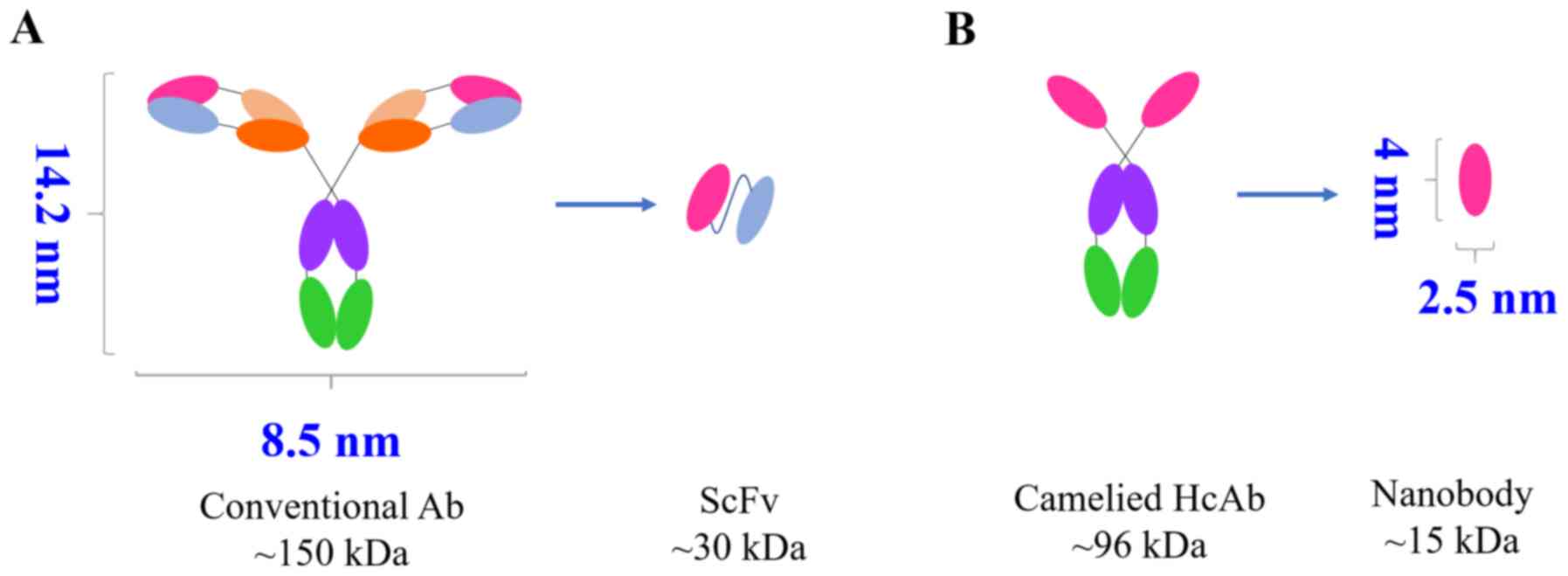
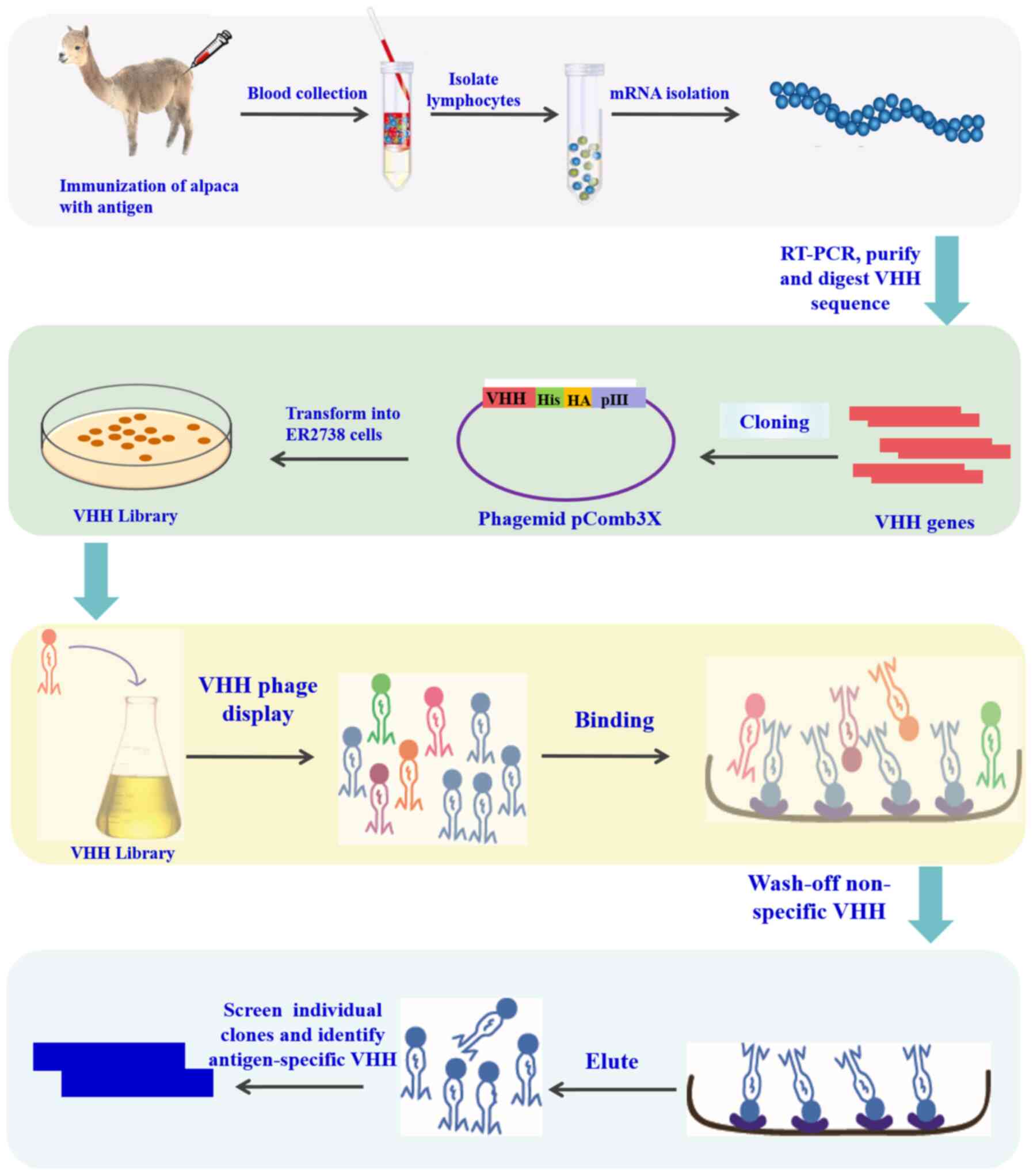
|
1
|
Frankel T, Lanfranca MP and Zou W: The
role of tumor micro-environment in cancer immunotherapy. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 1036:51–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fan CA, Reader J and Roque DM: Review of
immune therapies targeting ovarian cancer. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 19:742018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marin-Acevedo JA, Soyano AE, Dholaria B,
Knutson KL and Lou Y: Cancer immunotherapy beyond immune checkpoint
inhibitors. J Hematol Oncol. 11:82018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marin-Acevedo JA, Dholaria B, Soyano AE,
Knutson KL, Chumsri S and Lou Y: Next generation of immune
checkpoint therapy in cancer: New developments and challenges. J
Hematol Oncol. 11:392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ok CY and Young KH: Checkpoint inhibitors
in hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 10:1032017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baghdadi M, Takeuchi S, Wada H and Seino
K: Blocking mono-clonal antibodies of TIM proteins as orchestrators
of anti-tumor immune response. MAbs. 6:1124–1132. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rodallec A, Sicard G, Fanciullino R,
Benzekry S, Lacarelle B, Milano G and Ciccolini J: Turning cold
tumors into hot tumors: Harnessing the potential of tumor immunity
using nanoparticles. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 14:1139–1147.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nishino M, Ramaiya NH, Hatabu H and Hodi
FS: Monitoring immune-checkpoint blockade: Response evaluation and
biomarker development. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:655–668. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Darvin P, Toor SM, Sasidharan Nair V and
Elkord E: Immune checkpoint inhibitors: Recent progress and
potential biomarkers. Exp Mol Med. 50:1–11. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hargadon KM, Johnson CE and Williams CJ:
