|
1
|
Heare T, Hensley MA and Dell'Orfano S:
Bone tumors: Osteosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma. Curr Opin Pediatr.
21:365–372. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xiao X, Wang W, Li Y, Yang D, Li X, Shen
C, Liu Y, Ke X, Guo S and Guo Z: HSP90AA1-mediated autophagy
promotes drug resistance in osteosarcoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
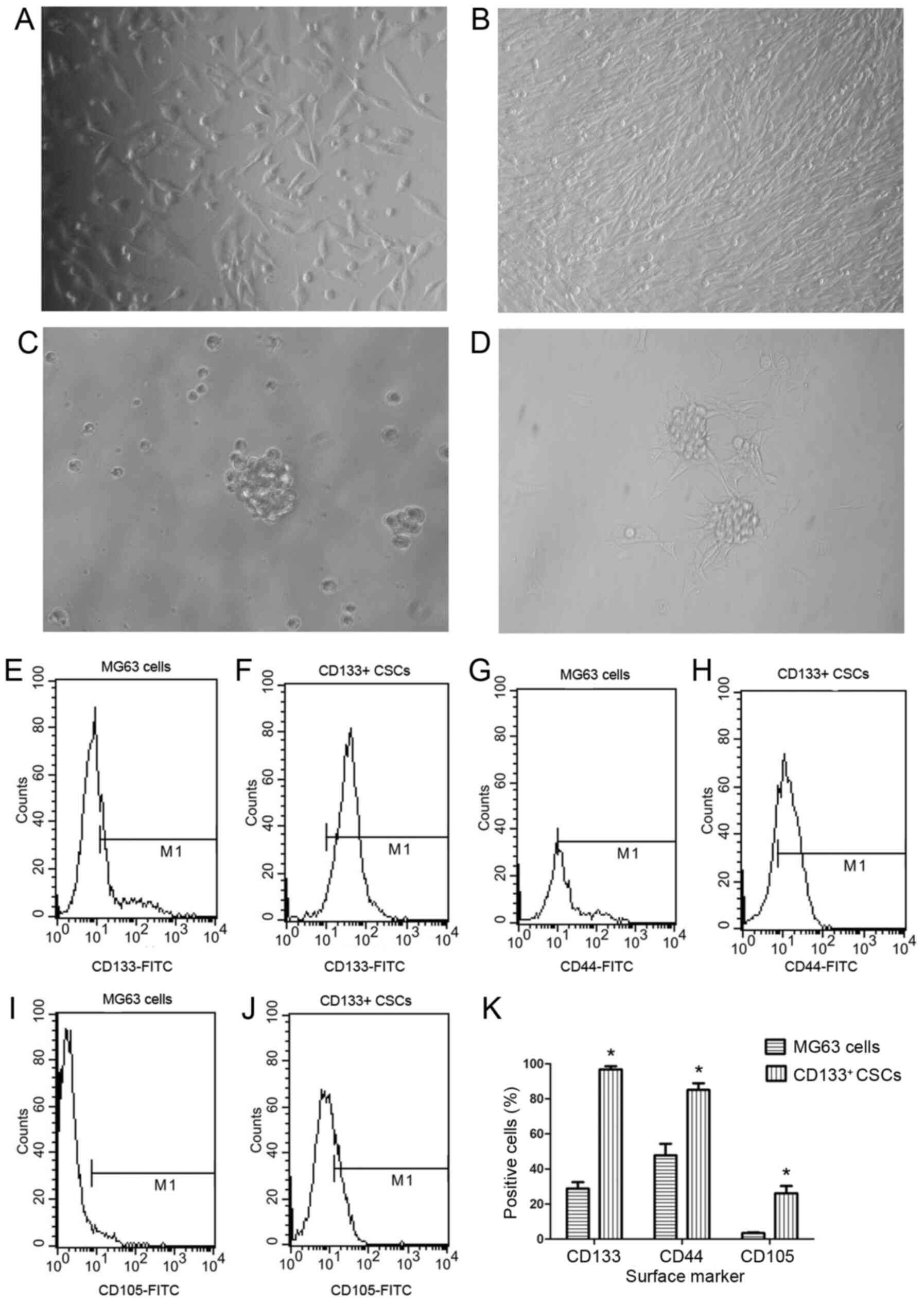
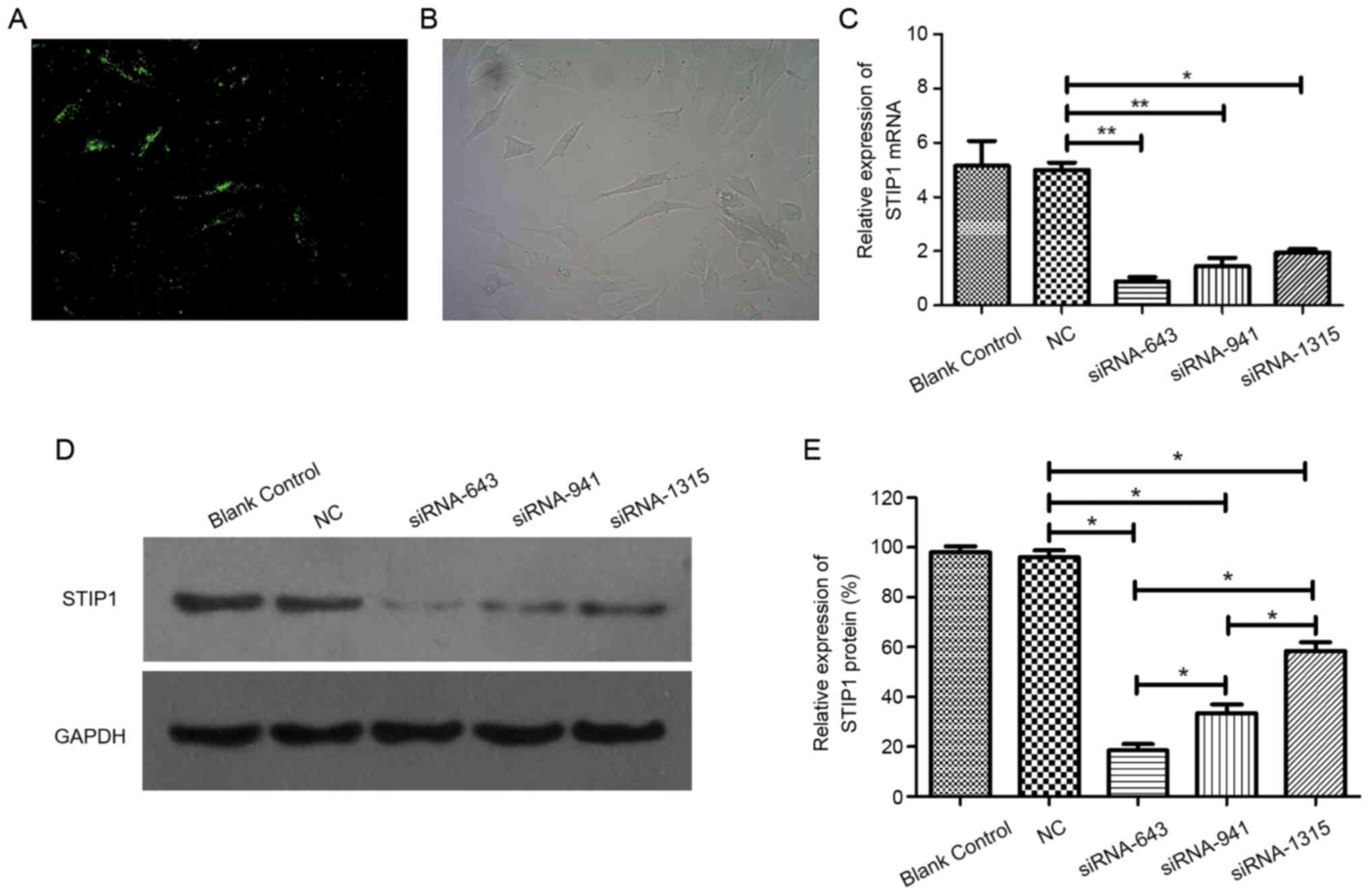
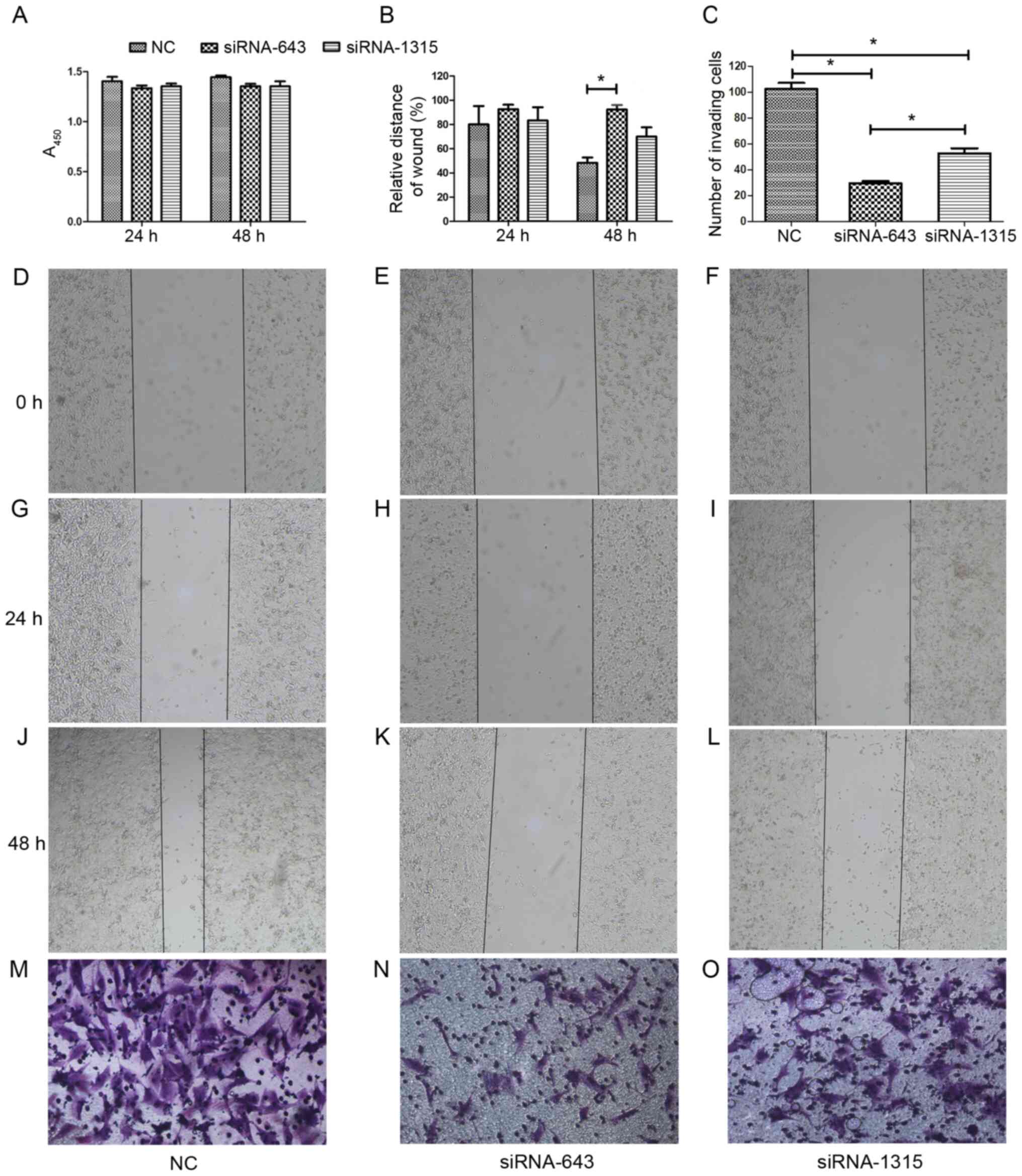
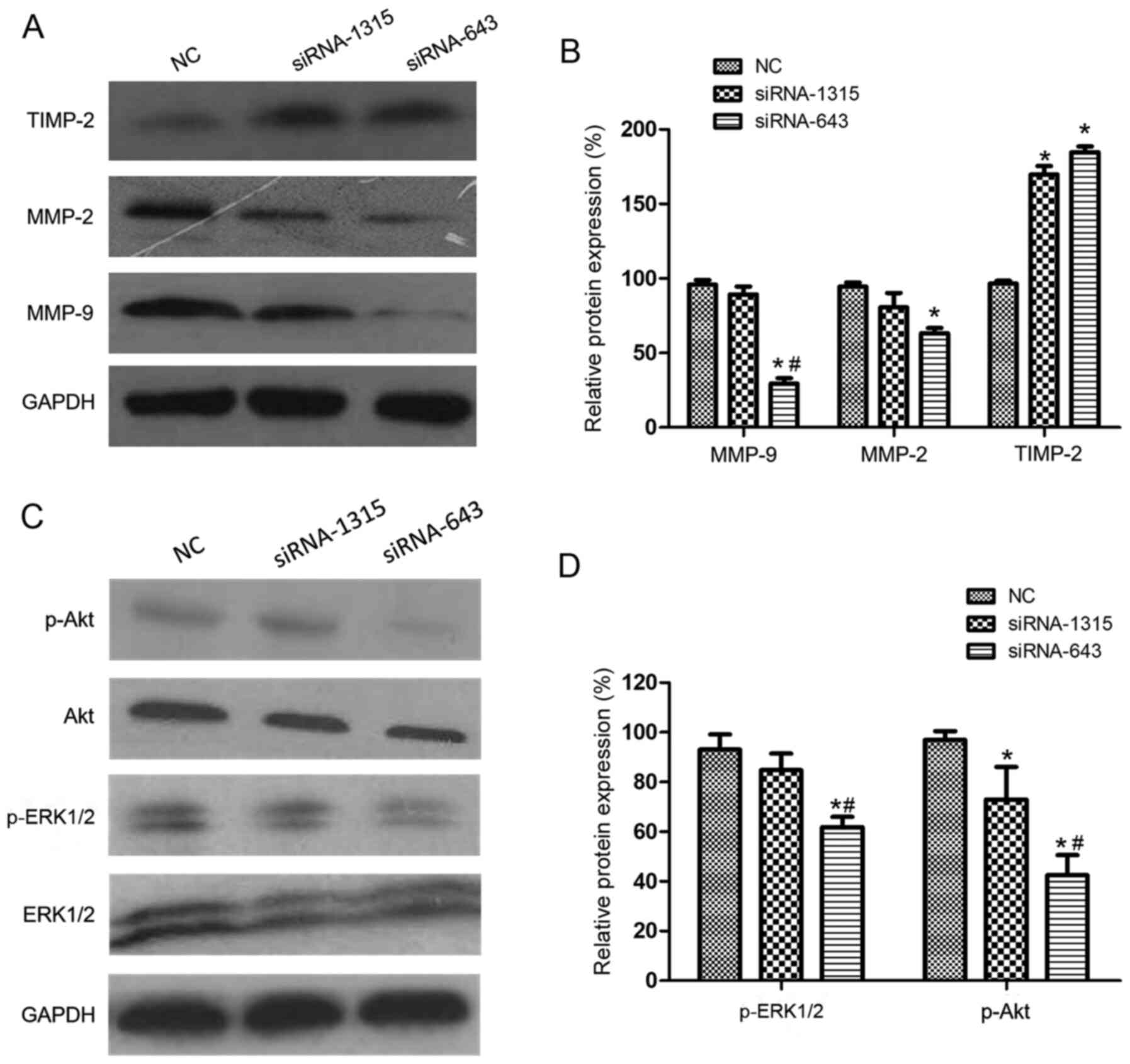
37:2012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ellis RJ: Molecular chaperones: Assisting
assembly in addition to folding. Trends Biochem Sci. 31:395–401.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Y and McAlpine SR: Regulating the
cytoprotective response in cancer cells using simultaneous
inhibition of Hsp90 and Hsp70. Org Biomol Chem. 13:2108–2116. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Longshaw VM, Baxter M, Prewitz M and
Blatch GL: Knockdown of the co-chaperone Hop promotes extranuclear
accumulation of Stat3 in mouse embryonic stem cells. Eur J Cell
Biol. 88:153–166. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Longshaw VM, Chapple JP, Balda MS,
Cheetham ME and Blatch GL: Nuclear translocation of the Hsp70/Hsp90
organizing protein mSTI1 is regulated by cell cycle kinases. J Cell
Sci. 117(Pt 5): 701–710. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhai E, Liang W, Lin Y, Huang L, He X, Cai
S, Chen J, Zhang N, Li J, Zhang Q, et al: HSP70/HSP90-Organizing
