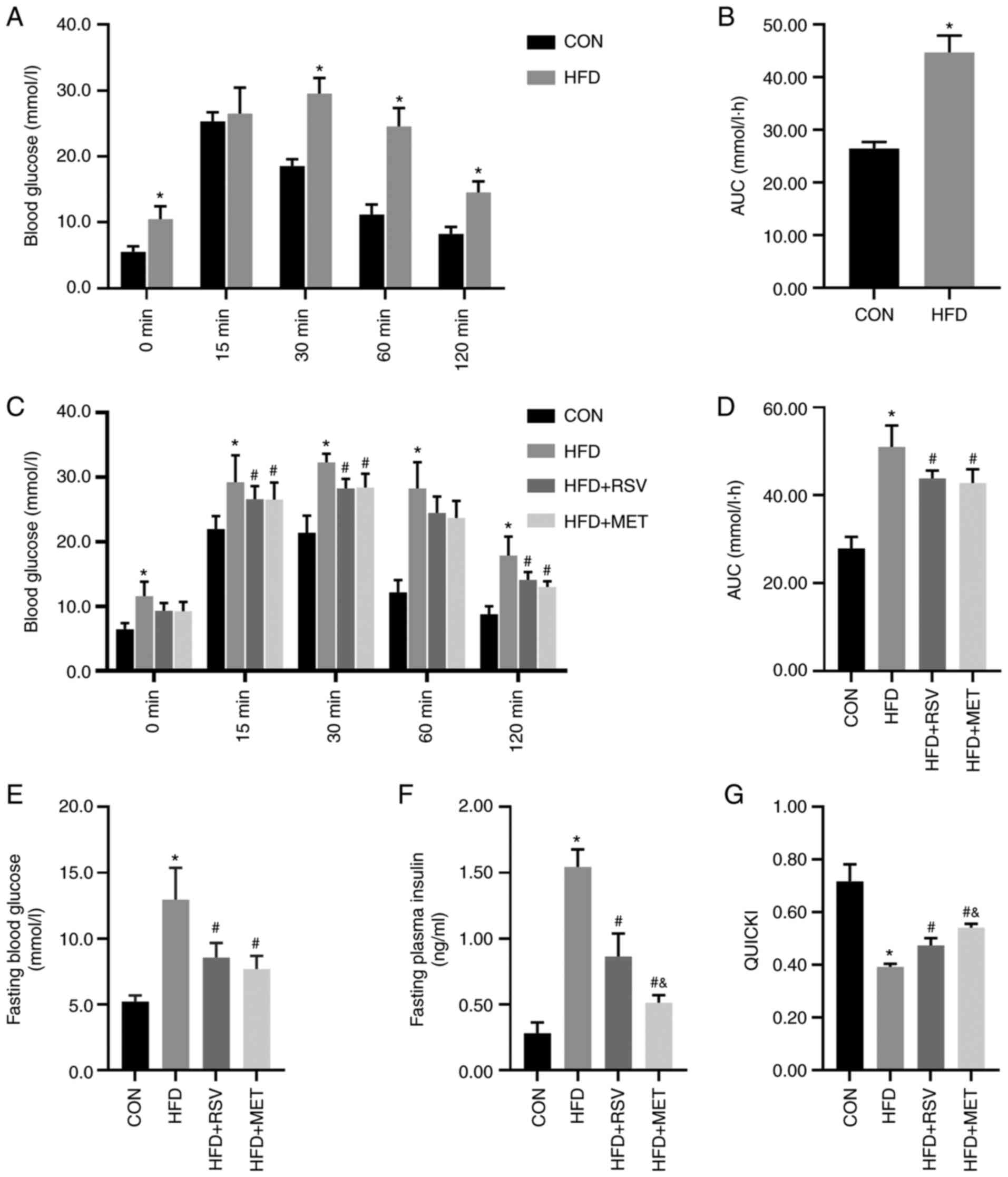
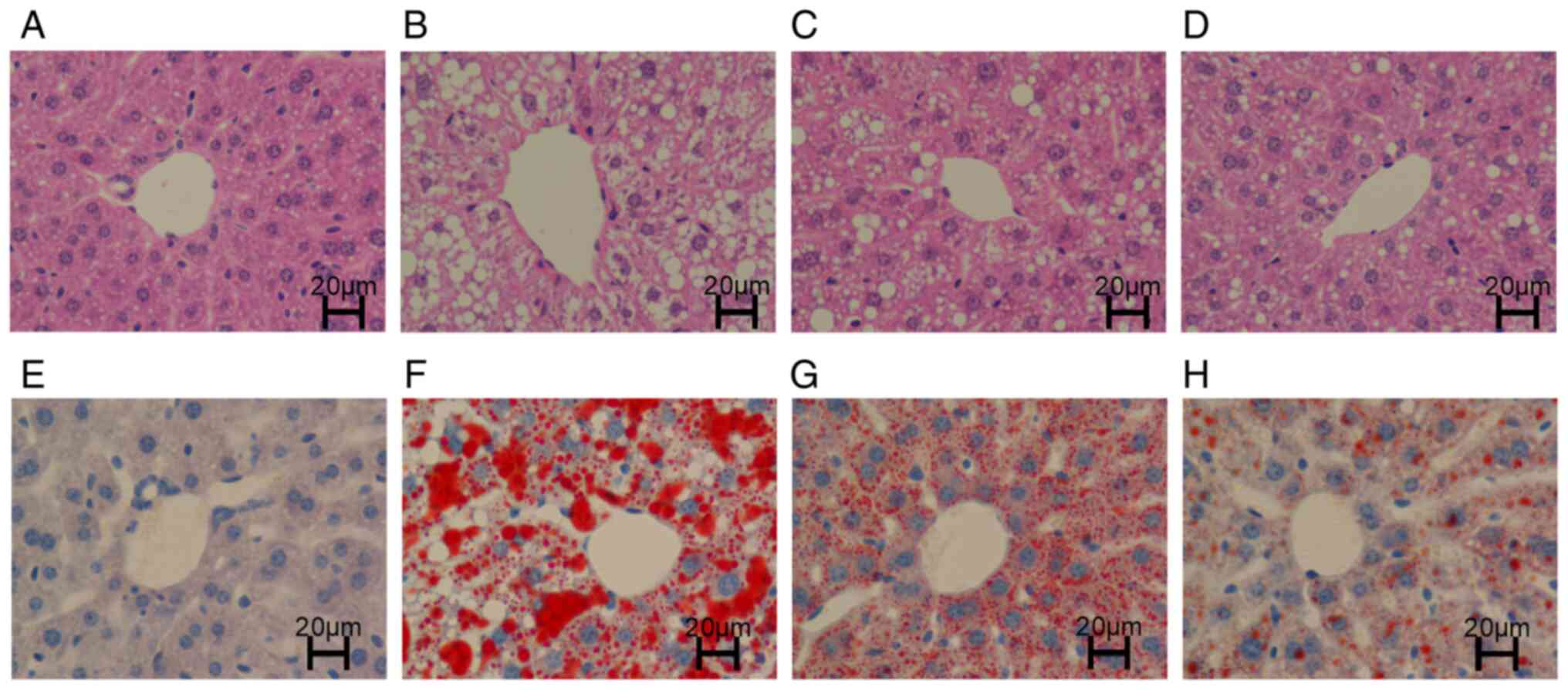
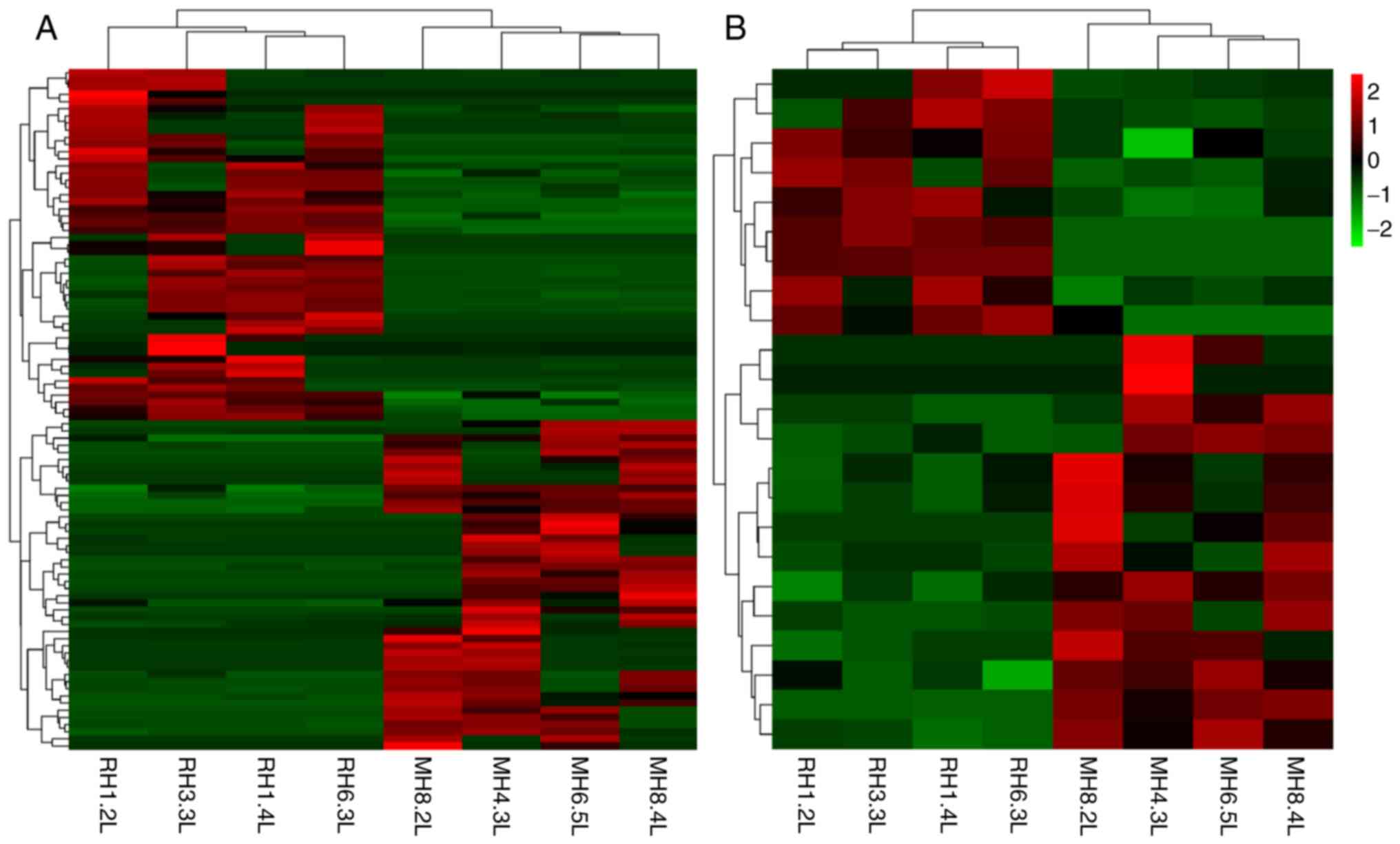
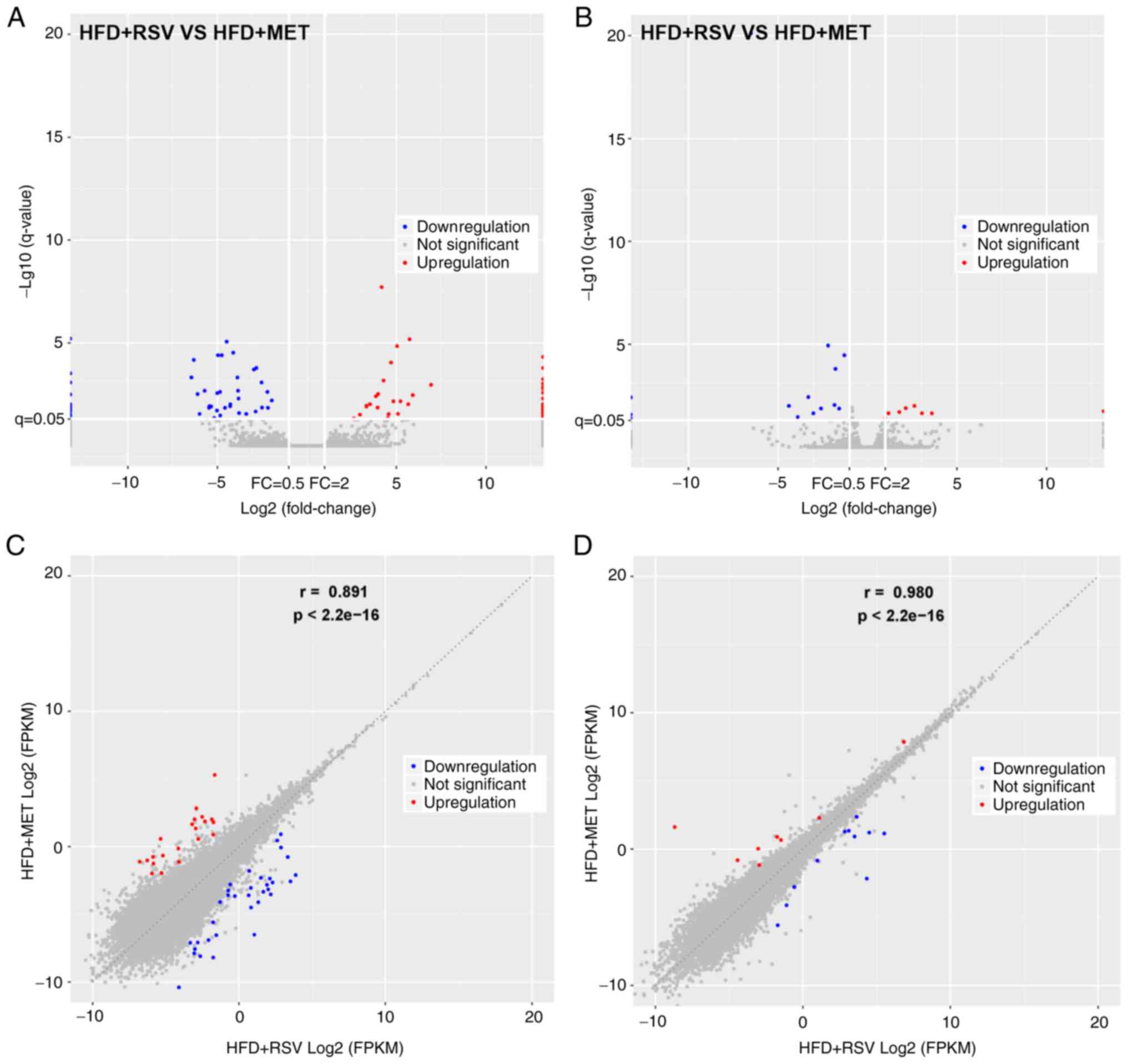
|
1
|
Kim J, Bilder D and Neufeld TP: Mechanical
stress regulates insulin sensitivity through integrin-dependent
control of insulin receptor localization. Genes Dev. 32:156–164.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Biasutto L, Mattarei A, Azzolini M, La
Spina M, Sassi N, Romio M, Paradisi C and Zoratti M: Resveratrol
derivatives as a pharmacological tool. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1403:27–37. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Weiskirchen S and Weiskirchen R:
Resveratrol: How much wine do you have to drink to stay healthy?
Adv Nutr. 7:706–718. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kai Y, Kawano Y, Yamamoto H and Narahara
H: A possible role for AMP-activated protein kinase activated by
metformin and AICAR in human granulosa cells. Reprod Biol
Endocrinol. 13:272015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Abbasi Oshaghi E, Goodarzi MT, Higgins V
and Adeli K: Role of resveratrol in the management of insulin
resistance and related conditions: Mechanism of action. Crit Rev
Clin Lab Sci. 54:267–293. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhao W, Li A, Feng X, Hou T, Liu K, Liu B
and Zhang N: Metformin and resveratrol ameliorate muscle insulin
resistance through preventing lipolysis and inflammation in hypoxic
adipose tissue. Cell Signal. 28:1401–1411. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu XF, Hao JL, Xie T, Pant OP, Lu CB, Lu
CW and Zhou DD: The BRAF activated non-coding RNA: A pivotal long
non-coding RNA in human malignancies. Cell Prolif. 51:e124492018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang X, Chang X, Zhang P, Fan L, Zhou T
and Sun K: Aberrant expression of long non-coding RNAs in newly
diagnosed type 2 diabetes indicates potential roles in chronic
inflammation and insulin resistance. Cell Physiol Biochem.
43:2367–2378. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Shu L, Hou G, Zhao H, Huang W, Song G and
Ma H: Long non-coding RNA expression profiling following treatment
with resveratrol to improve insulin resistance. Mol Med Rep.
22:1303–1316. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhao H, Zhang Y, Shu L, Song G and Ma H:
Resveratrol reduces liver endoplasmic reticulum stress and improves
insulin sensitivity in vivo and in vitro. Drug Des Devel Ther.