Immune checkpoint blockade therapy for cancer: An overview of
FDA-approved immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int Immunopharmacol.
62:29–39. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shen H, Yang ES, Conry M, Fiveash J,
Contreras C, Bonner JA and Shi LZ: Predictive biomarkers for immune
checkpoint blockade and opportunities for combination therapies.
Genes Dis. 6:232–246. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kamath SD, Kalyan A and Benson AB III:
Pembrolizumab for the treatment of gastric cancer. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 18:1177–1187. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hsu FS, Su CH and Huang KH: A
comprehensive review of US FDA-approved immune checkpoint
inhibitors in urothelial carcinoma. J Immunol Res.
2017:69405462017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Song MK, Park BB and Uhm J: Understanding
immune evasion and therapeutic targeting associated with PD-1/PD-L1
pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int J Mol Sci.
20:13262019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Michot JM, Bigenwald C, Champiat S,
Collins M, Carbonnel F, Postel-Vinay S, Berdelou A, Varga A,
Bahleda R, Hollebecque A, et al: Immune-related adverse events with
immune checkpoint blockade: A comprehensive review. Eur J Cancer.
54:139–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bannas P, Hambach J and Koch-Nolte F:
Nanobodies and nanobody-based human heavy chain antibodies as
antitumor therapeutics. Front Immunol. 8:16032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ubah OC, Buschhaus MJ, Ferguson L,
Kovaleva M, Steven J, Porter AJ and Barelle CJ: Next-generation
flexible formats of VNAR domains expand the drug platform's utility
and developability. Biochem Soc Trans. 46:1559–1565. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang H, Meng AM, Li SH and Zhou XL: A
nanobody targeting carcinoembryonic antigen as a promising
molecular probe for non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Med Rep.
