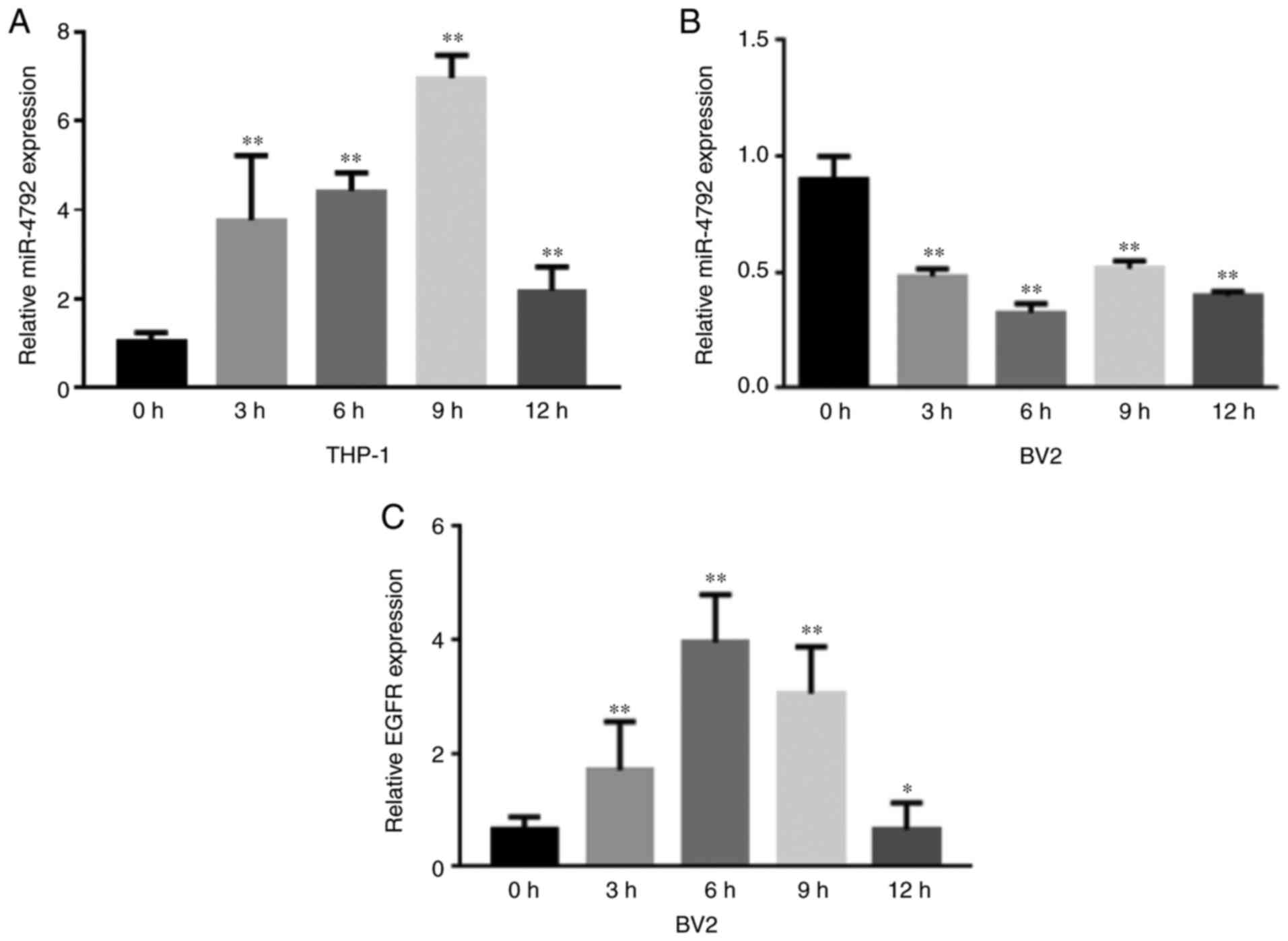
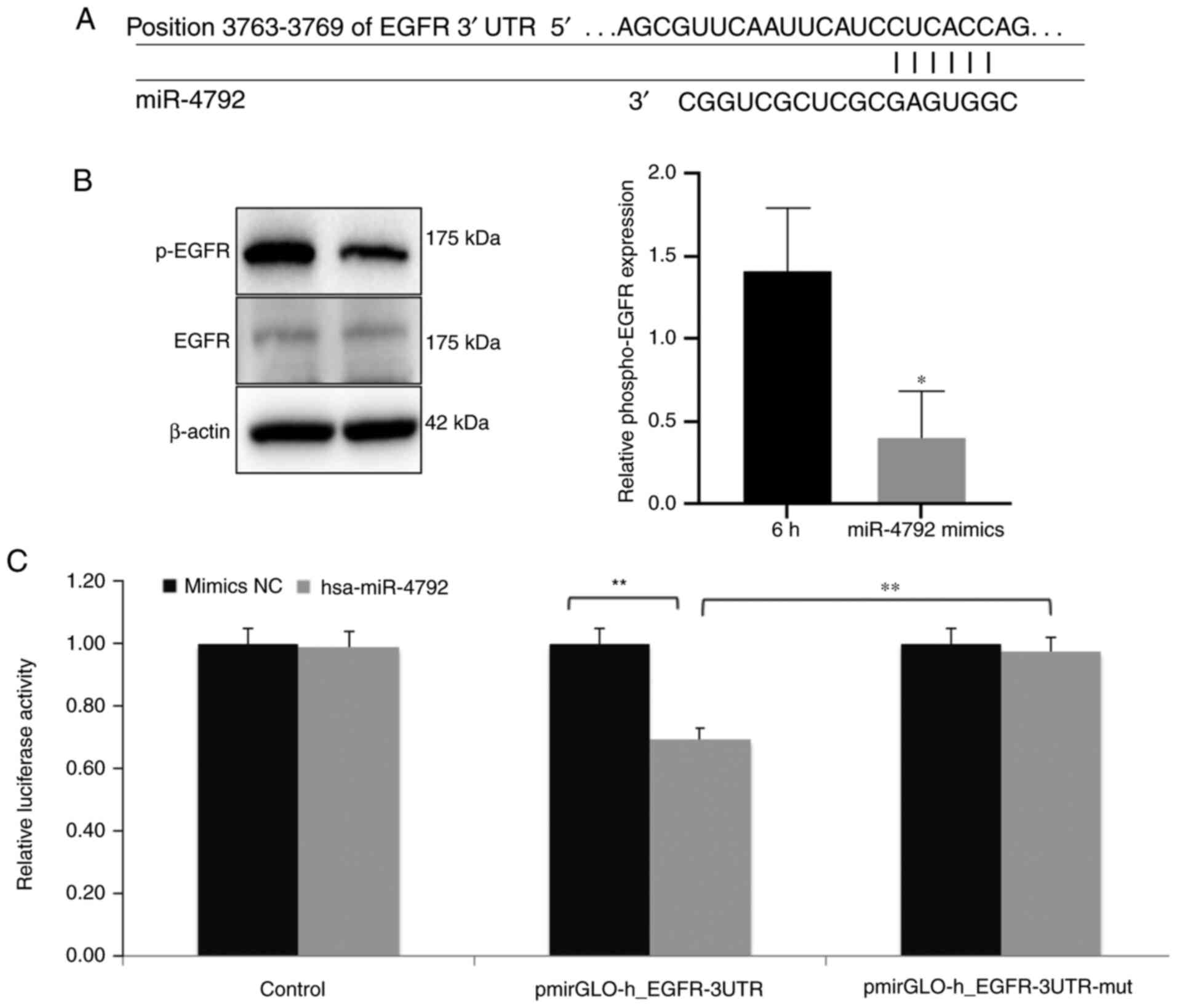
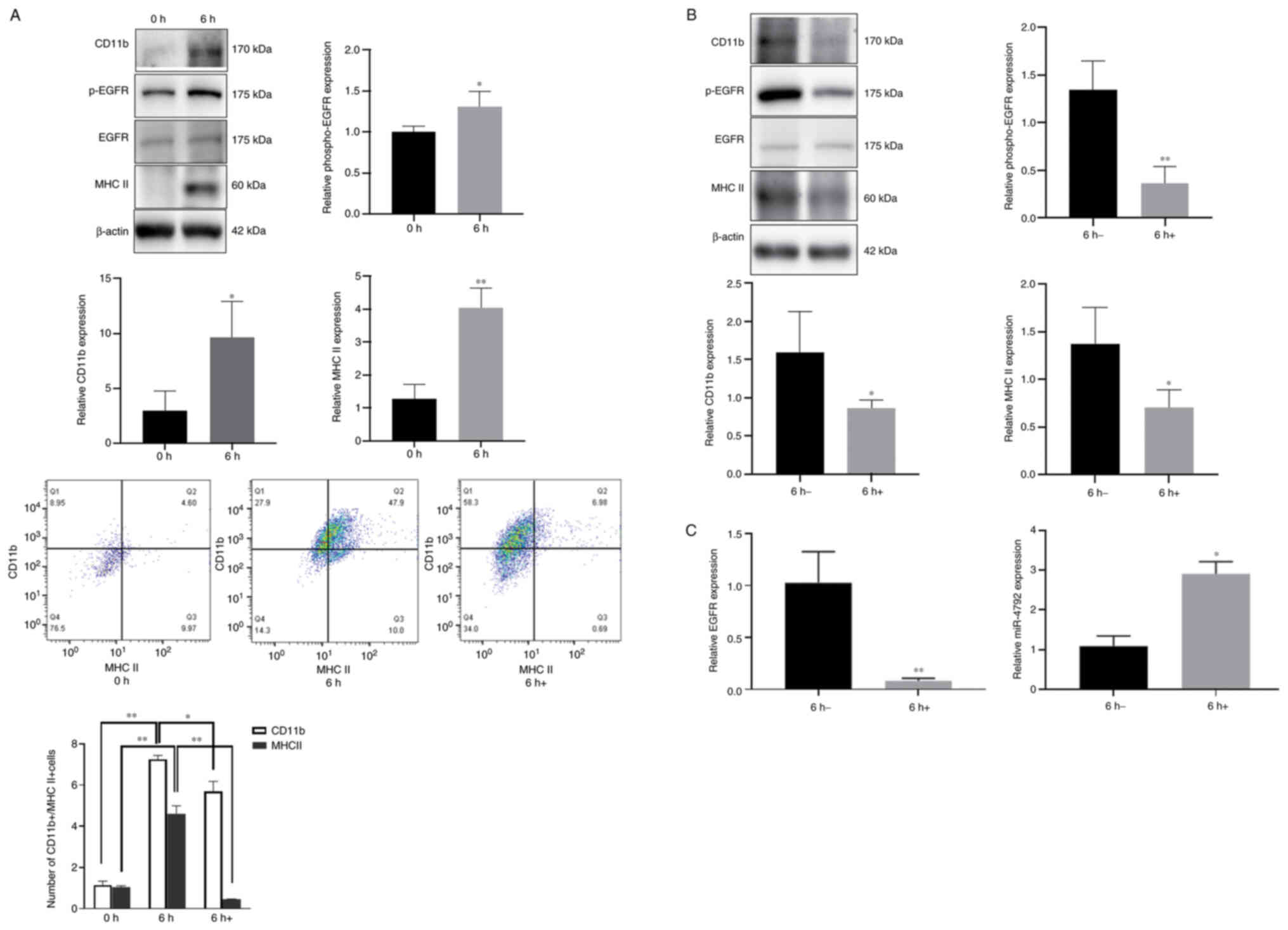
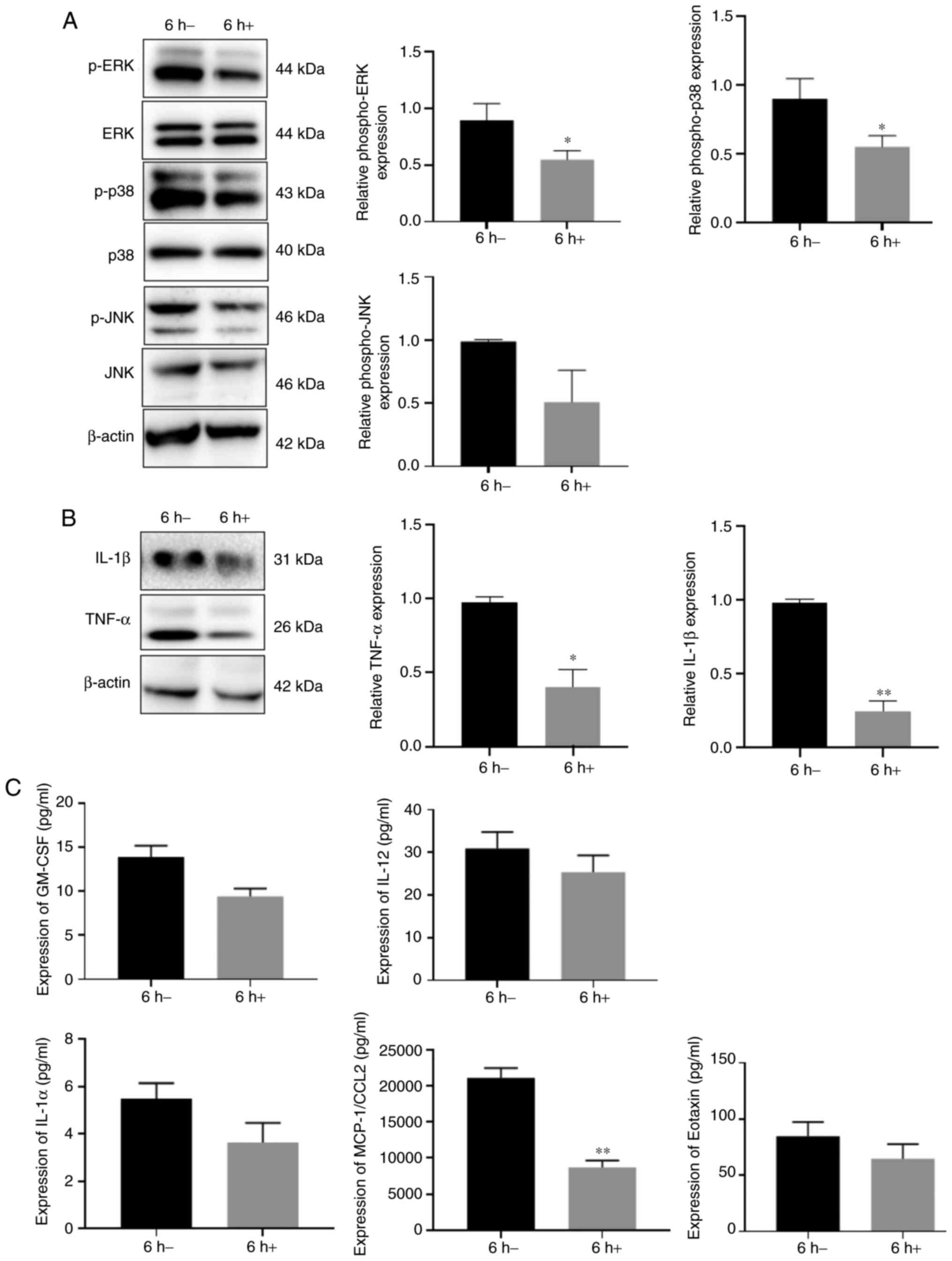
|
1
|
Pappas PG: Cryptococcal infections in
non-HIV-infected patients. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 124:61–79.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rajasingham R, Smith RM, Park BJ, Jarvis
JN, Govender NP, Chiller TM, Denning DW, Loyse A and Boulware DR:
Global burden of disease of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis:
An updated analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 17:873–881. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wu B, Liu H, Huang J, Zhang W and Zhang T:
Pulmonary cryptococcosis in non-AIDS patients. Clin Invest Med.