protein contributes to gastric cancer progression in an autocrine
fashion and predicts poor survival in gastric cancer. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 47:879–892. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Walsh N, Larkin A, Swan N, Conlon K,
Dowling P, McDermott R and Clynes M: RNAi knockdown of Hop
(Hsp70/Hsp90 organising protein) decreases invasion via MMP-2 down
regulation. Cancer Lett. 306:180–189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Baindur-Hudson S, Edkins AL and Blatch GL:
Hsp70/Hsp90 organising protein (hop): Beyond interactions with
chaperones and prion proteins. Subcell Biochem. 78:69–90. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu B, Ma W, Jha RK and Gurung K: Cancer
stem cells in osteosarcoma: Recent progress and perspective. Acta
Oncol. 50:1142–1150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang M, Yan M, Zhang R, Li J and Luo Z:
Side population cells isolated from human osteosarcoma are enriched
with tumor-initiating cells. Cancer Sci. 102:1774–1781. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gibbs CP, Kukekov VG, Reith JD,
Tchigrinova O, Suslov ON, Scott EW, Ghivizzani SC, Ignatova TN and
Steindler DA: Stem-like cells in bone sarcomas: Implications for
tumorigenesis. Neoplasia. 7:967–976. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Koka P, Mundre RS, Rangarajan R,
Chandramohan Y, Subramanian RK and Dhanasekaran A: Uncoupling
Warburg effect and stemness in CD133+ve cancer stem
cells from Saos-2 (osteosarcoma) cell line under hypoxia. Mol Biol