16:625–630. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Broos K, Lecocq Q, Raes G, Devoogdt N,
Keyaerts M and Breckpot K: Noninvasive imaging of the PD-1:PD-L1
immune checkpoint: Embracing nuclear medicine for the benefit of
personalized immunotherapy. Theranostics. 8:3559–3570. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mayer AT, Natarajan A, Gordon SR, Maute
RL, McCracken MN, Ring AM, Weissman IL and Gambhir SS: Practical
immuno-PET radiotracer design considerations for human immune
checkpoint imaging. J Nucl Med. 58:538–546. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Natarajan A, Mayer AT, Reeves RE, Nagamine
CM and Gambhir SS: Development of novel ImmunoPET tracers to image
human PD-1 checkpoint expression on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
in a humanized mouse model. Mol Imaging Biol. 19:903–914. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li M, Ehlerding EB, Jiang D, Barnhart TE,
Chen W, Cao T, Engle JW and Cai W: In vivo characterization of
PD-L1 expression in breast cancer by immuno-PET with
89Zr-labeled avelumab. Am J Transl Res. 12:1862–1872.
2020.
|
|
23
|
Kikuchi M, Clump DA, Srivastava RM, Sun L,
Zeng D, Diaz-Perez JA, Anderson CJ, Edwards WB and Ferris RL:
Preclinical immunoPET/CT imaging using Zr-89-labeled anti-PD-L1
monoclonal antibody for assessing radiation-induced PD-L1
upregulation in head and neck cancer and melanoma. Oncoimmunology.
6:e13290712017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li D, Zou S, Cheng S, Song S, Wang P and
Zhu X: Monitoring the response of PD-L1 expression to epidermal
growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in nonsmall-cell
lung cancer xenografts by immuno-PET imaging. Mol Pharm.
16:3469–3476. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
González Trotter DE, Meng X, McQuade P,
Rubins D, Klimas M, Zeng Z, Connolly BM, Miller PJ, O'Malley SS,
Lin SA, et al: In vivo imaging of the programmed death ligand 1 by
18F PET. J Nucl Med. 58:1852–1857. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hettich M, Braun F, Bartholomä MD,
Schirmbeck R and Niedermann G: High-resolution PET imaging with
therapeutic antibody-based PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint tracers.
Theranostics. 6:1629–1640. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heskamp S, Hobo W, Molkenboer-Kuenen JD,
Olive D, Oyen WJ, Dolstra H and Boerman OC: Noninvasive imaging of
tumor PD-L1 expression using radiolabeled anti-PD-L1 antibodies.
Cancer Res. 75:2928–2936. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li D, Cheng S, Zou S, Zhu D, Zhu T, Wang P
and Zhu X: Immuno-PET imaging of 89Zr labeled anti-PD-L1
domain anti-body. Mol Pharm. 15:1674–1681. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Josefsson A, Nedrow JR, Park S, Banerjee
SR, Rittenbach A, Jammes F, Tsui B and Sgouros G: Imaging,
biodistribution, and dosimetry of radionuclide-labeled PD-L1
antibody in an immunocompetent mouse model of breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 76:472–479. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Natarajan A, Patel CB, Habte F and Gambhir
SS: Dosimetry prediction for clinical translation of
64Cu-pembrolizumab ImmunoPET targeting human PD-1
expression. Sci Rep. 8:6332018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Van Audenhove I and Gettemans J:
Nanobodies as versatile tools to understand, diagnose, visualize
and treat cancer. EBioMedicine. 8:40–48. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lecocq Q, De Vlaeminck Y, Hanssens H,
D'Huyvetter M, Raes G, Goyvaerts C, Keyaerts M, Devoogdt N and
Breckpot K: Theranostics in immunooncology using nanobody
derivatives. Theranostics. 9:7772–7791. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Hamers-Casterman C, Atarhouch T,
Muyldermans S, Robinson G, Hamers C, Songa EB, Bendahman N and
Hamers R: Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains.
Nature. 363:446–448. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Muyldermans S: Nanobodies: Natural
single-domain antibodies. Annu Rev Biochem. 82:775–797. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Könning D, Zielonka S, Grzeschik J,
Empting M, Valldorf B, Krah S, Schröter C, Sellmann C, Hock B and
Kolmar H: Camelid and shark single domain antibodies: Structural
features and therapeutic potential. Curr Opin Struct Biol.
45:10–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Krah S, Schröter C, Zielonka S, Empting M,
Valldorf B and Kolmar H: Single-domain antibodies for biomedical
applications. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 38:21–28. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Steeland S, Vandenbroucke RE and Libert C:
Nanobodies as therapeutics: Big opportunities for small antibodies.
Drug Discov Today. 21:1076–1113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Stijlemans B, De Baetselier P, Caljon G,
Van Den Abbeele J, Van Ginderachter JA and Magez S: Nanobodies as
tools to understand, diagnose, and treat African trypanosomiasis.
Front Immunol. 8:7242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hassanzadeh-Ghassabeh G, Devoogdt N, De
Pauw P, Vincke C and Muyldermans S: Nanobodies and their potential
applications. Nanomedicine (Lond). 8:1013–1026. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Arezumand R, Alibakhshi A, Ranjbari J,
Ramazani A and Muyldermans S: Nanobodies as novel agents for
targeting angio-genesis in solid cancers. Front Immunol.
