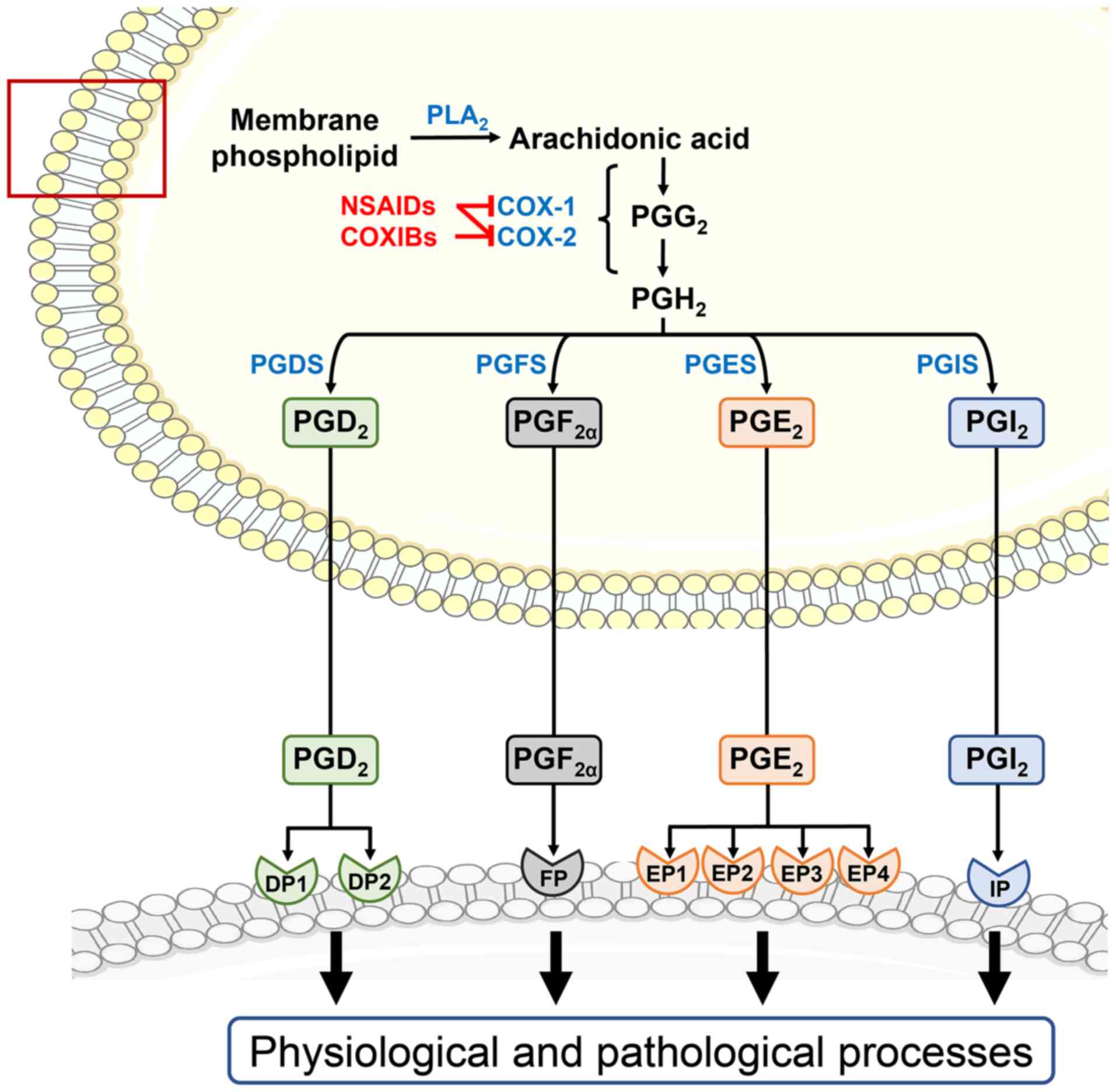
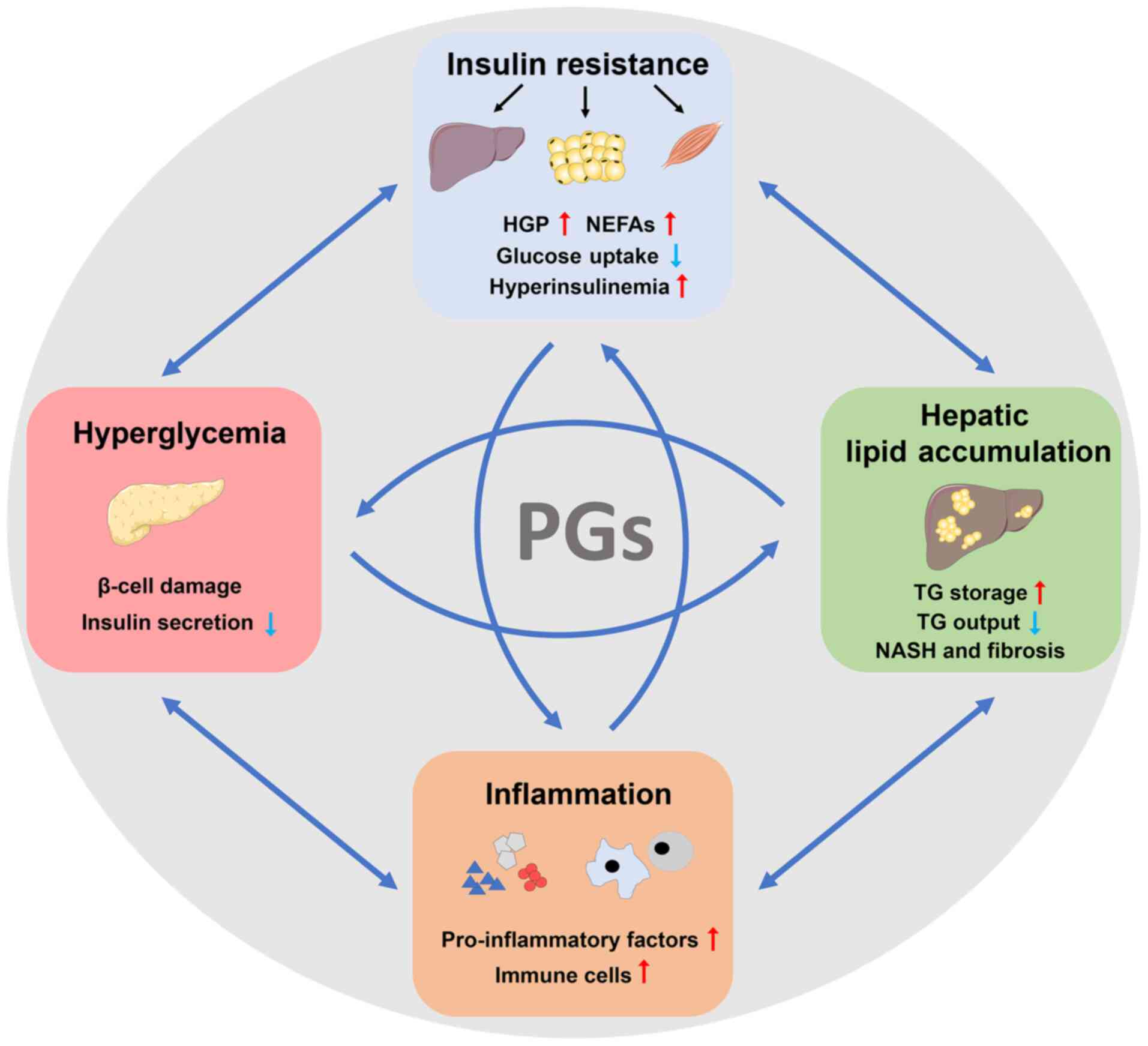
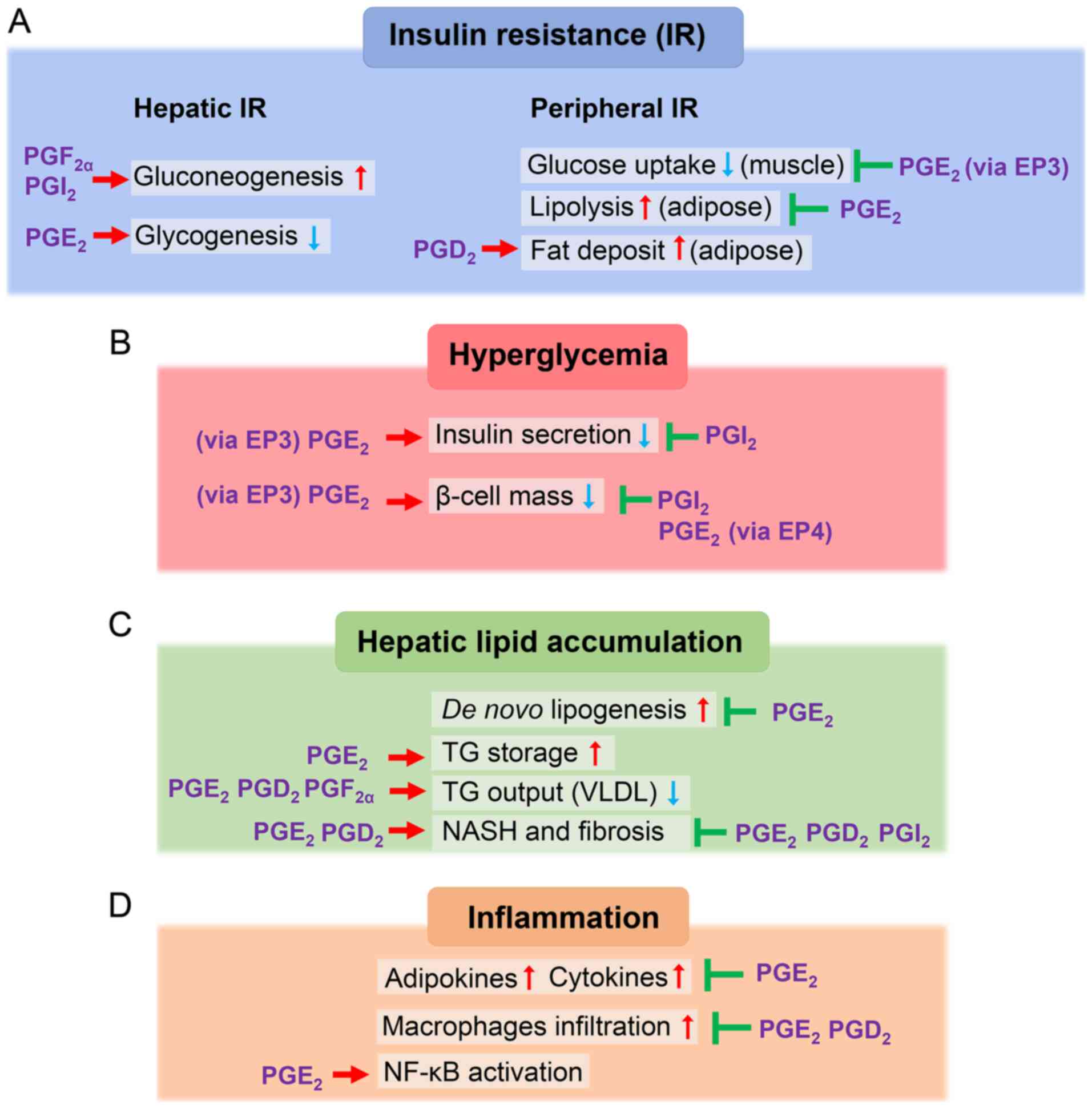
|
1
|
International Diabetes Federation(IDF):
IDF diabetes atlas. 9th edition. IDF; Brussels: 2019
|
|
2
|
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel
Y, Henry L and Wymer M: Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence,
and outcomes. Hepatology. 64:73–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chatterjee S, Khunti K and Davies MJ: Type
2 diabetes. Lancet. 389:2239–2251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy
T, Henry L, Eslam M, George J and Bugianesi E: Global burden of
NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention.
Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:11–20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhou F, Zhou J, Wang W, Zhang XJ, Ji YX,
Zhang P, She ZG, Zhu L, Cai J and Li H: Unexpected rapid increase
in the burden of NAFLD in China from 2008 to 2018: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Hepatology. 70:1119–1133. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Younossi ZM, Golabi P, de Avila L, Paik
JM, Srishord M, Fukui N, Qiu Y, Burns L, Afendy A and Nader F: The
global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2
diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol.
71:793–801. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sung KC, Jeong WS, Wild SH and Byrne CD:
Combined influence of insulin resistance, overweight/obesity, and
fatty liver as risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care.
35:717–722. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wild SH, Morling JR, McAllister DA,
