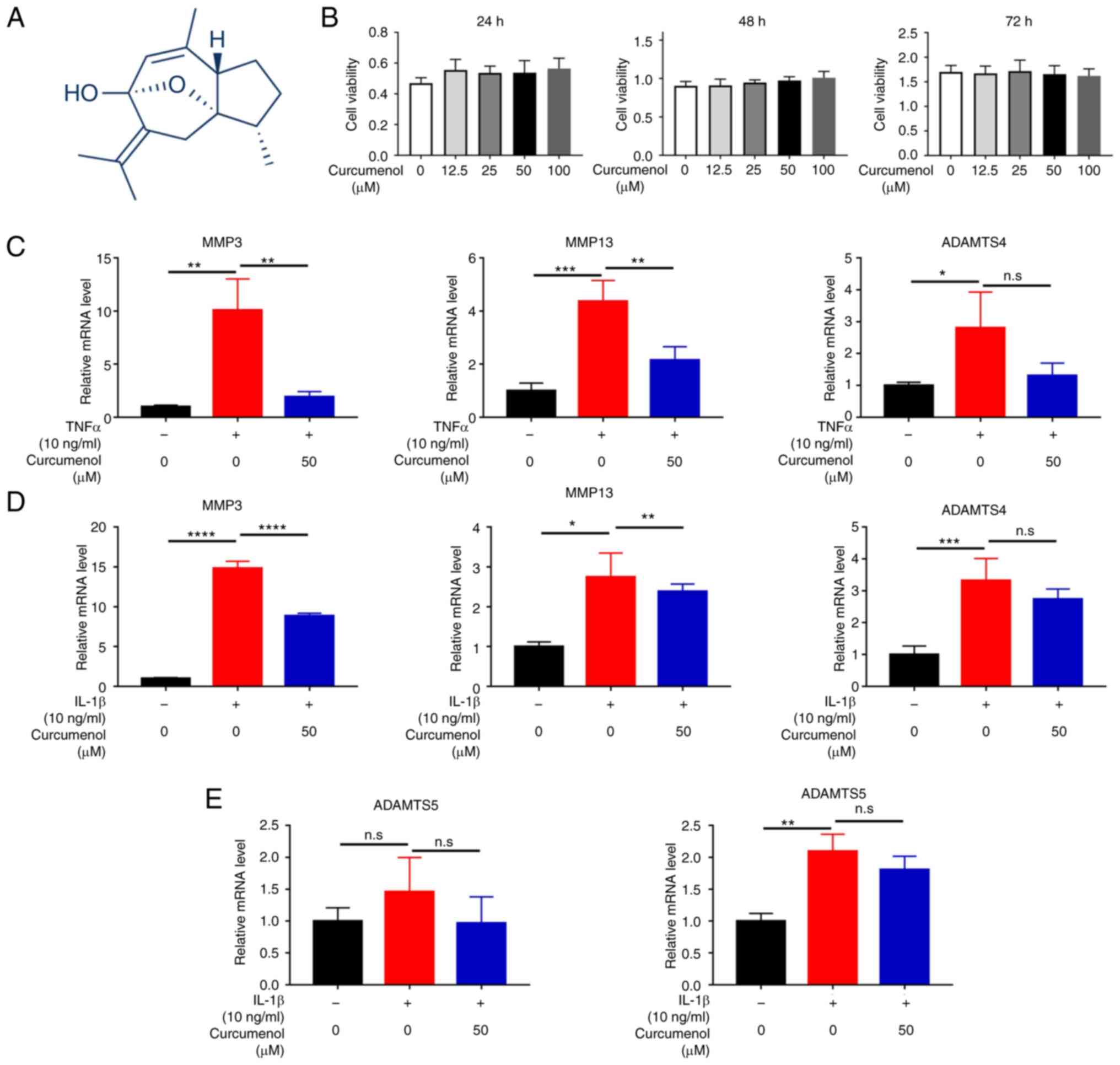
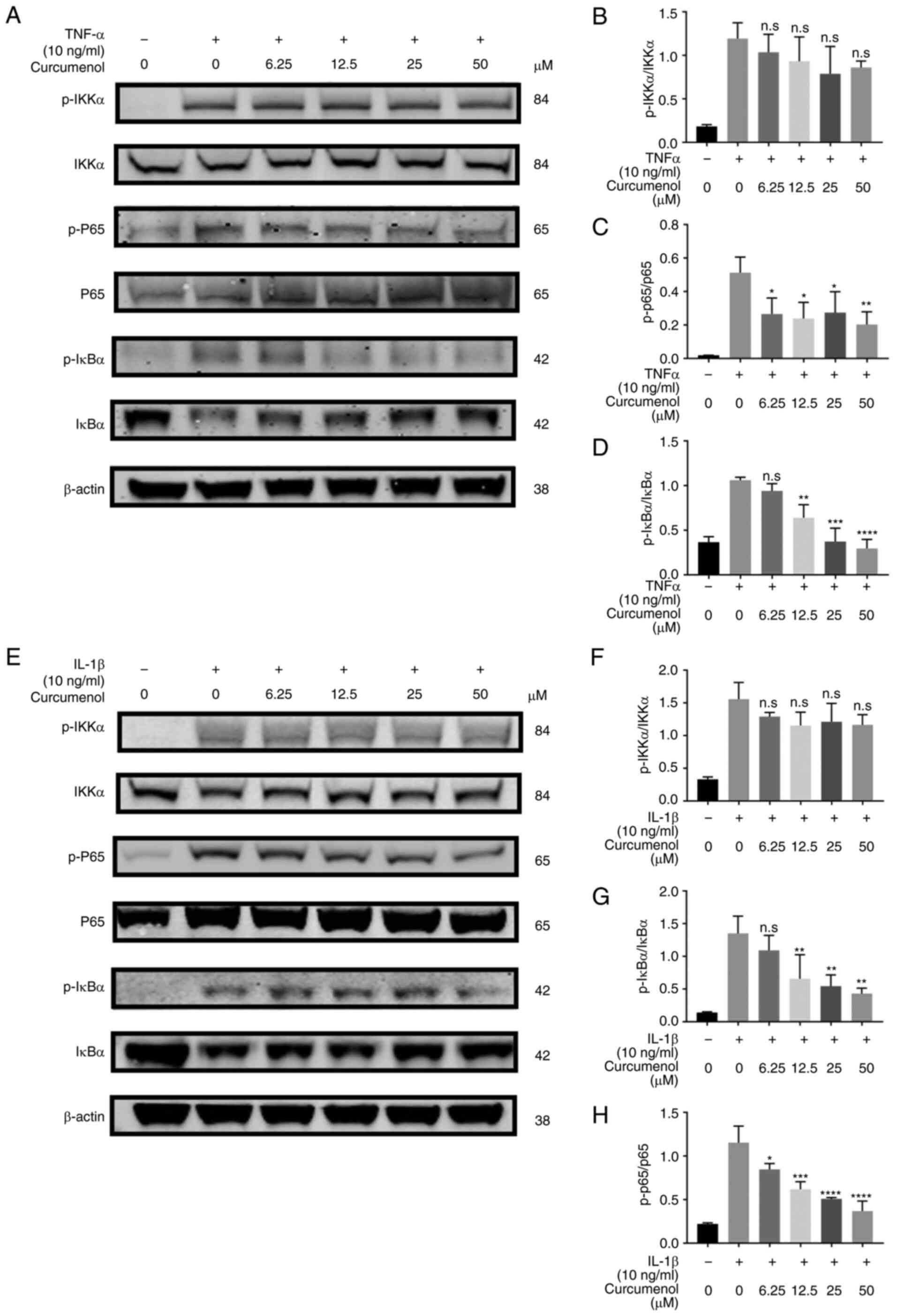
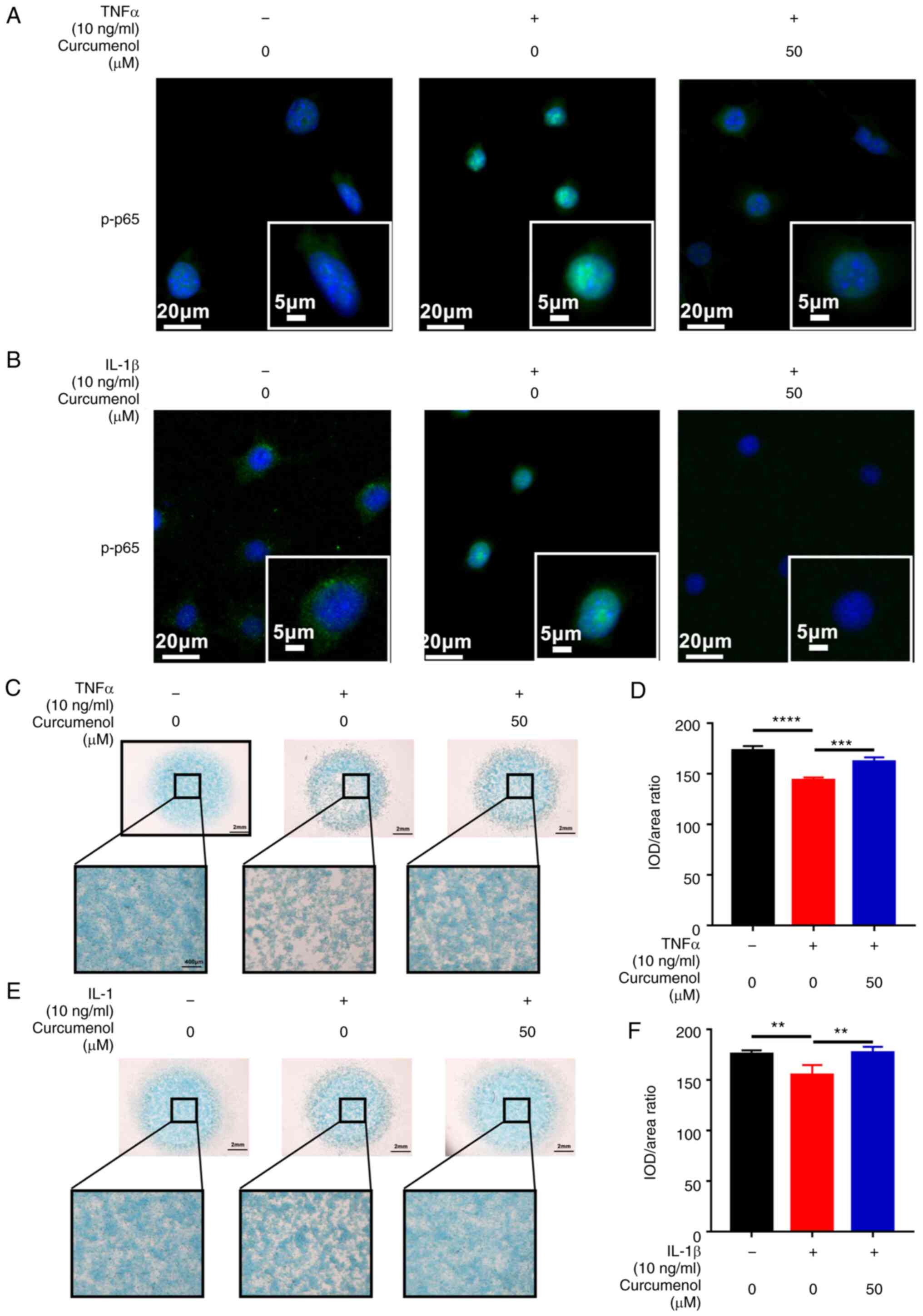
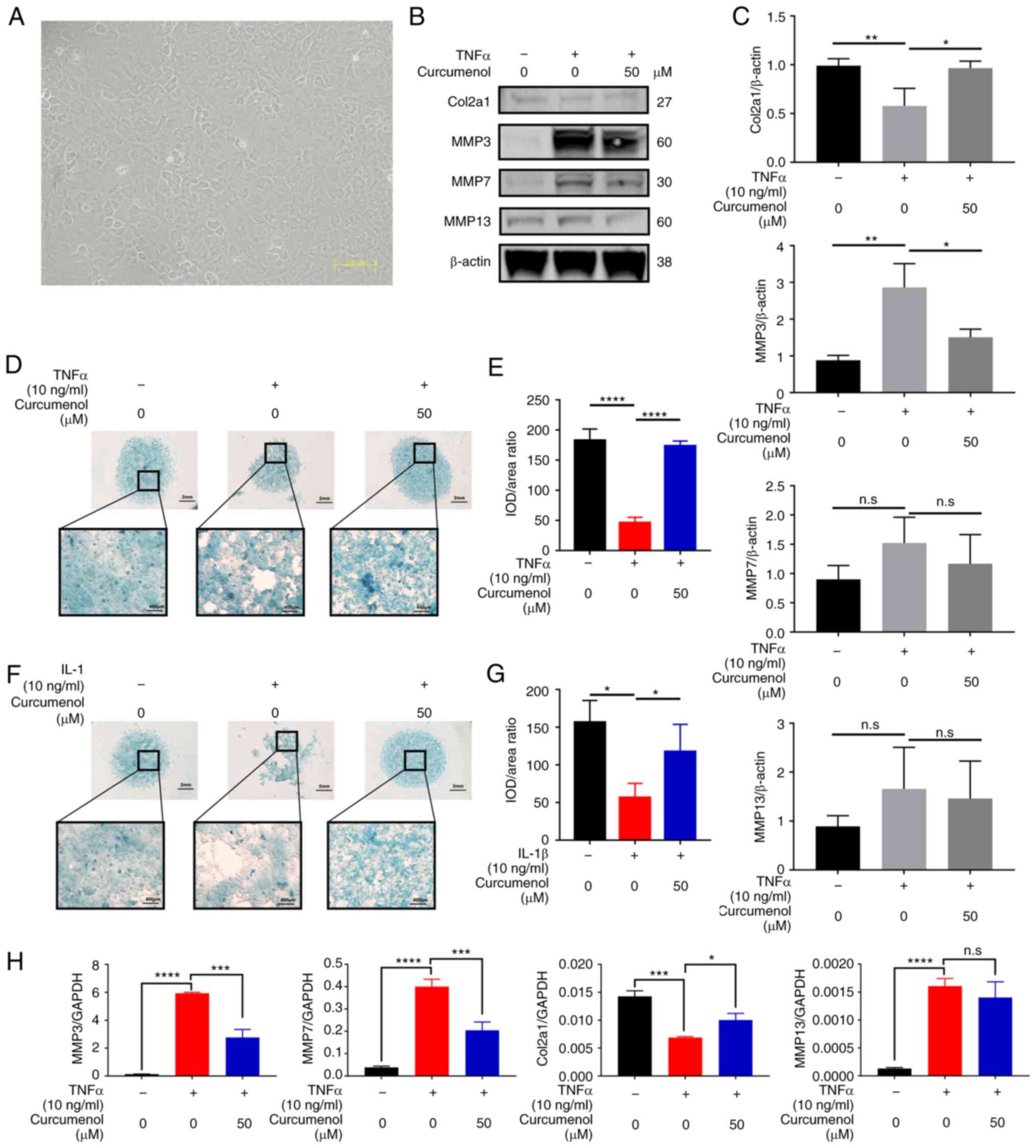
|
1
|
Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R, Price
AJ, Vincent TL, Weinans H and Carr AJ: Osteoarthritis. Lancet.
386:376–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang Z, Huang C, Jiang Q, Zheng Y, Liu Y,
Liu S, Chen Y, Mei Y, Ding C, Chen M, et al: Guidelines for the
diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis in China (2019 edition).
Ann Transl Med. 8:12132020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hiligsmann M, Cooper C, Arden N, Boers M,
Branco JC, Luisa Brandi M, Bruyère O, Guillemin F, Hochberg MC,
Hunter DJ, et al: Health economics in the field of osteoarthritis:
An expert's consensus paper from the European society for clinical
and economic aspects of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis (ESCEO).
Semin Arthritis Rheum. 43:303–313. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Agricola R, Heijboer MP, Roze RH, Reijman
M, Bierma-Zeinstra SMA, Verhaar JAN, Weinans H and Waarsing JH:
Pincer deformity does not lead to osteoarthritis of the hip whereas
acetabular dysplasia does: Acetabular coverage and development of
osteoarthritis in a nationwide prospective cohort study (CHECK).
