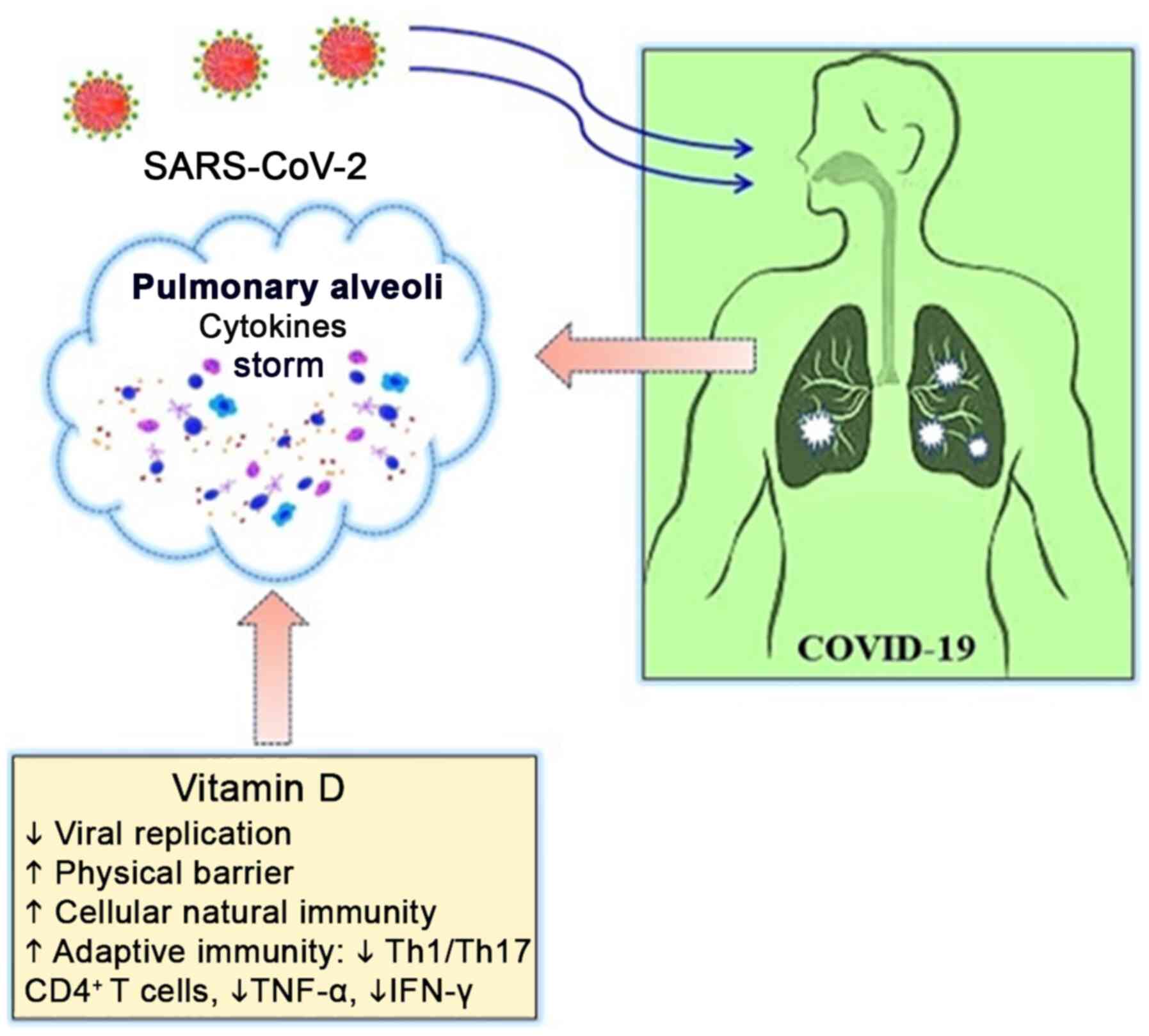
|
1
|
Guo YR, Cao QD, Hong ZS, Tan YY, Chen SD,
Jin HJ, Tan KS, Wang DY and Yan Y: The origin, transmission and
clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak
- an update on the status. Mil Med Res. 7:112020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Docea AO, Tsatsakis A, Albulescu D,
Cristea O, Zlatian O, Vinceti M, Moschos SA, Tsoukalas D, Goumenou
M, Drakoulis N, et al: A new threat from an old enemy: Re-emergence
of coronavirus (Review). Int J Mol Med. 45:1631–1643.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lai CC, Wang CY, Wang YH, Hsueh SC, Ko WC
and Hsueh PR: Global epidemiology of coronavirus disease 2019
(COVID-19): Disease incidence, daily cumulative index, mortality,
and their association with country healthcare resources and
economic status. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 55:1059462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Goumenou M, Sarigiannis D, Tsatsakis A,
Anesti O, Docea AO, Petrakis D, Tsoukalas D, Kostoff R, Rakitskii
V, Spandidos DA, et al: COVID-19 in Northern Italy: An integrative
overview of factors possibly influencing the sharp increase of the
outbreak (Review). Mol Med Rep. 22:20–32. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stopsack KH, Mucci LA, Antonarakis ES,
Nelson PS and Kantoff PW: TMPRSS2 and COVID-19: Serendipity or
Opportunity for Intervention? Cancer Discov. 10:779–782. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tsatsakis A, Petrakis D, Nikolouzakis TK,
Docea AO, Calina D, Vinceti M, Goumenou M, Kostoff RN, Mamoulakis
C, Aschner M, et al: COVID-19, an opportunity to reevaluate the
correlation between long-term effects of anthropogenic pollutants
on viral epidemic/pandemic events and prevalence. Food Chem
Toxicol. 141:1114182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pareek M, Bangash MN, Pareek N, Pan D, Sze
S, Minhas JS, Hanif W and Khunti K: Ethnicity and COVID-19: An
urgent public health research priority. Lancet. 395:1421–1422.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nitulescu GM, Paunescu H, Moschos SA,
Petrakis D, Nitulescu G, Ion GND, Spandidos DA, Nikolouzakis TK,
