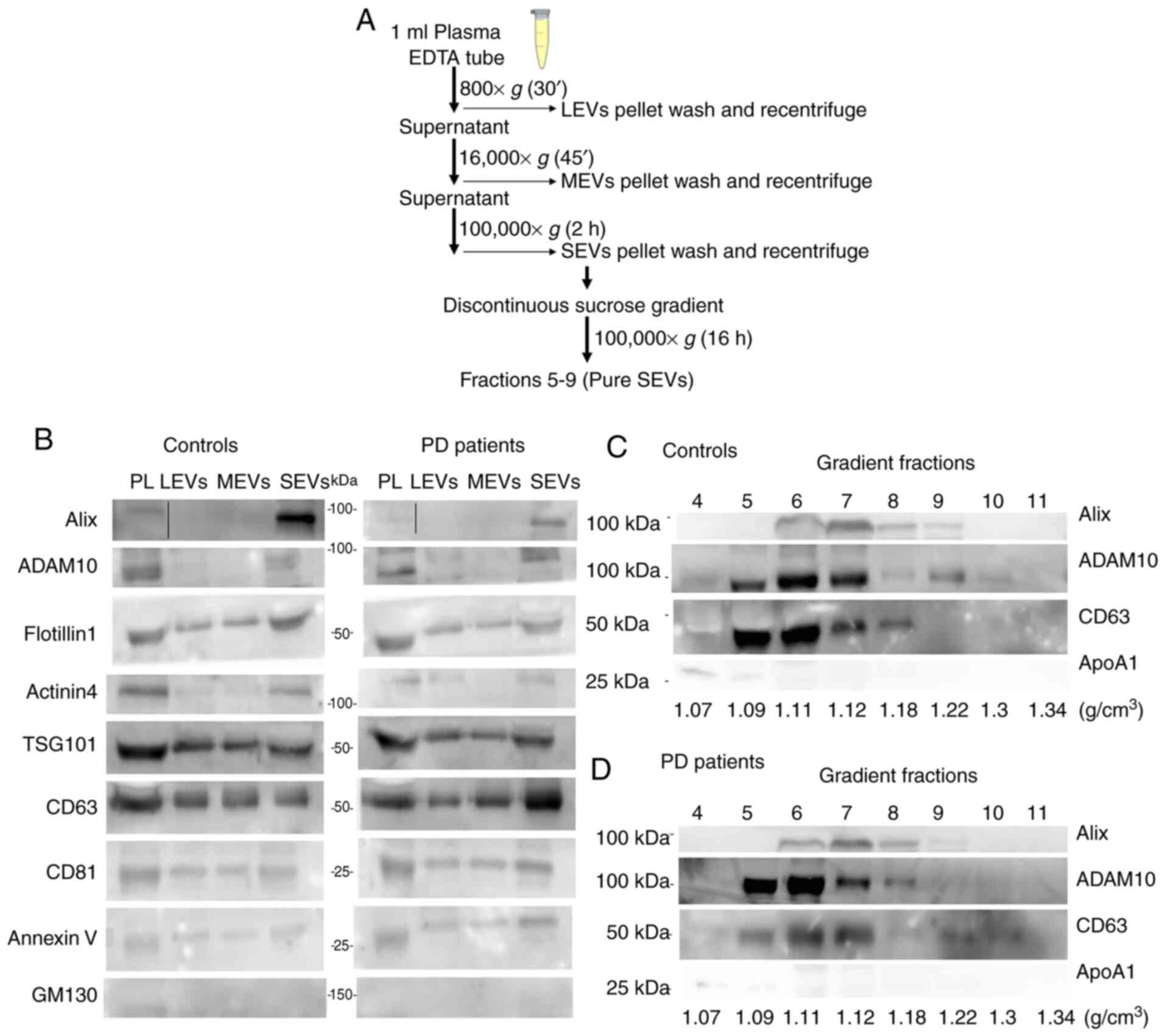
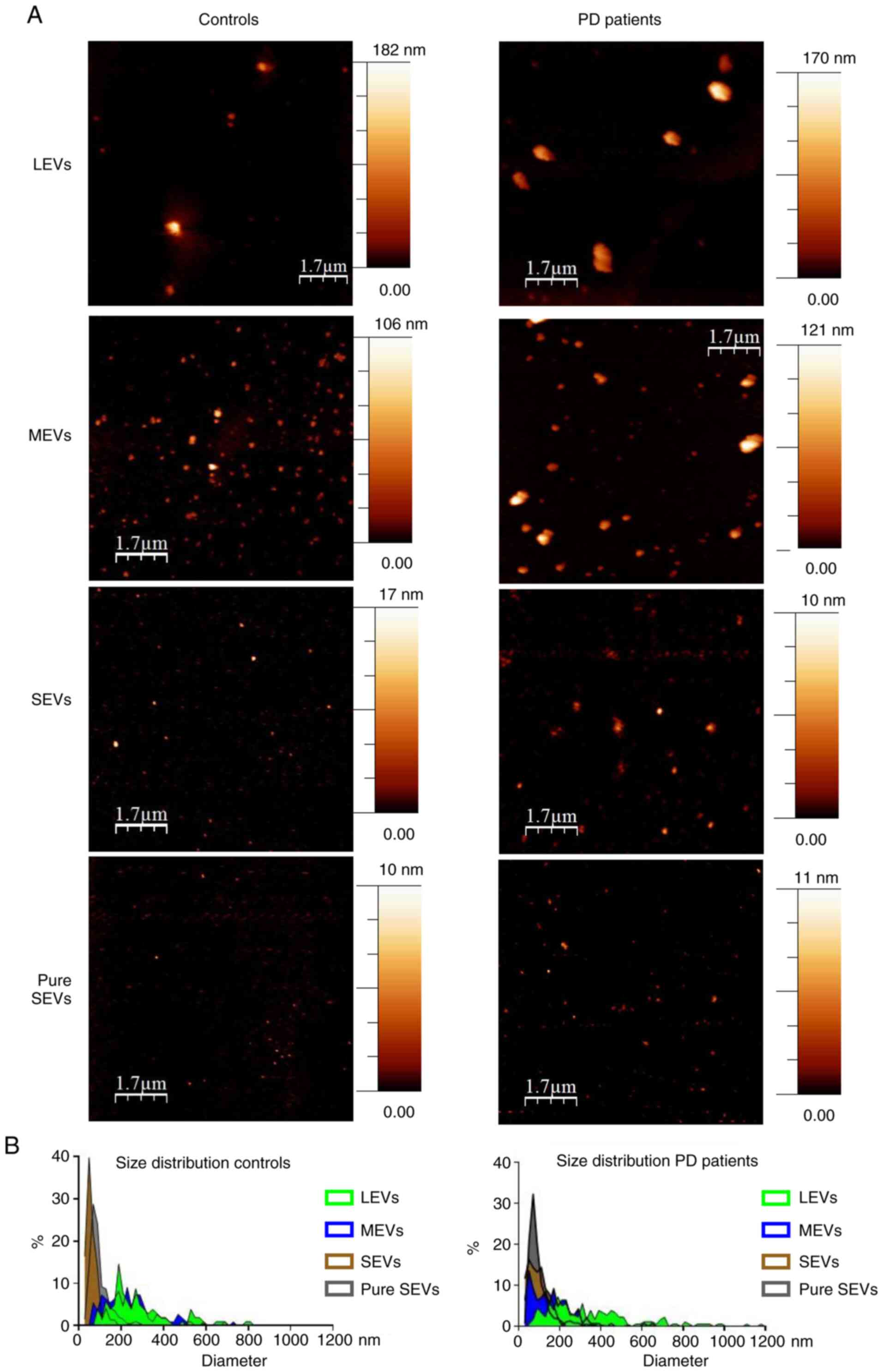
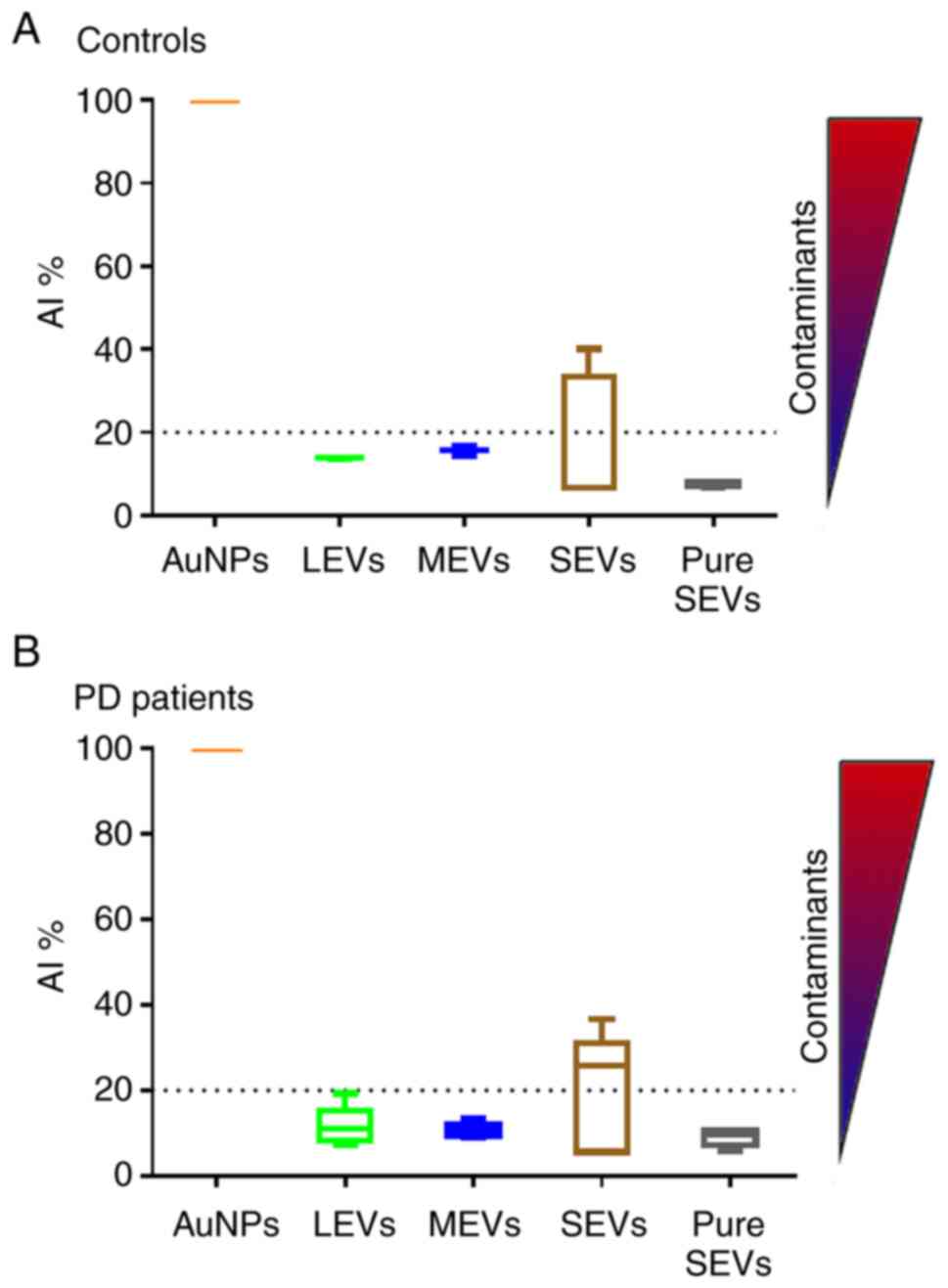
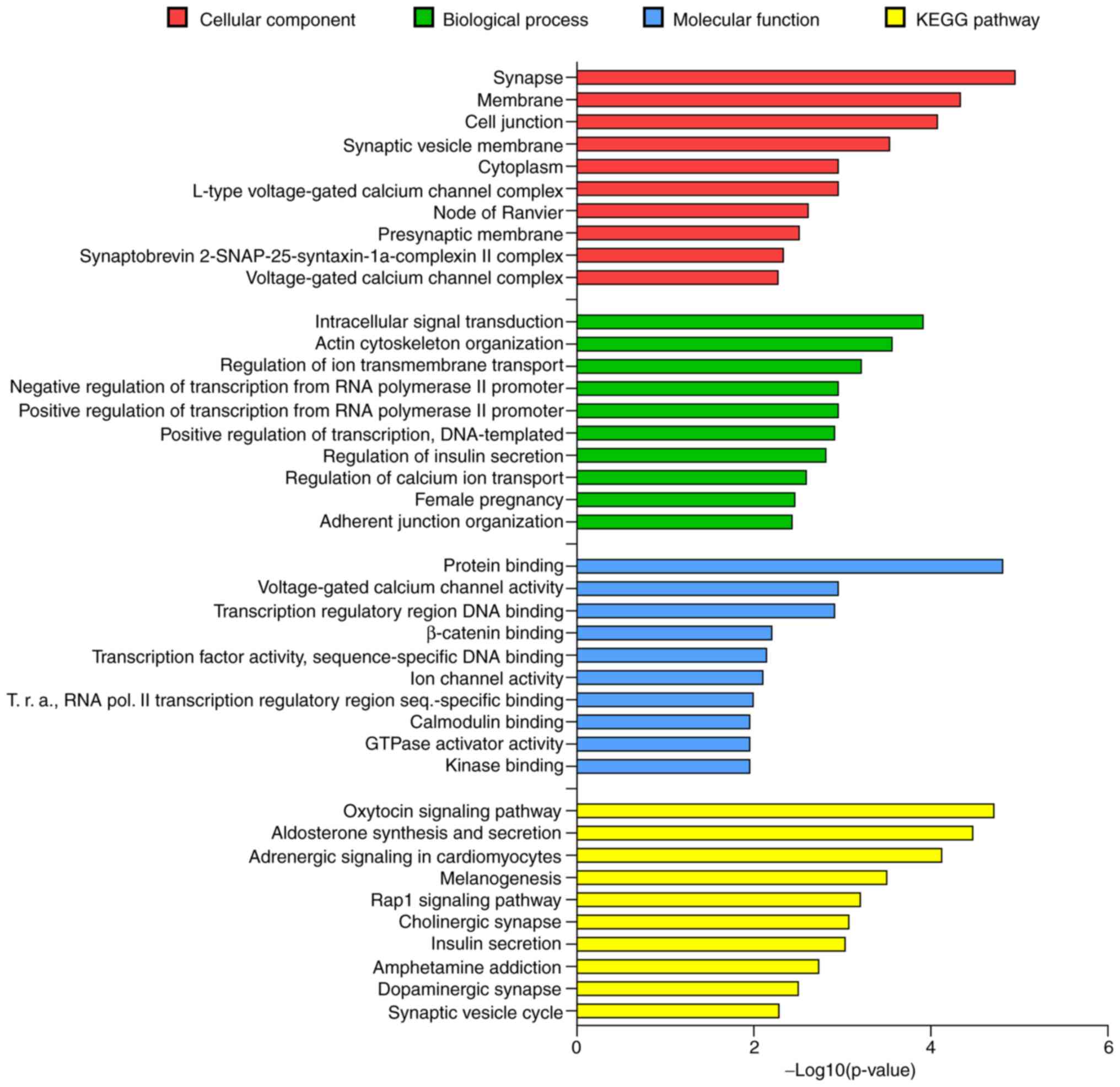
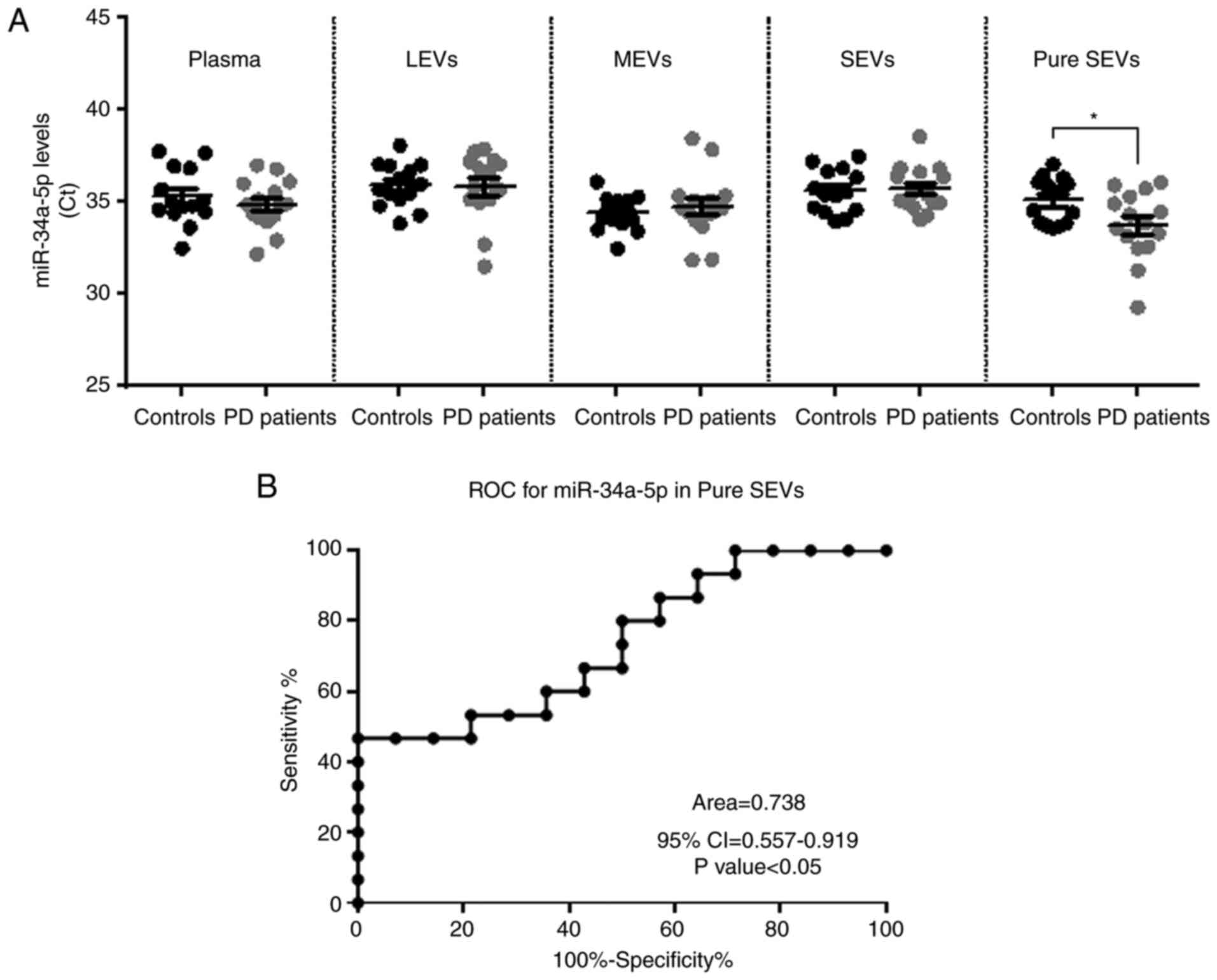
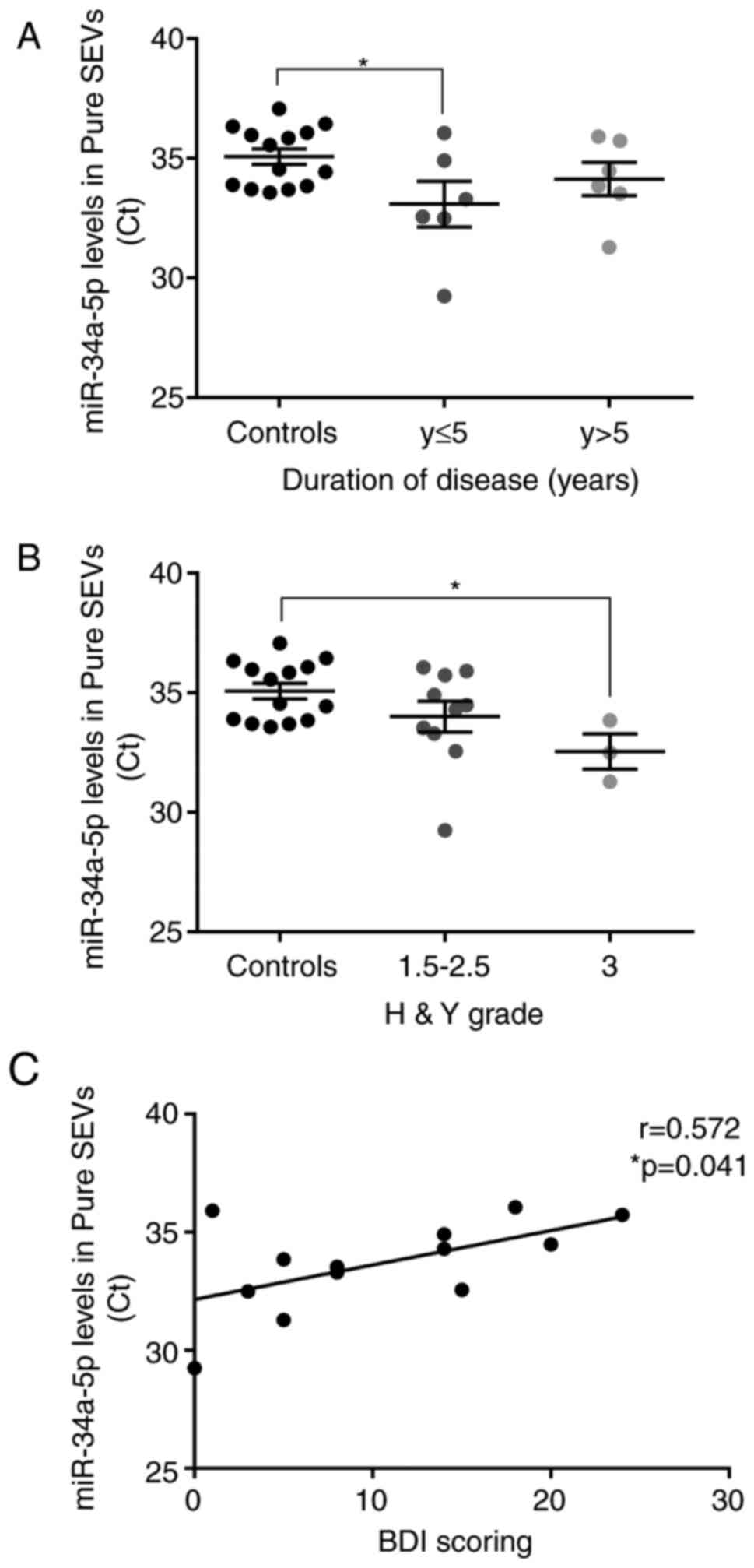
|
1
|
Tysnes OB and Storstein A: Epidemiology of
Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 12:901–905. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Spillantini MG and Goedert M:
Neurodegeneration and the ordered assembly of α-synuclein. Cell
Tissue Res. 373:137–148. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bellucci A, Mercuri NB, Venneri A,
Faustini G, Longhena F, Pizzi M, Missale C and Spano P: parkinson's
disease: From synaptic loss to connectome dysfunction. Neuropathol
Appl Neurobiol. 42:77–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Thompson AG, Gray E, Heman-Ackah SM, Mäger
I, Talbot K, El Andaloussi S, Wood MJ and Turner MR: Extracellular
vesicles in neurodegenerative disease-pathogenesis to biomarkers.
Nat Rev Neurol. 12:346–357. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tofaris GK: A critical assessment of
exosomes in the pathogenesis and stratification of parkinson's
disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 7:569–579. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Paolini L, Federici S, Consoli G, Arceri
D, Radeghieri A, Alessandri I and Bergese P: Fourier-Transform
infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy fingerprints subpopulations of
extracellular vesicles of different sizes and cellular origin. J
Extracell Vesicles. 9:17411742020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tomlinson PR, Zheng Y, Fischer R, Heidasch
R, Gardiner C, Evetts S, Hu M, Wade-Martins R, Turner MR, Morris J,
et al: Identification of distinct circulating exosomes in
parkinson's disease. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2:353–361. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gui YX, Liu H, Zhang LS, Lv W and Hu XY:
Altered microRNA profiles in cerebrospinal fluid exosome in
parkinson disease and alzheimer disease. Oncotarget.