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:1514–1521. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tsuchiya H, Ota M, Sumitomo S, Ishigaki K,
Suzuki A, Sakata T, Tsuchida Y, Inui H, Hirose J, Kochi Y, et al:
Parsing multiomics landscape of activated synovial fibroblasts
highlights drug targets linked to genetic risk of rheumatoid
arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. Nov 2–2020.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
6
|
Myers J, Wielage RC, Han B, Price K, Gahn
J, Paget MA and Happich M: The efficacy of duloxetine,
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and opioids in
osteoarthritis: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 15:762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McAlindon TE, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC,
Arden NK, Berenbaum F, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, Hawker GA, Henrotin Y,
Hunter DJ, Kawaguchi H, et al: OARSI guidelines for the
non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 22:363–388. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Pas HI, Winters M, Haisma HJ, Koenis MJ,
Tol JL and Moen MH: Stem cell injections in knee osteoarthritis: A
systematic review of the literature. Br J Sports Med. 51:1125–1133.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hached F, Vinatier C, Le Visage C, Gondé
H, Guicheux J, Grimandi G and Billon-Chabaud A:
Biomaterial-assisted cell therapy in osteoarthritis: From
mesenchymal stem cells to cell encapsulation. Best Pract Res Clin
Rheumatol. 31:730–745. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Liao T, Wan C, Yang X, Zhao J, Fu
R, Yao Z, Huang Y, Shi Y, Chang G, et al: Efficient generation of
human primordial germ cell-like cells from pluripotent stem cells
in a methylcellulose-based 3D system at large scale. PeerJ.
6:e61432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hikino H, Sakurai Y, Numabe S and Takemoto
T: Structure of curcumenol. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 16:39–42.
1968. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xu J, Ji F, Kang J, Wang H, Li S, Jin DQ,
Zhang Q, Sun H and Guo Y: Absolute configurations and NO inhibitory
activities of terpenoids from curcuma longa. J Agric Food Chem.
63:5805–5812. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Assis A, Brito V, Bittencourt M, Silva L,
Oliveira F and Oliveira R: Essential oils composition of four Piper
species from Brazil. J Essential Oil Res. 25:203–209. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Saikia AK, Sarma SK, Strano T and Ruberto
G: Essential oil from piper pedicellatum C. DC. Collected in
North-East India. J Essential Oil Bearing Plants. 18:314–319. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sun DX, Fang ZZ, Zhang YY, Cao YF, Yang L
and Yin J: Inhibitory effects of curcumenol on human liver
cytochrome P450 enzymes. Phytother Res. 24:1213–1216. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pintatum A, Maneerat W, Logie E, Tuenter
E, Sakavitsi ME, Pieters L, Berghe WV, Sripisut T, Deachathai S and
Laphookhieo S: In Vitro anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, and
cytotoxic activities of four species and the isolation of compounds
from rhizome. Biomolecules. 10:7992020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Oh CD, Im HJ, Suh J, Chee A, An H and Chen
D: Rho-associated kinase inhibitor immortalizes rat nucleus
pulposus and annulus fibrosus cells: Establishment of
intervertebral disc cell lines with novel approaches. Spine (Plila
Pa 1976). 41:E255–E261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Johnson M, Zaretskaya I, Raytselis Y,
Merezhuk Y, McGinnis S and Madden TL: NCBI BLAST: A better web
interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 36(Web Server issue): W5–W9. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shi JW, Zhang TT, Liu W, Yang J, Lin XL,
Jia JS, Shen HF, Wang SC, Li J, Zhao WT, et al: Direct conversion
of pig fibroblasts to chondrocyte-like cells by c-Myc. Cell Death
Discov. 5:552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Glasson SS, Blanchet TJ and Morris EA: The
surgical destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) model of
osteoarthritis in the 129/SvEv mouse. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
15:1061–1069. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang M, Sampson ER, Jin H, Li J, Ke QH, Im
HJ and Chen D: MMP13 is a critical target gene during the
progression of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 15:R52013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Loeser RF, Kelley KL, Armstrong A, Collins
JA, Diekman BO and Carlson CS: Deletion of JNK enhances senescence
in joint tissues and increases the severity of age-related
osteoarthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 72:1679–1688. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sohara Y, Shimada H, Scadeng M, Pollack H,
Yamada S, Ye W, Reynolds CP and DeClerck YA: Lytic bone lesions in
human neuroblastoma xenograft involve osteoclast recruitment and
are inhibited by bisphosphonate. Cancer Res. 63:3026–3031.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sharma L: Osteoarthritis of the knee. N
Engl J Med. 384:51–59. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Thorlund JB, Juhl CB, Roos EM and
Lohmander LS: Arthroscopic surgery for degenerative knee:
Systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits and harms. BMJ.
