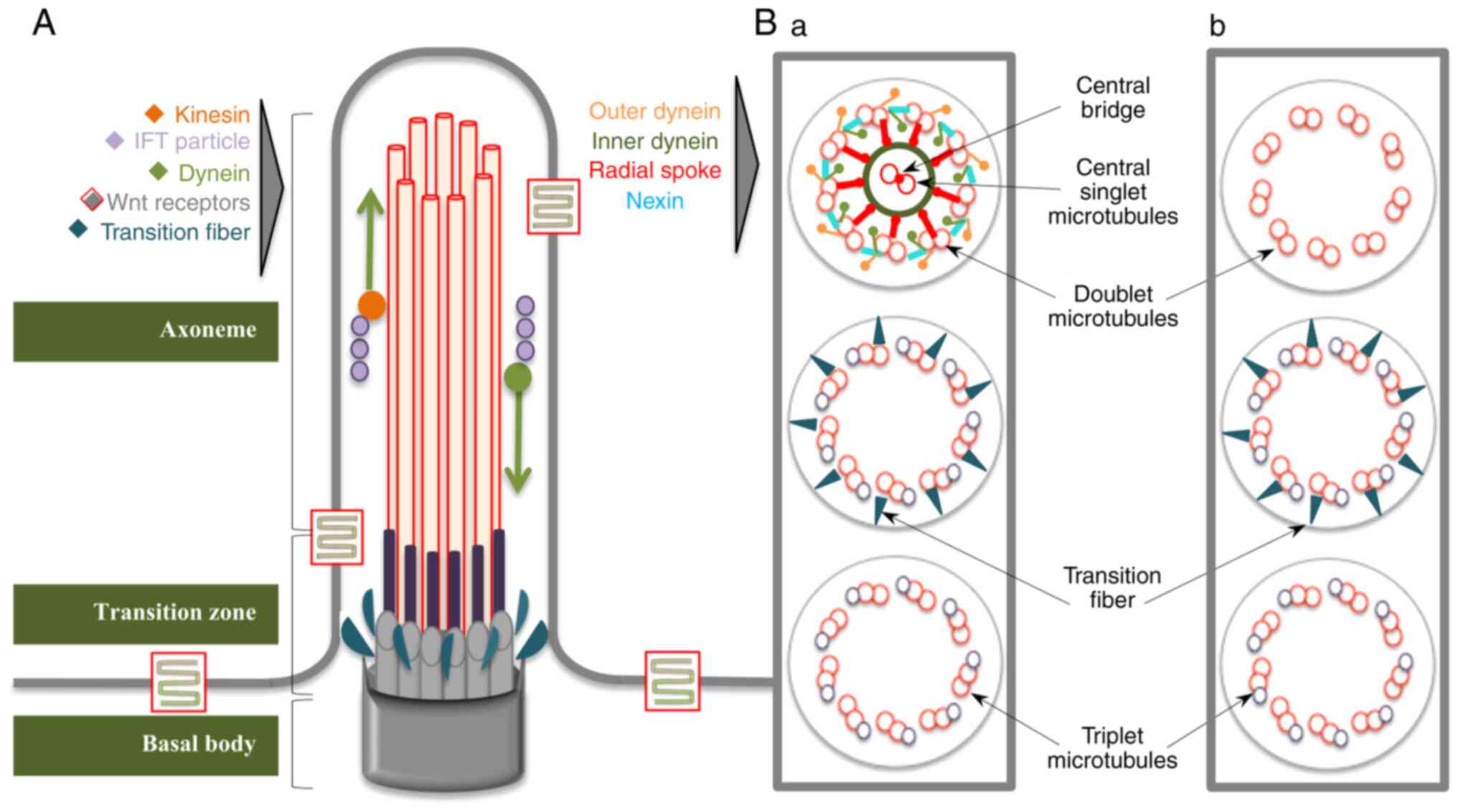
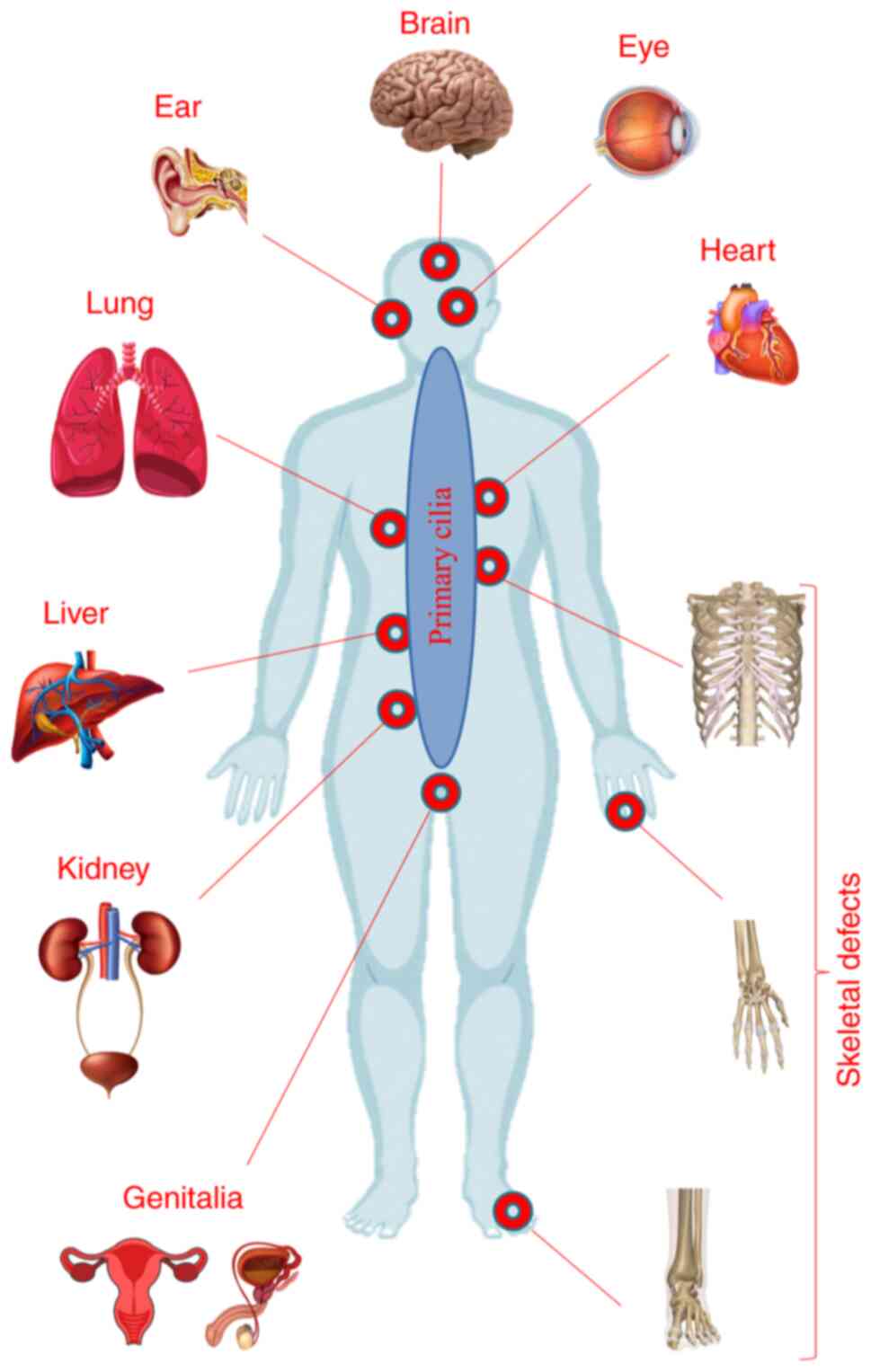
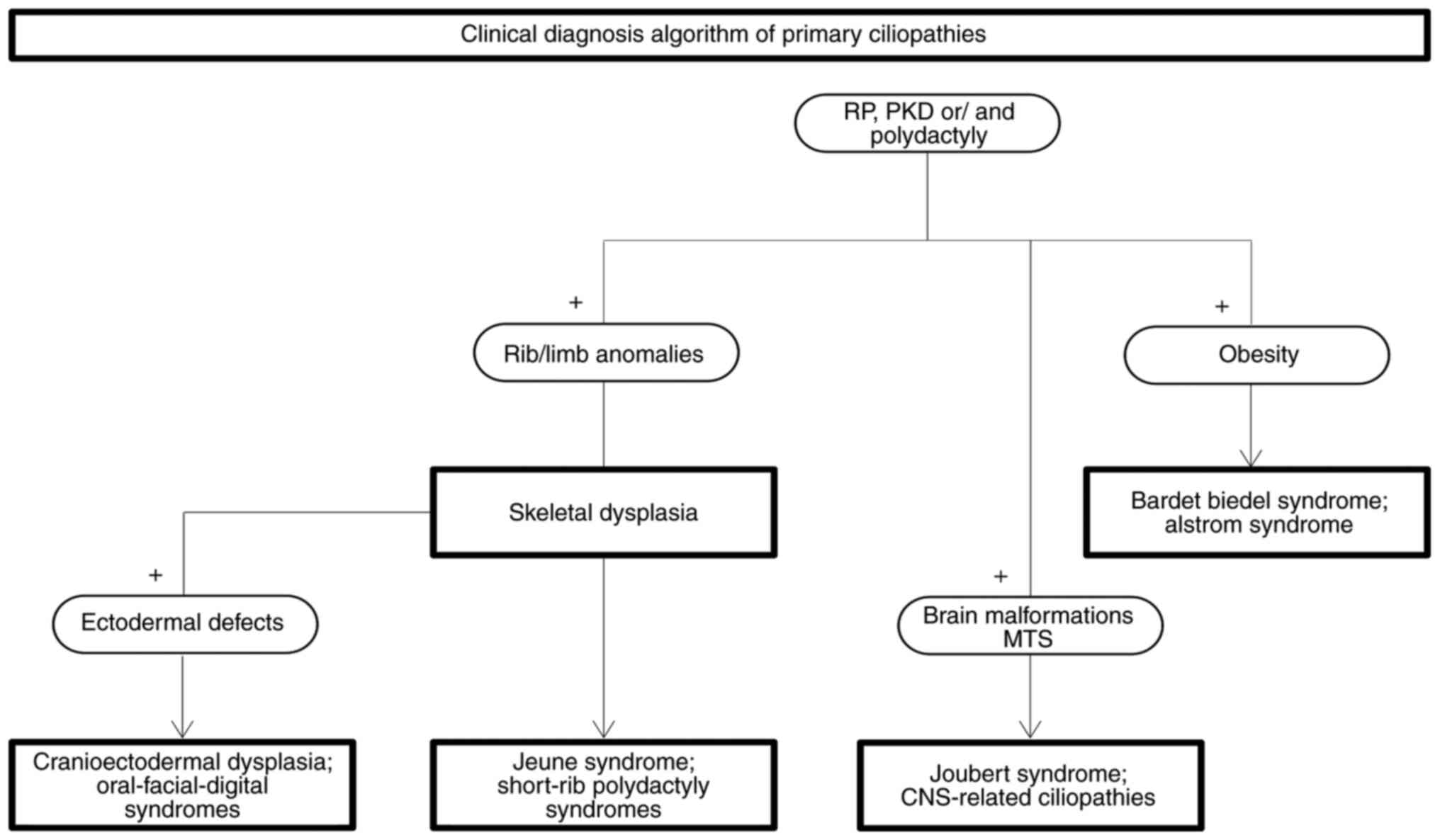
|
1
|
Badano JL, Mitsuma N, Beales PL and
Katsanis N: The ciliopathies: An emerging class of human genetic
disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 7:125–148. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Waters AM and Beales PL: Ciliopathies: An
expanding disease spectrum. Pediatr Nephrol. 26:1039–1056. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Moore A, Escudier E, Roger G, Tamalet A,
Pelosse B, Marlin S, Clément A, Geremek M, Delaisi B, Bridoux AM,
et al: RPGR is mutated in patients with a complex X linked
phenotype combining primary ciliary dyskinesia and retinitis
pigmentosa. J Med Genet. 43:326–333. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Budny B, Chen W, Omran H, Fliegauf M,
Tzschach A, Wisniewska M, Jensen LR, Raynaud M, Shoichet SA, Badura
M, et al: A novel X-linked recessive mental retardation syndrome
comprising macrocephaly and ciliary dysfunction is allelic to
oral-facial-digital type I syndrome. Hum Genet. 120:171–178. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Moalem S, Keating S, Shannon P, Thompson
M, Millar K, Nykamp K, Forster A, Noor A and Chitayat D: Broadening
the ciliopathy spectrum: Motile cilia dyskinesia, and
nephronophthisis associated with a previously unreported homozygous
mutation in the INVS/NPHP2 gene. Am J Med Genet A. 161A:1792–1796.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Shapiro AJ, Zariwala MA, Ferkol T, Davis
SD, Sagel SD, Dell SD, Rosenfeld M, Olivier KN, Milla C, Daniel SJ,
et al: Diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of primary ciliary
dyskinesia: PCD foundation consensus recommendations based on state
of the art review. Pediatr Pulmonol. 51:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tobin JL and Beales PL: The nonmotile
ciliopathies. Genet Med. 11:386–402. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Leeuwenhoek AV: Observations, communicated