Drakoulis N and Tsatsakis A: Comprehensive analysis of drugs to
treat SARS-CoV-2 infection: Mechanistic insights into current
COVID-19 therapies (Review). Int J Mol Med. 46:467–488. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calina D, Sarkar C, Arsene AL, Salehi B,
Docea AO, Mondal M, Islam MT, Zali A and Sharifi-Rad J: Recent
advances, approaches and challenges in targeting pathways for
potential COVID-19 vaccines development. Immunol Res. 68:315–324.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kostoff RN, Kanduc D, Porter AL, Shoenfeld
Y, Calina D, Briggs MB, Spandidos DA and Tsatsakis A: Vaccine- and
natural infection-induced mechanisms that could modulate vaccine
safety. Toxicol Rep. 7:1448–1458. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Calina D, Docea AO, Petrakis D, Egorov A
M, Ishmukhametov AA, Gabibov AG, Shtilman MI, Kostoff R, Carvalho
F, Vinceti M, et al: Towards effective COVID-19 vaccines: Updates,
perspectives and challenges (Review). Int J Mol Med. 46:3–16. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Calina D, Hartung T, Docea AO, Spandidos
DA, Egorov AM, Shtilman MI, Carvalho F and Tsatsakis A: COVID-19
vaccines: Ethical framework concerning human challenge studies.
Daru. Aug 27–2020.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Arboleda JF, Urcuqui-Inchima S and Vitamin
D: Vitamin D Supplementation: A Potential Approach for
Coronavirus/COVID-19 Therapeutics? Front Immunol. 11:15232020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Martineau AR and Forouhi NG: Vitamin D for
COVID-19: A case to answer? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 8:735–736.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Benskin LL: A Basic Review of the
Preliminary Evidence That COVID-19 Risk and Severity Is Increased
in Vitamin D Deficiency. Front Public Health. 8:5132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ali N: Role of vitamin D in preventing of
COVID-19 infection, progression and severity. J Infect Public
Health. 13:1373–1380. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Laird E, Rhodes J and Kenny RA: Vitamin D
and inflammation: potential implications for severity of Covid-19.