32:E70–E77. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kishi K, Homma S, Kurosaki A, Kohno T,
Motoi N and Yoshimura K: Clinical features and high-resolution CT
findings of pulmonary cryptococcosis in non-AIDS patients. Respir
Med. 100:807–812. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chang YC, Stins MF, McCaffery MJ, Miller
GF, Pare DR, Dam T, Paul-Satyaseela M, Kim KS and Kwon-Chung KJ:
Cryptococcal yeast cells invade the central nervous system via
transcellular penetration of the blood-brain barrier. Infect Immun.
72:4985–4995. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ngamskulrungroj P, Chang Y, Sionov E and
Kwon-Chung KJ: The primary target organ of Cryptococcus gattii is
different from that of Cryptococcus neoformans in a murine model.
mBio. 3:e00103–e00112. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chang YC, Bien CM, Lee H, Espenshade PJ
and Kwon-Chung KJ: Sre1p, a regulator of oxygen sensing and sterol
homeostasis, is required for virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans.
Mol Microbiol. 64:614–629. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ribes S, Ebert S, Regen T, Agarwal A,
Tauber SC, Czesnik D, Spreer A, Bunkowski S, Eiffert H, Hanisch UK,
et al: Toll-like receptor stimulation enhances phagocytosis and
intracellular killing of nonencapsulated and encapsulated
Streptococcus pneumoniae by murine microglia. Infect Immun.
78:865–871. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Redlich S, Ribes S, Schütze S, Eiffert H
and Nau R: Toll-like receptor stimulation increases phagocytosis of
Cryptococcus neoformans by microglial cells. J Neuroinflammation.
10:712013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gebert L and MacRae IJ: Regulation of
microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:21–37.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rupaimoole R and Frank J: Slack MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chen H, Jin Y, Chen H, Liao N, Wang Y and
Chen J: MicroRNA-mediated inflammatory responses induced by
Cryptococcus neoformans are dependent on the NF-κB pathway in human
monocytes. Int J Mol Med. 39:1525–1532. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
De Lacorte Singulani J, De Fátima Da Silva
J, Gullo FP, Costa MC, Fusco-Almeida AM, Enguita FJ and
Mendes-Giannini MJS: Preliminary evaluation of circulating
microRNAs as potential biomarkers in paracoccidioidomycosis. Biomed
Rep. 6:353–357. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kumar M, Ahmad T, Sharma A, Mabalirajan U,
Kulshreshtha A, Agrawal A and Ghosh B: Let-7 microRNA-mediated
regulation of IL-13 and allergic airway inflammation. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 128:1077–1085. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Essandoh K, Li Y, Huo J and Fan GC:
miRNA-mediated macrophage polarization and its potential role in
the regulation of inflammatory response. Shock. 46:122–131. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nahid MA, Yao B, Dominguez-Gutierrez PR,
Kesavalu L, Satoh M and Chan EK: Regulation of TLR2-mediated
tolerance and cross-tolerance through IRAK4 modulation by miR-132
and miR-212. J Immunol. 190:1250–1263. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Testa U, Pelosi E, Castelli G and Labbaye
C: miR-146 and miR-155: two key modulators of immune response and
tumor development. Noncoding RNA. 3:22201.