10:37043–37053. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cao XY, Lu JM, Zhao ZQ, Li MC, Lu T, An XS
and Xue LJ: MicroRNA biomarkers of Parkinson's disease in serum
exosome-like microvesicles. Neurosci Lett. 644:94–99. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yao YF, Qu MW, Li GC, Zhang FB and Rui HC:
Circulating exosomal miRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers in parkinson's
disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:5278–5283. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mateescu B, Kowal EJ, van Balkom BW,
Bartel S, Bhattacharyya SN, Buzás EI, Buck AH, de Candia P, Chow
FW, Das S, et al: Obstacles and opportunities in the functional
analysis of extracellular vesicle RNA-an ISEV position paper. J
Extracell vesicles. 6:12860952017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chua CE and Tan BL: MiR-34a in
neurophysiology and neuropathology. J Mol Neurosci. 67:235–246.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
van den Berg MM, Krauskopf J, Ramaekers
JG, Kleinjans JC, Prickaerts J and Briedé JJ: Circulating microRNAs
as potential biomarkers for psychiatric and neurodegenerative
disorders. Prog Neurobiol. 185:1017322020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Goetz CG, Fahn S, Martinez-Martin P, Poewe
W, Sampaio C, Stebbins GT, Stern MB, Tilley BC, Dodel R, Dubois B,
et al: Movement disorder society-sponsored revision of the unified
parkinson's disease rating scale (MDS-UPDRS): Process, format, and
clinimetric testing plan. Mov Disord. 22:41–47. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Goetz CG, Poewe W, Rascol O, Sampaio C,
Stebbins GT, Counsell C, Giladi N, Holloway RG, Moore CG, Wenning
GK, et al: Movement disorder society task force report on the hoehn
and yahr staging scale: Status and recommendations. Mov Disord.
19:1020–1028. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J and
Erbaugh J: An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen
Psychiatry. 4:561–571. 1961. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Witwer KW, Buzás EI, Bemis LT, Bora A,
Lässer C, Lötvall J, Nolte-'t Hoen EN, Piper MG, Sivaraman S, Skog
J, et al: Standardization of sample collection, isolation and
analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell
Vesicles. 2:272013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Coumans FA, Brisson AR, Buzas EI,
Dignat-George F, Drees EE, El-Andaloussi S, Emanueli C, Gasecka A,
Hendrix A, Hill AF, et al: Methodological guidelines to study
extracellular vesicles. Circ Res. 120:1632–1648. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lacroix R, Judicone C, Mooberry M,
Boucekine M, Key NS and Dignat-George F; The ISTH SSC Workshop:
Standardization of pre-analytical variables in plasma microparticle
determination: Results of the international society on thrombosis
and haemostasis SSC collaborative workshop. J Thromb Haemost.
11:11902013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Van Deun J, Mestdagh P, Agostinis P, Akay
Ö, Anand S, Anckaert J, Martinez ZA, Baetens T, Beghein E, Bertier
L, et al: EV-TRACK: Transparent reporting and centralizing
knowledge in extracellular vesicle research. Nat Methods.
28:228–232. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Paolini L, Zendrini A, Di Noto G, Busatto
S, Lottini E, Radeghieri A, Dossi A, Caneschi A, Ricotta D and
Bergese P: Residual matrix from different separation techniques
impacts exosome biological activity. Sci Rep. 6:235502016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Di Noto G, Chiarini M, Paolini LL,
Mazzoldi EL, Giustini V, Radeghieri A, Caimi L and Ricotta D:
Immunoglobulin free light chains and GAGs mediate multiple myeloma
extracellular vesicles uptake and secondary NfκB nuclear
translocation. Front Immunol. 5:5172014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Di Noto G, Paolini L, Zendrini A,
Radeghieri A, Caimi L and Ricotta D: C-Src enriched serum
microvesicles are generated in malignant plasma cell dyscrasia.
PLoS One. 8:e708112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paolini L, Radeghieri A, Civini S, Caimi L
and Ricotta D: The epsilon hinge-ear region regulates membrane
localization of the AP-4 complex. Traffic. 12:1604–1619. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alvisi G, Paolini L, Contarini A, Zambarda
C, Di Antonio V, Colosini A, Mercandelli N, Timmoneri M, Palù G,
Caimi L, et al: Intersectin goes nuclear: Secret life of an
endocytic protein. Biochem J. 475:1455–1472. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jeppesen DK, Fenix AM, Franklin JL,
Higginbotham JN, Zhang Q, Zimmerman LJ, Liebler DC, Ping J, Liu Q,
Evans R, et al: Reassessment of exosome composition. Cell.
