control systems and decision making for antibody
production. Nat Immunol. 11:681–688. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Carotta S, Willis SN, Hasbold J, Inouye M,
Pang SH, Emslie D, Light A, Chopin M, Shi W, Wang H, et al: The
transcription factors IRF8 and PU.1 negatively regulate plasma cell
differen-tiation. J Exp Med. 211:2169–2181. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Willis SN, Tellier J, Liao Y, Trezise S,
Light A, O'Donnell K, Garrett- Sinha LA, Shi W, Tarlinton DM and
Nutt SL: Environmental sensing by mature B cells is controlled by
the transcription factors PU.1 and SpiB. Nat Commun. 8:14262017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Batista CR, Li SK, Xu LS, Solomon LA and
DeKoter RP: PU.1 regulates Ig light chain transcription and
rearrangement in Pre-B cells during B cell development. J Immunol.
198:1565–1574. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ochiai K, Maienschein-Cline M, Simonetti
G, Chen J, Rosenthal R, Brink R, Chong AS, Klein U, Dinner AR,
Singh H and Sciammas R: Transcriptional regulation of germinal
center B and plasma cell fates by dynamical control of IRF4.
Immunity. 38:918–929. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Pang SH, Minnich M, Gangatirkar P, Zheng
Z, Ebert A, Song G, Dickins RA, Corcoran LM, Mullighan CG,
Busslinger M, et al: PU.1 cooperates with IRF4 and IRF8 to suppress
pre-B-cell leukemia. Leukemia. 30:1375–1387. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Scialdone A, Khazaei S, Hasni MS,
Lennartsson A, Gullberg U and Drott K: Depletion of the
transcriptional coactivators CREB-binding protein or EP300
downregulates CD20 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells and
impairs the cytotoxic effects of anti-CD20 antibodies. Exp Hematol.
79:35–46.e1. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Soodgupta D, White LS, Yang W, Johnston R,
Andrews JM, Kohyama M, Murphy KM, Mosammaparast N, Payton JE and
Bednarski JJ: RAG-mediated DNA breaks attenuate PU.1 activity in
early B cells through activation of a SPIC-BCLAF1 complex. Cell
Rep. 29:829–843.e5. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Rogers JH, Owens KS, Kurkewich J,
Klopfenstein N, Iyer SR, Simon MC and Dahl R: E2A antagonizes PU.1
activity through inhibition of DNA binding. Biomed Res Int.
2016:39836862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Laslo P, Spooner CJ, Warmflash A, Lanck
DW, Lee HJ, Sciammas R, Gantner BN, Dinner AR and Singh H:
Multilineage transcriptional priming and determination of alternate
hematopoietic cell fates. Cell. 126:755–766. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|