Rep. 45:1653–1662. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ni M, Xiong M, Zhang X, Cai G, Chen H,
Zeng Q and Yu Z: Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles
conjugated with CD133 aptamers for targeted salinomycin delivery to
CD133+ osteosarcoma cancer stem cells. Int J
Nanomedicine. 10:2537–2554. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Yang J, Guo W, Wang L, Yu L, Mei H, Fang
S, Ji P, Liu Y, Liu G and Song Q: Cisplatin-resistant osteosarcoma
cells possess cancer stem cell properties in a mouse model. Oncol
Lett. 12:2599–2605. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brown HK, Tellez-Gabriel M and Heymann D:
Cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett. 386:189–195. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li K, Li X, Tian J, Wang H, Pan J and Li
J: Downregulation of DNA-PKcs suppresses P-gp expression via
inhibition of the Akt/NF-κB pathway in CD133-positive osteosarcoma
MG-63 cells. Oncol Rep. 36:1973–1980. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gong C, Liao H, Guo F, Qin L and Qi J:
Implication of expression of Nanog in prostate cancer cells and
their stem cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
32:242–246. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gong C, Liao H, Wang J, Lin Y, Qi J, Qin
L, Tian LQ and Guo FJ: LY294002 induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis of cancer stem-like cells from human osteosarcoma via