to the publisher by Mr. Antony van Leewenhoeck, in a dutch letter
of the 9th Octob. 1676. Here English'd: Concerning little animals
by him observed in rain-well-seaand snow water; as also in water
wherein pepper had lain infused. Philosophical Transactions.
12:821–831. 1677. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lee L: Mechanisms of mammalian ciliary
motility: Insights from primary ciliary dyskinesia genetics. Gene.
473:57–66. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Guo J, Higginbotham H, Li J, Nichols J,
Hirt J, Ghukasyan V and Anton ES: Developmental disruptions
underlying brain abnormalities in ciliopathies. Nat Commun.
6:78572015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chang CF, Schock EN, Attia AC, Stottmann
RW and Brugmann SA: The ciliary baton: Orchestrating neural crest
cell development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 111:97–134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mirvis M, Stearns T and James Nelson W:
Cilium structure, assembly, and disassembly regulated by the
cytoskeleton. Biochem J. 475. pp. 2329–2353. 2018, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Marshall WF and Nonaka S: Cilia: Tuning in
to the cell's antenna. Curr Biol. 16:R604–R614. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Roberts AJ, Kon T, Knight PJ, Sutoh K and
Burgess SA: Functions and mechanics of dynein motor proteins. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:713–726. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Linck R, Fu X, Lin J, Ouch C, Schefter A,
Steffen W, Warren P and Nicastro D: Insights into the structure and
function of ciliary and flagellar doublet microtubules: Tektins,
Ca2+-binding proteins, and stable protofilaments. J Biol
Chem. 289:17427–17444. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Reiter JF, Blacque OE and Leroux MR: The
base of the cilium: Roles for transition fibres and the transition
zone in ciliary formation, maintenance and compartmentalization.
