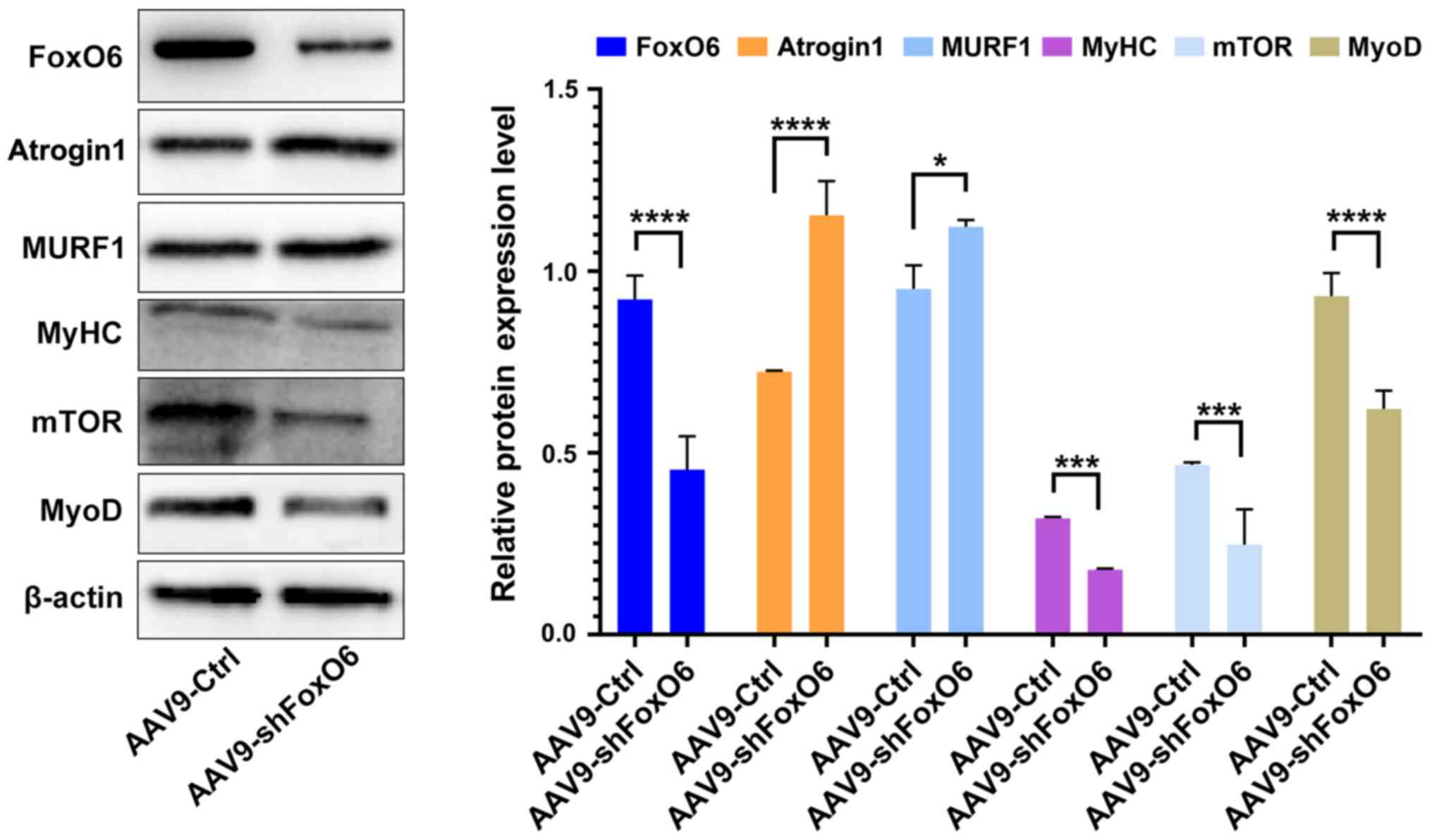
|
1
|
Sandri M: Autophagy in skeletal muscle.
FEBS Lett. 584:1411–1416. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lecker SH, Goldberg AL and Mitch WE:
Protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in normal
and disease states. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:1807–1819. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Gilbert A, Gomes M,
Baracos V, Bailey J, Price SR, Mitch WE and Goldberg AL: Multiple
types of skeletal muscle atrophy involve a common program of
changes in gene expression. FASEB J. 18:39–51. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fappi A, de Carvalho Neves J, Sanches LN,
Silva PV, Sikusawa GY, Brandão TPC, Chadi G and Zanoteli E:
Skeletal muscle response to deflazacort, dexamethasone and
methylprednisolone. Cells. 8:4062019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Gupta A and Gupta Y:
Glucocorticoid-Induced myopathy: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and
treatment. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 17:913–916. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cohen S, Nathan JA and Goldberg AL: Muscle
wasting in disease: Molecular mechanisms and promising therapies.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 14:58–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jagoe RT and Goldberg AL: What do we
really know about the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in muscle
atrophy? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab. 4:183–190. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jagoe RT, Lecker SH, Gomes M and Goldberg
AL: Patterns of gene expression in atrophying skeletal muscles: The
response to food deprivation. FASEB J. 16:1697–1712. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gomes MD, Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Navon A and
Goldberg AL: Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly
expressed during muscle atrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:14440–14445. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK,
Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K,
et al: Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal
muscle atrophy. Science. 294:1704–1708. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Megeney LA, Kablar B, Garrett K, Anderson
JE and Rudnicki MA: MyoD is required for myogenic stem cell
function in adult skeletal muscle. Genes Dev. 10:1173–1183. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bodine SC, Stitt TN, Gonzalez M, Kline WO,
Stover GL, Bauerlein R, Zlotchenko E, Scrimgeour A, Lawrence JC,
Glass DJ and Yancopoulos GD: Akt/mTOR pathway is a crucial
regulator of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and can prevent muscle
atrophy in vivo. Nat Cell Biol. 3:1014–1019. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Agbulut O, Noirez P, Beaumont F and
Butler-Browne G: Myosin heavy chain isoforms in postnatal muscle
development of mice. Biol Cell. 95:399–406. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hannenhalli S and Kaestner KH: The
evolution of fox genes and their role in development and disease.
