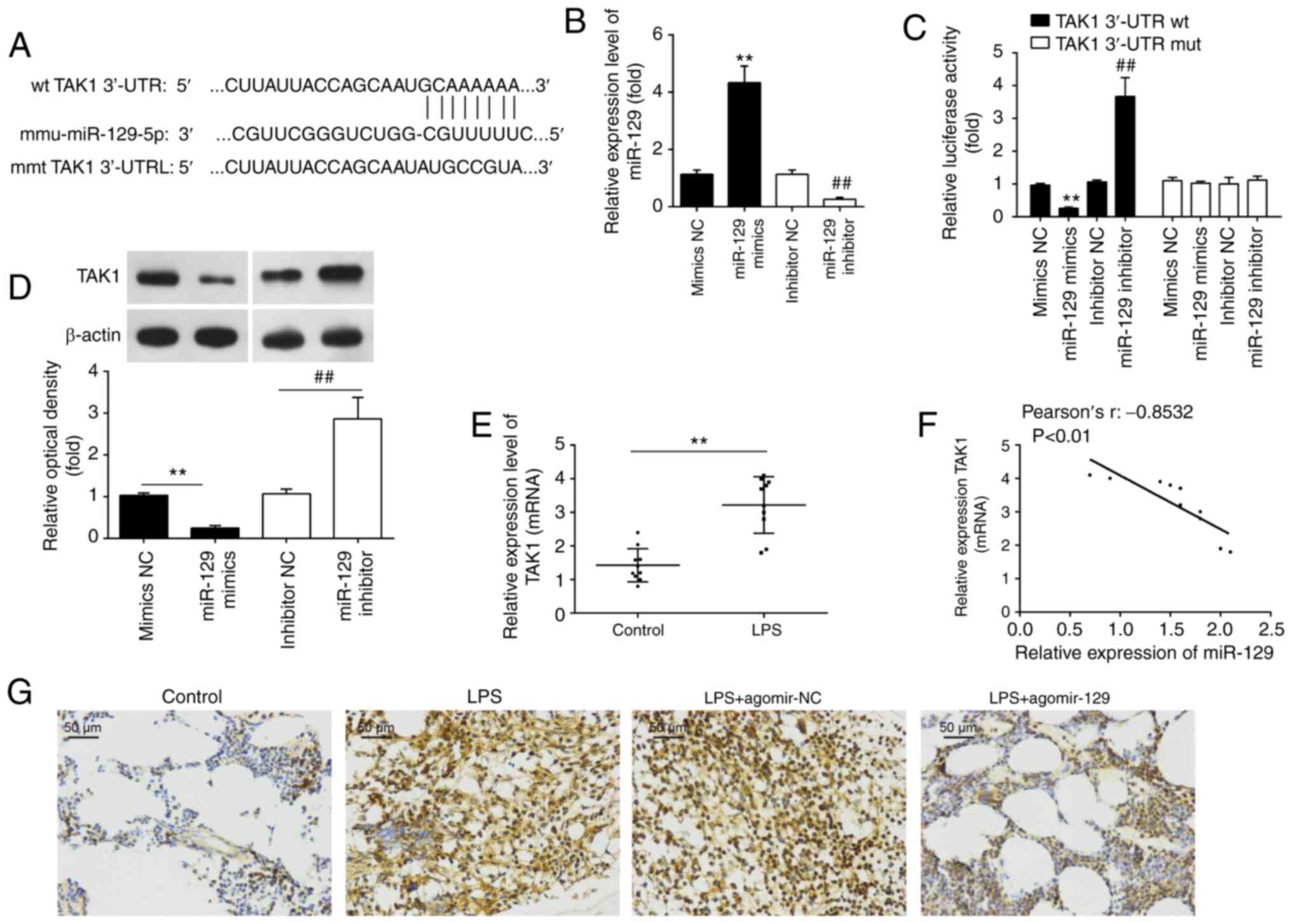
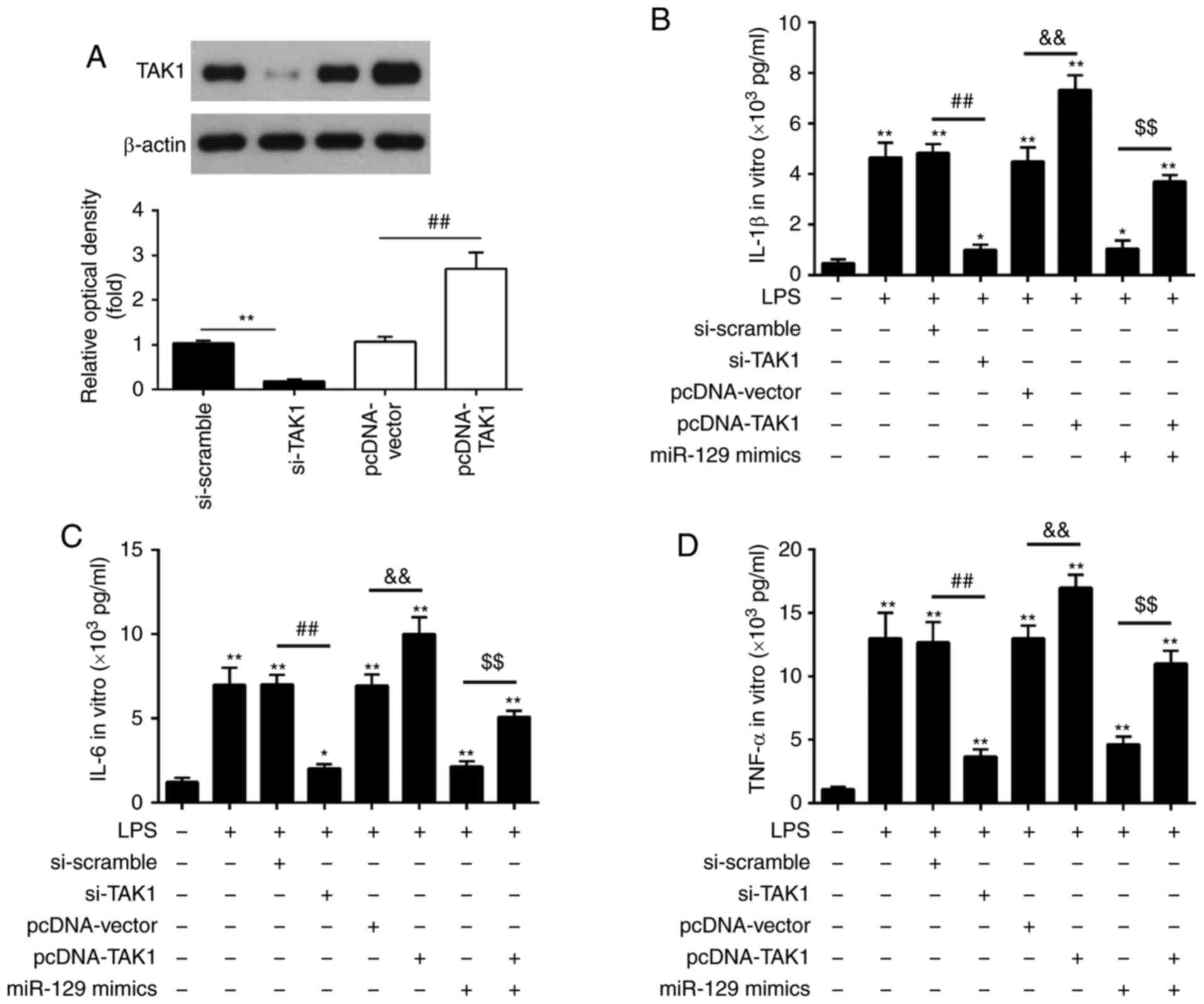
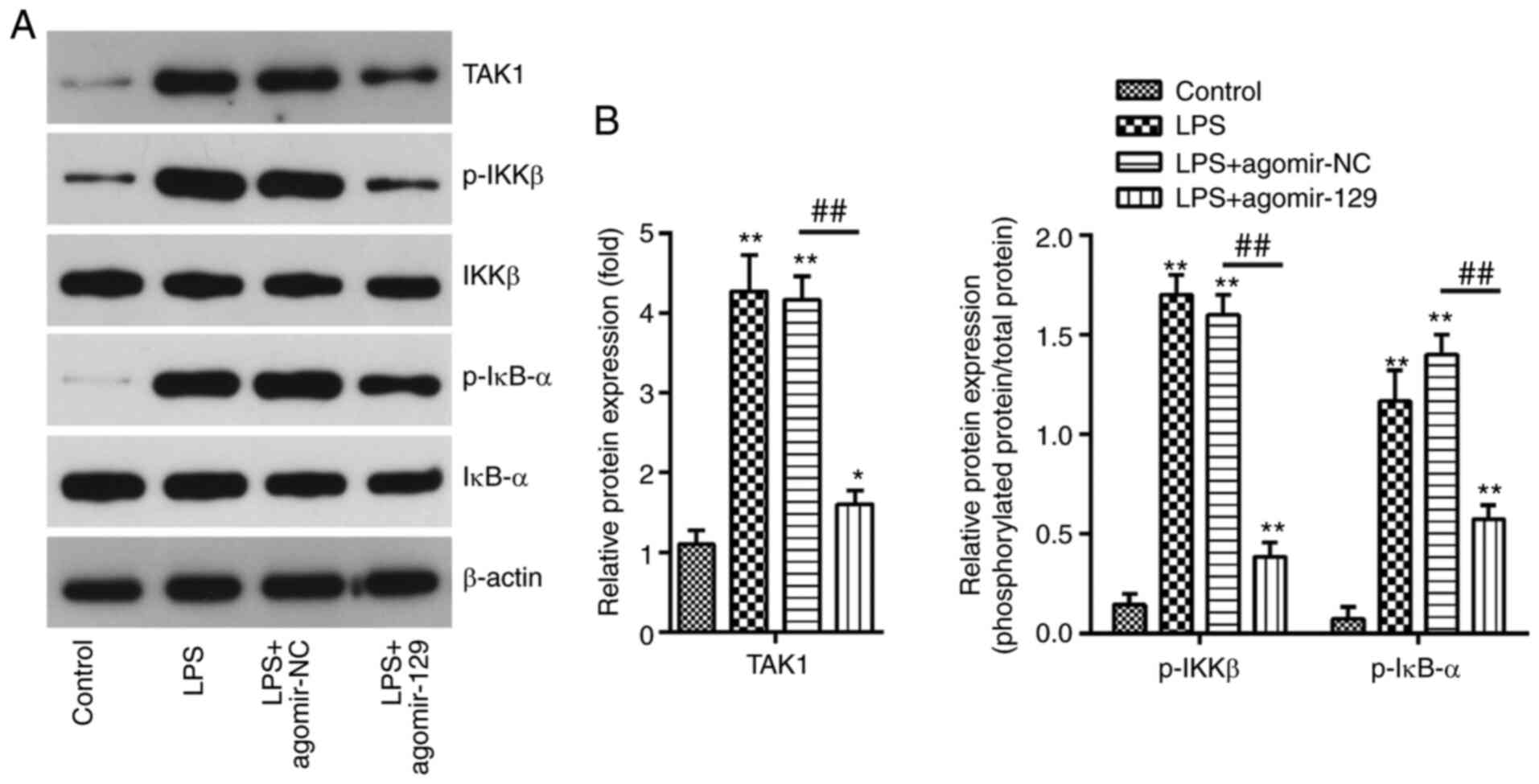
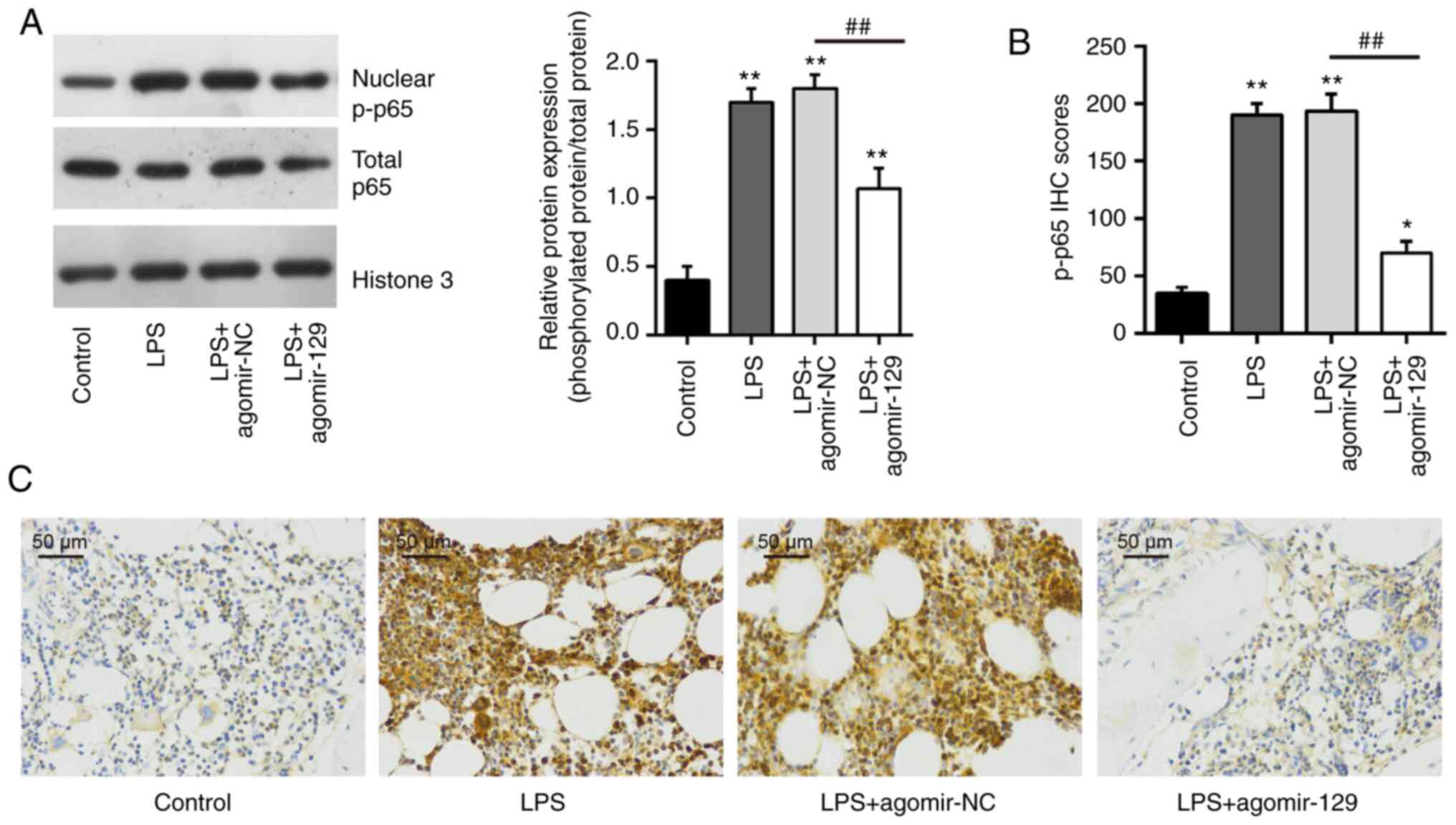
|
1
|
Hoesel LM, Neff TA, Neff SB, Younger JG,
Olle EW, Gao H, Pianko MJ, Bernacki KD, Sarma JV and Ward PA:
Harmful and protective roles of neutrophils in sepsis. Shock.
24:40–47. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Villar J, Blanco J, Añón JM, Santos-Bouza
A, Blanch L, Ambrós A, Gandía F, Carriedo D, Mosteiro F, Basaldúa
S, et al: The ALIEN study: Incidence and outcome of acute
respiratory distress syndrome in the era of lung protective
ventilation. Intensive Care Med. 37:1932–1941. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gill SE, Taneja R, Rohan M, Wang L and
Mehta S: Pulmonary microvascular albumin leak is associated with
endothelial cell death in murine sepsis-induced lung injury in
vivo. PLoS One. 9:e885012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jiang C, Ting AT and Seed B: PPAR-gamma
agonists inhibit production of monocyte inflammatory cytokines.
Nature. 391:82–86. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Strieter RM, Belperio JA and Keane MP:
Cytokines in innate host defense in the lung. J Clin Invest.