down-regulation of PI3K activity. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:3103–3107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li J, Sun X, Wang Z, Chen L, Li D, Zhou J
and Liu M: Regulation of vascular endothelial cell polarization and
migration by Hsp70/Hsp90-organizing protein. PLoS One.
7:e363892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Abarrategi A, Tornin J, Martinez-Cruzado
L, Hamilton A, Martinez-Campos E, Rodrigo JP, González MV, Baldini
N, Garcia-Castro J and Rodriguez R: Osteosarcoma: Cells-of-Origin,
cancer stem cells, and targeted therapies. Stem Cells Int.
2016:36317642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qi XT, Li YL, Zhang YQ, Xu T, Lu B, Fang
L, Gao JQ, Yu LS, Zhu DF, Yang B, et al: KLF4 functions as an
oncogene in promoting cancer stem cell-like characteristics in
osteosarcoma cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 40:546–555. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Chang Y, Zhao Y, Zhan H, Wei X, Liu T and
Zheng B: Bufalin inhibits the differentiation and proliferation of
human osteosarcoma cell line hMG63-derived cancer stem cells.
Tumour Biol. 35:1075–1082. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen F, Zeng Y, Qi X, Chen Y, Ge Z, Jiang
Z, Zhang X, Dong Y, Chen H and Yu Z: Targeted salinomycin delivery
with EGFR and CD133 aptamers based dual-ligand lipid-polymer
nanoparticles to both osteosarcoma cells and cancer stem cells.
Nanomedicine. 14:2115–2127. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu YW, Liu CT, Huang XY, Huang LS, Luo YH,
Hong CQ, Guo HP, Xu LY, Peng YH and Li EM: Serum Autoantibodies
