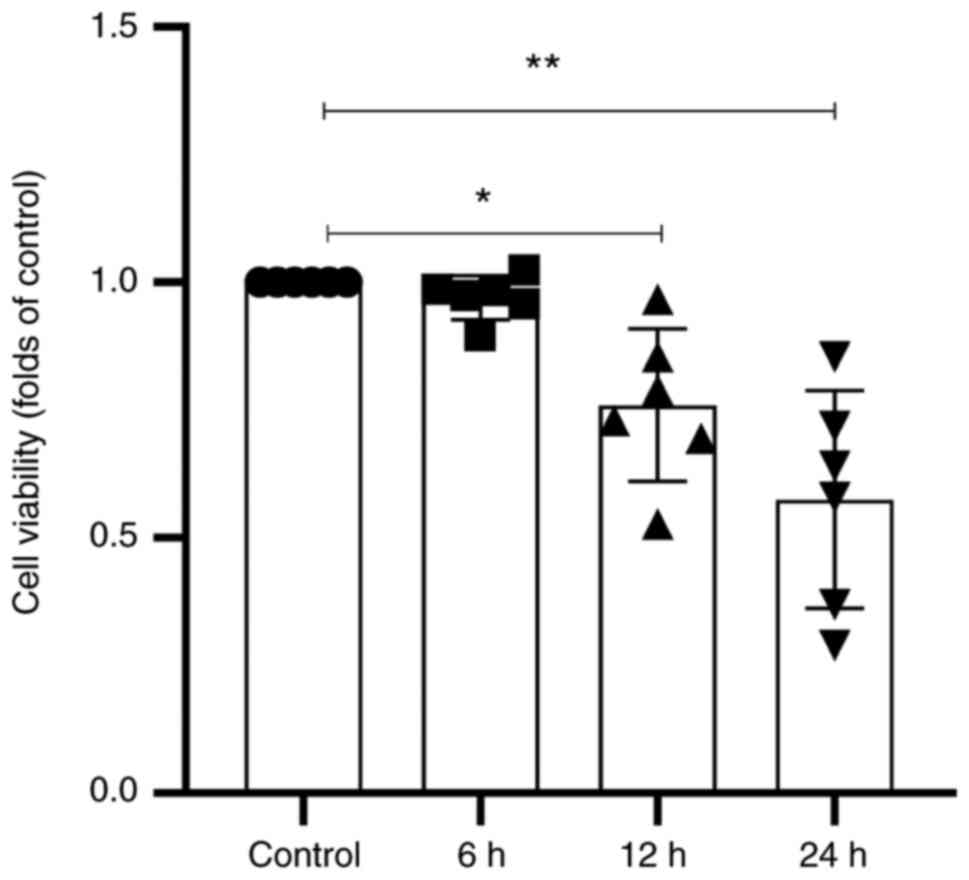
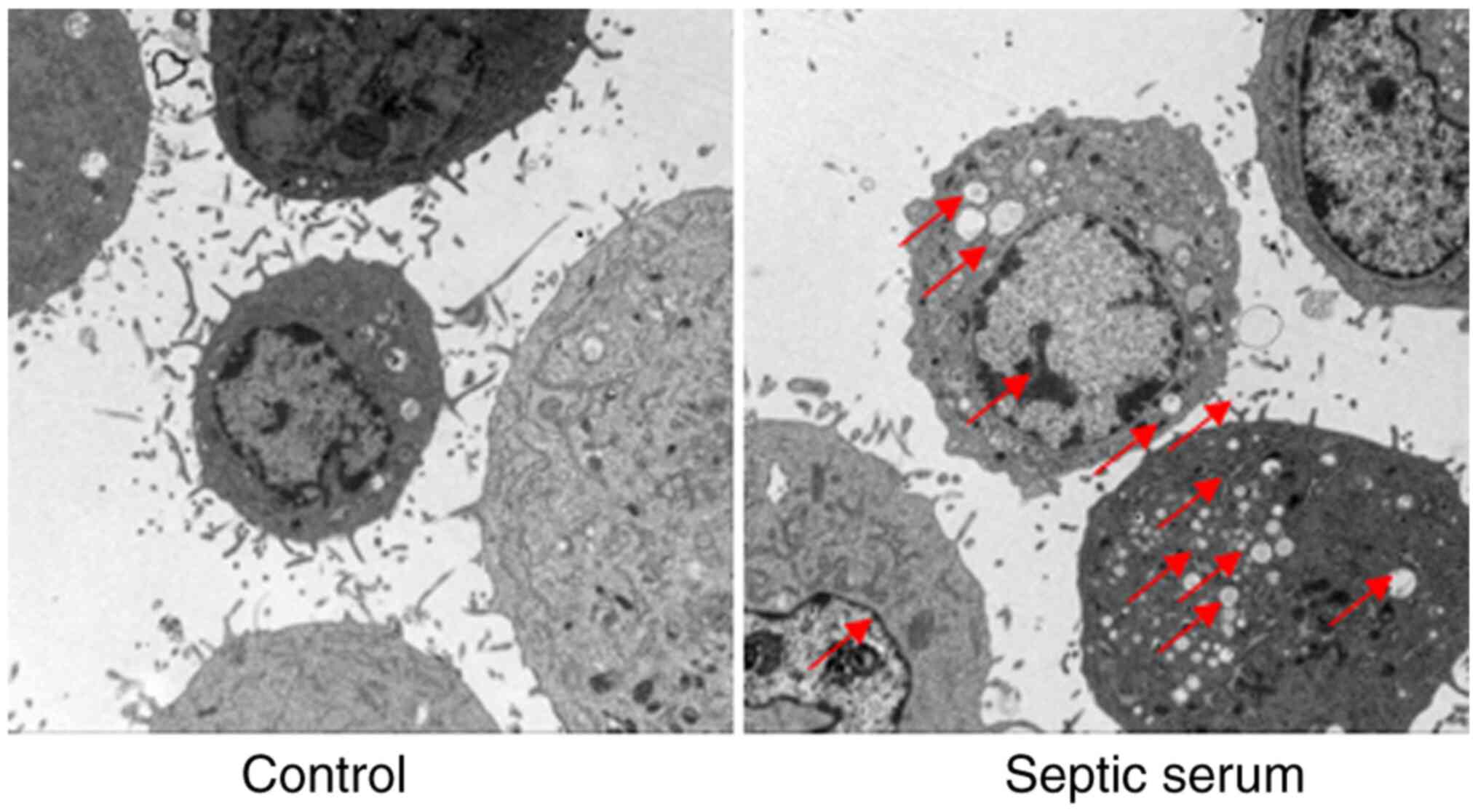
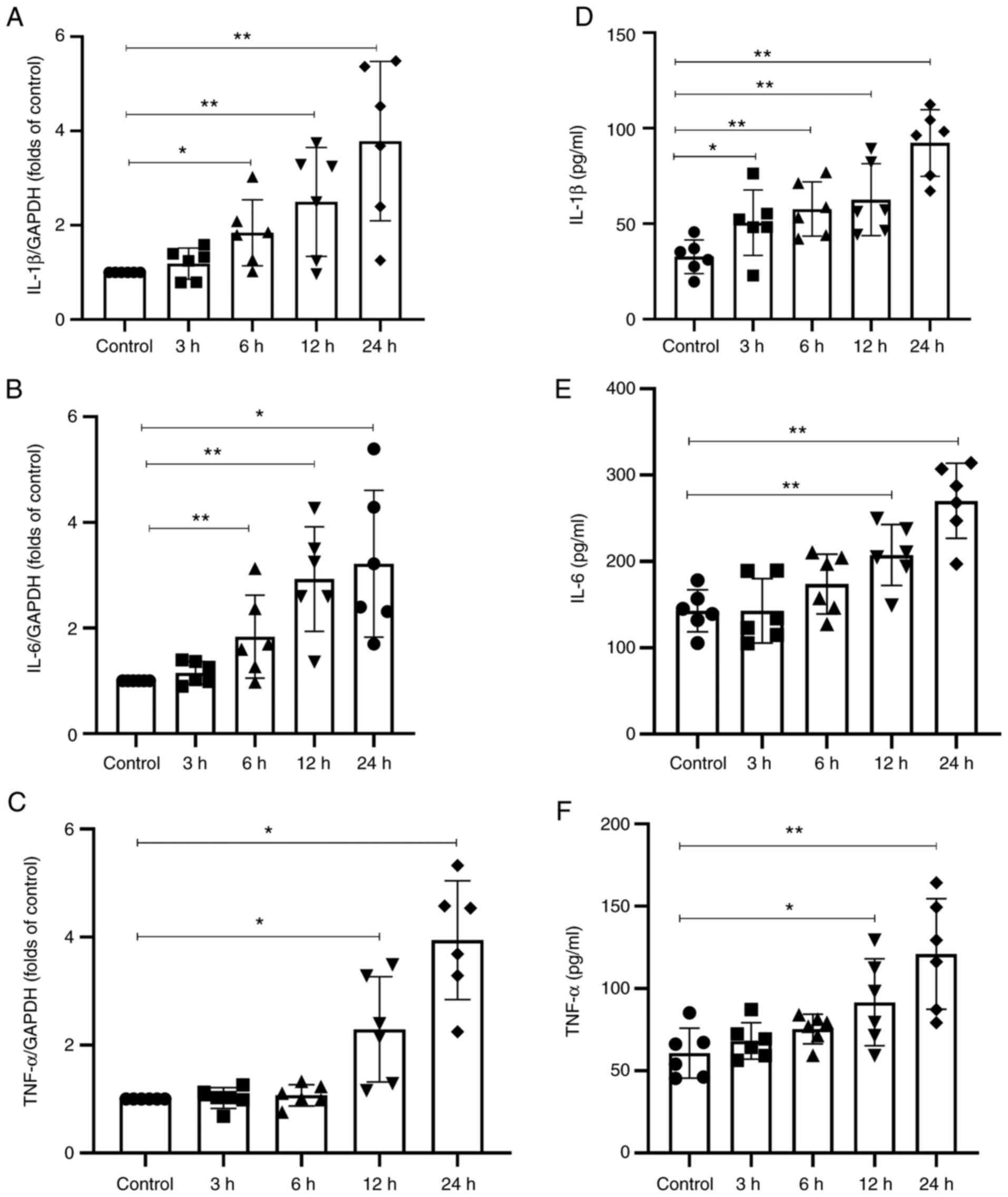
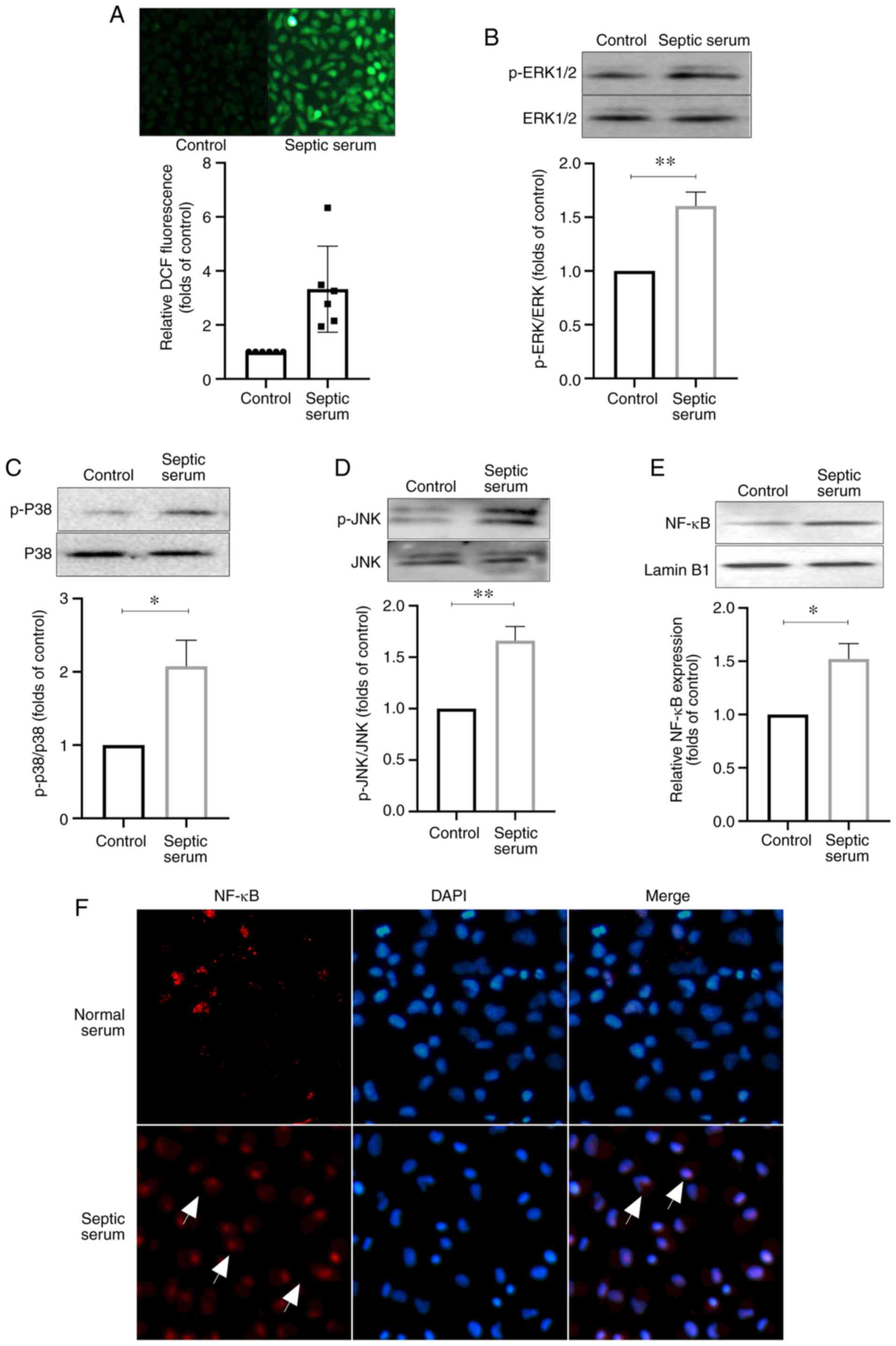
|
1
|
Colbert JF, Schmidt EP, Faubel S and Ginde
AA: Severe sepsis outcomes among hospitalizations with inflammatory
bowel disease. Shock. 47:128–131. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cepinskas G and Wilson JX: Inflammatory
response in micro-vascular endothelium in sepsis: Role of oxidants.
J Clin Biochem Nutr. 42:175–184. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
De Blasi RA, Palmisani S, Alampi D,