Ir Med J. 113:812020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Darling AL, Ahmadi KR, Ward KA, Harvey NC,
Alves AC, Dunn-Waters DK, Lanham-New SA, Cooper C and Blackbourn
DJ: Vitamin D status, body mass index, ethnicity and COVID-19:
Initial analysis of the first-reported UK Biobank COVID-19 positive
cases 580 compared with negative controls 723. MedRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.29.20084277urisimplehttps://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.29.20084277.
|
|
19
|
Patel P, Hiam L, Sowemimo A, Devakumar D
and McKee M: Ethnicity and covid-19. BMJ. 369:m22822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Grant WB, Lahore H, McDonnell SL, Baggerly
CA, French CB, Aliano JL and Bhattoa HP: Evidence that Vitamin D
Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19
Infections and Deaths. Nutrients. 12:9882020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Martineau AR, Jolliffe DA, Hooper RL,
Greenberg L, Aloia JF, Bergman P, Dubnov-Raz G, Esposito S, Ganmaa
D, Ginde AA, et al: Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute
respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis
of individual participant data. BMJ. 356:i65832017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pike JW and Christakos S: Biology and
mechanisms of action of the vitamin D hormone. Endocrinol Metab
Clin North Am. 46:815–843. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song
J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, et al: China Novel Coronavirus
Investigating and Research Team: A novel coronavirus from patients
with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 382:727–733. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu
Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, et al: Clinical features of patients
infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet.
395:497–506. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsatsakis A, Calina D, Falzone L, Petrakis
D, Mitrut R, Siokas V, Pennisi M, Lanza G, Libra M, Doukas SG, et
al: SARS-CoV-2 pathophysiology and its clinical implications: An
integrative overview of the pharmacotherapeutic management of
COVID-19. Food Chem Toxicol. 146:1117692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lanza K, Perez LG, Costa LB, Cordeiro TM,
Palmeira VA and Ribeiro VT: Covid-19: The renin-angiotensin system
imbalance hypothesis. Clin Sci (Lond). 134:1259–1264. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Aldridge RW, Lewer D, Katikireddi SV,
Mathur R, Pathak N, Burns R, Fragaszy EB, Johnson AM, Devakumar D,
Abubakar I, et al: Black, Asian and Minority Ethnic groups in
England are at increased risk of death from COVID-19: Indirect
standardisation of NHS mortality data. Wellcome Open Res. 5:882020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Khunti K, Singh AK, Pareek M and Hanif W:
Is ethnicity linked to incidence or outcomes of covid-19? BMJ.
369:m15482020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pan D, Sze S, Minhas JS, Bangash MN,
Pareek N, Divall P, Williams CM, Oggioni MR, Squire IB, Nellums LB,
et al: The impact of ethnicity on clinical outcomes in COVID-19: A
systematic review. EClinicalMedicine. 23:1004042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sze S, Pan D, Gray LJ, Nevill CR, Martin
CA, Nazareth J, Minhas JS, Divall P, Khunti K, Abrams K, et al:
Ethnicity and clinical outcomes in COVID-19: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine. Nov 12–2020.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vahidy FS, Nicolas JC, Meeks JR, Khan O,
Pan A, Jones SL, Masud F, Sostman HD, Phillips R, Andrieni JD, et
al: Racial and ethnic disparities in SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: Analysis
of a COVID-19 observational registry for a diverse US metropolitan
population. BMJ Open. 10:e0398492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Clemens TL, Adams JS, Henderson SL and
Holick MF: Increased skin pigment reduces the capacity of skin to
synthesise vitamin D3. Lancet. 1:74–76. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pavan WJ and Sturm RA: The Genetics of
Human Skin and Hair Pigmentation. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet.
20:41–72. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abdel-Malek ZA and Swope VB: Epidermal
melanocytes: regulation of their survival, proliferation, and
function in human skin. Melanoma Development. Springer; Vienna: pp.
7–33. 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rees JL: Genetics of hair and skin color.
Annu Rev Genet. 37:67–90. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Del Bino S, Duval C and Bernerd F:
Clinical and biological characterization of skin pigmentation
diversity and its consequences on UV impact. Int J Mol Sci.