8:17462017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Van Heeke G, Allosery K, De Brabandere V,
De Smedt T, Detalle L and de Fougerolles A: Nanobodies®
as inhaled biotherapeutics for lung diseases. Pharmacol Ther.
169:47–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Massa S, Xavier C, Muyldermans S and
Devoogdt N: Emerging site-specific bioconjugation strategies for
radioimmunotracer development. Expert Opin Drug Deliv.
13:1149–1163. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Massa S, Vikani N, Betti C, Ballet S,
Vanderhaegen S, Steyaert J, Descamps B, Vanhove C, Bunschoten A,
van Leeuwen FW, et al: Sortase A-mediated site-specific labeling of
camelid single-domain antibody-fragments: A versatile strategy for
multiple molecular imaging modalities. Contrast Media Mol Imaging.
11:328–339. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Oliveira S, Heukers R, Sornkom J, Kok RJ,
van Bergen EN and Henegouwen PM: Targeting tumors with nanobodies
for cancer imaging and therapy. J Control Release. 172:607–617.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Iezzi ME, Policastro L, Werbajh S,
Podhajcer O and Canziani GA: Single-domain antibodies and the
promise of modular targeting in cancer imaging and treatment. Front
Immunol. 9:2732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hu Y, Liu C and Muyldermans S:
Nanobody-based delivery systems for diagnosis and targeted tumor
therapy. Front Immunol. 8:14422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Beghein E and Gettemans J: Nanobody
technology: A versatile toolkit for microscopic imaging,
protein-protein interaction analysis, and protein function
exploration. Front Immunol. 8:7712017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Menzel S, Rissiek B, Haag F, Goldbaum FA
and Koch-Nolte F: The art of blocking ADP-ribosyltransferases
(ARTs): Nanobodies as experimental and therapeutic tools to block
mammalian and toxin ARTs. FEBS J. 280:3543–3550. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Unger M, Eichhoff AM, Schumacher L,
Strysio M, Menzel S, Schwan C, Alzogaray V, Zylberman V, Seman M,
Brandner J, et al: Selection of nanobodies that block the
enzy-matic and cytotoxic activities of the binary clostridium
difficile toxin CDT. Sci Rep. 5:78502015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Mars A, Bouhaouala-Zahar B and Raouafi N:
Ultrasensitive sensing of androctonus australis hector scorpion
venom toxins in biological fluids using an electrochemical graphene
quantum dots/nanobody-based platform. Talanta. 190:182–187. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Singh A, Pasha SK, Manickam P and Bhansali
S: Single-domain antibody based thermally stable electrochemical
immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 83:162–168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhu Z, Shi L, Feng H and Zhou HS: Single
domain antibody coated gold nanoparticles as enhancer for
Clostridium difficile toxin detection by electrochemical impedance
immunosensors. Bioelectrochemistry. 101:153–158. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Li G, Zhu M, Ma L, Yan J, Lu X, Shen Y and
Wan Y: Generation of small single domain nanobody binders for
sensitive detection of testosterone by electrochemical impedance
spectroscopy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 8:13830–13839. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li H, Sun Y, Elseviers J, Muyldermans S,
Liu S and Wan Y: A nanobody-based electrochemiluminescent
immunosensor for sensitive detection of human procalcitonin.
Analyst. 139:3718–3721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu X, Wen Y, Wang W, Zhao Z, Han Y, Tang
K and Wang D: Nanobody-based electrochemical competitive
immunosensor for the detection of AFB1 through
AFB1-HCR as signal amplifier. Mikrochim Acta.
187:3522020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Liu A, Yin K, Mi L, Ma M, Liu Y, Li Y, Wei
W, Zhang Y and Liu S: A novel photoelectrochemical immunosensor by
integration of nanobody and ZnO nanorods for sensitive detection of
nucleoside diphosphatase kinase-A. Anal Chim Acta. 973:82–90. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou Q, Li G, Zhang Y, Zhu M, Wan Y and
Shen Y: Highly selective and sensitive electrochemical immunoassay
of Cry1C using nanobody and π-π stacked graphene oxide/thionine
assembly. Anal Chem. 88:9830–9836. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Steeland S, Puimège L, Vandenbroucke RE,
Van Hauwermeiren F, Haustraete J, Devoogdt N, Hulpiau P,
Leroux-Roels G, Laukens D, Meuleman P, et al: Generation and
characterization of small single domain antibodies inhibiting human
tumor necrosis factor receptor 1. J Biol Chem. 290:4022–4037. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
59
|
Kazemi-Lomedasht F, Pooshang-Bagheri K,
Habibi-Anbouhi M, Hajizadeh-Safar E, Shahbazzadeh D, Mirzahosseini
H and Behdani M: In vivo immunotherapy of lung cancer using
cross-species reactive vascular endothelial growth factor
nano-bodies. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 20:489–496. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Salvador JP, Vilaplana L and Marco MP:
Nanobody: Outstanding features for diagnostic and therapeutic
applications. Anal Bioanal Chem. 411:1703–1713. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
De Munter S, Van Parys A, Bral L, Ingels
J, Goetgeluk G, Bonte S, Pille M, Billiet L, Weening K, Verhee A,
et al: Rapid and effective generation of nanobody based CARs using
PCR and gibson assembly. Int J Mol Sci. 21:8832020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
62
|
Ren W, Li Z, Xu Y, Wan D, Barnych B, Li Y,
Tu Z, He Q, Fu J and Hammock BD: One-step ultrasensitive
bioluminescent enzyme immunoassay based on nanobody/nanoluciferase
fusion for detection of aflatoxin B1 in cereal. J Agric
Food Chem. 67:5221–5229. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Allegra A, Innao V, Gerace D, Vaddinelli
D, Allegra AG and Musolino C: Nanobodies and cancer: Current status
and new perspectives. Cancer Invest. 36:221–237. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
De Genst E, Chan PH, Pardon E, Hsu SD,
Kumita JR, Christodoulou J, Menzer L, Chirgadze DY, Robinson CV,
Muyldermans S, et al: A nanobody binding to non-amyloido-genic
regions of the protein human lysozyme enhances partial unfolding
but inhibits amyloid fibril formation. J Phys Chem B.