Kerssens J, Fischbacher C, Parkes J, Roderick PJ, Sattar N and
Byrne CD; Scottish and Southampton Diabetes and Liver Disease
Group: Scottish Diabetes Research Network Epidemiology Group: Type
2 diabetes and risk of hospital admission or death for chronic
liver diseases. J Hepatol. 64:1358–1364. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leite NC, Villela-Nogueira CA, Pannain VL,
Bottino AC, Rezende GF, Cardoso CR and Salles GF: Histopathological
stages of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes:
Prevalences and correlated factors. Liver Int. 31:700–706. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Prashanth M, Ganesh HK, Vima MV, John M,
Bandgar T, Joshi SR, Shah SR, Rathi PM, Joshi AS, Thakkar H, et al:
Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with
type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Assoc Physicians India. 57:205–210.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dam-Larsen S, Franzmann M, Andersen IB,
Christoffersen P, Jensen LB, Sørensen TI, Becker U and Bendtsen F:
Long term prognosis of fatty liver: Risk of chronic liver disease
and death. Gut. 53:750–755. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ratziu V, Bonyhay L, Di Martino V,
Charlotte F, Cavallaro L, Sayegh-Tainturier MH, Giral P, Grimaldi
A, Opolon P and Poynard T: Survival, liver failure, and
hepatocellular carcinoma in obesity-related cryptogenic cirrhosis.
Hepatology. 35:1485–1493. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ekstedt M, Franzén LE, Mathiesen UL,
Thorelius L, Holmqvist M, Bodemar G and Kechagias S: Long-term
follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes.