19:26682018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Costin GE and Hearing VJ: Human skin
pigmentation: Melanocytes modulate skin color in response to
stress. FASEB J. 21:976–994. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Serre C, Busuttil V and Botto JM:
Intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of human skin melanogenesis and
pigmentation. Int J Cosmet Sci. 40:328–347. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu LH, Fan X, Li HT, An XX and Yang RY:
Angiotensin II promotes melanogenesis via angiotensin II type 1
receptors in human melanocytes. Mol Med Rep. 12:651–656. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu LH, Fan X, Xia ZK, An XX and Yang RY:
Angiotensin II stimulates melanogenesis via the protein kinase C
pathway. Exp Ther Med. 10:1528–1532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Steckelings UM, Wollschläger T, Peters J,
Henz BM, Hermes B and Artuc M: Human skin: Source of and target
organ for angiotensin II. Exp Dermatol. 13:148–154. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Brenner M and Hearing VJ: The protective
role of melanin against UV damage in human skin. Photochem
Photobiol. 84:539–549. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Solano F: Photoprotection and skin
pigmentation: melanin-related molecules and some other new agents
obtained from natural sources. Molecules. 25:15372020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Rocha J: The evolutionary history of human
skin pigmentation. J Mol Evol. 88:77–87. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Slominski A and Postlethwaite AE: Skin
under the sun: when melanin pigment meets vitamin D. Endocrinology.
156:1–4. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Bikle DD: Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism
of action, and clinical applications. Chem Biol. 21:319–329. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pearce SH and Cheetham TD: Diagnosis and
management of vitamin D deficiency. BMJ. 340:b56642010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Webb AR, Kazantzidis A, Kift RC, Farrar
MD, Wilkinson J and Rhodes LE: Meeting vitamin D requirements in
White Caucasians at UK latitudes: Providing a choice. Nutrients.
10:4972018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Farrar MD, Kift R, Felton SJ, Berry JL,
Durkin MT, Allan D, Vail A, Webb AR and Rhodes LE: Recommended
summer sunlight exposure amounts fail to produce sufficient vitamin
D status in UK adults of South Asian origin. Am J Clin Nutr.
94:1219–1224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bonilla C, Ness AR, Wills AK, Lawlor DA,
Lewis SJ and Davey Smith G: Skin pigmentation, sun exposure and
vitamin D levels in children of the Avon Longitudinal Study of
Parents and Children. BMC Public Health. 14:5972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hameed A and Akhtar N: The skin melanin:
an inhibitor of vitamin-D3 biosynthesis: with special emphasis with
structure of skin. A mini review Dermatol Case Rep. 4:12019.
|
|
52
|
Richard A, Rohrmann S and Quack Lötscher
KC: Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its associations with
skin color in pregnant women in the first trimester in a sample
from Switzerland. Nutrients. 9:2602017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
53
|
Alzaman NS, Dawson-Hughes B, Nelson J,
D'Alessio D and Pittas AG: Vitamin D status of black and white
Americans and changes in vitamin D metabolites after varied doses
of vitamin D supplementation. Am J Clin Nutr. 104:205–214. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Harris SS: Vitamin D and African
Americans. J Nutr. 136:1126–1129. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
ElObeid AS, Kamal-Eldin A, Abdelhalim MAK
and Haseeb AM: Pharmacological properties of melanin and its
function in health. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 120:515–522.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Mednick AJ, Nosanchuk JD and Casadevall A:
Melanization of Cryptococcus neoformans affects lung inflammatory
responses during cryptococcal infection. Infect Immun.