350:h27472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rasmussen-Barr E, Held U, Grooten WJA,
Roelofs PDDM, Koes BW, van Tulder MW and Wertli MM: Nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs for sciatica: An updated cochrane review.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 42:586–594. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Derry S, Wiffen PJ, Kalso EA, Bell RF,
Aldington D, Phillips T, Gaskell H and Moore RA: Topical analgesics
for acute and chronic pain in adults-an overview of cochrane
reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 5:CD0086092017.
|
|
29
|
Marmon P, Owen SF and Margiotta-Casaluci
L: Pharmacology-informed prediction of the risk posed to fish by
mixtures of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in the
environment. Environ Int. 146:1062222021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Chen J, Xuan J, Gu YT, Shi KS, Xie JJ,
Chen JX, Zheng ZM, Chen Y, Chen XB, Wu YS, et al: Celastrol reduces
IL-1β induced matrix catabolism, oxidative stress and inflammation
in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral
disc degeneration in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 91:208–219. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Y, Deng SJ, Zhang Z, Gu Y, Xia SN, Bao
XY, Cao X and Xu Y: 6-Gingerol attenuates microglia-mediated
neuroinflammation and ischemic brain injuries through
Akt-mTOR-STAT3 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 883:1732942020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Lin S, Liu P, Huang J, Qiu J, Wen Z,
Yuan J, Qiu H, Liu Y, Liu Q, et al: Carnosol suppresses
RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and attenuates titanium
particles-induced osteolysis. J Cell Physiol. 236:1950–1966. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lo JY, Kamarudin MNA, Hamdi OAA, Awang K
and Kadir HA: Curcumenol isolated from curcuma zedoaria suppresses
Akt-mediated NF-κB activation and p38 MAPK signaling pathway in
LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells. Food Funct. 6:3550–3559.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Z, Jones G, Winzenberg T, Cai G,
Laslett LL, Aitken D, Hopper I, Singh A, Jones R, Fripp J, et al:
Effectiveness of extract for the treatment of symptoms and
effusion-synovitis of knee osteoarthritis : A randomized trial. Ann
Intern Med. 173:861–869. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kapoor M, Martel-Pelletier J, Lajeunesse
D, Pelletier JP and Fahmi H: Role of proinflammatory cytokines in
the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 7:33–42.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Rodriguez-Trillo A, Mosquera N, Pena C,
Rivas-Tobío F, Mera-Varela A, Gonzalez A and Conde C: Non-Canonical
WNT5A signaling through RYK contributes to aggressive phenotype of
the rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Front Immunol.
11:5552452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao X, Meng F, Hu S, Yang Z, Huang H,
Pang R, Wen X, Kang Y and Zhang Z: The synovium attenuates
cartilage degeneration in KOA through activation of the
Smad2/3-Runx1 cascade and chondrogenesis-related miRNAs. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 22:832–845. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Baker RG, Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB,
inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 13:11–22. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Moqbel SAA, Xu K, Chen Z, Xu L, He Y, Wu
Z, Ma C, Ran J, Wu L and Xiong Y: Tectorigenin alleviates
inflammation, apoptosis, and ossification in rat tendon-derived
stem cells modulating NF-Kappa B and MAPK pathways. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 8:5688942020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang Q, Lenardo MJ and Baltimore D: 30
Years of NF-κB: A blossoming of relevance to human pathobiology.
Cell. 168:37–57. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhongyi S, Sai Z, Chao L and Jiwei T:
Effects of nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in human
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
40:224–232. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Baldwin AS: The NF-kappa B and I kappa B
proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol.
14:649–683. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun Z, Yin Z, Liu C, Liang H, Jiang M and
Tian J: IL-1β promotes ADAMTS enzyme-mediated aggrecan degradation
through NF-κB in human intervertebral disc. J Orthop Surg Res.
10:1592015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tu J, Li W, Zhang Y, Wu X, Song Y, Kang L,
Liu W, Wang K, Li S, Hua W and Yang C: Simvastatin inhibits
IL-1β-induced apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation by
suppressing the NF-kB and MAPK pathways in nucleus pulposus cells.
