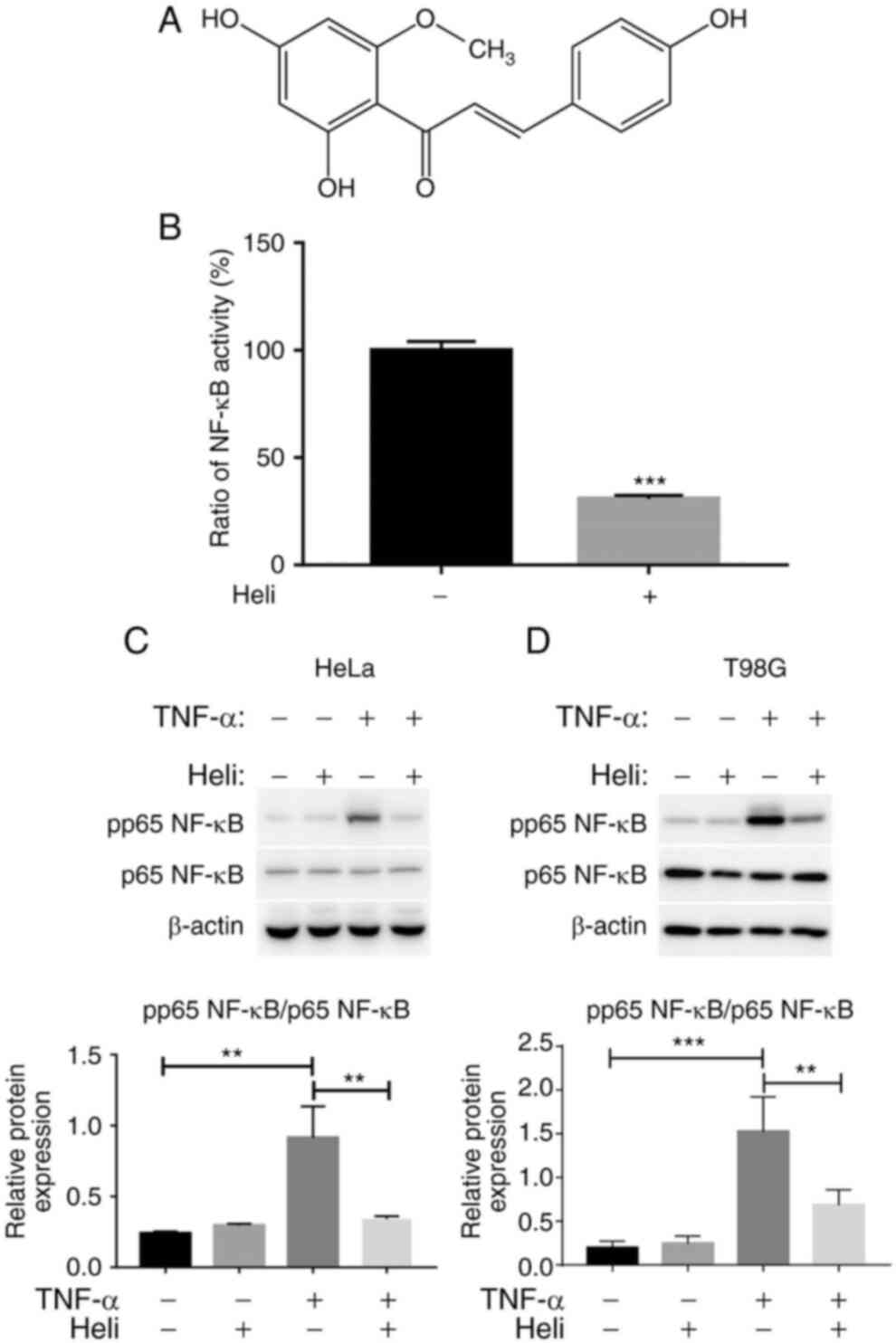
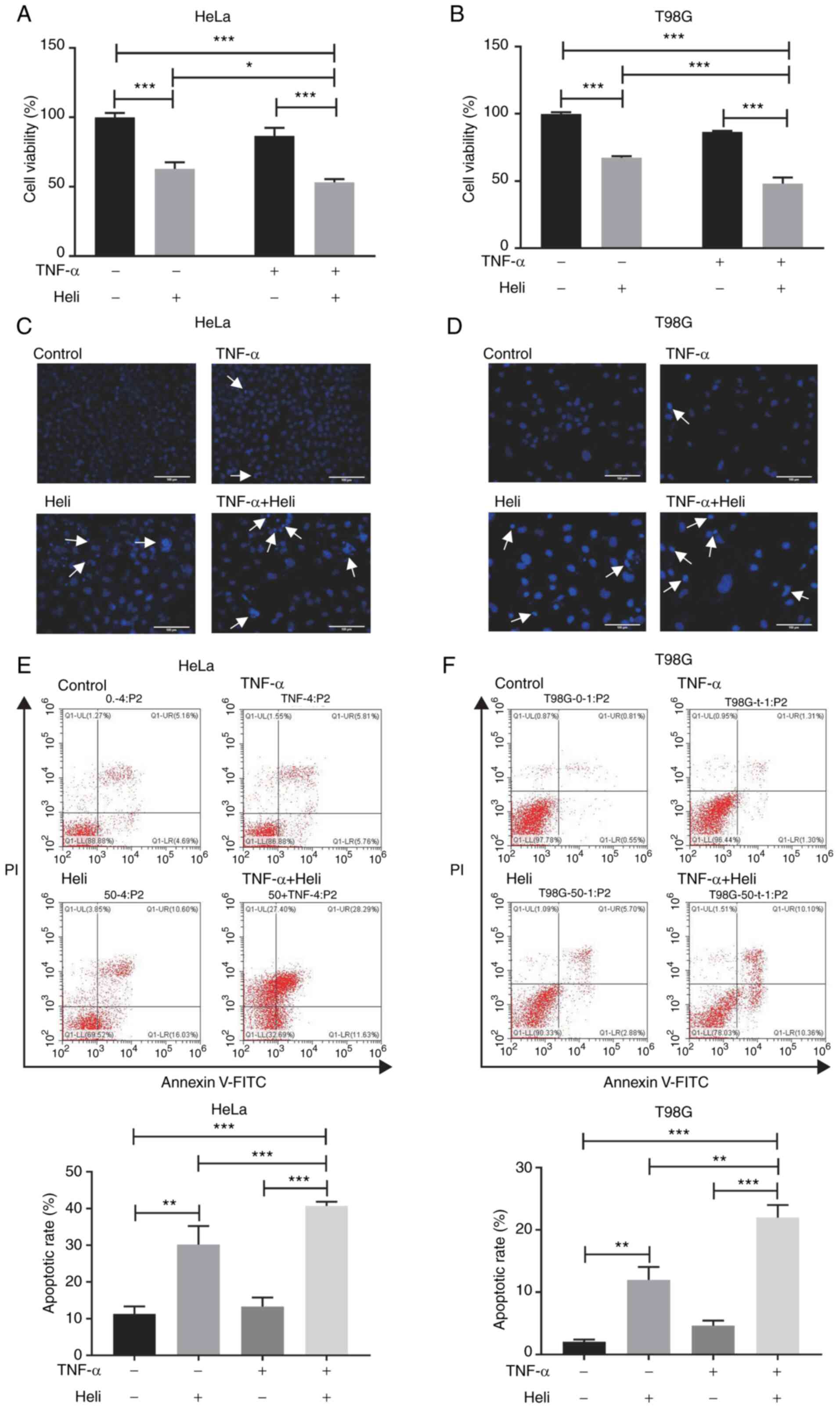
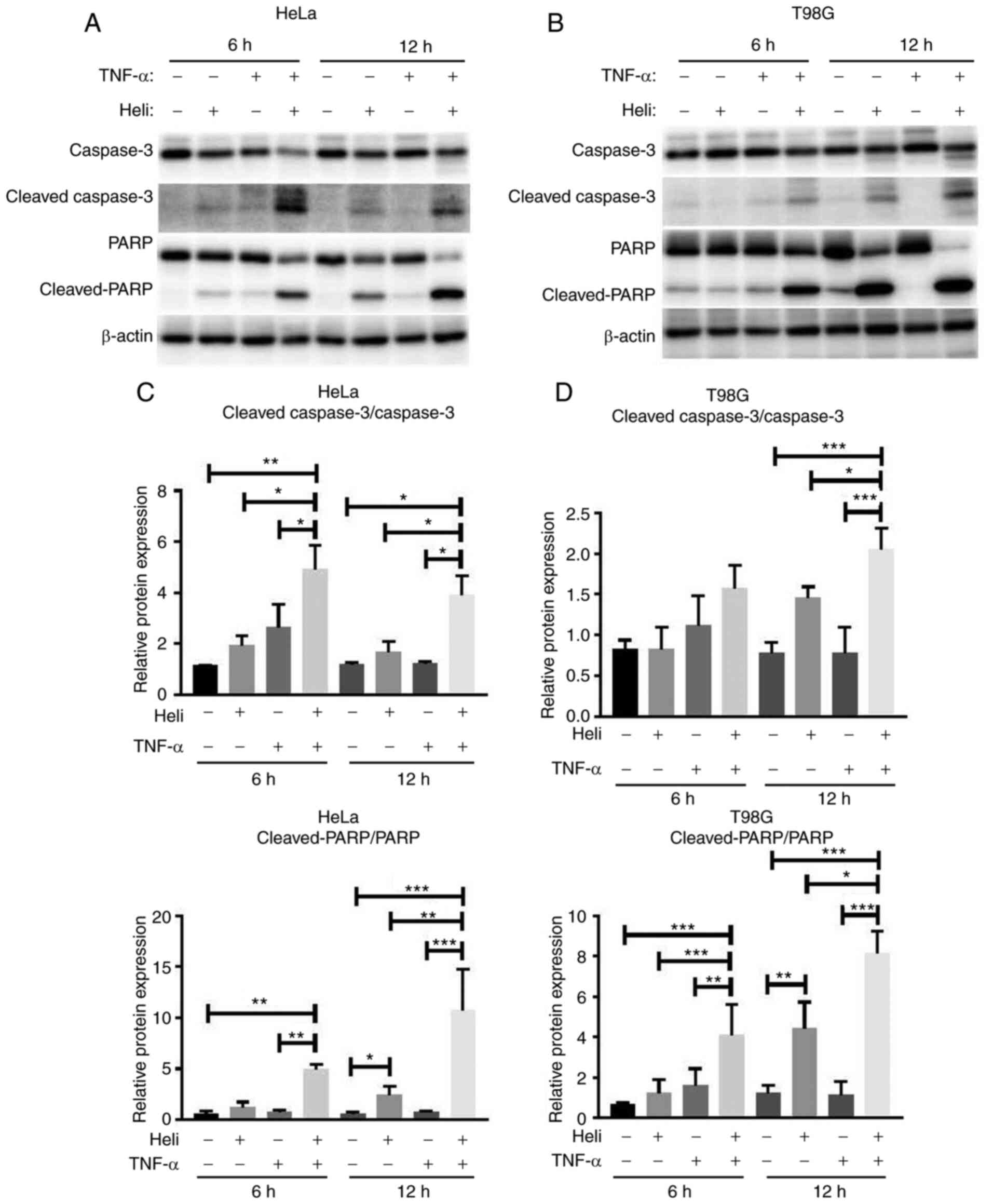
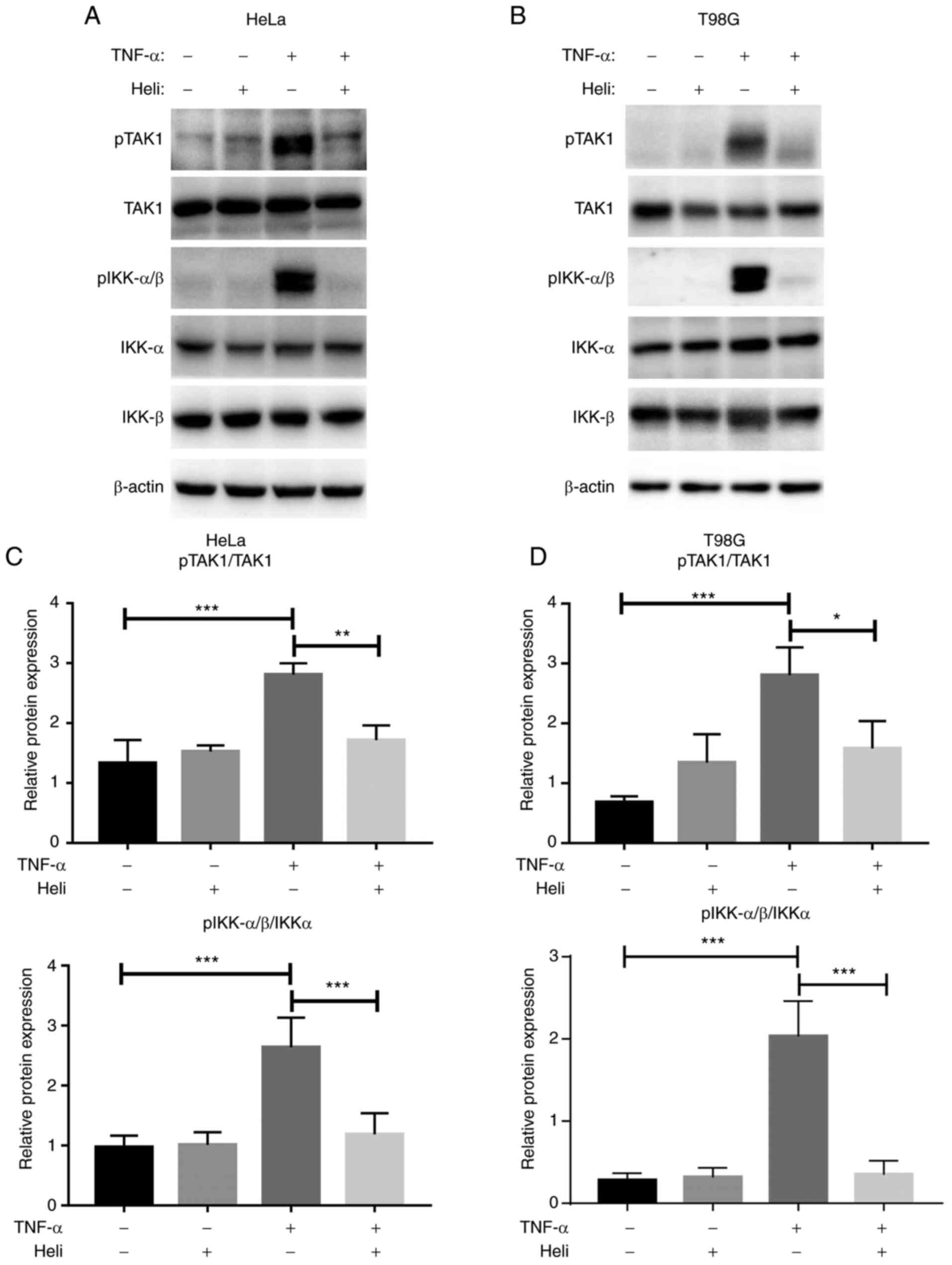
|
1
|
Sakurai H: Targeting of TAK1 in
inflammatory disorders and cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
33:522–530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Crusz SM and Balkwill FR: Inflammation and
cancer: Advances and new agents. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 12:584–596.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
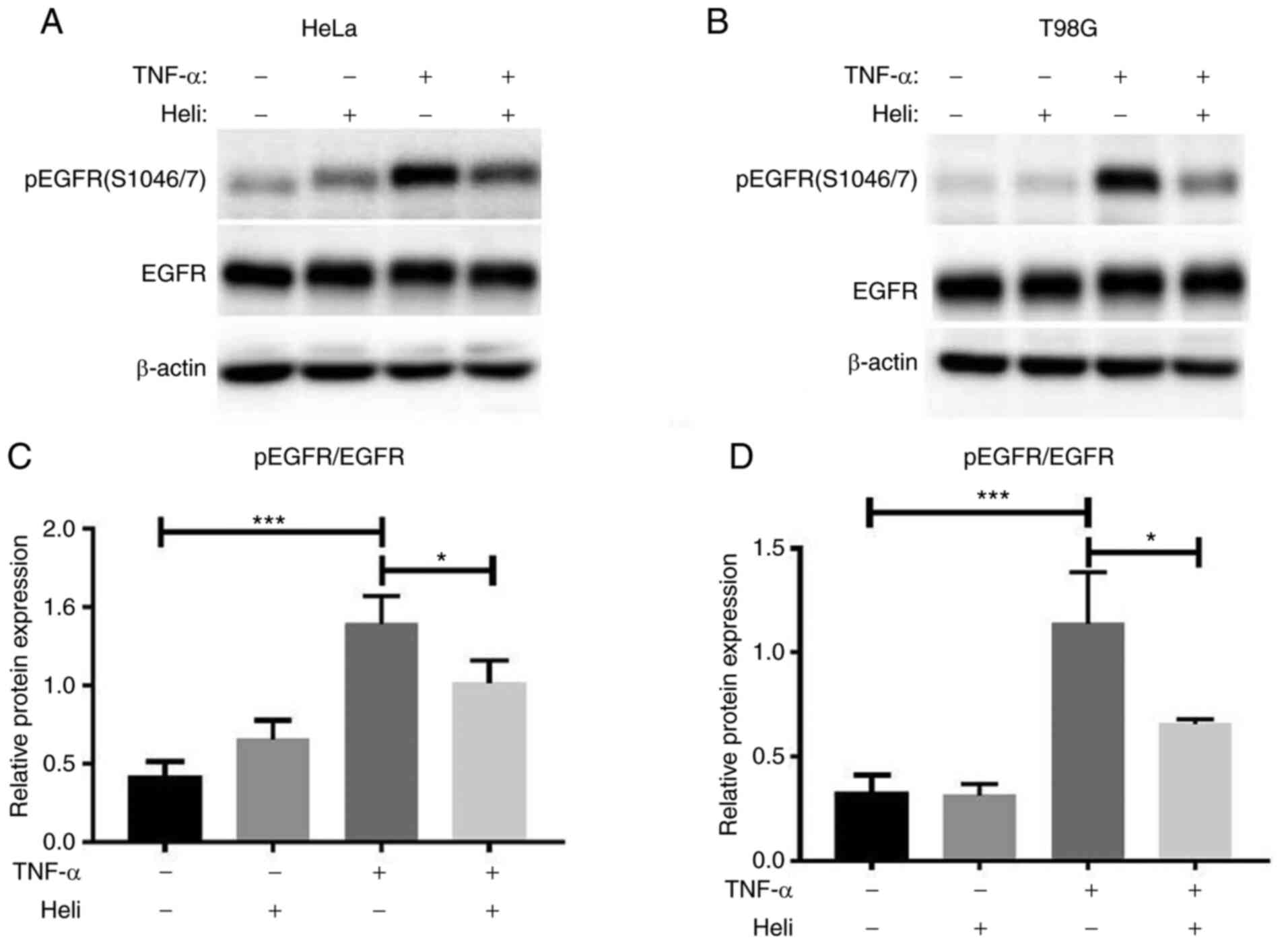
|
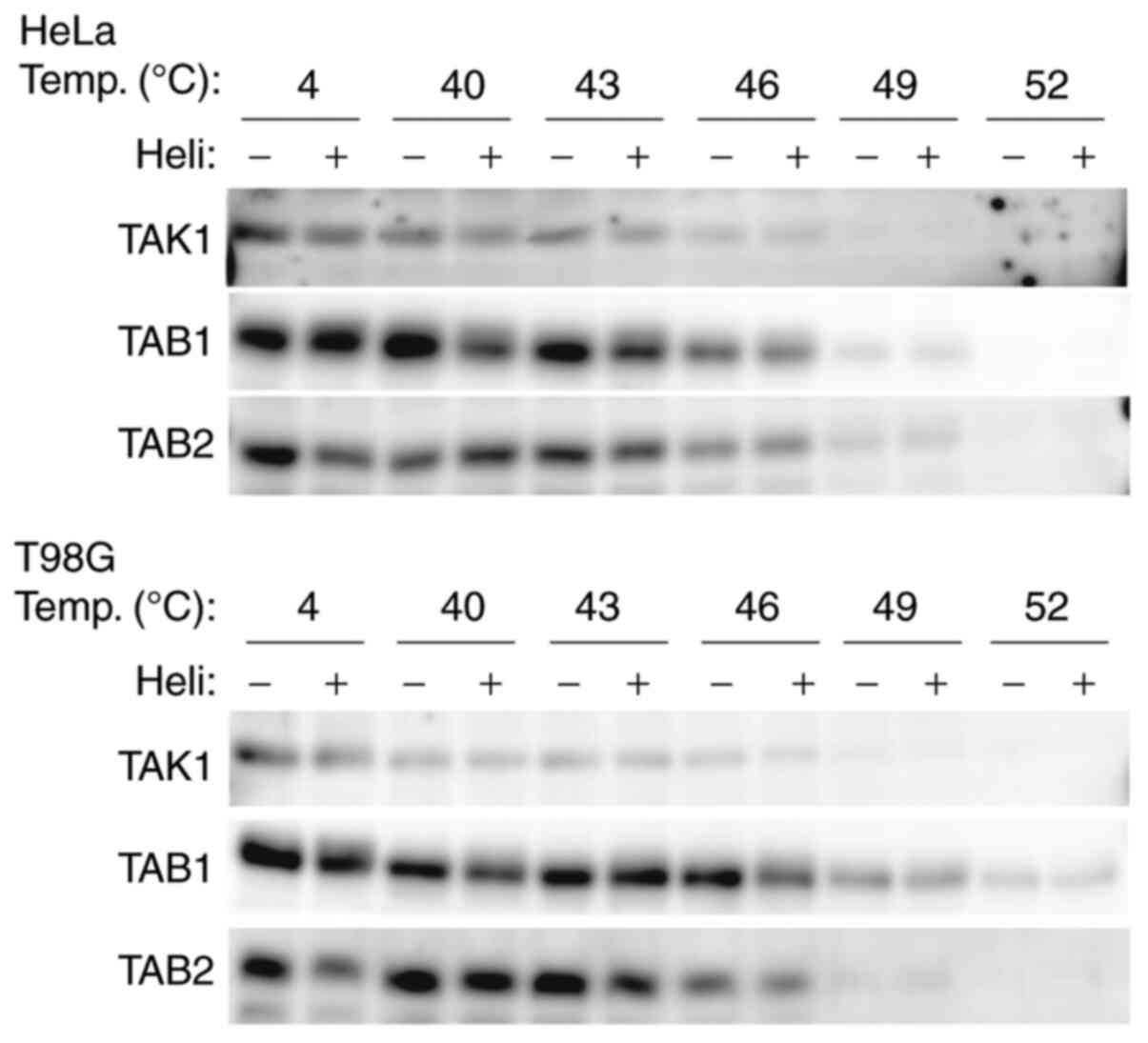
3
|
Karin M: Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer
development and progression. Nature. 441:431–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wajant H, Pfizenmaier K and Scheurich P:
Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ. 10:45–65. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
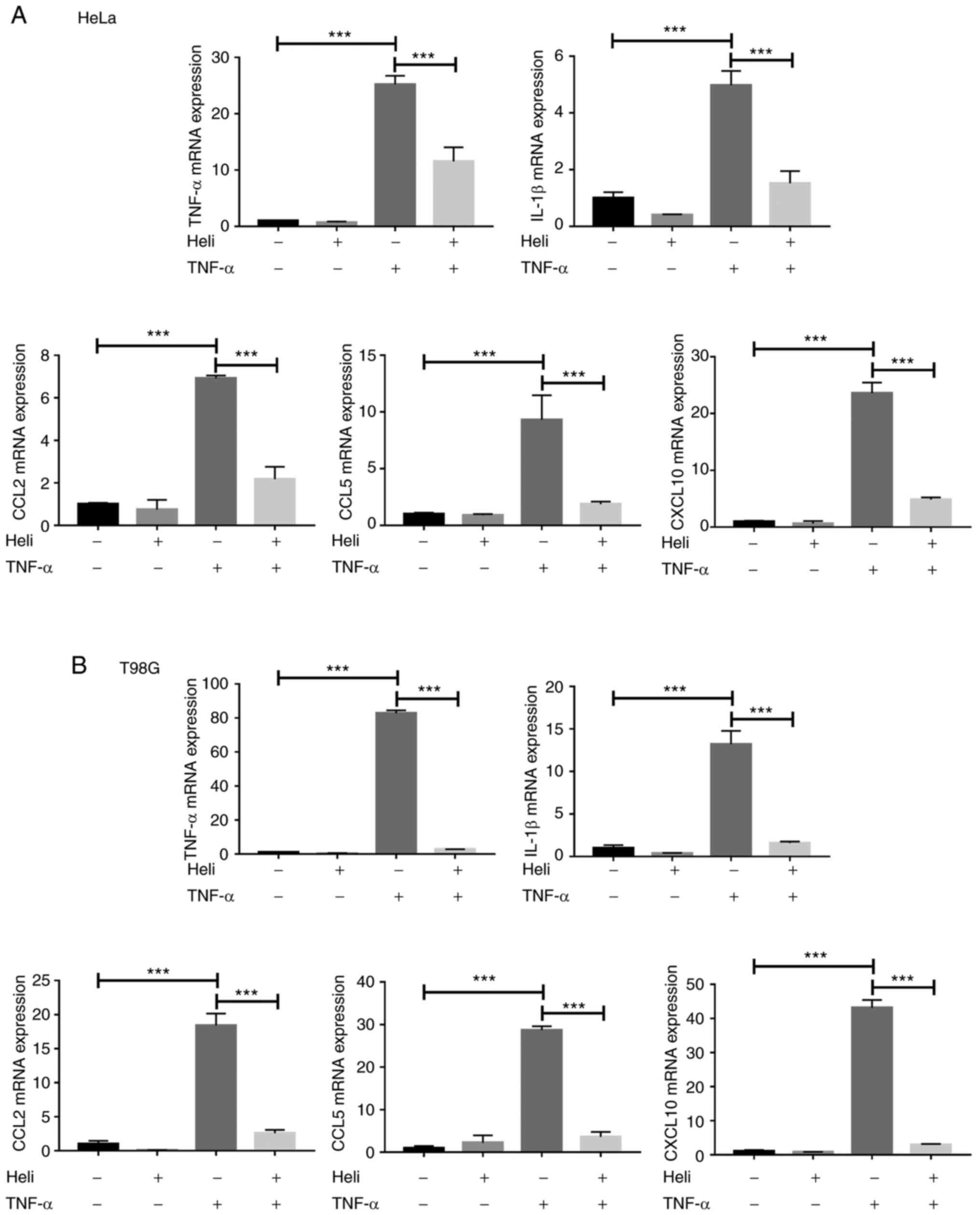
|
|
5
|
Bodmer JL, Holler N, Reynard S,
Vinciguerra P, Schneider P, Juo P, Blenis J and Tschopp J: TRAIL
receptor-2 signals apoptosis through FADD and caspase-8. Nat Cell
Biol. 2:241–243. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Morris G, Walker AJ, Berk M, Maes M and
Puri BK: Cell death pathways: A novel therapeutic approach for
neuroscientists. Mol Neurobiol. 55:5767–5786. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Varfolomeev E and Vucic D: Intracellular
