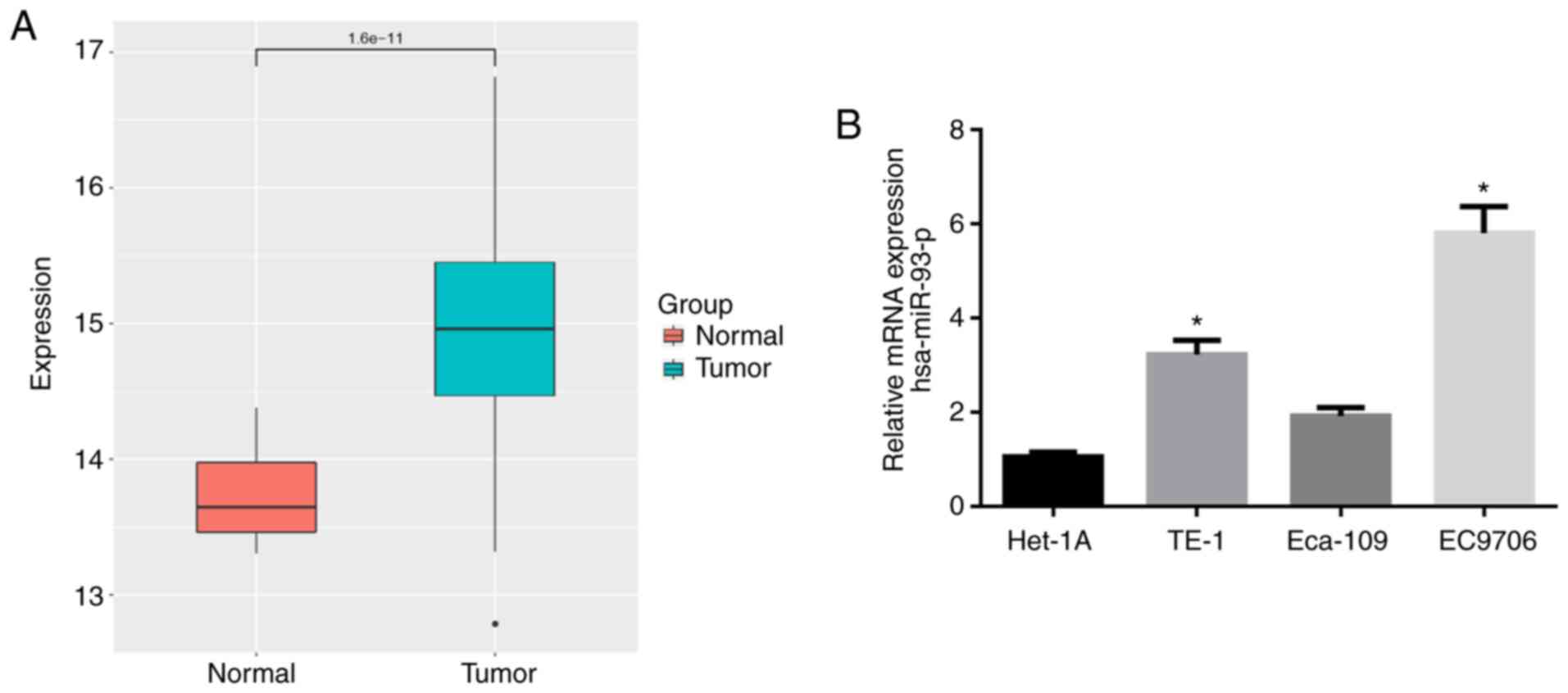
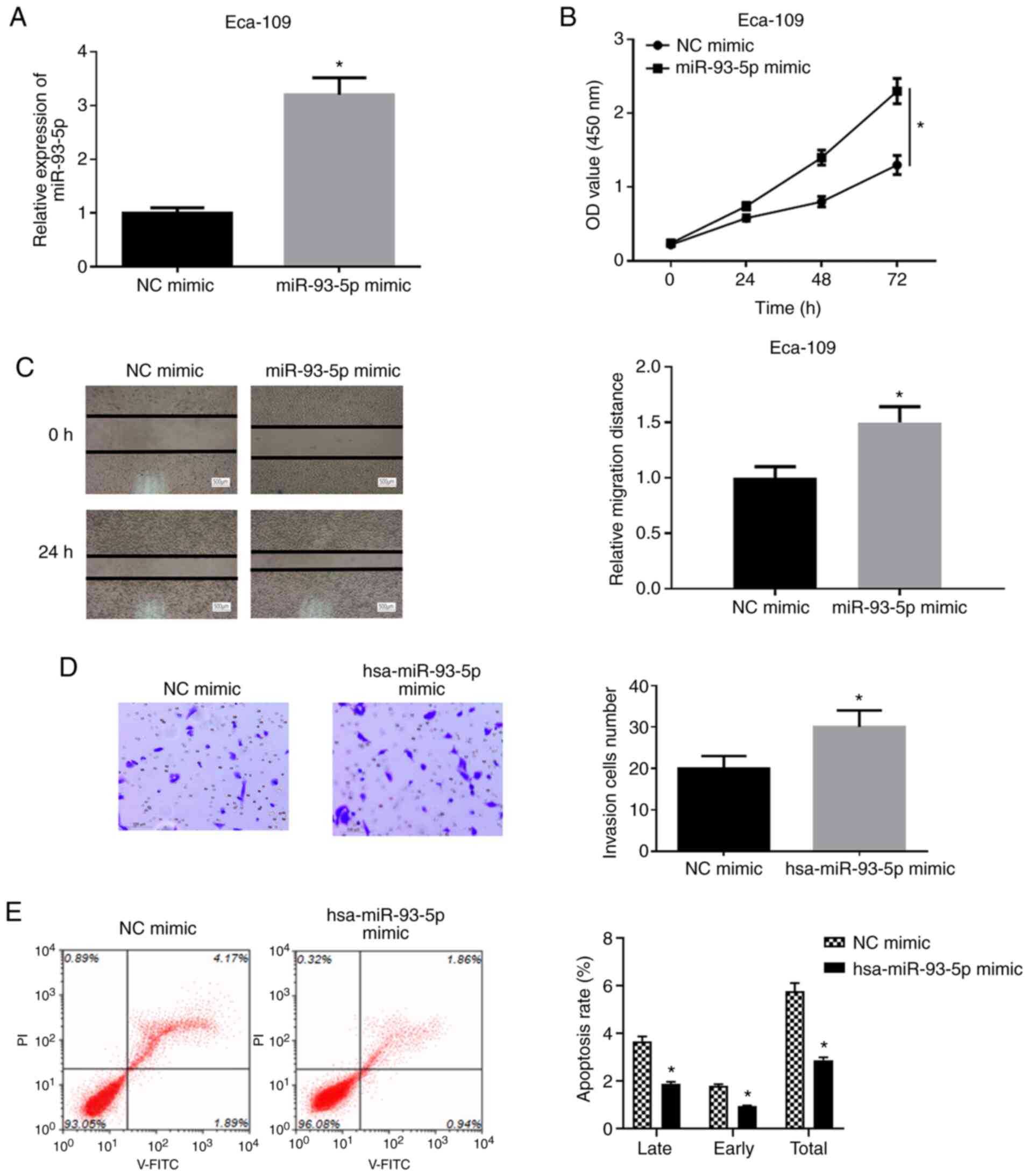
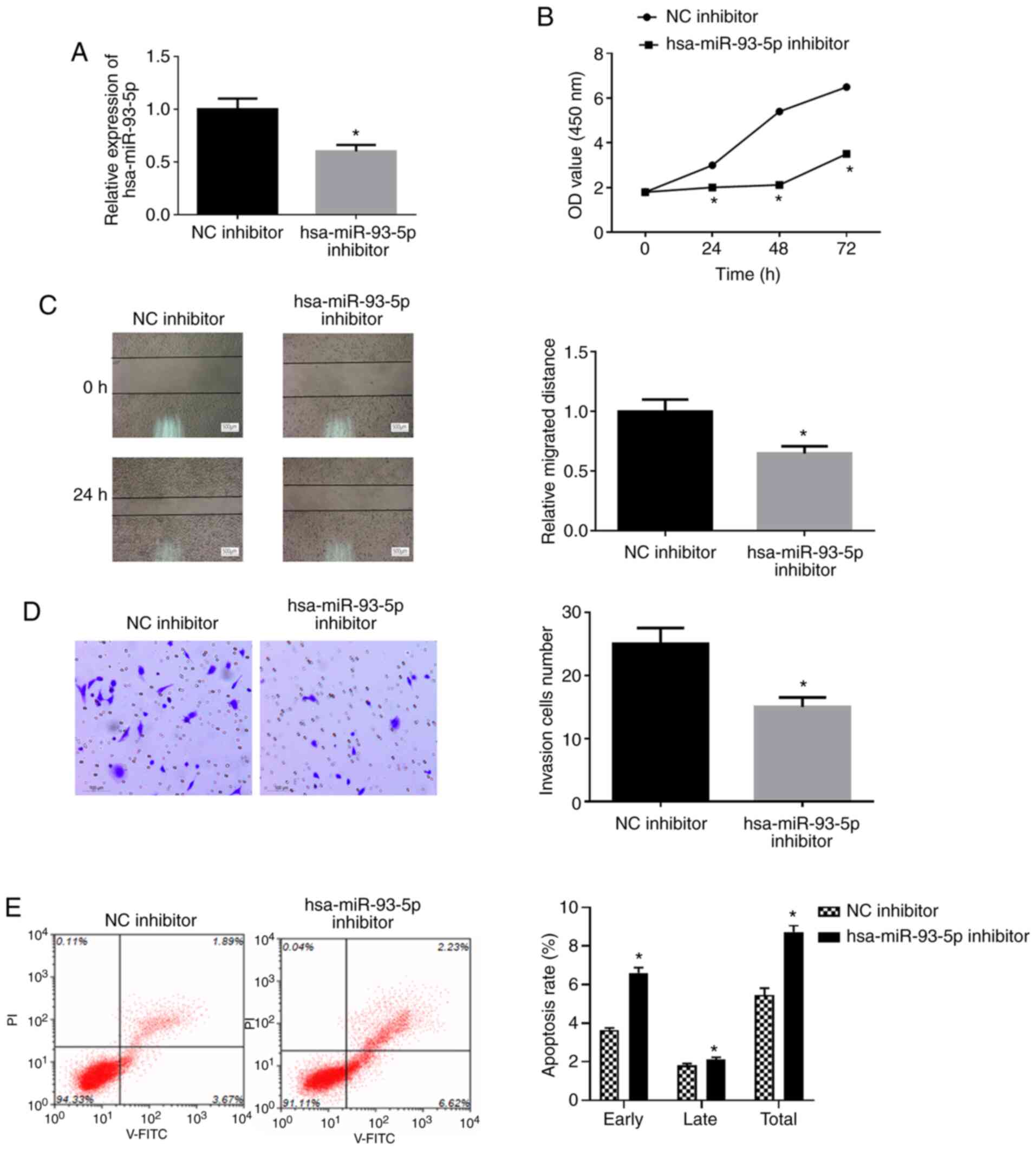
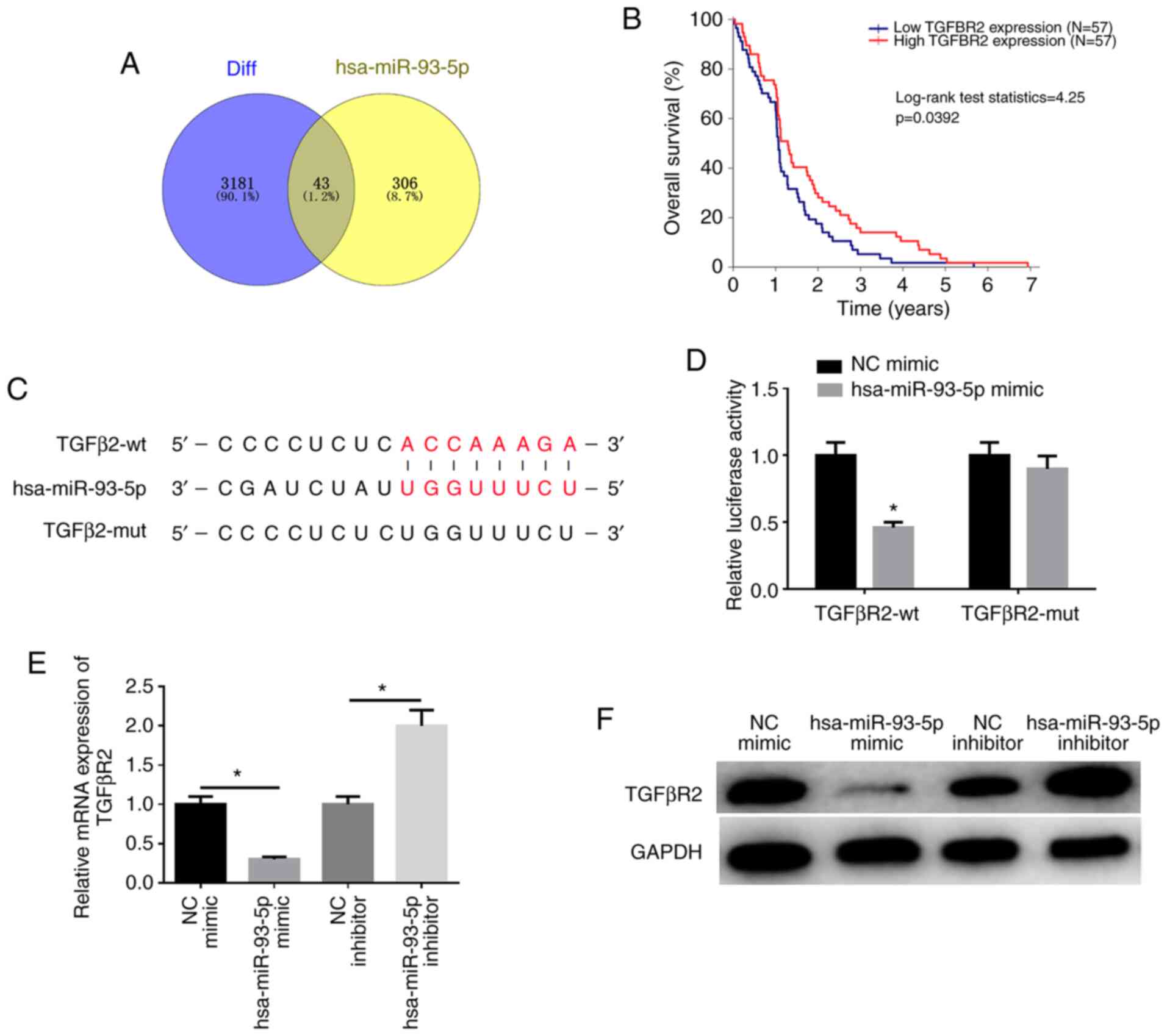