Nat Rev Genet. 10:233–240. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Link W: Introduction to FOXO biology.
Methods Mol Biol. 1890:1–9. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Monsalve M and Olmos Y: The complex
biology of FOXO. Curr Drug Targets. 12:1322–1350. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jacobs FM, van der Heide LP, Wijchers PJ,
Burbach JPH, Hoekman MFM and Smidt MP: FoxO6, a novel member of the
foxo class of transcription factors with distinct shuttling
dynamics. J Biol Chem. 278:35959–35967. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu W, Li Y and Luo B: Current perspective
on the regulation of FOXO4 and its role in disease progression.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:651–663. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Reed SA, Sandesara PB, Senf SM and Judge
AR: Inhibition of FoxO transcriptional activity prevents muscle
fiber atrophy during cachexia and induces hypertrophy. FASEB J.
26:987–1000. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Sandri M, Sandri C, Gilbert A, Skurk C,
Calabria E, Picard A, Walsh K, Schiaffino S, Lecker SH and Goldberg
AL: Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin
ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell.
117:399–412. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kamei Y, Miura S, Suzuki M, Kai Y,
Mizukami J, Taniguchi T, Mochida K, Hata T, Matsuda J, Aburatani H,
et al: Skeletal muscle FOXO1 (FKHR) transgenic mice have less
skeletal muscle mass, down-regulated type I (slow twitch/red
muscle) fiber genes, and impaired glycemic control. J Biol Chem.
279:41114–41123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu J, Li RS, Workeneh B, Dong Y, Wang X
and Zhaoyong Hu: Transcription factor FoxO1, the dominant mediator
of muscle wasting in chronic kidney disease, is inhibited by
microRNA-486. Kidney Int. 82:401–411. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao J, Brault JJ, Schild A, Cao P, Sandri
M, Schiaffino S, Lecker SH and Goldberg AL: FoxO3 coordinately
activates protein degradation by the autophagic/lysosomal and
proteasomal pathways in atrophying muscle cells. Cell Metabol.
6:472–483. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mammucari C, Milan G, Romanello V, Masiero
E, Rudolf R, Piccolo PD, Burden SJ, Lisi RD, Sandri C, Zhao JH, et
al: Foxo3 controls autophagy in skeletal muscle in vivo. Cell
Metabol. 6:458–471. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Moylan JS, Smith JD, Chambers MA,
McLoughlin TJ and Reid MB: TNF induction of atrogin-1/MAFbx mRNA
depends on Foxo4 expression but not AKT-Foxo1/3 signaling. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 295:C986–C993. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hoekman MF, Jacobs FM, Smidt MP and
Burbach JP: Spatial and temporal expression of FoxO transcription
factors in the developing and adult murine brain. Gene Expr
Patterns. 6:134–140. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Salih DA, Rashid AJ, Colas D, de la
Torre-Ubieta L, Zhu RP, Morgan AA, Santo EE, Ucar D, Devarajan K,
Cole CJ, et al: FoxO6 regulates memory consolidation and synaptic
function. Genes Dev. 26:2780–2801. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chung SY, Huang WC, Su CW, Lee KW, Chi HS,
Lin CT, Chen ST, Huang KM, Tsai MS, Yu HP and Chen SL: FoxO6 and
PGC-1α form a regulatory loop in myogenic cells. Biosci Rep.
33:e000452013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sun Z, da Fontoura CSG, Moreno M, Holton
NE, Sweat M, Sweat Y, Lee MK, Arbon J, Bidlack FB, Thedens DR, et
al: FoxO6 regulates hippo signaling and growth of the craniofacial
complex. PLoS Genet. 14:e10076752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-(-Delta Delta C(T))method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Eley HL, Russell ST and Tisdale MJ:
Mechanism of attenuation of muscle protein degradation induced by
tumor necrosis factor-alpha and angiotensin II by
beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
295:E1417–E1426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen X, Wu Y, Yang T, Wei M, Wang Y, Deng
X, Shen C, Li W, Zhang H, Xu W, et al: Salidroside alleviates
cachexia symptoms in mouse models of cancer cachexia via activating
mTOR signalling. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 7:225–232. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mandai S, Mori T, Nomura N, Furusho T,
Arai Y, Kikuchi H, Sasaki E, Sohara E, Rai T, Uchida S, et al: WNK1
regulates skeletal muscle cell hypertrophy by modulating the
nuclear localization and transcriptional activity of FOXO4. Sci
Rep. 14:91012018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Derde S, Hermans G, Derese I, Güiza F,
Hedström Y, Wouters PJ, Bruyninckx F, D'Hoore A, Larsson L, Van den
Berghe G and Vanhorebeek I: Muscle atrophy and preferential loss of
myosin in prolonged critically ill patients. Crit Care Med.
40:79–89. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Banduseela V, Ochala J, Lamberg K, Kalimo
H and Larsson L: Muscle paralysis and myosin loss in a patient with
cancer cachexia. Acta Myol. 26:136–144. 2007.
|
|
36
|
Risson V, Mazelin L, Roceri M, Sanchez H,
Moncollin V, Corneloup C, Richard-Bulteau H, Vignaud A, Baas D,
Defour A, et al: Muscle inactivation of mTOR causes metabolic and
dystrophin defects leading to severe myopathy. J Cell Biol.
187:859–874. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|