109:699–705. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hoesel B and Schmid JA: The complexity of
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:862013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jiang T, Tian F, Zheng H, Whitman SA, Lin
Y, Zhang Z, Zhang N and Zhang DD: Nrf2 suppresses lupus nephritis
through inhibition of oxidative injury and the NF-κB-mediated
inflammatory response. Kidney Int. 85:333–343. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gross CM, Kellner M, Wang T, Lu Q, Sun X,
Zemskov EA, Noonepalle S, Kangath A, Kumar S, Gonzalez-Garay M, et
al: LPS-induced acute lung injury involves NF-κB-mediated down-
regulation of SOX18. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 58:614–624. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Yang H, Lv H, Li H, Ci X and Peng L:
Oridonin protects LPS-induced acute lung injury by modulating
Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress and Nrf2-independent NLRP3 and NF-κB
pathways. Cell Commun Signal. 17:622019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang KY, Arcaroli JJ and Abraham E: Early
alterations in neutrophil activation are associated with outcome in
acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 167:1567–1574. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schwartz MD, Moore EE, Moore FA, Shenkar
R, Moine P, Haenel JB and Abraham E: Nuclear factor-kappa B is
activated in alveolar macrophages from patients with acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 24:1285–1292. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang S, Yu Z, Yuan T, Wang L, Wang X, Yang
H, Sun L, Wang Y and Du G: Therapeutic effect of methyl salicylate
2-O-β-d-lactoside on LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting
TAK1/NF-kappaB phosphorylation and NLRP3 expression. Int
Immunopharmacol. 40:219–228. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo Z, Gu Y, Wang C, Zhang J, Shan S, Gu
X, Wang K, Han Y and Ren T: Enforced expression of miR-125b
attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury. Immunol Lett. 162:18–26.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Xie Y, Zhang L and Zhao H:
MicroRNA-155 participates in smoke-inhalation-induced acute lung
injury through inhibition of SOCS-1. Molecules. 25:10222020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Wan G, An Y, Tao J, Wang Y, Zhou Q, Yang R
and Liang Q: MicroRNA-129-5p alleviates spinal cord injury in mice
via suppressing the apoptosis and inflammatory response through
HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Biosci Rep. 40:BSR201933152020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li XQ, Chen FS, Tan WF, Fang B, Zhang ZL
and Ma H: Elevated microRNA-129-5p level ameliorates
neuroinflammation and blood-spinal cord barrier damage after
ischemia-reperfusion by inhibiting HMGB1 and the TLR3-cytokine
pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 14:2052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zeng Z, Liu Y, Zheng W, Liu L, Yin H,
Zhang S, Bai H, Hua L, Wang S, Wang Z, et al: MicroRNA-129-5p
alleviates nerve injury and inflammatory response of Alzheimer's
disease via downregulating SOX6. Cell cycle. 18:3095–3110. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen ZX, He D, Mo QW, Xie LP, Liang JR,
Liu L and Fu WJ: MiR-129-5p protects against myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury via targeting HMGB1. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 24:4440–4450. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu Z, Zhang C, Cheng L, Hu M, Tao H and
Song L: The microRNA miR-17 regulates lung FoxA1 expression during
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 445:48–53. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carbone L, Carbone ET, Yi EM, Bauer DB,
Lindstrom KA, Parker JM, Austin JA, Seo Y, Gandhi AD and Wilkerson
JD: Assessing cervical dislocation as a humane euthanasia method in
mice. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 51:352–356. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li C, Yang D, Cao X, Wang F, Jiang H, Guo
H, Du L, Guo Q and Yin X: LFG-500, a newly synthesized flavonoid,
attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and
inflammation in mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 113:57–69. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lei C, Jiao Y, He B, Wang G, Wang Q and
Wang J: RIP140 down-regulation alleviates acute lung injury via the
inhibition of LPS-induced PPARγ promoter methylation. Pulm
Pharmacol Ther. 37:57–64. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ayaz G, Halici Z, Albayrak A, Karakus E
and Cadirci E: Evaluation of 5-HT7 receptor trafficking on in vivo
and in vitro model of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory
cell injury in rats and LPS-treated A549 cells. Biochem Genet.