Hepatology. 44:865–873. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rafiq N, Bai C, Fang Y, Srishord M,
McCullough A, Gramlich T and Younossi ZM: Long-term follow-up of
patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
7:234–238. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Targher G, Bertolini L, Padovani R,
Rodella S, Tessari R, Zenari L, Day C and Arcaro G: Prevalence of
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its association with
cardiovascular disease among type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes
Care. 30:1212–1218. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ryysy L, Häkkinen AM, Goto T, Vehkavaara
S, Westerbacka J, Halavaara J and Yki-Järvinen H: Hepatic fat
content and insulin action on free fatty acids and glucose
metabolism rather than insulin absorption are associated with
insulin requirements during insulin therapy in type 2 diabetic
patients. Diabetes. 49:749–758. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lomonaco R, Bril F, Portillo-Sanchez P,
Ortiz-Lopez C, Orsak B, Biernacki D, Lo M, Suman A, Weber MH and
Cusi K: Metabolic impact of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in obese
patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 39:632–638. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G,
Tomassetti S, Bugianesi E, Lenzi M, McCullough AJ, Natale S,
Forlani G and Melchionda N: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A
feature of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes. 50:1844–1850. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cai D, Yuan M, Frantz DF, Melendez PA,
Hansen L, Lee J and Shoelson SE: Local and systemic insulin
resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-beta and
NF-kappaB. Nat Med. 11:183–190. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun G, Jackson CV, Zimmerman K, Zhang LK,
Finnearty CM, Sandusky GE, Zhang G, Peterson RG and Wang YJ: The
FATZO mouse, a next generation model of type 2 diabetes, develops
NAFLD and NASH when fed a Western diet supplemented with fructose.
BMC Gastroenterol. 19:412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Garcia-Jaramillo M, Spooner MH, Löhr CV,
Wong CP, Zhang W and Jump DB: Lipidomic and transcriptomic analysis
of western diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in
female Ldlr-/-mice. PLoS One. 14:e02143872019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Verboven M, Deluyker D, Ferferieva V,
Lambrichts I, Hansen D, Eijnde BO and Bito V: Western diet given to
healthy rats mimics the human phenotype of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
J Nutr Biochem. 61:140–146. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hernandez-Rodas MC, Valenzuela R and
Videla LA: Relevant aspects of nutritional and dietary
interventions in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci.
16:25168–25198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Valenzuela R and Videla LA: The importance
of the long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid n-6/n-3 ratio in
development of non-alcoholic fatty liver associated with obesity.
Food Funct. 2:644–648. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Taha AY, Cheon Y, Faurot KF, Macintosh B,
Majchrzak-Hong SF, Mann JD, Hibbeln JR, Ringel A and Ramsden CE:
Dietary omega-6 fatty acid lowering increases bioavailability of
omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in human plasma lipid pools.
Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 90:151–157. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wood KE, Lau A, Mantzioris E, Gibson RA,
Ramsden CE and Muhlhausler BS: A low omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty
acid (n-6 PUFA) diet increases omega-3 (n-3) long chain PUFA status
in plasma phospholipids in humans. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent
Fatty Acids. 90:133–138. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xia F, He C, Ren M, Xu FG and Wan JB:
Quantitative profiling of eicosanoids derived from n-6 and n-3
polyunsaturated fatty acids by twin derivatization strategy
combined with LC-MS/MS in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Anal Chim Acta. 1120:24–35. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li N, Yue H, Jia M, Liu W, Qiu B, Hou H,
Huang F and Xu T: Effect of low-ratio n-6/n-3 PUFA on blood
glucose: A meta-analysis. Food Funct. 10:4557–4565. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu HQ, Qiu Y, Mu Y, Zhang XJ, Liu L, Hou
XH, Zhang L, Xu XN, Ji AL, Cao R, et al: A high ratio of dietary
n-3/n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids improves obesity-linked
inflammation and insulin resistance through suppressing activation
of TLR4 in SD rats. Nutr Res. 33:849–858. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shrestha N, Cuffe JSM, Holland OJ, Perkins
AV, McAinch AJ and Hryciw DH: Linoleic acid increases prostaglandin
E2 release and reduces mitochondrial respiration and cell viability
in human trophoblast-like cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 52:94–108.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kliewer SA, Lenhard JM, Willson TM, Patel
I, Morris DC and Lehmann JM: A prostaglandin J2 metabolite binds
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and promotes
adipocyte differentiation. Cell. 83:813–819. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hennig B, Toborek M, Joshi-Barve S, Barger
SW, Barve S, Mattson MP and McClain CJ: Linoleic acid activates
nuclear transcription factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B) and induces
NF-kappa B-dependent transcription in cultured endothelial cells.
Am J Clin Nutr. 63:322–328. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Seo MJ and Oh DK: Prostaglandin synthases:
Molecular characterization and involvement in prostaglandin
biosynthesis. Prog Lipid Res. 66:50–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schaid MD, Zhu Y, Richardson NE,
Patibandla C, Ong IM, Fenske RJ, Neuman JC, Guthery E, Reuter A,
Sandhu HK, et al: Systemic metabolic alterations correlate with
islet-level prostaglandin E2 production and signaling mechanisms
that predict β-cell dysfunction in a mouse model of type 2
diabetes. Metabolites. 11:582021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nasrallah R, Robertson SJ, Karsh J and
Hébert RL: Celecoxib modifies glomerular basement membrane,
mesangium and podocytes in OVE26 mice, but ibuprofen is more
detrimental. Clin Sci (Lond). 124:685–694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chan PC, Hsiao FC, Chang HM, Wabitsch M
and Hsieh PS: Importance of adipocyte cyclooxygenase-2 and
prostaglandin E2-prostaglandin E receptor 3 signaling in the
development of obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation and
insulin resistance. FASEB J. 30:2282–2297. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hsieh PS, Jin JS, Chiang CF, Chan PC, Chen
CH and Shih KC: COX-2-mediated inflammation in fat is crucial for
obesity-linked insulin resistance and fatty liver. Obesity (Silver
Spring). 17:1150–1157. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Szerafin T, Erdei N, Fulop T, Pasztor ET,
Edes I, Koller A and Bagi Z: Increased cyclooxygenase-2 expression
and prostaglandin-mediated dilation in coronary arterioles of
patients with diabetes mellitus. Circ Res. 99:e12–e17. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang T, Cai H, Zheng W, Michel A, Pawlita
M, Milne G, Xiang YB, Gao YT, Li HL, Rothman N, et al: A
prospective study of urinary prostaglandin E2 metabolite,
helicobacter pylori antibodies, and gastric cancer risk. Clin
Infect Dis. 64:1380–1386. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Na YR, Jung D, Stakenborg M, Jang H, Gu
GJ, Jeong MR, Suh SY, Kim HJ, Kwon YH, Sung TS, et al:
Prostaglandin E2 receptor PTGER4-expressing macrophages promote
intestinal epithelial barrier regeneration upon inflammation. Gut.