against STIP1 as a potential biomarker in the diagnosis of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Markers. 2017:53840912017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang L, Zhai E, Cai S, Lin Y, Liao J, Jin
H, Peng S, Xu L, Chen M and Zeng Z: Stress-inducible Protein-1
promotes metastasis of gastric cancer via Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:62018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Iglesia RP, Prado MB, Cruz L, Martins VR,
Santos TG and Lopes MH: Engagement of cellular prion protein with
the co-chaperone Hsp70/90 organizing protein regulates the
proliferation of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Stem Cell Res Ther.
8:762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang HS, Tsai CL, Chang PY, Chao A, Wu RC,
Chen SH, Wang CJ, Yen CF, Lee YS and Wang TH: Positive associations
between upregulated levels of stress-induced phosphoprotein 1 and
matrix metalloproteinase-9 in endometriosis/adenomyosis. PLoS One.
13:e1905732018.
|
|
30
|
Erlich RB, Kahn SA, Lima FR, Muras AG,
Martins RA, Linden R, Chiarini LB, Martins VR and Moura Neto V:
STI1 promotes glioma proliferation through MAPK and PI3K path-ways.
Glia. 55:1690–1698. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsai CL, Chao A, Jung SM, Tsai CN, Lin CY,
Chen SH, Sue SC, Wang TH, Wang HS and Lai CH: Stress-induced
phospho-protein-1 maintains the stability of JAK2 in cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 7:50548–50563. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|