EMBO Rep. 13:608–618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vertii A, Hung HF, Hehnly H and Doxsey S:
Human basal body basics. Cilia. 5:132016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Satir P and Christensen ST: Overview of
structure and function of mammalian cilia. Annu Rev Physiol.
69:377–400. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hu Q, Milenkovic L, Jin H, Scott MP,
Nachury MV, Spiliotis ET and Nelson WJ: A septin diffusion barrier
at the base of the primary cilium maintains ciliary membrane
protein distribution. Science. 329. pp. 436–439. 2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Fisch C and Dupuis-Williams P:
Ultrastructure of cilia and flagella-back to the future! Biol Cell.
103:249–270. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Czarnecki PG and Shah JV: The ciliary
transition zone: From morphology and molecules to medicine. Trends
Cell Biol. 22:201–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Nonaka S, Tanaka Y, Okada Y, Takeda S,
Harada A, Kanai Y, Kido M and Hirokawa N: Randomization of
left-right asymmetry due to loss of nodal cilia generating leftward
flow of extraembryonic fluid in mice lacking KIF3B motor protein.
Cell. 95:829–837. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Afzelius BA: Cilia-related diseases. J
Pathol. 204:470–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Dabdoub A and Kelley MW: Planar cell
polarity and a potential role for a Wnt morphogen gradient in
stereociliary bundle orientation in the mammalian inner ear. J
Neurobiol. 64:446–457. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hirokawa N, Tanaka Y, Okada Y and Takeda
S: Nodal flow and the generation of left-right asymmetry. Cell.
125:33–45. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hamada H: Roles of motile and immotile
cilia in left-right symmetry breaking. Etiology and Morphogenesis
of Congenital Heart Disease: From Gene Function and Cellular
Interaction to Morphology. Nakanishi T, Markwald RR, Baldwin HS,
Keller BB, Srivastava D and Yamagishi H: Springer; Tokyo: pp.
57–65. 2016, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bloodgood RA: From central to rudimentary
to primary: The history of an underappreciated organelle whose time
has come. The primary cilium. Methods Cell Biol. 94:3–52. 2009.
|
|
28
|
Webber WA and Lee J: Fine structure of
mammalian renal cilia. Anat Rec. 182:339–343. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Pazour GJ, Dickert BL, Vucica Y, Seeley
ES, Rosenbaum JL, Witman GB and Cole DG: Chlamydomonas IFT88 and
its mouse homologue, polycystic kidney disease gene tg737, are
required for assembly of cilia and flagella. J Cell Biol.
151:709–718. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pazour GJ, San Agustin JT, Follit JA,
Rosenbaum JL and Witman GB: Polycystin-2 localizes to kidney cilia
and the ciliary level is elevated in orpk mice with polycystic
kidney disease. Curr Biol. 12:R378–R380. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gradilone SA, Masyuk AI, Splinter PL,
Banales JM, Huang BQ, Tietz PS, Masyuk TV and Larusso NF:
Cholangiocyte cilia express TRPV4 and detect changes in luminal
tonicity inducing bicarbonate secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:19138–19143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mansini AP, Peixoto E, Jin S, Richard S
and Gradilone SA: The chemosensory function of primary cilia
regulates cholangiocyte migration, invasion, and tumor growth.
Hepatology. 69:1582–1598. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Masyuk AI, Gradilone SA, Banales JM, Huang
BQ, Masyuk TV, Lee SO, Splinter PL, Stroope AJ and Larusso NF:
Cholangiocyte primary cilia are chemosensory organelles that detect
biliary nucleotides via P2Y12 purinergic receptors. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 295:G725–G734. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Praetorius HA and Spring KR: Bending the
MDCK cell primary cilium increases intracellular calcium. J Membr
Biol. 184:71–79. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hou Y and Witman GB: Dynein and
intraflagellar transport. Exp Cell Res. 334:26–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Pedersen LB and Rosenbaum JL:
Intraflagellar transport (IFT) role in ciliary assembly, resorption
and signalling. Curr Top Dev Biol. 85:23–61. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Christensen ST, Clement CA, Satir P and
Pedersen LB: Primary cilia and coordination of receptor tyrosine
kinase (RTK) signalling. J Pathol. 226:172–184. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wheway G, Nazlamova L and Hancock JT:
Signaling through the primary cilium. Front Cell Dev Biol. 6:82018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Veland IR, Awan A, Pedersen LB, Yoder BK
and Christensen ST: Primary cilia and signaling pathways in
mammalian development, health and disease. Nephron Physiol.
111:39–53. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Cardenas-Rodriguez M and Badano JL:
Ciliary biology: Understanding the cellular and genetic basis of
human ciliopathies. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 151C:263–280.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Grigoryan T, Wend P, Klaus A and
Birchmeier W: Deciphering the function of canonical Wnt signals in
development and disease: Conditional loss- and gain-of-function
mutations of beta-catenin in mice. Genes Dev. 22:2308–2341. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Reya T, Duncan AW, Ailles L, Domen J,
Scherer DC, Willert K, Hintz L, Nusse R and Weissman IL: A role for
Wnt signalling in self-renewal of haematopoietic stem cells.
Nature. 423:409–414. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Komiya Y and Habas R: Wnt signal
transduction pathways. Organogenesis. 4:68–75. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Abdelhamed ZA, Wheway G, Szymanska K,
Natarajan S, Toomes C, Inglehearn C and Johnson CA: Variable
expressivity of ciliopathy neurological phenotypes that encompass
Meckel-Gruber syndrome and Joubert syndrome is caused by complex
de-regulated ciliogenesis, Shh and Wnt signalling defects. Hum Mol
Genet. 22:1358–1372. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wheway G, Abdelhamed Z, Natarajan S,
Toomes C, Inglehearn C and Johnson CA: Aberrant Wnt signalling and
cellular over-proliferation in a novel mouse model of Meckel-Gruber
syndrome. Dev Biol. 377:55–66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lin F, Hiesberger T, Cordes K, Sinclair
AM, Goldstein LS, Somlo S and Igarashi P: Kidney-specific
inactivation of the KIF3A subunit of kinesin-II inhibits renal
ciliogenesis and produces polycystic kidney disease. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 100:5286–5291. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Anvarian Z, Mykytyn K, Mukhopadhyay S,
Pedersen LB and Christensen ST: Cellular signalling by primary
cilia in development, organ function and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol.
15:199–219. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
von Maltzahn J, Chang NC, Bentzinger CF
and Rudnicki MA: Wnt signaling in myogenesis. Trends Cell Biol.
22:602–609. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Salinas PC: Wnt signaling in the
vertebrate central nervous system: From axon guidance to synaptic
function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:a0080032012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Eggenschwiler JT and Anderson KV: Cilia
and developmental signaling. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:345–373.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Varjosalo M and Taipale J: Hedgehog:
Functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev. 22:2454–2472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Schneider L, Clement CA, Teilmann SC,
Pazour GJ, Hoffmann EK, Satir P and Christensen ST: PDGFRalphaalpha
signaling is regulated through the primary cilium in fibroblasts.