Feb 7–2021.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
McCoy JM, Wicks JR and Audoly LP: The role
of prostaglandin E2 receptors in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid
arthritis. J Clin Invest. 110:651–658. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fajt ML, Gelhaus SL, Freeman B, Uvalle CE,
Trudeau JB, Holguin F and Wenzel SE: Prostaglandin D2
pathway upregulation: Relation to asthma severity, control, and TH2
inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 131:1504–1512. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hoshino T, Nakaya T, Homan T, Tanaka K,
Sugimoto Y, Araki W, Narita M, Narumiya S, Suzuki T and Mizushima
T: Involvement of prostaglandin E2 in production of amyloid-beta
peptides both in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 282:32676–32688.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Feingold KR, Doerrler W, Dinarello CA,
Fiers W and Grunfeld C: Stimulation of lipolysis in cultured fat
cells by tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, and the interferons
is blocked by inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. Endocrinology.
130:10–16. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yokota T, Meka CS, Medina KL, Igarashi H,
Comp PC, Takahashi M, Nishida M, Oritani K, Miyagawa J, Funahashi
T, et al: Paracrine regulation of fat cell formation in bone marrow
cultures via adiponectin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest.
109:1303–1310. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Forman BM, Tontonoz P, Chen J, Brun RP,
Spiegelman BM and Evans RM: 15-Deoxy-delta 12, 14-prostaglandin J2
is a ligand for the adipocyte determination factor PPAR gamma.
Cell. 83:803–812. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Litherland SA, Xie XT, Hutson AD,
Wasserfall C, Whittaker DS, She JX, Hofig A, Dennis MA, Fuller K,
Cook R, et al: Aberrant prostaglandin synthase 2 expression defines
an antigen-presenting cell defect for insulin-dependent diabetes
mellitus. J Clin Invest. 104:515–523. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yasui M, Tamura Y, Minami M, Higuchi S,
Fujikawa R, Ikedo T, Nagata M, Arai H, Murayama T and Yokode M: The
prostaglandin E2 receptor EP4 regulates obesity-related
inflammation and insulin sensitivity. PLoS One. 10:e01363042015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Edelman MJ, Wang X, Hodgson L, Cheney RT,
Baggstrom MQ, Thomas SP, Gajra A, Bertino E, Reckamp KL, Molina J,
et al: Phase III randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial
of celecoxib in addition to standard chemotherapy for advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer with cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression:
CALGB 30801 (Alliance). J Clin Oncol. 35:2184–2192. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pathan SA, Mitra B, Straney LD, Afzal MS,
Anjum S, Shukla D, Morley K, Al Hilli SA, Al Rumaihi K, Thomas SH
and Cameron PA: Delivering safe and effective analgesia for
management of renal colic in the emergency department: A
double-blind, multigroup, randomised controlled trial. Lancet.
387:1999–2007. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bath PM, Woodhouse LJ, Appleton JP,
Beridze M, Christensen H, Dineen RA, Duley L, England TJ, Flaherty
K, Havard D, et al: Antiplatelet therapy with aspirin, clopidogrel,
and dipyridamole versus clopidogrel alone or aspirin and
dipyridamole in patients with acute cerebral ischaemia (TARDIS): A
randomised, open-label, phase 3 superiority trial. Lancet.
391:850–859. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Norambuena F, Mackenzie S, Bell JG, Callol
A, Estévez A and Duncan N: Prostaglandin (F and E, 2- and 3-series)
production and cyclooxygenase (COX-2) gene expression of wild and
cultured broodstock of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Gen
Comp Endocrinol. 177:256–262. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang X, Lin H and Gu Y: Multiple roles of
dihomo-γ-linolenic acid against proliferation diseases. Lipids
Health Dis. 11:252012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sonnweber T, Pizzini A, Nairz M, Weiss G
and Tancevski I: Arachidonic acid metabolites in cardiovascular and
metabolic diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 19:32852018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
Cheng Z, Abayasekara DR and Wathes DC: The
effect of supplementation with n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids on
1-, 2- and 3-series prostaglandin F production by ovine uterine
epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1736:128–135. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Smith WL, Urade Y and Jakobsson PJ:
Enzymes of the cyclooxygenase pathways of prostanoid biosynthesis.
Chem Rev. 111:5821–5865. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Seibert K, Zhang Y, Leahy K, Hauser S,
Masferrer J, Perkins W, Lee L and Isakson P: Pharmacological and
biochemical demonstration of the role of cyclooxygenase 2 in
inflammation and pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:12013–12017.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kirkby NS, Zaiss AK, Urquhart P, Jiao J,
Austin PJ, Al-Yamani M, Lundberg MH, MacKenzie LS, Warner TD,
Nicolaou A, et al: LC-MS/MS confirms that COX-1 drives vascular
prostacyclin whilst gene expression pattern reveals non-vascular
sites of COX-2 expression. PLoS One. 8:e695242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kirkby NS, Chan MV, Zaiss AK, Garcia-Vaz
E, Jiao J, Berglund LM, Verdu EF, Ahmetaj-Shala B, Wallace JL,
Herschman HR, et al: Systematic study of constitutive
cyclooxygenase-2 expression: Role of NF-κB and NFAT transcriptional
pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci A. 113:434–439. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Smith WL, DeWitt DL and Garavito RM:
Cyclooxygenases: Structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu
Rev Biochem. 69:145–182. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tilg H, Moschen AR and Roden M: NAFLD and
diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:32–42. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Oakes ND, Cooney GJ, Camilleri S, Chisholm
DJ and Kraegen EW: Mechanisms of liver and muscle insulin
resistance induced by chronic high-fat feeding. Diabetes.
46:1768–1774. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Krssak M, Brehm A, Bernroider E, Anderwald
C, Nowotny P, Dalla Man C, Cobelli C, Cline GW, Shulman GI,
Waldhäusl W and Roden M: Alterations in postprandial hepatic
glycogen metabolism in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 53:3048–3056.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Smith GI, Shankaran M, Yoshino M,
Schweitzer GG, Chondronikola M, Beals JW, Okunade AL, Patterson BW,
Nyangau E, Field T, et al: Insulin resistance drives hepatic de
novo lipogenesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin
Invest. 130:1453–1460. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
65
|
McQuaid SE, Hodson L, Neville MJ, Dennis
AL, Cheeseman J, Humphreys SM, Ruge T, Gilbert M, Fielding BA,
Frayn KN and Karpe F: Downregulation of adipose tissue fatty acid
trafficking in obesity: A driver for ectopic fat deposition?
Diabetes. 60:47–55. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
66
|
Garcia-Monzón C, Lo Iacono O, Mayoral R,
González-Rodriguez A, Miquilena-Colina ME, Lozano-Rodriguez T,
Garcia-Pozo L, Vargas Castrillón J, Casado M, Boscá L, et al:
Hepatic insulin resistance is associated with increased apoptosis
and fibrogenesis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and chronic
hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 54:142–152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum
M, Leibel RL and Ferrante AW Jr: Obesity is associated with
macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest.
112:1796–1808. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D,
Chou CJ, Sole J, Nichols A, Ross JS, Tartaglia LA and Chen H:
Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development
of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest.