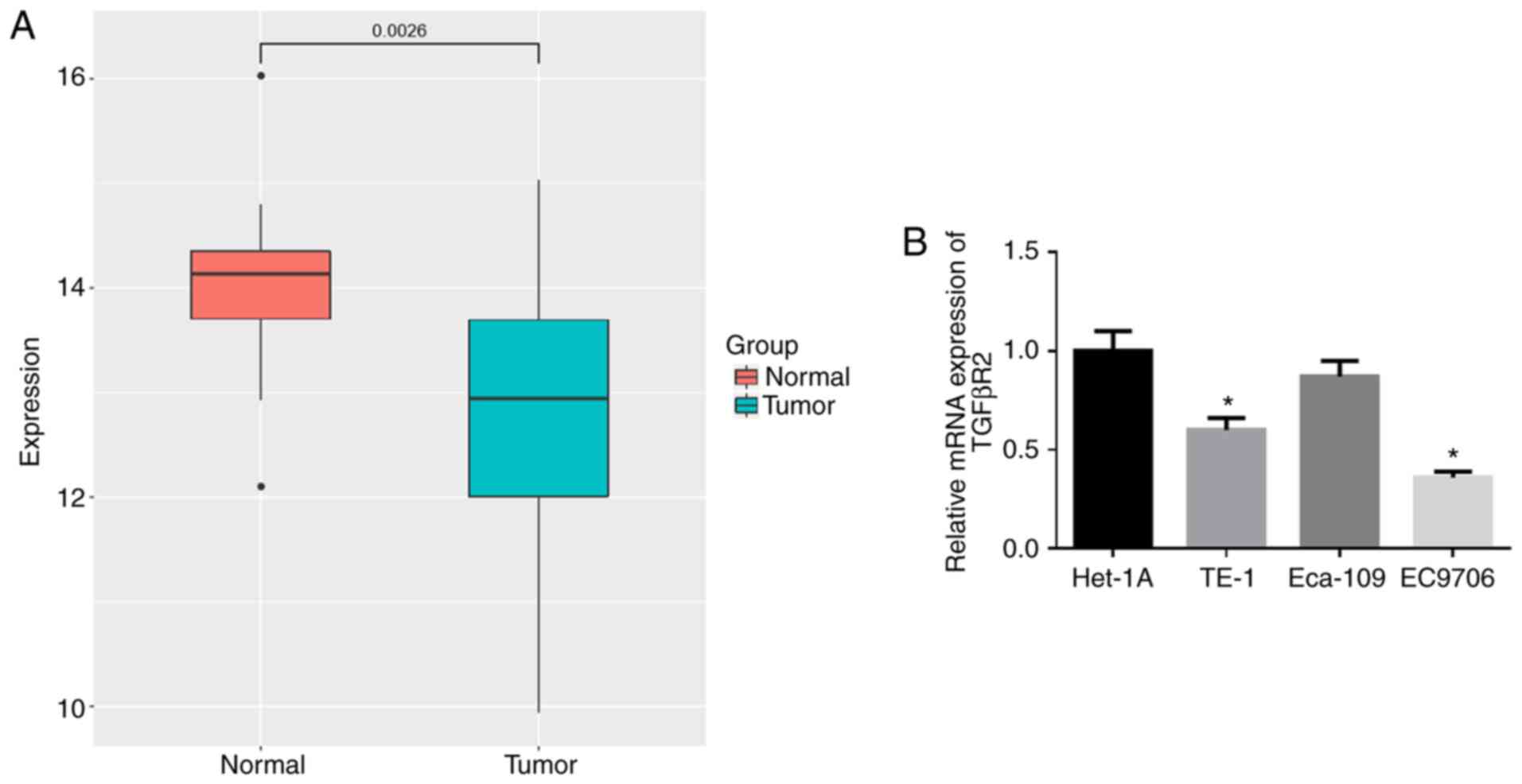
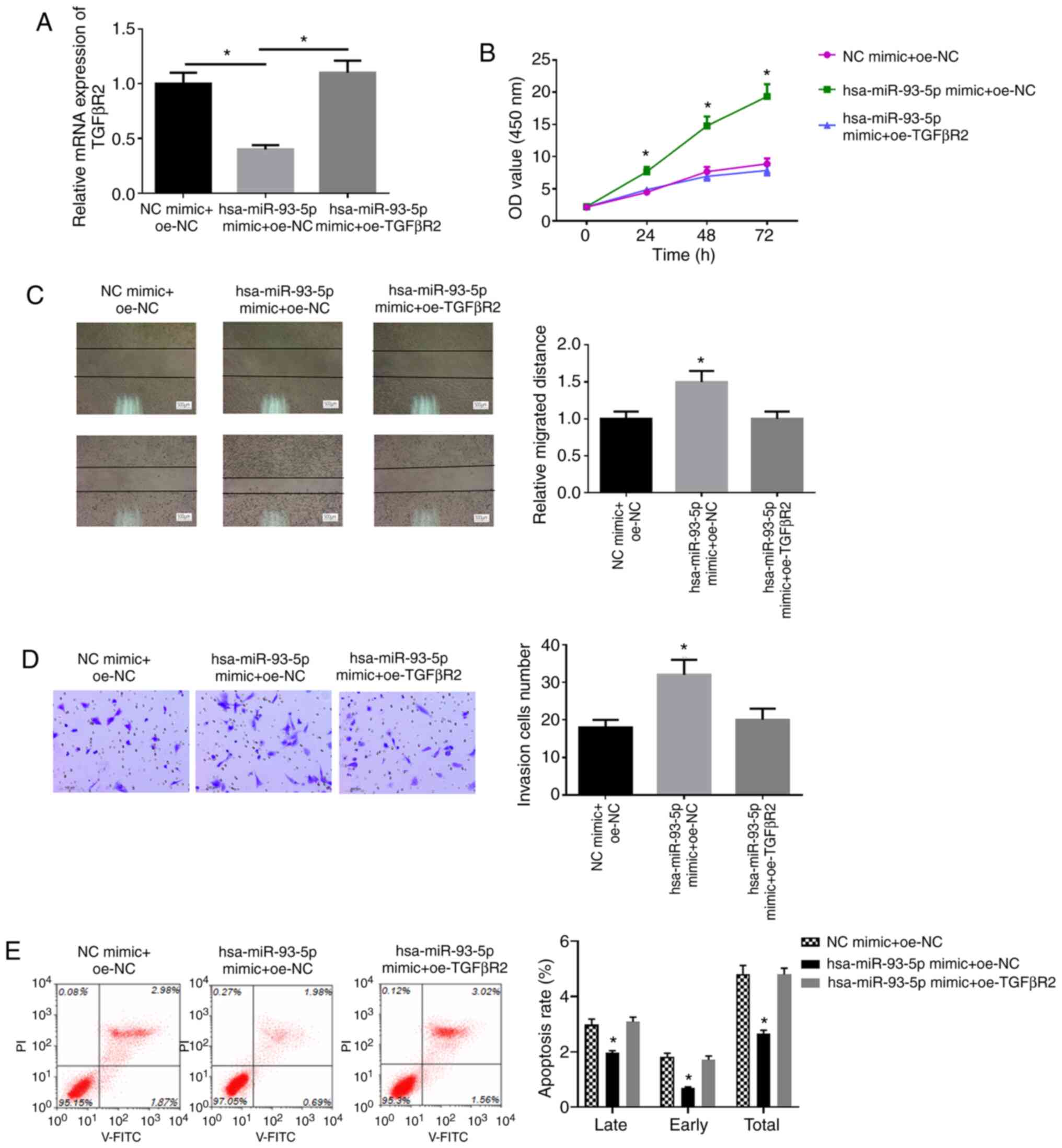
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nishimura T, Tamaoki M, Komatsuzaki R, Oue
N, Taniguchi H, Komatsu M, Aoyagi K, Minashi K, Chiwaki F,
Shinohara H, et al: SIX1 maintains tumor basal cells via
transforming growth factor-β pathway and associates with poor
prognosis in esophageal cancer. Cancer Sci. 108:216–225. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Wu K, He J, Pu W and Peng Y: The role of
exportin-5 in MicroRNA biogenesis and cancer. Genomics Proteomics
Bioinformatics. 16:120–126. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen S, Chen X, Sun KX, Xiu YL, Liu BL,
Feng MX, Sang XB and Zhao Y: MicroRNA-93 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of endometrial carcinoma cells.