Mercieri M, Romano R, Collini S and Pinto G: Microvascular
dysfunction and skeletal muscle oxygenation assessed by
phase-modulation near-infrared spectroscopy in patients with septic
shock. Intensive Care Med. 31:1661–1668. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford
KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer
S, et al: Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and
mortality, 1990-2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease
study. Lancet. 395:200–211. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kumar V: Sepsis roadmap: What we know,
what we learned, and where we are going. Clin Immunol.
210:1082642020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Martin JB and Badeaux JE: Interpreting
Laboratory tests in infection: Making sense of biomarkers in sepsis
and systemic inflammatory response syndrome for intensive care unit
patients. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 29:119–130. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Edul VK, Ferrara G and Dubin A:
Microcirculatory dysfunction in sepsis. Endocr Metab Immune Disord
Drug Targets. 10:235–246. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bro-Jeppesen J, Johansson PI, Kjaergaard
J, Wanscher M, Ostrowski SR, Bjerre M and Hassager C: Level of
systemic inflammation and endothelial injury is associated with
cardio-vascular dysfunction and vasopressor support in post-cardiac
arrest patients. Resuscitation. 121:179–186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iba T and Levy JH: Inflammation and
thrombosis: Roles of neutrophils, platelets and endothelial cells
and their interactions in thrombus formation during sepsis. J
Thromb Haemost. 16:231–241. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Uchimido R, Schmidt EP and Shapiro NI: The
glycocalyx: A novel diagnostic and therapeutic target in sepsis.