Curr Biol. 15:1861–1866. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Clement DL, Mally S, Stock C, Lethan M,
Satir P, Schwab A, Pedersen SF and Christensen ST: PDGFRα signaling
in the primary cilium regulates NHE1-dependent fibroblast migration
via coordinated differential activity of MEK1/2-ERK1/2-p90RSK and
AKT signaling pathways. J Cell Sci. 126:953–965. 2013.
|
|
55
|
Pala R, Alomari N and Nauli SM: Primary
cilium-dependent signaling mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 18:22722017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Heldin CH: Targeting the PDGF signaling
pathway in the treatment of non-malignant diseases. J Neuroimmune
Pharmacol. 9:69–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Nishimura Y, Kasahara K, Shiromizu T,
Watanabe M and Inagaki M: Primary cilia as signaling hubs in health
and disease. Adv Sci (Weinh). 6:18011382018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Schou KB, Pedersen LB and Christensen ST:
Ins and outs of GPCR signaling in primary cilia. EMBO Rep.
16:1099–1113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hilgendorf KI, Johnson CT and Jackson PK:
The primary cilium as a cellular receiver: Organizing ciliary GPCR
signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 39:84–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Ezratty EJ, Stokes N, Chai S, Shah AS,
Williams SE and Fuchs E: A role for the primary cilium in Notch
signaling and epidermal differentiation during skin development.
Cell. 145:1129–1141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Clement CA, Ajbro KD, Koefoed K,
Vestergaard ML, Veland IR, Henriques de Jesus MP, Pedersen LB,
Benmerah A, Andersen CY, Larsen LA and Christensen ST: TGF-β
signaling is associated with endocytosis at the pocket region of
the primary cilium. Cell Rep. 3:1806–1814. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Vestergaard ML, Awan A, Warzecha CB,
Christensen ST and Andersen CY: Immunofluorescence microscopy and
mRNA analysis of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) including
primary cilia associated signaling pathways. Methods Mol Biol.
1307:123–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Basten SG and Giles RH: Functional aspects
of primary cilia in signaling, cell cycle and tumorigenesis. Cilia.
2:62013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Zhong M, Zhao X, Li J, Yuan W, Yan G, Tong
M, Guo S, Zhu Y and Jiang Y, Liu Y and Jiang Y: Tumor suppressor
folliculin regulates mTORC1 through primary Cilia. J Biol Chem.
291:11689–11697. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Boehlke C, Kotsis F, Patel V, Braeg S,
Voelker H, Bredt S, Beyer T, Janusch H, Hamann C, Gödel M, et al:
Primary cilia regulate mTORC1 activity and cell size through Lkb1.
Nat Cell Biol. 12:1115–1122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Leitch CC and Zaghloul NA: BBS4 is
necessary for ciliary localization of TrkB receptor and activation
by BDNF. PLoS One. 9:e986872014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Lee JE and Gleeson JG: A systems-biology
approach to understanding the ciliopathy disorders. Genome Med.
3:592011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ansley SJ, Badano JL, Blacque OE, Hill J,
Hoskins BE, Leitch CC, Kim JC, Ross AJ, Eichers ER, Teslovich TM,
et al: Basal body dysfunction is a likely cause of pleiotropic
Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Nature. 425:628–633. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Laurence JZ and Moon RC: Four cases of
'retinitis pigmentosa' occurring in the same family, and
accompanied by general imperfections of development. 1866. Obes
Res. 3:400–403. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Moore SJ, Green JS, Fan Y, Bhogal AK,
Dicks E, Fernandez BA, Stefanelli M, Murphy C, Cramer BC, Dean JC,
et al: Clinical and genetic epidemiology of Bardet-Biedl syndrome
in Newfoundland: a 22-year prospective, population-based, cohort
study. Am J Med Genet A. 132A:352–360. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Mitchison HM and Valente EM: Motile and
non-motile cilia in human pathology: From function to phenotypes. J
Pathol. 241:294–309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Hildebrandt F and Zhou W:
Nephronophthisis-associated ciliopathies. J Am Soc Nephrol.
18:1855–1871. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Bergmann C: Early and severe polycystic
kidney disease and related ciliopathies: An emerging field of
interest. Nephron. 141:50–60. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Srivastava S, Molinari E, Raman S and
Sayer JA: Many Genes-One disease? Genetics of nephronophthisis
(NPHP) and NPHP-Associated disorders. Front Pediatr. 5:2872018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Bergmann C: Genetics of autosomal
recessive polycystic kidney disease and its differential diagnoses.
Front Pediatr. 5:2212018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Salomon R, Saunier S and Niaudet P:
Nephronophthisis. Pediatr Nephrol. 24:2333–2344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Srivastava S and Sayer JA:
Nephronophthisis. J Pediatr Genet. 3:103–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Jenkins D and Beales PL: Genes and
mechanisms in human ciliopathies. Emery and Rimoin's Principles and
Practice of Medical Genetics. Rimoin D, Pyeritz R and Korf B:
Academic Press; Oxford; pp. 1–36. 2013
|
|
79
|
Gunay-Aygun M: Liver and kidney disease in
ciliopathies. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 151C:296–306. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Brancati F, Iannicelli M, Travaglini L,
Mazzotta A, Bertini E, Boltshauser E, D'Arrigo S, Emma F, Fazzi E,
Gallizzi R, et al: MKS3/TMEM67 mutations are a major cause of COACH
Syndrome, a Joubert Syndrome related disorder with liver
involvement. Hum Mutat. 30:E432–E442. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Doherty D, Parisi MA, Finn LS, Gunay-Aygun
M, Al-Mateen M, Bates D, Clericuzio C, Demir H, Dorschner M, van
Essen AJ, et al: Mutations in 3 genes (MKS3, CC2D2A and RPGRIP1L)
cause COACH syndrome (Joubert syndrome with congenital hepatic
fibrosis). J Med Genet. 47:8–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Parisi MA: Clinical and molecular features
of Joubert syndrome and related disorders. Am J Med Genet C Semin
Med Genet. 151C:326–340. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Brancati F, Dallapiccola B and Valente EM:
Joubert Syndrome and related disorders. Orphanet J Rare Dis.
5:202010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Berger W, Kloeckener-Gruissem B and
Neidhardt J: The molecular basis of human retinal and vitreoretinal
diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res. 29:335–375. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Chung DC and Traboulsi EI: Leber
congenital amaurosis: Clinical correlations with genotypes, gene
therapy trials update, and future directions. J AAPOS. 13:587–592.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Wente S, Schroder S, Buckard J, Büttel HM,
von Deimling F, Diener W, Häussler M, Hübschle S, Kinder S,
Kurlemann G, et al: Nosological delineation of congenital ocular
motor apraxia type Cogan: An observational study. Orphanet J Rare
Dis. 11:1042016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Valente EM, Dallapiccola B and Bertini E:
Joubert syndrome and related disorders. Handb Clin Neurol.
113:1879–1888. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Poretti A, Snow J, Summers AC, Tekes A,
Huisman TAGM, Aygun N, Carson KA, Doherty D, Parisi MA, Toro C, et
al: Joubert syndrome: Neuroimaging findings in 110 patients in
correlation with cognitive function and genetic cause. J Med Genet.
54:521–529. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Romani M, Micalizzi A and Valente EM:
Joubert syndrome: Congenital cerebellar ataxia with the molar
tooth. Lancet Neurol. 12:894–905. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Poretti A, Boltshauser E, Loenneker T,
Valente EM, Brancati F, Il'yasov K and Huisman TA: Diffusion tensor
imaging in Joubert syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 28:1929–1933.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Valente EM, Brancati F and Dallapiccola B:
Genotypes and phenotypes of Joubert syndrome and related disorders.
