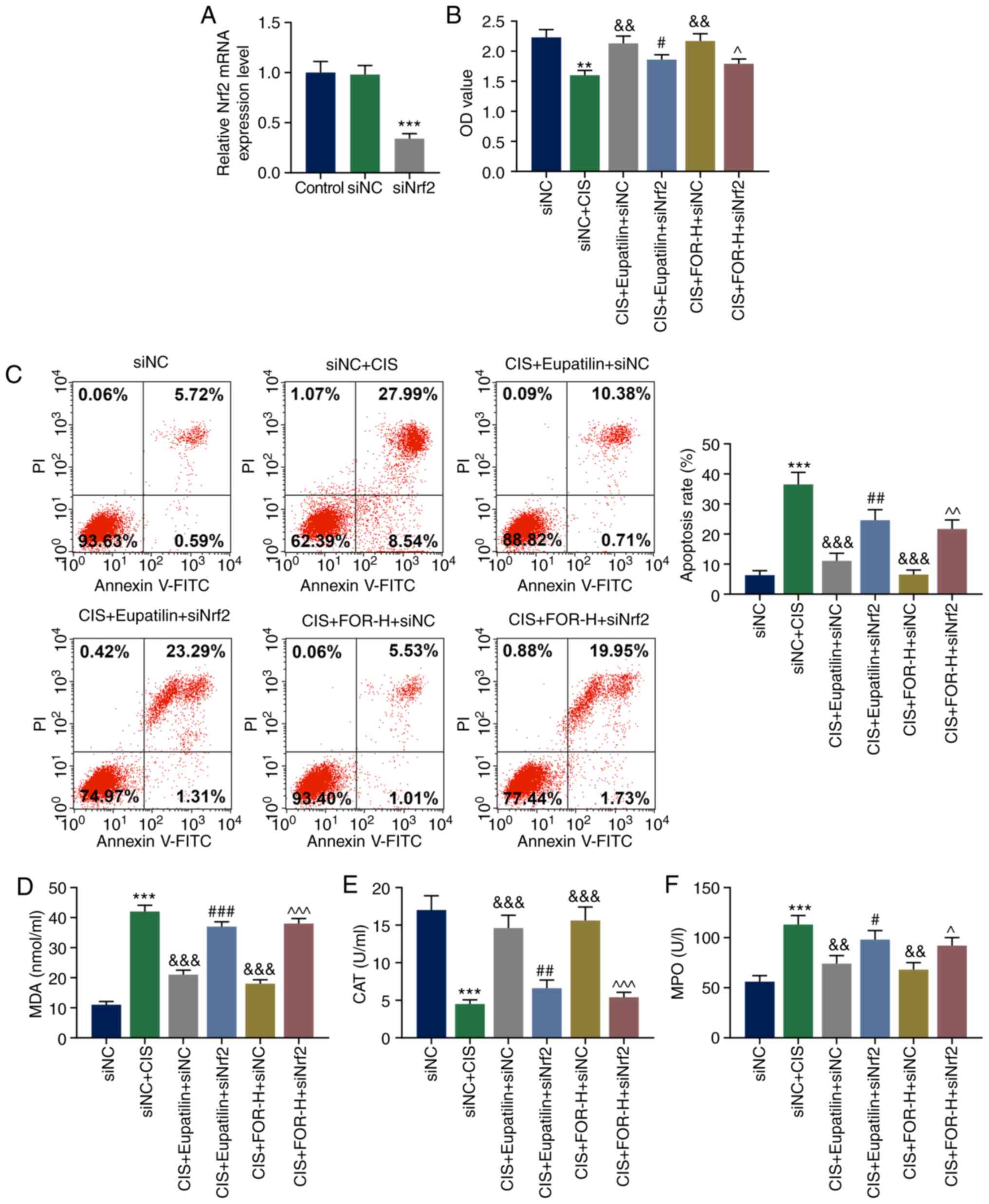
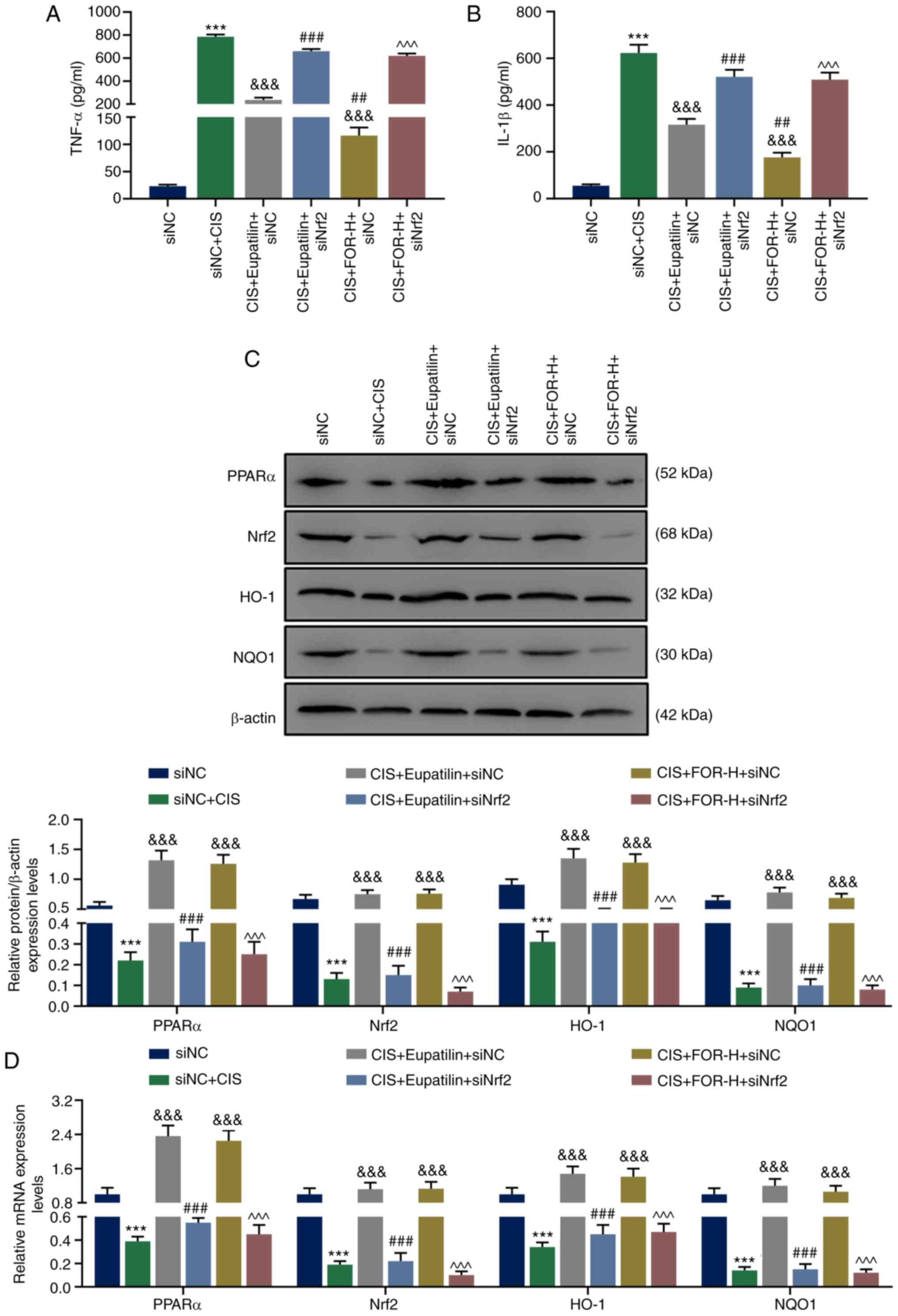
|
1
|
Lee YJ, Chan JP, Hsu WL, Lin KW and Chang
CC: Prognostic factors and a prognostic index for cats with acute
kidney injury. J Vet Intern Med. 26:500–505. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Farrar A: Acute kidney injury. Nurs Clin
North Am. 53:499–510. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brix S and Stahl R: Acute kidney injury.
Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 142:290–300. 2017.In German. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ni J, Hou X, Wang X, Shi Y, Xu L, Zheng X,
Liu N, Qiu A and Zhuang S: 3-deazaneplanocin A protects against
cisplatin-induced renal tubular cell apoptosis and acute kidney
injury by restoration of E-cadherin expression. Cell Death Dis.
10:3552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
de Almeida CDC, Simões E, Silva AC, de
Queiroz Oliveira JA, Batista ISF, Pereira FH, Gonçalves JE, Nobre V
and Martins MAP: Vancomycin-associated nephrotoxicity in
non-critically ill patients admitted in a Brazilian public
hospital: A prospective cohort study. PLoS One. 14:e02220952019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lameire NH, Bagga A, Cruz D, De Maeseneer
J, Endre Z, Kellum JA, Liu KD, Mehta RL, Pannu N, Van Biesen W and
Vanholder R: Acute kidney injury: An increasing global concern.
Lancet. 382:170–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rashid S, Nafees S, Siddiqi A, Vafa A,
Afzal SM, Parveen R, Ali N, Hasan SK, Barnwal P, Shahid A and
Sultana S: Partial protection by 18β glycrrhetinic acid against
cisplatin induced oxidative intestinal damage in wistar rats:
Possible role of NFkB and caspases. Pharmacol Rep. 69:1007–1013.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee H, Lee D, Kang KS, Song JH and Choi
YK: Inhibition of intracellular ROS accumulation by formononetin
attenuates cisplatin-mediated apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:8132018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Li J, Jiang K, Qiu X, Li M, Hao Q, Wei L,
Zhang W, Chen B and Xin X: Overexpression of CXCR4 is significantly
associated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy resistance and can be
a prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian cancer. BMB Rep.
47:33–38. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Park JY, Lee D, Jang HJ, Jang DS, Kwon HC,
Kim KH, Kim SN, Hwang GS, Kang KS and Eom DW: Protective effect of
artemisia asiatica extract and its active compound eupatilin
against cisplatin-induced renal damage. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2015:4839802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang YZ, Zhang J, Tan L, Xia Z, Wang CZ,
Zhou LD, Zhang Q and Yuan CS: Preparation and evaluation of
temperature and magnetic dual-responsive molecularly imprinted
polymers for the specific enrichment of formononetin. J Sep Sci.
41:3060–3068. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang D, Wang C, Duan Y, Meng Q, Liu Z,
Huo X, Sun H, Ma X and Liu K: Targeting Oct2 and P53: Formononetin
prevents cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 326:15–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chtourou Y, Aouey B, Aroui S, Kebieche M
and Fetoui H: Anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of
naringin on cisplatin-induced renal injury in the rat. Chem Biol
Interact. 243:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ning C, Gao X, Wang C, Huo X, Liu Z, Sun
H, Yang X, Sun P, Ma X, Meng Q and Liu K: Protective effects of
ginsenoside Rg1 against lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced
acute liver injury in mice through inhibiting toll-like receptor 4
signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 61:266–276. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hwang JS, Kang ES, Han SG, Lim DS, Paek
KS, Lee CH and Seo HG: Formononetin inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced release of high mobility group box 1 by
upregulating SIRT1 in a PPARδ-dependent manner. Peer J.
6:e42082018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mu H, Bai YH, Wang ST, Zhu ZM and Zhang
YW: Research on antioxidant effects and estrogenic effect of
formononetin from Trifolium pratense (red clover). Phytomedicine.
16:314–319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nguyen LTH, Nguyen UT, Kim YH, Shin HM and
Yang IJ: Astragali Radix and its compound formononetin ameliorate
diesel particulate matter-induced skin barrier disruption by
regulation of keratinocyte proliferation and apoptosis. J
Ethnopharmacol. 228:132–141. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Huang D, Wang C, Meng Q, Liu Z, Huo X, Sun
H, Yang S, Ma X, Peng J and Liu K: Protective effects of
formononetin against rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury by
upregulating NRF2 in vivo and in vitro. RSC Adv. 6:110874–110883.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gonzalez-Manan D, D'Espessailles A, Dossi
CG, San Martin M, Mancilla RA and Tapia GS: Rosa mosqueta oil
prevents oxidative stress and inflammation through the upregulation
of PPAR-α and NRF2 in C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet. J Nutr.