55:34–47. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shao L, Meng D, Yang F, Song H and Tang D:
Irisin-mediated protective effect on LPS-induced acute lung injury
via suppressing inflammation and apoptosis of alveolar epithelial
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 487:194–200. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Z, Yan J, Yang F, Wang D, Lu Y and
Liu L: MicroRNA-326 prevents sepsis-induced acute lung injury via
targeting TLR4. Free Radic Res. 54:408–418. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bian B, Yu XF, Wang GQ and Teng TM: Role
of miRNA-1 in regulating connexin 43 in ischemia-reperfusion heart
injury: A rat model. Cardiovasc Pathol. 27:37–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Moitra J, Sammani S and Garcia JG:
Re-evaluation of evans blue dye as a marker of albumin clearance in
murine models of acute lung injury. Transl Res. 150:253–265. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Villar J, Cabrera-Benitez NE, Valladares
F, García-Hernández S, Ramos-Nuez Á, Martín-Barrasa JL, Muros M,
Kacmarek RM and Slutsky AS: Tryptase is involved in the development
of early ventilator-induced pulmonary fibrosis in sepsis-induced
lung injury. Crit Care. 19:1382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Varghese F, Bukhari AB, Malhotra R and De
A: IHC Profiler: An open source plugin for the quantitative
evaluation and automated scoring of immunohistochemistry images of
human tissue samples. PLoS One. 9:e968012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu G, Li X, Li M and Zhang Z: Long
non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes the proliferation and migration of
Schwann cells by elevating BDNF through sponging miR-129-5p. Exp
Cell Res. 390:1119372020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ju M, Liu B, He H, Gu Z, Liu Y, Su Y, Zhu
D, Cang J and Luo Z: MicroRNA-27a alleviates LPS-induced acute lung
injury in mice via inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis through
modulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Cell Cycle. 17:2001–2018.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Li P, Yao Y, Ma Y and Chen Y: MiR-150
attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury via targeting AKT3. Int
Immunopharmacol. 75:1057942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xie W, Lu Q, Wang K, Lu J, Gu X, Zhu D,
Liu F and Guo Z: miR-34b-5p inhibition attenuates lung inflammation
and apoptosis in an LPS-induced acute lung injury mouse model by
targeting progranulin. J Cell Physiol. 233:6615–6631. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Yan Y, Lou Y and Kong J: MiR-155 expressed
in bone marrow-derived lymphocytes promoted
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through Ang-2-Tie-2
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 510:352–357. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vaporidi K, Vergadi E, Kaniaris E,
Hatziapostolou M, Lagoudaki E, Georgopoulos D, Zapol WM, Bloch KD
and Iliopoulos D: Pulmonary microRNA profiling in a mouse model of
ventilator-induced lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
303:L199–L207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ma R, Chen X, Ma Y, Bai G and Li DS:
MiR-129-5p alleviates myocardial injury by targeting suppressor of
cytokine signaling 2 after ischemia/reperfusion. Kaohsiung J Med
Sci. 36:599–606. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang X, Hou X, Chuan L, Wei S, Wang J,
Yang X and Ru J: miR-129-5p alleviates LPS-induced acute kidney
injury via targeting HMGB1/TLRs/NF-kappaB pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 89:1070162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fang Y, Gao F, Hao J and Liu Z:
microRNA-1246 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary
endothelial cell apoptosis and acute lung injury by targeting
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Am J Transl Res. 9:1287–1296.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tianzhu Z and Shumin W: Esculin inhibits
the inflammation of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via
regulation of TLR/NF-κB pathways. Inflammation. 38:1529–1536. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mei SH, McCarter SD, Deng Y, Parker CH,
Liles WC and Stewart DJ: Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung
injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing
angiopoietin 1. PLoS Med. 4:e2692007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cheng KT, Xiong S, Ye Z, Hong Z, Di A,
Tsang KM, Gao X, An S, Mittal M, Vogel SM, et al:
Caspase-11-mediated endothelial pyroptosis underlies
endotoxemia-induced lung injury. J Clin Invest. 127:4124–4135.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu H, Lin Z and Ma Y: Suppression of Fpr2
expression protects against endotoxin-induced acute lung injury by
interacting with Nrf2-regulated TAK1 activation. Biomed
Pharmacother. 125:1099432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gao D, Wang R, Li B, Yang Y, Zhai Z and
Chen DY: WDR34 is a novel TAK1-associated suppressor of the
IL-1R/TLR3/TLR4-induced NF-kappaB activation pathway. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 66:2573–2584. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen Q, Wu S, Wu Y, Chen L and Pang Q:
MiR-149 suppresses the inflammatory response of chondrocytes in
osteoarthritis by down-regulating the activation of TAK1/NF-κB.