73:2012–2019. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Patsakas A, Demetriou N and Angelopoulos
A: Melanin pigmentation and inflammation in human gingiva. J
Periodontol. 52:701–704. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Smith JR, Rosenbaum JT and Williams KA:
Experimental melanin-induced uveitis: Experimental model of human
acute anterior uveitis. Ophthalmic Res. 40:136–140. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kaya M, Edward DP, Tessler H and Hendricks
RL: Augmentation of intraocular inflammation by melanin. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 33:522–531. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Pugh ND, Balachandran P, Lata H, Dayan FE,
Joshi V, Bedir E, Makino T, Moraes R, Khan I and Pasco DS: Melanin:
Dietary mucosal immune modulator from Echinacea and other botanical
supplements. Int Immunopharmacol. 5:637–647. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wilms H, Rosenstiel P, Sievers J, Deuschl
G, Zecca L and Lucius R: Activation of microglia by human
neuromelanin is NF-kappaB dependent and involves p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase: Implications for Parkinson's
disease. FASEB J. 17:500–502. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Feller L, Masilana A, Khammissa RA, Altini
M, Jadwat Y and Lemmer J: Melanin: the biophysiology of oral
melanocytes and physiological oral pigmentation. Head Face Med.
10:82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Fritz MA, Roehm PC, Bannan MA and Lalwani
AK: Extracellular and intracellular melanin in inflammatory middle
ear disease. Laryngoscope. 124:E241–E244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Na JY, Kim YH, Choi YD and Lee JS:
Melanotic oncocytic metaplasia of the nasopharynx: A report of
three cases and review of the literature. Korean J Pathol.
46:201–204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hossein-nezhad A and Holick MF: Vitamin D
for health: A global perspective. Mayo Clin Proc. 88:720–755. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wacker M and Holick MF: Sunlight and
vitamin D: A global perspective for health. Dermatoendocrinol.
5:51–108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Holick MF: Vitamin D: Extraskeletal
health. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 39:381–400. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Schwalfenberg GK: A review of the critical
role of vitamin D in the functioning of the immune system and the
clinical implications of vitamin D deficiency. Mol Nutr Food Res.
55:96–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Zdrenghea MT, Makrinioti H, Bagacean C,
Bush A, Johnston SL and Stanciu LA: Vitamin D modulation of innate
immune responses to respiratory viral infections. Rev Med Virol.
27:e19092017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Prietl B, Treiber G, Pieber TR and Amrein
K: Vitamin D and immune function. Nutrients. 5:2502–2521. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hoeck AD and Pall ML: Will vitamin D
supplementation ameliorate diseases characterized by chronic
inflammation and fatigue? Med Hypotheses. 76:208–213. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Jolliffe D, Camargo CA, Sluyter J, Aglipay
M, Aloia J, Bergman P, Damsgaard C, Dubnov-Raz G, Esposito S,
Ganmaa D, et al: Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute
respiratory infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of
aggregate data from randomised controlled trials. medRxiv.
https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.14.20152728urisimplehttps://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.14.20152728.
|
|
73
|
Azmi H, Najwa H and Ennaji MM: Vitamin D
Immunomodulatory Role in Chronic and Acute Viral Diseases. Emerging
and Reemerging Viral Pathogens. Academic Press; 489. pp.
5062020
|
|
74
|
Beard JA, Bearden A and Striker R: Vitamin
D and the anti-viral state. J Clin Virol. 50:194–200. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Greiller CL and Martineau AR: Modulation
of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D.
Nutrients. 7:4240–4270. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Abhimanyu and Coussens AK: The role of UV
radiation and vitamin D in the seasonality and outcomes of
infectious disease. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 16:314–338. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lang PO, Aspinall R and Vitamin D: Vitamin
D status and the host resistance to infections: What it is
currently (not) understood. Clin Ther. 39:930–945. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gruber-Bzura BM: Vitamin D and
influenza-prevention or therapy? Int J Mol Sci. 19:24192018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Rondanelli M, Miccono A, Lamburghini S,
Avanzato I, Riva A, Allegrini P, Faliva MA, Peroni G, Nichetti M
and Perna S: Self-Care for Common Colds: The pivotal role of
Vitamin D, Vitamin C, Zinc, and Echinacea in three main immune
inter-active clusters (physical barriers, innate and adaptive
immunity) involved during an episode of common colds-practical
advice on dosages and on the time to take these
nutrients/botanicals in order to prevent or treat common colds.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018:58130952018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Gombart AF, Pierre A and Maggini S: A
review of micronutrients and the immune system-working in harmony
to reduce the risk of infection. Nutrients. 12:2362020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Teymoori-Rad M, Shokri F, Salimi V and
Marashi SM: The interplay between vitamin D and viral infections.