Crit Care. 23:162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Houschyar KS, Pyles MN, Rein S,
Nietzschmann I, Duscher D, Maan ZN, Weissenberg K, Philipps HM,
Strauss C, Reichelt B and Siemers F: Continuous hemoadsorption with
a cytokine adsorber during sepsis-a review of the literature. Int J
Artif Organs. 40:205–211. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Farley KS, Wang LF, Law C and Mehta S:
Alveolar macrophage inducible nitric oxide synthase-dependent
pulmonary micro-vascular endothelial cell septic barrier
dysfunction. Microvasc Res. 76:208–216. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Berger C, Rossaint J, Van Aken H, Westphal
M, Hahnenkamp K and Zarbock A: Lidocaine reduces neutrophil
recruitment by abolishing chemokine-induced arrest and
transendothelial migration in septic patients. J Immunol.
192:367–376. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lambertucci F, Motino O, Villar S, Rigalli
JP, de Luján Alvarez M, Catania VA, Martín-Sanz P, Carnovale CE,
Quiroga AD, Francés DE and Ronco MT: Benznidazole, the trypanocidal
drug used for Chagas disease, induces hepatic NRF2 activation and
attenuates the inflammatory response in a murine model of sepsis.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 315:12–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li HR, Liu J, Zhang SL, Luo T, Wu F, Dong
JH, Guo YJ and Zhao L: Corilagin ameliorates the extreme
inflammatory status in sepsis through TLR4 signaling pathways. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 17:182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Top AP, Ince C, de Meij N, van Dijk M and
Tibboel D: Persistent low microcirculatory vessel density in
nonsurvivors of sepsis in pediatric intensive care. Crit Care Med.
39:8–13. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
O'Sullivan AW, Wang JH and Redmond HP:
NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK inhibition improve survival in endotoxin
shock and in a cecal ligation and puncture model of sepsis in
combination with antibiotic therapy. J Surg Res. 152:46–53. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Flierl MA and
Ward PA: Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and
puncture. Nat Protoc. 4:31–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao J, Xu SZ and Liu J: Fibrinopeptide A
induces C-reactive protein expression through the
ROS-ERK1/2/p38-NF-κB signal pathway in the human umbilical vascular
endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 234:13481–13492. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kyriazopoulou E, Leventogiannis K,
Norrby-Teglund A, Dimopoulos G, Pantazi A, Orfanos SE, Rovina N,
Tsangaris I, Gkavogianni T, Botsa E, et al: Macrophage
activation-like syndrome: An immunological entity associated with
rapid progression to death in sepsis. BMC Med. 15:1722017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sturtzel C: Endothelial Cells. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1003:71–91. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Garrean S, Gao XP, Brovkovych V, Shimizu
J, Zhao YY, Vogel SM and Malik AB: Caveolin-1 regulates NF-kappaB
activation and lung inflammatory response to sepsis induced by
lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 177:4853–4860. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
McCuskey RS, Nishida J, McDonnell D, Baker
GL, Urbaschek R and Urbaschek B: Effect of immunoglobulin G on the
hepatic microvascular inflammatory response during sepsis. Shock.
5:28–33. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Orfanos SE, Kotanidou A, Glynos C,
Athanasiou C, Tsigkos S, Dimopoulou I, Sotiropoulou C, Zakynthinos
S, Armaganidis A, Papapetropoulos A and Roussos C: Angiopoietin-2
is increased in severe sepsis: Correlation with inflammatory
mediators. Crit Care Med. 35:199–206. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yoo JW, Moon JY, Hong SB, Lim CM, Koh Y
and Huh JW: Clinical significance of circulating endothelial cells
in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Infect Dis (Lond).