117:13245–13258. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gonzalez-Sapienza G, Rossotti MA and
Tabares-da Rosa S: Single-domain antibodies as versatile affinity
reagents for analytical and diagnostic applications. Front Immunol.
8:9772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Akazawa-Ogawa Y, Uegaki K and Hagihara Y:
The role of intra-domain disulfide bonds in heat-induced
irreversible denaturation of camelid single domain VHH antibodies.
J Biochem. 159:111–121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
67
|
Goldman ER, Liu JL, Zabetakis D and
Anderson GP: Enhancing stability of camelid and shark single domain
antibodies: An overview. Front Immunol. 8:8652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kunz P, Zinner K, Mücke N, Bartoschik T,
Muyldermans S and Hoheisel JD: The structural basis of nanobody
unfolding reversibility and thermoresistance. Sci Rep. 8:79342018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Schumacher D, Helma J, Schneider AFL,
Leonhardt H and Hackenberger CPR: Nanobodies: Chemical
functionalization strategies and intracellular applications. Angew
Chem Int Ed Engl. 57:2314–2333. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
70
|
Wang Y, Fan Z, Shao L, Kong X, Hou X, Tian
D, Sun Y, Xiao Y and Yu L: Nanobody-derived nanobiotechnology tool
kits for diverse biomedical and biotechnology applications. Int J
Nanomedicine. 11:3287–3303. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jovčevska I and Muyldermans S: The
therapeutic potential of nanobodies. BioDrugs. 34:11–26. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Zottel A, Jovčevska I, Šamec N, Mlakar J,
Šribar J, Križaj I, Skoblar Vidmar M and Komel R: Anti-vimentin,
anti-TUFM, anti-NAP1L1 and anti-DPYSL2 nanobodies display cytotoxic
effect and reduce glioblastoma cell migration. Ther Adv Med Oncol.
12:17588359209153022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Peyron I, Kizlik-Masson C, Dubois MD,
Atsou S, Ferrière S, Denis CV, Lenting PJ, Casari C and Christophe
OD: Camelid-derived single-chain antibodies in hemostasis:
Mechanistic, diagnostic, and therapeutic applications. Res Pract
Thromb Haemost. 4:1087–1110. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kijanka M, Dorresteijn B, Oliveira S and
van Bergen en Henegouwen PM: Nanobody-based cancer therapy of solid
tumors. Nanomedicine (Lond). 10:161–174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Huen J, Yan Z, Iwashkiw J, Dubey S,
Gimenez MC, Ortiz ME, Patel SV, Jones MD, Riazi A, Terebiznik M, et
al: A novel single domain antibody targeting FliC flagellin of
salmonella enterica for effective inhibition of host cell invasion.
Front Microbiol. 10:26652019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
76
|
Zavrtanik U, Lukan J, Loris R, Lah J and
Hadži S: Structural basis of epitope recognition by heavy-chain
camelid antibodies. J Mol Biol. 430:4369–4368. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lauwereys M, Arbabi Ghahroudi M, Desmyter
A, Kinne J, Hölzer W, De Genst E, Wyns L and Muyldermans S: Potent
enzyme inhibitors derived from dromedary heavy-chain anti-bodies.
EMBO J. 17:3512–3520. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Arbabi-Ghahroudi M: Camelid single-domain
antibodies: Historical perspective and future outlook. Front
Immunol. 8:15892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Muruganandam A, Tanha J, Narang S and
Stanimirovic D: Selection of phage-displayed llama single-domain
antibodies that transmigrate across human blood-brain barrier
endothelium. FASEB J. 16:240–242. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Abulrob A, Sprong H, Van Bergen en
Henegouwen P and Stanimirovic D: The blood-brain barrier
transmigrating single domain antibody: Mechanisms of transport and
antigenic epitopes in human brain endothelial cells. J Neurochem.
