|
1
|
World Health Organization (WHO): Weekly
Epidemiological Update on COVID-19. WHO; Geneva: 2021
|
|
2
|
Docea AO, Tsatsakis A, Albulescu D,
Cristea O, Zlatian O, Vinceti M, Moschos SA, Tsoukalas D, Goumenou
M, Drakoulis N, et al: A new threat from an old enemy: Re-emergence
of coronavirus (Review). Int J Mol Med. 45:1631–1643.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Calina D, Hartung T, Docea AO, Spandidos
DA, Egorov AM, Shtilman MI, Carvalho F and Tsatsakis A: COVID-19
vaccines: Ethical framework concerning human challenge studies.
Daru. 28:807–812. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kostoff RN, Kanduc D, Porter AL, Shoenfeld
Y, Calina D, Briggs MB, Spandidos DA and Tsatsakis A: Vaccine- and
natural infection-induced mechanisms that could modulate vaccine
safety. Toxicol Rep. 7:1448–1458. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Calina D, Docea AO, Petrakis D, Egorov AM,
Ishmukhametov AA, Gabibov AG, Shtilman MI, Kostoff R, Carvalho F,
Vinceti M, et al: Towards effective COVID-19 vaccines: Updates,
perspectives and challenges (Review). Int J Mol Med. 46:3–16. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calina D, Sarkar C, Arsene AL, Salehi B,
Docea AO, Mondal M, Islam MT, Zali A and Sharifi-Rad J: Recent
advances, approaches and challenges in targeting pathways for
potential COVID-19 vaccines development. Immunol Res. 68:315–324.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Voysey M, Clemens SAC, Madhi SA, Weckx LY,
Folegatti PM, Aley PK, Angus B, Baillie VL, Barnabas SL, Bhorat QE,
et al Oxford COVID Vaccine Trial Group: Safety and efficacy of the
ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim
analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South
Africa, and the UK. Lancet. 397:99–111. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S,
Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH,
Nitsche A, et al: SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2
and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell.
181:271–280.e8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shang J, Ye G, Shi K, Wan Y, Luo C, Aihara
H, Geng Q, Auerbach A and Li F: Structural basis of receptor
recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature. 581:221–224. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iwata-Yoshikawa N, Okamura T, Shimizu Y,
Hasegawa H, Takeda M and Nagata N: TMPRSS2 contributes to virus
spread and immunopathology in the airways of murine models after
coronavirus infection. J Virol. 93:e01815–e01818. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Katopodis P, Anikin V, Randeva HS,
Spandidos DA, Chatha K, Kyrou I and Karteris E: Pan-cancer analysis
of transmembrane protease serine 2 and cathepsin L that mediate
cellular SARS-CoV-2 infection leading to COVID-19. Int J Oncol.
57:533–539. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bittmann S, Weissenstein A, Villalon G,
Moschuring-Alieva E and Luchter E: Simultaneous treatment of
COVID-19 with serine protease inhibitor camostat and/or cathepsin L
inhibitor? J Clin Med Res. 12:320–322. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cantuti-Castelvetri L, Ojha R, Pedro LD,
Djannatian M, Franz J, Kuivanen S, Kallio K, Kaya T, Anastasina M,
Smura T, et al: Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and
provides a possible pathway into the central nervous system.
bioRxiv. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.07.137802.
|
|
14
|
Daly JL, Simonetti B, Klein K, Chen KE,
Williamson MK, Anton-Plagaro C, Shoemark DK, Simon-Gracia L, Bauer
M, Hollandi R, et al: Neuropilin-1 is a host factor for SARS-CoV-2
infection. Science. 370:861–865. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zang R, Gomez Castro MF, McCune BT, Zeng
Q, Rothlauf PW, Sonnek NM, Liu Z, Brulois KF, Wang X, Greenberg HB,
et al: TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human
small intestinal enterocytes. Sci Immunol. 5:1–15. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lee JJ, Kopetz S, Vilar E, Shen JP, Chen K
and Maitra A: Relative abundance of SARS-CoV-2 entry genes in the
enterocytes of the lower gastrointestinal tract. Genes (Basel).
11:6452020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He
JX, Liu L, Shan H, Lei CL, Hui DSC, et al: China Medical Treatment
Expert Group for Covid-19: Clinical characteristics of coronavirus
disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 382:1708–1720. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kerslake R, Hall M, Randeva HS, Spandidos
DA, Chatha K, Kyrou I and Karteris E: Co-expression of peripheral
olfactory receptors with SARS-CoV-2 infection mediators: Potential
implications beyond loss of smell as a COVID-19 symptom. Int J Mol
Med. 46:949–956. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ng SC and Tilg H: COVID-19 and the
gastrointestinal tract: More than meets the eye. Gut. 69:973–974.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Almeida JFM and Chehter EZ: COVID-19 and
the gastrointestinal tract: What do we already know? Einstein (Sao
Paulo). 18:eRW59092020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Syed A, Khan A, Gosai F, Asif A and
Dhillon S: Gastrointestinal pathophysiology of SARS-CoV2 - a
literature review. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect.