regulation of TNF activity in health and disease. Cytokine.
101:26–32. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Camara-Clayette V, Lecluse Y, Schrader C,
Klapper W, Vainchenker W, Hermine O and Ribrag V: The NF-κB pathway
is rarely spontaneously activated in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)
cell lines and patient's samples. Eur J Cancer. 50:159–169. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
He A, Ji R, Shao J, He C, Jin M and Xu Y:
TLR4-MyD88= TRAF6-TAK1 complex-mediated NF-κB activation contribute
to the anti-inflammatory effect of V8 in LPS-induced human cervical
cancer SiHa cells. Inflammation. 39:172–181. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nighot M, Rawat M, Al-Sadi R, Castillo EF,
Nighot P and Ma TY: Lipopolysaccharide-Induced increase in
intestinal permeability is mediated by TAK-1 activation of IKK and
MLCK/MYLK gene. Am J Pathol. 189:797–812. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Taniguchi K and Karin M: NF-κB,
inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:309–324. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Capece D, Verzella D, Tessitore A, Alesse
E, Capalbo C and Zazzeroni F: Cancer secretome and inflammation:
The bright and the dark sides of NF-κB. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
78:51–61. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Morandell S, Stasyk T, Skvortsov S, Ascher
S and Huber LA: Quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomics
reveal novel insights into complexity and dynamics of the EGFR
signaling network. Proteomics. 8:4383–4401. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nishimura M, Shin MS, Singhirunnusorn P,
Suzuki S, Kawanishi M, Koizumi K, Saiki I and Sakurai H:
TAK1-Mediated serine/threonine phosphorylation of epidermal growth
factor receptor via p38/extracellular signal-regulated kinase:
NF-{kappa}B-independent survival pathways in tumor necrosis factor
alpha signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 29:5529–5539. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shin MS, Shinghirunnusorn P, Sugishima Y,
Nishimura M, Suzuki S, Koizumi K, Saiki I and Sakurai H: Cross