|
|
18
|
Li Y and Chen X: miR-4792 inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma by targeting FOXC1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
468:863–869. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Georgieva B, Milev I, Minkov I, Dimitrova
I, Bradford AP and Baev V: Characterization of the uterine
leiomyoma microR-NAome by deep sequencing. Genomics. 99:275–281.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chickooree D, Zhu K, Ram V, Wu HJ, He ZJ
and Zhang S: A preliminary microarray assay of the miRNA expression
signatures in buccal mucosa of oral submucous fibrosis patients. J
Oral Pathol Med. 45:691–697. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gabrusiewicz K, Rodriguez B, Wei J,
Hashimoto Y, Healy LM, Maiti SN, Thomas G, Zhou S, Wang Q, Elakkad
A, et al: Glioblastoma-infiltrated innate immune cells resemble M0
macrophage phenotype. JCI Insight. 1:e858412016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li CC, Eaton SA, Young PE, Lee M,
Shuttleworth R, Humphreys DT, Grau GE, Combes V, Bebawy M, Gong J,
et al: Glioma microvesicles carry selectively packaged coding and
non-coding RNAs which alter gene expression in recipient cells. RNA
Biol. 10:1333–1344. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Liu G, Jiang C, Li D, Wang R and Wang W:
MiRNA-34a inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent MMP7 activation in
gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 35:9801–9806. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen S, Zhang Z, Chen L and Zhang J: miRNA
101 3p.1 as an independent diagnostic biomarker aggravates chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease via activation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 20:4293–4302. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma HP, Kong WX, Li XY, Li W, Zhang Y and
Wu Y: miRNA-223 is an anticancer gene in human non-small cell lung
cancer through the PI3K/AKT pathway by targeting EGFR. Oncol Rep.
41:1549–1559. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Williamson PR: The relentless march of
cryptococcal meningitis. Lancet Infect Dis. 17:790–791. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bocchini V, Mazzolla R, Barluzzi R, Blasi
E, Sick P and Kettenmann H: An immortalized cell line expresses
properties of activated microglial cells. J Neurosci Res.
31:616–621. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sheng W, Zong Y, Mohammad A, Ajit D, Cui
J, Han D, Hamilton JL, Simonyi A, Sun AY, Gu Z, et al:
Pro-inflammatory cytokines and lipopolysaccharide induce changes in
cell morphology, and upregulation of ERK1/2, iNOS and sPLA2-IIA
expression in astrocytes and microglia. J Neuroinflammation.
8:1212011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Saag MS, Graybill RJ, Larsen RA, Pappas
PG, Perfect JR, Powderly WG, Sobel JD and Dismukes WE: Practice
guidelines for the management of cryptococcal disease. Infectious
diseases society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 30:710–718. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jin Y, Yao G, Wang Y, Teng L, Wang Y, Chen
H, Gao R, Lin W, Wang Z and Chen J: MiR-30c-5p mediates
inflammatory responses and promotes microglia survival by targeting
eIF2α during Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Microb Pathog.
141:1039592020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang WY, Tan MS, Yu JT and Tan L: Role of
pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer's
disease. Ann Transl Med. 3:1362015.
|
|
33
|
Jin X and Yamashita T: Microglia in
central nervous system repair after injury. J Biochem. 159:491–496.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kraft AD and Harry GJ: Features of
microglia and neuroinflammation relevant to environmental exposure
and neurotoxicity. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 8:2980–3018.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
O'Sullivan JB, Ryan KM, Curtin NM, Harkin
A and Connor TJ: Noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors limit
neuroinflammation in rat cortex following a systemic inflammatory
challenge: Implications for depression and neurodegeneration. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 12:687–699. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Loane DJ and Byrnes KR: Role of microglia
in neurotrauma. Neurotherapeutics. 7:366–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bachstetter AD, Xing B, de Almeida L,
Dimayuga ER, Watterson DM and Van Eldik LJ: Microglial p38alpha
MAPK is a key regulator of proinflammatory cytokine up-regulation
induced by toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands or beta-amyloid (Aβ). J
Neuroinflammation. 8:792011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xu L, Huang Y, Yu X, Yue J, Yang N and Zuo
P: The influence of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor
on synthesis of inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha
in spinal cord of rats with chronic constriction injury. Anesth
Analg. 105:1838–1844. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kim SH, Smith CJ and Van Eldik LJ:
Importance of MAPK pathways for microglial pro-inflammatory
cytokine IL-1 beta production. Neurobiol Aging. 25:431–439. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Qu WS, Tian DS, Guo ZB, Fang J, Zhang Q,
Yu ZY, Xie MJ, Zhang HQ, Lü JG and Wang W: Inhibition of EGFR/MAPK
signaling reduces microglial inflammatory response and the
associated secondary damage in rats after spinal cord injury. J
Neuroinflammation. 9:1782012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yamauchi T, Ueki K, Tobe K, Tamemoto H,
Sekine N, Wada M, Honjo M, Takahashi M, Takahashi T, Hirai H, et
al: Growth hormone-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of EGF receptor
as an essential element leading to MAP kinase activation and gene
expression. Endocr J. 45(Suppl): S27–S31. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Goel S, Hidalgo M and Perez-Soler R: EGFR
inhibitor-mediated apoptosis in solid tumors. J Exp Ther Oncol.