112:1821–1830. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Cook JR, Langlet F, Kido Y and Accili D:
Pathogenesis of selective insulin resistance in isolated
hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 290:13972–13980. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Cao Z, Mulvihill MM, Mukhopadhyay P, Xu H,
Erdélyi K, Hao E, Holovac E, Haskó G, Cravatt BF, Nomura DK and
Pacher P: Monoacylglycerol lipase controls endocannabinoid and
eicosanoid signaling and hepatic injury in mice. Gastroenterology.
144:808–817.e15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Henkel J, Gärtner D, Dorn C, Hellerbrand
C, Schanze N, Elz SR and Püschel GP: Oncostatin M produced in
Kupffer cells in response to PGE2: Possible contributor to hepatic
insulin resistance and steatosis. Lab Invest. 91:1107–1117. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Henkel J, Neuschäfer-Rube F,
Pathe-Neuschäfer-Rube A and Püschel GP: Aggravation by
prostaglandin E2 of interleukin-6-dependent insulin resistance in
hepatocytes. Hepatology. 50:781–790. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Bock G, Chittilapilly E, Basu R, Toffolo
G, Cobelli C, Chandramouli V, Landau BR and Rizza RA: Contribution
of hepatic and extrahepatic insulin resistance to the pathogenesis
of impaired fasting glucose: Role of increased rates of
gluconeogenesis. Diabetes. 56:1703–1711. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wang Y, Yan S, Xiao B, Zuo S, Zhang Q,
Chen G, Yu Y, Chen D, Liu Q, Liu Y, et al: Prostaglandin
F2α facilitates hepatic glucose production through
CaMKIIγ/p38/FOXO1 signaling pathway in fasting and obesity.
Diabetes. 67:1748–1760. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yan S, Zhang Q, Zhong X, Tang J, Wang Y,
Yu J, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Guo F, Liu Y, et al: I prostanoid
receptor-mediated inflammatory pathway promotes hepatic
gluconeogenesis through activation of PKA and inhibition of AKT.
Diabetes. 63:2911–2923. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Francés DE, Motiño O, Agrá N,
González-Rodríguez Á, Fernández-Álvarez A, Cucarella C, Mayoral R,
Castro-Sánchez L, García-Casarrubios E, Boscá L, et al: Hepatic
cyclooxygenase-2 expression protects against diet-induced
steatosis, obesity, and insulin resistance. Diabetes. 64:1522–1531.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Petersen KF, Dufour S, Savage DB, Bilz S,
Solomon G, Yonemitsu S, Cline GW, Befroy D, Zemany L, Kahn BB, et
al: The role of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in the
pathogenesis of the metabolic syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:12587–12594. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Banhos Danneskiold-Samsøe N, Sonne SB,
Larsen JM, Hansen AN, Fjære E, Isidor MS, Petersen S, Henningsen J,
Severi I, Sartini L, et al: Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 in
adipocytes reduces fat accumulation in inguinal white adipose
tissue and hepatic steatosis in high-fat fed mice. Sci Rep.
9:89792019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ceddia RP, Lee D, Maulis MF, Carboneau BA,
Threadgill DW, Poffenberger G, Milne G, Boyd KL, Powers AC,
McGuinness OP, et al: The PGE2 EP3 receptor regulates dietinduced
adiposity in male mice. Endocrinology. 157:220–232. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Garcia-Alonso V, Titos E, Alcaraz-Quiles
J, Rius B, Lopategi A, López-Vicario C, Jakobsson PJ, Delgado S,
Lozano J and Clària J: Prostaglandin E2 exerts multiple regulatory
actions on human obese adipose tissue remodeling, inflammation,
adaptive thermogenesis and lipolysis. PLoS One. 11:e01537512016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Fujitani Y, Aritake K, Kanaoka Y, Goto T,
Takahashi N, Fujimori K and Kawada T: Pronounced adipogenesis and
increased insulin sensitivity caused by overproduction of
prostaglandin D2 in vivo. FEBS J. 277:1410–1419. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Virtue S, Masoodi M, de Weijer BA, van
Eijk M, Mok CY, Eiden M, Dale M, Pirraco A, Serlie MJ, Griffin JL
and Vidal-Puig A: Prostaglandin profiling reveals a role for
haematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase in adipose tissue
macrophage polarisation in mice and humans. Int J Obes (Lond).
39:1151–1160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Hernandez-Carretero A, Weber N, La Frano
MR, Ying W, Lantero Rodriguez J, Sears DD, Wallenius V, Borgeson E,
Newman JW and Osborn O: Obesity-induced changes in lipid mediators
persist after weight loss. Int J Obes (Lond). 42:728–736. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Fujimori K, Aritake K, Oishi Y, Nagata N,
Maehara T, Lazarus M and Urade Y: L-PGDS-produced PGD2 in
premature, but not in mature, adipocytes increases obesity and
insulin resistance. Sci Rep. 9:19312019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
85
|
Fujimori K, Maruyama T, Kamauchi S and
Urade Y: Activation of adipogenesis by lipocalin-type prostaglandin
D synthase-generated Δ¹2-PGJ2 acting through
PPARγ-dependent and independent pathways. Gene. 505:46–52. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wakai E, Aritake K, Urade Y and Fujimori
K: Prostaglandin D2 enhances lipid accumulation through suppression
of lipolysis via DP2 (CRTH2) receptors in adipocytes. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 490:393–399. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Groop LC, Bonadonna RC, DelPrato S,
Ratheiser K, Zyck K, Ferrannini E and DeFronzo RA: Glucose and free
fatty acid metabolism in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Evidence for multiple sites of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest.
84:205–213. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Skurk T, Alberti-Huber C, Herder C and
Hauner H: Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine
expression and secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 92:1023–1033.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Lê KA, Mahurkar S, Alderete TL, Hasson RE,
Adam TC, Kim JS, Beale E, Xie C, Greenberg AS, Allayee H and Goran
MI: Subcutaneous adipose tissue macrophage infiltration is
associated with hepatic and visceral fat deposition,
hyperinsulinemia, and stimulation of NF-κB stress pathway.
Diabetes. 60:2802–2809. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Utriainen T, Takala T, Luotolahti M,
Rönnemaa T, Laine H, Ruotsalainen U, Haaparanta M, Nuutila P and
Yki-Järvinen H: Insulin resistance characterizes glucose uptake in
skeletal muscle but not in the heart in NIDDM. Diabetologia.
41:555–559. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Pratipanawatr W, Pratipanawatr T, Cusi K,
Berria R, Adams JM, Jenkinson CP, Maezono K, DeFronzo RA and
Mandarino LJ: Skeletal muscle insulin resistance in normoglycemic
subjects with a strong family history of type 2 diabetes is
associated with decreased insulin-stimulated insulin receptor
substrate-1 tyrosine phosphorylation. Diabetes. 50:2572–2578. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Weyer C, Bogardus C, Mott DM and Pratley
RE: The natural history of insulin secretory dysfunction and
insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
J Clin Invest. 104:787–794. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Dietze G, Wicklmayr M, Böttger I and Mayer
L: Insulin action on glucose uptake into skeletal muscle:
Inhibition of endogenous biosynthesis of prostaglandins. FEBS Lett.