interference with TNF-alpha-induced TAK1 activation via
EGFR-mediated p38 phosphorylation of TAK1-binding protein 1.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:1156–1164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qiao C, Han Q, Song J, Wang Z, Xu L and Xu
H: Analysis of eight bioactive compounds in alpinia species by
HPLC-DAD. Nat Prod Res Dev. 20:422–426. 2008.
|
|
17
|
Jaidee W, Andersen RJ, Chavez MAG, Wang
YA, Patrick BO, Pyne SG, Muanprasat C, Borwornpinyo S and
Laphookhieo S: Amides and flavonoids from the fruit and leaf
extracts of melodorum siamensis. J Nat Prod. 82:283–292. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ho YF, Karsani SA, Yong WK and Abd Malek
SN: Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle blockade by helichrysetin
in a549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2013:8572572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fong HY, Abd Malek SN, Yee HS and Karsani
SA: Helichrysetin induces DNA damage that triggers JNK-mediated
apoptosis in ca ski cells. Pharmacogn Mag. 13:607–612. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Doug H, Chen SX, Xu HX, Kadota S and Namba
T: A new antiplatelet diarylheptanoid from alpinia blepharocalyx. J
Nat Prod. 61:142–144. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vogel S, Ohmayer S, Brunner G and Heilmann
J: Natural and non-natural prenylated chalcones: Synthesis,
cytotoxicity and anti-oxidative activity. Bioorg Med Chem.