Inflammation. 40:725–734. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen J, Garssen J and Redegeld F: The
efficacy of bortezomib in human multiple myeloma cells is enhanced
by combination with omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA: Timing is
essential. Clin Nutr. 40:1942–1953. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Pham TH, Hagenbeek TJ, Lee HJ, Li J, Rose
CM, Lin E, Yu M, Martin SE, Piskol R, Lacap JA, et al: Machine
learning and chemico-genomics approach defines and predicts
cross-talk of Hippo and MAPK pathways. Cancer Discov. 11:778–793.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Cao C, Wu F, Niu X, Hu X, Cheng J, Zhang
Y, Li C, Duan X, Fu X, Zhang J, et al: Cadherin-11 cooperates with
inflammatory factors to promote the migration and invasion of
fibroblast-like synoviocytes in pigmented villonodular synovitis.
Theranostics. 10:10573–10588. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Séguin CA, Bojarski M, Pilliar RM,
Roughley PJ and Kandel RA: Differential regulation of matrix
degrading enzymes in a TNFalpha-induced model of nucleus pulposus
tissue degeneration. Matrix Biol. 25:409–418. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang G, Chen S, Xie Z, Shen S, Xu W, Chen
W, Li X, Wu Y, Li L, Liu B, et al: TGFβ attenuates cartilage
extracellular matrix degradation via enhancing FBXO6-mediated MMP14
ubiquitination. Ann Rheum Dis. 79:1111–1120. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
He L, He T, Xing J, Zhou Q, Fan L, Liu C,
Chen Y, Wu D, Tian Z, Liu B and Rong L: Bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve
knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 11:2762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Inoue R, Ishibashi Y, Tsuda E, Yamamoto Y,
Matsuzaka M, Takahashi I, Danjo K, Umeda T, Nakaji S and Toh S:
Knee osteoarthritis, knee joint pain and aging in relation to
increasing serum hyaluronan level in the Japanese population.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 19:51–57. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Lamo-Espinosa JM, Blanco JF, Sánchez M,
Moreno V, Granero-Moltó F, Sánchez-Guijo F, Crespo-Cullel I, Mora
G, Vicente DDS, Pompei-Fernández O, et al: Phase II multicenter
randomized controlled clinical trial on the efficacy of
intra-articular injection of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells with platelet rich plasma for the treatment of knee
osteoarthritis. J Transl Med. 18:3562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hubbard JS, Chen PH and Boyd KL: Effects
of repeated intraperitoneal injection of pharmaceutical-grade and
nonpharmaceutical-grade corn oil in female C57BL/6J mice. J Am
Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 56:779–785. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Alsina-Sanchis E, Mülfarth R, Moll I,
Mogler C, Rodriguez-Vita J and Fischer A: Intraperitoneal oil
application causes local inflammation with depletion of resident
peritoneal macrophages. Mol Cancer Res. 19:288–300. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Wang S, Ma Q, Xie Z, Shen Y, Zheng B,
Jiang C, Yuan P, An Q, Fan S and Jie Z: An antioxidant
sesquiterpene inhibits osteoclastogenesis via blocking IPMK/TRAF6
and counteracts OVX-induced osteoporosis in mice. J Bone Miner Res.
May 6–2021.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Kompel AJ, Roemer FW, Murakami AM, Diaz
LE, Crema MD and Guermazi A: Intra-articular corticosteroid
injections in the hip and knee: Perhaps not as safe as we thought?
Radiology. 293:656–663. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mehta PN and Ghadially FN: Articular
cartilage in corn oil-induced lipoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis.
32:75–82. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bagi CM, Berryman ER, Teo S and Lane NE:
Oral administration of undenatured native chicken type II collagen
(UC-II) diminished deterioration of articular cartilage in a rat
model of osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
25:2080–2090. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Runhaar J, Rozendaal RM, van Middelkoop M,
Bijlsma HJW, Doherty M, Dziedzic KS, Lohmander LS, McAlindon T,
Zhang W and Zeinstra SB: Subgroup analyses of the effectiveness of
oral glucosamine for knee and hip osteoarthritis: A systematic
review and individual patient data meta-analysis from the OA trial
bank. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:1862–1869. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|