177:428–445. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kowal J, Arras G, Colombo M, Jouve M,
Morath JP, Primdal-Bengtson B, Dingli F, Loew D, Tkach M and Théry
C: Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize
heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:E968–E977. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Radeghieri A, Savio G, Zendrini A, Di Noto
G, Salvi A, Bergese P and Piovani G: Cultured human amniocytes
express hTERT, which is distributed between nucleus and cytoplasm
and is secreted in extracellular vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 483:706–711. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Berardocco M, Radeghieri A, Busatto S,
Gallorini M, Raggi C, Gissi C, D'Agnano I, Bergese P, Felsani A and
Berardi AC: RNA-Seq reveals distinctive RNA profiles of small
extracellular vesicles from different human liver cancer cell
lines. Oncotarget. 8:82920–82939. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vescovi R, Monti M, Moratto D, Paolini L,
Consoli F, Benerini L, Melocchi L, Calza S, Chiudinelli M, Rossi G,
et al: Collapse of the plasmacytoid dendritic cell compartment in
advanced cuta-neous melanomas by components of the tumor cell
secretome. Cancer Immunol Res. 7:12–28. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Horcas I, Fernández R, Gómez-Rodríguez JM,
Colchero J, Gómez-Herrero J and Baro AM: WSXM: A software for
scanning probe microscopy and a tool for nanotechnology. Rev Sci
Instrum. 78:0137052007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maiolo D, Paolini L, Di Noto G, Zendrini
A, Berti D, Bergese P and Ricotta D: Colorimetric nanoplasmonic
assay to determine purity and titrate extracellular vesicles. Anal
Chem. 87:4168–4176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zendrini A, Paolini L, Busatto S,
Radeghieri A, Romano M, Wauben MH, van Herwijnen MJ, Nejsum P,
Borup A, Ridolfi A, et al: Augmented COlorimetric NANoplasmonic
(CONAN) method for grading purity and determine concentration of EV
microliter volume solutions. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 7:4522019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Salvi A, Vezzoli M, Busatto S, Paolini L,
Faranda T, Abeni E, Caracausi M, Antonaros F, Piovesan A, Locatelli
C, et al: Analysis of a nanoparticle-enriched fraction of plasma
reveals miRNA candidates for down syndrome pathogenesis. Int J Mol
Med. 43:2303–2318. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sticht C, De La Torre C, Parveen A and
Gretz N: Mirwalk: An online resource for prediction of microrna
binding sites. PLoS One. 18:e02062392018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Dennis G, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J,
Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Grossi I, Salvi A, Abeni E, Marchina E and
De Petro G: Biological function of MicroRNA193a-3p in health and
disease. Int J Genomics. 2017:59131952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Faranda T, Grossi I, Manganelli M,
Marchina E, Baiocchi G, Portolani N, Crosatti M, De Petro G and
Salvi A: Differential expression profiling of long non-coding RNA
GAS5 and miR-126-3p in human cancer cells in response to sorafenib.
Sci Rep. 9:91182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Grossi I, Arici B, Portolani N, De Petro G
and Salvi A: Clinical and biological significance of miR-23b and
miR-193a in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:6955–6969. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ,
Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, Antoniou A, Arab T, Archer F,
Atkin-Smith GK, et al: Minimal information for studies of
extra-cellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of
the international society for extracellular vesicles and update of
the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 7:15357502018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Mollinari C, Racaniello M, Berry A, Pieri
M, De Stefano MC, Cardinale A, Zona C, Cirulli F, Garaci E and
Merlo D: MiR-34a regulates cell proliferation, morphology and
function of newborn neurons resulting in improved behavioural
outcomes. Cell Death Dis. 6:e16222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Agostini M, Tucci P, Steinert JR,
Shalom-Feuerstein R, Rouleau M, Aberdam D, Forsythe ID, Young KW,
Ventura A, Concepcion CP, et al: microRNA-34a regulates neurite
outgrowth, spinal morphology, and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:21099–21104. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Morgado AL, Xavier JM, Dionísio PA,
Ribeiro MF, Dias RB, Sebastião AM, Solá S and Rodrigues CM:
MicroRNA-34a modulates neural stem cell differentiation by
regulating expression of synaptic and autophagic proteins. Mol
Neurobiol. 51:1168–11183. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Bavamian S, Mellios N, Lalonde J, Fass DM,
Wang J, Sheridan SD, Madison JM, Zhou F, Rueckert EH, Barker D, et
al: Dysregulation of miR-34a links neuronal development to genetic
risk factors for bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 20:573–584.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Modi PK, Jaiswal S and Sharma P:
Regulation of neuronal cell cycle and apoptosis by MicroRNA 34a.
Mol Cell Biol. 36:84–94. 2016.
|
|
46
|
Wang X, Liu P, Zhu H, Xu Y, Ma C, Dai X,
Huang L, Liu Y, Zhang L and Qin C: MiR-34a, a microRNA up-regulated
in a double transgenic mouse model of alzheimer's disease, inhibits
bcl2 translation. Brain Res Bull. 28:268–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Aranha MM, Santos DM, Solá S, Steer CJ and
Rodrigues MP: MiR-34a regulates mouse neural stem cell
differentiation. PLoS One. 6:e213962011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dias BG, Goodman JV, Ahluwalia R, Easton
AE, Andero R and Ressler KJ: Amygdala-Dependent Fear Memory
Consolidation via miR-34a and Notch Signaling. Neuron. 20:906–918.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Liu N, Landreh M, Cao K, Abe M, Hendriks
GJ, Kennerdell JR, Zhu Y, Wang LS and Bonini NM: The microRNA
miR-34 modulates ageing and neurodegeneration in drosophila.
Nature. 15:519–523. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kennerdell JR, Liu N and Bonini NM: MiR-34
inhibits poly-comb repressive complex 2 to modulate chaperone
expression and promote healthy brain aging. Nat Commun.
10:41882018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Cheng L, Sharples RA, Scicluna BJ and Hill
AF: Exosomes provide a protective and enriched source of miRNA for
biomarker profiling compared to intracellular and cell-free blood.
J Extracell Vesicles. 3:262014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Leggio L, Vivarelli S, L'Episcopo F,
Tirolo C, Caniglia S, Testa N, Marchetti B and Iraci N: MicroRNAs
in parkinson's disease: From pathogenesis to novel diagnostic and
therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 18:26982017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wang L and Zhang L: Circulating exosomal
miRNA as diag-nostic biomarkers of neurodegenerative diseases.