16:4286–4293. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ali MS, Tezuka Y, Awale S, Banskota AH and
Kadota S: Six new diarylheptanoids from the seeds of alpinia
blepharocalyx. J Nat Prod. 64:289–293. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gewali MB, Tezuka Y, Banskota AH, Ali MS,
Saiki I, Dong H and Kadota S: Epicalyxin F and calyxin I: Two novel
antiproliferative diarylheptanoids from the seeds of alpinia
blepharocalyx. Org Lett. 1:1733–1736. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Giuggioli D,
Ferrannini E, Ferri C and Fallahi P: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand
(CXCL)10 in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 13:272–280. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Somade OT, Ajayi BO, Safiriyu OA, Oyabunmi
OS and Akamo AJ: Renal and testicular up-regulation of
pro-inflammatory chemokines (RANTES and CCL2) and cytokines (TNF-α,
IL-1β, IL-6) following acute edible camphor administration is
through activation of NF-kB in rats. Toxicol Rep. 6:759–767. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Barruet E, Morales BM, Cain CJ, Ton AN,
Wentworth KL, Chan TV, Moody TA, Haks MC, Ottenhoff TH, Hellman J,
et al: NF-κB/MAPK activation underlies ACVR1-mediated inflammation
in human heterotopic ossification. JCI Insight. 3:2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Babapour N, Mehramiz M, Moghadam AR,
Behboodi N, Yousefi Z, Maftouh M, Talebian S, Khazaei M, Jafarian
A, Sharifi-Sistani N, et al: Association of TNF-308 G>A
polymorphism located in tumor necrosis factor a with the risk of
developing cervical cancer and results of pap smear. J Cell
Biochem. 120:5444–5448. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Borghi A, Verstrepen L and Beyaert R:
TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-κB, MAP
kinases and cell death. Biochem Pharmacol. 116:1–10. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fernald K and Kurokawa M: Evading
apoptosis in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 23:620–633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Annibaldi A and Meier P: Checkpoints in
TNF-induced cell death: Implications in inflammation and cancer.
Trends Mol Med. 24:49–65. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sun LR, Zhou W, Zhang HM, Guo QS, Yang W,
Li BJ, Sun ZH, Gao SH and Cui RJ: Modulation of multiple signaling
pathways of the plant-derived natural products in cancer. Front
Oncol. 9:11532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jandial DD, Blair CA, Zhang S, Krill LS,
Zhang YB and Zi X: Molecular targeted approaches to cancer therapy
and prevention using chalcones. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
14:181–200. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu M, Hansen PE, Wang G, Qiu L, Dong J,
Yin H, Qian Z, Yang M and Miao J: Pharmacological profile of
xanthohumol, a prenylated flavonoid from hops (Humulus lupulus).
Molecules. 20:754–779. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao W, Li H, Hou Y, Jin Y and Zhang L:
Combined administration of poly-ADP-ribose polymerase-1 and
caspase-3 inhibitors alleviates neuronal apoptosis after spinal
cord injury in rats. World Neurosurg. 127:e346–e352. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Malojirao VH, Vigneshwaran V, Thirusangu
P, Mahmood R and Prabhakar BT: The tumor antagonistic steroidal
alkaloid solanidine prompts the intrinsic suicidal signal mediated
DFF-40 nuclear import and nucleosomal disruption. Life Sci.
199:139–150. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ma Y, Wang Y and Song B:
Griffipavixanthone induces apoptosis of human breast cancer MCF-7
cells in vitro. Breast Cancer. 26:190–197. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
McElroy SJ, Frey MR, Yan F, Edelblum KL,
Goettel JA, John S and Polk DB: Tumor necrosis factor inhibits
ligand-stimulated EGF receptor activation through a TNF receptor
1-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
295:G285–G293. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chariot A: The NF-kappaB-independent
functions of IKK subunits in immunity and cancer. Trends Cell Biol.
19:404–413. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schlessinger J: Receptor tyrosine kinases:
Legacy of the first two decades. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
6:a0089122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lemmon MA and Schlessinger J: Cell
signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 141:1117–1134. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tan X, Lambert PF, Rapraeger AC and
Anderson RA: Stress-Induced EGFR trafficking: Mechanisms,
functions, and therapeutic implications. Trends Cell Biol.
26:352–366. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|