6:305–320. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pinheiro SB, Sousa ES, Cortez ACA, da
Silva Rocha DF, Menescal LSF, Chagas VS, Gómez ASP, Cruz KS, Santos
LO, Alves MJ, et al: Cryptococcal meningitis in non-HIV patients in
the State of Amazonas, Northern Brazil. J Microbiol. 52:279–288.
2021.
|
|
44
|
Martinez-Nunez RT, Louafi F and
Sanchez-Elsner T: The interleukin 13 (IL-13) pathway in human
macrophages is modulated by microRNA-155 via direct targeting of
interleukin 13 receptor alpha1 (IL13Ralpha1). J Biol Chem.
286:1786–1794. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Roy S: miRNA in macrophage development and
function. Antioxid Redox Signal. 25:795–804. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Sabiiti W, Robertson E, Beale MA, Johnston
SA, Brouwer AE, Loyse A, Jarvis JN, Gilbert AS, Fisher MC, Harrison
TS, et al: Efficient phagocytosis and laccase activity affect the
outcome of HIV-associated cryptococcosis. J Clin Invest.
124:2000–2008. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Alanio A, Desnos-Ollivier M and Dromer F:
Dynamics of Cryptococcus neoformans-macrophage interactions reveal
that fungal background influences outcome during cryptococcal
meningoencephalitis in humans. mBio. 2:e00158–e00111. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ji RR, Nackley A, Huh Y, Terrando N and
Maixner W: Neuroinflammation and central sensitization in chronic
and widespread pain. Anesthesiology. 129:343–366. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lyman M, Lloyd DG, Ji X, Vizcaychipi MP
and Ma D: Neuroinflammation: The role and consequences. Neurosci
Res. 79:1–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kim YK, Na KS, Myint AM and Leonard BE:
The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in neuroinflammation,
neurogenesis and the neuroendocrine system in major depression.
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 64:277–284. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Henn A, Lund S, Hedtjärn M, Schrattenholz
A, Pörzgen P and Leist M: The suitability of BV2 cells as
alternative model system for primary microglia cultures or for
animal experiments examining brain inflammation. ALTEX. 26:83–94.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Stansley B, Post J and Hensley K: A
comparative review of cell culture systems for the study of
microglial biology in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuroinflammation.
9:1152012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kofler J and Wiley CA: Microglia: Key
innate immune cells of the brain. Toxicol Pathol. 39:103–114. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Rock RB, Gekker G, Hu S, Sheng WS, Cheeran
M, Lokensgard JR and Peterson PK: Role of microglia in central
nervous system infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 17:942–964. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Barluzzi R, Brozzetti A, Delfino D,
Bistoni F and Blasi E: Role of the capsule in microglial
cell-Cryptococcus neoformans interaction: Impairment of antifungal
activity but not of secretory functions. Med Mycol. 36:189–197.