92:294–298. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Leighton B, Budohoski L, Lozeman FJ,
Challiss RA and Newsholme EA: The effect of prostaglandins E1, E2
and F2 alpha and indomethacin on the sensitivity of glycolysis and
glycogen synthesis to insulin in stripped soleus muscles of the
rat. Biochem J. 227:337–340. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Coll T, Palomer X, Blanco-Vaca F,
Escolà-Gil JC, Sánchez RM, Laguna JC and Vázquez-Carrera M:
Cyclooxygenase 2 inhibition exacerbates palmitate-induced
inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells.
Endocrinology. 151:537–548. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Smith GI, Polidori DC, Yoshino M, Kearney
ML, Patterson BW, Mittendorfer B and Klein S: Influence of
adiposity, insulin resistance, and intrahepatic triglyceride
content on insulin kinetics. J Clin Invest. 130:3305–3314. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Solomon TP, Knudsen SH, Karstoft K,
Winding K, Holst JJ and Pedersen BK: Examining the effects of
hyperglycemia on pancreatic endocrine function in humans: Evidence
for in vivo glucotoxicity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:4682–4691.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Hughan KS, Bonadonna RC, Lee S,
Michaliszyn SF and Arslanian SA: β-Cell lipotoxicity after an
overnight intravenous lipid challenge and free fatty acid elevation
in African American versus American white overweight/obese
adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98:2062–2069. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Goodpaster BH, Thaete FL and Kelley DE:
Thigh adipose tissue distribution is associated with insulin
resistance in obesity and in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Clin
Nutr. 71:885–892. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Solini A, Rossi C, Duranti E, Taddei S,
Natali A and Virdis A: Saxagliptin prevents vascular remodeling and
oxidative stress in db/db mice. Role of endothelial nitric oxide
synthase uncoupling and cyclooxygenase. Vascul Pharmacol. 76:62–71.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Hundal RS, Petersen KF, Mayerson AB,
Randhawa PS, Inzucchi S, Shoelson SE and Shulman GI: Mechanism by
which high-dose aspirin improves glucose metabolism in type 2
diabetes. J Clin Invest. 109:1321–1326. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Helmersson J, Vessby B, Larsson A and Basu
S: Association of type 2 diabetes with cyclooxygenase-mediated
inflammation and oxidative stress in an elderly population.
Circulation. 109:1729–1734. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Kimple ME, Keller MP, Rabaglia MR, Pasker
RL, Neuman JC, Truchan NA, Brar HK and Attie AD: Prostaglandin E2
receptor, EP3, is induced in diabetic islets and negatively
regulates glucose- and hormone-stimulated insulin secretion.
Diabetes. 62:1904–1912. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Batchu SN, Majumder S, Bowskill BB, White
KE, Advani SL, Brijmohan AS, Liu Y, Thai K, Azizi PM, Lee WL and
Advani A: Prostaglandin I2 receptor agonism preserves β-cell
function and attenuates albuminuria through nephrin-dependent
mechanisms. Diabetes. 65:1398–1409. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Arablou T, Aryaeian N, Valizadeh M,
Sharifi F, Hosseini A and Djalali M: The effect of ginger
consumption on glycemic status, lipid profile and some inflammatory
markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Food Sci
Nutr. 65:515–520. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zhu CF, Li GZ, Peng HB, Zhang F, Chen Y
and Li Y: Treatment with marine collagen peptides modulates glucose
and lipid metabolism in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 35:797–804. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Ceddia RP, Downey JD, Morrison RD, Kraemer
MP, Davis SE, Wu J, Lindsley CW, Yin H, Daniels JS and Breyer RM:
The effect of the EP3 antagonist DG-041 on male mice with
diet-induced obesity. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat.
144:1063532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Weir GC, Gaglia J and Bonner-Weir S:
Inadequate β-cell mass is essential for the pathogenesis of type 2
diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 8:249–256. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Grodsky GM: A threshold distribution
hypothesis for packet storage of insulin and its mathematical
modeling. J Clin Invest. 51:2047–2059. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Persaud SJ, Muller D, Belin VD,
Kitsou-Mylona I, Asare-Anane H, Papadimitriou A, Burns CJ, Huang
GC, Amiel SA and Jones PM: The role of arachidonic acid and its
metabolites in insulin secretion from human islets of langerhans.
Diabetes. 56:197–203. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Tran PO, Gleason CE, Poitout V and
Robertson RP: Prostaglandin E(2) mediates inhibition of insulin
secretion by interleukin-1beta. J Biol Chem. 274:31245–31248. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Tran PO, Gleason CE and Robertson RP:
Inhibition of interleukin-1beta-induced COX-2 and EP3 gene
expression by sodium salicylate enhances pancreatic islet beta-cell
function. Diabetes. 51:1772–1778. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Shanmugam N, Todorov IT, Nair I, Omori K,
Reddy MA and Natarajan R: Increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2
in human pancreatic islets treated with high glucose or ligands of
the advanced glycation endproduct-specific receptor (AGER), and in
islets from diabetic mice. Diabetologia. 49:100–107. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Persaud SJ, Burns CJ, Belin VD and Jones
PM: Glucose-induced regulation of COX-2 expression in human islets
of langerhans. Diabetes. 53(Suppl 1): S190–S192. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Shridas P, Zahoor L, Forrest KJ, Layne JD
and Webb NR: Group X secretory phospholipase A2 regulates insulin
secretion through a cyclooxygenase-2-dependent mechanism. J Biol
Chem. 289:27410–27417. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Seaquist ER, Walseth TF, Nelson DM and
Robertson RP: Pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein mediation of PGE2
inhibition of cAMP metabolism and phasic glucose-induced insulin
secretion in HIT cells. Diabetes. 38:1439–1445. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Carboneau BA, Allan JA, Townsend SE,
Kimple ME, Breyer RM and Gannon M: Opposing effects of
prostaglandin E2 receptors EP3 and EP4 on mouse and human β-cell
survival and proliferation. Mol Metab. 6:548–559. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Meng ZX, Sun JX, Ling JJ, Lv JH, Zhu DY,
Chen Q, Sun YJ and Han X: Prostaglandin E2 regulates Foxo activity
via the Akt pathway: Implications for pancreatic islet beta cell
dysfunction. Diabetologia. 49:2959–2968. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Anderson SL, Trujillo JM, McDermott M and
Saseen JJ: Determining predictors of response to exenatide in type
2 diabetes. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 52. pp. 466–471. 2012,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Kimple ME, Moss JB, Brar HK, Rosa TC,
Truchan NA, Pasker RL, Newgard CB and Casey PJ: Deletion of GαZ
protein protects against diet-induced glucose intolerance via
expansion of β-cell mass. J Biol Chem. 287:20344–20355. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Zawalich WS, Zawalich KC and Yamazaki H:
Divergent effects of epinephrine and prostaglandin E2 on
glucose-induced insulin secretion from perifused rat islets.