Front Mol Neurosci. 13:532020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Crescitelli R, Lässer C, Szabó TG, Kittel
A, Eldh M, Dianzani I, Buzás EI and Lötvall J: Distinct RNA
profiles in subpopulations of extracellular vesicles: Apoptotic
bodies, microvesicles and exosomes. J Extracell vesicles. 2:122013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Lunavat TR, Cheng L, Kim DK, Bhadury J,
Jang SC, Lässer C, Sharples RA, López MD, Nilsson J, Gho YS, et al:
Small RNA deep sequencing discriminates subsets of extracellular
vesicles released by melanoma cells-Evidence of unique microRNA
cargos. RNA Biol. 12:810–823. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
56
|
Enderle D, Spiel A, Coticchia CM, Berghoff
E, Mueller R, Schlumpberger M, Sprenger-Haussels M, Shaffer JM,
Lader E, Skog J and Noerholm M: Characterization of RNA from
exosomes and other extracellular vesicles isolated by a novel spin
column-based method. PLoS One. 10:e01361332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ravanidis S, Bougea A, Papagiannakis N,
Maniati M, Koros C, Simitsi A, Bozi M, Pachi I, Stamelou M,
Paraskevas GP, et al: Circulating brain-enriched MicroRNAs for
detection and discrimination of idiopathic and genetic parkinson's
disease. Mov Disord. 35:457–467. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Bak M, Silahtaroglu A, Møller M,
Christensen M, Rath MF, Skryabin B, Tommerup N and Kauppinen S:
MicroRNA expression in the adult mouse central nervous system. RNA.
14:432–444. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jauhari A, Singh T, Singh P, Parmar D and
Yadav S: Regulation of miR-34 family in neuronal development. Mol
Neurobiol. 55:936–945. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Sarkar S, Jun S, Rellick S, Quintana DD,
Cavendish JZ and Simpkins JW: Expression of microRNA-34a in
alzheimer's disease brain targets genes linked to synaptic
plasticity, energy metabolism, and resting state network activity.
Brain Res. 1646:139–151. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Agostini M, Tucci P, Killick R, Candi E,
Sayan BS, di Val Cervo PR, Nicoterad P, McKeon F, Knight RA, Mak TW
and Melino G: Neuronal differentiation by TAp73 is mediated by
microRNA-34a regulation of synaptic protein targets. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:21093–21098. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Briggs CE, Wang Y, Kong B, Woo TU, Iyer LK
and Sonntag KC: Midbrain dopamine neurons in parkinson's disease
exhibit a dysregulated miRNA and target-gene network. Brain Res.
1618:111–121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Delavar RM, Baghi M, Safaeinejad Z,
Kiani-Esfahani A, Ghaedi K and Nasr-Esfahani MH: Differential
expression of miR-34a, miR-141, and miR-9 in
MPP+-treated differentiated PC12 cells as a model of
parkinson's disease. Gene. 662:54–65. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Horst CH, Schlemmer F, de Aguiar
Montenegro N, Domingues AC, Ferreira GG, da Silva Ribeiro CY, de
Andrade RR, Del Bel Guimarães E, Titze-de-Almeida SS and
Titze-de-Almeida R: Signature of aberrantly expressed microRNAs in
the striatum of rotenone-induced parkinsonian rats. Neurochem Res.
43:2132–2140. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ba Q, Cui C, Wen L, Feng S, Zhou J and
Yang K: Schisandrin B shows neuroprotective effect in
6-OHDA-induced parkinson's disease via inhibiting the negative
modulation of miR-34a on Nrf2 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
75:165–172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Alural B, Ozerdem A, Allmer J, Genc K and
Genc S: Lithium protects against paraquat neurotoxicity by NRF2
activation and miR-34a inhibition in SH-SY5Y cells. Front Cell
Neurosci. 9:2092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Horst CH, Titze-De-Almeida R and
Titze-De-Almeida SS: The involvement of eag1 potassium channels and
miR-34a in rotenone-induced death of dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells.
Mol Med Rep. 15:1479–1488. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Cosín-Tomás M, Antonell A, Lladó A,
Alcolea D, Fortea J, Ezquerra M, Lleó A, Martí MJ, Pallàs M,
Sanchez-Valle R, et al: Plasma miR-34a-5p and miR-545-3p as early
biomarkers of alzheimer's disease: Potential and limitations. Mol
Neurobiol. 54:5550–5562. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Mao S, Sun Q, Xiao H, Zhang C and Li L:
Secreted miR-34a in astrocytic shedding vesicles enhanced the
vulnerability of dopaminergic neurons to neurotoxins by targeting
Bcl-2. Protein Cell. 6:529–540. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wan Y, Liu Y, Wang X, Wu J, Liu K, Zhou J,
Liu L and Zhang C: Identification of differential microRNAs in
cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with major depressive
disorder. PLoS One. 10:e01219752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ohmichi T, Mitsuhashi M, Tatebe H, Kasai
T, El-Agnaf OA and Tokuda T: Quantification of brain-derived
extracellular vesicles in plasma as a biomarker to diagnose
parkinson's and related diseases. Park Relat Disord. 61:82–87.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|