Rev Med Virol. 29:e20322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Shi YY, Liu TJ, Fu JH, Xu W, Wu LL, Hou AN
and Xue XD: Vitamin D/VDR signaling attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by maintaining the
integrity of the pulmonary epithelial barrier. Mol Med Rep.
13:1186–1194. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
83
|
White JH: Vitamin D as an inducer of
cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide expression: Past, present and
future. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 121:234–238. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Cantorna MT, Snyder L, Lin YD and Yang L:
Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D regulation of T cells.
Nutrients. 7:3011–3021. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Wu D, Lewis ED, Pae M and Meydani SN:
Nutritional modulation of immune function: analysis of evidence,
mechanisms, and clinical relevance. Front Immunol. 9:31602019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Xu S, Chen YH, Tan ZX, Xie DD, Zhang C,
Xia MZ, Wang H, Zhao H, Xu DX and Yu DX: Vitamin D3 pretreatment
alleviates renal oxidative stress in lipopolysaccharide-induced
acute kidney injury. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 152:133–141. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Shi Y, Liu T, Yao L, Xing Y, Zhao X, Fu J
and Xue X: Chronic vitamin D deficiency induces lung fibrosis
through activation of the renin-angiotensin system. Sci Rep.
7:33122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kong J, Zhu X, Shi Y, Liu T, Chen Y, Bhan
I, Zhao Q, Thadhani R and Li YC: VDR attenuates acute lung injury
by blocking Ang-2-Tie-2 pathway and renin-angiotensin system. Mol
Endocrinol. 27:2116–2125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Ferder M, Inserra F, Manucha W and Ferder
L: The world pandemic of vitamin D deficiency could possibly be
explained by cellular inflammatory response activity induced by the
renin-angiotensin system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
304:C1027–C1039. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Ajabshir S, Asif A and Nayer A: The
effects of vitamin D on the renin-angiotensin system. J
Nephropathol. 3:41–43. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Li YC: Vitamin D regulation of the
renin-angiotensin system. J Cell Biochem. 88:327–331. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Li YC, Kong J, Wei M, Chen ZF, Liu SQ and
Cao LP: 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3) is a negative endocrine
regulator of the renin-angiotensin system. J Clin Invest.
110:229–238. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Imai Y, Kuba K, Rao S, Huan Y, Guo F, Guan
B, Yang P, Sarao R, Wada T, Leong-Poi H, et al:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung
failure. Nature. 436:112–116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Treml B, Neu N, Kleinsasser A, Gritsch C,
Finsterwalder T, Geiger R, Schuster M, Janzek E, Loibner H,
Penninger J, et al: Recombinant angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
improves pulmonary blood flow and oxygenation in
lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in piglets. Crit Care Med.
38:596–601. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Nair R, Maseeh A and Vitamin D: Vitamin D:
The 'sunshine' vitamin. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 3:118–126.
2012.
|
|
96
|
Holick MF: The vitamin D deficiency
pandemic: Approaches for diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Rev
Endocr Metab Disord. 18:153–165. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Melamed ML, Michos ED, Post W and Astor B:
25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and the risk of mortality in the general
population. Arch Intern Med. 168:1629–1637. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Mitchell F: Vitamin-D and COVID-19: Do
deficient risk a poorer outcome? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.
8:5702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
House N, Holborn H and Wc L: ICNARC report
on COVID-19 in critical care. ICNARC. 17:1–26. 2020.
|
|
100
|
Ilie PC, Stefanescu S and Smith L: The
role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019
infection and mortality. Aging Clin Exp Res. 32:1195–1198. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Mok CK, Ng YL, Ahidjo BA, Lee RC, Loe MW,
Liu J, Tan KS, Kaur P, Chng WJ, Wong JE, et al: Calcitriol, the
active form of vitamin D, is a promising candidate for COVID-19
prophylaxis. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.21.162396urisimplehttps://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.21.162396.
|
|
102
|
Daneshkhah A, Agrawal V, Eshein A,
Subramanian H, Roy HK and Backman V: Evidence for possible
association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated
inflammation in COVID-19 patients. Aging Clin Exp Res.
32:2141–2158. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|