Metabolism. 56:12–18. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Igoillo-Esteve M, Marselli L, Cunha DA,
Ladrière L, Ortis F, Grieco FA, Dotta F, Weir GC, Marchetti P,
Eizirik DL and Cnop M: Palmitate induces a pro-inflammatory
response in human pancreatic islets that mimics CCL2 expression by
beta cells in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 53:1395–1405. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Gokulakrishnan K, Mohanavalli KT,
Monickaraj F, Mohan V and Balasubramanyam M: Subclinical
inflammation/oxidation as revealed by altered gene expression
profiles in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and Type 2
diabetes patients. Mol Cell Biochem. 324:173–181. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Wang G, Liang R, Liu T, Wang L, Zou J, Liu
N, Liu Y, Cai X, Liu Y, Ding X, et al: Opposing effects of
IL-1β/COX-2/PGE2 pathway loop on islets in type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Endocr J. 66:691–699. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE
and Ridker PM: C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of
developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 286:327–334. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Abou-Shousha S, Abd El-Megeed MH and
Sultan HK: Interleukin-8, ferritin and soluble transferrin
receptors in type II diabetes mellitus. Egypt J Immunol. 13:19–25.
2006.
|
|
127
|
Cai W, Qiu C, Zhang H, Chen X, Zhang X,
Meng Q and Wei J: Detection of circulating natural antibodies to
inflammatory cytokines in type-2 diabetes and clinical
significance. J Inflamm (Lond). 14:242017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Rahier J, Guiot Y, Goebbels RM, Sempoux C
and Henquin JC: Pancreatic beta-cell mass in European subjects with
type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 10(Suppl 4): S32–S42. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel
R, Rizza RA and Butler PC: Beta-cell deficit and increased
beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes.
52:102–110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Oshima H, Taketo MM and Oshima M:
Destruction of pancreatic beta-cells by transgenic induction of
prostaglandin E2 in the islets. J Biol Chem. 281:29330–29336. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Kimple ME, Nixon AB, Kelly P, Bailey CL,
Young KH, Fields TA and Casey PJ: A role for G(z) in pancreatic
islet beta-cell biology. J Biol Chem. 280:31708–31713. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Amior L, Srivastava R, Nano R, Bertuzzi F
and Melloul D: The role of Cox-2 and prostaglandin E2 receptor EP3
in pancreatic β-cell death. FASEB J. 33:4975–4986. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Lewis B, Mancini M, Mattock M, Chait A and
Fraser TR: Plasma triglyceride and fatty acid metabolism in
diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Invest. 2:445–453. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Diraison F, Moulin P and Beylot M:
Contribution of hepatic de novo lipogenesis and reesterification of
plasma non esterified fatty acids to plasma triglyceride synthesis
during non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Metab.
29:478–485. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Tirosh A, Shai I, Bitzur R, Kochba I,
Tekes-Manova D, Israeli E, Shochat T and Rudich A: Changes in
triglyceride levels over time and risk of type 2 diabetes in young
men. Diabetes Care. 31:2032–2037. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Kashyap S, Belfort R, Gastaldelli A,
Pratipanawatr T, Berria R, Pratipanawatr W, Bajaj M, Mandarino L,
DeFronzo R and Cusi K: A sustained increase in plasma free fatty
acids impairs insulin secretion in nondiabetic subjects genetically
predisposed to develop type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 52:2461–2474.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Sakurai M, Takamura T, Ota T, Ando H,
Akahori H, Kaji K, Sasaki M, Nakanuma Y, Miura K and Kaneko S:
Liver steatosis, but not fibrosis, is associated with insulin
resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol.
42:312–317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Svegliati-Baroni G, Saccomanno S,
Rychlicki C, Agostinelli L, De Minicis S, Candelaresi C, Faraci G,
Pacetti D, Vivarelli M, Nicolini D, et al: Glucagon-like peptide-1
receptor activation stimulates hepatic lipid oxidation and restores
hepatic signalling alteration induced by a high-fat diet in
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 31:1285–1297. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR, Maeda S,
Li ZW, Long JM, Wynshaw-Boris A, Poli G, Olefsky J and Karin M:
IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance.
Nat Med. 11:191–198. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Henkel J, Frede K, Schanze N, Vogel H,
Schürmann A, Spruss A, Bergheim I and Püschel GP: Stimulation of
fat accumulation in hepatocytes by PGE2-dependent
repression of hepatic lipolysis, β-oxidation and VLDL-synthesis.
Lab Invest. 92:1597–1606. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Pérez S, Aspichueta P, Ochoa B and Chico
Y: The 2-series prostaglandins suppress VLDL secretion in an
inflammatory condition-dependent manner in primary rat hepatocytes.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1761:160–171. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Chung MY, Mah E, Masterjohn C, Noh SK,
Park HJ, Clark RM, Park YK, Lee JY and Bruno RS: Green tea lowers
hepatic COX-2 and prostaglandin E2 in rats with dietary fat-induced
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Med Food. 18:648–655. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Nassir F, Adewole OL, Brunt EM and Abumrad
NA: CD36 deletion reduces VLDL secretion, modulates liver
prostaglandins, and exacerbates hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice. J
Lipid Res. 54:2988–2997. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Sato N, Kaneko M, Tamura M and Kurumatani
H: The prostacyclin analog beraprost sodium ameliorates
characteristics of metabolic syndrome in obese Zucker (fatty) rats.
Diabetes. 59:1092–1100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Duncan BB, Schmidt MI, Pankow JS,
Ballantyne CM, Couper D, Vigo A, Hoogeveen R, Folsom AR and Heiss
G; Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study: Low-grade systemic
inflammation and the development of type 2 diabetes: The
atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes. 52:1799–1805.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Haukeland JW, Damås JK, Konopski Z, Løberg
EM, Haaland T, Goverud I, Torjesen PA, Birkeland K, Bjøro K and
Aukrust P: Systemic inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease is characterized by elevated levels of CCL2. J Hepatol.