Eur J Med Genet. 51:1–23. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Akizu N, Silhavy JL, Rosti RO, Scott E,
Fenstermaker AG, Schroth J, Zaki MS, Sanchez H, Gupta N, Kabra M,
et al: Mutations in CSPP1 lead to classical Joubert syndrome. Am J
Hum Genet. 94:80–86. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Khan S, Lin S, Harlalka GV, Ullah A, Shah
K, Khalid S, Mehmood S, Hassan MJ, Ahmad W, Self JE, et al: BBS5
and INPP5E mutations associated with ciliopathy disorders in
families from Pakistan. Ann Hum Genet. 83:477–482. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Srour M, Schwartzentruber J, Hamdan FF,
Ospina LH, Patry L, Labuda D, Massicotte C, Dobrzeniecka S,
Capo-Chichi JM, Papillon-Cavanagh S, et al: Mutations in C5ORF42
cause Joubert syndrome in the French Canadian population. Am J Hum
Genet. 90:693–700. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Verma PK and El-Harouni AA: Review of
literature: Genes related to postaxial polydactyly. Front Pediatr.
3:82015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Marion V, Stutzmann F, Gerard M, De Melo
C, Schaefer E, Claussmann A, Hellé S, Delague V, Souied E, Barrey
C, et al: Exome sequencing identifies mutations in LZTFL1, a BBSome
and smoothened trafficking regulator, in a family with
Bardet--Biedl syndrome with situs inversus and insertional
polydactyly. J Med Genet. 49:317–321. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Figuera LE, Rivas F and Cantu JM:
Oral-facial-digital syndrome with fibular aplasia: A new variant.
Clin Genet. 44:190–192. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Kannu P, McFarlane JH, Savarirayan R and
Aftimos S: An unclassifiable short rib-polydactyly syndrome with
acromesomelic hypomineralization and campomelia in siblings. Am J
Med Genet A. 143A:2607–2611. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Schmidts M and Mitchison HM: Severe
skeletal abnormalities caused by defects in retrograde
intraflagellar transport dyneins. King SM: Academic Press; pp.
356–401. 2018
|
|
100
|
Schmidts M: Clinical genetics and
pathobiology of ciliary chondrodysplasias. J Pediatr Genet.
3:46–94. 2014.
|
|
101
|
Hartill V, Szymanska K, Sharif SM, Wheway
G and Johnson CA: Meckel-Gruber syndrome: An update on diagnosis,
clinical management, and research advances. Front Pediatr.
5:2442017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Doherty D, Glass IA, Siebert JR, Strouse
PJ, Parisi MA, Shaw DW, Chance PF, Barr M Jr and Nyberg D: Prenatal
diagnosis in pregnancies at risk for Joubert syndrome by ultrasound
and MRI. Prenat Diagn. 25:442–447. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Sepulveda W, Sebire NJ, Souka A, Snijders
RJ and Nicolaides KH: Diagnosis of the Meckel-Gruber syndrome at
eleven to fourteen weeks' gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
176:316–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Reece EA and Goldstein I: Early prenatal
diagnosis of hydrocephalus. Am J Perinatol. 14:69–73. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
den Hollander NS, Robben SG, Hoogeboom AJ,
Niermeijer MF and Wladimiroff JW: Early prenatal sonographic
diagnosis and follow-up of Jeune syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet
Gynecol. 18:378–383. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Poretti A, Brehmer U, Scheer I, Bernet V
and Boltshauser E: Prenatal and neonatal MR imaging findings in
oral-facial-digital syndrome type VI. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
29:1090–1091. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Beales PL and Kenny TD: Towards the
diagnosis of a ciliopathy. Ciliopathies: A Reference for
Clinicians. Oxford University Press; Oxford; pp. 1–7. 2013
|
|
108
|
Katsanis N, Beales PL, Woods MO, Lewis RA,
Green JS, Parfrey PS, Ansley SJ, Davidson WS and Lupski JR:
Mutations in MKKS cause obesity, retinal dystrophy and renal
malformations associated with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Nat Genet. 26.
pp. 67–70. 2000, View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Slavotinek AM, Stone EM, Mykytyn K,
Heckenlively JR, Green JS, Heon E, Musarella MA, Parfrey PS,
Sheffield VC and Biesecker LG: Mutations in MKKS cause Bardet-Biedl
syndrome. Nat Genet. 26. pp. 15–16. 2000, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Reiter JF and Leroux MR: Genes and
molecular pathways underpinning ciliopathies. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 18:533–547. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Shaheen R, Szymanska K, Basu B, Patel N,
Ewida N, Faqeih E, Al Hashem A, Derar N, Alsharif H, Aldahmesh MA,
et al: Characterizing the morbid genome of ciliopathies. Genome
Biol. 17:2422016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Lindstrand A, Davis EE, Carvalho CM,
Pehlivan D, Willer JR, Tsai IC, Ramanathan S, Zuppan C, Sabo A,
Muzny D, et al: Recurrent CNVs and SNVs at the NPHP1 locus
contribute pathogenic alleles to Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Am J Hum
Genet. 94:745–754. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Lindstrand A, Frangakis S, Carvalho CM,
Richardson EB, McFadden KA, Willer JR, Pehlivan D, Liu P,
Pediaditakis IL, Sabo A, et al: Copy-Number variation contributes
to the mutational load of Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Am J Hum Genet.
99:318–336. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Fauser S, Munz M and Besch D: Further
support for digenic inheritance in Bardet-Biedl syndrome. J Med
Genet. 40:e1042003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Katsanis N: The oligogenic properties of
Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 13(Spec No 1): R65–R71. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Katsanis N, Ansley SJ, Badano JL, Eichers
ER, Lewis RA, Hoskins BE, Scambler PJ, Davidson WS, Beales PL and
Lupski JR: Triallelic inheritance in Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a
Mendelian recessive disorder. Science. 293. pp. 2256–2259. 2001,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Katsanis N, Eichers ER, Ansley SJ, Lewis
RA, Kayserili H, Hoskins BE, Scambler PJ, Beales PL and Lupski JR:
BBS4 is a minor contributor to Bardet-Biedl syndrome and may also
participate in triallelic inheritance. Am J Hum Genet. 71. pp.
22–29. 2002, View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Beales PL, Badano JL, Ross AJ, Ansley SJ,
Hoskins BE, Kirsten B, Mein CA, Froguel P, Scambler PJ, Lewis RA,
et al: Genetic interaction of BBS1 mutations with alleles at other
BBS loci can result in non-Mendelian Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Am J
Hum Genet. 72:1187–1199. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Abu-Safieh L, Al-Anazi S, Al-Abdi L,
Hashem M, Alkuraya H, Alamr M, Sirelkhatim MO, Al-Hassnan Z,
Alkuraya B, Mohamed JY, et al: In search of triallelism in
Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 20:420–427. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Delvallée C, Nicaise S, Antin M, Leuvrey
AS, Nourisson E, Leitch CC, Kellaris G, Stoetzel C, Geoffroy V,
Scheidecker S, et al: A BBS1 SVA F retrotransposon insertion is a
frequent cause of Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Clin Genet. 99:318–324.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Davis EE and Katsanis N: The ciliopathies:
A transitional model into systems biology of human genetic disease.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 22:290–303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Badano JL, Kim JC, Hoskins BE, Lewis RA,
Ansley SJ, Cutler DJ, Castellan C, Beales PL, Leroux MR and
Katsanis N: Heterozygous mutations in BBS1, BBS2 and BBS6 have a
potential epistatic effect on Bardet-Biedl patients with two
mutations at a second BBS locus. Hum Mol Genet. 12. pp. 1651–1659.