1998.
|
|
56
|
Neal LM, Xing E, Xu J, Kolbe JL,
Osterholzer JJ, Segal BM, Williamson PR and Olszewski MA:
CD4+T cells orchestrate lethal immune pathology despite
fungal clearance during Cryptococcus neoformans
meningoencephalitis. mBio. 11:e01415–e01417. 2017.
|
|
57
|
Adami C, Sorci G, Blasi E, Agneletti AL,
Bistoni F and Donato R: S100B expression in and effects on
microglia. Glia. 33:131–142. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Song X, Tanaka S, Cox D and Lee SC: Fc
gamma receptor signaling in primary human microglia: Differential
roles of PI-3K and Ras/ERK MAPK pathways in phagocytosis and
chemokine induction. J Leukoc Biol. 75:1147–1155. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Preissler J, Grosche A, Lede V, Le Duc D,
Krügel K, Matyash V, Szulzewsky F, Kallendrusch S, Immig K,
Kettenmann H, et al: Altered microglial phagocytosis in
GPR34-deficient mice. Glia. 63:206–215. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Lee SC, Kress Y, Dickson DW and Casadevall
A: Human microglia mediate anti-Cryptococcus neoformans activity in
the presence of specific antibody. J Neuroimmunol. 62:43–52. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Lee SC, Kress Y, Zhao ML, Dickson DW and
Casadevall A: Cryptococcus neoformans survive and replicate in
human microglia. Lab Invest. 73:871–879. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Popovich PG, Guan Z, Wei P, Huitinga I,
van Rooijen N and Stokes BT: Depletion of hematogenous macrophages
promotes partial hindlimb recovery and neuroanatomical repair after
experimental spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 158:351–365. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Stirling DP, Khodarahmi K, Liu J, McPhail
LT, McBride CB, Steeves JD, Ramer MS and Tetzlaff W: Minocycline
treatment reduces delayed oligodendrocyte death, attenuates axonal
dieback, and improves functional outcome after spinal cord injury.
J Neurosci. 24:2182–2190. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Tian DS, Xie MJ, Yu ZY, Zhang Q, Wang YH,
Chen B, Chen C and Wang W: Cell cycle inhibition attenuates
microglia induced inflammatory response and alleviates neuronal
cell death after spinal cord injury in rats. Brain Res.
1135:177–185. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Gomez-Pinilla F, Knauer DJ and
Nieto-Sampedro M: Epidermal growth factor receptor immunoreactivity
in rat brain. Development and cellular localization. Brain Res.
438:385–390. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Erschbamer M, Pernold K and Olson L:
Inhibiting epidermal growth factor receptor improves structural,
locomotor, sensory, and bladder recovery from experimental spinal
cord injury. J Neurosci. 27:6428–6435. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Jung HW, Son HY, Minh CV, Kim YH and Park
YK: Methanol extract of ficus leaf inhibits the production of
nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated
microglia via the MAPK pathway. Phytother Res. 22:1064–1069. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Correia I, Prieto D, Román E, Wilson D,
Hube B, Alonso-Monge R and Pla J: Cooperative role of MAPK pathways
in the interaction of Candida albicans with the host epithelium.
Microorganisms. 25:482019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Uenotsuchi T, Takeuchi S, Matsuda T, Urabe
K, Koga T, Uchi H, Nakahara T, Fukagawa S, Kawasaki M, Kajiwara H,
et al: Differential induction of Th1-prone immunity by human
dendritic cells activated with sporothrix schenckii of cutaneous
and visceral origins to determine their different virulence. Int
Immunol. 18:1637–1646. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Liu P, Pu J, Zhang J, Chen Z, Wei K and
Shi L: Bioinformatic analysis of mir-4792 regulates Radix
Tetrastigma hemsleyani flavone to inhibit proliferation, invasion,
and induce apoptosis of a549 cells. Onco Targets Ther.
12:1401–1412. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Lindell DM, Ballinger MN, McDonald RA,
Toews GB and Huffnagle GB: Immunologic homeostasis during
infection: coexistence of strong pulmonary cell-mediated immunity
to secondary Cryptococcus neoformans infection while the primary
infection still persists at low levels in the lungs. J Immunol.
177:4652–4661. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Lindell DM, Ballinger MN, McDonald RA,
Toews GB and Huffnagle GB: Diversity of the T-cell response to
pulmonary Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Infect Immun.
74:4538–4548. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Eastman AJ, Osterholzer JJ and Olszewski
MA: Role of dendritic cell-pathogen interactions in the immune
response to pulmonary cryptococcal infection. Future Microbiol.
10:1837–1857. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|