44:1167–1174. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Kamari Y, Shaish A, Vax E, Shemesh S,
Kandel-Kfir M, Arbel Y, Olteanu S, Barshack I, Dotan S, Voronov E,
et al: Lack of interleukin-1α or interleukin-1β inhibits
transformation of steatosis to steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis
in hypercholesterolemic mice. J Hepatol. 55:1086–1094. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Masters SL, Dunne A, Subramanian SL, Hull
RL, Tannahill GM, Sharp FA, Becker C, Franchi L, Yoshihara E, Chen
Z, et al: Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by islet amyloid
polypeptide provides a mechanism for enhanced IL-1β in type 2
diabetes. Nat Immunol. 11:897–904. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Chitturi S, Abeygunasekera S, Farrell GC,
Holmes-Walker J, Hui JM, Fung C, Karim R, Lin R, Samarasinghe D,
Liddle C, et al: NASH and insulin resistance: Insulin
hypersecretion and specific association with the insulin resistance
syndrome. Hepatology. 35:373–379. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Sanyal AJ, Campbell-Sargent C, Mirshahi F,
Rizzo WB, Contos MJ, Sterling RK, Luketic VA, Shiffman ML and Clore
JN: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Association of insulin resistance
and mitochondrial abnormalities. Gastroenterology. 120:1183–1192.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Yang ZH, Miyahara H, Takeo J and Katayama
M: Diet high in fat and sucrose induces rapid onset of
obesity-related metabolic syndrome partly through rapid response of
genes involved in lipogenesis, insulin signalling and inflammation
in mice. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 4:322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Ren LP, Chan SM, Zeng XY, Laybutt DR,
Iseli TJ, Sun RQ, Kraegen EW, Cooney GJ, Turner N and Ye JM:
Differing endoplasmic reticulum stress response to excess
lipogenesis versus lipid oversupply in relation to hepatic
steatosis and insulin resistance. PLoS One. 7:e308162012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Brunt EM, Kleiner DE, Wilson LA, Unalp A,
Behling CE and Lavine JE: Portal chronic inflammation in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A histologic marker of
advanced NAFLD-clinicopathologic correlations from the nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis clinical research network. Hepatology. 49:809–820.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Angulo P, Keach JC, Batts KP and Lindor
KD: Independent predictors of liver fibrosis in patients with
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 30:1356–1362. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Hossain N, Afendy A, Stepanova M, Nader F,
Srishord M, Rafiq N, Goodman Z and Younossi Z: Independent
predictors of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:1224–1229. 1229.e1–e2. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Zeyda M, Farmer D, Todoric J, Aszmann O,
Speiser M, Györi G, Zlabinger GJ and Stulnig TM: Human adipose
tissue macrophages are of an anti-inflammatory phenotype but
capable of excessive pro-inflammatory mediator production. Int J
Obes (Lond). 31:1420–1428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Itani SI, Ruderman NB, Schmieder F and
Boden G: Lipid-induced insulin resistance in human muscle is
associated with changes in diacylglycerol, protein kinase C, and
IkappaB-alpha. Diabetes. 51:2005–2011. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF,
Atkinson RL and Spiegelman BM: Increased adipose tissue expression
of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin
resistance. J Clin Invest. 95:2409–2415. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
du Plessis J, van Pelt J, Korf H, Mathieu
C, van der Schueren B, Lannoo M, Oyen T, Topal B, Fetter G, Nayler
S, et al: Association of adipose tissue inflammation with
histologic severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Gastroenterology. 149:635–648.e14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Paradis V, Perlemuter G, Bonvoust F,
Dargere D, Parfait B, Vidaud M, Conti M, Huet S, Ba N, Buffet C and
Bedossa P: High glucose and hyperinsulinemia stimulate connective
tissue growth factor expression: A potential mechanism involved in
progression to fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Hepatology. 34:738–744. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Ota T, Takamura T, Kurita S, Matsuzawa N,
Kita Y, Uno M, Akahori H, Misu H, Sakurai M, Zen Y, et al: Insulin
resistance accelerates a dietary rat model of nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 132:282–293. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Henkel J, Coleman CD, Schraplau A, Jöhrens
K, Weiss TS, Jonas W, Schürmann A and Püschel GP: Augmented liver
inflammation in a microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1
(mPGES-1)-deficient diet-induced mouse NASH model. Sci Rep.
8:161272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Loomba R, Quehenberger O, Armando A and
Dennis EA: Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolites as novel
lipidomic biomarkers for noninvasive diagnosis of nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. J Lipid Res. 56:185–192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
164
|
Motiño O, Agra N, Brea Contreras R,
Dominguez-Moreno M, Garcia-Monzón C, Vargas-Castrillón J, Carnovale
CE, Boscá L, Casado M, Mayoral R, et al: Cyclooxygenase-2
expression in hepatocytes attenuates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
and liver fibrosis in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1862:1710–1723.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Kumar S, Srivastava A, Palaia T, Hall C,
Lee J, Stevenson M, Zhao CL and Ragolia L: Lipocalin-type
prostaglandin D2 synthase deletion induces dyslipidemia and
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Prostaglandins Other Lipid
Mediat. 149:1064292020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Kumei S, Yuhki KI, Kojima F, Kashiwagi H,
Imamichi Y, Okumura T, Narumiya S and Ushikubi F: Prostaglandin
I2 suppresses the development of diet-induced
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. FASEB J. 32:2354–2365. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Meng F, Wang K, Aoyama T, Grivennikov SI,
Paik Y, Scholten D, Cong M, Iwaisako K, Liu X, Zhang M, et al:
Interleukin-17 signaling in inflammatory, Kupffer cells, and
hepatic stellate cells exacerbates liver fibrosis in mice.
Gastroenterology. 143:765–776.e3. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Ikejima K, Takei Y, Honda H, Hirose M,
Yoshikawa M, Zhang YJ, Lang T, Fukuda T, Yamashina S, Kitamura T
and Sato N: Leptin receptor-mediated signaling regulates hepatic
fibrogenesis and remodeling of extracellular matrix in the rat.
Gastroenterology. 122:1399–1410. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Kim SM, Park KC, Kim HG and Han SJ: Effect
of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor meloxicam on liver fibrosis
in rats with ligated common bile ducts. Hepatol Res. 38:800–809.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Yu J, Ip E, Dela Peña A, Hou JY, Sesha J,
Pera N, Hall P, Kirsch R, Leclercq I and Farrell GC: COX-2
induction in mice with experimental nutritional steatohepatitis:
Role as pro-inflammatory mediator. Hepatology. 43:826–836. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Paik YH, Kim JK, Lee JI, Kang SH, Kim DY,
An SH, Lee SJ, Lee DK, Han KH, Chon CY, et al: Celecoxib induces
hepatic stellate cell apoptosis through inhibition of Akt
activation and suppresses hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gut.
58:1517–1527. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Simon TG, Henson J, Osganian S, Masia R,
Chan AT, Chung RT and Corey KE: Daily aspirin use associated with
reduced risk for fibrosis progression in patients with nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:2776–2784.e4.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Vilar-Gomez E and Chalasani N: Daily
aspirin use reduces risk of fibrosis progression in patients with
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, providing new uses for an old
drug. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:2651–2653. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Sui G, Cheng G, Yuan J, Hou X, Kong X and
Niu H: Interleukin (IL)-13, Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and
Prostacyclin 2 (PGI2) Activate Hepatic Stellate Cells via Protein
kinase C (PKC) pathway in hepatic fibrosis. Med Sci Monit.
24:2134–2141. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Hanson A, Wilhelmsen D and DiStefano JK:
The role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the development and
progression of fibrosis associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease (NAFLD). Noncoding RNA. 4:182018.
|
|
176
|
Kamada Y, Mori K, Matsumoto H, Kiso S,
Yoshida Y, Shinzaki S, Hiramatsu N, Ishii M, Moriwaki K, Kawada N,
et al: N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase V regulates TGF-β response
in hepatic stellate cells and the progression of steatohepatitis.
Glycobiology. 22:778–787. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Hui AY, Leung WK, Chan HL, Chan FK, Go MY,
Chan KK, Tang BD, Chu ES and Sung JJ: Effect of celecoxib on
experimental liver fibrosis in rat. Liver Int. 26:125–136. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Brea R, Motiño O, Francés D, García-Monzón
C, Vargas J, Fernández-Velasco M, Boscá L, Casado M, Martín-Sanz P
and Agra N: PGE2 induces apoptosis of hepatic stellate
cells and attenuates liver fibrosis in mice by downregulating
miR-3a-5p and miR-28a-5p. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1864:325–337. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
179
|
Hui AY, Dannenberg AJ, Sung JJ,
Subbaramaiah K, Du B, Olinga P and Friedman SL: Prostaglandin E2
inhibits transforming growth factor beta 1-mediated induction of
collagen alpha 1(I) in hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol.
41:251–258. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|