2003, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Badano JL, Leitch CC, Ansley SJ,
May-Simera H, Lawson S, Lewis RA, Beales PL, Dietz HC, Fisher S and
Katsanis N: Dissection of epistasis in oligogenic Bardet-Biedl
syndrome. Nature. 439. pp. 326–330. 2006, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Slavotinek A and Biesecker LG: Genetic
modifiers in human development and malformation syndromes,
including chaperone proteins. Hum Mol Genet. 12(Spec No 1):
R45–R50. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Hildebrandt F, Benzing T and Katsanis N:
Ciliopathies. N Engl J Med. 364:1533–1543. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Novarino G, Akizu N and Gleeson JG:
Modeling human disease in humans: The ciliopathies. Cell.
147:70–79. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Zaki MS, Sattar S, Massoudi RA and Gleeson
JG: Co-occurrence of distinct ciliopathy diseases in single
families suggests genetic modifiers. Am J Med Genet A.
155A:3042–3049. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Khanna H, Davis EE, Murga-Zamalloa CA,
Estrada-Cuzcano A, Lopez I, den Hollander AI, Zonneveld MN, Othman
MI, Waseem N, Chakarova CF, et al: A common allele in RPGRIP1L is a
modifier of retinal degeneration in ciliopathies. Nat Genet.
41:739–745. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Bujakowska KM, Liu Q and Pierce EA:
Photoreceptor cilia and retinal ciliopathies. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 9:a0282742017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Goldberg AF, Moritz OL and Williams DS:
Molecular basis for photoreceptor outer segment architecture. Prog
Retin Eye Res. 55:52–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Estrada-Cuzcano A, Roepman R, Cremers FP,
den Hollander AI and Mans DA: Non-syndromic retinal ciliopathies:
Translating gene discovery into therapy. Hum Mol Genet.
21:R111–R124. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
den Hollander AI, Roepman R, Koenekoop RK
and Cremers FP: Leber congenital amaurosis: Genes, proteins and
disease mechanisms. Prog Retin Eye Res. 27:391–419. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Adams NA, Awadein A and Toma HS: The
retinal ciliopathies. Ophthalmic Genet. 28:113–125. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Marshall JD, Muller J, Collin GB, Milan G,
Kingsmore SF, Dinwiddie D, Farrow EG, Miller NA, Favaretto F,
Maffei P, et al: Alstrom syndrome: Mutation spectrum of ALMS1. Hum
Mutat. 36:660–668. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Ronquillo CC, Bernstein PS and Baehr W:
Senior-Loken syndrome: A syndromic form of retinal dystrophy
associated with nephronophthisis. Vision Res. 75:88–97. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Braun DA and Hildebrandt F: Ciliopathies.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 9:a0281912017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Saigusa T and Bell PD: Molecular pathways
and therapies in autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Physiology (Bethesda). 30:195–207. 2015.
|
|
138
|
Bergmann C: ARPKD and early manifestations
of ADPKD: The original polycystic kidney disease and phenocopies.
Pediatr Nephrol. 30:15–30. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Chebib FT and Torres VE: Autosomal
dominant polycystic kidney disease: Core Curriculum 2016. Am J
Kidney Dis. 67:792–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Wolf MT and Hildebrandt F:
Nephronophthisis. Pediatr Nephrol. 26:181–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Konig J, Kranz B, Konig S, Schlingmann KP,
Titieni A, Tönshoff B, Habbig S, Pape L, Häffner K, Hansen M, et
al: Phenotypic spectrum of children with nephronophthisis and
related ciliopathies. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 12:1974–1983. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Zaghloul NA and Katsanis N: Mechanistic
insights into Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a model ciliopathy. J Clin
Invest. 119:428–437. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Forsythe E and Beales PL: Bardet-Biedl
syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 21:8–13. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Forsythe R and Gunay-Aygun M: Bardet-Biedl
syndrome overview. Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al:
GeneReviews® [Internet]. University of Washington; Seattle, WA:
2003, updated July 23, 2020.
|
|
145
|
Bujakowska KM, Zhang Q, Siemiatkowska AM,
Liu Q, Place E, Falk MJ, Consugar M, Lancelot ME, Antonio A, Lonjou
C, et al: Mutations in IFT172 cause isolated retinal degeneration
and Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 24:230–242. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Alazami AM, Alshammari MJ, Salih MA,
Alzahrani F, Hijazi H, Seidahmed MZ, Abu Safieh L, Aldosary M, Khan
AO and Alkuraya FS: Molecular characterization of Joubert syndrome
in Saudi Arabia. Hum Mutat. 33:1423–1428. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Stephen J, Vilboux T, Mian L, Kuptanon C,
Sinclair CM, Yildirimli D, Maynard DM, Bryant J, Fischer R,
Vemulapalli M, et al: Mutations in KIAA0753 cause Joubert syndrome
associated with growth hormone deficiency. Hum Genet. 136:399–408.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Shaheen R, Jiang N, Alzahrani F, Ewida N,
Al-Sheddi T, Alobeid E, Musaev D, Stanley V, Hashem M, Ibrahim N,
et al: Bi-allelic Mutations in FAM149B1 cause abnormal primary
cilium and a range of ciliopathy phenotypes in humans. Am J Hum
Genet. 104:731–737. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Radha Rama Devi A, Naushad SM and Lingappa
L: Clinical and molecular diagnosis of joubert syndrome and related
disorders. Pediatr Neurol. 106:43–49. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Oka M, Shimojima K, Yamamoto T, Hanaoka Y,
Sato S, Yasuhara T, Yoshinaga H and Kobayashi K: A novel HYLS1
homozygous mutation in living siblings with Joubert syndrome. Clin
Genet. 89:739–743. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Beck BB, Phillips JB, Bartram MP, Wegner
J, Thoenes M, Pannes A, Sampson J, Heller R, Göbel H, Koerber F, et
al: Mutation of POC1B in a severe syndromic retinal ciliopathy. Hum
Mutat. 35:1153–1162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Bachmann-Gagescu R, Dempsey JC, Phelps IG,
O'Roak BJ, Knutzen DM, Rue TC, Ishak GE, Isabella CR, Gorden N,
Adkins J, et al: Joubert syndrome: A model for untangling recessive
disorders with extreme genetic heterogeneity. J Med Genet.
52:514–522. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Schmidts M: Jeune syndrome and the ciliary
chondrodysplasias. Ciliopathies. Oxford University Press; Oxford;
pp. 30–63. 2013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Haycraft CJ, Zhang Q, Song B, Jackson WS,
Detloff PJ, Serra R and Yoder BK: Intraflagellar transport is
essential for endochondral bone formation. Development.
134:307–316. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
St-Jacques B, Hammerschmidt M and McMahon
AP: Indian hedgehog signaling regulates proliferation and
differentiation of chondrocytes and is essential for bone
formation. Genes Dev. 13:2072–2086. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Schmidts M, Hou Y, Cortes CR, Mans DA,
Huber C, Boldt K, Patel M, van Reeuwijk J, Plaza JM, van Beersum
SE, et al: TCTEX1D2 mutations underlie Jeune asphyxiating thoracic
dystrophy with impaired retrograde intraflagellar transport. Nat
Commun. 6:70742015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Zhang W, Taylor SP, Ennis HA, Forlenza KN,
Duran I, Li B, Sanchez JAO, Nevarez L, Nickerson DA and Bamshad M:
Expanding the genetic architecture and phenotypic spectrum in the
skeletal ciliopathies. Hum Mutat. 39:152–166. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Ellis RW and van Creveld S: A syndrome
characterized by ectodermal dysplasia, polydactyly,
Chondro-Dysplasia and congenital Morbus Cordis: Report of three
cases. Arch Dis Child. 15:65–84. 1940. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
McKusick VA, Eldridge R, Hostetler JA and
Egeland JA: Dwarfism in the Amish. Trans Assoc Am Physicians.