95:1201–1214. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Menzel S, Schwarz N, Haag F and Koch-Nolte
F: Nanobody-based biologics for modulating purinergic signaling in
inflammation and immunity. Front Pharmacol. 9:2662018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhu M, Hu Y, Li G, Ou W, Mao P, Xin S and
Wan Y: Combining magnetic nanoparticle with biotinylated nanobodies
for rapid and sensitive detection of influenza H3N2. Nanoscale Res
Lett. 9:5282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zarschler K, Witecy S, Kapplusch F,
Foerster C and Stephan H: High-yield production of functional
soluble single-domain antibodies in the cytoplasm of Escherichia
coli. Microb Cell Fact. 12:972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
He T, Zhu J, Nie Y, Hu R, Wang T, Li P,
Zhang Q and Yang Y: Nanobody technology for mycotoxin detection in
the field of food safety: Current status and prospects. Toxins
(Basel). 10:1802018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Detalle L, Stohr T, Palomo C, Piedra PA,
Gilbert BE, Mas V, Millar A, Power UF, Stortelers C, Allosery K, et
al: Generation and characterization of ALX-0171, a potent novel
therapeutic nanobody for the treatment of respiratory syncytial
virus infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 60:6–13. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Sheng Y, Wang K, Lu Q, Ji P, Liu B, Zhu J,
Liu Q, Sun Y, Zhang J, Zhou EM and Zhao Q: Nanobody-horseradish
peroxidase fusion protein as an ultrasensitive probe to detect
antibodies against newcastle disease virus in the immunoassay. J
Nanobiotechnology. 17:352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wang L, Liu X, Zhu X, Wang L, Wang W, Liu
C, Cui H, Sun M and Gao B: Generation of single-domain antibody
multimers with three different self-associating peptides. Protein
Eng Des Sel. 26:417–423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Behdani M, Zeinali S, Karimipour M,
Khanahmad H, Schoonooghe S, Aslemarz A, Seyed N, Moazami-Godarzi R,
Baniahmad F, Habibi-Anbouhi M, et al: Development of
VEGFR2-specific nanobody pseudomonas exotoxin A conjugated to
provide efficient inhibition of tumor cell growth. N Biotechnol.
30:205–209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Sadeghnezhad G, Romão E, Bernedo-Navarro
R, Massa S, Khajeh K, Muyldermans S and Hassania S: Identification
of new DR5 agonistic nanobodies and generation of multivalent
nanobody constructs for cancer treatment. Int J Mol Sci.
20:48182019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
90
|
Huet HA, Growney JD, Johnson JA, Li J,
Bilic S, Ostrom L, Zafari M, Kowal C, Yang G, Royo A, et al:
Multivalent nano-bodies targeting death receptor 5 elicit superior
tumor cell killing through efficient caspase induction. Mabs.
6:1560–1570. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Liu W, Song H, Chen Q, Yu J, Xian M, Nian
R and Feng D: Recent advances in the selection and identification
of antigen-specific nanobodies. Mol Immunol. 96:37–47. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wagner HJ, Wehrle S, Weiss E, Cavallari M
and Weber W: A two-step approach for the design and generation of
nanobodies. Int J Mol Sci. 19:34442018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
93
|
Yan J, Wang P, Zhu M, Li G, Romão E, Xiong
S and Wan Y: Characterization and applications of nanobodies
against human procalcitonin selected from a novel naïve Nanobody
phage display library. J Nanobiotechnology. 13:332015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Itoh K, Reis AH, Hayhurst A and Sokol SY:
Isolation of nanobodies against xenopus embryonic antigens using
immune and nonimmune phage display libraries. PLoS One.
14:e02160832019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Yan J, Li G, Hu Y, Ou W and Wan Y:
Construction of a synthetic phage-displayed Nanobody library with
CDR3 regions randomized by trinucleotide cassettes for diagnostic
applications. J Transl Med. 12:3432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Cui Y, Li D, Morisseau C, Dong JX, Yang J,
Wan D, Rossotti MA, Gee SJ, González-Sapienza GG and Hammock BD:
Heavy chain single-domain antibodies to detect native human soluble
epoxide hydrolase. Anal Bioanal Chem. 407:7275–7283. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Gong X, Zhu M, Li G, Lu X and Wan Y:
Specific determination of influenza H7N2 virus based on
biotinylated single-domain antibody from a phage-displayed library.
Anal Biochem. 500:66–72. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Vincke C, Gutiérrez C, Wernery U, Devoogdt
N, Hassanzadeh-Ghassabeh G and Muyldermans S: Generation of single
domain antibody fragments derived from camelids and generation of
manifold constructs. Methods Mol Biol. 907:145–176. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Behar G, Sibéril S, Groulet A, Chames P,
Pugnière M, Boix C, Sautès-Fridman C, Teillaud JL and Baty D:
Isolation and characterization of anti-FcgammaRIII (CD16) llama
single-domain antibodies that activate natural killer cells.
Protein Eng Des Sel. 21:1–10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Maussang D, Mujić-Delić A, Descamps FJ,
Stortelers C, Vanlandschoot P, Stigter-van Walsum M, Vischer HF,
van Roy M, Vosjan M, Gonzalez-Pajuelo M, et al: Llama-derived
single variable domains (nanobodies) directed against chemokine
receptor CXCR7 reduce head and neck cancer cell growth in vivo. J
Biol Chem. 288:29562–29572. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Farajpour Z, Rahbarizadeh F, Kazemi B and
Ahmadvand D: A nanobody directed to a functional epitope on VEGF,
as a novel strategy for cancer treatment. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 446:132–136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Kim HJ, McCoy MR, Majkova Z, Dechant JE,
Gee SJ, Tabares-da Rosa S, González-Sapienza GG and Hammock BD:
Isolation of alpaca anti-hapten heavy chain single domain
antibodies for development of sensitive immunoassay. Anal Chem.