PLoS One. 11:e01657762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Paul S, Lakatos P, Hartmann A,
Schneider-Stock R and Vera J: Identification of miRNA-mRNA modules
in colorectal cancer using rough hypercuboid based supervised
clustering. Sci Rep. 7:428092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li N, Miao Y, Shan Y, Liu B, Li Y, Zhao L
and Jia L: MiR-106b and miR-93 regulate cell progression by
suppression of PTEN via PI3K/Akt pathway in breast cancer. Cell
Death Dis. 8:e27962017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Du L, Zhao Z, Ma X, Hsiao TH, Chen Y,
Young E, Suraokar M, Wistuba I, Minna JD and Pertsemlidis A:
miR-93-directed downregulation of DAB2 defines a novel oncogenic
pathway in lung cancer. Oncogene. 33:4307–4315. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhu W, He J, Chen D, Zhang B, Xu L, Ma H,
Liu X, Zhang Y and Le H: Expression of miR-29c, miR-93, and miR-429
as potential biomarkers for detection of early stage non-small lung
cancer. PLoS One. 9:e877802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kucuksayan H, Akgun S, Ozes ON, Alikanoglu
AS, Yildiz M, Dal E and Akca H: TGF-β-SMAD-miR-520e axis regulates
NSCLC metastasis through a TGFBR2-mediated negative-feedback loop.
Carcinogenesis. 40:695–705. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Malkoski SP, Haeger SM, Cleaver TG,
Rodriguez KJ, Li H, Lu SL, Feser WJ, Barón AE, Merrick D, Lighthall
JG, et al: Loss of transforming growth factor beta type II receptor
increases aggressive tumor behavior and reduces survival in lung
adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
18:2173–2183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fricke F, Lee J, Michalak M, Warnken U,
Hausser I, Suarez-Carmona M, Halama N, Schnölzer M, Kopitz J and
Gebert J: TGFBR2-dependent alterations of exosomal cargo and
functions in DNA mismatch repair-deficient HCT116 colorectal cancer
cells. Cell Commun Signal. 15:142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu JJ, Zhang X and Wu XH: miR-93 promotes
the growth and invasion of prostate cancer by upregulating its
target genes TGFBR2, ITGB8, and LATS2. Mol Ther Oncolytics.
11:14–19. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu YF, Yu JR, Yang Z, Zhu GX, Gao P, Wang
H, Chen SY, Zhang J, Liu MY, Niu Y, et al: Promoter hypomethylation
mediated upregulation of MicroRNA-10b-3p targets FOXO3 to promote
the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 37:3012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma DH, Li BS, Liu JJ, Xiao YF, Yong X,
Wang SM, Wu YY, Zhu HB, Wang DX and Yang SM: miR-93-5p/IFNAR1 axis
promotes gastric cancer metastasis through activating the STAT3
signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 408:23–32. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou H, Wu G, Ma X, Xiao J, Yu G, Yang C,
Xu N, Zhang B, Zhou J, Ye Z and Wang Z: Attenuation of TGFBR2
expression and tumour progression in prostate cancer involve
diverse hypoxia-regulated pathways. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:892018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schumacher K, Dagres N, Hindricks G,
Husser D, Bollmann A and Kornej J: Characteristics of PR interval
as predictor for atrial fibrillation: Association with biomarkers
and outcomes. Clin Res Cardiol. 106:767–775. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mishra S, Deng JJ, Gowda PS, Rao MK, Lin
CL, Chen CL, Huang T and Sun LZ: Androgen receptor and microRNA-21
axis downregulates transforming growth factor beta receptor II
(TGFBR2) expression in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 33:4097–4106.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lyu X, Fang W, Cai L, Zheng H, Ye Y, Zhang
L, Li J, Peng H, Cho WC, Wang E, et al: TGFβR2 is a major target of
miR-93 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma aggressiveness. Mol Cancer.
13:512014. View Article : Google Scholar
|