77:151–168. 1964.
|
|
160
|
Ruiz-Perez VL and Goodship JA: Ellis-van
Creveld syndrome and Weyers acrodental dysostosis are caused by
cilia-mediated diminished response to hedgehog ligands. Am J Med
Genet C Semin Med Genet. 151C:341–351. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Howard TD, Guttmacher AE, McKinnon W,
Sharma M, McKusick VA and Jabs EW: Autosomal dominant postaxial
polydactyly, nail dystrophy, and dental abnormalities map to
chromosome 4p16, in the region containing the Ellis-van Creveld
syndrome locus. Am J Hum Genet. 61:1405–1412. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Levin LS, Perrin JC, Ose L, Dorst JP,
Miller JD and McKusick VA: A heritable syndrome of
craniosynostosis, short thin hair, dental abnormalities, and short
limbs: Cranioectodermal dysplasia. J Pediatr. 90:55–61. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Lin AE, Traum AZ, Sahai I, Keppler-Noreuil
K, Kukolich MK, Adam MP, Westra SJ and Arts HH: Sensenbrenner
syndrome (Cranioectodermal dysplasia): Clinical and molecular
analyses of 39 patients including two new patients. Am Med Genet A.
161A:2762–2776. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Arts HH, Bongers EM, Mans DA, van Beersum
SE, Oud MM, Bolat E, Spruijt L, Cornelissen EA, Schuurs-Hoeijmakers
JH, de Leeuw N, et al: C14ORF179 encoding IFT43 is mutated in
Sensenbrenner syndrome. J Med Genet. 48:390–395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Huber C and Cormier-Daire V: Ciliary
disorder of the skeleton. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet.
160C:165–174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Mainzer F, Saldino RM, Ozonoff MB and
Minagi H: Familial nephropathy associatdd with retinitis
pigmentosa, cerebellar ataxia and skeletal abnormalities. Am J Med.
49:556–562. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Perrault I, Saunier S, Hanein S, Filhol E,
Bizet AA, Collins F, Salih MA, Gerber S, Delphin N, Bigot K, et al:
Mainzer-Saldino syndrome is a ciliopathy caused by IFT140
mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 90:864–870. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Beales PL, Bland E, Tobin JL, Bacchelli C,
Tuysuz B, Hill J, Rix S, Pearson CG, Kai M, Hartley J, et al:
IFT80, which encodes a conserved intraflagellar transport protein,
is mutated in Jeune asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy. Nat Genet.
39:727–729. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Tuysuz B, Baris S, Aksoy F, Madazli R,
Ungur S and Sever L: Clinical variability of asphyxiating thoracic
dystrophy (Jeune) syndrome: Evaluation and classification of 13
patients. Am J Med Genet A. 149A:1727–1733. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
170
|
Zhang W, Taylor SP, Nevarez L, Lachman RS,
Nickerson DA and Bamshad M: IFT52 mutations destabilize anterograde
complex assembly, disrupt ciliogenesis and result in short rib
polydactyly syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 25:4012–4020. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Duran I, Taylor SP, Zhang W, Martin J,
Qureshi F, Jacques SM, Wallerstein R, Lachman RS, Nickerson DA,
Bamshad M, et al: Mutations in IFT-A satellite core component genes
IFT43 and IFT121 produce short rib polydactyly syndrome with
distinctive campomelia. Cilia. 6:72017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Roosing S, Romani M, Isrie M, Rosti RO,
Micalizzi A, Musaev D, Mazza T, Al-Gazali L, Altunoglu U,
Boltshauser E, et al: Mutations in CEP120 cause Joubert syndrome as
well as complex ciliopathy phenotypes. J Med Genet. 53:608–615.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Bruel AL, Franco B, Duffourd Y, Thevenon
J, Jego L, Lopez E, Deleuze JF, Doummar D, Giles RH, Johnson CA, et
al: Fifteen years of research on oral-facial-digital syndromes:
From 1 to 16 causal genes. J Med Genet. 54:371–380. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Li C, Jensen VL, Park K, Kennedy J,
Garcia-Gonzalo FR, Romani M, De Mori R, Bruel AL, Gaillard D, Doray
B, et al: MKS5 and CEP290 dependent assembly pathway of the ciliary
transition zone. PLoS Biol. 14:e10024162016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Al-Qattan MM, Shaheen R and Alkuraya FS:
Expanding the allelic disorders linked to TCTN1 to include Varadi
syndrome (Orofaciodigital syndrome type VI). Am J Med Genet A.
173:2439–2441. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Franco B and Thauvin-Robinet C: Update on
oral-facial-digital syndromes (OFDS). Cilia. 5:122016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Toriello HV: Are the oral-facial-digital
syndromes ciliopathies? Am J Med Genet A. 149A:1089–1095. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Toriello HV, Franco B, Bruel AL and
Thauvin-Robinet C: Oral-Facial-Digital Syndrome Type I.
GeneReviews((R)). Adam MP, Ardinger HH and Pagon RA: University of
Washington; Seattle, WA: 1993
|
|
179
|
Shamseldin HE, Rajab A, Alhashem A,
Shaheen R, Al-Shidi T, Alamro R, Al Harassi S and Alkuraya FS:
Mutations in DDX59 implicate RNA helicase in the pathogenesis of
orofaciodigital syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 93:555–560. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
180
|
Toriyama M, Lee C, Taylor SP, Duran I,
Cohn DH, Bruel AL, Tabler JM, Drew K, Kelly MR, Kim S, et al: The
ciliopathy-associated CPLANE proteins direct basal body recruitment
of intraflagellar transport machinery. Nat Genet. 48:648–656. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Saari J, Lovell MA, Yu HC and Bellus GA:
Compound heterozygosity for a frame shift mutation and a likely
pathogenic sequence variant in the planar cell
polarity-ciliogenesis gene WDPCP in a girl with polysyndactyly,
coarctation of the aorta, and tongue hamartomas. Am J Med Genet A.
167A:421–427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Thevenon J, Duplomb L, Phadke S, Eguether
T, Saunier A, Avila M, Carmignac V, Bruel AL, St-Onge J, Duffourd
Y, et al: Autosomal recessive IFT57 hypomorphic mutation cause
ciliary transport defect in unclassified oral-facial-digital
syndrome with short stature and brachymesophalangia. Clin Genet.
90:509–517. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Baker K and Beales PL: Making sense of
cilia in disease: The human ciliopathies. Am J Med Genet C Semin
Med Genet. 151C:281–295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
184
|
Laquerriere A, Maluenda J, Camus A,
Fontenas L, Dieterich K, Nolent F, Zhou J, Monnier N, Latour P,
Gentil D, et al: Mutations in CNTNAP1 and ADCY6 are responsible for
severe arthrogryposis multiplex congenita with axoglial defects.
Hum Mol Genet. 23:2279–2289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Filges I, Bruder E, Brandal K, Meier S,
Undlien DE, Waage TR, Hoesli I, Schubach M, de Beer T, Sheng Y, et
al: Stromme syndrome is a ciliary disorder caused by mutations in
CENPF. Hum Mutat. 37:359–363. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
186
|
Waters AM, Asfahani R, Carroll P, Bicknell
L, Lescai F, Bright A, Chanudet E, Brooks A, Christou-Savina S,
Osman G, et al: The kinetochore protein, CENPF, is mutated in human
ciliopathy and microcephaly phenotypes. J Med Genet. 52. pp.
147–156. 2015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Luijten MN, Basten SG, Claessens T,
Vernooij M, Scott CL, Janssen R, Easton JA, Kamps MA, Vreeburg M,
Broers JL, et al: Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome is a novel ciliopathy.