10:523–528. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jin X, Lian JS, Hu JH, Gao J, Zheng L,
Zhang YM, Hao SR, Jia HY, Cai H, Zhang XL, et al: Epidemiological,
clinical and virological characteristics of 74 cases of
coronavirus-infected disease 2019 (COVID-19) with gastrointestinal
symptoms. Gut. 69:1002–1009. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
De Felice FG, Tovar-Moll F, Moll J, Munoz
DP and Ferreira ST: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
(SARS-CoV-2) and the central nervous system. Trends Neurosci.
43:355–357. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mao L, Jin H, Wang M, Hu Y, Chen S, He Q,
Chang J, Hong C, Zhou Y, Wang D, et al: Neurologic manifestations
of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan,
China. JAMA Neurol. 77:683–690. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Needham EJ, Chou SH-Y, Coles AJ and Menon
DK: Neurological implications of COVID-19 infections. Neurocrit
Care. 32:667–671. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mao XY and Jin WL: The COVID-19 pandemic:
consideration for brain infection. Neuroscience. 437:130–131. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu Q, Fan X, Hong H, Gu Y, Liu Z, Fang S,
Wang Q, Cai C and Fang J: Comprehensive assessment of side effects
in COVID-19 drug pipeline from a network perspective. Food Chem
Toxicol. 145:1117672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sidiropoulou P, Docea AO, Nikolaou V,
Katsarou MS, Spandidos DA, Tsatsakis A, Calina D and Drakoulis N:
Unraveling the roles of vitamin D status and melanin during
Covid-19 (Review). Int J Mol Med. 47:92–100. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Davies J, Randeva HS, Chatha K, Hall M,
Spandidos DA, Karteris E and Kyrou I: Neuropilin-1 as a new
potential SARS-CoV-2 infection mediator implicated in the
neurologic features and central nervous system involvement of
COVID-19. Mol Med Rep. 22:4221–4226. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matschke J, Lütgehetmann M, Hagel C,
Sperhake JP, Schröder AS, Edler C, Mushumba H, Fitzek A, Allweiss
L, Dandri M, et al: Neuropathology of patients with COVID-19 in
Germany: A post-mortem case series. Lancet Neurol. 19:919–929.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang K, Sheng Y, Huang C, Jin Y, Xiong N,
Jiang K, Lu H, Liu J, Yang J, Dong Y, et al: Clinical
characteristics, outcomes, and risk factors for mortality in
patients with cancer and COVID-19 in Hubei, China: A multicentre,
retrospective, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 21:904–913. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chai P, Yu J, Ge S, Jia R and Fan X:
Genetic alteration, RNA expression, and DNA methylation profiling
of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) receptor ACE2 in
malignancies: A pan-cancer analysis. J Hematol Oncol. 13:432020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Voinsky I and Gurwitz D: Smoking and
COVID-19: Similar bronchial ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression and higher
TMPRSS4 expression in current versus never smokers. Drug Dev Res.
81:1073–1080. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
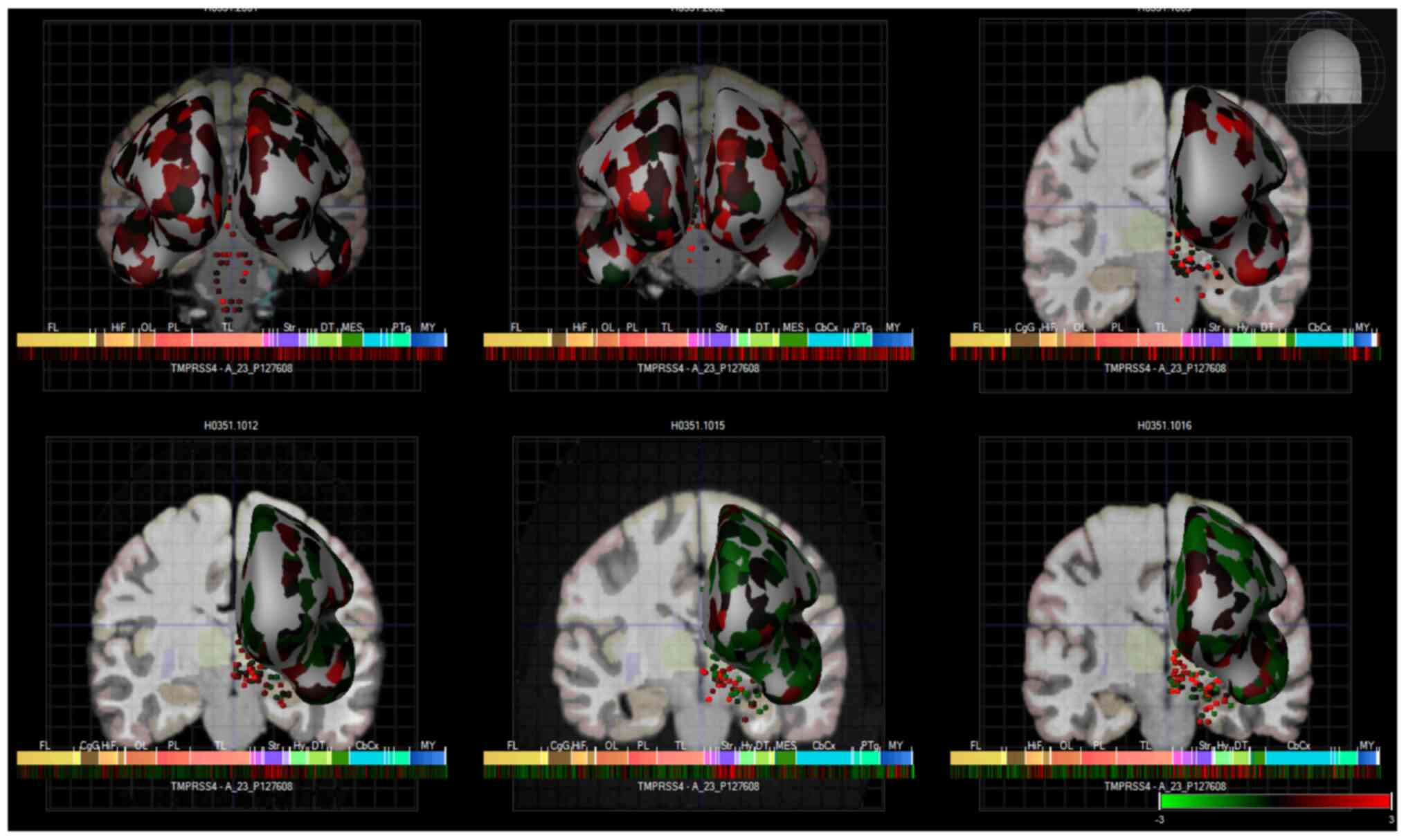
Hawrylycz MJ, Lein ES, Guillozet-Bongaarts
AL, Shen EH, Ng L, Miller JA, van de Lagemaat LN, Smith KA, Ebbert