47:393–398. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Constantino L, Gonçalves RC, Giombelli VR,
Tomasi CD, Vuolo F, Kist LW, de Oliveira GM, de Bittencourt
Pasquali MA, Bogo MR, Mauad T, et al: Regulation of lung oxidative
damage by endogenous superoxide dismutase in sepsis. Intensive Care
Med Exp. 2:172014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Schwalm MT, Pasquali M, Miguel SP, Dos
Santos JP, Vuolo F, Comim CM, Petronilho F, Quevedo J, Gelain DP,
Moreira JC, et al: Acute brain inflammation and oxidative damage
are related to long-term cognitive deficits and markers of
neurodegeneration in sepsis-survivor rats. Mol Neurobiol.
49:380–385. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Simon F and Fernández R: Early
lipopolysaccharide-induced reactive oxygen species production
evokes necrotic cell death in human umbilical vein endothelial
cells. J Hypertens. 27:1202–1216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bime C, Zhou T, Wang T, Slepian MJ, Garcia
JG and Hecker L: Reactive oxygen species-associated molecular
signature predicts survival in patients with sepsis. Pulm Circ.
6:196–201. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Forrester SJ, Kikuchi DS, Hernandes MS, Xu
Q and Griendling KK: Reactive oxygen species in metabolic and
inflammatory signaling. Circ Res. 122:877–902. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang J, Wang X, Vikash V, Ye Q, Wu D, Liu
Y and Dong W: ROS and ROS-mediated cellular signaling. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2016:43509652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Minutoli L, Puzzolo D, Rinaldi M, Irrera
N, Marini H, Arcoraci V, Bitto A, Crea G, Pisani A, Squadrito F, et
al: ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in brain, heart,
kidney, and testis ischemia/reperfusion injury. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2016:21830262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tejero J, Shiva S and Gladwin MT: Sources
of vascular nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species and their
regulation. Physiol Rev. 99:311–379. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Mittal M, Siddiqui MR, Tran K, Reddy SP
and Malik AB: Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue
injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:1126–1167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Ronco MT, Manarin R, Francés D, Serra E,
Revelli S and Carnovale C: Benznidazole treatment attenuates liver
NF-κB activity and MAPK in a cecal ligation and puncture model of
sepsis. Mol Immunol. 48:867–873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song GY, Chung CS, Chaudry IH and Ayala A:
Immune suppression in polymicrobial sepsis: Differential regulation
of Th1 and Th2 responses by p38 MAPK. Benznidazole treatment
attenuates liver NF-κB activity and MAPK in a cecal ligation and
puncture model of sepsis. J Surg Res. 91:141–146. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Song GY, Chung CS, Jarrar D, Chaudry IH
and Ayala A: Evolution of an immune suppressive macrophage
phenotype as a product of P38 MAPK activation in polymicrobial
sepsis. Shock. 15:42–48. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Song GY, Chung CS, Jarrar D, Cioffi WG and
Ayala A: Mechanism of immune dysfunction in sepsis: Inducible
nitric oxide-meditated alterations in p38 MAPK activation. J
Trauma. 53:276–282. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun Y, Li YH, Wu XX, Zheng W, Guo ZH, Li
Y, Chen T, Hua ZC and Xu Q: Ethanol extract from Artemisia vestita,
a traditional Tibetan medicine, exerts anti-sepsis action through
down-regulating the MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Int J Mol Med.
17:957–962. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim WH, An HJ, Kim JY, Gwon MG, Gu H, Lee
SJ, Park JY, Park KD, Han SM, Kim MK and Park KK: Apamin inhibits
TNF-α- and IFN-γ-induced inflammatory cytokines and chemokines via
suppressions of NF-κB signaling pathway and STAT in human
keratinocytes. Pharmacol Rep. 69:1030–1035. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Thoma A and Lightfoot AP: NF-κB and
inflammatory cytokine signalling: Role in skeletal muscle atrophy.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 1088:267–279. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|