Hum Mol Genet. 22:4383–4397. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
188
|
Jenkins D, Seelow D, Jehee FS, Perlyn CA,
Alonso LG, Bueno DF, Donnai D, Josifova D, Mathijssen IM, Morton
JE, et al: RAB23 mutations in Carpenter syndrome imply an
unexpected role for hedgehog signaling in cranial-suture
development and obesity. Am J Hum Genet. 80:1162–1170. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
189
|
Symoens S, Barnes AM, Gistelinck C,
Malfait F, Guillemyn B, Steyaert W, Syx D, D'hondt S, Biervliet M,
De Backer J, et al: Genetic defects in TAPT1 disrupt ciliogenesis
and cause a complex lethal osteochondrodysplasia. Am J Hum Genet.
97:521–534. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
190
|
Reijnders MR, Zachariadis V, Latour B,
Jolly L, Mancini GM, Pfundt R, Wu KM, van Ravenswaaij-Arts CM,
Veenstra-Knol HE, Anderlid BM, et al: De Novo Loss-of-Function
mutations in USP9X cause a Female-Specific recognizable syndrome
with developmental delay and congenital malformations. Am J Hum
Genet. 98:373–381. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
191
|
Twigg SRF, Hufnagel RB, Miller KA, Zhou Y,
McGowan SJ, Taylor J, Craft J, Taylor JC, Santoro SL, Huang T, et
al: A recurrent Mosaic Mutation in SMO, encoding the Hedgehog
signal transducer smoothened, is the major cause of Curry-Jones
syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 98:1256–1265. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
192
|
Ali BR, Silhavy JL, Akawi NA, Gleeson JG
and Al-Gazali L: A mutation in KIF7 is responsible for the
autosomal recessive syndrome of macrocephaly, multiple epiphyseal
dysplasia and distinctive facial appearance. Orphanet J Rare Dis.
7:272012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
193
|
Putoux A, Thomas S, Coene KL, Davis EE,
Alanay Y, Ogur G, Uz E, Buzas D, Gomes C, Patrier S, et al: KIF7
mutations cause fetal hydrolethalus and acrocallosal syndromes. Nat
Genet. 43:601–606. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
194
|
Dammermann A, Pemble H, Mitchell BJ,
McLeod I, Yates JR III, Kintner C, Desai AB and Oegema K: The
hydrolethalus syndrome protein HYLS-1 links core centriole
structure to cilia formation. Genes Dev. 23:2046–2059. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
195
|
Alby C, Piquand K, Huber C, Megarbané A,
Ichkou A, Legendre M, Pelluard F, Encha-Ravazi F, Abi-Tayeh G,
Bessières B, et al: Mutations in KIAA0586 cause lethal ciliopathies
ranging from a hydrolethalus phenotype to Short-Rib Polydactyly
syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 97:311–318. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
196
|
Demurger F, Ichkou A, Mougou-Zerelli S, Le
Merrer M, Goudefroye G, Delezoide AL, Quélin C, Manouvrier S,
Baujat G, Fradin M, et al: New insights into genotype-phenotype
correlation for GLI3 mutations. Eur J Hum Genet. 23:92–102. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
197
|
Oud MM, Bonnard C, Mans DA, Altunoglu U,
Tohari S, Ng AYJ, Eskin A, Lee H, Rupar CA, de Wagenaar NP, et al:
A novel ICK mutation causes ciliary disruption and lethal
endocrine-cerebro-osteodysplasia syndrome. Cilia. 5:82016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
198
|
Karaca E, Buyukkaya R, Pehlivan D, Charng
WL, Yaykasli KO, Bayram Y, Gambin T, Withers M, Atik MM, Arslanoglu
I, et al: Whole-exome sequencing identifies homozygous GPR161
mutation in a family with pituitary stalk interruption syndrome. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 100:E140–147. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
199
|
Guen VJ, Gamble C, Perez DE, Bourassa S,
Zappel H, Gärtner J, Lees JA and Colas P: STAR syndrome-associated
CDK10/Cyclin M regulates actin network architecture and
ciliogenesis. Cell Cycle. 15:678–688. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
200
|
Alessandri JL, Dagoneau N, Laville JM,
Baruteau J, Hébert JC and Cormier-Daire V: RAB23 mutation in a
large family from Comoros Islands with Carpenter syndrome. Am J Med
Genet A. 152A:982–986. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
201
|
Jenkins D, Baynam G, De Catte L, Elcioglu
N, Gabbett MT, Hudgins L, Hurst JA, Jehee FS, Oley C and Wilkie AO:
Carpenter syndrome: Extended RAB23 mutation spectrum and analysis
of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Hum Mutat. 32:E2069–E2078. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
202
|
Lefroy H, Hurst JA and Shears DJ: STAR
syndrome: A further case and the first report of maternal
mosaicism. Clin Dysmorphol. 26:157–160. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Ng SB, Bigham AW, Buckingham KJ, Hannibal
MC, McMillin MJ, Gildersleeve HI, Beck AE, Tabor HK, Cooper GM,
Mefford HC, et al: Exome sequencing identifies MLL2 mutations as a
cause of Kabuki syndrome. Nat Genet. 42:790–793. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
204
|
Miyake N, Koshimizu E, Okamoto N, Mizuno
S, Ogata T, Nagai T, Kosho T, Ohashi H, Kato M, Sasaki G, et al:
MLL2 and KDM6A mutations in patients with Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med
Genet A. 161A:2234–2243. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
205
|
Shaheen R, Rahbeeni Z, Alhashem A, Faqeih
E, Zhao Q, Xiong Y, Almoisheer A, Al-Qattan SM, Almadani HA,
Al-Onazi N, et al: Neu-Laxova syndrome, an inborn error of serine
metabolism, is caused by mutations in PHGDH. Am J Hum Genet.
94:898–904. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
206
|
Acuna-Hidalgo R, Schanze D, Kariminejad A,
Nordgren A, Kariminejad MH, Conner P, Grigelioniene G, Nilsson D,
Nordenskjöld M, Wedell A, et al: Neu-Laxova syndrome is a
heterogeneous metabolic disorder caused by defects in enzymes of
the L-serine biosynthesis pathway. Am J Hum Genet. 95:285–293.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
207
|
Duplomb L, Duvet S, Picot D, Jego G, El
Chehadeh-Djebbar S, Marle N, Gigot N, Aral B, Carmignac V, Thevenon
J, et al: Cohen syndrome is associated with major glycosylation
defects. Hum Mol Genet. 23:2391–2399. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
208
|
El Chehadeh S, Aral B, Gigot N,
Thauvin-Robinet C, Donzel A, Delrue MA, Lacombe D, David A, Burglen
L, Philip N, et al: Search for the best indicators for the presence
of a VPS13B gene mutation and confirmation of diagnostic criteria
in a series of 34 patients genotyped for suspected Cohen syndrome.
J Med Genet. 47:549–553. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
209
|
Emery NJ, Seed AM, von Bayern AM and
Clayton NS: Cognitive adaptations of social bonding in birds.
Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 362:489–505. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
210
|
Bozal-Basterra L, Martin-Ruiz I, Pirone L,
Liang Y, Sigurðsson JO, Gonzalez-Santamarta M, Giordano I,
Gabicagogeascoa E, de Luca A, Rodríguez JA, et al: Truncated SALL1
impedes primary cilia function in townes-brocks syndrome. Am J Hum
Genet. 102:249–265. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
211
|
Devlin LA and Sayer JA: Renal
ciliopathies. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 56:49–60. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|