84:1165–1171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
103
|
Li K, Zettlitz KA, Lipianskaya J, Zhou Y,
Marks JD, Mallick P, Reiter RE and Wu AM: A fully human scFv phage
display library for rapid antibody fragment reformatting. Protein
Eng Des Sel. 28:307–316. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Doshi R, Chen BR, Vibat CR, Huang N, Lee
CW and Chang G: In vitro nanobody discovery for integral membrane
protein targets. Sci Rep. 4:67602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Ferrari D, Garrapa V, Locatelli M and
Bolchi A: A novel nanobody scaffold optimized for bacterial
expression and suitable for the construction of ribosome display
libraries. Mol Biotechnol. 62:43–55. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Yau KY, Groves MA, Li S, Sheedy C, Lee H,
Tanha J, MacKenzie CR, Jermutus L and Hall JC: Selection of
hapten-specific single-domain antibodies from a non-immunized llama
ribosome display library. J Immunol Methods. 281:161–175. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Bencurova E, Pulzova L, Flachbartova Z and
Bhide M: A rapid and simple pipeline for synthesis of
mRNA-ribosome-V(H)H complexes used in single-domain antibody
ribosome display. Mol Biosyst. 11:1515–1524. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
McMahon C, Baier AS, Pascolutti R,
Wegrecki M, Zheng S, Ong JX, Erlandson SC, Hilger D, Rasmussen SGF,
Ring AM, et al: Yeast surface display platform for rapid discovery
of conformationally selective nanobodies. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
25:289–296. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Uchański T, Zögg T, Yin J, Yuan D,
Wohlkönig A, Fischer B, Rosenbaum DM, Kobilka BK, Pardon E and
Steyaert J: An improved yeast surface display platform for the
screening of nanobody immune libraries. Sci Rep. 9:3822019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Salema V and Fernández LÁ: Escherichia
coli surface display for the selection of nanobodies. Microb
Biotechnol. 10:1468–1484. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Salema V, Marín E, Martínez-Arteaga R,
Ruano-Gallego D, Fraile S, Margolles Y, Teira X, Gutierrez C,
Bodelón G and Fernández LÁ: Selection of single domain antibodies
from immune libraries displayed on the surface of E. coli cells
with two β-domains of opposite topologies. PLoS One. 8:e751262013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Salema V, Mañas C, Cerdán L, Piñero-Lambea
C, Marín E, Roovers RC, Van Bergen En Henegouwen PM and Fernández
LÁ: High affinity nanobodies against human epidermal growth factor
receptor selected on cells by E. coli display. MAbs. 8:1286–1301.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Tang J, Li J, Zhu X, Yu Y, Chen D, Yuan L,
Gu Z, Zhang X, Qi L, Gong Z, et al: Novel CD7-specific
nanobody-based immunotoxins potently enhanced apoptosis of
CD7-positive malignant cells. Oncotarget. 7:34070–34083. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Hassel JC, Heinzerling L, Aberle J, Bähr
O, Eigentler TK, Grimm MO, Grünwald V, Leipe J, Reinmuth N, Tietze
JK, et al: Combined immune checkpoint blockade
(anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4): Evaluation and management of adverse drug
reactions. Cancer Treat Rev. 57:36–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Gupta A, De Felice KM, Loftus EV Jr and
Khanna S: Systematic review: Colitis associated with anti-CTLA-4
therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 42:406–417. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Savoia P, Astrua C and Fava P: Ipilimumab
(Anti-Ctla-4 Mab) in the treatment of metastatic melanoma:
Effectiveness and toxicity management. Hum Vaccin Immunother.
12:1092–1101. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Gao X and McDermott DF: Ipilimumab in
combination with nivolumab for the treatment of renal cell
carcinoma. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 18:947–957. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Tang Z, Mo F, Liu A, Duan S, Yang X, Liang
L, Hou X, Yin S, Jiang X, Vasylieva N, et al: A nanobody against
cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated antigen-4 increases the
anti-tumor effects of specific CD8+ T cells. J Biomed
Nanotechnol. 15:2229–2239. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Mahoney KM, Freeman GJ and McDermott DF:
The next immune-checkpoint inhibitors: PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in
melanoma. Clin Ther. 37:764–782. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Broos K, Lecocq Q, Keersmaecker B, Raes G,
Corthals J, Lion E, Thielemans K, Devoogdt N, Keyaerts M and
Breckpot K: Single domain antibody-mediated blockade of programmed
death-ligand 1 on dendritic cells enhances CD8 T-cell activation
and cytokine production. Vaccines (Basel). 7:852019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Fang T, Li R, Li Z, Cho J, Guzman JS, Kamm
RD and Ploegh HL: Remodeling of the tumor microenvironment by a
chemokine/Anti-PD-L1 nanobody fusion protein. Mol Pharm.