A, Riley ZL, et al: An anatomically comprehensive atlas of the
adult human brain transcriptome. Nature. 489:391–399. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ma C, Cong Y and Zhang H: COVID-19 and the
digestive system. Am J Gastroenterol. 115:1003–1006. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Smillie CS, Biton M, Ordovas-Montanes J,
Sullivan KM, Burgin G, Graham DB, Herbst RH, Rogel N, Slyper M,
Waldman J, et al: Intra- and inter-cellular rewiring of the human
colon during ulcerative colitis. Cell. 178:714–730.e22. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Walker A, Pottinger G, Scott A and Hopkins
C: Anosmia and loss of smell in the era of covid-19. BMJ.
370:m28082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Veldhuizen MG and Small DM:
Modality-specific neural effects of selective attention to taste
and odor. Chem Senses. 36:747–760. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Darmanis S, Sloan SA, Zhang Y, Enge M,
Caneda C, Shuer LM, Hayden Gephart MG, Barres BA and Quake SR: A
survey of human brain transcriptome diversity at the single cell
level. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:7285–7290. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
de Aberasturi AL, Redrado M, Villalba M,
Larzabal L, Pajares MJ, Garcia J, Evans SR, Garcia-Ros D, Bodegas
ME, Lopez L, et al: TMPRSS4 induces cancer stem cell-like
properties in lung cancer cells and correlates with ALDH expression
in NSCLC patients. Cancer Lett. 370:165–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Larzabal L, Nguewa PA, Pio R, Blanco D,
Sanchez B, Rodríguez MJ, Pajares MJ, Catena R, Montuenga LM and
Calvo A: Overexpression of TMPRSS4 in non-small cell lung cancer is
associated with poor prognosis in patients with squamous histology.
Br J Cancer. 105:1608–1614. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Suzuki K, Nagai K, Yoshida J, Nishimura M,
Takahashi K, Yokose T and Nishiwaki Y: Conventional
clinicopathologic prognostic factors in surgically resected
nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. A comparison of prognostic factors
for each pathologic TNM stage based on multivariate analyses.
Cancer. 86:1976–1984. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Henarejos-Castillo I, Sebastian-Leon P,
Devesa-Peiro A, Pellicer A and Diaz-Gimeno P: SARS-CoV-2 infection
risk assessment in the endometrium: Viral infection-related gene
expression across the menstrual cycle. Fertil Steril. 114:223–232.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nikolich-Zugich J, Knox KS, Rios CT, Natt
B, Bhattacharya D and Fain MJ: SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in older
adults: What we may expect regarding pathogenesis, immune
responses, and outcomes. Geroscience. 42:505–514. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
Erratum. Geroscience. 42:10132020.
|
|
45
|
Guadarrama-Ortiz P, Choreño-Parra JA,
Sánchez-Martínez CM, Pacheco-Sánchez FJ, Rodríguez-Nava AI and
García-Quintero G: Neurological aspects of SARS-CoV-2 infection:
mechanisms and manifestations. Front Neurol. 11:10392020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Frank S: Catch me if you can: SARS-CoV-2
detection in brains of deceased patients with COVID-19. Lancet
Neurol. 19:883–884. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|