13:1473–1485. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang YJ, Zhao H, Dong L, Zhen YF, Xing
HY, Ma HJ and Song GY: Resveratrol ameliorates high-fat
diet-induced insulin resistance and fatty acid oxidation via
ATM-AMPK axis in skeletal muscle. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:9117–9125. 2019.
|
|
12
|
Beaudoin MS, Snook LA, Arkell AM, Simpson
JA, Holloway GP and Wright DC: Resveratrol supplementation improves
white adipose tissue function in a depot-specific manner in Zucker
diabetic fatty rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
305:R542–R551. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kristensen JM, Larsen S, Helge JW, Dela F
and Wojtaszewski JF: Two weeks of metformin treatment enhances
mitochondrial respiration in skeletal muscle of AMPK kinase dead
but not wild type mice. PLoS One. 13:e535332013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Cheng K, Song Z, Zhang H, Li S, Wang C,
Zhang L and Wang T: The therapeutic effects of resveratrol on
hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet-induced obese mice by improving
oxidative stress, inflammation and lipid-related gene
transcriptional expression. Med Mol Morphol. 52:187–197. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen K, Zhao H, Shu L, Xing H, Wang C, Lu
C and Song G: Effect of resveratrol on intestinal tight junction
proteins and the gut microbiome in high-fat diet-fed insulin
resistant mice. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 71:965–978. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hrebícek J, Janout V, Malincíková J,
Horáková D and Cízek L: Detection of insulin resistance by simple
quantitative insulin sensitivity check index QUICKI for
epidemiological assessment and prevention. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
87:144–147. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Buchfink B, Xie C and Huson DH: Fast and
sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods. 12:59–60.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zou Q, Mao Y, Hu L, Wu Y and Ji Z:
miRClassify: An advanced web server for miRNA family classification
and annotation. Comput Biol Med. 45:157–160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Staehr P, Hother-Nielsen O and
Beck-Nielsen H: The role of the liver in type 2 diabetes. Rev
Endocr Metab Disord. 5:105–110. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Petersen MC, Vatner DF and Shulman GI:
Regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in health and disease. Nat
Rev Endocrinol. 13:572–587. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Klover PJ and Mooney RA: Hepatocytes:
Critical for glucose homeostasis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
36:753–758. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hatting M, Tavares CDJ, Sharabi K, Rines
AK and Puigserver P: Insulin regulation of gluconeogenesis. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1411:21–35. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
McCurdy CE, Schenk S, Holliday MJ, Philp
A, Houck JA, Patsouris D, MacLean PS, Majka SM, Klemm DJ and
Friedman JE: Attenuated Pik3r1 expression prevents insulin
resistance and adipose tissue macrophage accumulation in
diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes. 61:2495–2505. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Langlet F, Haeusler RA, Lindén D, Ericson
E, Norris T, Johansson A, Cook JR, Aizawa K, Wang L, Buettner C and
Accili D: Selective inhibition of FOXO1 activator/repressor balance
modulates hepatic glucose handling. Cell. 171:824–835.e18. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Thiel G and Rössler OG: Resveratrol
regulates gene transcription via activation of stimulus-responsive
transcription factors. Pharmacol Res. 117:166–176. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li JY, Huang WQ, Tu RH, Zhong GQ, Luo BB
and He Y: Resveratrol rescues hyperglycemia-induced endothelial
dysfunction via activation of Akt. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:182–191.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X,
Fenyk-Melody J, Wu M, Ventre J, Doebber T, Fujii N, et al: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J
Clin Invest. 108:1167–1174. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sathishkumar C, Prabu P, Mohan V and
Balasubramanyam M: Linking a role of lncRNAs (long non-coding RNAs)
with insulin resistance, accelerated senescence, and inflammation
in patients with type 2 diabetes. Hum Genomics. 12:412018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gao Y, Wu F, Zhou J, Yan L, Jurczak MJ,
Lee HY, Yang L, Mueller M, Zhou XB, Dandolo L, et al: The H19/let-7
double-negative feedback loop contributes to glucose metabolism in
muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:13799–13811. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ding GL, Wang FF, Shu J, Tian S, Jiang Y,
Zhang D, Wang N, Luo Q, Zhang Y, Jin F, et al: Transgenerational
glucose intolerance with Igf2/H19 epigenetic alterations in mouse
islet induced by intrauterine hyperglycemia. Diabetes.
61:1133–1142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang Y, Wu H, Wang F, Ye M, Zhu H and Bu
S: Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 expression in patients with
gestational diabetes mellitus. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 140:164–169.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|