16:2838–2844. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhang F, Wei H, Wang X, Bai Y, Wang P, Wu
J, Jiang X, Wang Y, Cai H, Xu T and Zhou A: Structural basis of a
novel PD-L1 nanobody for immune checkpoint blockade. Cell Discov.
3:170042017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Xian Z, Ma L, Zhu M, Li G, Gai J, Chang Q,
Huang Y, Ju D and Wan Y: Blocking the PD-1-PD-L1 axis by a novel
PD-1 specific nanobody expressed in yeast as a potential
therapeutic for immunotherapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
519:267–273. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Li S, Jiang K, Wang T, Zhang W, Shi M,
Chen B and Hua Z: Nanobody against PDL1. Biotechnol Lett.
42:727–736. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Liu J, Zhang S, Hu Y, Yang Z, Li J, Liu X,
Deng L, Wang Y, Zhang X, Jiang T and Lu X: Targeting PD-1 and Tim-3
path-ways to reverse CD8 T-cell exhaustion and enhance ex vivo
T-cell responses to autologous dendritic/tumor vaccines. J
Immunother. 39:171–180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Liu JF, Ma SR, Mao L, Bu LL, Yu GT, Li YC,
Huang CF, Deng WW, Kulkarni AB, Zhang WF and Sun ZJ: T-cell
immu-noglobulin mucin 3 blockade drives an antitumor immune
response in head and neck cancer. Mol Oncol. 11:235–247. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Chang X, Lu X, Guo J and Teng GJ:
Interventional therapy combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors:
Emerging opportunities for cancer treatment in the era of
immunotherapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 74:49–60. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Ascione A, Arenaccio C, Mallano A, Flego
M, Gellini M, Andreotti M, Fenwick C, Pantaleo G, Vella S and
Federico M: Development of a novel human phage display-derived
anti-LAG3 scFv antibody targeting CD8+ T lymphocyte
exhaustion. BMC Biotechnol. 19:672019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Homayouni V, Ganjalikhani-Hakemi M, Rezaei
A, Khanahmad H, Behdani M and Lomedasht FK: Preparation and
characterization of a novel nanobody against T-cell immunoglobulin
and mucin-3 (TIM-3). Iran J Basic Med Sci. 19:1201–1208.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Ma LL, Zhu M, Li GH, Li YF, Gai JW and Wan
YK: Construction and screening of phage display library for TIM-3
nanobody. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. 53:388–395. 2018.
|
|
131
|
Long L, Zhang X, Chen F, Pan Q,
Phiphatwatchara P, Zeng Y and Chen H: The promising immune
checkpoint LAG-3: From tumor microenvironment to cancer
immunotherapy. Genes Cancer. 9:176–189. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Everett KL, Kraman M, Wollerton FPG,
Zimarino C, Kmiecik K, Gaspar M, Pechouckova S, Allen NL, Doody JF
and Tuna M: Generation of Fcabs targeting human and murine LAG-3 as
building blocks for novel bispecific antibody therapeutics.
Methods. 154:60–69. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Puhr HC and Ilhan-Mutlu A: New emerging
targets in cancer immunotherapy: The role of LAG3. ESMO Open.
4:e0004822019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Dmitriev OY, Lutsenko S and Muyldermans S:
Nanobodies as probes for protein dynamics in vitro and in cells. J
Biol Chem. 291:3767–3775. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
135
|
Chanier T and Chames P: Nanobody
engineering: Toward next generation immunotherapies and
immunoimaging of cancer. Antibodies (Basel). 8:132019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Lecocq Q, Zeven K, De Vlaeminck Y, Martens
S, Massa S, Goyvaerts C, Raes G, Keyaerts M, Breckpot K and
Devoogdt N: Noninvasive imaging of the immune checkpoint LAG-3
using nanobodies, from development to pre-clinical use.
Biomolecules. 9:5482019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
137
|
Lv G, Sun X, Qiu L, Sun Y, Li K, Liu Q,
Zhao Q, Qin S and Lin J: PET imaging of tumor PD-L1 expression with
a highly specific nonblocking single-domain antibody. J Nucl Med.
61:117–122. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
138
|
Broos K, Keyaerts M, Lecocq Q, Renmans D,
Nguyen T, Escors D, Liston A, Raes G, Breckpot K and Devoogdt N:
Non-invasive assessment of murine PD-L1 levels in syngeneic tumor
models by nuclear imaging with nanobody tracers. Oncotarget.
8:41932–41946. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Broos K, Lecocq Q, Xavier C, Bridoux J,
Nguyen TT, Corthals J, Schoonooghe S, Lion E, Raes G, Keyaerts M,
et al: Evaluating a single domain antibody targeting human PD-L1 as
a nuclear imaging and therapeutic agent. Cancers (Basel).
11:8722019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Wan R, Liu A, Hou X, Lai Z, Li J, Yang N,
Tan J, Mo F, Hu Z, Yang X, et al: Screening and antitumor effect of
an anti-CTLA-4 nanobody. Oncol Rep. 39:511–518. 2018.
|
|
141
|
Wang W, Hou X, Yang X, Liu A, Tang Z, Mo
F, Yin S and Lu X: Highly sensitive detection of CTLA-4-positive
T-cell subgroups based on nanobody and fluorescent carbon quantum
dots. Oncol Lett. 18:109–116. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|