147:579–588. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang WR, Liu EQ, Zhang JY, Li YX, Yang XF,
He YH, Zhang W, Jing T and Lin R: Activation of PPAR alpha by
fenofibrate inhibits apoptosis in vascular adventitial fibroblasts
partly through SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of FoxO1. Exp Cell Res.
338:54–63. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang S, Wei L, Xia R, Liu L, Chen Y, Zhang
W, Li Q, Feng K, Yu M, Zhang W, et al: Formononetin ameliorates
cholestasis by regulating hepatic SIRT1 and PPARα. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 512:770–778. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shen J, Rasmussen M, Dong QR, Tepel M and
Scholze A: Expression of the NRF2 target gene NQO1 is enhanced in
mono-nuclear cells in human chronic kidney disease. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2017:90918792017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cao SS, Yan M, Hou ZY, Chen Y, Jiang YS,
Fan XR, Fang PF and Zhang BK: Danshen modulates Nrf2-mediated
signaling pathway in cisplatin-induced renal injury. J Huazhong
Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 37:761–765. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shelton LM, Park BK and Copple IM: Role of
Nrf2 in protection against acute kidney injury. Kidney Int.
84:1090–1095. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ansari MA: Sinapic acid modulates
Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in
rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 93:646–653. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shen Y, Qiu T, Liu XH, Zhang L, Wang ZS
and Zhou JQ: Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury attenuated by
splenic ischemic preconditioning. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:2134–2142. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Method. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Camano S, Lazaro A, Moreno-Gordaliza E,
Torres AM, de Lucas C, Humanes B, Lazaro JA, Milagros Gomez-Gomez
M, Bosca L and Tejedor A: Cilastatin attenuates cisplatin-induced
proximal tubular cell damage. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 334:419–429.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pabla N and Dong Z: Cisplatin
nephrotoxicity: Mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney
Int. 73:994–1007. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Coelho S, Cabral G, Lopes JA and Jacinto
A: Renal regeneration after acute kidney injury. Nephrology
(Carlton). 23:805–814. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Iwaki T, Bennion BG, Stenson EK, Lynn JC,
Otinga C, Djukovic D, Raftery D, Fei L, Wong HR, Liles WC and
Standage SW: PPARα contributes to protection against metabolic and
inflammatory derangements associated with acute kidney injury in
experimental sepsis. Physiol Rep. 7:e140782019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kong W, Fu J, Liu N, Jiao C, Guo G, Luan
J, Wang H, Yao L, Wang L, Yamamoto M, et al: Nrf2 deficiency
promotes the progression from acute tubular damage to chronic renal
fibrosis following unilateral ureteral obstruction. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 33:771–783. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zoja C, Benigni A and Remuzzi G: The Nrf2
pathway in the progression of renal disease. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 29(Suppl 1): i19–i24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ruiz S, Pergola PE, Zager RA and Vaziri
ND: Targeting the transcription factor Nrf2 to ameliorate oxidative
stress and inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int.
83:1029–1041. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Aladaileh SH, Hussein OE, Abukhalil MH,
Saghir SAM, Bin-Jumah M, Alfwuaires MA, Germoush MO, Almaiman AA
and Mahmoud AM: Formononetin upregulates Nrf2/HO-1 signaling and
prevents oxidative stress, inflammation, and kidney injury in
methotrexate-induced rats. Antioxidants (Basel). 8:4302019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
AL Haithloul HAS, Alotaibi MF, Bin-Jumah
M, Elgebaly H and Mahmoud AM: Olea europaea leaf extract
up-regulates Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 signaling and attenuates
cyclophos-phamide-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and
apoptosis in rat kidney. Biomed Pharmacother. 111:676–685. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Gang GT, Kim YH, Noh JR, Kim KS, Jung JY,
Shong M, Hwang JH and Lee CH: Protective role of NAD(P)H:quinone
oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity.
Toxicol Lett. 221:165–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|