Biomed Pharmacother. 101:763–768. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nan CC, Zhang N, Cheung KCP, Zhang HD, Li
W, Hong CY, Chen HS, Liu XY, Li N and Cheng L: Knockdown of lncRNA
MALAT1 alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting
apoptosis through the miR-194-5p/FOXP2 axis. Front Cell Dev Biol.
8:5868692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang J, Ding C, Shao Q, Liu F, Zeng Z,
Nie C and Qian K: The protective effects of transfected
microRNA-146a on mice with sepsis-induced acute lung injury in
vivo. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 27:591–594. 2015.In
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cao X, Zhang C, Zhang X, Chen Y and Zhang
H: MiR-145 negatively regulates TGFBR2 signaling responsible for
sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 111:852–858.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li L, Wu W, Huang W, Hu G, Yuan W and Li
W: NF-κB RNAi decreases the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and inhibits
TNF-α-induced apoptosis in human alveolar epithelial cells. Inflamm
Res. 62:387–397. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gong Y, Lan H, Yu Z, Wang M, Wang S, Chen
Y, Rao H, Li J, Sheng Z and Shao J: Blockage of glycolysis by
targeting PFKFB3 alleviates sepsis-related acute lung injury via
suppressing inflammation and apoptosis of alveolar epithelial
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 491:522–529. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Albertine KH, Soulier MF, Wang Z, Ishizaka
A, Hashimoto S, Zimmerman GA, Matthay MA and Ware LB: Fas and fas
ligand are up-regulated in pulmonary edema fluid and lung tissue of
patients with acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Am J Pathol. 161:1783–1796. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kawasaki M, Kuwano K, Hagimoto N, Matsuba
T, Kunitake R, Tanaka T, Maeyama T and Hara N: Protection from
lethal apoptosis in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in
mice by a caspase inhibitor. Am J Pathol. 157:597–603. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yang R, Cai X, Li J, Liu F and Sun T:
Protective effects of MiR-129-5p on acute spinal cord injury rats.
Med Sci Monit. 25:8281–8288. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Du X, Tian D, Wei J, Yan C, Hu P, Wu X and
Yang W: MEG3 alleviated LPS-induced intestinal injury in sepsis by
modulating miR-129-5p and surfactant protein D. Mediators Inflamm.
2020:82327342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen Z, Zhang D, Li M and Wang B:
Costunolide ameliorates lipoteichoic acid-induced acute lung injury
via attenuating MAPK signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
61:283–289. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Fan C, Wu LH, Zhang GF, Xu F, Zhang S,
Zhang X, Sun L, Yu Y, Zhang Y and Ye RD: 4′-Hydroxywogonin
suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW
264.7 macrophages and acute lung injury mice. PLoS One.
12:e01811912017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Cai PC, Shi L, Liu VW, Tang HW, Liu IJ,
Leung TH, Chan KK, Yam JW, Yao KM, Ngan HY and Chan DW: Elevated
TAK1 augments tumor growth and metastatic capacities of ovarian
cancer cells through activation of NF-κB signaling. Oncotarget.
5:7549–7562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Meng Q, Wu W, Pei T, Xue J, Xiao P, Sun L,
Li L and Liang D: miRNA-129/FBW7/NF-κB, a novel regulatory pathway
in inflammatory bowel disease. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 19:731–740.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liu AH, Wu YT and Wang YP: MicroRNA-129-5p
inhibits the development of autoimmune encephalomyelitis-related
epilepsy by targeting HMGB1 through the TLR4/NF-kB signaling
pathway. Brain Res Bull. 132:139–149. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|